Loofah Sponge Has a Potential Multifunctional Role for Enhanced Tetracycline Biodegradation: Carrier, Putative Nutrient Releaser and Solubilizer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Lfr–ZY Complex
2.3. Removal of TC
2.4. Determination of Antioxidant Enzymes
2.5. Effects of Extract of Lfr on TC Removal
2.6. Adsorption of TC by Lfr
2.7. Reusability
2.8. Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
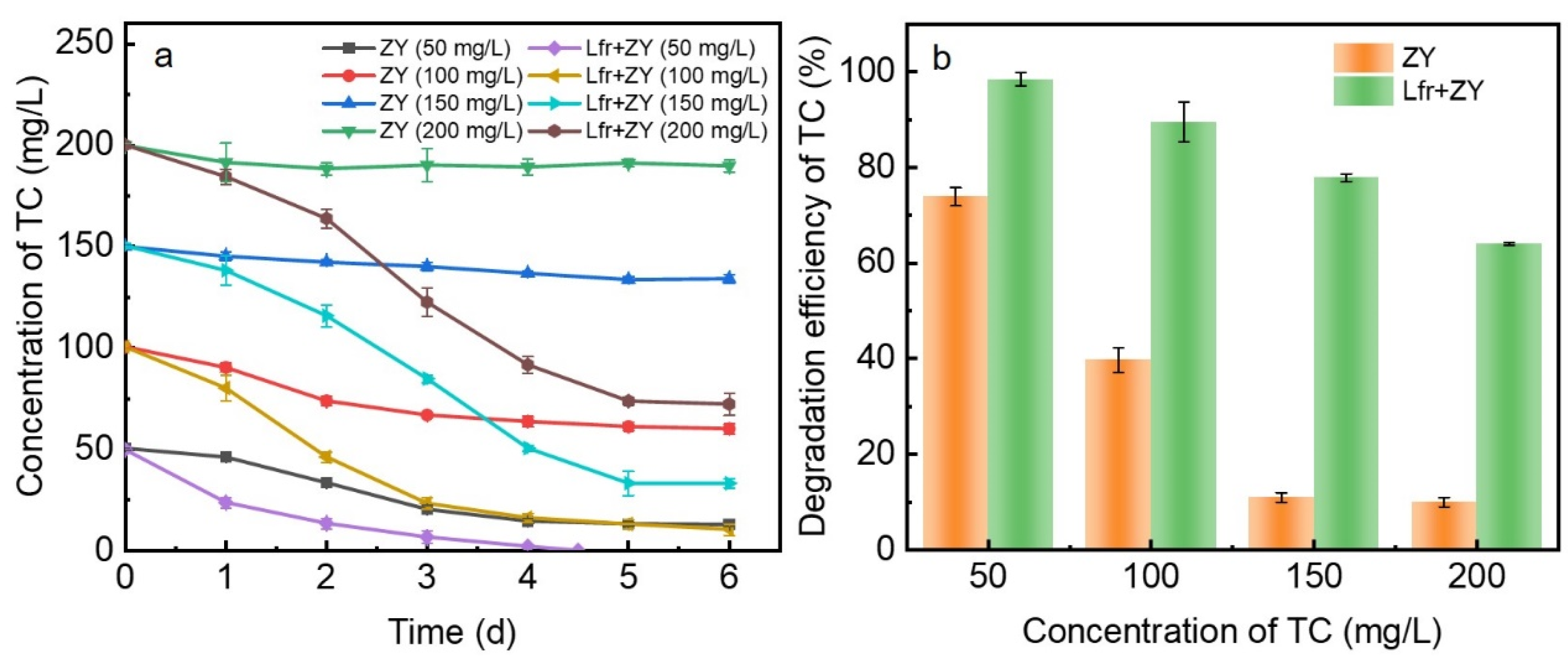
3.1. Removal of TC by ZY and Lfr-ZY
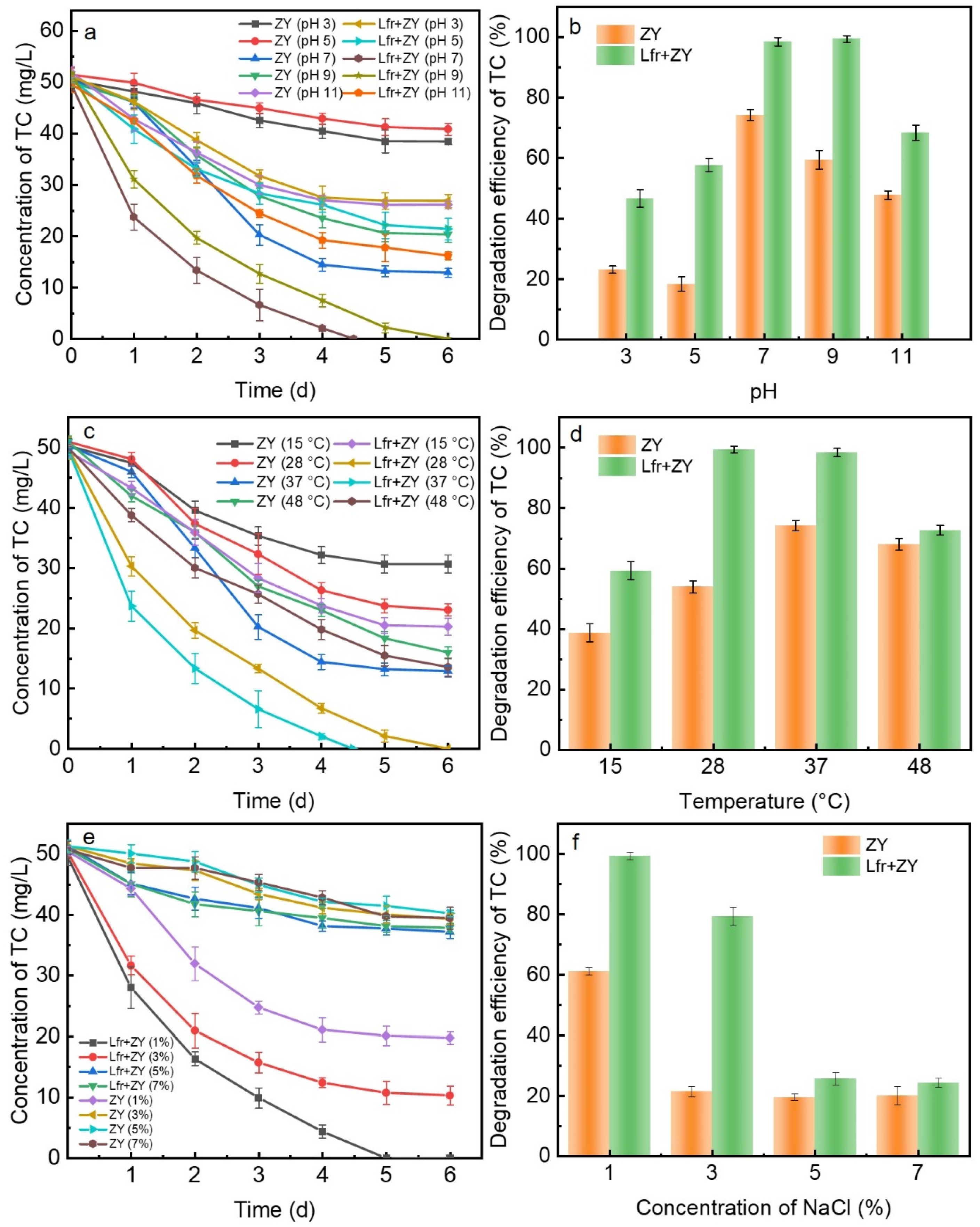
3.2. Influences
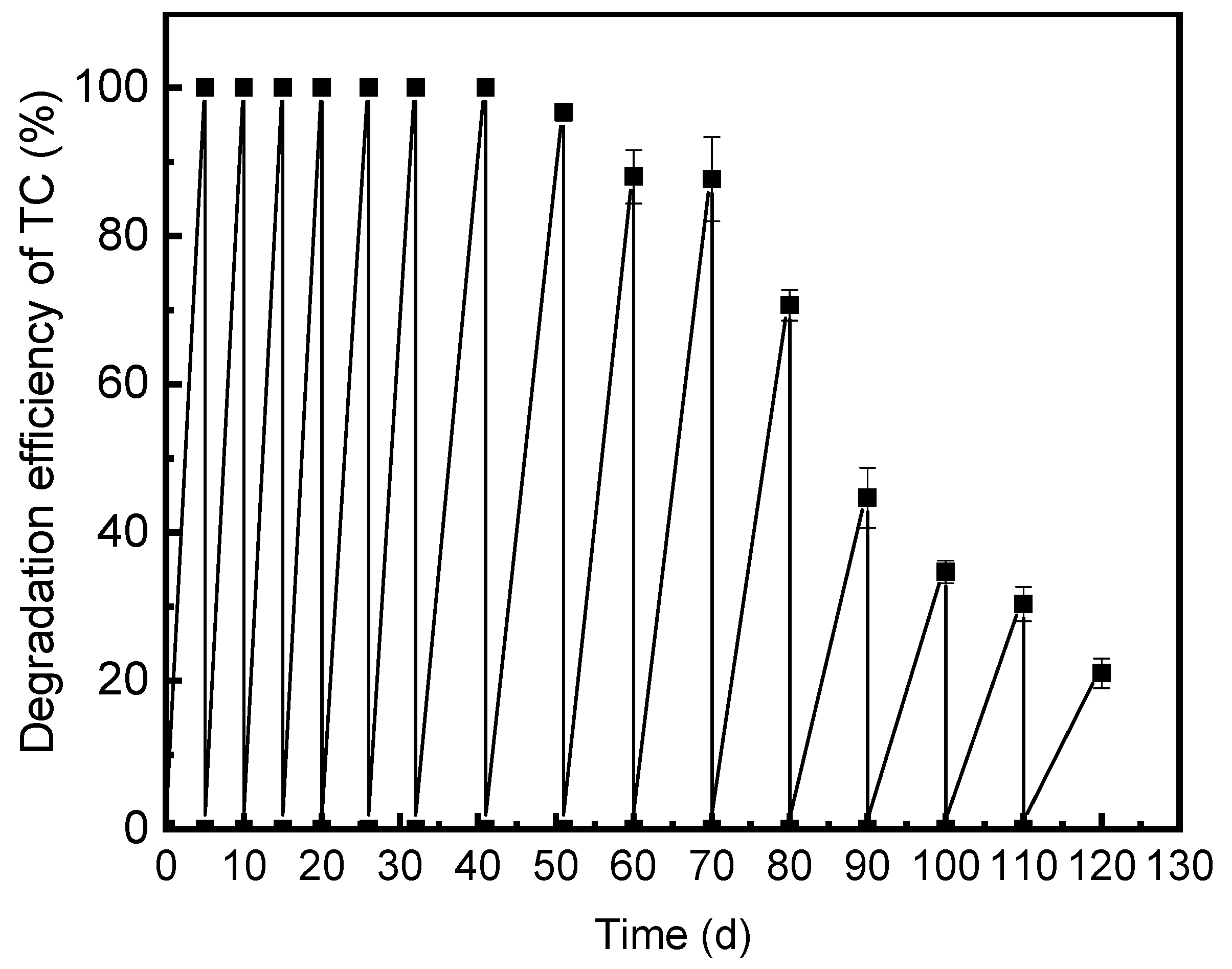
3.3. Cycling
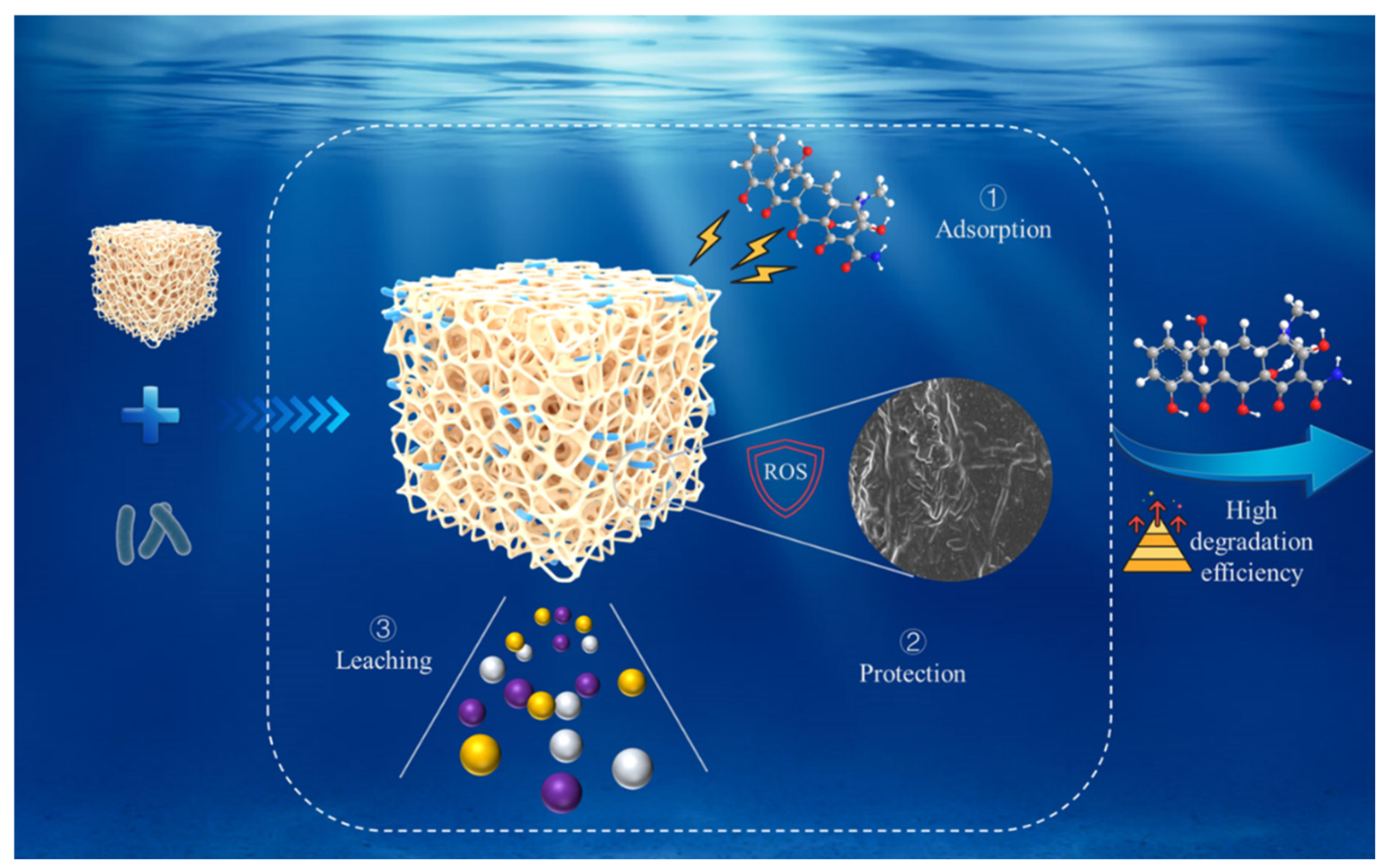
3.4. Mechanism of Lfr Assisting ZY to Enhance TC Removal
3.4.1. Protection of ZY by Lfr
3.4.2. Potential of Nutrient Supplement by Lfr
3.4.3. Potential Solubilizing Effect of Lfr
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.Y.; Du, B.; Wu, G.X. Powdered activated carbon facilitated degradation of complex organic compounds and tetracycline in stressed anaerobic digestion systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 400, 130672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leichtweis, J.; Vieira, Y.; Welter, N.; Silvestri, S.; Dotto, G.L.; Carissimi, E. A review of the occurrence, disposal, determination, toxicity and remediation technologies of the tetracycline antibiotic. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 160, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.X.; Lei, A.J.; Yang, S.; Chen, H.G.; Liu, X.Y.; Liu, L.W.; Kang, X.T. Biodegradation and bioaugmentation of tetracycline by Providencia stuartii TX2: Performance, degradation pathway, genetic background, key enzymes, and application risk assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 477, 135231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.N.; Ye, H.K.; Li, X.J.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, L.X.; Chen, Y.L.; Yang, P.P.; Weng, L.P.; Bai, M.H. Enhancing tetracycline removal: Performance and mechanisms of interspecies electron transfer in microbial consortia. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 492, 138302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, L.J.; Fang, Y.; Jia, X.B.; Chen, J.C. High temperatures can effectively degrade residual tetracyclines in chicken manure through composting. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 380, 120862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amangelsin, Y.; Semenova, Y.; Dadar, M.; Aljofan, M.; Bjorklund, G. The Impact of Tetracycline Pollution on the Aquatic Environment and Removal Strategies. