Abstract
In order to solve the problems of the poor adaptability to nonlinear systems, cumbersome parameter adjustment, and sensing-execution delay facing PID control for trawl winch tension control on fishing vessels, a prediction model for trawl winch cable tension was developed using a NARX neural network. The network was trained using historical data to achieve the accurate prediction of the trawl winch cable tension value in the future moment. The predicted value of the NARX neural network was introduced into the BP-PID controller as a feedforward quantity, and a BP-PID feedforward control strategy based on the prediction of the NARX neural network was designed. The simulation results in MATLAB software version: 9.13.0 (R2022b) show that, in comparison with the conventional PID control method, the BP-PID feedforward control strategy based on NARX neural network prediction substantially minimizes the fluctuation in trawl winch tension, enhances the control accuracy and robustness, and demonstrates excellent control performance under various sea states and load conditions.
1. Introduction
Trawling is a highly productive fishing method [1]. Trawl winch cable tension control is a key technology in trawl winches. The tension of the winch is affected by numerous uncertainties, including waves, ship steering, the weight of the catch, wind, and so on. This constant adjustment results in the increased wear and tear of the cable, potentially leading to incorrect rope selection, biting, and breaking, which significantly impact the performance and service life of the trawl winch as well as the safety of the fishing vessel’s operators.
Currently, there are two mainstream tension control methods: hydraulic differential control and PID control. Although hydraulic differential control [2,3,4,5] regulates tension, its dynamic response speed is limited by the compression of the hydraulic oil and the elasticity of the pipeline, the system stability is poor, being prone to jitter or instability phenomena. The PID control method [6,7,8] for momentary changes in tension parameters needs to be adjusted frequently, reducing the practicality and robustness of the system, and coping with the nonlinear change in the trawl winch cable tension is also a challenge. In addition to this, the time delay between sensor measurement and controller actuation can lead to poor control [9].
For the prediction of variables, Xu [9] proposed an integrated framework for decision making and motion planning with non-oscillatory capability, which improves the computational efficiency by constructing a state transfer model based on the prediction uncertainty. Li [10] designed an output feedback stabilization controller based on the predictor. Xiong [11] proposed a parametric adaptive sliding mode control strategy based on a radial basis function neural network (RBFNN) to track and control the trajectory of a UAV.
Nonlinear autoregressive exogenous input (NARX) neural networks have been widely used in the field of time-series forecasting due to their superior dynamic data processing capabilities [12]. The model significantly improves the prediction accuracy of complex nonlinear series by introducing a memory mechanism for historical data and has demonstrated excellent prediction performance in multidisciplinary fields [12,13,14,15,16].
It is worth noting that the operating environment at sea has significant variability and uncertainty: on the one hand, the actual sea state shows dynamic changes (not a single sea state), and there are significant fluctuations in the catch; on the other hand, the operation process may encounter sudden severe wind, waves, and other extreme working conditions. This puts higher demands on the trawl winch tension prediction model, which needs to adapt to different environmental conditions and load changes to ensure prediction accuracy. In this study, a NARX prediction model with environmental-adaptive capability was constructed based on typical sea state data for 2~5 levels and multi-scale catch samples.
The BP-PID feedforward control strategy based on NARX neural network prediction ensures good control accuracy and robustness in the face of different sea-state conditions and catches and reduces tension fluctuations, thus improving fishing efficiency and extending the service life of the equipment to protect the safety of fishing vessel operators.
2. Neural Network
2.1. Artificial Neural Networks
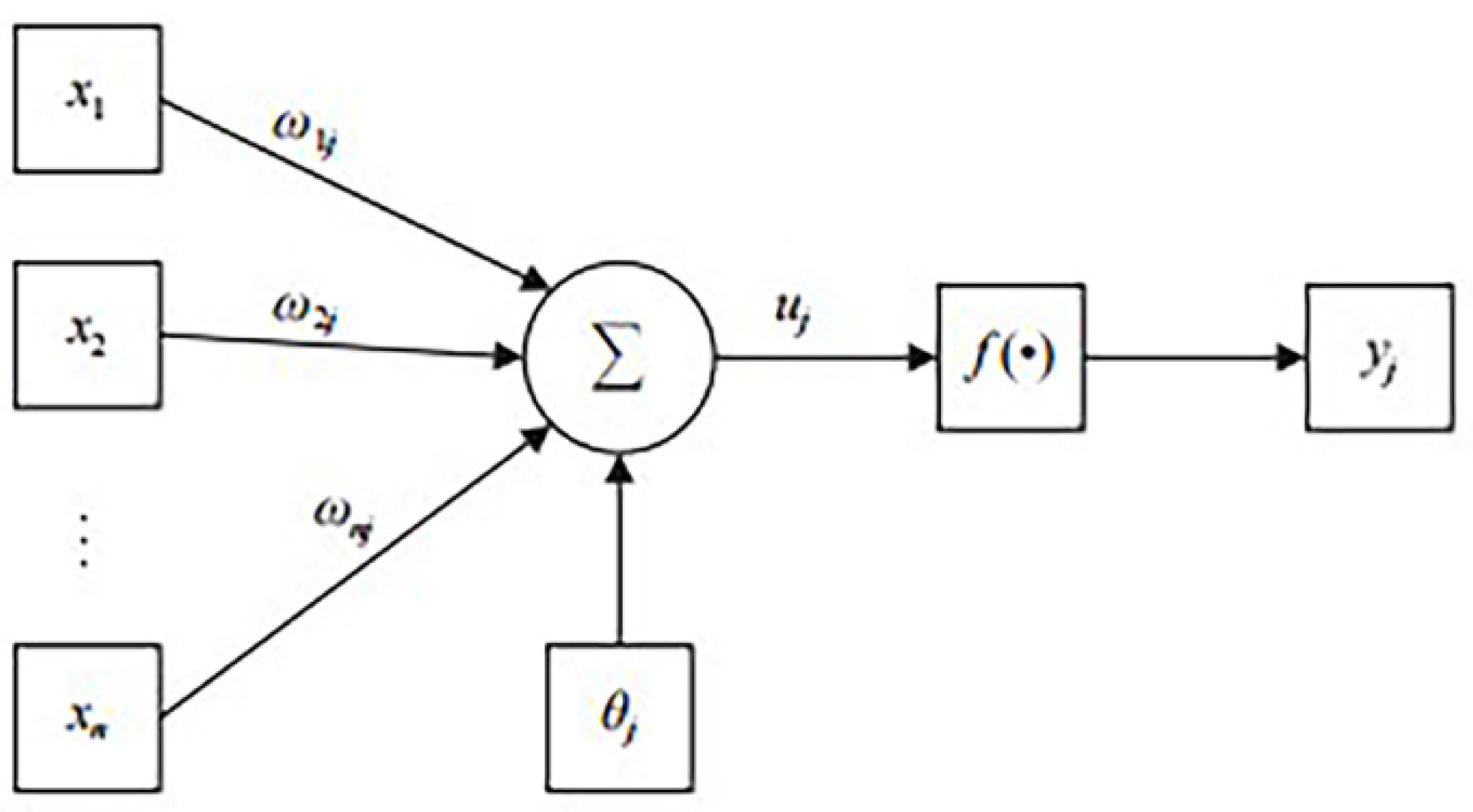
A neural network is a complex network structure constructed by countless basic neurons connected with each other. In Figure 1, a schematic representation of the neuron structure is provided, thereby demonstrating the process of data transmission among neuron nodes. The figure shows that are the input values of the J^{th} neuron; are the weights corresponding to the input values; is the weighted sum of the input values; is the bias of this neuron; and is the output value of this neuron.
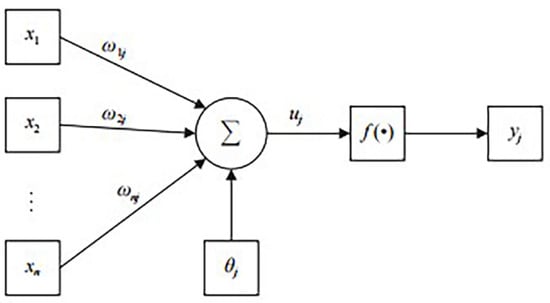
Figure 1.
A model of the neuron structure.
The computational rules for the neuron nodes in a neural network [17] are as follows:
In Equations (1) and (2), is the number of inputs to the neuron; is the J^{th} input value of the neuron; is the bias of this neuron; is the J^{th} input weight of the neuron; is the activation function.
2.2. NARX Neural Network
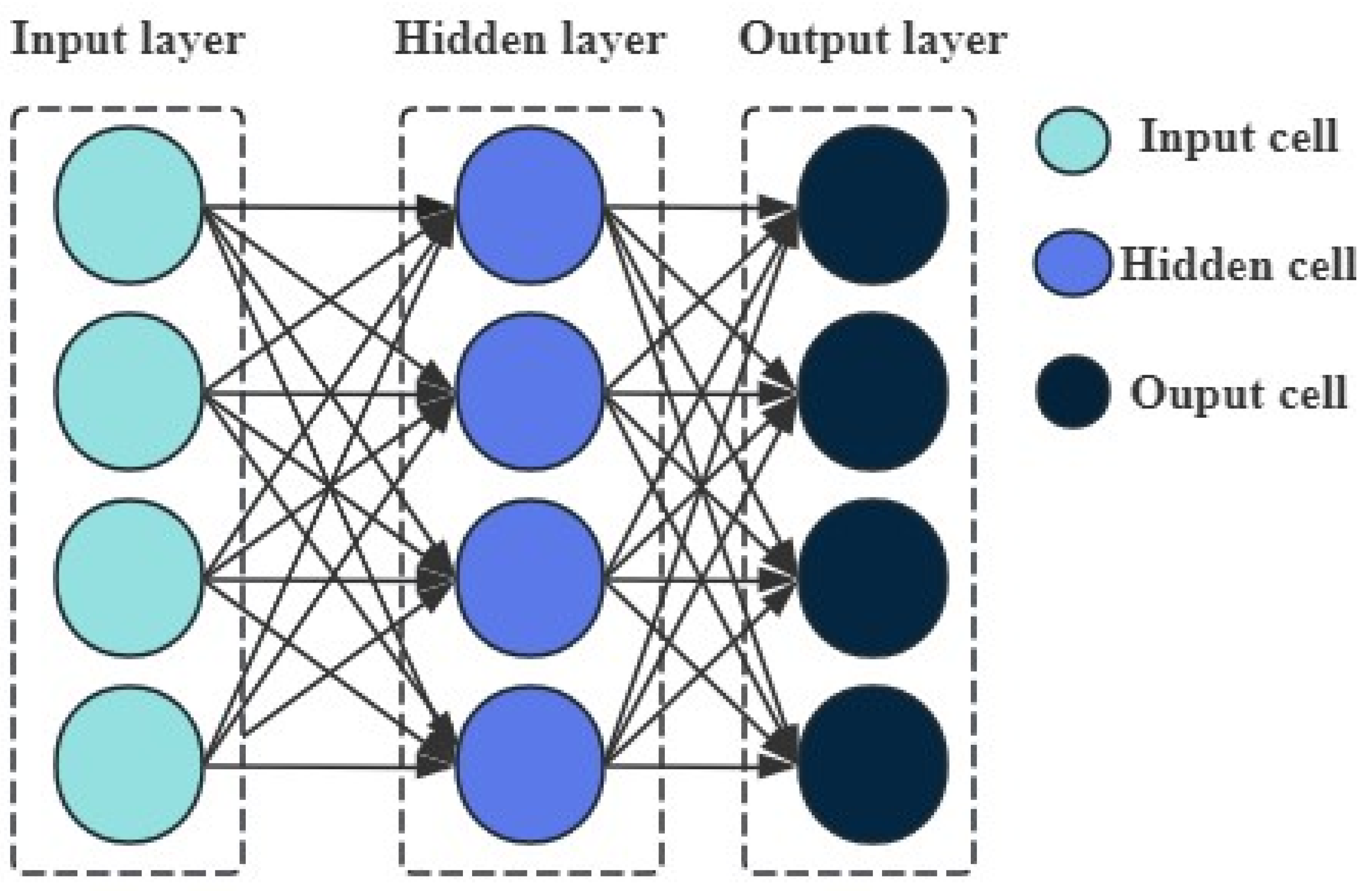
The NARX neural network is able to effectively capture the historical data information in a system due to its memory mechanism [18], thus more accurately describing the dynamic time-varying characteristics, which makes it perform well in the modeling and prediction of complex dynamic systems [19]. Figure 2 illustrates the basic composition and hierarchical structure of the NARX neural network, which consists of a three-layer structure: the input layer, the hidden layer, and the output layer.
