Abstract
Introduction: Tuberculosis affects commonly the lungs, but any other organs can be affected as well. Urogenital tuberculosis is usually misdiagnosed. In this perspective, we aimed to give an update on the epidemiological, clinical and evolutionary features of urogenital tuberculosis in Southern Tunisia. Methods: We conducted a retrospective study including all patients with extrapulmonary tuberculosis notified during the period from 1992 to 2017 in Southern Tunisia. We specified the particularities of urogenital tuberculosis cases, and we compared them with other extrapulmonary tuberculosis cases. Results: Overall, we analyzed 240 cases with urogenital tuberculosis, among 1702 patients with extrapulmonary tuberculosis (14.1%). There were 121 women (50.4%). The mean age was 49±17 years. Multifocal tuberculosis was noted in 29 cases (12.1%). There were 169 cases with urinary tract tuberculosis (70.4%). Chronological trends analysis showed that the median age at diagnosis increased significantly (Rho = 0.41; p = 0.039) and the number of urogenital tuberculosis declined during the study period, without a statistical significance (Rho = −0.07; p = 0.721). Compared to other extrapulmonary tuberculosis sites, patients aged 60 years and above (OR = 2.7; p < 0.001) and coming from rural areas (OR = 1.4; p = 0.021) were more frequently diagnosed with urogenital tuberculosis. Treatment duration was significantly longer in patients with urogenital tuberculosis (10.13 ± 3.79 vs. 9.20 ± 3.77 months; p < 0.001). As for the disease evolution, relapse was significantly more frequent in patients with urogenital tuberculosis (OR = 4.1; p = 0.045). Conclusions: Although decreasing trends over time were noted, the prognosis of urogenital tuberculosis was more severe compared to other extrapulmonary tuberculosis sites.
Introduction
Tuberculosis (TB) remains an unresolved public health issue affecting annually millions of people [1]. In 2017, an estimated 10 million people developed TB worldwide and 1.6 million people died from the disease [1]. Targets of halving TB incidence, prevalence and mortality rates by 2015 compared with their levels in 1990 were set and were globally achieved [1]. The World Health Organization aims to end the TB epidemic by 2030, according to the Sustainable Development Goals [2].
TB is a multisystem disease that affects commonly the lungs, but any other organ can be affected as well. Urogenital tuberculosis (UGTB) is the second and the third most common extrapulmonary tuberculosis (EPTB) site in developing and developed countries, respectively [3,4]. It represented 20 to 40% of all EPTB cases, while isolated genital TB represented 9% of all EPTB cases [4,5]. Previous studies showed that both urinary and genital organs were involved in more than half of the cases [4]. The kidneys, the most commonly involved site in UGTB, were affected in 80% of the cases, while the epididymis was the most commonly affected genital organ in about 22-55% of the cases [4,6]. In the 2019 Global TB report, TB incidence in Tunisia was 35 cases / 100 000 population [7], and EPTB cases noted an increase through the few last years, reaching 20 to 40% of all TB cases [8]. The late onset of symptoms of UGTB, its myriad presentations and the insidious evolution explained the diagnosis and treatment delay. As a result, urogenital organ destruction and serious complications may occur such as chronic renal failure and infertility.
In Southern Tunisia, a highly endemic region for TB [9], updated and exhaustive UGTB data are lacking. Identifying its particularities would help both physicians and authorities to improve UGTB management. In this perspective, the aim of this work was to give an update on the epidemiological, clinical and evolutionary features of UGTB in the South of Tunisia.
Methods
Study design
We conducted a retrospective study including all patients diagnosed with EPTB over a 26-year period, from January 1992 to December 2017 in the South of Tunisia. We specified the particularities of UGTB cases, and we compared them with other EPTB cases.
Data collection and case definitions
We collected data from the regional tuberculosis register of Southern Tunisia, which was implemented as an integrate part of the National TB program. The center of TB received notified cases from both private and public healthcare structure. Exhaustive cases coming from both urban and rural districts were notified. Socio-demographic characteristics including age, gender and urbanity of residence were reviewed. Clinical and evolutionary features, such as diagnostic methods, clinical presentation, treatment, the follow up duration and the disease outcome were recorded. Recovery was defined as a urine negative sample for Mycobacterium, if it was previously isolated, and/or the stability or the absence of evolutionary lesions on radiological imaging.