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Song, X.; Miao, J.W.; Ma, Y.F.; Zhao, T.; Yin, M.Y. Removal of tetracycline from water by adsorption with biochar: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 60, 105215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Lin, H.; Ma, J.W.; Zhu RRSun, W.C.; Lin, X.Y.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, H.B.; Zhang, X. Degradation of tetracycline antibiotics by Arthrobacter nicotianae OTC-16. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shen, W.; Chen, J.F.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, C.; Xie, S.G. Tetracycline biotransformation by a novel bacterial strain Alcaligenes sp. T17. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 155130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, P.; Jeon, C.H.; Kim, W. Tetracycline bioremediation using the novel Serratia marcescens strain WW1 isolated from a wastewater treatment plant. Chemosphere 2022, 298, 134344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Dou, X.; Huang, L.; Wang, L.; Meng, D.; Zhai, L.X.; Shen, Y.; You, C.P.; Guan, Z.B.; Liao, X.R. Characterization of a robust cold-adapted thermostable laccase from Pycnoporus sp SYBC-L10 with a strong ability for the degradation of tetracycline oxytetracycline by laccase-mediated oxidation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 382, 121084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.V.; Hsu, F.Y.; Liao, H.Y. Biodegradation of three tetracyclines in swine wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2014, 49, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, Y.Y.; Ke, Y.C.; Chen, C.; Xie, S.G. A comprehensive review on biodegradation of tetracyclines: Current research progress and prospect. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 152852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Gu, Y.C.; Wu, X.Y.; Zhou, X.Y.; Zhou, H.; Amanze, C.; Shen, L.; Zeng, W.M. Construction of a Tetracycline Degrading Bacterial Consortium and Its Application Evaluation in Laboratory-Scale Soil Remediation. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, X.Y.; Feng, F.X.; Xu, X.P. Biodegradation of tetracycline by the yeast strain Trichosporon mycotoxinivorans XPY-10. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 46, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.; Bao, J.G.; Chang, G.F.; Zheng, H.; Li, X.X.; Du, J.K.; Snow, D.; Li, X. Biotransformation of tetracycline by a novel bacterial strain Stenotrophomonas maltophilia DT1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 318, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wu, X.; Shen, L.; Li, J.; Yu, R.