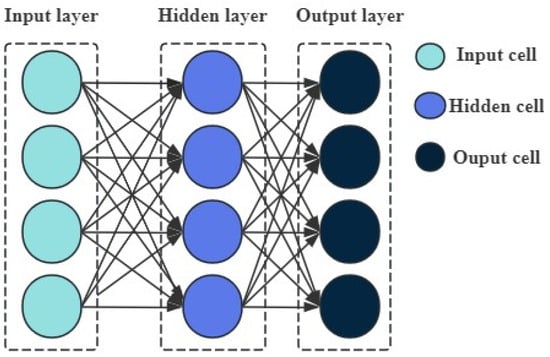
Figure 2.
A schematic diagram of the NARX neural network structure.
The neural network attains a complex mapping relationship from input to output through the interconnection of multiple basic neurons combined with a hierarchical structure. This hierarchical structure enables the neural network to gradually extract and abstract the features of the data to achieve efficient learning and inference [20]. The NARX neural network has been shown to exhibit superior convergence and learning rate [21,22], and its neural network model is as follows:
In Equation (3), and denote the input and output values at moment t, respectively. denotes the maximum order of the input delay, denotes the maximum order of the output delay, is the historical output relative to moment t, is the historical input relative to moment t, and is the nonlinear function of the prediction model.
2.3. NARX Tension Compensation Value Prediction Model
Ideally, the lifting and lowering motion of a fishing vessel can be simplified as sine or cosine motion, which are two forms of periodic motion that can effectively simulate the effect of waves on trawl winch cable tension. In this paper, to simplify the model and facilitate the calculation, the wave motion is set to be sinusoidal. The process of trawl winch towing under the sea is the main research object, in which the tension of the trawl winch cable comes from the trawl net, the weight of the catch itself, the tension of the fishing vessel by the action of the rising and sinking of the waves, the buoyancy of the sea water, and the resistance of the trawl movement. The formula for tension calculation is given in Equation (4) [23] below:
In Equation (4), H denotes the wave height, T signifies the period, μ represents the ratio of lift displacement to wave height, m is the trawl and catch mass, is the trawl winch cable tension, θ is the angle between the cable and the trawl winch, and g is the acceleration of gravity. is the drag coefficient, ρ is the density of seawater (), V is the speed of the trawl, and A is the transverse sectional area of the submerged part of the trawl.
When combined with the wave parameters enumerated in Table 1 for each sea state, the wave height time-series values of the simulated waves for each sea state can be calculated from the wave spectrum.

Table 1.
Definition of sea states.
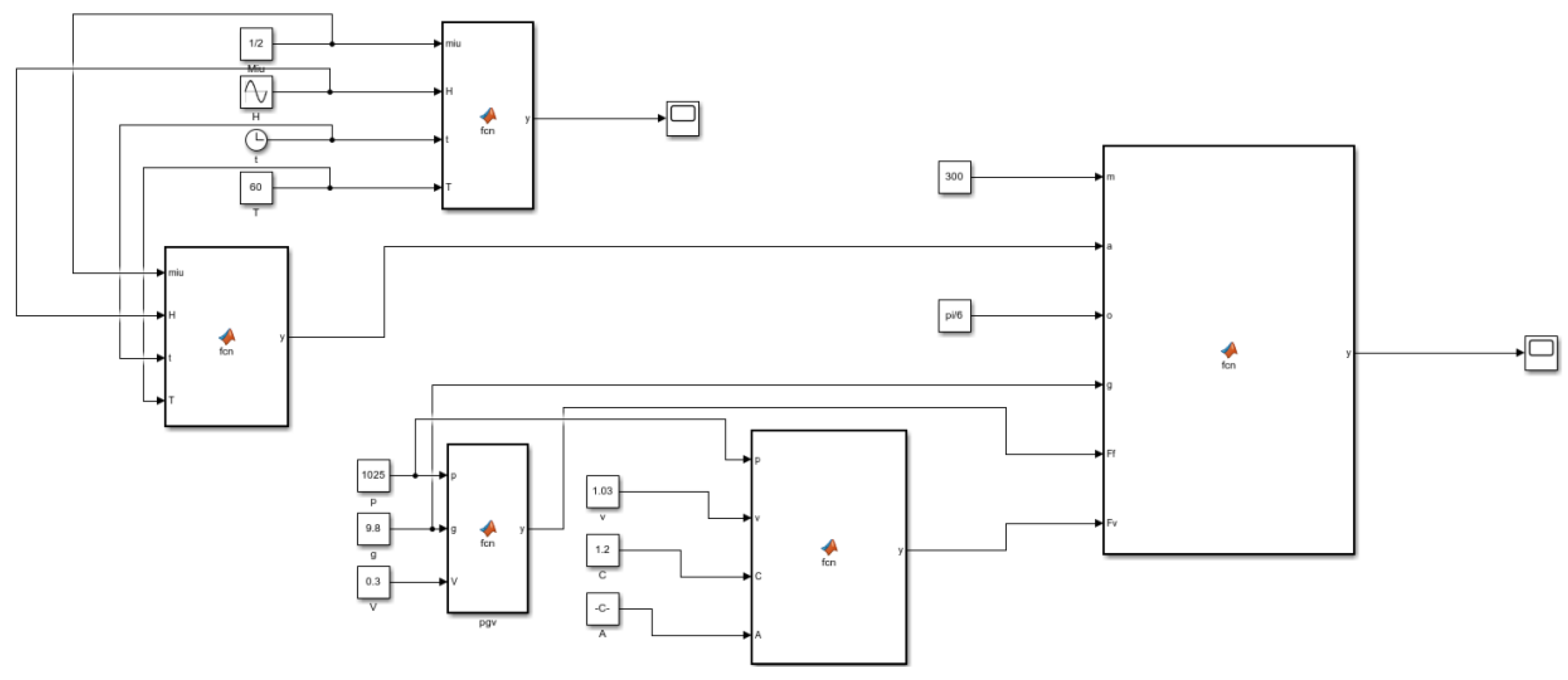
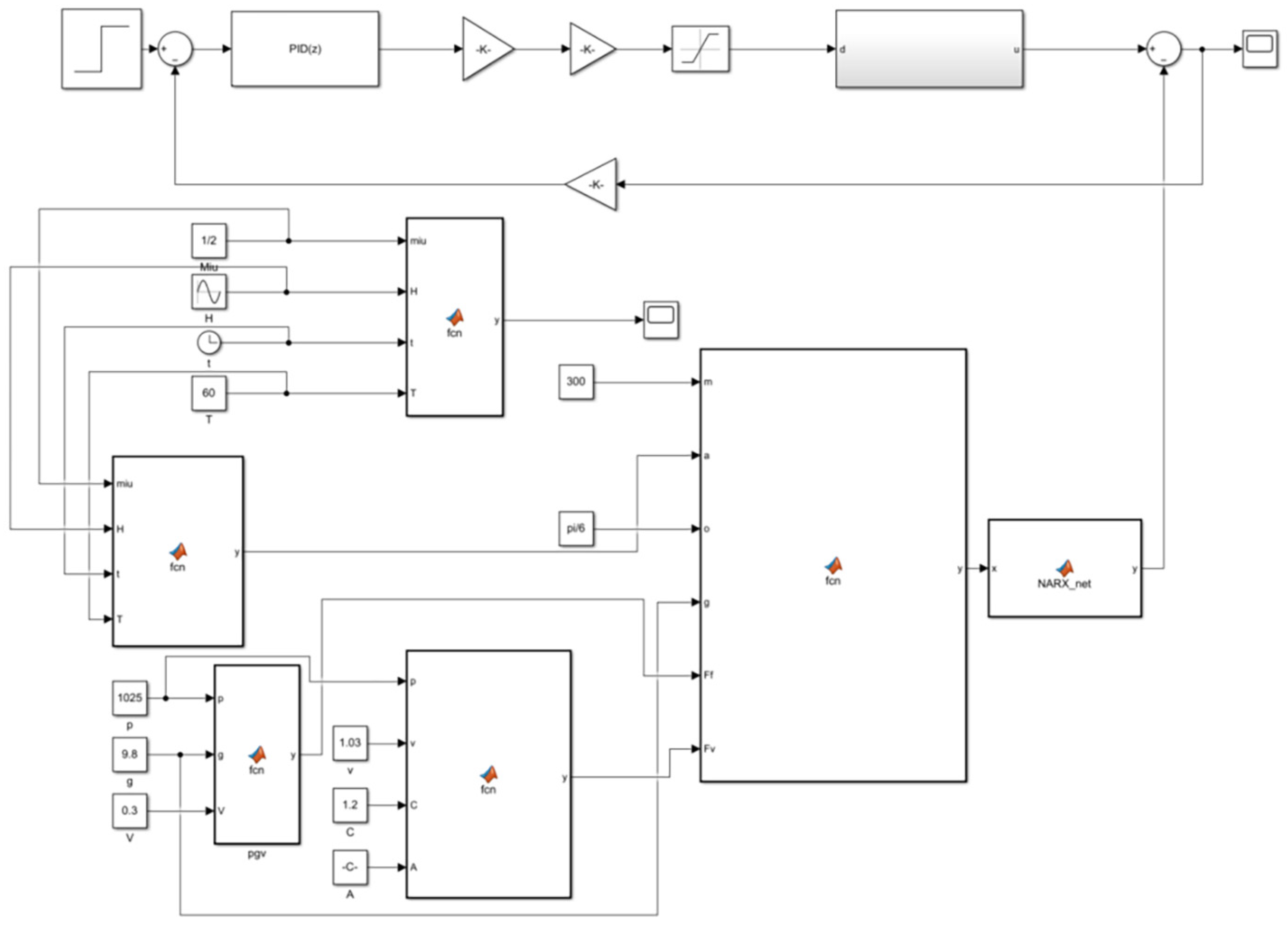
Through the mechanical analysis of trawl winch cable tension, the model of fishing vessel lift displacement and the cable tension compensation value was built in the simulation software MATLAB [24], as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3.
Model of cable tension compensation value.
The time series of the trawl winch cable tension under different sea states and catches, obtained by the trawl winch cable tension compensation simulation model, were used as the dataset for the prediction model. The cable tension time series was 200 s long, and the data sampling interval was 0.02 s. The 3000 data points in the first 65 s were used as the training dataset, and the remaining data were used as the test dataset. The Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm, which has good convergence speed, was used for training. It is standard practice to over-normalize the input and output data prior to training and prediction, and back-normalize the results when predicting [25]. This is to circumvent the impact of the distribution and range differences in the data during neural network training, thereby preventing imbalanced weight updates and enhancing the convergence rate. The normalization equation is presented in Equation (5).
In Equation (5), denotes the input data, signifies the minimum value of the input data, represents the maximum value of the input data, and is the normalized value of the data.