All new cases of tuberculosis were included in our study. The diagnosis of UGTB was confirmed by microbiological and /or histological proof. In the remaining cases, it was based on clinical signs and imaging followed by an adequate response to antitubercular therapy.
Urinary tract TB included renal, ureteral and/ or bladder TB [10]. The female genital organs affected by Mycobacterium were represented by the fallopian tubes, uterine endometrium or myometrium, ovaries, cervix and vagina/vulva [5]. Male genital TB involved the epididymis, testis, prostate, seminal vesicle, vas deferens, urethra and penis [4,11]. Multifocal TB was defined as concurrent tubercular involvement of two or more non-contiguous organs [9,12].
Other EPTB sites included cases of lymph node TB, abdominal TB, osteoarticular TB, tuberculous meningitis and cutaneous TB.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS 20 software (IMB Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Categorical variables were expressed as numbers and percentages, while continuous variables were expressed by means and standard deviations, if they were normally distributed. Median and interquartile ranges (IQR) were used for non-normally distributed data. To compare two frequencies, we used Chi square test, while T-test was used to compare two means in independent samples. We calculated the correlation coefficient of Spearman (Rho) to analyze chronological trends over time. The odds ratio was used to measure the association between an exposure and an outcome. The difference between the groups was considered significant when p<0.05.
