Characteristics of Nanosecond Bipolar Pulsed Water Electrode Dielectric Barrier Discharge for Ozone Generation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Electrical Characteristics
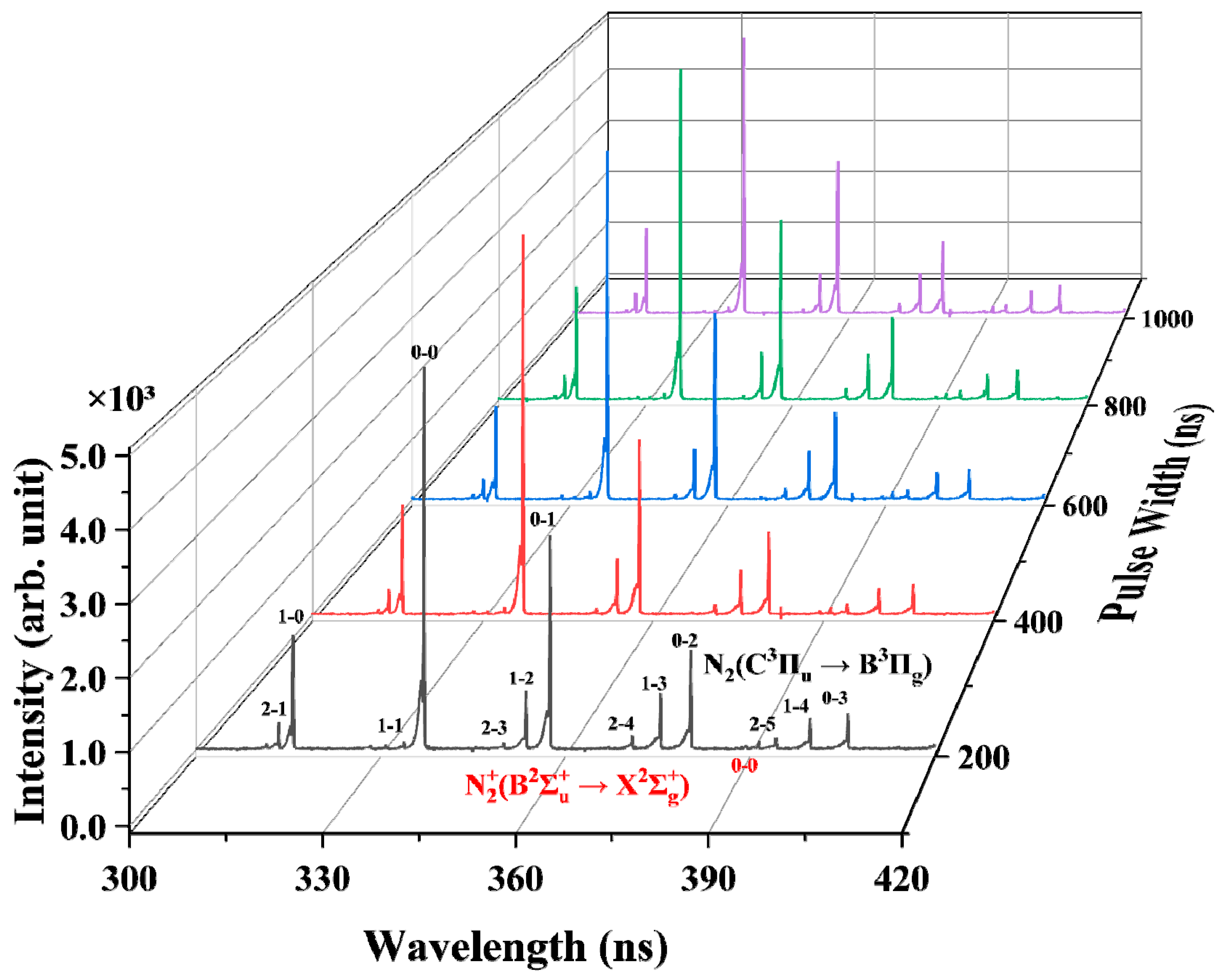