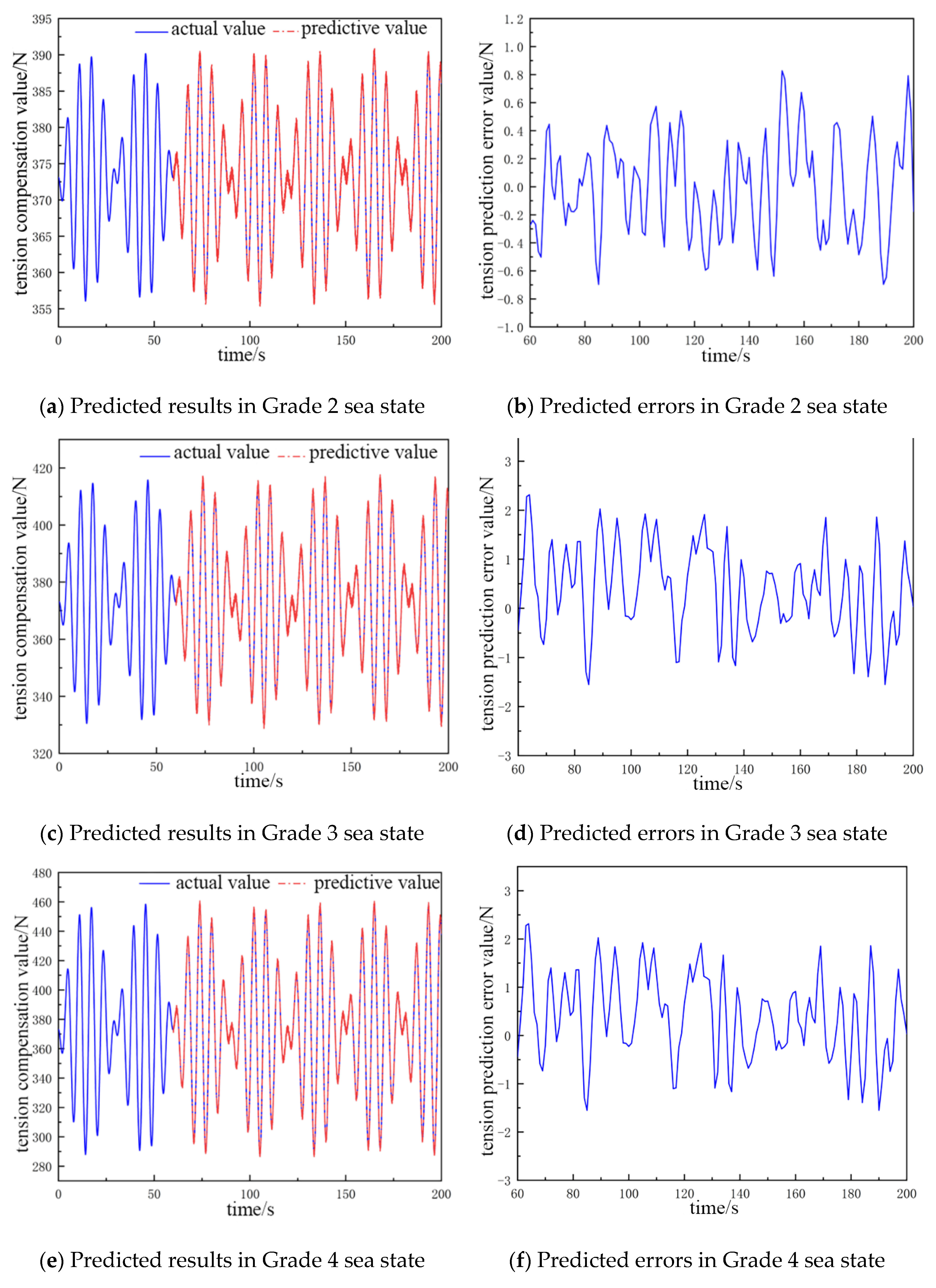
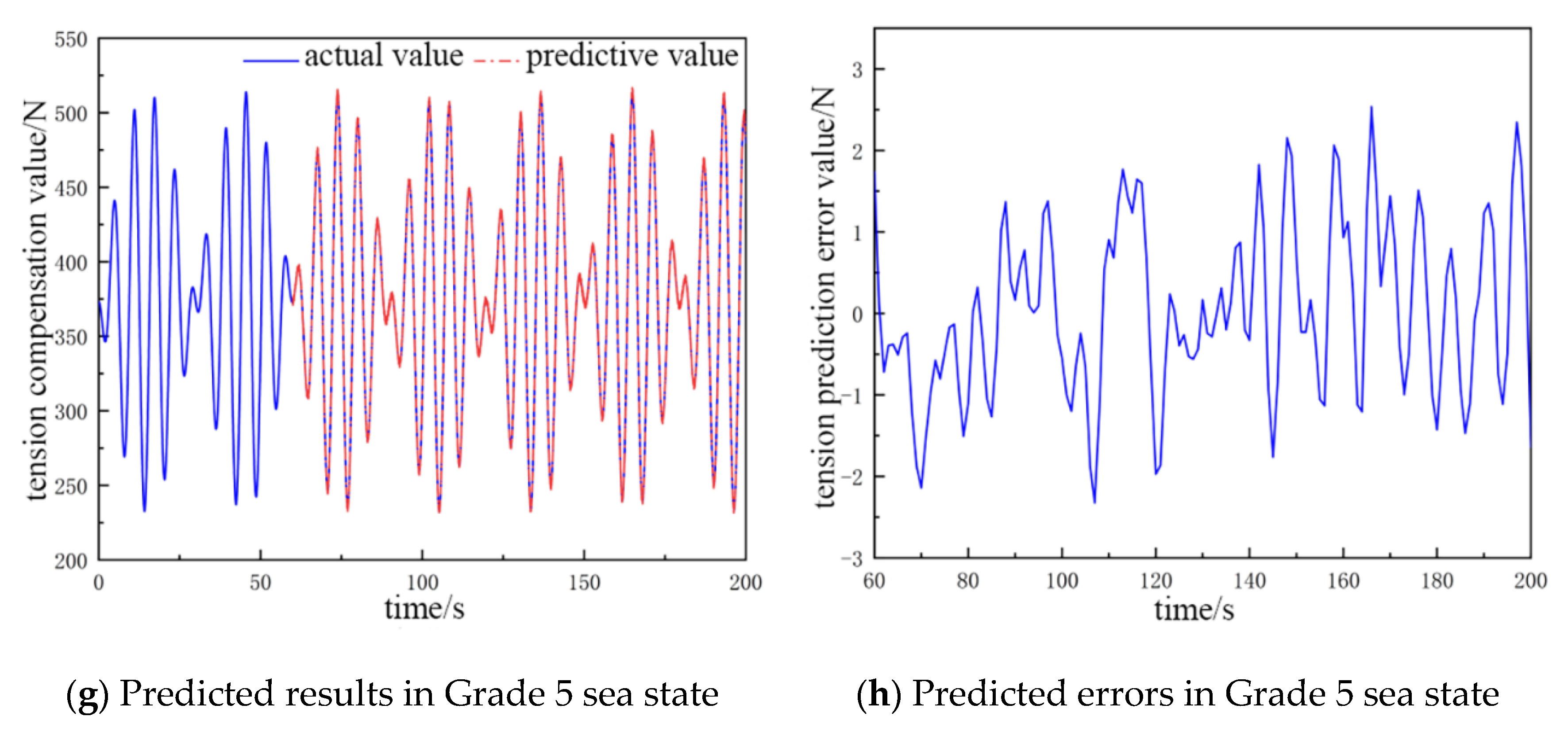
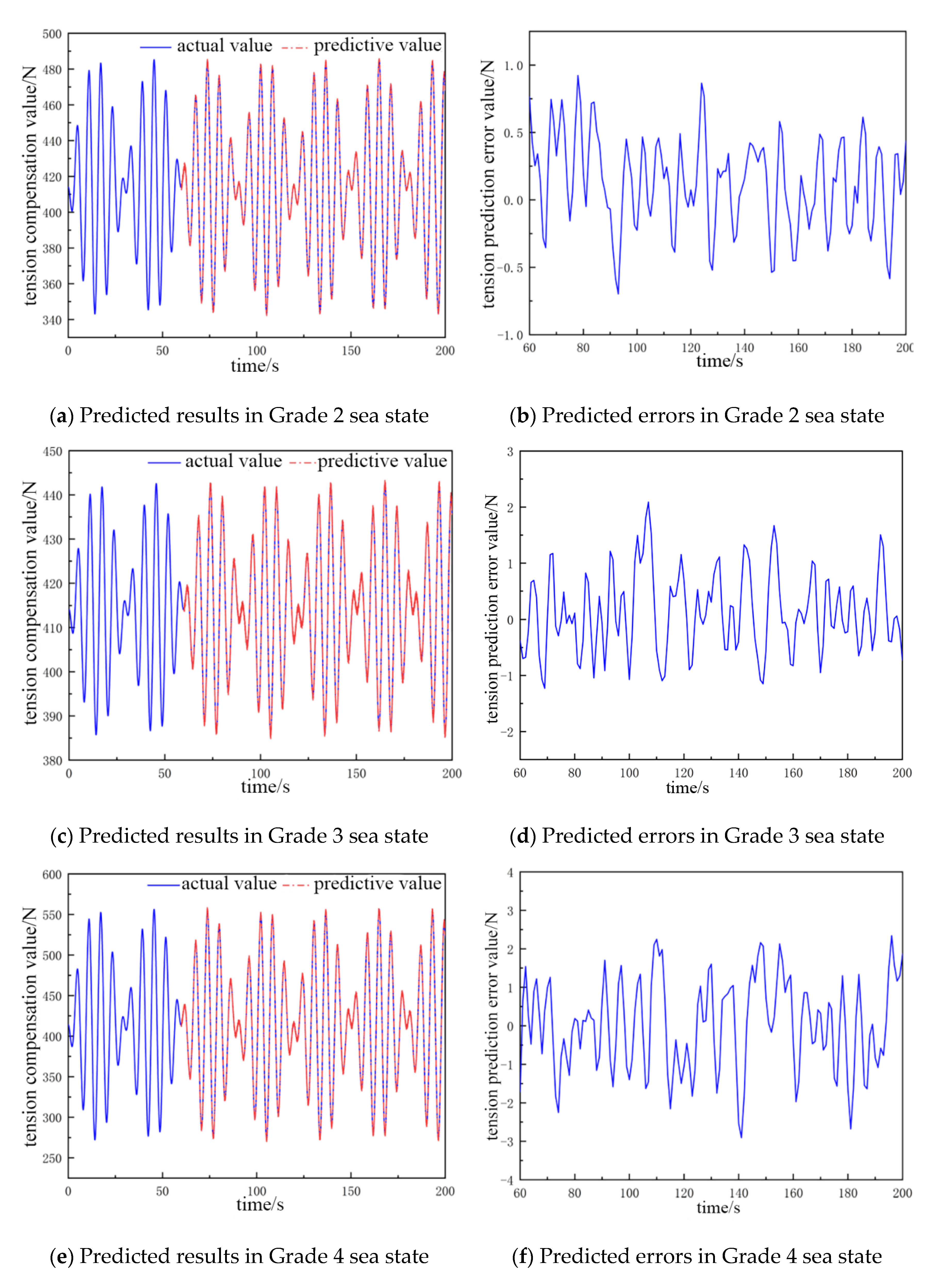
By comparing and analyzing the predicted cable tension compensation value and the true value in the next 135 s, the comparative analysis plots of the NARX neural network prediction results for different catch weights and different sea conditions were obtained, as shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5.