Results
Patients’ characteristics
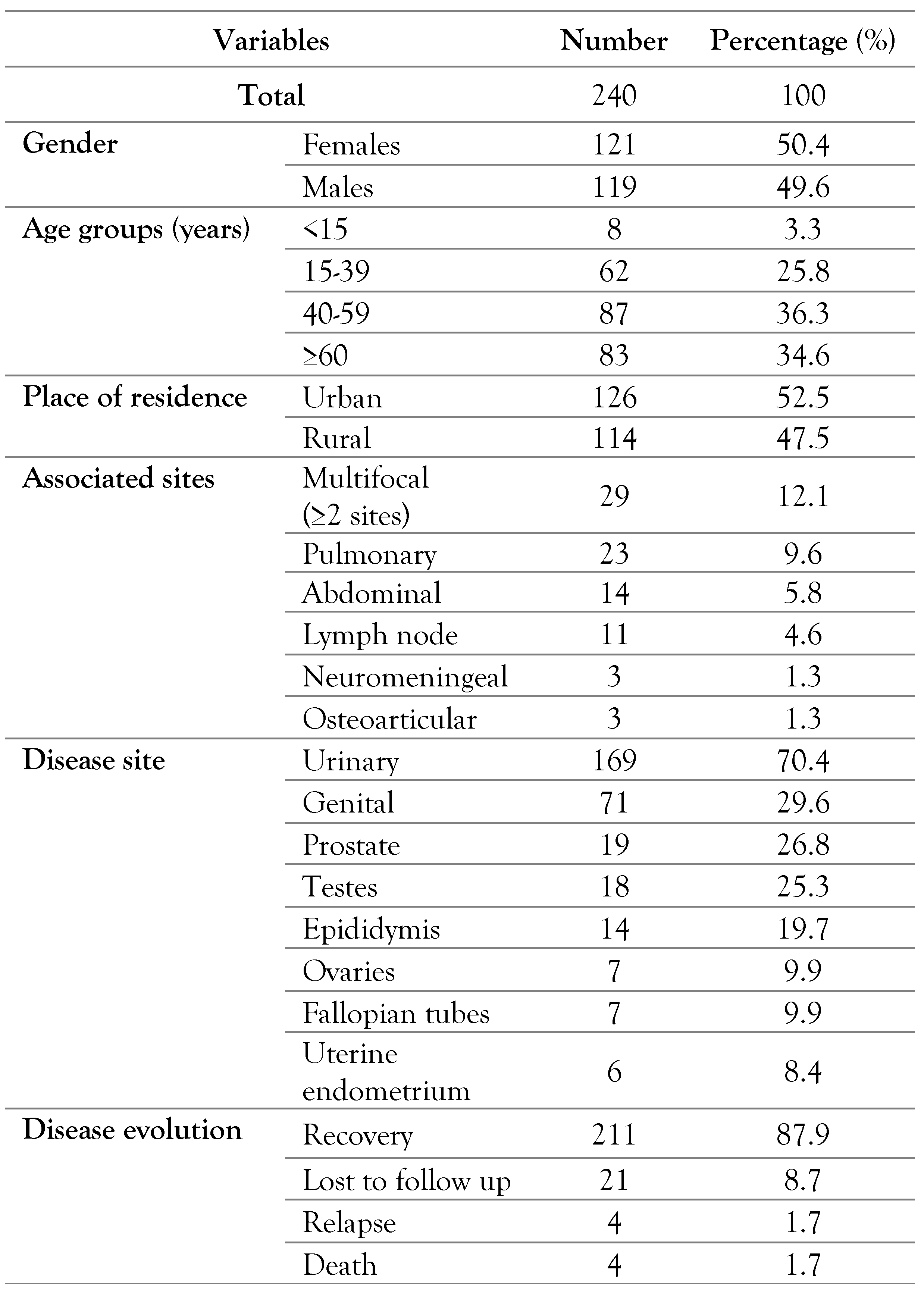
Over a 26-year period, 240 patients were diagnosed with UGTB, among 1702 patients with EPTB (14.1%), occupying the second most common EPTB site after lymph node TB. There were 121 women (50.4%). The mean age was 49±17 years. Eighty-seven patients were aged between 40 and 60 years (36.3%). According to the place of residence, 114 patients came from rural areas (47.5%). Multifocal TB was noted in 29 cases (12.1%). There were 23 cases (9.6%) with pulmonary TB associated with UGTB, among whom 16 cases (6.7%) had miliary TB. Abdominal and lymph node TB were associated to UGTB in 14 (5.8%) and 11 cases (4.6%), respectively.
There were 169 cases (70.4%) with urinary tract TB and 71 cases (29.6%) with genital TB. We noted 19 cases (26.8%) with prostate TB, 18 cases (25.3%) with testicular TB and 14 cases (19.7%) with epididymis TB.
The diagnosis of UGTB was based on histological evidence and microbiological evidence in 56.6% and 35.1% of the cases, respectively. Intradermal tuberculin reaction was positive in 75.7% of the cases. Antitubercular therapy was based on fixed drug combination in 37 cases (20.4%) and on separate drugs preparation in 203 cases (84.6%). The mean duration of treatment was 10±3 months. Recovery was noted in 211 cases (87.9%). Twenty-one patients were lost to follow-up (8.7%). We noted 4 relapsing cases (1.7%) and 4 deaths (1.7%) – Table 1.

Table 1.
Socio-demographic, clinical and evolutionary characteristics of patients with urogenital tuberculosis.
