Abstract
Coal is one of the most important sources for energy generation. In order to reach buyer or legislation requirements, and prevent environmental pollution, coal must be washed by processes such as froth flotation to remove mineral matter and to increase the coal quality. Different techniques such as X-ray diffraction and artificial vision are employed to monitor coal flows during the washing process; nevertheless, these techniques require high-cost equipment and qualified personnel to perform the analysis; also, data interpretation is a time-consuming task. The use of non-conventional sensors, such as a solid–liquid electrical conductivity sensor, to forecast the quality of coal offers an easy to employ method to monitor the process in real time, take corrective actions and improve the resulting coal grade, reduce the loss of valuable material and reduce pollution, increasing the sustainability of the process. For this research, coal samples from Región Carbonífera in Coahuila, Mexico were analyzed to obtain their intrinsic characteristics and their electrical conductivity. It was found that the electrical conductivity value is directly proportional to the calorific value and inversely proportional to the ash content. A conductivity value increase from 25 to 30 µS/cm was obtained when using a surfactant modified coal pulp.
1. Introduction
The mining industry, specifically coal mining, presents important areas of opportunity for process optimization as well as for pollution reduction. Coal is considered as the most important source of energy all over the world; it is used in the metallurgical industry to produce pig iron as well as in the electrical industry to produce electricity. It is utilized in thermoelectric industries as one of the most important sources of energy, producing almost 60% of the world’s energy consumption. Coal is subdivided into four different types: lignite, sub-bituminous, bituminous and anthracite; this classification is dependent on the amount of fixed carbon found in coal, from lower to higher quantity, respectively [1]; industries prefer one coal type over others depending on its characteristics, price and availability; in general, the bituminous coal is used in the metallurgical industry, while the remaining three kinds go to different industries as some type of fuel [2,3,4].
Coal is an organic sedimentary rock that contains, in different amounts, a wide variety of elements such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur, in addition to other compounds that include mineral matter, as well as methane, which is found within the pore systems of the coal. Both the organic and inorganic matter found in coal define all aspects of its classification and utilization. Physical properties of coal like its calorific value, volatile matter, inorganic matter and agglomeration character vary systematically with the coal rank [1,5,6].
In order to prevent environmental pollution, as well as to increase the quality of coal, it is necessary to carry out a cleaning process before utilization. Coal washing is a process by which mineral matter is removed from coal using various methods to leave it as mineral-free as possible, increasing its grade in order to achieve the buyer or legislation requirements [6,7,8,9]. There are different stages to clean coal. Gravimetric separation (jig, spirals, shaking tables) processes separate coal in the range of 100 mm to 0.5 mm from the high-density gangue but do not produce a clean coal; dense medium separation for sizes bigger than half a millimeter (gravitational vessels, centrifugal separators) also separate high-density gangue, and fine separation for sizes under 0.5 mm (froth flotation process), generates the highest quality coal, since the particle size allows the liberation of coal from inorganic matter [10].
The froth flotation process is employed to increase the grade of the coal fine particles. Froth flotation is a complex process involving an aqueous medium, solid particles and air bubbles; it is a physicochemical-based process that takes advantage of the hydrophobicity of minerals to perform the separation of valuable ore from the gangue.
In an ideal froth flotation process, air bubbles are injected into the column from the bottom, the pulp enters into contact with the ascending air bubbles, and the valuable mineral (hydrophobic material) is attached to them to form a bubble–particle aggregate that will rise to the top of the column; meanwhile, the gangue (hydrophilic material) travels to the bottom of the column in a stream called tailings. In the coal washing process, the particles under 0.5 mm, which are around 25 wt. % of the feed material, are processed in a flotation cell or column [3]. In practice, prior to the introduction of the pulp into the column, the pulp must be conditioned with an appropriate chemical reagent that modifies the surface of the coal, increasing its hydrophobic behavior to improve the recovery of the valuable mineral. When the bubble–particle aggregate reaches the surface, the bubble will support the coal particles only if they form a stable froth; otherwise, the bubbles will burst and release the coal back into the pulp. Froth stability is affected by the coal concentration, size and shape [11,12,13,14].
