Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Modelling and Application for Sterilization of Foods: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Backgrounds for Thermal Treatment of Foods
Thermal Inactivation of Microorganisms
3. The Governing Equations in Thermal Processing
4. Turbulence Modelling
5. Applications of CFD Models in the Thermal Processing of Foods
5.1. Constitution of the CFD Model
5.2. Solid and Very Viscous Foods
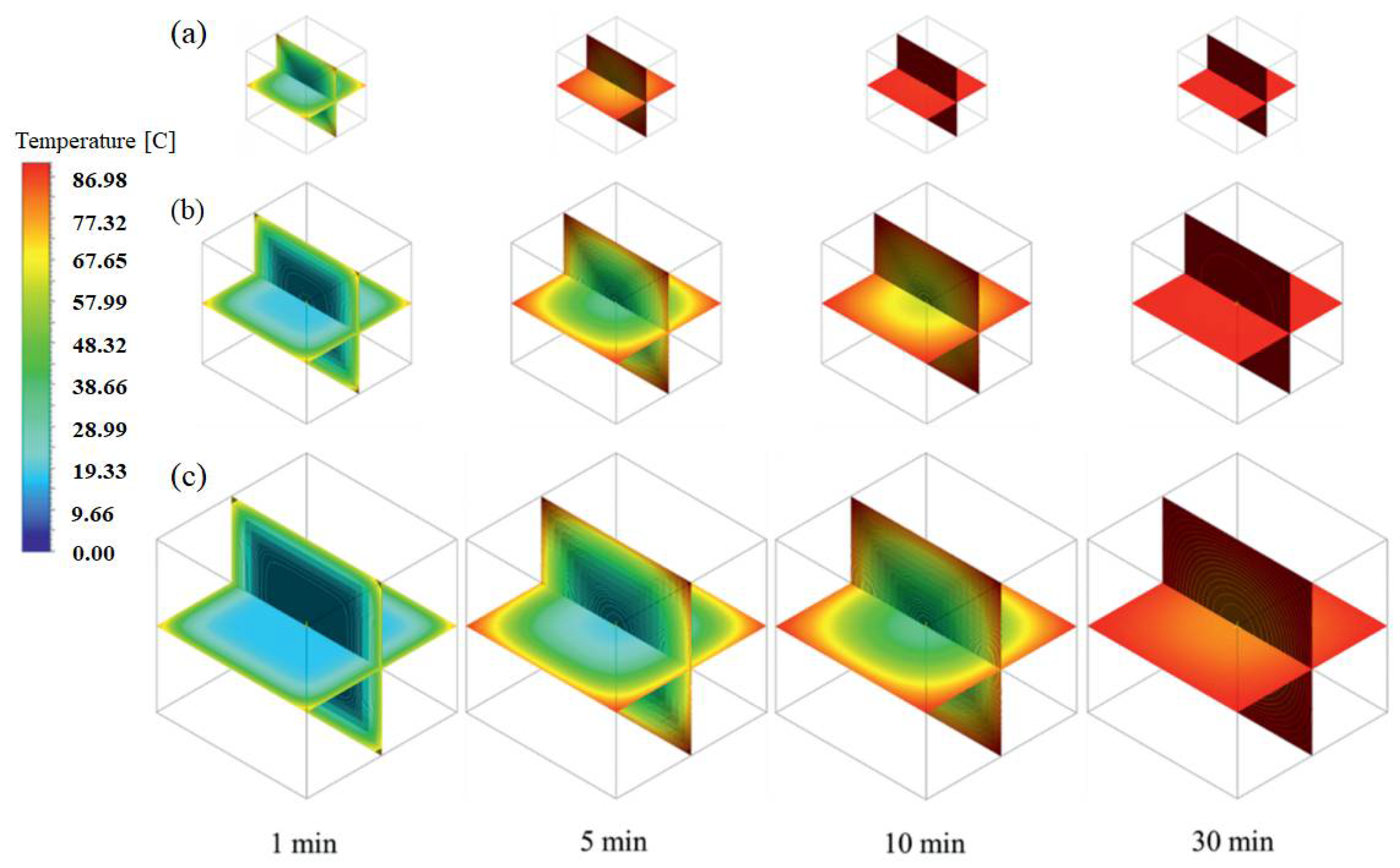
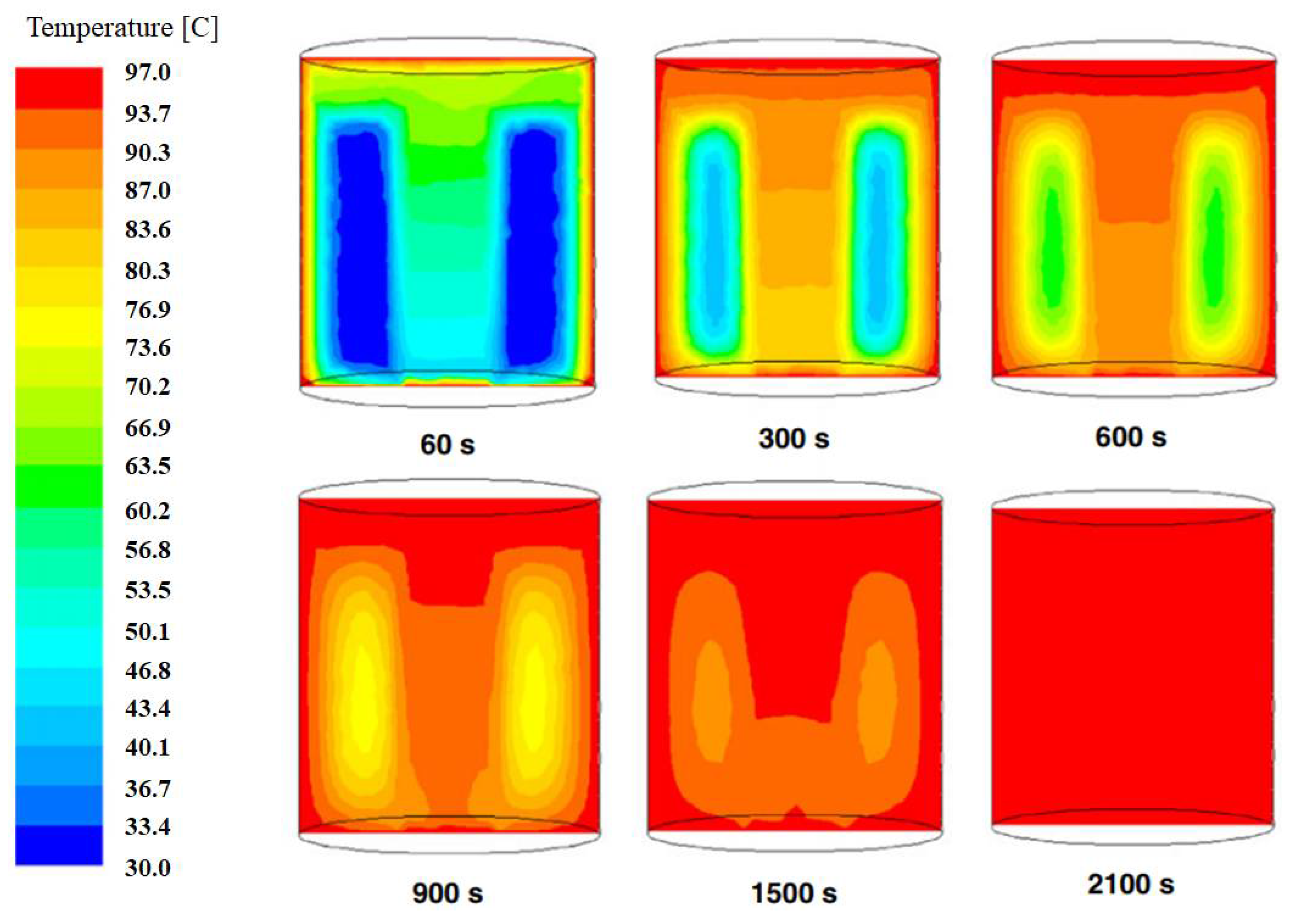
5.3. Liquid Foods
5.4. Liquid-Solid Foods
5.5. CFD Studies on Microbial Inactivation
6. Current Limitations and Future Trends of CFD Modeling in Thermal Processing
7. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Specific heat capacity (W·kg−1·K−1) | |
| Acceleration of gravity (m·s−2) | |
| Heat source (W·m−3) | |
| Temperature (K) | |
| Time (min) | |
| Velocity component (m·s−1) | |
| Greek symbols | |
| Thermal expansion coefficient (K−1) | |
| Density (kg·m−3) | |
| Thermal conductivity (W·m−1·K−1) | |
| Subscripts | |
| Cartesian coordinate index | |
| Reference | |
References
- Stumbo, C.R.; Purohit, K.S.; Ramakrishnan, T.V. Thermal process lethality guide for low-acid foods in metal containers. J. Food Sci. 1975, 40, 1316–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, R.; Teixeira, A.A. Optimization of canned food processing. In Optimization in Food Engineering; Erdogdu, F., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 561–596. [Google Scholar]
- Ghani, A.G.A.; Farid, M.M. Thermal sterilization of food using CFD. In Computational Fluid Dynamics in Food Processing; Sun, D., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 331–345. [Google Scholar]
- Datta, A.K.; Teixeira, A.A. Numerically predicted transient temperature and velocity profiles during natural convection heating of canned liquid foods. J. Food Sci. 1988, 53, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Bhattacharya, M.; Blaylock, J. Numerical simulation of natural convection heating of canned thick viscous liquid food products. J. Food Sci. 1990, 55, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Bhattacharya, M. Transient temperature and velocity profiles in a canned non-Newtonian liquid food during sterilization in a still-cook retort. Int. J. Heat Mass. Transf. 1991, 34, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuvaneswari, E.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Heat transfer analysis of pasteurization of bottled beer in a tunnel pasteurizer using computational fluid dynamics. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2014, 23, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogdu, F.; Uyar, R.; Palazoglu, T.K. Experimental comparison of natural convection and conduction heat transfer. J. Food Process. Eng. 2010, 33, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, A.G.A.; Farid, M.M. A numerical simulation study on thermal sterilization of food in pouches using computational fluid dynamics (CFD). Assoc. Comput. Mach. N. Z. Bull. 2005, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kiziltas, S.; Erdogdu, F.; Palazoglu, T.K. Simulation of heat transfer for solid-liquid food mixtures in cans and model validation under pasteurization conditions. J. Food Eng. 2010, 97, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koribilli, N.; Aravamudan, K.; Varadhan, M.A. Quantifying enhancement in heat transfer due to natural convection during canned food thermal sterilization in a still retort. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2011, 4, 429–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lespinard, A.R.; Mascheroni, R.H. Influence of the geometry aspect of jars on the heat transfer and flow pattern during sterilization of liquid foods. J. Food Process. Eng. 2012, 35, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawajfeh, K.; Albaali, A.G.; Saidan, M.; Abureden, S. Modeling of natural convection heating and biochemical changes in a viscous liquid canned food using computational fluid dynamics. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. Eng. 2013, 3, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Shafiekhani, S.; Zamindar, N.; Hojatoleslami, M.; Toghraie, D. Numerical simulation of transient temperature profiles for canned apple puree in semi-rigid aluminum based packaging during pasteurization. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 2770–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanu, S.; Vignali, G. Modelling and multi-objective optimisation of the VHP pouch packaging sterilisation process. Int. J. Food Eng. 2016, 12, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, J.R.; Graves, R.H.; Szemplenski, T. Handbook of Aseptic Processing and Packaging, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; ISBN 9781138199071. [Google Scholar]
- Euler, L. Principia motus fluidorum. Novi Comment. Acad. Sci. Petropol. 1761, 6, 271–311. [Google Scholar]
- Navier, C.L.M.H. Memoire sur les lois du mouvement des fluids. Mem. I’Acad. R. Sci. I’Inst. France 1823, 6, 389–440. [Google Scholar]
- Stokes, G.G. On the Effect of the Internal Friction Fluids on the Motion of Pendulums; Pitt Press: Cambridge, UK, 1851; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.G.; Yoon, W.B. Developing an effective method to determine the deviation of F value upon the location of a still can during convection heating using CFD and subzones. J. Food Process Eng. 2014, 37, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazdidi-Tehrani, F.; Moghaddam, S.; Aghaamini, M. On the validity of Boussinesq approximation in variable property turbulent mixed convection channel flows. Heat Transfer Eng. 2018, 39, 473–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdsworth, S.D.; Simpson, R. Computational fluid dynamics in thermal food processing. In Thermal Processing of Packaged Foods; Holdsworth, S.D., Simpson, R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 369–381. ISBN 9783319249025. [Google Scholar]
- Cordioli, M.; Rinaldi, M.; Copelli, G.; Casoli, P.; Barbanti, D. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modelling and experimental validation of thermal processing of canned fruit salad in glass jar. J. Food Eng. 2015, 150, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosna, D.; Vignali, G. Three-dimensional CFD simulation of a “steam water spray” retort process for food vegetable products. Int. J. Food Eng. 2015, 11, 715–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.W.; Yoon, W.B. Effects of air movement in a hot air dryer on the drying characteristics of colored potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) using computational fluid dynamics. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2018, 11, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versteeg, H.; Malalasekera, W. An Introductioto Computational Fluid Dynamic; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1995; Chaper 9. [Google Scholar]