Chronological trends of urogenital tuberculosis between 1992 and 2017
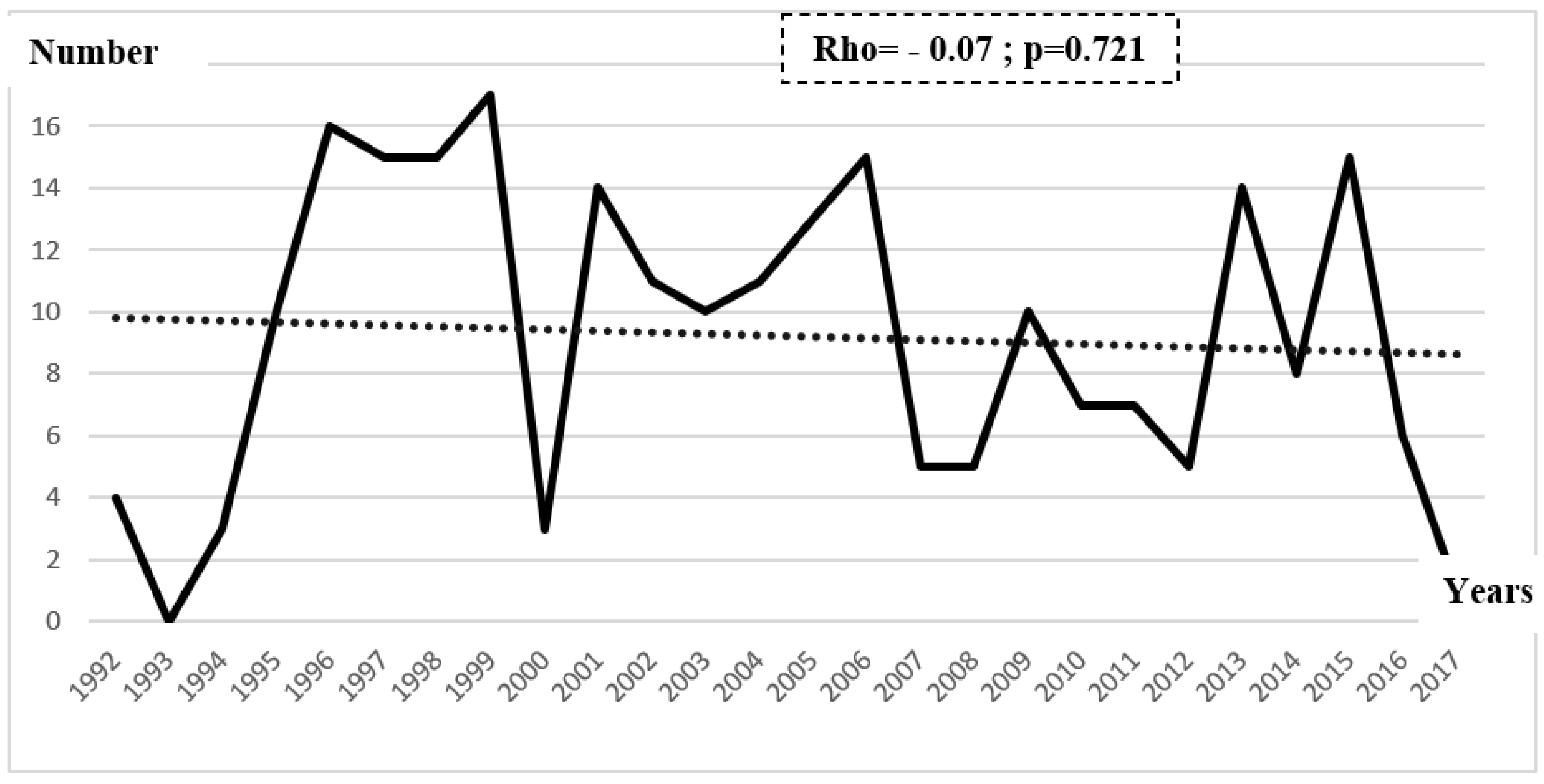
Chronological trends analysis showed that the number of UGTB new cases declined during the study period, without a statistical significance (Rho = -0.07; p=0.721) – Figure 1.
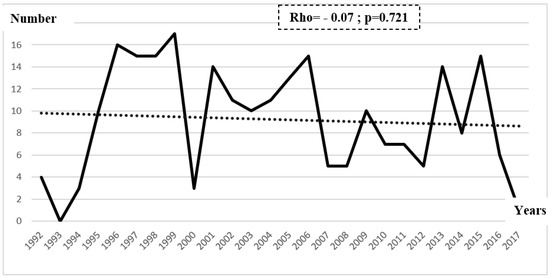
Figure 1.
Chronological trends of urogenital tuberculosis new cases between 1992 and 2017.