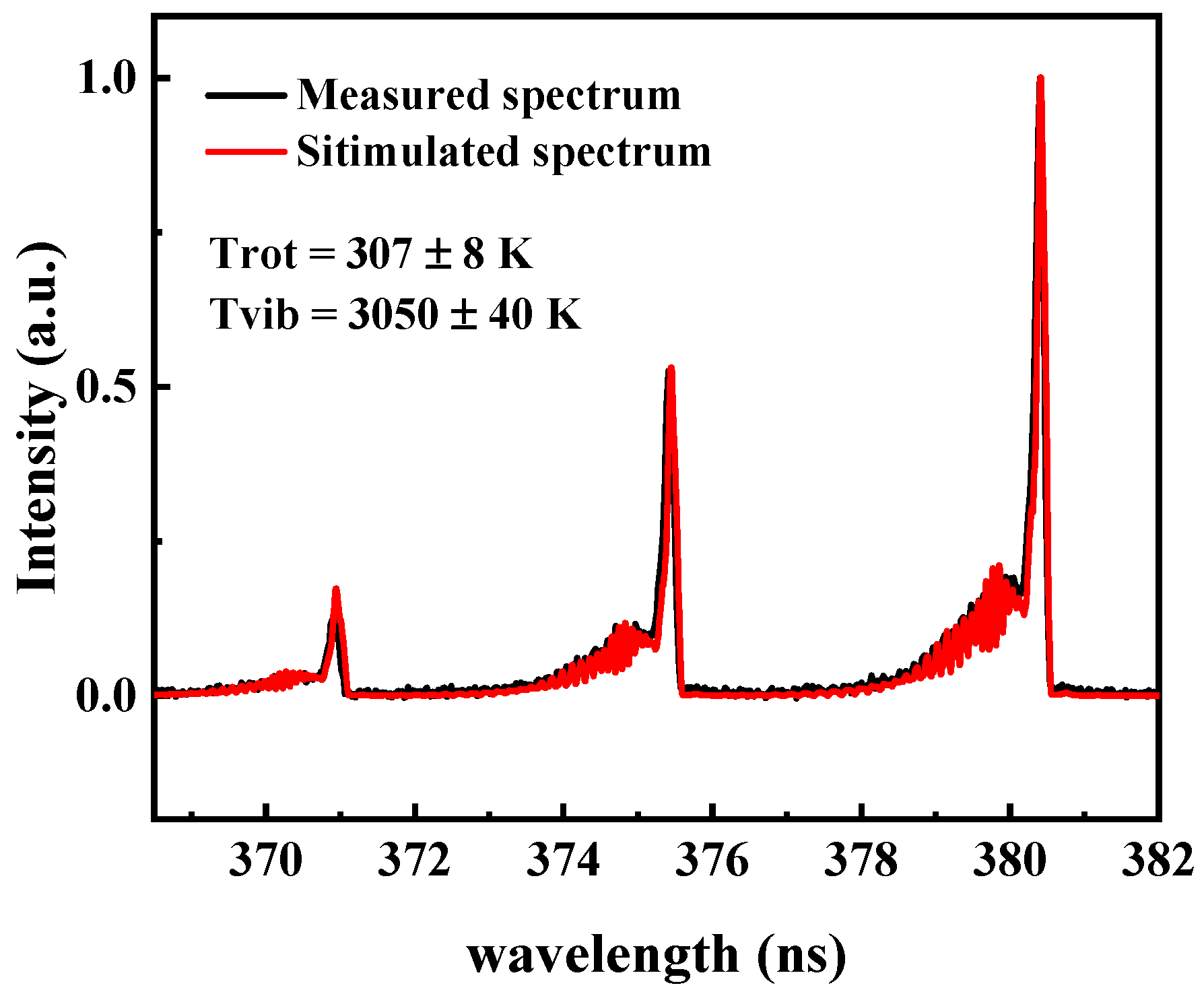
3.2. The Optical Emission Spectroscopy and Gas Temperature
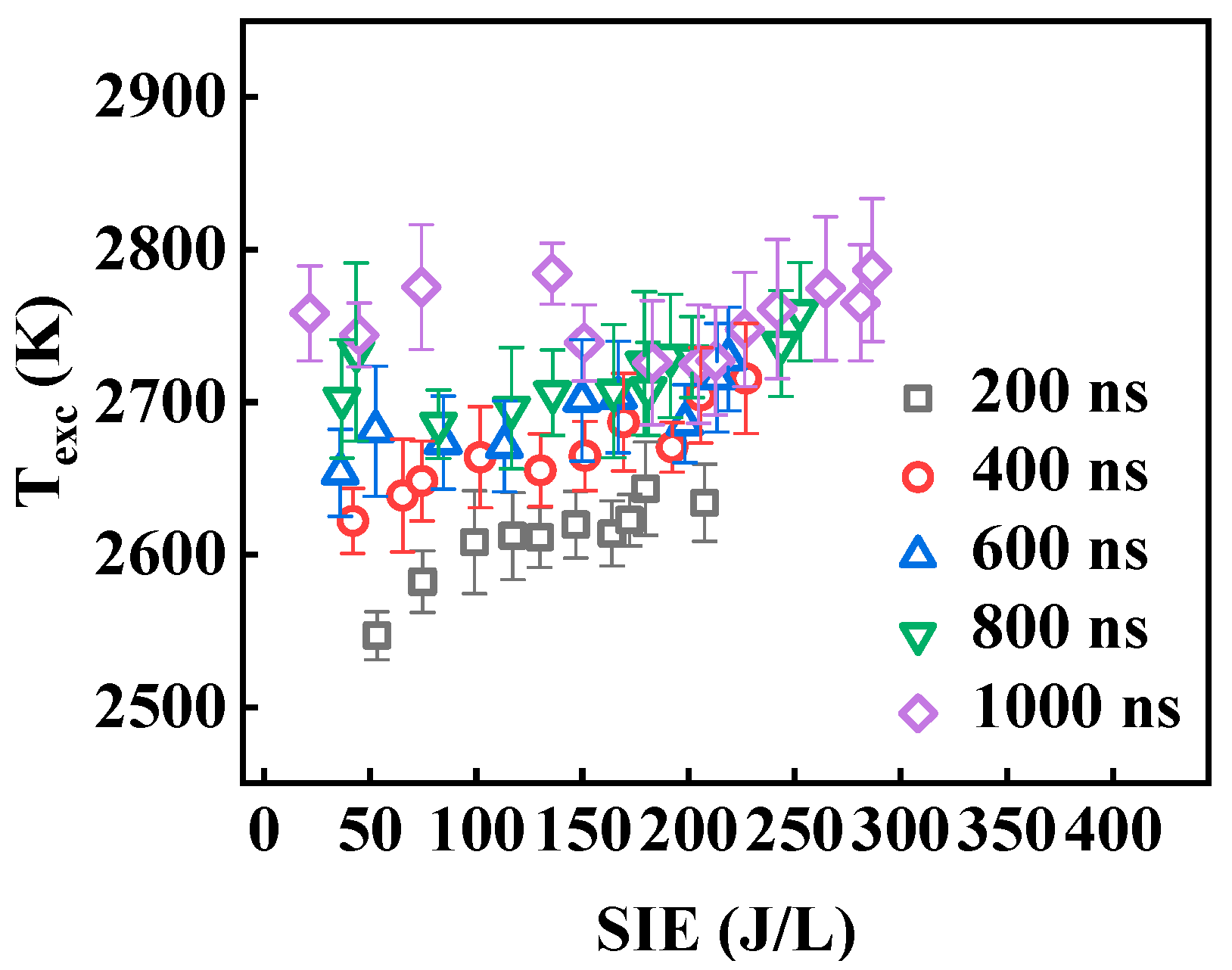
3.3. The Electron Excitation Temperature
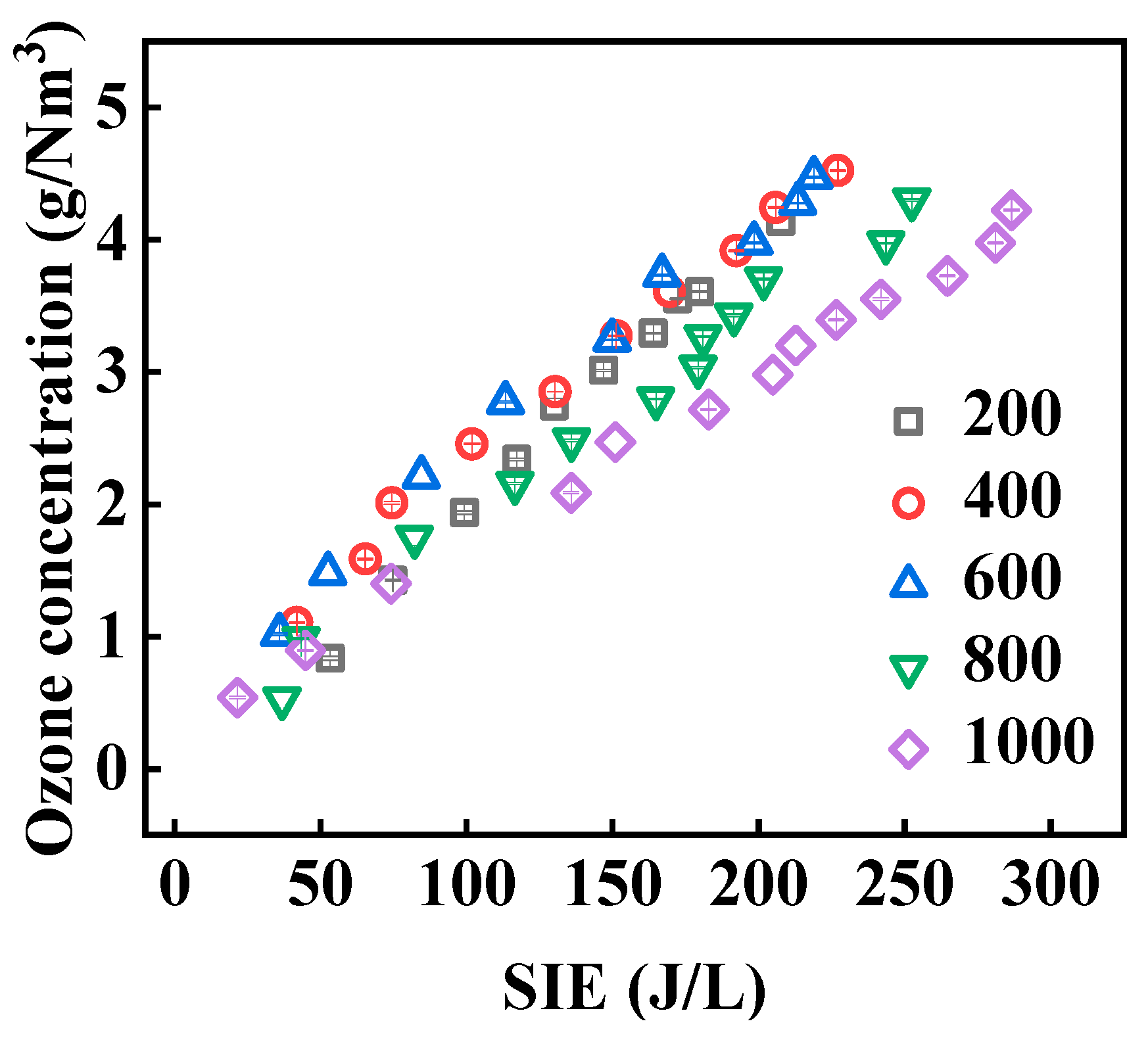