Monitoring of the washing process to determine the correct separation of the coal and gangue is a crucial part of coal separation technology. Typically, the samples to evaluate the performance of the process are obtained at defined times during the day, these samples require processing times to be evaluated and to have the results compared and, if any perturbance in the process is detected, corrective adjustments are performed; this implies that while the sampling is performed, an incorrect washing process can potentially result generating losses and pollution, which is a remanent pollution associated with the coal that remains in the gangue.
It is difficult to monitor and control the process in situ; nevertheless, many studies have been conducted to develop the monitoring of the flotation process [9,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. Artificial vision, X-ray diffraction, X-ray fluorescence and electrical conductivity of the froth surface and collection zone are some of the techniques employed to monitor and adjust the process variables; the equipment employed is relatively expensive to maintain and requires, in general, qualified personnel to perform the analysis [8,16,26].
Artificial vision is employed since froth images are related with the working condition of the process; the color, shape, size and texture of the froth are analyzed, indicating the performance of the froth flotation process. In order to relate the process with the froth images, a statistical analysis is required; the gray level co-occurrence and neighboring gray level dependence matrix are commonly employed for the recognition of the froth flotation condition. Bubble stability measurement and froth velocity are also employed to evaluate the process variables. These methods are time consuming and unstable under illumination variations [9,17].
X-ray diffraction provides information of chemical species found at the analyzed zone in the flotation process; samples must be collected and sent to the laboratory to make the X-ray analysis; this process is time consuming. X-ray fluorescence performs available elemental analysis on the flow streams of the flotation process; this technique is also time consuming [27].
Electrical conductivity in a froth flotation column has been applied to monitor variables like froth depth, gas holdup, and bias rate in an easy and fast way [11,28]. After the coal is washed, some tests are carried out to determine its characteristics like calorific value, volatile matter, sulfur content, and ash content.
The aim of this work is to evaluate the performance of a solid–liquid electrical conductivity sensor on a pulp of coal fine particles and relate it with coal characteristics, such as calorific value and ash content. During the coal washing using a froth flotation process, a solid–liquid electrical conductivity non-conventional sensor could be employed in situ at the concentration and tails streams to monitor and control the process, allowing for it to be modified in shorter times whenever a perturbance is detected, generating lower coal losses in the gangue product.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterization
The raw material used for this research was obtained from the coal region of northern Coahuila, Mexico, named Región Carbonífera de Coahuila, México. A total of four samples of mineral coal were collected, grinded, and separated in different fractions. The fraction with particle sizes between 74 and 45 μm was taken for analysis; this particle size is the one employed in the fine separation by froth flotation in the mineral coal industry.
Microstructural analysis was carried out using Scanning Electron Microscopy in a 20 kV powered JEOL JSM 6610LV microscope. Micrographs, to obtain the morphology of the samples, were acquired at 50x. Samples were spread out in a double-sided carbon tape attached to an aluminum stub. The chemical analysis was determined by energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) using an Oxford Inca X-Ray energy dispersive spectrometer attached to the microscope system. X-ray diffraction, in a diffractometer Rigaku Ultima IV with a Cu kα 1.54056 Å radiation, operated at 40 kV and 44 mA, step size and collection time set at 0.05° and 50 s, respectively, was used to obtain the crystal characteristics of the coal samples in the 2θ range of 10 to 80 degrees. Fourier Transform InfraRed (FTIR) spectra were collected with a Thermo Scientific Nicolet iS10 spectrometer with the ATR modality to identify the functional groups present in each sample in the 4000 to 450 cm−1 length wave range with a scan time of 32 s; it was used to detect organic functional groups in coal samples and evaluate the chemical composition of the samples. The calorific value, sulfur content, volatile matter and ash content were obtained with a calorimeter LECO AC500, a Sulfur Analyzer ELTRA model SC-580, a Quincy Lab 40GC gravity convection Lab oven, and a THERMOLYNE Ash Furnace, respectively.