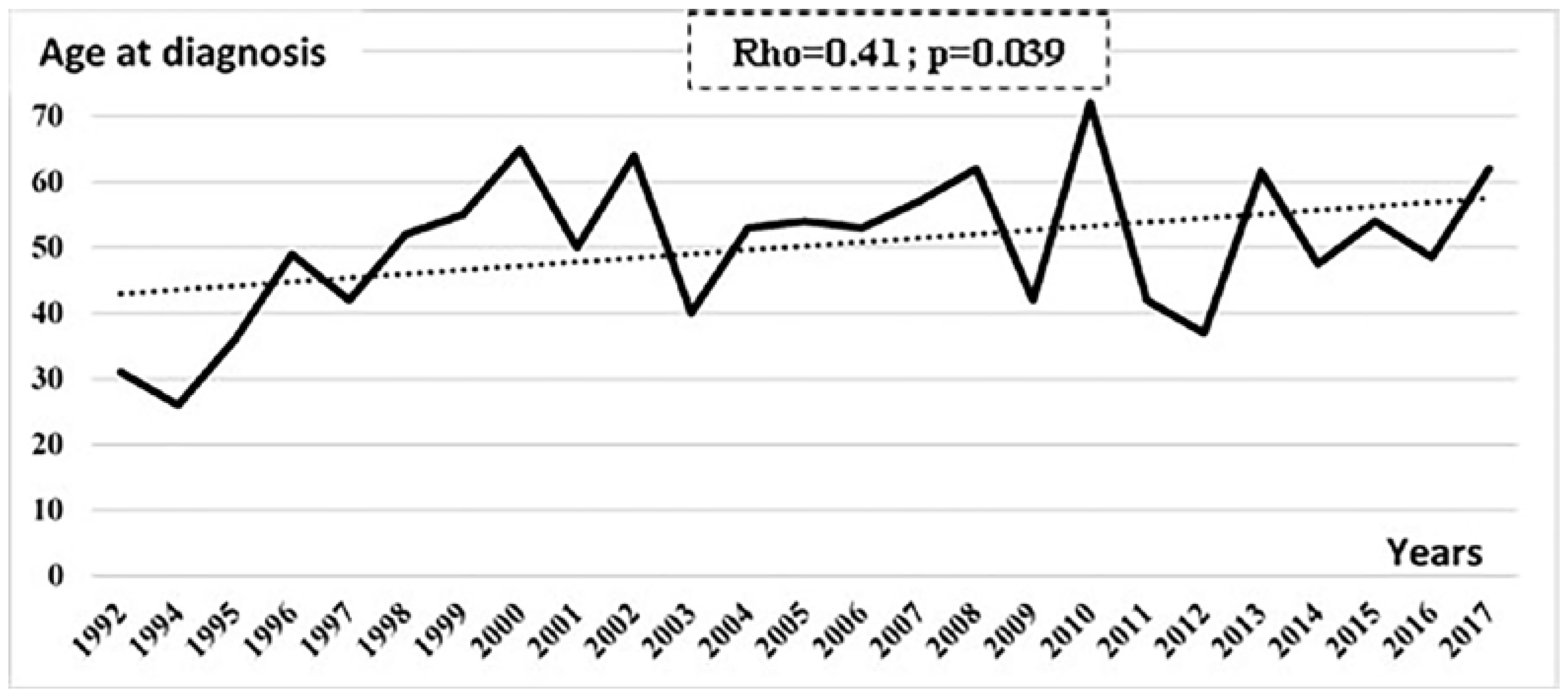
The case notification of UGTB increased significantly with increasing age between 1992 and 2017 (Rho=0.41; p=0.039) – Figure 2.
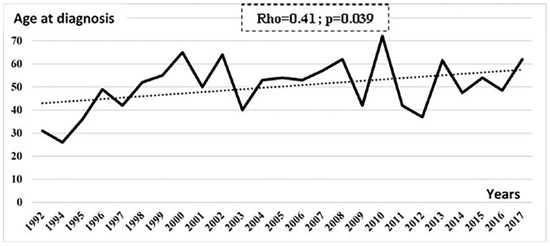
Figure 2.
Chronological trends of age at diagnosis of patients with urogenital tuberculosis between 1992 and 2017.
Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of urogenital tuberculosis
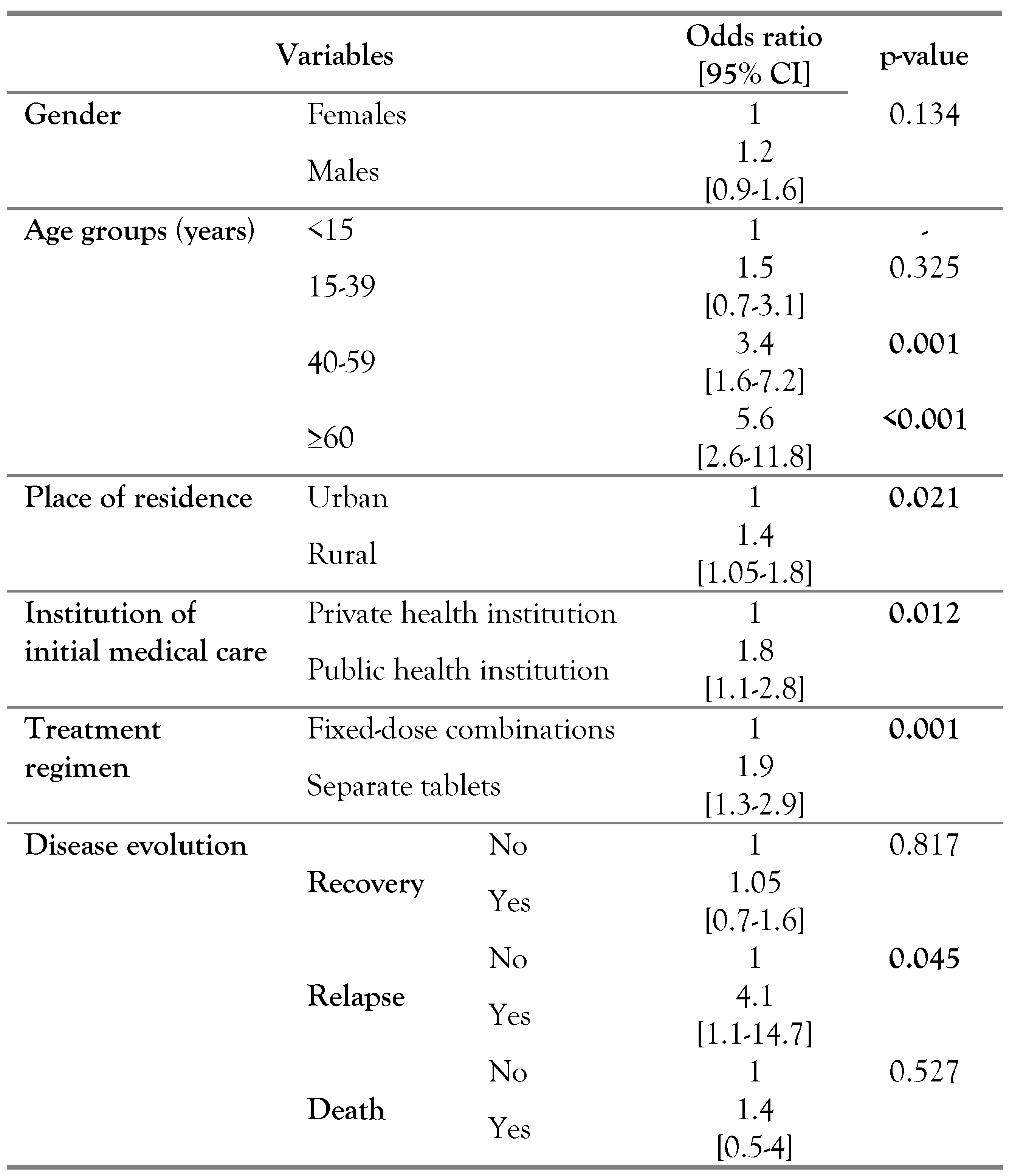
The mean age at diagnosis of UGTB was significantly higher than in other EPTB sites (49.5±18 vs 38.7±19.6, p<0.001). Patients aged 60 years and above (OR=2.7; p<0.001), coming from rural areas (OR=1.4; p=0.021), and referring to a public health institution (OR=1.8; p=0.012) were more frequently diagnosed with UGTB. Treatment regimen of separate tablets was significantly more prescribed for patients with UGTB (OR=1.9; p<0.001). Treatment duration was significantly longer in UGTB (10.13±3.79 vs 9.20±3.77 months; p<0.001). According to the disease evolution, relapse was significantly more frequent in UGTB patients (OR=4.1; p=0.045) – Table 2.