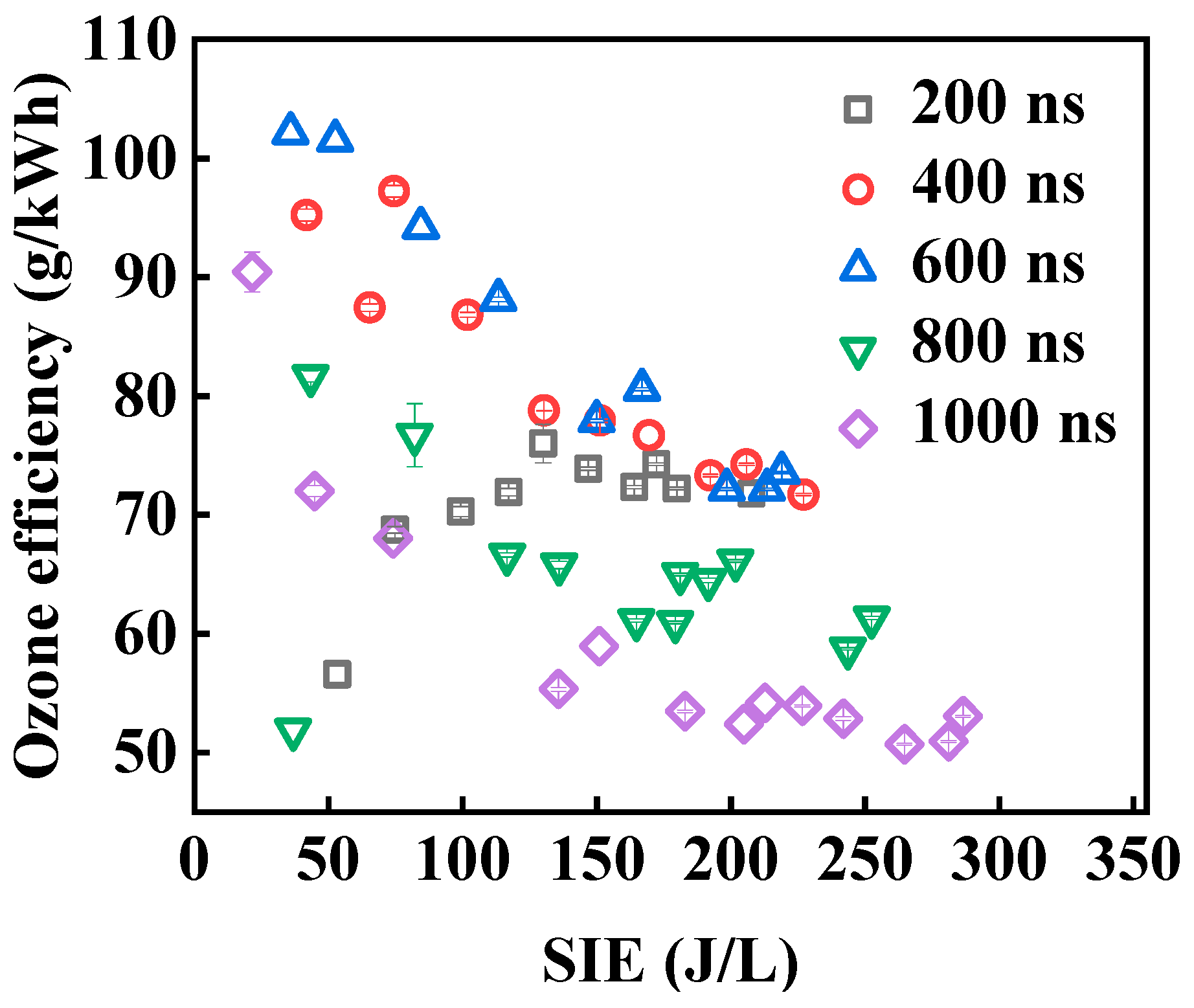
3.4. The Ozone Production
4. Conclusions
- The bipolar pulse voltage alternates symmetrically, with the Trot maintained between 307–310 K, and the Tvib remains stable at 3120 ± 50 K. This thermal stability outperforms Jiang et al.’s cylindrical metal-electrode bipolar pulse DBD and Zhang et al. ’s conventional DBD, effectively suppressing ozone decomposition while ensuring sufficient O2 dissociation energy, addressing a long-standing trade-off in pulse DBD ozone generation
- The Texc increases as SIE and Tp increase: when SIE = 200 J/L, Tp extends from 200 ns to 1000 ns, and Texc rises from 2633 K to 2724 K.