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, G.; Zeng, W. Whole Genome Sequencing and Comparative Genomics Analyses of Pandoraea sp. XY-2, a New Species Capable of Biodegrade Tetracycline. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, J. Removal of chlortetracycline from water by immobilized Bacillus subtilis on honeysuckle residue–derived biochar. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Dai, Y.J. Phosphoric acid activation of cow dung biochar for adsorbing enrofloxacin in water: Icing on the cake. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 341, 122887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Dai, Y.J. Vitamin C modified crayfish shells biochar efficiently remove tetracycline from water: A good medicine for water restoration. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 136884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, Y.B.; Liu, G.; Fang, J. Study on a novel immobilized microbe pellets constructed with Alcaligenes sp R3, its ability to remove tetracycline. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristak, L.; Kubovsky, I.; Réh, R. New Challenges in Wood and Wood-Based Materials. Polymers 2021, 13, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Sablani, S. Biodegradable packaging reinforced with plant-based food waste and by-products. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Xiao, D.L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H.C.; Nan, H.Y.; Li DPKan, Y.; Cao, X.D. Biochar as simultaneous shelter, adsorbent, pH buffer, and substrate of Pseudomonas citronellolis to promote biodegradation of high concentrations of phenol in wastewater. Water Res. 2020, 172, 115494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Chen, N.; Feng, C.P. Performance and enhancement mechanism of corncob guiding chromium (VI) bioreduction. Water Res. 2021, 197, 117057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias Padró, M.D.; Caboni, E.; Morin, K.A.S.; Mercado, M.A.M.; Olalde-Portugal, V. Effect of Bacillus subtilis on antioxidant enzyme activities in tomato grafting. PeerJ 2021, 9, 10984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-X.; Xu, Q.M.; Yu, S.C.; Cheng, J.S.; Yuan, Y.J. Bio-removal of tetracycline antibiotics under the consortium with probiotics Bacillus clausii T and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens producing biosurfactants. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Hu, Y.Y.; Cheng, J.H.; Chen, Y.C. Degradation of oxytetracycline (OTC) and nitrogen conversion characteristics using a novel strain. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyanju, C.A.; Ogunniyi, S.; Ighalo, J.O.; Adeniyi, A.G.; Abdulkareem, S. A review on Luffa fibres and their polymer composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 2797. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cao, F. The highly enhanced Cr(VI) photoreduction removal by oxalic acid coordinated with iron-loaded waste Loofah. Environ. Res. 2022, 205, 112456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Liang, J.; Li, Y. Adsorption of tetracycline by polycationic straw: Density functional theory calculation for mechanism and machine learning prediction for tetracyclines’ remediation. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 340, 122869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, G.; Chen, H.; Tang, S. Combining biological chemical methods to disassemble of cellulose from corn straw for the preparation of porous carbons with enhanced adsorption performance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Hu, Y.Y.; Cheng, C.; Cheng, J.H.; Chen, Y.C. Simultaneous degradation of tetracycline and denitrification by a novel bacterium, Klebsiella sp. SQY5. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, Y.B.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.C.; Chen, Z.L.; Shen, J.M. Screen and Study of Tetracycline-Degrading Bacteria from Activated Sludge and Granular Sludge. CLEAN Soil Air Water 2018, 46, 1700411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahumada-Rudolph, R.; Novoa, V.; Becerra, J.; Cespedes, C.; Cabrera-Pardo, J.R. Mycoremediation of oxytetracycline by marine fungi mycelium isolated from salmon farming areas in the south of Chile. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 152, 112198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, S.; Can, K. Pyophage cocktail for the biocontrol of membrane fouling and its effect in aerobic microbial biofilm community during the treatment of antibiotics. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 318, 123965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wei, Y.S.; Zheng, J.X.; Zhao, X.; Zhong, W.K. The behavior of tetracyclines and their degradation products during swine manure composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Tang, F.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Zhao, C.; Li, L. A novel chitosan-biochar immobilized microorganism strategy to enhance bioremediation of crude oil in soil. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkermans, S.; Van Impe, J.F. Mechanistic modelling of the inhibitory effect of pH on microbial growth. Food Microbiol. 