Combustion Enhancement of Pulverized Coal with Targeted Oxygen-Enrichment in an Ironmaking Blast Furnace
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geometry and Operating Condition
3. Model Description
3.1. Basic Equations
3.2. Reaction Process
4. Results and Discussion
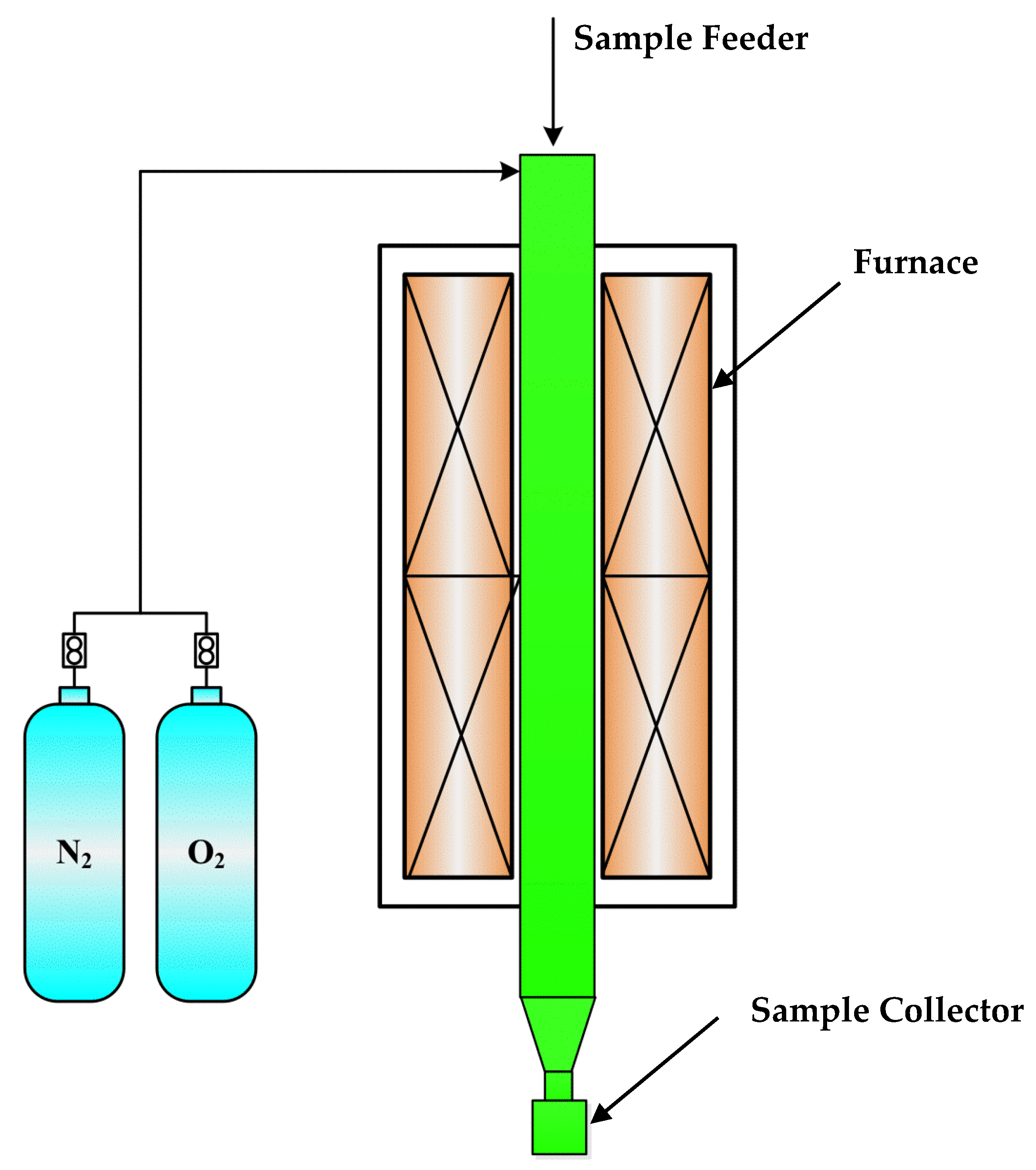
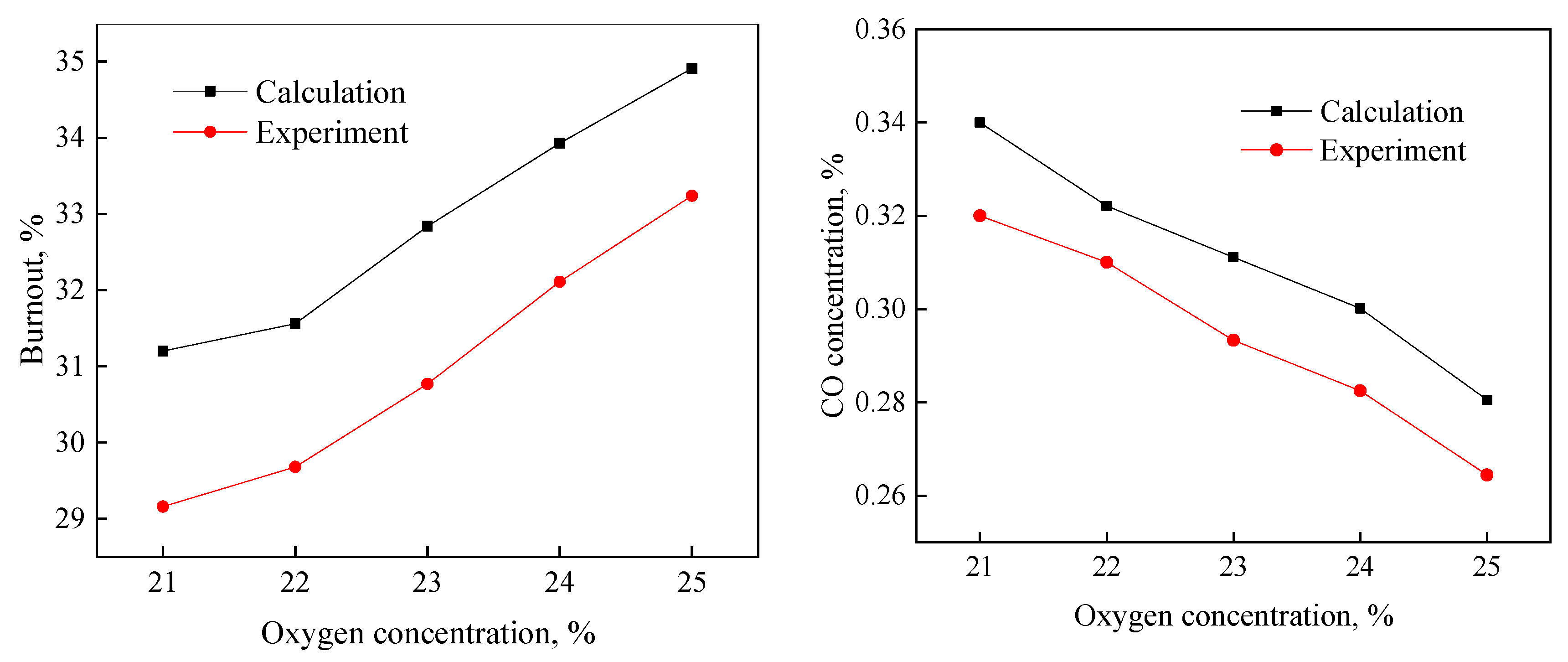
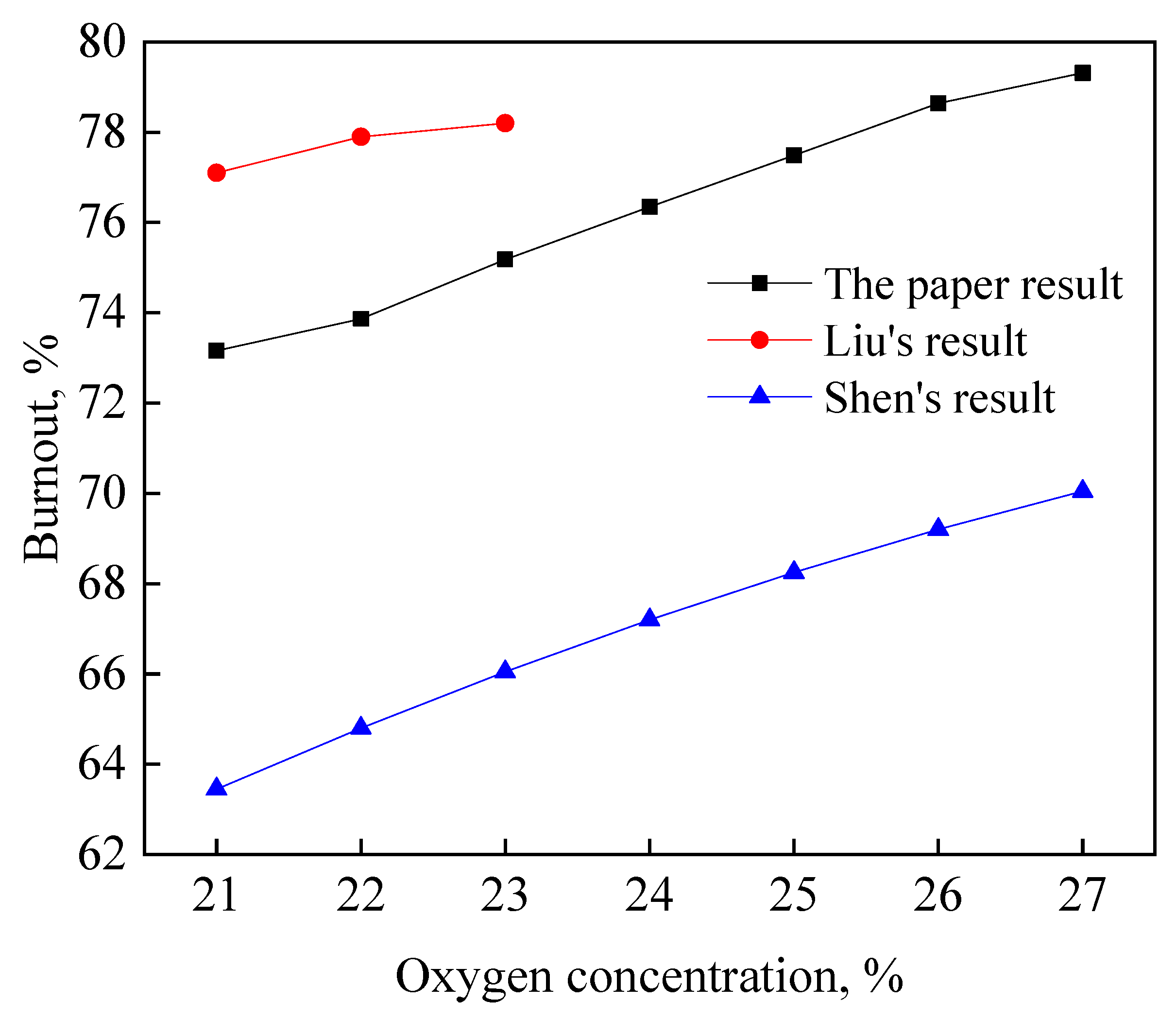
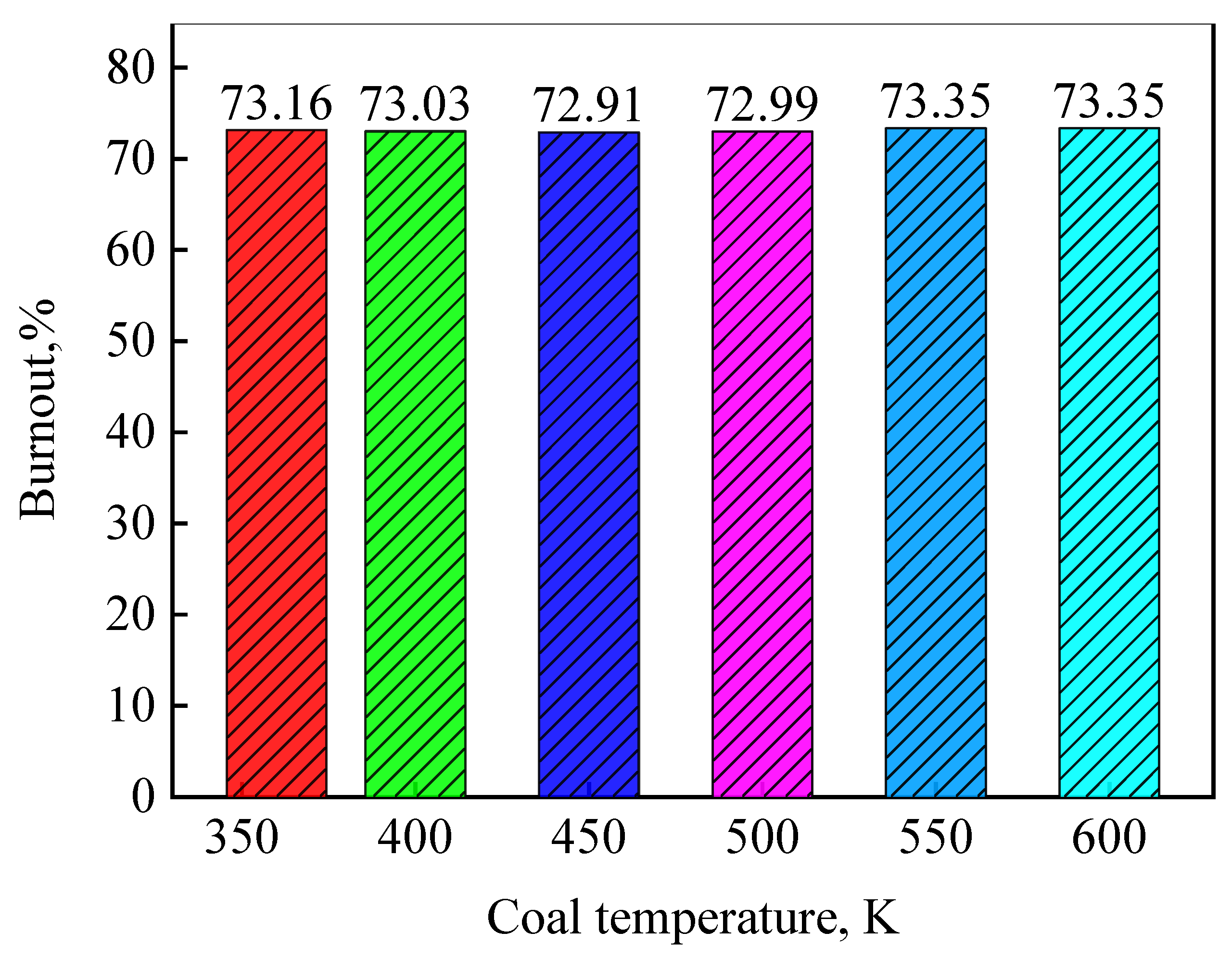