- The ozone generation efficiency exhibits a “first increases, then decreases” trend with respect to Tp: the optimal Tp is between 500–600 ns, where the maximum efficiency reaches 102 g/kWh (corresponding to SIE = 35.95 J/L), slightly higher than the peak efficiency of 99.64 ± 0.87 g/kWh (corresponding to SIE = 33.60 ± 1.53 J/L) in the single-pulse-driven water electrode reactor. When Tp exceeds 600 ns, excess energy deposition results in an increase in discharge temperature, leading to a decrease in efficiency. This result confirms the originality of bipolar pulses in improving energy utilization, while the low SIE (35.95 J/L) and air-fed compatibility endow the system with practical value for industrial on-site ozone generation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kogelschatz, U. Dielectric-barrier discharges: Their history, discharge physics, and industrial applications. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2003, 23, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, G.; Wang, T.; MacGregor, S.J.; Ren, Q.; Wilson, M.P.; Timoshkin, I.V. Optimization of ozone generation by investigation of filament current characteristics under dielectric barrier discharge. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2016, 44, 2129–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, J.; Lv, H.; Zeng, X.; Ling, Z.; Ding, L.; Jin, C.J.P. Advances in Ozone Technology for Environmental, Energy, Food and Medical Applications. Processes 2025, 13, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanos, J.C.; Wabner, D.W. Elektrochemische abscheidung von sauerstoff und ozon an bleidioxid und platin-anoden in wässrigen elektrolyten mit 18O-markiertem wasser. Electrochim. Acta 1985, 30, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, B.; Kogelschatz, U. Ozone generation with narrow–band UV radiation. Ozone Sci. Eng. 1991, 13, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabuchi, R.; Nakata, Y.; Kageyama, T.; Teranishi, K.; Shimomura, N. Investigation of ozone production using nanosecond pulsed power to increase ozone concentration. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Power Modulator and High Voltage Conference (IPMHVC), San Diego, CA, USA, 3–7 June 2012; pp. 512–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.-C.; Wang, W.-C.; Zhang, S.; Jia, L.; Yang, D.-Z.; Tang, K.; Liu, Z.-J. An uniform DBD plasma excited by bipolar nanosecond pulse using wire-cylinder electrode configuration in atmospheric air. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 122, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, D.; Ding, C.; He, Y.; Wang, Z.; Kumar, S.; Zhu, Y.; Cen, K. Characteristics of dielectric barrier discharge ozone synthesis for different pulse modes. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2017, 37, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Yun, U.-H.; Kim, J.-G. Characteristics of high-repetition-rate bipolar pulse DBD under various electrical conditions in atmospheric-pressure air. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2023, 57, 125206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, X.; Yuan, D.; Wang, L.; Xie, L.; Wei, L.; Zhang, G.J.V. Enhancing ozone production in dielectric barrier discharge utilizing water as electrode. Vacuum 2023, 212, 112047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, K.; Yuan, D.; Jin, C.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Peng, B.; Wei, L.J.V. Ozone production in nanosecond pulsed dielectric barrier discharge in synthetic air: The effect of pulse width. Vacuum 2024, 230, 113688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Yuan, D.; Wang, L.; Zhang, G.; Peng, B.; Wei, L.; Ling, Z. A novel dielectric barrier discharge ozone generator with excellent microdischarge temperature behavior. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 250, 123453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shang, K.; Duan, L.; Li, Y.; An, J.; Zhang, C.; Lu, N.; Li, J.; Wu, Y. Influence of power supply on the generation of ozone and degradation of phenol in a surface discharge reactor. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 418, 012131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Lin, F.; Peng, B.; Wei, L.; Ling, Z.; Zeng, X.; Yuan, D.J.V. Nanosecond pulsed multi-hollow surface dielectric barrier discharge for ozone production. Vacuum 2025, 238, 114252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, M.; Li, X. A pulsed bipolar current-mode power supply with high power factor in a single stage for dielectric barrier discharge application. Circuit World 2025, 51, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, H.T.; Uesugi, Y.; Nguyen, X.B. Mechanisms of low-frequency dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma driven by unipolar pulses and bipolar pulses. AIP Adv. 2021, 11, 025022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, B.; Zhang, Q.; Bogaerts, A.J.C. Mode transition of filaments in packed-bed dielectric barrier discharges. Catalysts 2018, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenhao, Z.; Zhang, D.; Xiaohui, D.; Xi, Z.; Feng, L.; Zhi, F. Effect of dielectric material on the uniformity of nanosecond pulsed dielectric barrier discharge. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2024, 26, 094008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jia, L.; Wang, W.-c.; Yang, D.-z.; Tang, K.; Liu, Z.-J. The influencing factors of nanosecond pulse homogeneous dielectric barrier discharge in air. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 117, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yao, J.; He, F.; Ouyang, J. Comparison of ozone production in planar DBD of different modes. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2024, 44, 891–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-H.; Abdelaziz, A.A.; Teramoto, Y.; Nozaki, T.; Kim, D.-Y.; Brandenburg, R.; Schiorlin, M.; Hensel, K.; Song, Y.-H.; Lee, D.; et al. Revisiting why DBDs can generate O 3 against the thermodynamic limit. Int. J. Plasma Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 17, e02004. [Google Scholar]
- Jodzis, S.; Baran, K. The influence of gas temperature on ozone generation and decomposition in ozone generator. How Is Ozone Decomposed? Vacuum 2022, 195, 110647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodzis, S.; Barczyński, T. Ozone synthesis and decomposition in oxygen-fed pulsed DBD system: Effect of ozone concentration, power density, and residence time. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2019, 41, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, N.; Shang, K.; Wu, Y. Diagnosis of electronic excitation temperature in surface dielectric barrier discharge plasmas at atmospheric pressure. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2014, 16, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsheng, W.; Liang, X.; Zhang, Y. Numerical investigation on the effect of gas parameters on ozone generation in pulsed dielectric barrier discharge. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2018, 20, 125505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Jin, C.; Li, Y.; Zeng, X.; Wei, L.; Ling, Z.; Lin, F. Advanced ozone generator for efficient NOx oxidation: Enhanced energy efficiency with optimal microdischarge temperature. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2025, 65, 103954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lee, B.J.; Im, H.G.; Cha, M.S. Ozone production with dielectric barrier discharge: Effects of power source and humidity. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2016, 44, 2288–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Researchers | Type of DBD | Gas Source | Power Supply | SIE (J/L) | Ozone Generation Efficiency (g/kWh) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wu et al., 2025 | Single-water electrode DBD | Air | Bipolar Pulse | 35.95 | 102 | This work |
| Yuan et al., 2025 | Double-water electrode DBD | Air | Pulse | 176.9 | 312 | [26] |
| Ji et al., 2024 | Single-water electrode DBD | Air | Pulse | 33.6 | 99.64 | [11] |
| Zhang et al., 2016 | Conventional DBD | Air (Dry/Humid) | Pulse | 23 | 80 | [27] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, W.; Jin, C.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, X.; Wei, L.; Ling, Z.; Wang, L. Characteristics of Nanosecond Bipolar Pulsed Water Electrode Dielectric Barrier Discharge for Ozone Generation. Processes 2025, 13, 3619. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113619
Wu W, Jin C, Wu Y, Zeng X, Wei L, Ling Z, Wang L. Characteristics of Nanosecond Bipolar Pulsed Water Electrode Dielectric Barrier Discharge for Ozone Generation. Processes. 2025; 13(11):3619. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113619
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Weitian, Chenyang Jin, Yifan Wu, Xianyang Zeng, Linsheng Wei, Zhongqian Ling, and Lijian Wang. 2025. "Characteristics of Nanosecond Bipolar Pulsed Water Electrode Dielectric Barrier Discharge for Ozone Generation" Processes 13, no. 11: 3619. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113619
APA StyleWu, W., Jin, C., Wu, Y., Zeng, X., Wei, L., Ling, Z., & Wang, L. (2025). Characteristics of Nanosecond Bipolar Pulsed Water Electrode Dielectric Barrier Discharge for Ozone Generation. Processes, 13(11), 3619. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113619