Table 2.
Epidemiological, therapeutic and evolutionary factors associated with urogenital tuberculosis in comparison with the other extrapulmonary tuberculosis forms.
Discussion
This study illustrated the potential burden of UGTB in Southern Tunisia during the last two decades. Compared to other EPTB forms, UGTB had a poorer prognosis and affected more commonly high-risk patients. A high incidence of UGTB was reported, ranking the second most common EPTB site after lymph node TB. In Poland, it occupied the third place after pleural and lymph node TB [13]. As for Europe and North America, it ranked fourth, representing 1.3% to 14.3% of all EPTB cases [14]. Actually, UGTB results from hematogenous spread of Mycobacterium, which usually occurs secondary to TB in other sites, mostly the lungs [14,15]. Primary tuberculous infection might be asymptomatic and undiagnosed until the reactivation of quiescent bacterium. In Japan, 31% of UGTB patients had a history of TB [16]. Previous research showed that UGTB occurred in 2 to 20% of pulmonary TB patients, worldwide [16]. Besides, 28% of patients with pulmonary TB had prostate TB [3], which was higher than our results. This might be explained by the misdiagnosis and the underestimation of UGTB cases among patients with pulmonary TB, which took all the attention. Another form of TB transmission to the urogenital tract was described in literature, the intravesical administration of Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG), which was used as a therapy for superficial bladder cancer [14,17].
According to age categories, the occurrence of UGTB increased with increasing age. This might be related to the diagnosis delay, since UGTB, usually asymptomatic, is known for its insidious evolution and its myriad presentations leading therefore to dissemination of the infection [14,18]. In fact, it has been reported that the latency period between pulmonary infection and clinical UGTB was 22 years on average [18].
UGTB was significantly more frequent in rural areas, which was concordant with results noted in the literature [19]. This might be explained by the different lifestyle, the low socio-economic status and the different environmental variables. In this context, it has been shown that TB was more common among groups living in conditions of malnutrition, poverty, unemployment, political instability and especially poor health education [19]. These results were in contrast with those noted in Poland, where a ratio of 4.12 urban to rural areas was noted [13]. Therefore, implementing a preventive strategy and strengthening TB care in both rural and urban areas are highly recommended in the local area.
Treatment duration was significantly longer in UGTB compared to other EPTB sites. In a previous Tunisian study, anti-tubercular therapy was required for a 12 months duration [8]. However, 6 months duration was considered adequate in most forms of EPTB, except for tuberculous meningitis as well as bone and joint TB [20]. On the other hand, other studies showed that 6 months duration was as effective as 9 months duration for the treatment of female genital TB [21]. In light of the lack of standard recommendations for adequate treatment duration of UGTB, physicians opt for a prolonged therapy in order to ensure recovery.
The localization of UGTB was a predictor of relapse in our study population. In fact, relapse was significantly more frequent among patients with UGTB than other EPTB sites, which might be explained, firstly, by the insufficient duration of treatment as well as the diagnosis and treatment delay and secondly by malnutrition and poor social conditions [22].
During the study period, chronological trends analysis showed that the number of UGTB new cases declined, without a statistical significance, which differs from other EPTB sites. In fact, previous studies reported a significant growing trend in the TB incidence rate, all forms combined, as well as EPTB cases, between 1995 and 2016, in south of Tunisia [23].
Conclusions
Our study highlighted the substantial burden of UGTB in Southern Tunisia. Although decreasing trends over time were noted, the prognosis of UGTB was more severe compared to other EPTB sites. Therefore, multi-sectorial interventions including physicians, microbiologists and epidemiologists should be integrated in the first line and primary healthcare structures in order to improve access to treatment and early screening of TB cases. It should be diagnosed and managed with adequate anti-tubercular therapy at an early state so as to avoid serious complications and relapse.