4.1. Model Validation
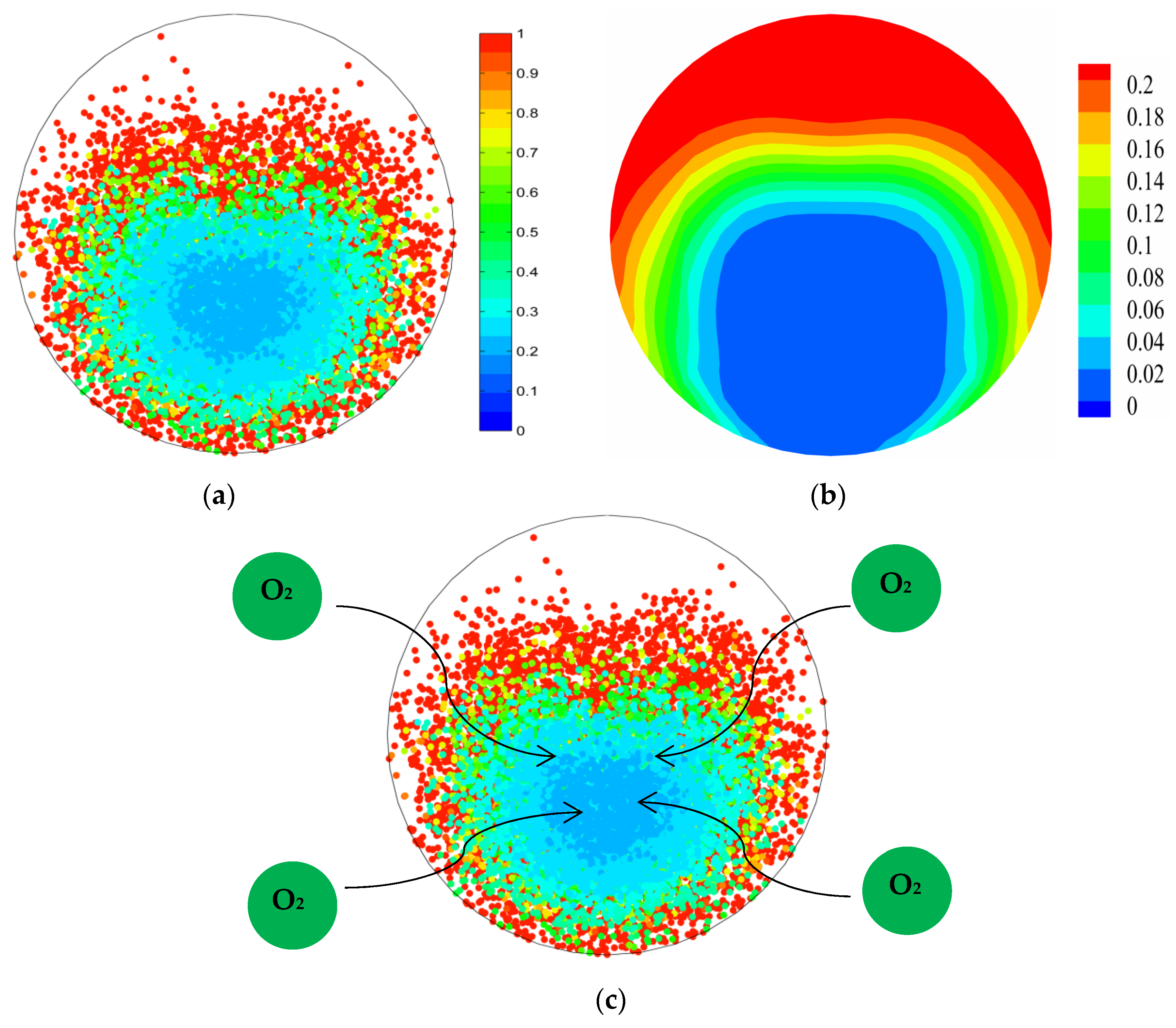
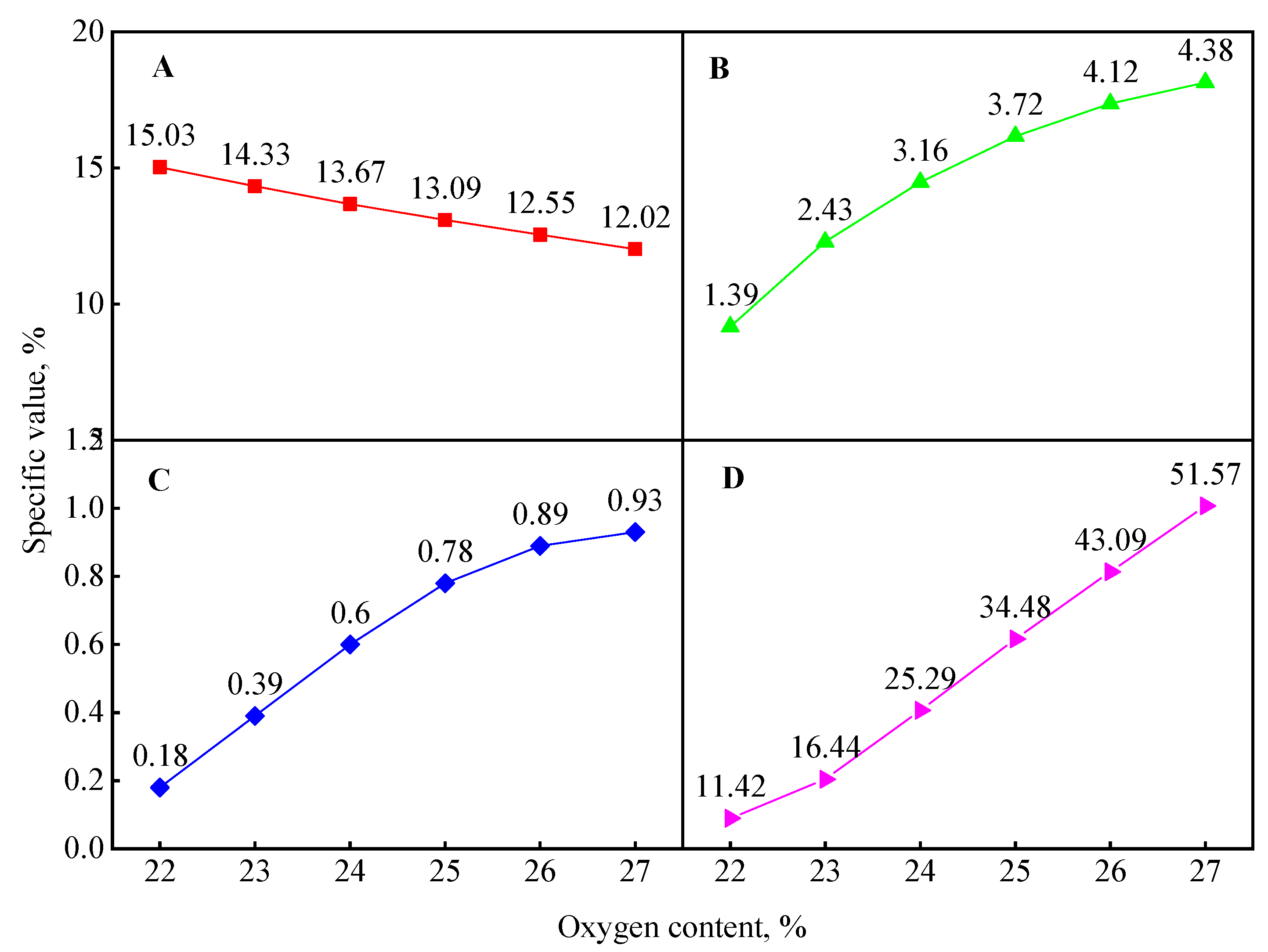
4.2. Concept of Targeted Oxygen-Enrichment
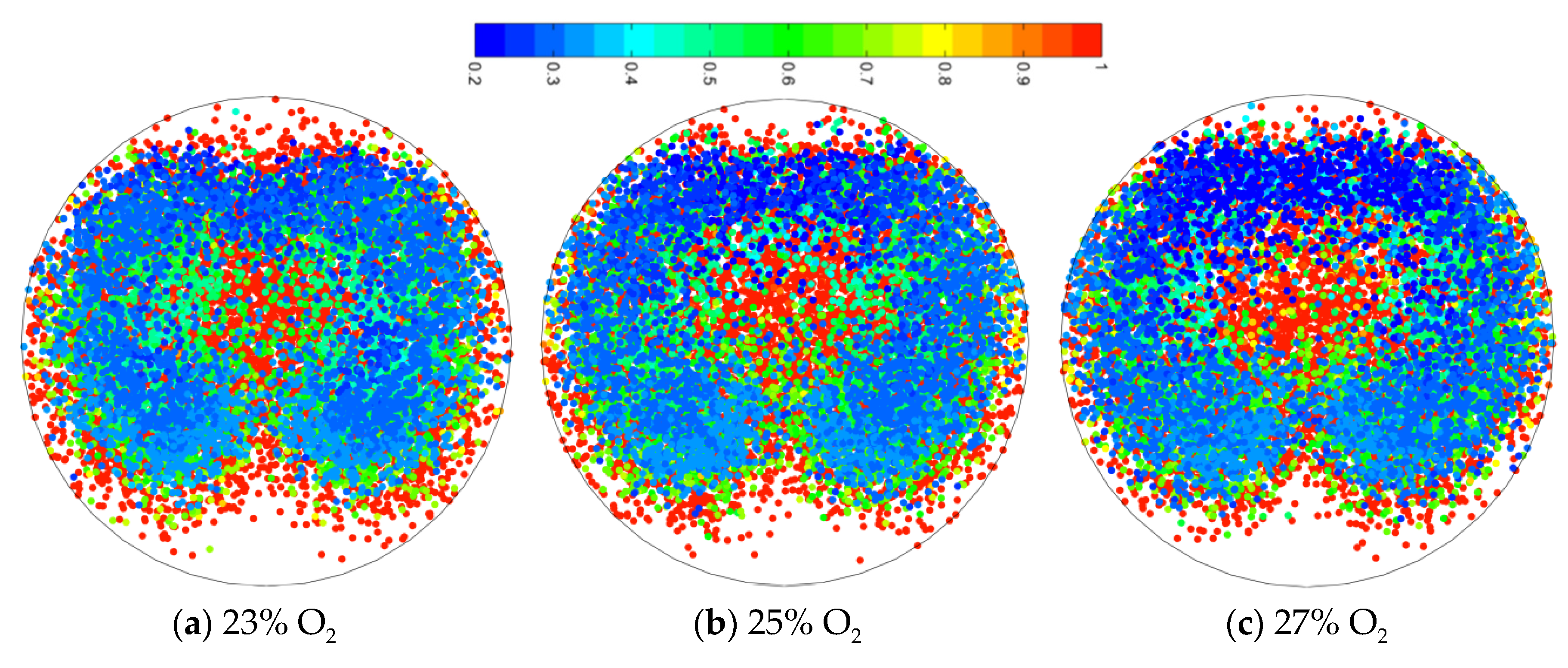
4.3. Coal Combustion Characteristics