Molecular Interaction of Water-Soluble Resorcinarenes for Potential Choline Detectors
Abstract
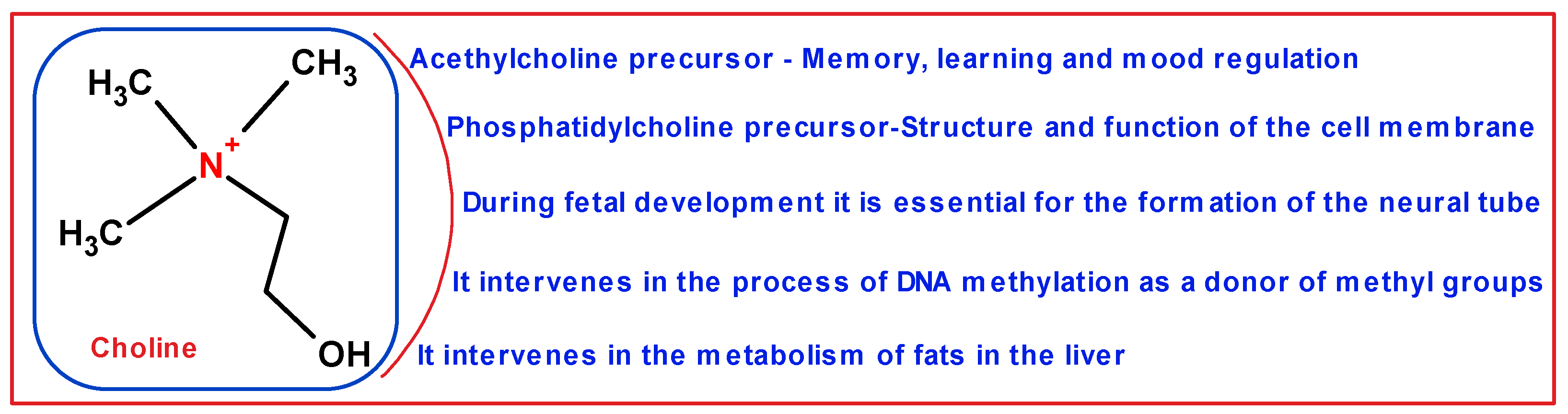
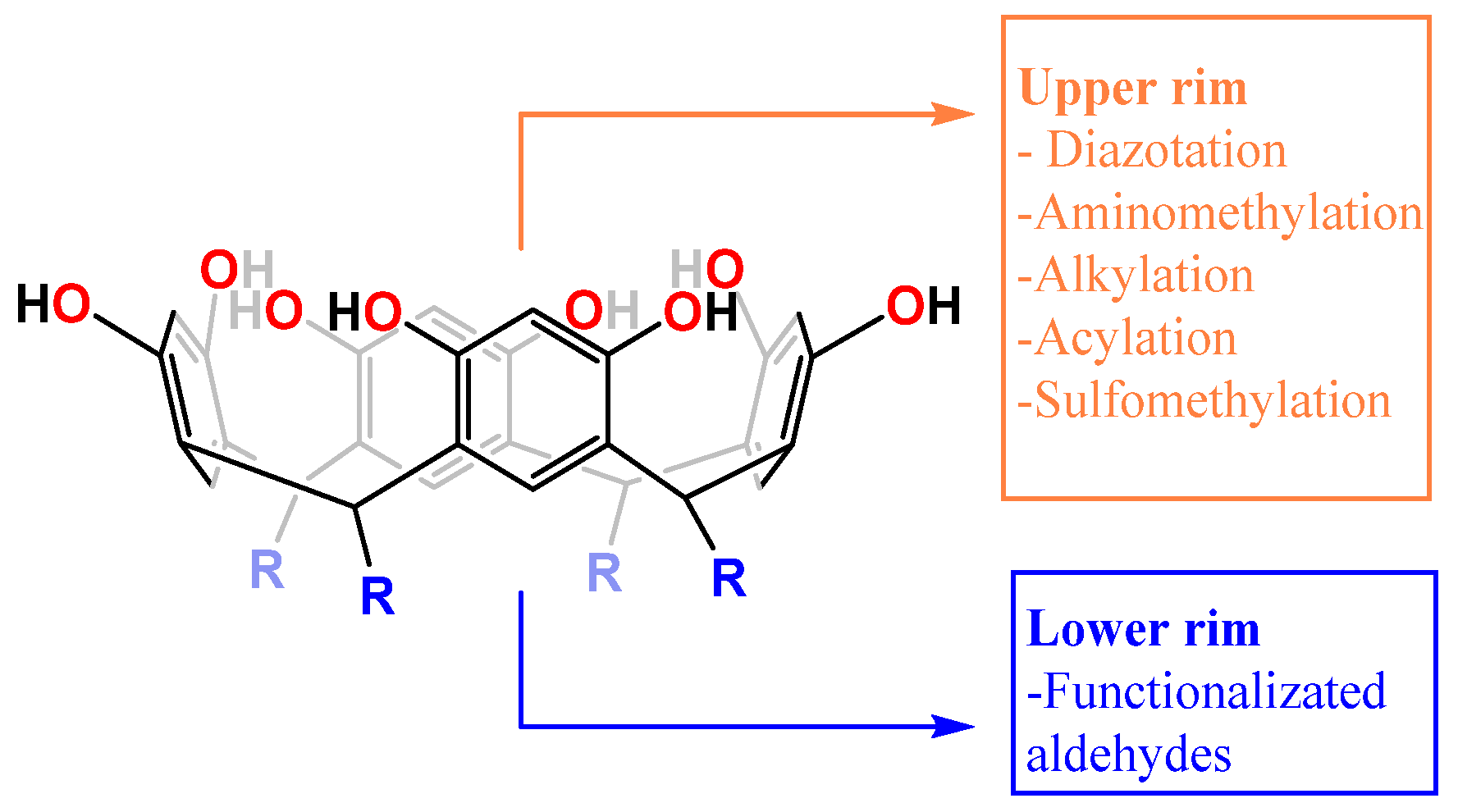
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
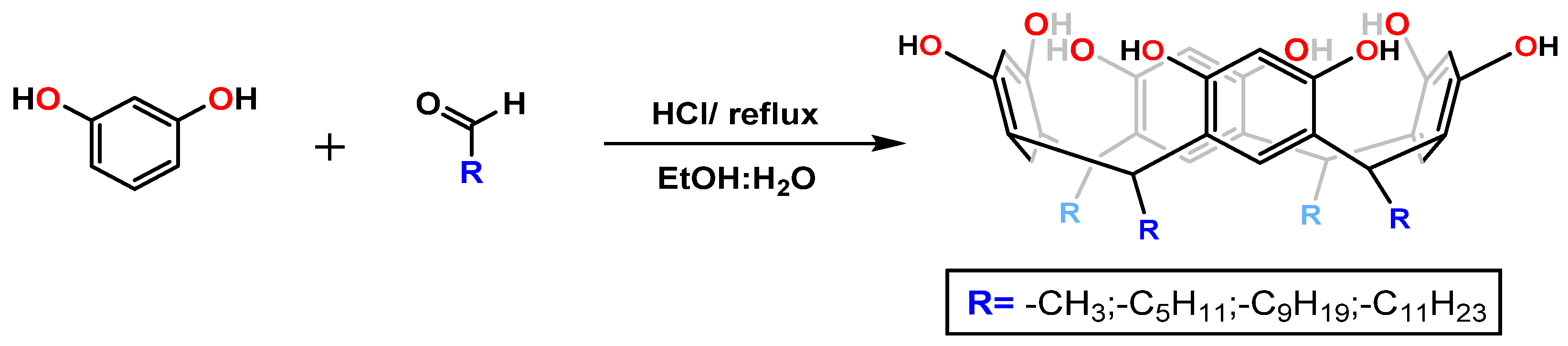
2.1. General Procedure for Synthesis of Resorcinarenes
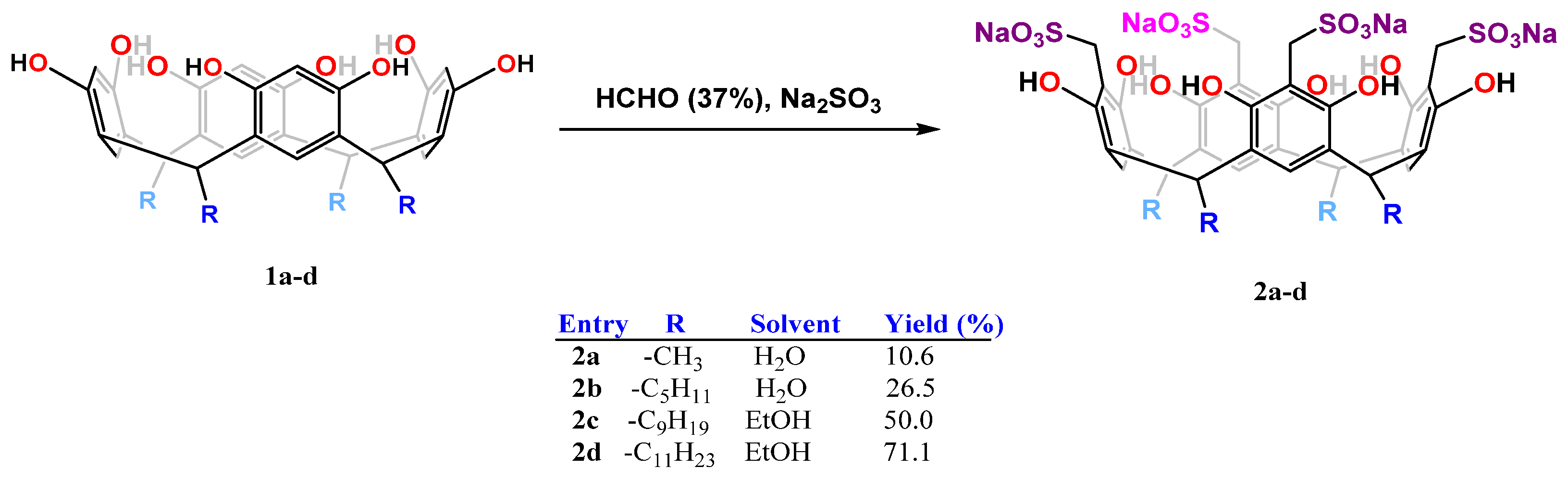
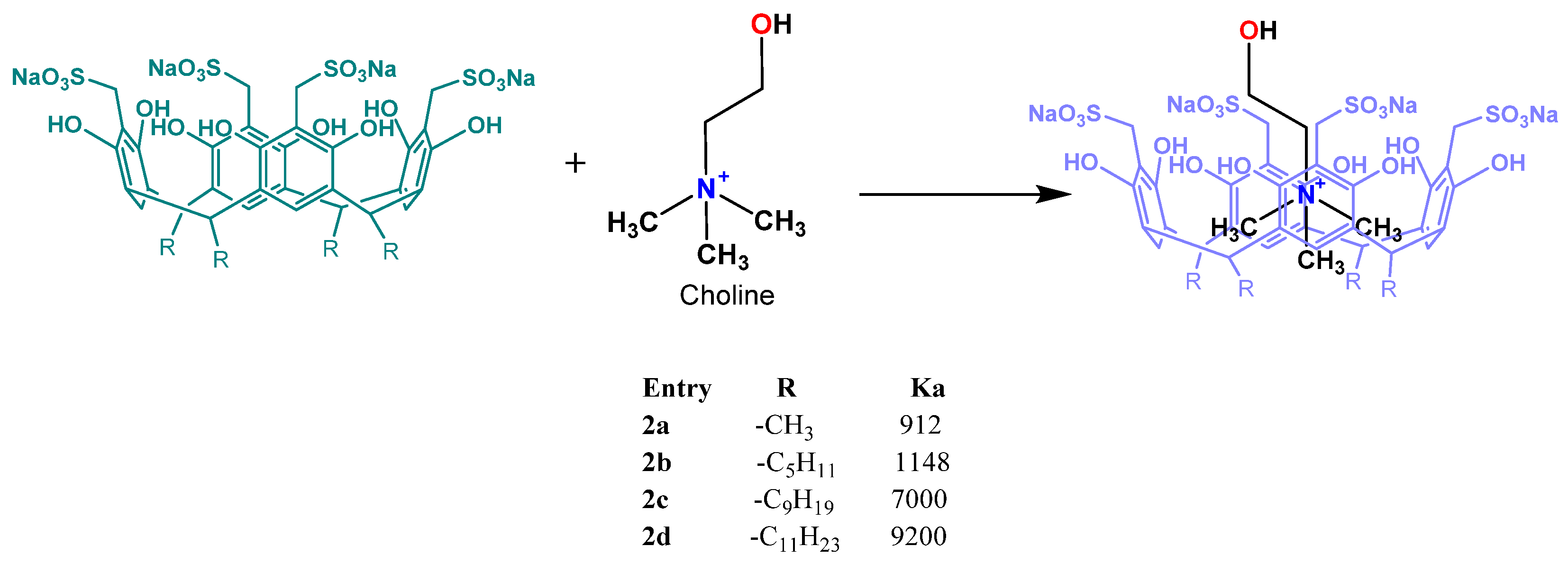
2.2. General Procedure for Sulfomethylation of Resorcinarenes
2.3. ATR-IR Analysis
2.4. Conductimetric Titrations
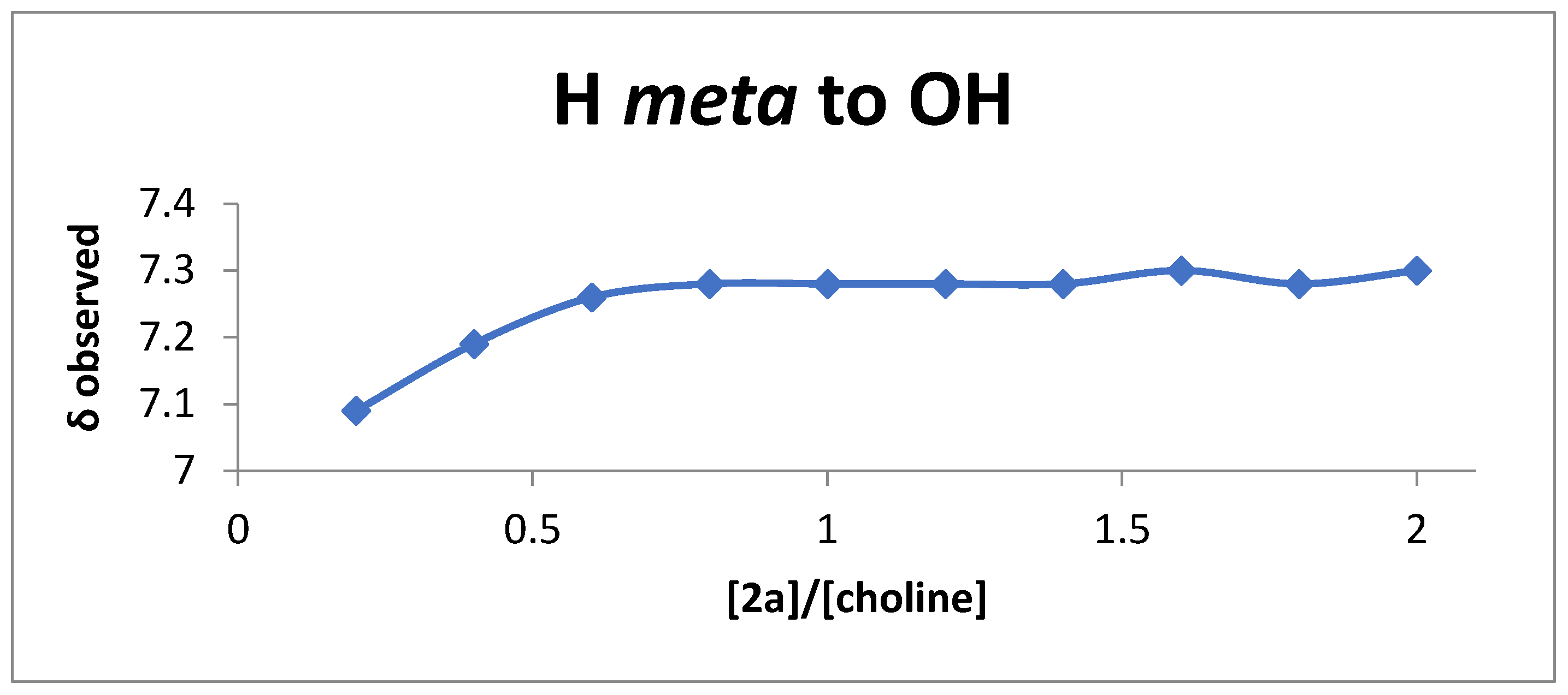
2.5. NMR Titrations
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeisel, S.H.; da Costa, K.A. Choline: An essential nutrient for public health. Nutr. Rev. 2009, 67, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisel, S.H.; Blusztajn, J.K. Choline and human nutrition. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1994, 14, 269–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwagi, Y.; Ono, T.; Sato, F.; Kumano, M.; Yoshida, K.; Dairaku, T.; Sasano, Y.; Iwabuchi, Y.; Sato, K. Electrochemical determination of choline using nortropine-N-oxyl for a non-enzymatic system. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2019, 27, 100302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisel, S.H. Choline: Critical role during fetal development and dietary requirements in adults. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2006, 26, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Rahman, M.K.A.; Mazzone, G.