Author Contributions
FH, MK, CM, JD and MBJ designed and supervised the study and drafted the manuscript. FH, MK, HBA and KR collected and analyzed the data and performed the background literature review for the manuscript. FH, MK, HBA, MaBJ, MBH, MT and MBJ carried out the laboratory work, conducted the statistical analyses and drafted the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
None to declare.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors – none to declare.
References
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report. 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/ (accessed on 4 February 2020).
- United Nations. Ensure Healthy Lives and Promote Wellbeing for All at All Ages. Sustainable Development Goals. 2018. Available online: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/health/ (accessed on 4 February 2020).
- Kulchavenya, E.; Kholtobin, D. Diseases masking and delaying the diagnosis of urogenital tuberculosis. Ther Adv Urol 2015, 7, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Singh, P.; Hemal, A.; Kumar, R. Genital tuberculosis: Current status of diagnosis and management. Transl Androl Urol 2017, 6, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, G.A.; Devaleenal, D.B.; Natrajan, M. Genital tuberculosis in females. Indian J Med Res 2017, 145, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.J.; Lee, W.; Jeong, W.Y.; et al. Chronic kidney disease with genitourinary tuberculosis: Old disease but ongoing complication. BMC Nephrol 2018, 19, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report. 2019. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/329368/9789241565714-eng.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 15 June 2020).
- Zayet, S.; Berriche, A.; Ammari, L.; et al. [Epidemio-clinical features of genital tuberculosis among Tunisian women: A series of 47 cases]. Pan Afr Med J 2018, 30, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigui, M.; Ben Ayed, H.; Koubaa, M.; et al. Multifocal tuberculosis in southern Tunisia what is specific with? J Tuberc 2018, 2, 1006. [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor, R.; Ansari, M.S.; Mandhani, A.; Gulia, A. Clinical presentation and diagnostic approach in cases of genitourinary tuberculosis. Indian J Urol 2008, 24, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhonkar, A.; Tambe, S.; Aswani, Y.; Nayak, C.S. Case series of genital tuberculosis. Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS 2017, 38, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Patil, T.B.; Lalla, R. Disseminated tuberculosis manifesting as pulmonary, meningeal and spinal tuberculosis in an immunocompetent patient. BMJ Case Rep 2012, 2012, bcr2012007778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagodziński, J.; Zielonka, T.M.; Peplińska, K.; Życińska, K. Tuberculosis of the urogenital tract in adults in a tertiary referral center. Adv Exp Med Biol 2018, 1040, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillion, A.; Koutlidis, N.; Froissart, A.; Fantin, B. [Investigation and management of genito-urinary tuberculosis]. Rev Med Interne 2014, 35, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J. Genitourinary presentation of tuberculosis. Rev Urol 2015, 17, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakane, K.; Yasuda, M.; Deguchi, T.; et al. Nationwide survey of urogenital tuberculosis in Japan. Int J Urol 2014, 21, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Jacoiste Asín, M.A.; Fernández-Ruiz, M.; López Medrano, F.; et al. Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) infection following intravesical BCG administration as adjunctive therapy for bladder cancer: Incidence, risk factors, and outcome in a single-institution series and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 2014, 93, 236–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, A.A.; Lucon, A.M.; Junior, R.F.; Srougi, M. Epidemiology of urogenital tuberculosis worldwide. Int J Urol 2008, 15, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghinejad, J.; Sadeghi Oroumiyeh, A.; Barati, B.; Karimi, S.; Jahantab, M.; Molayi Kohneshahri, S. Epidemiologic study of tuberculosis during 2006–2015 in Salmas, Iran. Int J Health Life Sci 2018, 4, e80210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y. Diagnosis and treatment of extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul) 2015, 78, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, J.B.; Singh, N.; Dharmendra, S.; et al. Six months versus nine months anti-tuberculous therapy for female genital tuberculosis: A randomized controlled trial. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2016, 203, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokce, G.; Kilicarslan, H.; Ayan, S.; et al. Genitourinary tuberculosis: A review of 174 cases. Scand J Infect Dis 2002, 34, 338–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Ayed, H.; Koubaa, M.; Gargouri, L.; et al. Epidemiology and disease burden of tuberculosis in south of Tunisia over a 22-year period: Current trends and future projections. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© GERMS 2020.