2018, 72, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Esmail, G.A.; Arasu, M.V. Effective degradation of tetracycline by manganese peroxidase producing Bacillus velezensis strain Al-Dhabi 140 from Saudi Arabia using fibrous-bed reactor. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 128726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Kong, D.L.; Ma, Q.Y.; Li, Q.Q.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Z.Y.; Parales, R.E.; Ruan, Z.Y. Biodegradation of Tetracycline Antibiotics by the Yeast Strain Cutaneotrichosporon dermatis M503. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, L.; Yang, L.T.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, J.; He, L.; Cui, J.Q.; Shen, J.; Wang, Z. Recoverable magnetic Fe-MOF immobilized carrier to immobilize two microorganisms for reduction of heavy oil viscosity and oilfield wastewater COD. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 56, 104459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Wu, Y.L.; Zhou, H.L.; Yan, H.J.; Liao, Y.; Mao, H. Plant tannin foam anchored iron nanoparticles: Efficient recyclable degradation of tetracycline anti-biotics under high salt conditions. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 426, 139188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, K.; Deng, T.; Ji, B.; Shang, Y.; Wang, H.Y. Immobilization of halophilic yeast for effective removal of phenol in hypersaline conditions. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, Y.; Shi, M.; Wu, Y.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liang, J. Bioengineering a loofah sponge mediated system for enhanced phenol bioremoval: pH-responsive microenvironment construction and electron transport mediation. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 76, 108111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lin, H.; Dong, Y.B.; Li, B.; Liu, C.J.; Yin, T.T. Mechanisms underlying enhanced bioremediation of sulfamethoxazole and zinc(II) by Bacillus sp. SDB4 immobilized on biochar. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 370, 133483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Liang, Y.P.; Wu, Z.N.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.W.; Li, Q.F.; Chen, X.; Guo, W.L.; Jiang, L.N. Effects of tetracycline on growth, oxidative stress response, and metabolite pattern of ryegrass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 380, 120885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Yang, J.; Zhao, S.R.; Wang, X.Y.; Xie, Z.X. Toxic Effects of Tetracycline and Its Removal by the Freshwater Microalga Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, G.; Qi, W.Y.; Chen, W.Z.