under Targeted Oxygen-Enrichment
4.4. Effect of Coal Particles Temperature
5. Conclusions
- (1)
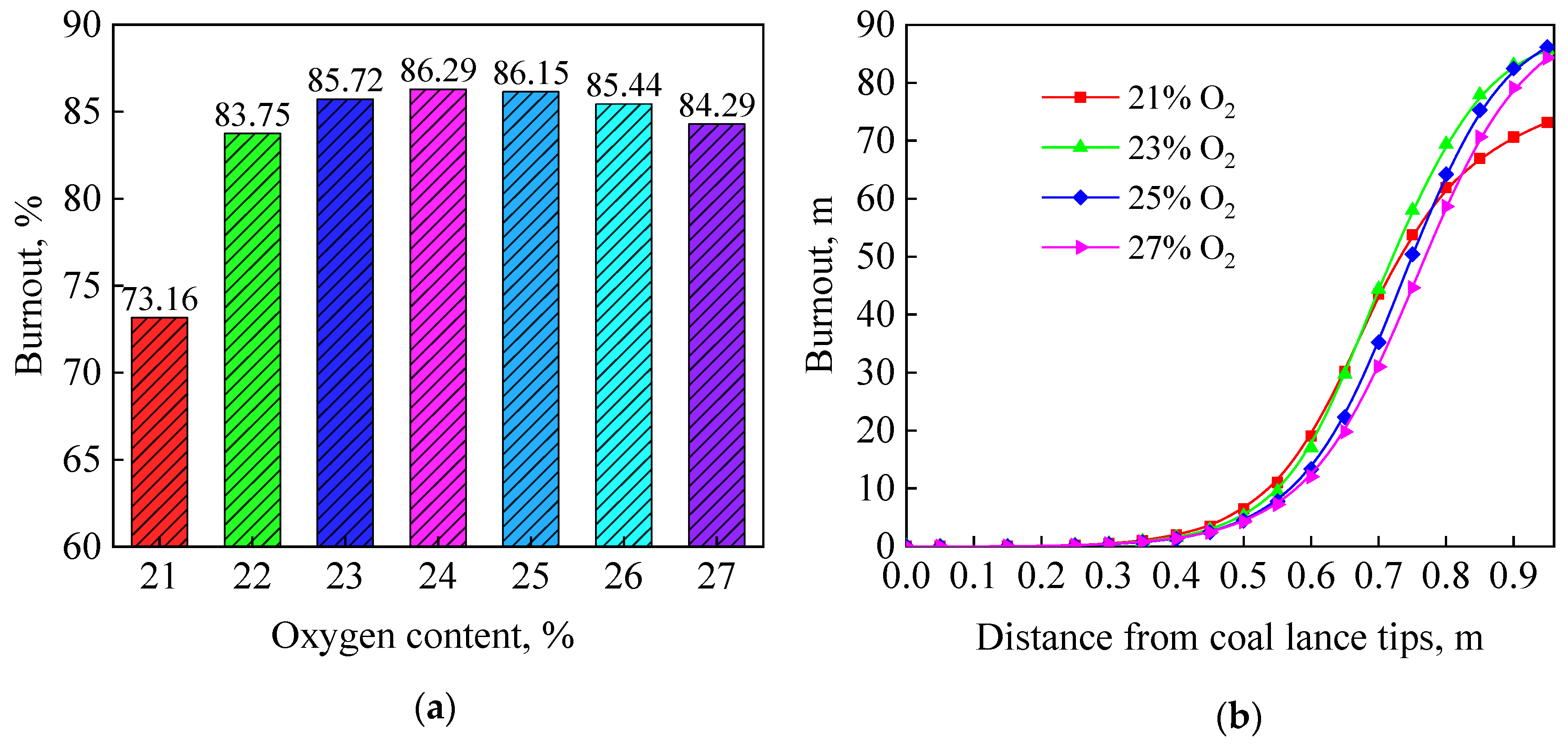
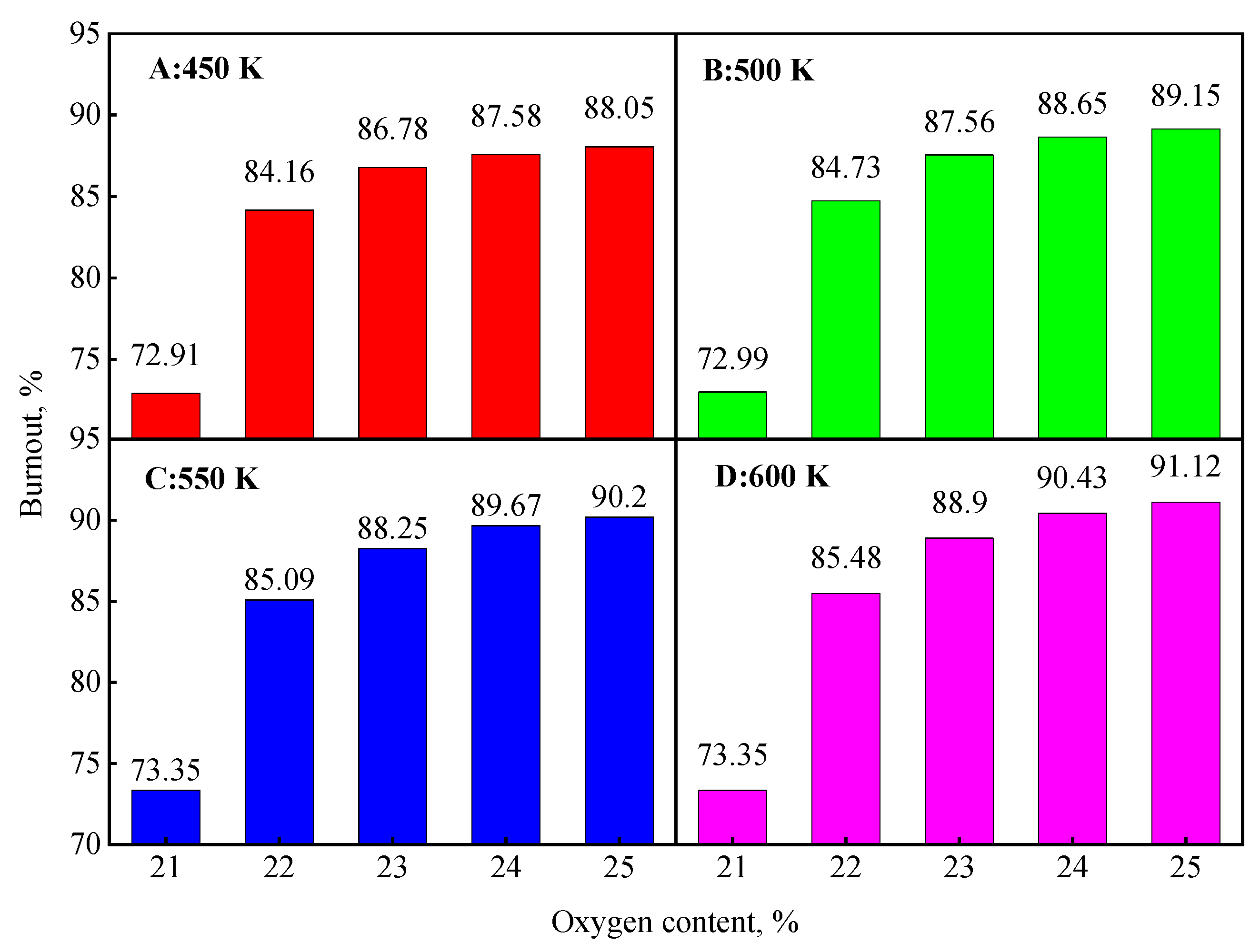
- The coal burnout increases significantly under targeted oxygen-enrichment. When the oxygen concentration is 22%, the coal burnout has an increase of 10.59%; when the oxygen concentration is 24%, the coal burnout has an increase of 13.13%, which is the maximum.