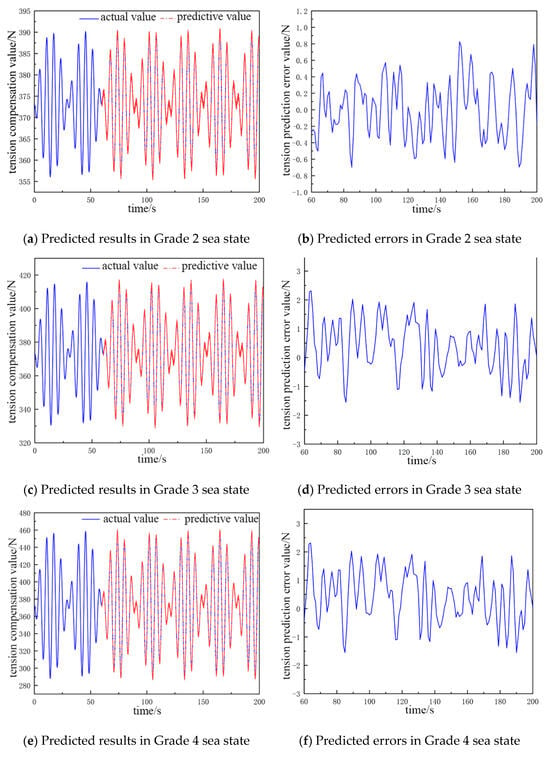
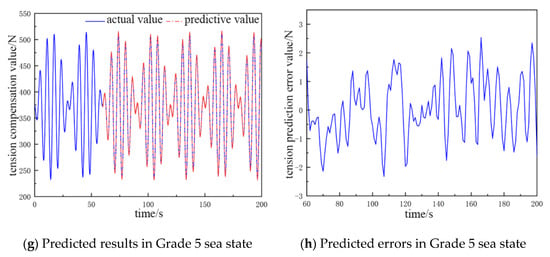
Figure 4.
The predicted value and error value of cable tension compensation for a 300 kg catch.
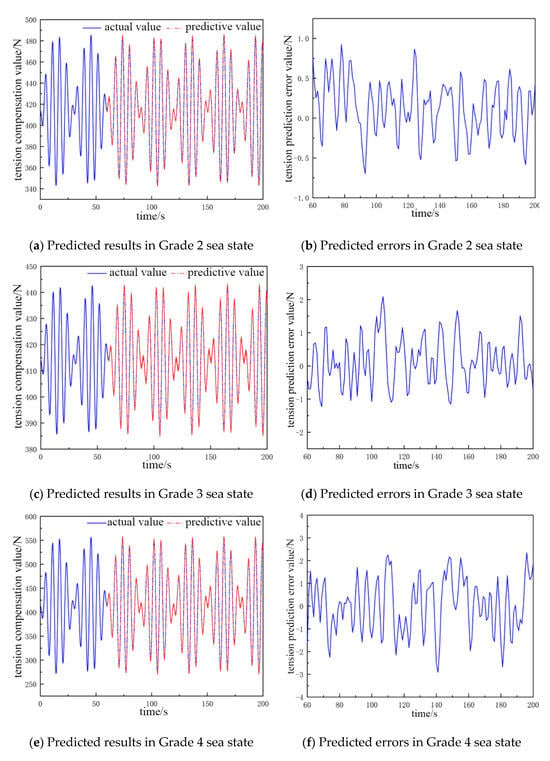
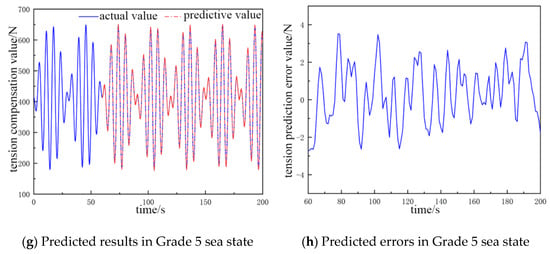
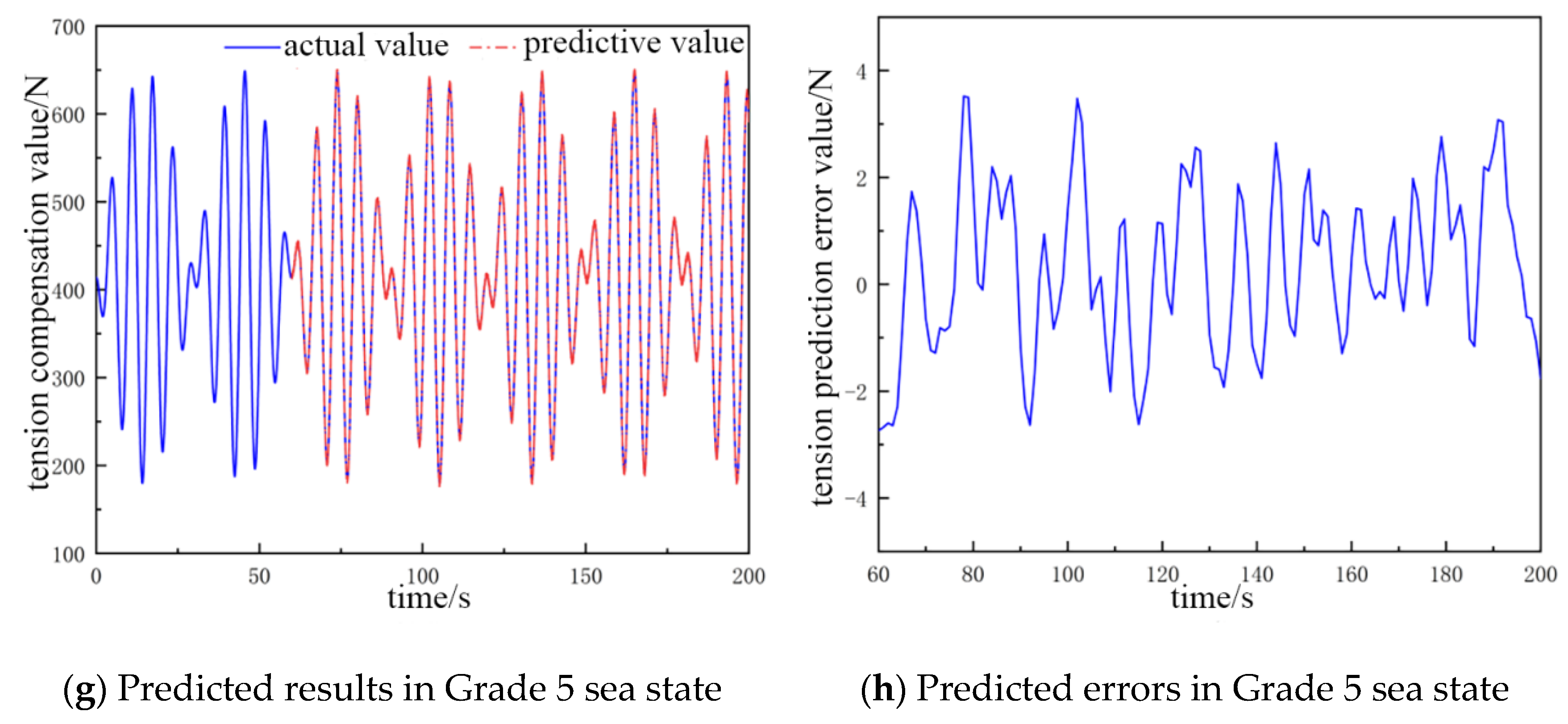
Figure 5.
The predicted value and error value of the cable tension compensation for a 500 kg catch.
The fluctuation in the cable tension compensation value in Figure 4a,b ranges from 356 to 390 N, and the error of the tension prediction value ranges from −0.7 to 0.85 N. In Figure 4c,d, the fluctuation in the cable tension compensation value ranges from 350 to 415 N, and the error of tension prediction value is from −1.52 to 1.9 N. In Figure 4e,f, the fluctuation in the cable tension compensation value ranges from 290 to 455 N, and the error in the tension prediction value ranges from −1.51 to 2.4 N. In Figure 4g,h, the fluctuation range in the cable tension compensation value ranges from 230 to 510 N, and the error range of the tension prediction value is −2.51 to 2.5 N.
In Table 2, the network structure is 12-5-1 for sea state Grade 2, the average error is about 0.45 N, and the prediction accuracy is 95.3%. The input layers of the neural network structure increase to 13 for sea state Grade 3; the average error is 0.92 N, which is 0.47 N more than that of Grade 2; and the prediction accuracy is 96.1%. The accuracy increases by 0.8% relative to Grade 2. The input layers of the neural network structure increase to 15; the hidden layers increase to 6; the average error is 1.29 N, which is 0.37 N more than that of Grade 3; and the prediction accuracy increases by 0.8%. The input layers of the neural network structure increase to 15, and the hidden layers increase to 6 in Grade 4; the average error is 1.29 N, which is 0.37 N more than that in Grade 3; the prediction accuracy is 97.6%; and the accuracy is 1.5% more than that in Grade 3. The input layers of the neural network structure increase to 16 in Grade 5, and the average error is 1.35 N, which is 0.06% more than that in Grade 4. The average error is 1.35 N, which is 0.06 N higher than that in Grade 4, and the prediction accuracy is 98.3%, which is 0.7% higher than that in Grade 4.

Table 2.
The prediction error of the NARX model for a 300 kg catch.
In Figure 5a,b, the fluctuation range of the cable tension compensation value is 385 to 443 N, and the error of the tension prediction value ranges from −0.73 to 0.9 N. In Figure 5c,d, the fluctuation range of the cable tension compensation value is 343 to 483 N, and the error of tension prediction value ranges from −1.25 to 2.2 N. In Figure 5e,f, the fluctuation range of the cable tension compensation value is 275 to 560 N, and the error of the tension prediction value ranges from −3.1 to 2.2 N. In Figure 5g,h, the fluctuation range of the cable tension compensation value is 180 to 650 N. and the error of the tension prediction value ranges from −2.8 to 3.4 N.
In Table 3, the structure of the network in the Grade 2 sea state is 15-6-1, the average error is about 0.47 N, and the prediction accuracy is 97.1%. There are seven hidden layers in the neural network structure in the Grade 3 sea state, and the average error is 0.48 N, which is 0.01 N more than that in the Grade 2 sea state, and the prediction accuracy is 97.5%, and the accuracy is 0.4% more than that in the Grade 2 sea state. The input layers of the neural network structure increase to 16 in the Grade 4 sea state, and the average error is 1.67 N, which is 1.19 N more than that in the Grade 3 sea state. The prediction accuracy is 98.2%, and the accuracy is 0.7% more than that in the Grade 3 sea state. The input layers of the neural network structure increase to 17 in the Grade 5 sea state, and the average error is 2.01 N, which is 0.34 N more than that in the Grade 4 sea state. The prediction accuracy is 98.7%, and the accuracy increases by 0.5% relative to the Grade 4 sea state.

Table 3.
The prediction error of the NARX model for a 500 kg catch.
From Figure 4 and Figure 5, it can be concluded that the fluctuation range of the cable tension compensation value is larger when the weight of the catch is larger and the sea-state grade is higher. Concurrently, the error of the predicted tension value also increase, which is more obvious in the high-grade sea state. However, they are all within the range of the accuracy requirement. Furthermore, an analysis of Table 2 and Table 3 reveals that increases in catch weight and sea state result in an escalation in the number of nodes necessary for the output and hidden layers of the neural network. However, the number of nodes required for the input layer remains consistent; when this number increases, the amount of computation required by the neural network increases. It is therefore necessary to take into account the prediction accuracy of the neural network and the amount of computation as well as to adjust to the optimal number of nodes of the input layer and the hidden layer.
The findings of the present study indicate that the prediction accuracy of the NARX time-series neural network is 95.3% at the lowest and 98.7% at the highest for different catch weights and sea-state levels. This is in accordance with the expected results of the experiment and thus verifies the feasibility of the prediction model for feedforward control.