- Launder, B.E.; Spalding, D.B. The numerical computation of turbulent flows. Numer. Predict. Flow Heat Transf. Turbul. Combust. 1983, 96–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, M.; Safaei, M.R.; Vafai, K.; Ahmadi, G.; Dahari, M.; Kazi, S.N.; Jomhari, N. Investigation of nanofluid mixed convection in a shallow cavity using a two phase mixture model. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2014, 75, 204–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansoni, J.L.; Seleghim, P., Jr. Optimal industrial reactor design: Development of a multiobjective optimization method based on a posteriori performance parameters calculated from CFD flow solutions. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016, 91, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlin, P. Modeling of Generation and Distribution of Steam in an Autoclave-A CFD Analysis. Master’s Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Goteborg, Sweden, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier, L.; Moreau, A.; Ronse, G.; Six, T.; Petit, J.; Delaplace, G. A CFD model as a tool to simulate β-lactoglobulin heat-induced denaturation and aggregation in a plate heat exchanger. J. Food Eng. 2014, 136, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendekar, A.; Sawant, V.B. Heat transfer optimization of shell and tube heat exchanger through CFD analysis. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Recent Trends in Engineering Science and management, Bundi, India, 10 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Eiamsa-ard, S.; Promvonge, P. Numerical study on heat transfer of turbulent channel flow over periodic grooves. Int. Commun. Heat Mass. Transfer 2008, 35, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Mahmud, T.; Heggs, P.J.; Ghadiri, M.; Bayly, A.; Ahmadian, H.; de Juan, M. CFD modeling of a pilot-scale countercurrent spray drying tower for the manufacture of detergent powder. Dry. Technol. 2017, 35, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moureh, J.; Flick, D. Airflow characteristics within a slot-ventilated enclosure. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2005, 26, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouaud, O.; Havet, M. Computation of the airflow in a pilot scale clean room using k-ϵ turbulence models. Int. J. Refrig. 2002, 25, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, M.L.; Verboven, P.; de Baerdemaeker, J.; Nicolai, B.M. Analysis of the air flow in a cold store by means of computational fluid dynamics. Int. J. Refrig. 2000, 23, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirade, P.S.; Daudin, J.D. Computational fluid dynamics prediction and validation of gas circulation in a cheese-ripening room. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahor, H.B.; Hoang, M.L.; Verboven, P.; Baelmans, M.; Nicolai, B.M. CFD model of the airflow, heat and mass transfer in cool stores. Int. J. Refrig. 2005, 28, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, A.G.A.; Farid, M.M.; Chen, X.D.; Richards, P. Numerical simulation of natural convection heating of canned food by computational fluid dynamics. J. Food Eng. 1999, 41, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, M.; Ghani, A.A. A new computational technique for the estimation of sterilization time in canned food. Chem. Eng. Process. 