- (2)
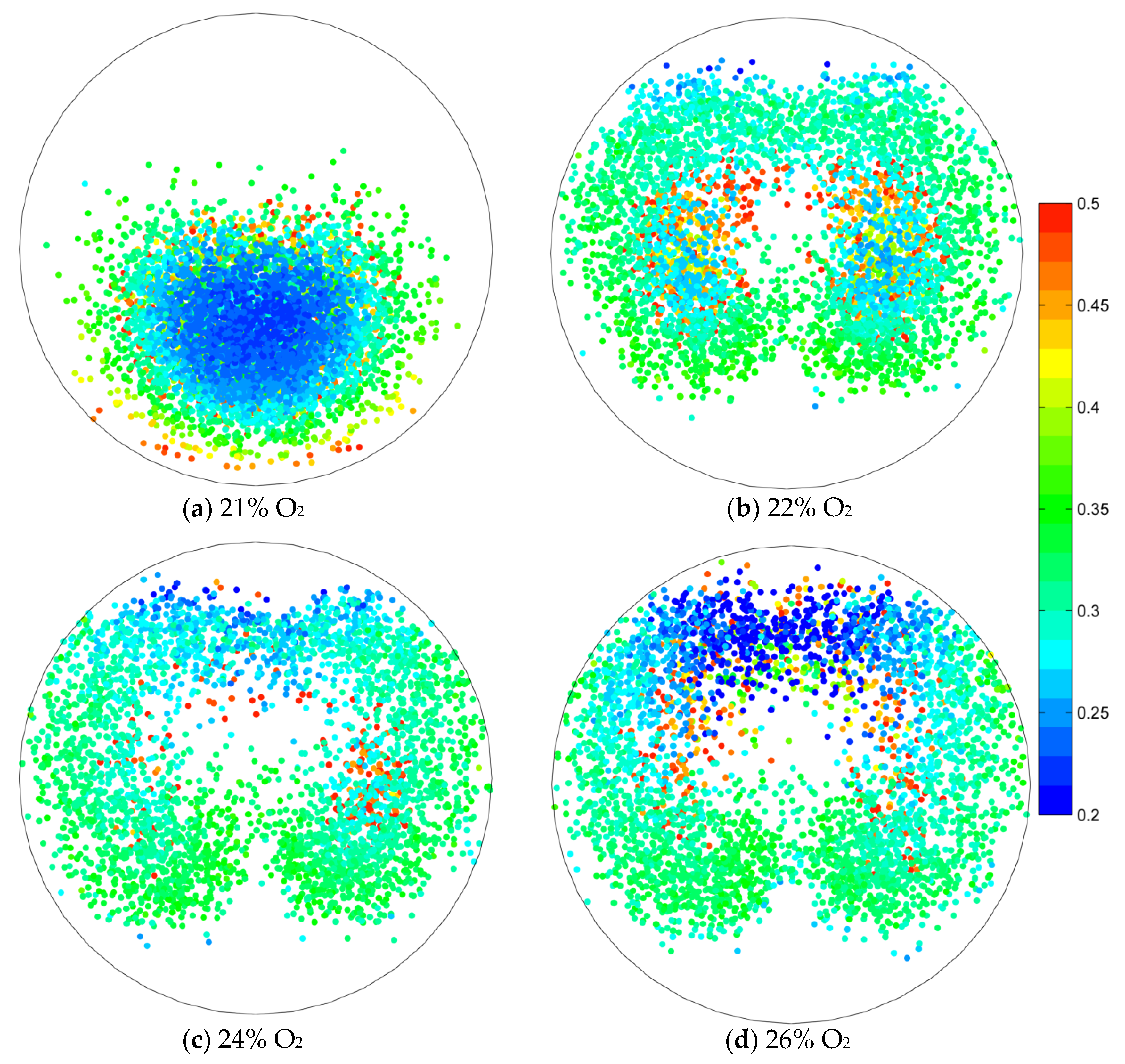
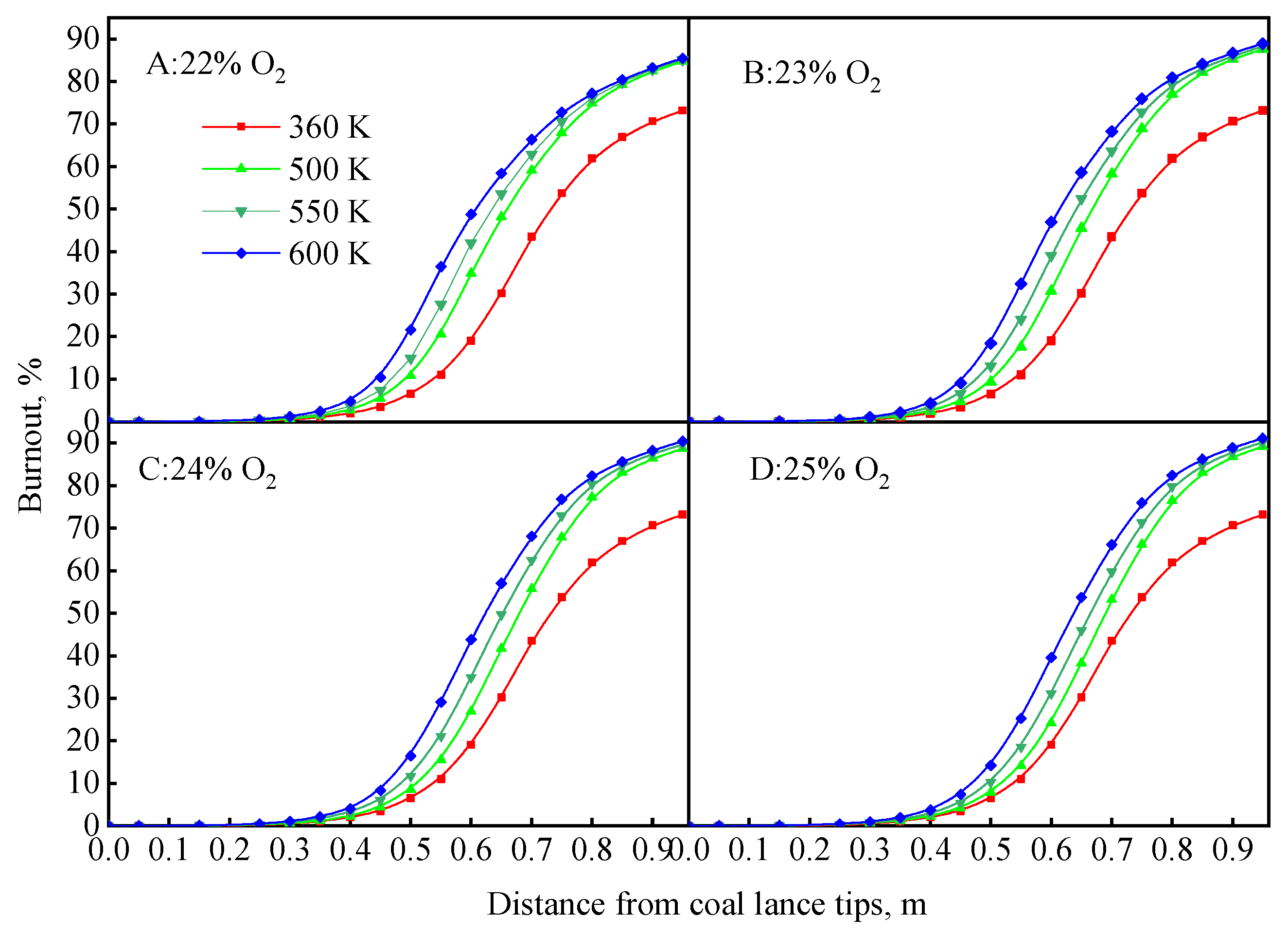
- The coal will increase only by increasing the oxygen concentration of the lower-burnout region. The oxygen concentration of the lower-burnout region is greatly increased under targeted oxygen-enrichment, while the coal particles are more dispersed under the effect of the oxygen stream.