3. NARX-Based Trawl Winch Tension Control System Design
3.1. Mathematical Modeling of Trawl Winch
It is evident that the motor is invariably subject to direct-current (DC) torque control during the process of cable collection by the trawl winch. Consequently, the trawl winch torque balance [26] Equation (6) can be derived.
In Equation (6), the variable signifies the torque exerted by the trawl winch drum. denotes the viscous damping coefficient of the trawl winch drum. is the rotational inertia of the trawl winch drum, and is the radius of the drum. is the trawl winch drum angle of rotation.
The Laplace transform of Equation (6) is equivalent to Equation (7).
When the trawl winch collects the cable, the length of the cable changes due to the lifting and sinking motion of the fishing vessel, so the following Equation (8) is obtained.
In Equation (8), the variable denotes the elasticity coefficient of the cable, is the Young’s modulus of the cable, signifies the cross-sectional area of the cable, and represents the length of the cable.
The transfer function between the trawl winch and the torque, , is thereby demonstrated.
The inverter is controlled by means of direct-current (DC) torque, and the transfer function between it and the motor is .
In Equation (10), N is the output torque of the drive; U is the value of the signal voltage.
The transfer function of the motor reducer in the trawl winch is .
In Equation (11), is the reduction ratio of the reducer; is the transmission efficiency of the reducer
3.2. Conventional PID Controller Design
The PID controller has been shown to possess a number of advantageous qualities, including good stability, a wide range of applications, and the capacity for real-time control. Consequently, it is employed extensively in industrial control systems [27,28,29,30]. The conventional PID control method comprises three elements: proportional, integral, and differential. These are adjusted to modify the size of the parameters, which are then multiplied by the system’s weighting coefficients. This results in the control of the controlled object.
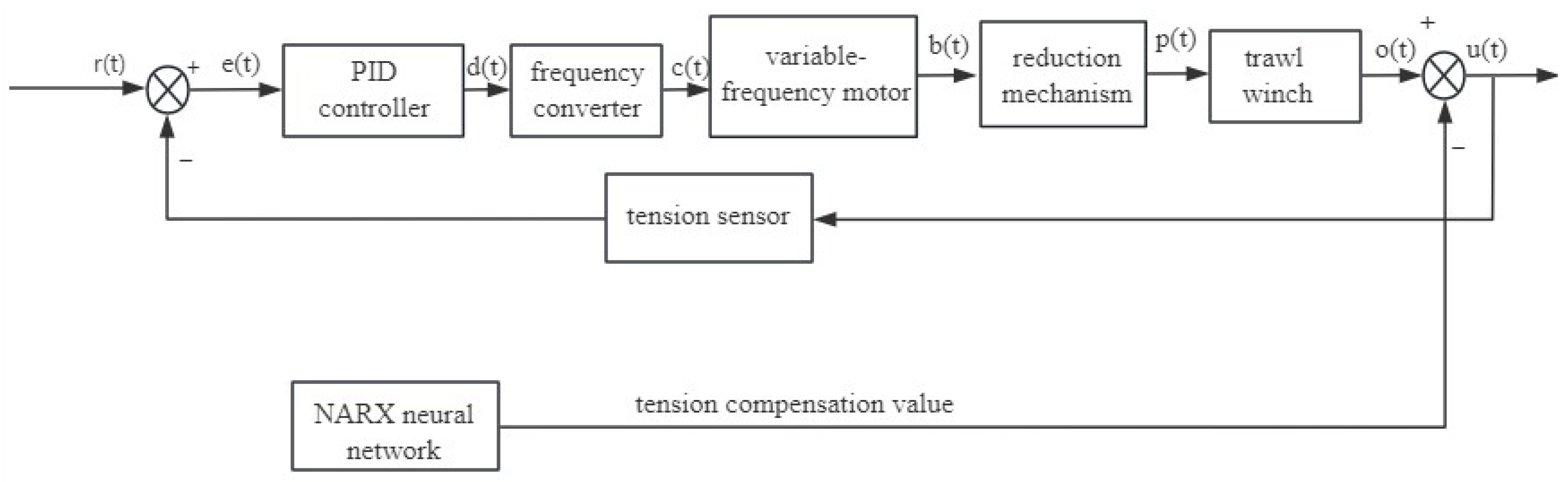
The cable tension control system incorporates a controller, trawl winches, and detection devices. Cable tension is influenced by the weight of the catch, the wave conditions, and the trawl winch’s output torque. The tension control system in the cable tension control involves the real-time monitoring of cable tension via a detection device, with the resulting feedback signal directing the controller to regulate the output of the inverter motor. This maintains the cable tension within the safety range and maintains constant performance. The transfer function of the controller, trawl winch, and detection device establishes the conventional PID control block diagram of the trawl winch, as illustrated in Figure 6.
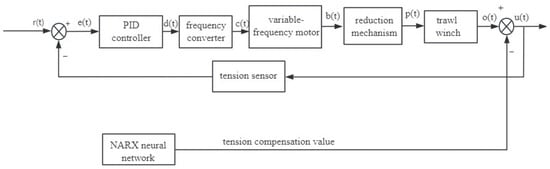
Figure 6.
Conventional PID control of trawl winch.
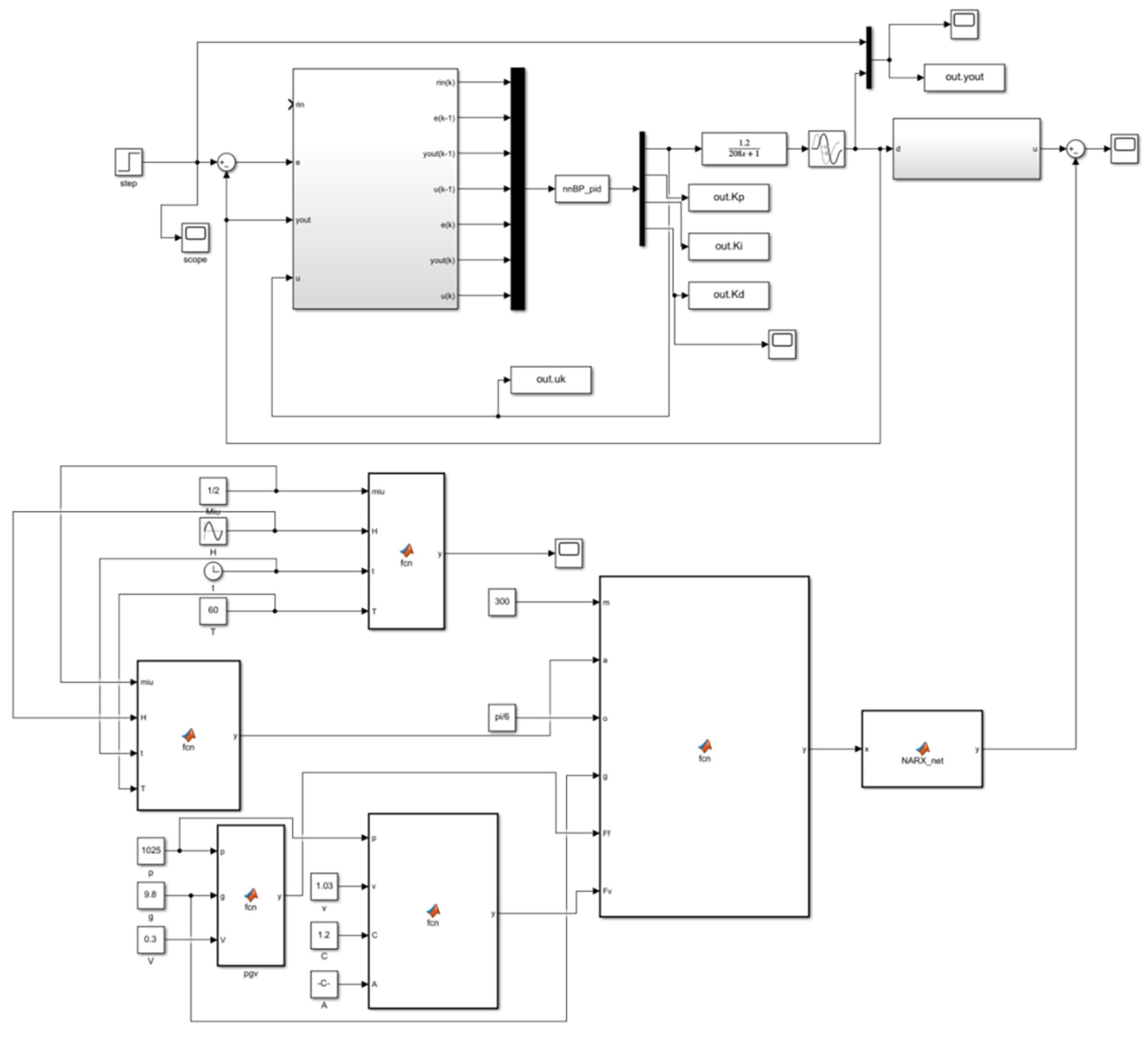
The cable tension compensation value prediction model is predicated on a combination of a NARX time-series neural network and traditional PID control. The model was constructed in a MATLAB/Simulink trawl winch cable constant tension control system, as illustrated in Figure 7.
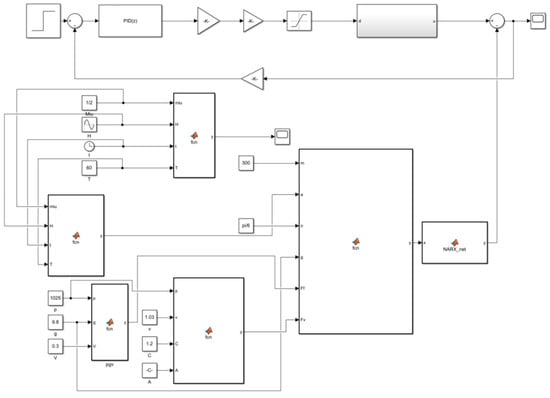
Figure 7.
Simulation of trawl winch control system based on conventional PID control.
PID control is a linear controller in essence; however, in the context of cable tension control systems, the presence of external uncertainties renders the system nonlinear, thereby impeding the efficacy of traditional PID control. The PID control process necessitates experience and testing when regulating the proportional, integral, and differential parameters. When the trawl winch collects the cable, the error generated is not only the change in the output torque of the drum but also the change in the weight of the catch and so on. If only the error generated by the controller is considered, it is difficult to achieve the desired control accuracy. The time lag between sensor measurement and controller execution also affects the response speed of the system.