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Sicilia, E.; Shoeib, T. Novel choline selective electrochemical membrane sensor with application in milk powders and infant formulas. Talanta 2020, 221, 121409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubrich, D.R.; Gerber, N.; Pflueger, A.B.; Zweig, M. Tissue Choline Studied Using a Simple Chemical Assay. J. Neurochem. 1981, 36, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, J.L.F.C.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Vaz, M.C.V.F. Enzymatic determination of choline in milk using a FIA system with potentiometric detection. Analyst 2000, 125, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ding, S.; Shan, D.; Sun, Y. Bioelectrochemical response of a choline biosensor fabricated by using polyaniline. Sci. China Chem. 2009, 52, 2275–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheipesh, T.; Mchedlov–Petrossyan, N.; Bogdanova, L.; Kharchenko, D.; Roshal, A.; Vodolazkaya, N.; Taranets, Y.; Shekhovtsov, S.; Rodik, R.; Kalchenko, V. Aggregates of cationic calix[4]arenes in aqueous solution as media for governing protolytic equilibrium, fluorescence, and kinetics. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 366, 119940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Fang, Y.; Dehaen, W. Macrocyclic arenes functionalized with BODIPY: Rising stars among chemosensors and smartmaterials. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V.K.; Kanaiya, P.H. Chemistry of calix[4]resorcinarenes. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2011, 80, 75–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmerman, P.; Verboom, W.; Reinhoudt, D.N. Resorcinarenes. Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 2663–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Aguirre, A.A.; Monroy, Z.J.R.; Maldonado, M. Analysis by RP-HPLC and Purification by RP-SPE of the C -Tetra(p -hydroxyphenyl)resorcinolarene Crown and Chair Stereoisomers. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2019, 2019, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziaja, P.; Krogul, A.; Pawłowski, T.S.; Litwinienko, G. Structure and stoichiometry of resorcinarene solvates as host–guest complexes—NMR, X-ray and thermoanalytical studies. Thermochim. Acta 2016, 623, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmadi, S.; Mohamad, S.; Maah, M.J. Comparative study of tributyltin adsorption onto mesoporous silica functionalized with calix[4]arene, p-tert-butylcalix[4]arene and p-sulfonatocalix[4]arene. Molecules 2014, 19, 4524–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruderisch, A.; Pfeiffer, J.; Schurig, V. Synthesis of an enantiomerically pure resorcinarene with pendant l-valine residues and its attachment to a polysiloxane (Chirasil-Calix). Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2001, 12, 2025–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Harrison, R.G.; Lamb, J.D. Application of resorcinarene derivatives in chemical separations. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2013, 78, 39–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, A.; Stavens, K.B.; Pusztay, S.V.; Andres, R.P. Synthesis and Characterization of Resorcinarene-Encapsulated Nanoparticles. MRS Proc. 1999, 581, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.M.; Soh, S.F.; Zhao, J.; Yong, E.L.; Gong, Y. Preparation and application of methylcalix[4]resorcinarene-bonded silica particles as chiral stationary phase in high-performance liquid chromatography. Chirality 2011, 23, E91–E97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, G.; Cadavid-Montoya, N.A.; Maldonado, M. Evaluation of a Resorcinarene-Based Sorbent as a Solid-Phase Extraction Material for the Enrichment of L-Carnitine from Aqueous Solutions. Processes 2023, 11, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, N.; Brenner, E.; Sémeril, D.; Matt, D.; Harrowfield, J. The Use of Resorcinarene Cavitands in Metal-Based Catalysis. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 2017, 6100–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, N.; Sémeril, D.; Brenner, E.; Matt, D.; Özdemir, I.; Kaya, C.; Toupet, L. Resorcinarene-Functionalised Imidazolium Salts as Ligand Precursors for Palladium-Catalysed Suzuki–Miyaura Cross-Couplings. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, U.; Modi, K.; Panchal, M.; Mehta, V.; Jain, V.K. Catalytic activity of recyclable resorcinarene-protected antibacterial Pd nanoparticles in C-C coupling reactions. Chin. J. Catal. 2016, 37, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, W.-Y.; Xu, G.; Yang, J.; Wu, H.; Chen, B.; Zhou, W.; Ma, J.-F. Versatile Assembly of Metal-Coordinated Calix[4]resorcinarene Cavitands and Cages Through Ancillary Linker Tuning. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 7648–7656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, A.V.; Han, S.; Balasubramanian, R. Rapid selective colorimetric sensing of polyphosphates by ionic resorcinarene cavitand interdigitated gold nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 247, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehbie, M.; Arrachart, G.; Cruz, C.A.; Karamé, I.; Ghannam, L.; Pellet-Rostaing, S. Organization of diglycolamides on resorcinarene cavitand and its effect on the selective extraction and separation of HREEs. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 187, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollok, C.H.; Zhang, Q.; Tiefenbacher, K.; Merten, C. Chirality Induction from a Chiral Guest to the Hydrogen-Bonding Network of Its Hexameric Resorcinarene Host Capsule. Chemphyschem 2017, 18, 1987–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Catti, L.; Kaila, V.R.I.; Tiefenbacher, K. To catalyze or not to catalyze: Elucidation of the subtle differences between the hexameric capsules of pyrogallolarene