2004, 43, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, M.N.; Kannan, A. CFD studies on natural convective heating of canned food in conical and cylindrical containers. J. Food Eng. 2006, 77, 1024–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, A.; Sandaka, P.C.G. Heat transfer analysis of canned food sterilization in a still retort. J. Food Eng. 2008, 88, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutar, M.; Erdogdu, F. Numerical simulation for heat transfer and velocity field characteristics of two-phase flow systems in axially rotating horizontal cans. J. Food Eng. 2012, 111, 366–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortella, G. CFD-aided retail cabinets design. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2002, 34, 43–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, A.; Datta, A.K. Two-dimensional CFD modeling and simulation of crustless bread baking process. J. Food Eng. 2010, 99, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.; Zhou, W.; Hua, J. CFD modeling of an industrial continuous bread-baking process involving U-movement. J. Food Eng. 2007, 78, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, A.M.; Madge, M.; Evans, J.A. The use of CFD to improve the performance of a chilled multi-deck retail display cabinet. Int. J. Refrig. 2005, 28, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirade, P.S.; Kondjoyan, A.; Daudin, J.D. Three-dimensional CFD calculations for designing large food chillers. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2002, 34, 67–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, A.; Sankaran, V. Mesh quality effects on the accuracy of CFD solutions on unstructured meshes. J. Comput. Phys. 2011, 230, 7670–7686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boz, Z.; Erdogdu, F.; Tutar, M. Effects of mesh refinement, time step size and numerical scheme on the computational modeling of temperature evolution during natural-convection heating. J. Food Eng. 2014, 123, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courant, R.; Friedrichs, K.; Lewy, H. Die partiellen differenzengleichungen der mathematischen Pysik. Math. Ann. 1928, 100, 32–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Moin, P. Application of a fractional-step method to imcompressible Navier-Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 1985, 59, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobin, A.; Neau, H.; Simonin, O.; Llinas, J.R.; Reiling, V.; Selo, J.L. Fluid dynamic numerical simulation of a gas phase polymerization reactor. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2003, 43, 1199–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strouhal, V. Über eine besondere Art der Tonerregung. Ann. Phys. 1878, 241, 216–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.; Moin, P.; Kim, J. Direct numerical simulation of turbulent flow over a backward-facing step. J. Fluid Mech. 1997, 330, 349–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Mose, A.; Gubler, D.; Schaelin, A. Influence of time step length and sub-iteration number on the convergence behavior and numerical accuracy for transient CFD. In Proceedings of the 11th Annual Conference of the CFD Society of Canada, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 28–30 May 2003; pp. 480–485. [Google Scholar]