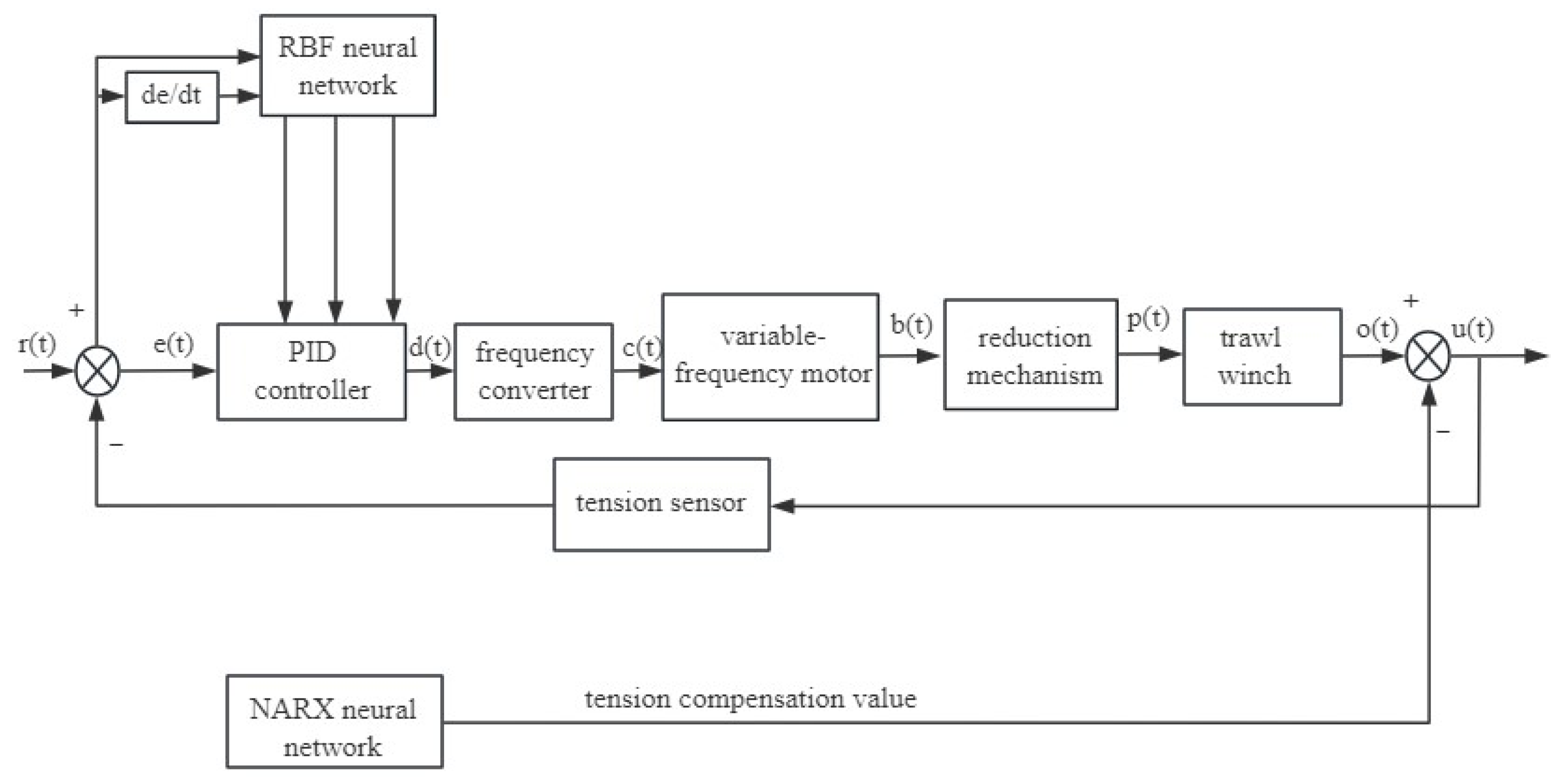
3.3. RBF Neural Network-Based PID Controller Design
The radial basis function (RBF) neural network is a type of artificial neural network that uses radial basis functions as activation functions. Its core feature is the use of radial basis functions as activation mechanisms. This type of network structure demonstrates excellent nonlinear mapping capabilities, outstanding interference resistance, and high-precision approximation effects when solving regression analysis problems [31,32,33].
As demonstrated above, conventional PID control is deficient in its capacity to address nonlinear challenges and exhibits an absence of adaptive capability in adjusting parameters [34]. In practical applications, the control system is susceptible to uncertainty due to external variables, resulting in suboptimal performance outcomes [35]. Consequently, a combination of the radial basis RBF neural network and conventional PID control was used to construct a PID controller based on an RBF neural network, as illustrated in Figure 8.
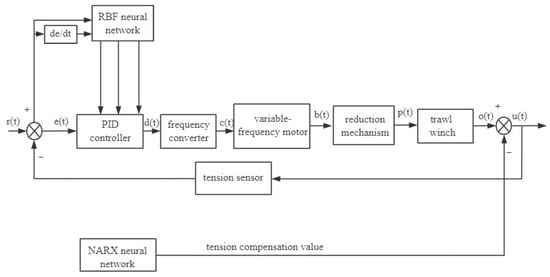
Figure 8.
RBF-PID control of trawl winch.
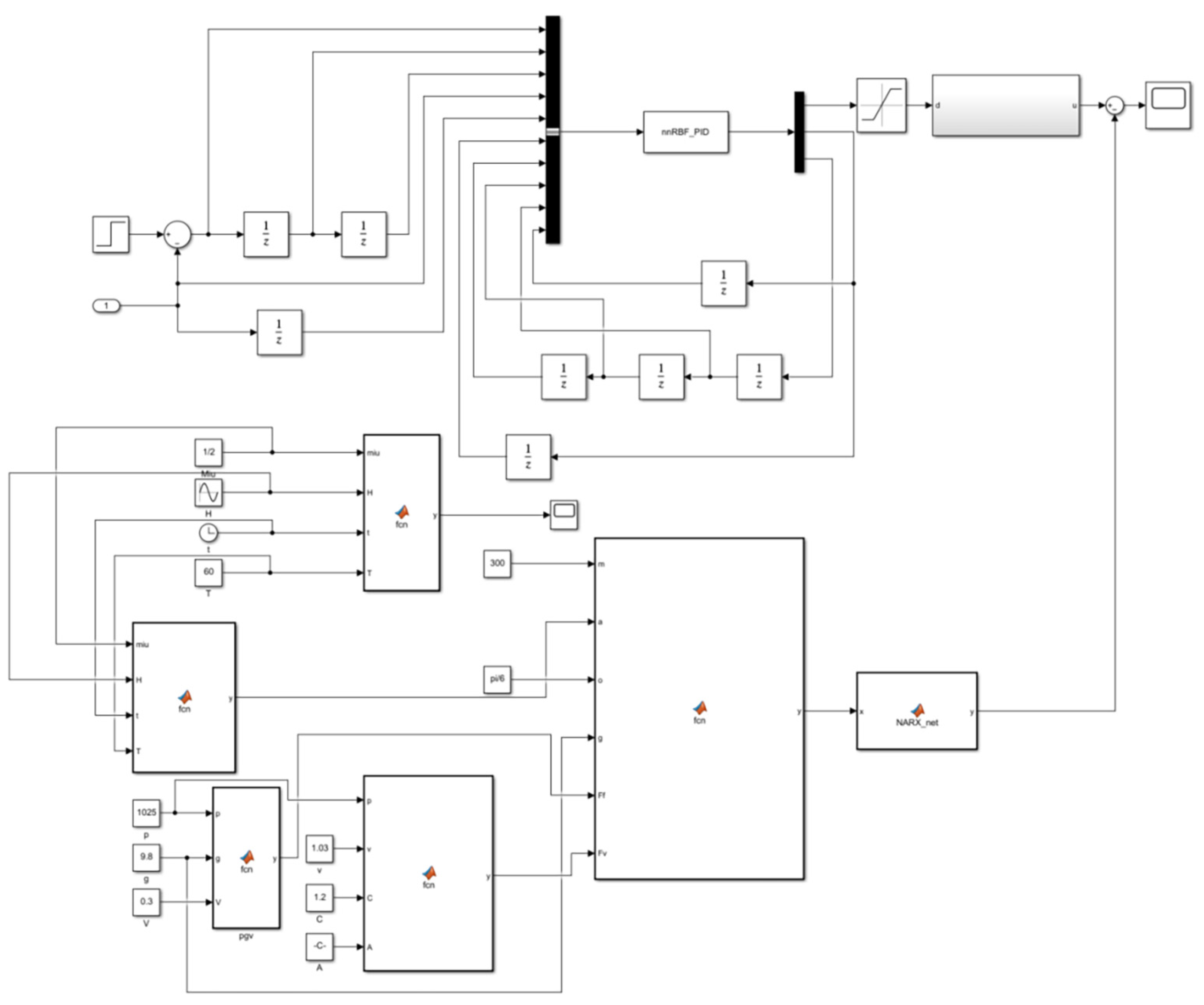
In order to verify the constant tension control of the cable based on an RBF neural network PID controller, a system simulation model was built in MATLAB/Simulink, as demonstrated in Figure 9.
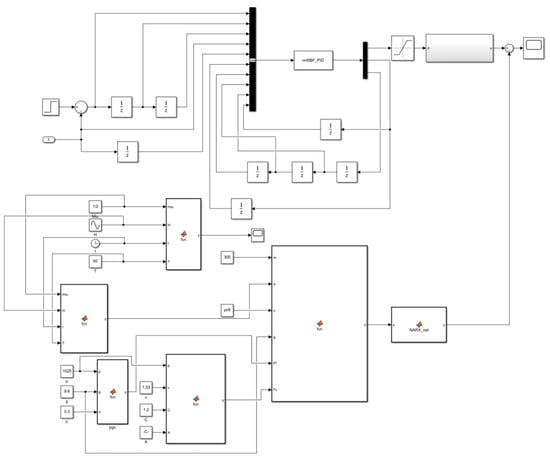
Figure 9.
Simulation of trawl winch control system based on RBF neural network PID control.
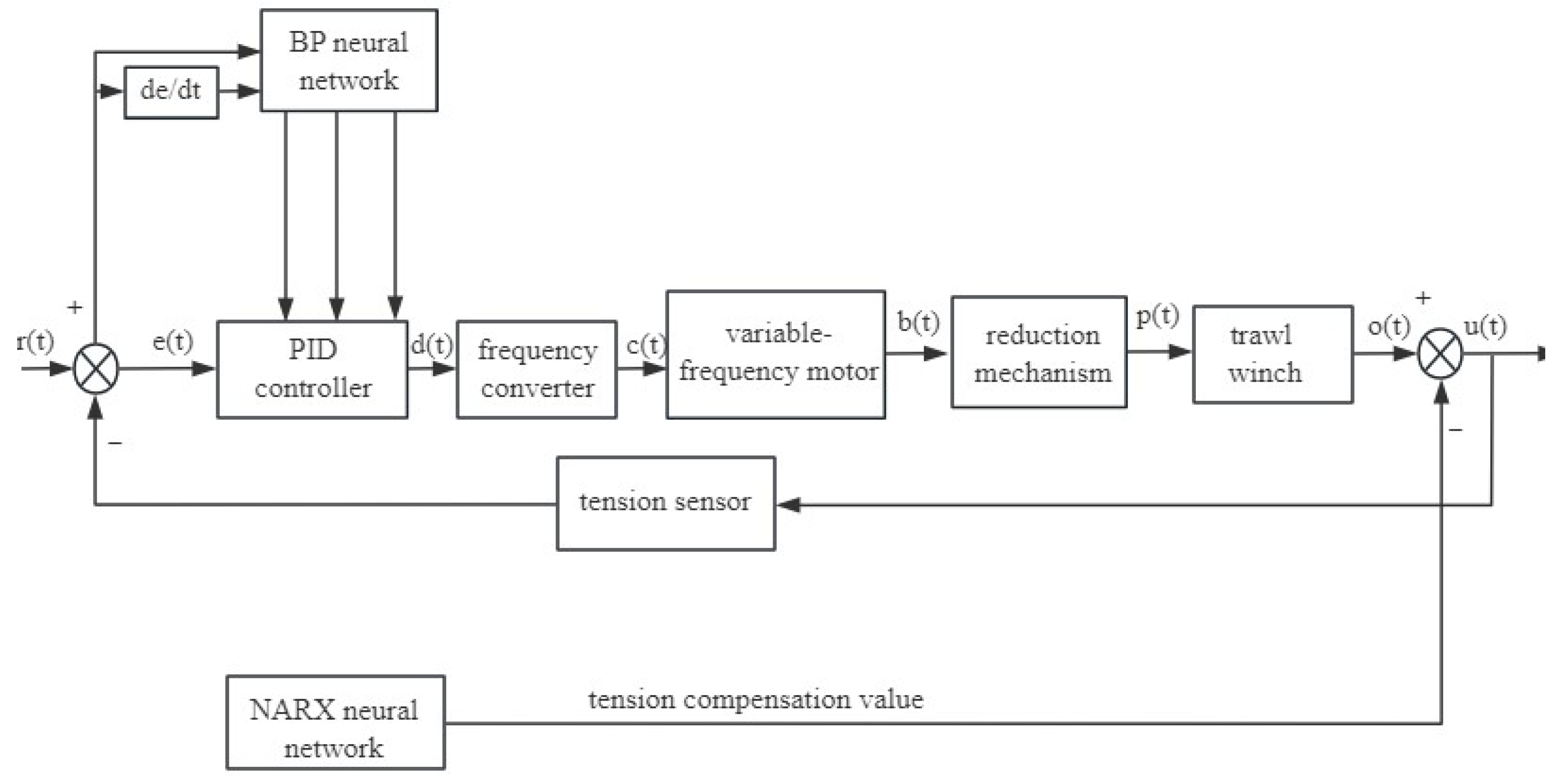
3.4. BP Neural Network-Based PID Controller Design
Back propagation (BP) neural networks are neural networks trained by using a back propagation algorithm to learn the mapping relationship between the input data and output data through the training process [36]. BP neural networks use the gradient descent method to make the change in the weights always improve in the direction of the error becoming smaller, ultimately achieving the minimum error [37,38,39].
