Infective Endocarditis by Proteus Species: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Introduction
Methods
Data search
Study selection
Outcomes of interest
Data extraction and definitions
Statistical analysis
Results
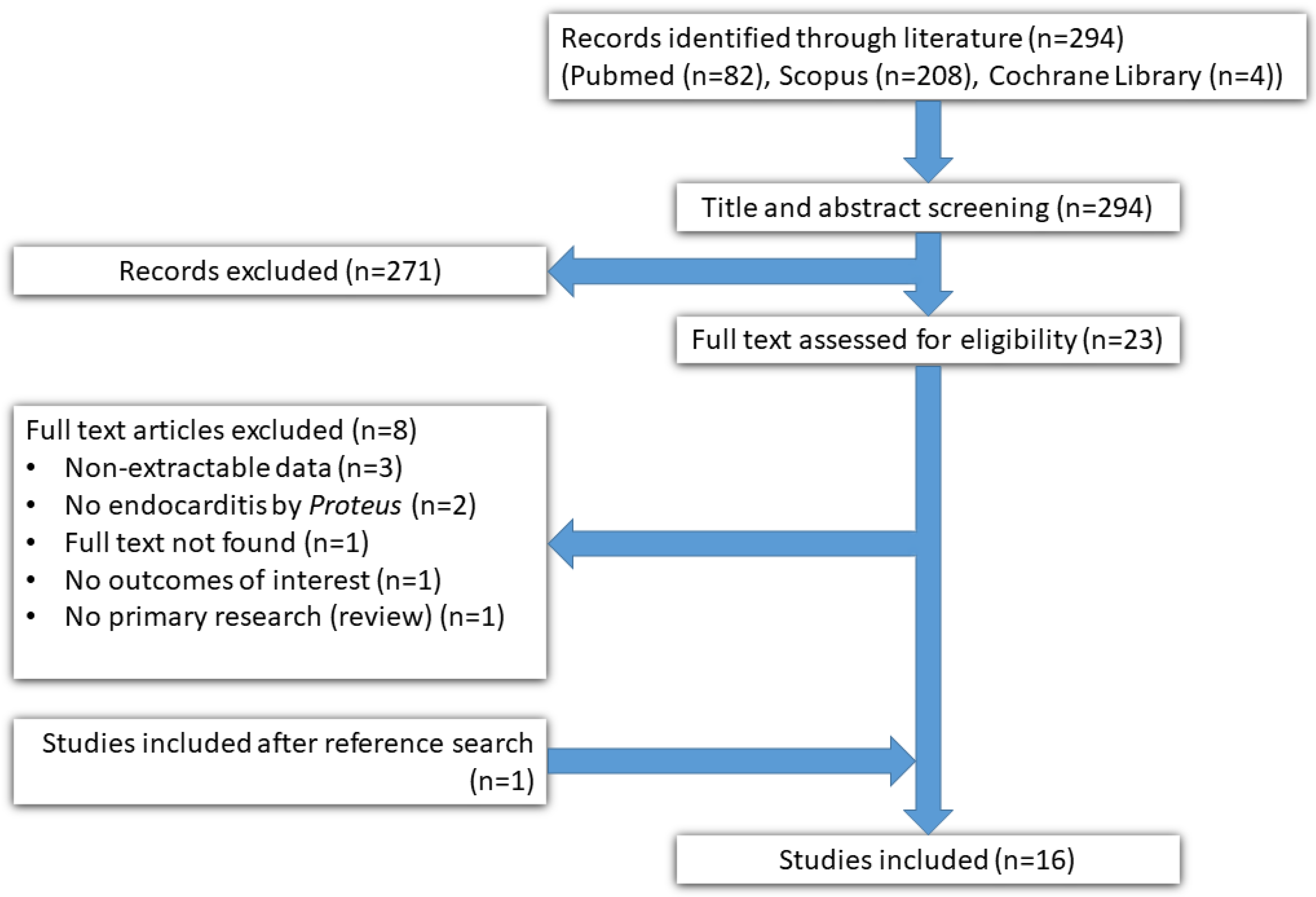
Literature search
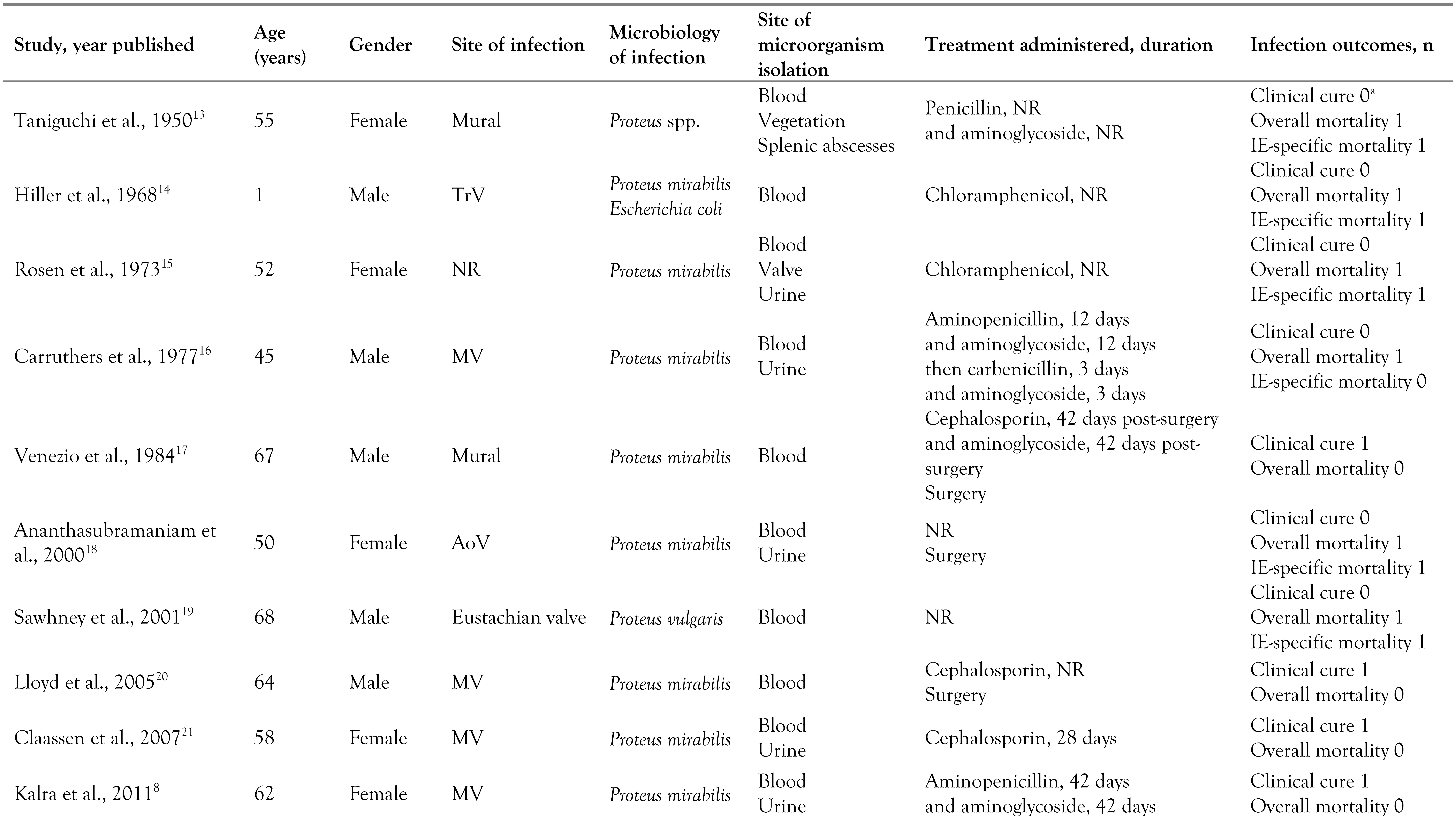
Included studies’ characteristics
Epidemiology of IE by Proteus species
Microbiology of IE and antimicrobial resistance of Proteus species
Diagnosis of IE by Proteus species
Clinical characteristics of IE by Proteus species
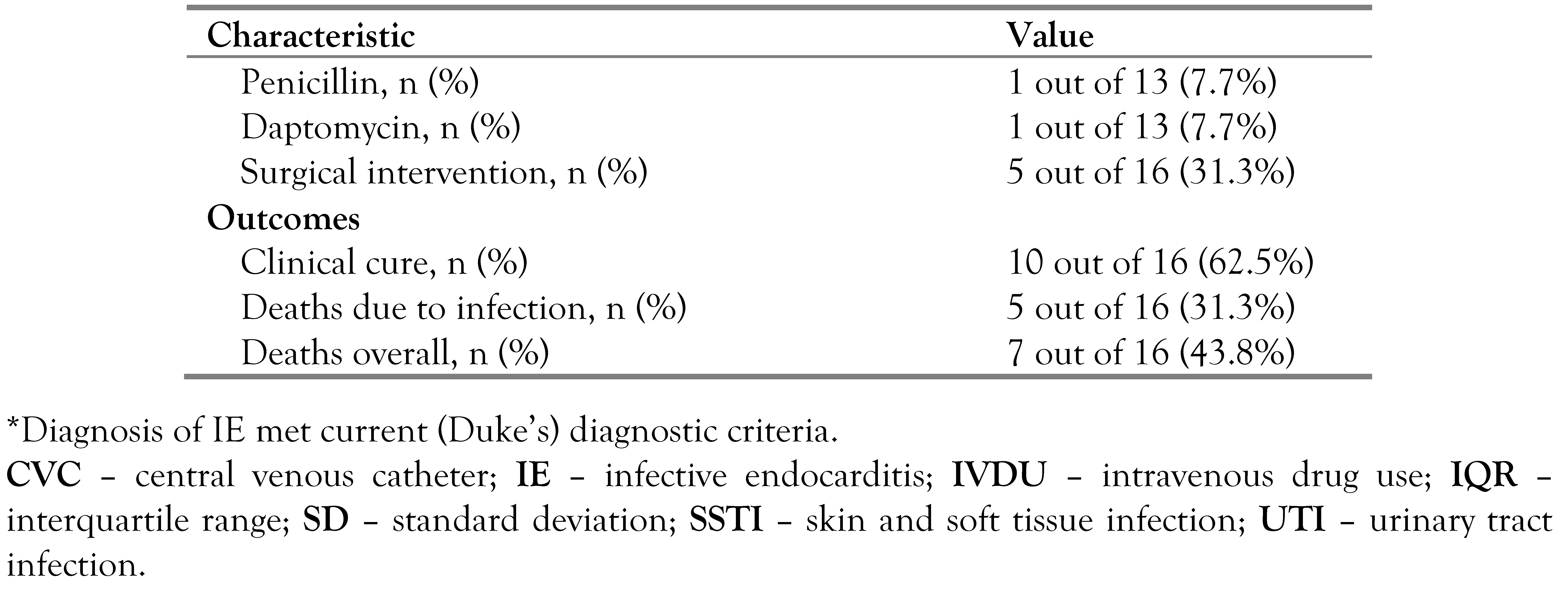
Treatment and outcomes of IE by Proteus species
Statistical analysis of IE by Proteus species
Discussion
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of interest
Appendix
 |
 |
 |
 |
References
- Donnenberg, M. Enterobacteriaceae. In Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases., 8th ed.; Bennett, J.E., Ed.; Elsevier/Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015; p. 2516. [Google Scholar]
- Armbruster, C.E.; Mobley, H.L. Merging mythology and morphology: The multifaceted lifestyle of Proteus mirabilis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, J.N.; Pearson, M.M. Proteus mirabilis and urinary tract infections. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3, 10.1128/microbiolspec.UTI-0017-2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbruster, C.E.; Mobley, H.L.T.; Pearson, M.M. Pathogenesis of Proteus mirabilis Infection. EcoSal. Plus. 2018, 8, 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0009-2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiecińska-Piróg, J.; Skowron, K.; Gospodarek-Komkowska, E. Primary and secondary bacteremia caused by Proteus spp.: Epidemiology, strains susceptibility and biofilm formation. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Gaca, J.G.; Chu, V.H. Management considerations in infective endocarditis: A review. JAMA 2018, 320, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddour, L.M.; Wilson, W.R.; Bayer, A.S.; et al. Infective endocarditis in adults: Diagnosis, antimicrobial therapy, and management of complications: A scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2015, 132, 1435–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, A.; Cooley, C.; Tsigrelis, C. Treatment of endocarditis due to Proteus species: A literature review. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 15, e222–e225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroup, D.F.; Berlin, J.A.; Morton, S.C.; et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: A proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 2000, 283, 2008–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, B.C.; Small, K.; Brodley, C.E.; Lau, J.; Trikalinos, T.A. Deploying an interactive machine learning system in an evidence-based practice center: Abstrackr. In Proceedings of the 2nd ACM SIGHIT International Health Informatics Symposium; 2012; pp. 819–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.S.; Sexton, D.J.; Mick, N.; et al. Proposed modifications to the Duke criteria for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 30, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Vist, G.E.; et al. GRADE: An emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2008, 336, 924–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, T.; Murphy, F.D. Mural bacterial endocarditis produced by Proteus. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1950, 143, 427–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiller, E.J. Bristle in the heart. Br. Med. J. 1968, 4, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rosen, P.; Armstrong, D. Infective endocarditis in patients treated for malignant neoplastic diseases: A postmortem study. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1973, 60, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, M.M. Endocarditis due to enteric bacilli other than Salmonellae: Case reports and literature review. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1977, 273, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venezio, F.R.; Thompson, J.E.; Sullivan, H.; Subramanian, R.; Ritzman, P.; Gunnar, R.M. Infection of a ventricular aneurysm and cardiac mural thrombus. Survival after surgical resection. Am. J. Med. 1984, 77, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthasubramaniam, K.; Karthikeyan, V. Aortic ring abscess and aortoatrial fistula complicating fulminant prosthetic valve endocarditis due to Proteus mirabilis. J. Ultrasound Med. 2000, 19, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawhney, N.; Palakodeti, V.; Raisinghani, A.; Rickman, L.S.; DeMaria, A.N.; Blanchard, D.G. Eustachian valve endocarditis: A case series and analysis of the literature. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2001, 14, 1139–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, M.; Satterwhite, L.; Lerakis, S. Successfully treated mitral valve Proteus mirabilis endocarditis. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2005, 329, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claassen, D.O.; Batsis, J.A.; Orenstein, R. Proteus mirabilis: A rare cause of infectious endocarditis. Scand J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 39, 373–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Chang, W.J.; Chin, C. An unusual cause of infective endocarditis: Proteus mirabilis bacteremia from an infected pressure ulcer. Int. J. Gerontol. 2015, 9, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, R.; Sekar, B.; Payne, M.N. Proteus endocarditis in an intravenous drug user. BMJ Case Rep. 2015, 2015, bcr2015212447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimoldi, S.G.; De Vecchi, E.; Pagani, C.; et al. Use of dithiothreitol to dislodge bacteria from the biofilm on an aortic valve in the operating theatre: A case of infective endocarditis caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Proteus mirabilis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2016, 102, e357–e359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotzki, C.R.; Mergenhagen, K.A.; Bulman, Z.P.; Tsuji, B.T.; Berenson, C.S. Native valve Proteus mirabilis endocarditis: Successful treatment of a rare entity formulated by in vitro synergy antibiotic testing. BMJ Case Rep. 2016, 2016, bcr2016215956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salsano, A.; Sportelli, E.; Borile, S.; Santini, F. Proteus mirabilis bioprosthetic tricuspid valve endocarditis with massive right ventricular vegetation: A new entity in the prosthetic valve endocarditis aetiology. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2016, 50, 581–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, I.; Silva, A.R.; Carreira, M.S.; Friões, F. Proteus mirabilis endocarditis. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e230575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morpeth, S.; Murdoch, D.; Cabell, C.H.; et al. Non-HACEK gram-negative bacillus endocarditis. Ann. Int. Med. 2007, 147, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, M.; Tiseo, G.; Durante-Mangoni, E.; et al. Risk factors and outcomes of endocarditis due to non-HACEK gram-negative bacilli: Data from the prospective multicenter Italian endocarditis study cohort. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02208-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polewczyk, A.; Janion, M.; Podlaski, R.; Kutarski, A. Clinical manifestations of lead-dependent infective endocarditis: Analysis of 414 cases. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavan, T.; Quinn, E.L.; Freimer, E.; et al. Clinical studies of cefazolin and comparison with other cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973, 4, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tolan, R.W., Jr.; Kleiman, M.B.; Frank, M.; King, H.; Brown, J.W. Operative intervention in active endocarditis in children: Report of a series of cases and review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1992, 14, 852–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Juanatey, J.R.; Garcia-Acuna, J.M.; Garcia-Bengoechea, J.; et al. Endocarditis with pericardial bioprostheses: Clinico-pathologic characteristics, immediate and long term prognosis. J. Heart Valve Dis. 1994, 3, 172–178. [Google Scholar]