- Pflug, I.J. Procedures for Carrying Out a Heat Penetration Test and Analysis of the Resulting Data; Department of Food Science and Nutrition, University of Minnesota: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Tattiyakul, J.; Rao, M.A.; Datta, A.K. Simulation of heat transfer to a canned corn starch dispersion subjected to axial rotation. Chem. Eng. Process. 2001, 40, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tattiyakul, J.; Rao, M.A.; Datta, A.K. Heat transfer to three canned fluids of different thermos-rheological behavior under intermittent agitation. Food Bioprod. Process. 2002, 80, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatankhah, H.; Zamindar, N.; Baghekhandan, M.S. Heat transfer simulation and retort program adjustment for thermal processing of wheat based Haleem in semi-rigid aluminum containers. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 6798–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.G.; Yoon, W.B. Developing an effective method to determine the heat transfer model in fish myofibrillar protein paste with computer simulation considering the phase transition on various dimensions. Int. J. Food Eng. 2016, 12, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.A.; Anantheswaran, R.C. Convective heat transfer to fluid foods in cans. Adv. Food Res. 1988, 32, 39–84. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, G.; Richardson, P. The application of computational fluid dynamics in the food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1997, 8, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, P.E.D.; Pinheiro, T.F.; Cristianini, M. Using computational fluid-dynamics (CFD) for the evaluation of beer pasteurization: Effect of orientation of cans. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 30, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.D.; Huang, H.; Ghani, A.G. Thermal sterilization of liquid foods in a sealed container – developing simple correlations to account for natural convection. Int. J. Food Eng. 2005, 1, 1556–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraga, N.; Torres, A.; Guarda, A.; Galotto, M.J. Non-Newtonian canned liquid food, unsteady fluid mechanics and heat transfer prediction for pasteurization and sterilization. J. Food Process. Eng. 2011, 35, 2000–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.A.; Anishaparvin, A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Computational fluid dynamics studies on pasteurization of canned milk. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2011, 64, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwattanayotin, S.; Yoovidhya, T.; Meepadung, T.; Ruenglertpanyakul, W. Simulation of sterilization of canned liquid food using sucrose degradation as an indicator. J. Food Eng. 2006, 73, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogdu, F.; Tutar, M. Velocity and temperature field characteristics of water and air during natural convection heating in cans. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghani, A.G.A.; Farid, M.M.; Chen, X.D. Numerical simulation of transient temperature and velocity profiles in a horizontal can during sterilization using computational fluid dynamics. J. Food Eng. 2002, 51, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boz, Z.; Erdogdu, F. Evaluation of two-dimensional approach for computational modelling of heat and momentum transfer in liquid containing horizontal cans and experimental validation. Food Bioprod. Process. 