Figure 10 illustrates a block diagram of the PID based on BP neural network; the network typically comprises three layers, with the number of nodes in the input and output layers being predetermined.
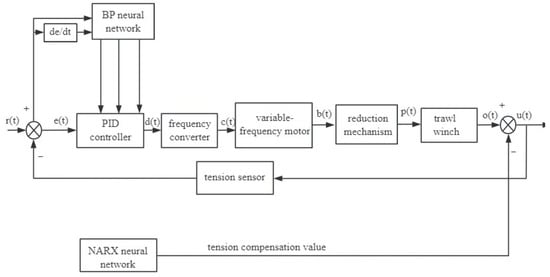
Figure 10.
BP-PID control of trawl winch.
When the output of the BP neural network does not match the expected true value, the neural network readjusts and enters the back propagation process. The error generated in the output layer is passed back to the input layer in a reverse manner. In the back propagation process, the error is first calculated and stored in the output layer. The error is passed layer-by-layer, passing through each neuron node in the hidden layer and finally reaching the input layer. In this process, each neuron receives the error signal from the next layer and adjusts its own weights and bias based on this signal using the gradient descent method. After many iterations, the error also gradually reduces, and the output data of the neural network gradually approach the real value. When the error is reduced to a certain degree, the neural network can be considered to have completed training.
In order to verify the constant tension control performance of a cable using the BP neural network PID controller, a system simulation model was built in MATLAB/Simulink, as illustrated in Figure 11.
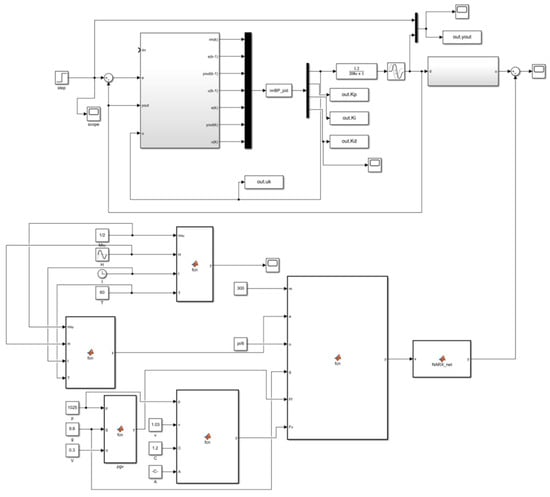
Figure 11.
Simulation of trawl winch control system based on BP neural network PID control.
3.5. Analysis of Simulation Results
Three cable tension control methods were used from the MATLAB/Simulink simulation, and the results were compared and analyzed. The findings indicate that the PID control system based on the BP neural network demonstrates the most effective performance in achieving the constant tension regulation of the cable. The PID control system based on RBF neural network exhibits suboptimal performance; however, both systems exhibit superior performance in comparison to the conventional PID control system.
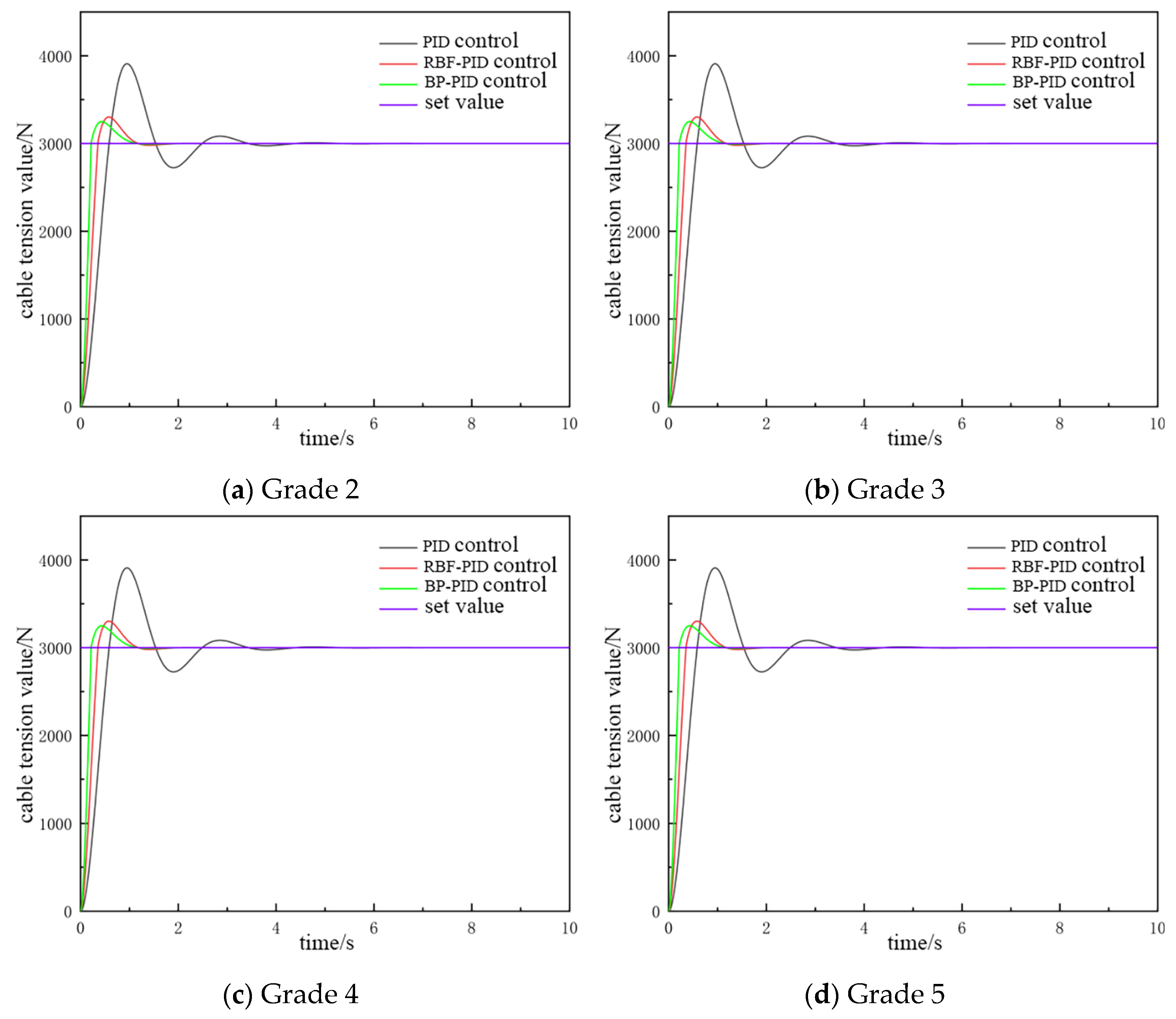
As demonstrated in Figure 12, when the catch weight is set at 300 kg, the overshooting of the conventional PID control is approximately 26%, while the overshooting of the PID control based on the RBF neural network and the PID based on the BP neural network is approximately 10% and 8%, respectively. With regard to the time required for the system to reach a steady state, conventional PID control takes longer than PID control based on the RBF neural network and PID control based on the BP neural network. In terms of oscillation, PID control based on the RBF neural network and PID control based on the BP neural network demonstrate superior performance compared to conventional PID control. Additionally, PID control based on the BP neural network exhibits slightly superior response speed compared to PID control based on the RBF neural network. Furthermore, the steady-state performance of the PID control based on the BP neural network is shown to be superior to that of the PID control based on the RBF neural network under various sea states.
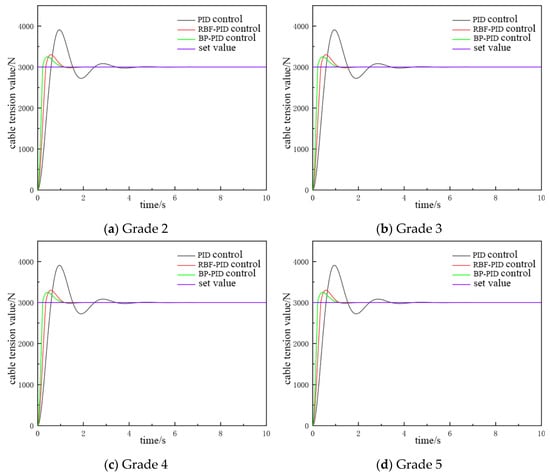
Figure 12.
The catch weighs 300 kg with the cable tension controlled.
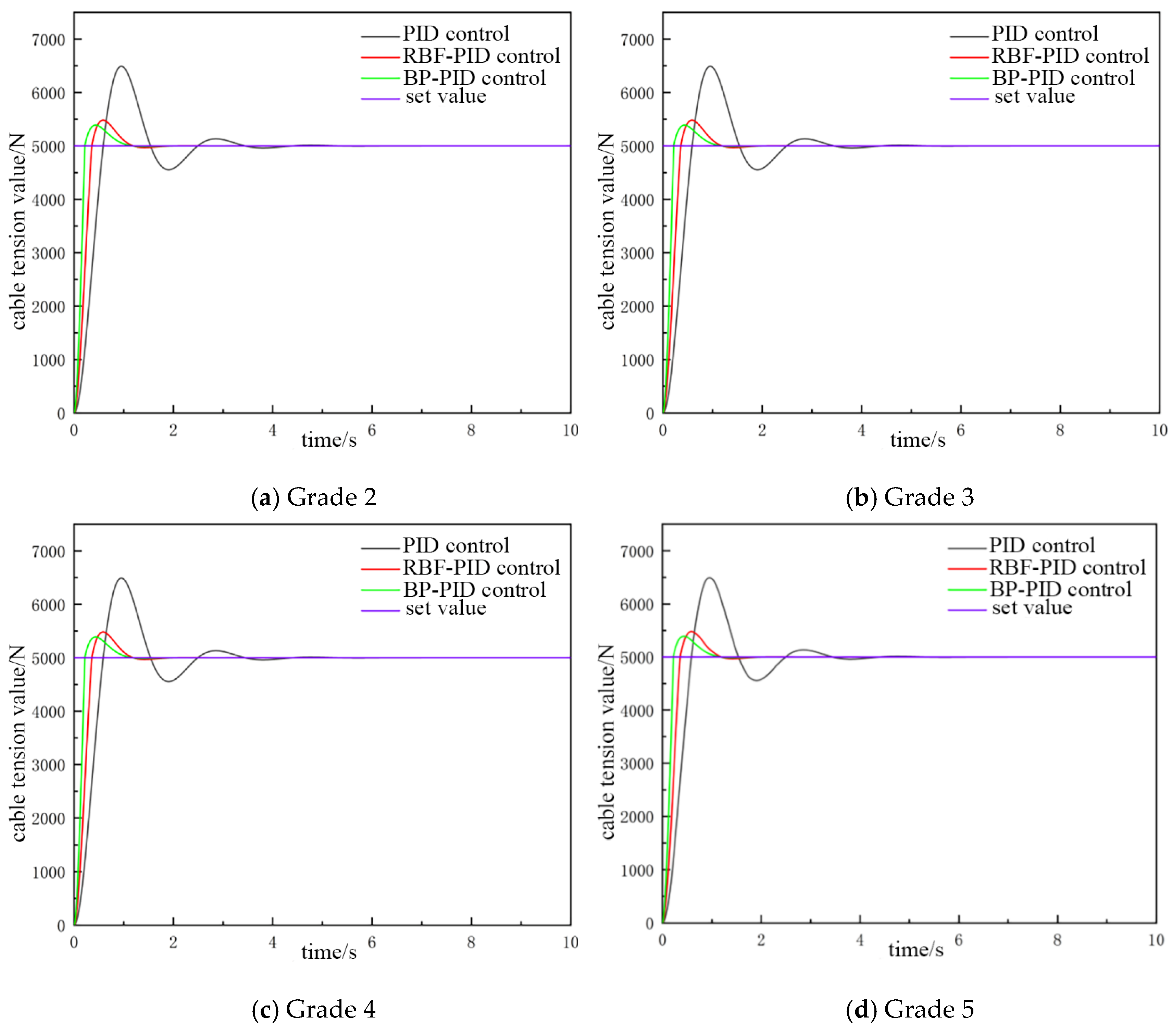
As demonstrated in Figure 13, when the catch weight is set at 500 kg, the overshooting amount and the time to enter the smooth state under the three control modes exhibit minimal variation. This observation suggests that the system possesses the capability to effectively regulate cable tension when the catch weight alters. Furthermore, it is evident from Figure 12 and Figure 13 that all three PID control methods exhibit overshooting behavior during cable tension control. However, moderate overshooting was shown to enhance the dynamic response speed and stability of the system. Nevertheless, it is imperative to avoid excessive overshooting, as it can compromise system stability.