and resorcinarene. Chem. Sci. 2016, 8, 1653–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdurakhmanova, E.R.; Mondal, D.; Jędrzejewska, H.; Cmoch, P.; Danylyuk, O.; Chmielewski, M.J.; Szumna, A. Supramolecular umpolung: Converting electron-rich resorcin[4]arenes into potent CH-bonding anion receptors and transporters. Chem 2024, 10, 1910–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanabria, E.; Esteso, M.A.; Vargas, E.F. Recognition of Heavy Metals by Using Resorcin[4]arenes Soluble in Water. Toxics 2022, 10, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro-Hernández, L.D.; Martínez-Klimova, E.; Cortez-Maya, S.; Mendoza-Cardozo, S.; Ramírez-Ápan, T.; Martínez-García, M. Synthesis, Characterization, and Nanomedical Applications of Conjugates Between Resorcinarene-Dendrimers and Ibuprofen. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijanova, I.V.; Moggio, I.; Arias, E.; Klimova, T.; Martínez-García, M. Resorcinarene-dendrimers with stilbene moieties for optoelectronics. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 10258–10266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Aguirre, A.; Maldonado, M.; Esteso, M.A. Removal of Toxic Metal Ions Using Poly(BuMA–co–EDMA) Modified with C-Tetra(nonyl)calix[4]resorcinarene. Toxics 2022, 10, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazakova, E.K.; Makarova, N.A.; Ziganshina, A.U.; Muslinkina, L.A.; Muslinkin, A.A.; Habicher, W.D. Novel water-soluble tetrasulfonatomethylcalix[4]resorcinarenes. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 41, 10111–10115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.; Jiang, K.; Fan, Z.; Wang, D.; Gu, P.; Zhou, S.; Li, Z. Post-synthetic sulfonation of resorcinarene-based porous organic polymer for superfast adsorption of diverse organic pollutants. Polymer 2024, 313, 127738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, J.H.; Wishard, A.; Mague, J.T.; Gibb, B.C. Binding properties and supramolecular polymerization of a water-soluble resorcin[4]arene. Org. Chem. Front. 2019, 6, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.C.; Edionwe, E.; Michel, B. Conductimetric Titrations: A Predict−Observe−Explain Activity for General Chemistry. J. Chem. Educ. 2010, 87, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas-Hinestroza, J.L.; Pérez-Redondo, A.; Maldonado, M. Inclusion complexation between neurotransmitters with polyacetylated calix[4]pyrogallolarenes: 1H-NMR and crystallographic analysis. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2022, 48, 3091–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ©2018 Hyperquad Limited, Equilibrium Constants from Averaged Chemical Shifts. Available online: http://www.hyperquad.co.uk/ (accessed on 21 January 2025).
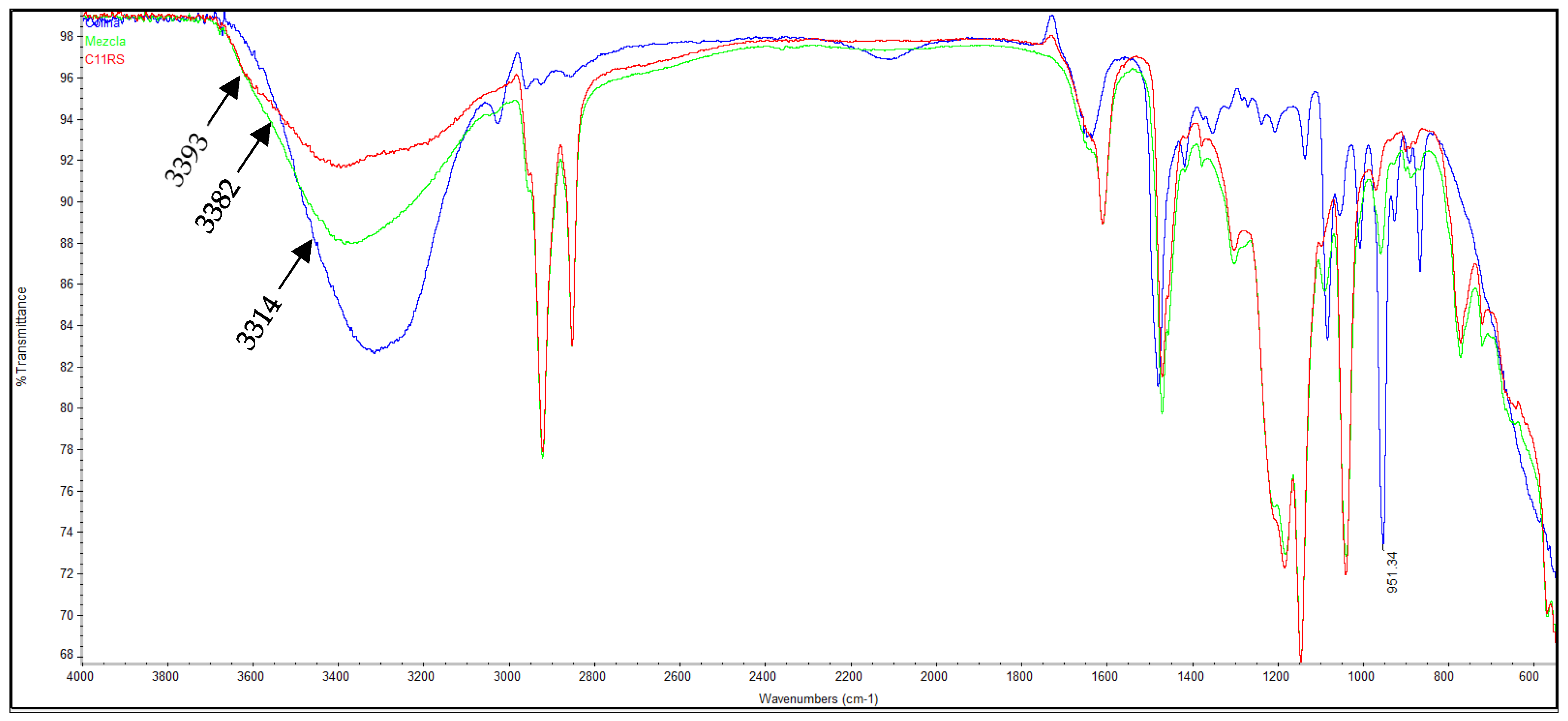
 ), Sulfomethylated resorcinarene (2d) (red,
), Sulfomethylated resorcinarene (2d) (red,  ) and equimolar mixture (green,
) and equimolar mixture (green,  ).