2013, 91, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimou, A.; Panagou, E.; Stoforos, N.G.; Yanniotis, S. Analysis of thermal processing of table olives using computational fluid dynamics. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmavati, R.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Computational fluid dynamics modeling of the thermal processing of canned pineapple slices and titbits. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 882–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, A.A.; Farid, M.M. Using the computational fluid dynamics to analyze the thermal sterilization of solid–liquid food mixture in cans. Innovative Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2006, 7, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimou, A.; Stoforos, N.G.; Yanniotis, S. Effect of particle orientation during thermal processing of canned peach halves: A CFD simulation. Foods 2014, 3, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimou, A.; Yanniotis, S. 3D numerical simulation of asparagus sterilization in a still can using computational fluid dynamics. J. Food Eng. 2011, 104, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, A.G.; Farid, M.M.; Chen, X.D. Theoretical and experimental investigation of the thermal inactivation of Bacillus stearothermophilus in food pouches. J. Food Eng. 2002, 51, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, A.G.; Farid, M.M.; Chen, X.D. Theoretical and experimental investigation of the thermal destruction of Vitamin C in food pouches. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2002, 34, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, S.; Varney, C.; Barbosa-Canovas, G.V.; Tang, J.; Selim, F.; Sablani, S.S. Pressure-assisted thermal sterilization effects on gas barrier, morphological, and free volume properties of multilayer EVOH films. J. Food Eng. 2014, 128, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempe, L.L.; Graikoski, J.T.; Bonventre, P.F. Combined Irradiation-Heat Processing of Canned Foods: I. Cooked Ground Beef Inoculated with Clostridium botulinum Spores. Appl. Microbiol. 1957, 5, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zenker, M.; Heinz, V.; Knorr, D. Application of ultrasound-assisted thermal processing for preservation and quality retention of liquid foods. J. Food Protect. 2003, 66, 1642–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, H.W.; Yoon, W.B. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Modelling and Application for Sterilization of Foods: A Review. Processes 2018, 6, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr6060062
Park HW, Yoon WB. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Modelling and Application for Sterilization of Foods: A Review. Processes. 2018; 6(6):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr6060062
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Hyeon Woo, and Won Byong Yoon. 2018. "Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Modelling and Application for Sterilization of Foods: A Review" Processes 6, no. 6: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr6060062
APA StylePark, H. W., & Yoon, W. B. (2018). Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Modelling and Application for Sterilization of Foods: A Review. Processes, 6(6), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr6060062