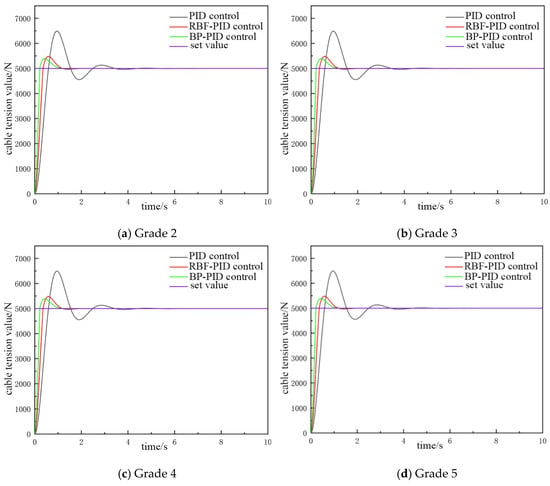
Figure 13.
The catch weighs 500 kg with the cable tension controlled.
4. Results
To this end, a cable tension prediction method was proposed, utilizing a NARX neural network. This approach was designed to effectively compensate for the nonlinear fluctuations in cable tension during the take-up and put-down processes. Concurrently, a tension control system based on BP-PID was designed to address the limitations of conventional PID control under complex working conditions. Through simulation verification and prediction result analysis, the following conclusions were drawn:
Firstly, the NARX tension compensation value prediction model is shown to accurately learn the dynamic characteristics of the cable tension system of the trawl winch and to predict the cable tension value with minimal prediction error. This lends support to the hypothesis that the model is a viable feedforward control method. Secondly, the predicted value of the NARX neural network is introduced into the BP-PID controller as a feedforward quantity. This effectively compensates for system perturbation and model error; significantly improves system response speed, control accuracy, and robustness; and reduces cable tension fluctuation. It also demonstrates superior control performance under different sea states and load conditions, which is evidently better than the traditional PID control method. Nevertheless, the implementation of constant tension control in the fishing boat trawl winch to a certain extent simplifies the mechanical model of the cable. This can be advantageous in terms of facilitating the incorporation of additional influential factors in the cable mechanical model, thereby enhancing its accuracy. However, due to the constraints imposed by the conditions, this study only conducted a simulation; it did not perform a real ship test.
5. Discussion
This paper proposes a method for the precise regulation of nonlinear, time-varying systems through the combination of neural network prediction (NARX) and feedforward control (BP-PID). Its application is not only limited to fishery but can also be extended to the field of ocean engineering, polar research, and energy, which require highly dynamic tension control. However, there are some limitations in this paper: the mechanical model of the cable was simplified to facilitate the analysis when the cable tension compensation model was constructed. In addition, due to the limitation of the conditions, this paper only completed a simulation analysis and did not carry out an actual ship test. In the future, further optimization of the cable tension compensation model can be considered to better fit the conditions in reality.
Author Contributions
Y.W.: writing—review and editing, writing—original draft, software, visualization; Q.L.: project administration, supervision, resources; M.X.: conceptualization, methodology, validation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by [2023 Zhejiang Ocean University Science and Technology Special Project] grant number [2023C41002] and the APC was funded by [2023 Zhejiang Ocean University Science and Technology Special Project].
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, Z.; Tang, H.; Xu, L.; Zhang, J. A review on fishing gear in China: Selectivity and application. Aquac. Fish. 2022, 7, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Wei, Y.; Han, H.; Guan, L.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X. Ocean wave active compensation analysis of inverse kinematics for hybrid boarding system based on fuzzy algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2018 OCEANS-MTS/IEEE Kobe Techno-Oceans (OTO), Kobe, Japan, 28–31 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, R.; Yang, J.; Yu, X.; Xu, J. Review of recent advances in the drive method of hydraulic control valve. Processes 2023, 11, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciatti, F.; Tamburrano, P.; Distaso, E.; Amirante, R. Digital hydraulic valves: Advancements in research. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, H.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, H. Pressure Control of Multi-Mode Variable Structure Electro–Hydraulic Load Simulation System. Sensors 2024, 24, 7400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Zhu, N.; Sun, Z.; Tan, S.; Tian, R. Research on the intelligent control strategy of pressurizer pressure in PWRs based on a fuzzy neural network PID controller. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2025, 433, 113875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phu, N.D.; Hung, N.N.; Ahmadian, A.; Senu, N. A new fuzzy PID control system based on fuzzy PID controller and fuzzy control process. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 22, 2163–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borase, R.P.; Maghade, D.K.; Sondkar, S.Y.; Pawar, S.N. A review of PID control, tuning methods and applications. Int. J. Dyn. Control 2021, 9, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, B. PDE-based observation and predictor-based control for linear systems with distributed infinite input and output delays. Automatica 2024, 170, 111845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hu, J.; Leng, B.; Xiong, L.; Fu, Z. An integrated of decision making and motion planning framework for enhanced oscillation-free capability. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 25, 5718–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.-J.; Chen, Y. RBFNN-Based Parameter Adaptive Sliding Mode Control for an Uncertain TQUAV With Time-Varying Mass. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2025, 35, 4658–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, S.M.; Paz, J.O.; Tagert, M.L.M. The use of NARX neural networks to forecast daily groundwater levels. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 1591–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzeldin, R.; Hatata, A. Application of NARX neural network model for discharge prediction through lateral orifices. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 57, 2991–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beintema, G.I.; Schoukens, M.; Tóth, R. Deep subspace encoders for nonlinear system identification. Automatica 2023, 156, 111210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Karimi, S.; Mohammadi, A.A.; Moghanlo, S.; Alavinejad, M.; Saleh, H.N.; Mohammadi, H.; Hashemi, M.N.; Kisi, O. Prediction of climate change on surface water using NARX neural network model: A case study on Ghezel Ozan River, Northwest, Iran. Desalination Water Treat. 2023, 304, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Shan, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G.; Fan, J. Research on identification and active vibration control of cantilever structure based on NARX neural network. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 171, 108872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, M.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Chen, R.; Ge, T. A real-time prediction method for ship heave motion using NARX neural network. Chin. J. Ship Res. 2020, 15, 48–55, 67. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Hong, Z.; Huang, S.; Li, Q. Full Feedback Dynamic Neural Network with Exogenous Inputs for Dynamic Data-Driven Modeling in Nonlinear Dynamic Power Systems. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2023, 18, 876–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Li, L.; Yin, J.; Lyu, W.; Zhang, W. A modular tide level prediction method based on a NARX neural network. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 147416–147429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, N.; Yao, Q.; Wu, Z.; Jin, W. Real-time moisture control in sintering process using offline–online NARX neural networks. Neurocomputing 2020, 396, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Sulaiman, M.; Tavera Romero, C.A.; Alarfaj, F.K. Theoretical analysis on absorption of carbon dioxide (CO2) into solutions of phenyl glycidyl ether (PGE) using nonlinear autoregressive exogenous neural networks. Molecules 2021, 26, 6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefraoui, A.; Kandoussi, K.; Louzazni, M.; Boutahar, A.; Elotmani, R.; Daya, A. Optimal battery state of charge parameter estimation and forecasting using non-linear autoregressive exogenous. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2023, 6, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X. Hydrodynamics in the Deployment of Major Components of the 1000-Metre Sea Trial System for Deep-Sea Mining. Ph.D. Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- MATLAB, version: 9.13.0 (R2022b); The MathWorks Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2022.
- Preetha, P.; Mallika, R. Normalization and deep learning based attention deficit hyperactivity disorder classification. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 40, 7613–7621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-M.; Li, C.; Deng, Y.-P. Modeling and Simulation Analysis on the Control System of Marine Shipborne Electric Driven Winch. Comput. Simul. 2016, 11, 244–249. [Google Scholar]
- Aboelhassan, A.; Abdelgeliel, M.; Zakzouk, E.E.; Galea, M. Design and Implementation of model predictive control based PID controller for industrial applications. Energies 2020, 13, 6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, I.A.; Irani, R.A. A generalized approach to anti-sway control for shipboard cranes. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 148, 107168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Kang, J.; Fu, C. Tunnel fire smoke control based on the PID method: A numerical study. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 124, 104450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantopoulos, G.C.; Baldivieso-Monasterios, P.R. State-limiting PID controller for a class of nonlinear systems with constant uncer-tainties. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2020, 30, 1770–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Song, Q.; Ma, S.; Ma, W.; Yin, C.; Cao, D.; Yu, H. A new adaptive sliding mode controller based on the RBF neural network for an electro-hydraulic servo system. ISA Trans. 2022, 129, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Cai, M.; Xu, W. Predictive control of air-fuel ratio in aircraft engine on fuel-powered unmanned aerial vehicle using fuzzy-RBF neural network. J. Frankl. Inst. 2020, 357, 8342–8363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Zhu, L.; Shu, C.; Sekar, V. An efficient multilayer RBF neural network and its application to regression problems. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 4133–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wu, S.; Lu, R.; Gao, F. Predictive control optimization based PID control for temperature in an industrial surfactant reactor. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2014, 135, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogru, O.; Velswamy, K.; Ibrahim, F.; Wu, Y.; Sundaramoorthy, A.S.; Huang, B.; Xu, S.; Nixon, M.; Bell, N. Reinforcement learning approach to autonomous PID tuning. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2022, 161, 107760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Z.; Xiong, J. The investigation into the failure criteria of concrete based on the BP neural network. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2022, 275, 108835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Hou, B.; Zhou, G.; Shen, L.; Wei, C.; Li, Q. Variable pitch active disturbance rejection control of wind turbines based on BP neural network PID. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 71782–71797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, F.; Li, R.; Han, P.; Xue, D. Research on autonomous walking performance and electromechanical characteristics of mining double-track chassis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0312096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Z.-Y. The application of immune genetic algorithm in main steam temperature of PID control of BP network. Phys. Procedia 2012, 24, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).