- Abela, G.S.; Majmudar, B.; Felner, J.M. Myocardial abscesses unassociated with infective endocarditis. South. Med. J. 1981, 74, 432–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, L. Infective endocarditis: Past, present and future. J. R. Coll. Physicians Lond. 1972, 6, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahill, T.J.; Prendergast, B.D. Infective endocarditis. Lancet 2016, 387, 882–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loubet, P.; Lescure, F.X.; Lepage, L.; et al. Endocarditis due to gram-negative bacilli at a French teaching hospital over a 6-year period: Clinical characteristics and outcome. Infect. Dis. (Lond.) 2015, 47, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertugrul Mercan, M.; Arslan, F.; Ozyavuz Alp, S.; et al. Non-HACEK Gram-negative bacillus endocarditis. Med. Mal. Infect. 2019, 49, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veve, M.P.; McCurry, E.D.; Cooksey, G.E.; Shorman, M.A. Epidemiology and outcomes of non-HACEK infective endocarditis in the southeast United States. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.F.; Liou, M.L.; Kuo, C.H.; Lin, Y.Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Kuo, H.Y. Antimicrobial susceptibility and molecular epidemiology of Proteus mirabilis isolates from three hospitals in northern Taiwan. Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 1338–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© GERMS 2020.
Share and Cite
Ioannou, P.; Vougiouklakis, G. Infective Endocarditis by Proteus Species: A Systematic Review. Germs 2020, 10, 229-239. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2020.1209
Ioannou P, Vougiouklakis G. Infective Endocarditis by Proteus Species: A Systematic Review. Germs. 2020; 10(3):229-239. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2020.1209
Chicago/Turabian StyleIoannou, Petros, and Georgios Vougiouklakis. 2020. "Infective Endocarditis by Proteus Species: A Systematic Review" Germs 10, no. 3: 229-239. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2020.1209
APA StyleIoannou, P., & Vougiouklakis, G. (2020). Infective Endocarditis by Proteus Species: A Systematic Review. Germs, 10(3), 229-239. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2020.1209