- (3)
- When more oxygen is added, the increase of coal burnout is unclear. The coal burnout of 22% O2 is 83.75%, but the value of 23% O2 is only 85.72%. This is because the new lower-burnout region appears and is more dispersed under the effect of oxygen stream. This will be the main direction for future investigations to promote the dispersion of oxygen.
- (4)
- The hysteresis of the coal combustion process caused by the room-temperature oxygen disappears and the coal burnout is further increased by increasing coal particle temperature. When the coal particle temperature was 600 K, the coal burnout was 85.48% at 1% oxygen enrichment, an increase of 12.13%; the coal burnout was 91.12% at 4% oxygen enrichment, an increase of 17.96%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geerdes, M.; van Laar, R.; Vaynshteyn, R. Low-cost hot metal: The future of blast furnace ironmaking. Iron Steel Technol. 2011, 8, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.-H.; Du, S.-W.; Tsai, C.-H.; Wang, Z.-Y. Torrefied biomasses in a drop tube furnace to evaluate their utility in blast furnaces. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 111, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suopajarvi, H.; Pongrácz, E.; Fabritius, T. Bioreducer use in Finnish blast furnace ironmaking–Analysis of CO2 emission reduction potential and mitigation cost. Appl. Energy 2014, 124, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.; Wu, S.; Zhu, H.; Yu, A.; Tsai, S. Experimental and numerical investigations of gouge formation related to blast furnace bur-den distribution. Miner. Eng. 2009, 22, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-T.; Zhao, W.; Chu, M.-S.; Feng, C.; Liu, Z.-G.; Tang, J. Current status and development trends of innovative blast furnace ironmaking technologies aimed to environmental harmony and operation intellectualization. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2017, 24, 751–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushnir, D.; Hansen, T.; Vogl, V.; Ahman, M. Adopting hydrogen direct reduction for the Swedish steel industry: A technological innovation system (TIS) study. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Yu, A. Modelling of injecting a ternary coal blend into a model ironmaking blast furnace. Miner. Eng. 2016, 90, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-H.; Cheng, W.-Y.; Lu, K.-M.; Huang, Y.-P. An evaluation on improvement of pulverized biomass property for solid fuel through torrefaction. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 3636–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.-W.; Wang, J.-S.; Lan, R.-Z.; Han, Y.-H.; Xue, Q.-G. Softening and Melting Behavior of Mixed Burden for Oxygen Blast Furnace. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2013, 20, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.S.; Maldonado, D.; Guo, B.Y.; Yu, A.B.; Austin, P.; Zulli, P. Computational Fluid Dynamics Study of Pulverized Coal Combustion in Blast Furnace Raceway. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 10314–10323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shen, Y. CFD study of charcoal combustion in a simulated ironmaking blast furnace. Fuel Process. Technol. 2019, 191, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.-W.; Yeh, C.-P.; Chen, W.-H.; Tsai, C.-H.; Lucas, J.A. Burning characteristics of pulverized coal within blast furnace raceway at various injection operations and ways of oxygen enrichment. Fuel 2015, 143, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.-P.; Du, S.-W.; Tsai, C.-H.; Yang, R.-J. Numerical analysis of flow and combustion behavior in tuyere and raceway of blast furnace fueled with pulverized coal and recycled top gas. Energy 2012, 42, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeski, A.; Runstedtler, A.; D’Alessio, J.; MacFadyen, N. Injection of Pulverized Coal and Natural Gas into Blast Furnaces for Iron-making: Lance Positioning and Design. ISIJ Int. 2015, 55, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhou, P.; Yan, H.; Shi, P.; Zhou, C.Q. Numerical investigation of the effects of size segregation on pulverized coal combus-tion in a blast furnace. Powder Technol. 2019, 342, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shen, Y. Three-dimensional modelling of charcoal combustion in an industrial scale blast furnace. Fuel 2019, 258, 116088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhu, J.; Wu, S.; Shen, Y. Co-combustion of semicoke and coal in an industry ironmaking blast furnace: Lab experiments, model study and plant tests. Fuel Process. Technol. 