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Gao, S.J.; Wang, Q.Z.; Gao, C.; Gao, M.C. Metagenomic insights into the nitrogen metabolism, antioxidant pathway, and antibiotic resistance genes of activated sludge from a sequencing batch reactor under tetracycline stress. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 462, 132788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.J.; Li, Q.Z.; Song, C.Y.; Shang, X.D.; Bao, D.P.; Tan, Q.; Chen, H.Y.; Lv, B.B. Corncob as a Substrate for the Cultivation of Lentinula edodes. Waste Biomass Valorization 2022, 13, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuña-Rodríguez, I.S.; Acuña-Rodríguez, I.S.; Newsham, K.K.; Gundel, P.E.; Torres-Díaz, C.; Molina-Montenegro, M.A. Functional roles of microbial symbionts in plant cold tolerance. Ecol. Lett. 2020, 23, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.J.; Jia, X.Q. The composition analysis and preliminary cultivation optimization of a PHA-producing microbial consortium with xylose as a sole carbon source. Waste Manag. 2016, 52, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltroche-Llacsahuanga, H.; Hauk, C.J.; Kock, R.; Lampert, F.; Lütticken, R.; Haase, G. Assessment of Acid Production by Various Human Oral Micro-organisms when Palatinose or Leucrose is Utilized. J. Dent. Res. 2001, 80, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucar, R.A.; Pérez-Díaz, I.M.; Dean, L.L. Gentiobiose and cellobiose content in fresh and fermenting cucumbers and utilization of such di-saccharides by lactic acid bacteria in fermented cucumber juice medium. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Q.; Li, G.B.; Gong, Z.Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, F.; Fan, J.; Wang, W.M. Stachyose is a preferential carbon source utilized by the rice false smut pathogen, Villosiclava virens. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 96, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y.; Fan, Z.; Wang, T.C.; Zhang, G.L. Cometabolic degradation of p-chloroaniline by the genus Brevibacillus bacteria with extra carbon sources. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 383, 121198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, S.; Hu, Y.Y.; Cheng, J.H.; Chen, Y.C. Effects of carbon source, nitrogen source, and natural algal powder-derived carbon source on biodegradation of tetracycline (TEC). Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 121567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Z.; Abdoulahi, M.H.; Yang, X.Y.; Zhu, Y.M.; Gong, B.N.; Li, Y.T. Carbon source type can affect tetracycline removal by Pseudomonas sp. TC952 through regulation of extracellular polymeric substances composition and production. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 149907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Li, S.X.; Qv, M.; Wang, W.; Wu, Q.R.; Nugroho, Y.K.; Huang, L.Z.; Zhu, L.D. Urea addition as an enhanced strategy for degradation of petroleum contaminants during co-composting of straw and pig manure: Evidences from microbial community and enzyme activity evaluation. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 393, 130135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, C.; Bahadur, K.; Briess, L.; Dussling, M.; Kohler, F.; Weinsheimer, S.; Wichern, F. Mitigating Negative Microbial Effects of p-Nitrophenol, Phenol, Copper and Cadmium in a Sandy Loam Soil Using Biochar. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subashchandrabose, S.R.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Naidu, R.; Megharaj, M. Biodegradation of high-molecular weight PAHs by Rhodococcus wratislaviensis strain 9: Overexpression of amidohydrolase induced by pyrene and BaP. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Components | Rt(s) | m/z | Relative Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oleic acid | 43.16 | 282.29 | 20.00% |
| Betaine | 381.36 | 160.14 | 1.95% |
| Erucamide | 42.24 | 338.35 | 0.31% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Liang, J. Loofah Sponge Has a Potential Multifunctional Role for Enhanced Tetracycline Biodegradation: Carrier, Putative Nutrient Releaser and Solubilizer. Processes 2025, 13, 3567. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113567
Yu L, Zheng Y, Liang J. Loofah Sponge Has a Potential Multifunctional Role for Enhanced Tetracycline Biodegradation: Carrier, Putative Nutrient Releaser and Solubilizer. Processes. 2025; 13(11):3567. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113567
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Lei, Yujing Zheng, and Jing Liang. 2025. "Loofah Sponge Has a Potential Multifunctional Role for Enhanced Tetracycline Biodegradation: Carrier, Putative Nutrient Releaser and Solubilizer" Processes 13, no. 11: 3567. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113567
APA StyleYu, L., Zheng, Y., & Liang, J. (2025). Loofah Sponge Has a Potential Multifunctional Role for Enhanced Tetracycline Biodegradation: Carrier, Putative Nutrient Releaser and Solubilizer. Processes, 13(11), 3567. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113567