).
 ), Sulfomethylated resorcinarene (2d) (red,
), Sulfomethylated resorcinarene (2d) (red,  ) and equimolar mixture (green,
) and equimolar mixture (green,  ).
).



| 2a | 2b | 2c | 2d | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IR (ATR/cm−1) | (O-H) | 3401 | 3414 | 3418 | 3393 |
| (ArC-H), | 3070 | 3050 | 3050 | 3055 | |
| (aliphatic C-H) | 2932 | 2927 | 2921 | 2851 | |
| (S=O) | 1075 | 1046 | 1038 | 1039 | |
| (S-O) | 780 | 757 | 706 | 770 | |
| 13C and 1H NMR * | (C-OHa) | --- (C) 149.7 | --- (C) 153.9 | (s, 8H) 9.73 (C) 150.1 | (s, 8H) 9.72 (C) 150.4 |
| (C-Hb) | (s, 4H) 6.59 (C) 109.1 | (s, 4H) 7.17 (C) 110.7 | (s, 4H) 7.13 (C) 109.1 | (s, 4H) 7.23 (C) 109.6 | |
| (C-Hc) | (s, 8H) 4.29 (C) 48.1 | (s, 8H) 3.95 (C) 52.9 | (s, 4H) 3.82 (C) 48.3 | (s, 8H) 3.85 (C) 48.7 | |
| (C-Hd), | (t, 4H) 4.51 (C) 28.4 | (t, 4H) 4.29 (C) 35.8 | (t, 4H) 4.18 (C) 34.1 | (t, 4H) 4.20 (C) 32.3 | |
| (Alkyl chain), CH2 | --- | (32H) 1.23–2.71 (C) 23.7–35.8 | (64H) 1.24–2.18 (C) 22.1–31.3 | (80H) 1.25–2.18 (C) 22.6–32.3 | |
| (C-H), CH3 | (t, 12H) 1.40 (C) 20.2 | (t, 12H) 0.85 (C) 14.0 | (t, 12H) 0.84 (C) 13.9 | (t, 12H) 0.83 (C) 14.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Urquijo, C.; Vela, M.; Sarmiento, R.; Maldonado, M. Molecular Interaction of Water-Soluble Resorcinarenes for Potential Choline Detectors. Processes 2025, 13, 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13020553
Urquijo C, Vela M, Sarmiento R, Maldonado M. Molecular Interaction of Water-Soluble Resorcinarenes for Potential Choline Detectors. Processes. 2025; 13(2):553. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13020553
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrquijo, Cielo, Miguel Vela, Roger Sarmiento, and Mauricio Maldonado. 2025. "Molecular Interaction of Water-Soluble Resorcinarenes for Potential Choline Detectors" Processes 13, no. 2: 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13020553
APA StyleUrquijo, C., Vela, M., Sarmiento, R., & Maldonado, M. (2025). Molecular Interaction of Water-Soluble Resorcinarenes for Potential Choline Detectors. Processes, 13(2), 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13020553