2019, 196, 106165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.-W.; Chen, W.-H.; Lucas, J. Performances of pulverized coal injection in blowpipe and tuyere at various operational conditions. Energy Convers. Manage. 2007, 48, 2069–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhou, P.; Zhou, C.Q. Evaluation of pulverized coal utilization in a blast furnace by numerical simulation and grey relation-al analysis. Appl. Energy 2019, 250, 1686–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Guo, B.; Yu, A.; Zulli, P. Model Study of the Effects of Coal Properties and Blast Conditions on Pulverized Coal Combustion. ISIJ Int. 2009, 49, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, R.; Kashihara, Y.; Murao, A.; Sato, M. Convergent-divergent injection lance for the enhancement of combustion efficiency of pulverized coal at blast furnace. ISIJ Int. 2016, ISIJINT-2015-556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Huo, H.; Wang, G.; Xue, Q.; She, X.; Wang, J. Effect of Oxygen-Coal Lance Configurations on Coal Combustion Behavior. Steel Res. Int. 2016, 88, 1600197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Shiozawa, T.; Austin, P.; Yu, A. Model study of the effect of bird’s nest on transport phenomena in the raceway of an ironmaking blast furnace. Miner. Eng. 2014, 63, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Xue, Q.; Li, C.; Wang, G.; She, X.; Wang, J. Coal flow and combustion characteristics under oxygen enrichment way of oxygencoal double lance. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 123, 1096–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayanta, A.T.; Alam, S.; Nakaso, K.; Fukai, J.; Kunitomo, K.; Shimizu, M. Combustibility of biochar injected into the raceway of a blast furnace. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 117, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Shang, T.; Zeng, J.; Wang, S.; Gong, Y.; Hui, S.E. Effect of Pulverized Coal Preheating on NO x Reduction during Combustion. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 4436–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
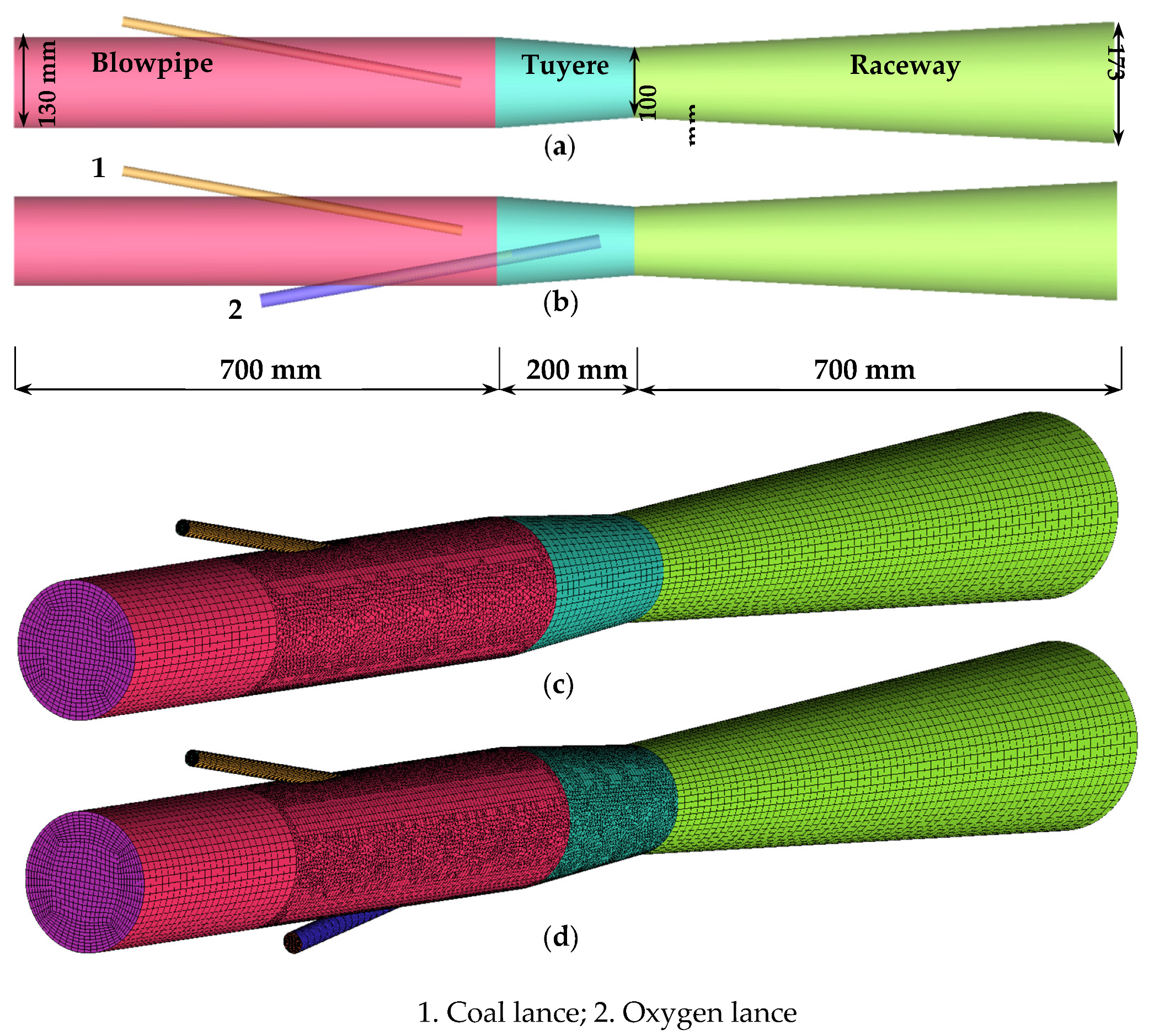



| (a) | |||
| Number of mesh | 171,014 | 260,414 | 361,322 |
| Burnout | 73.28 | 73.16 | 73.24 |
| (b) | |||
| Number of mesh | 254,021 | 403,621 | 577,334 |
| Burnout | 83.66 | 83.75 | 83.72 |
| Hot blast | |
| Temperature, K | 1473 |
| Volume, Nm3/t·HM | 1127 |
| Velocity, m/s | 93.05 |
| Oxygen content, % | 21 |
| Coal | |
| Coal rate, kg/s | 0.091 |
| Coal ratio, kg/t·HM | 150 |
| Oxygen | |
| Temperature, K | 298 |
| Content, % | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 |
| Velocity, m/s | 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48 |
| (a) | |
| Mass | |
| Momentum | |
| Energy | |
| Gas species | |
| Turbulent kinetic energy | |
| Turbulent dissipation rate | |
| (b) | |
| Mass | |
| Momentum | |
| Energy | |
| Reacions | Reaction Rate | Reaction Kinetics |
|---|---|---|
| Raw coal→VM+Char R1 | ||
|
VM+O2→CO+H2O+N2 R2 CO+0.5O2= CO2 R3 H2+0.5O2= H2O R4 VM+18O2→C18O+H218O+N2 R5 C18O+0.518O2= C18O2 R6 C18O+0.5O2= C18OO R7 CO+0.518O2= C18OO R8 H2+0.518O2= H218O R9 | ||
| Φchar+O2→2(Φ-1)CO+(2-Φ)CO2 R10 | ||
| Φchar+18O2→2(Φ-1)C18O+(2-Φ)C18O2 R11 | ||
| Φchar+C18O2→2C18O R12 | ||
| Φchar+C18OO→C18O+CO R13 | ||
| Φchar+H218O→C18O+H2 R14 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Z.; Wang, R.; Yi, Q.; Wang, G.; Ma, C. Combustion Enhancement of Pulverized Coal with Targeted Oxygen-Enrichment in an Ironmaking Blast Furnace. Processes 2021, 9, 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9030440
Zhou Z, Wang R, Yi Q, Wang G, Ma C. Combustion Enhancement of Pulverized Coal with Targeted Oxygen-Enrichment in an Ironmaking Blast Furnace. Processes. 2021; 9(3):440. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9030440
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Zhenfeng, Ruihao Wang, Qiujie Yi, Guang Wang, and Chunyuan Ma. 2021. "Combustion Enhancement of Pulverized Coal with Targeted Oxygen-Enrichment in an Ironmaking Blast Furnace" Processes 9, no. 3: 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9030440
APA StyleZhou, Z., Wang, R., Yi, Q., Wang, G., & Ma, C. (2021). Combustion Enhancement of Pulverized Coal with Targeted Oxygen-Enrichment in an Ironmaking Blast Furnace. Processes, 9(3), 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9030440