2.2. Solid–Liquid Electrical Conductivity
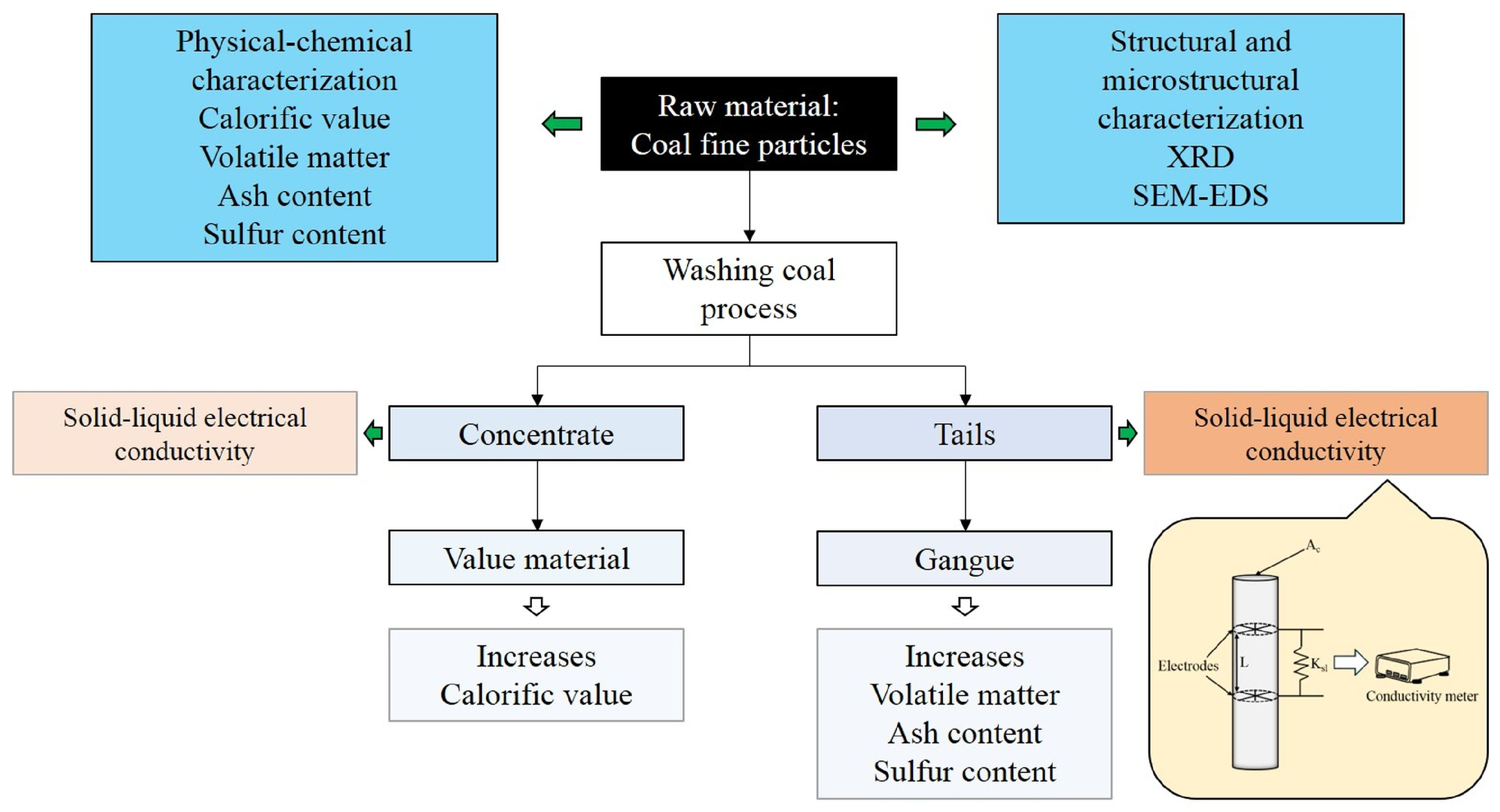
With the aim of obtaining the solid–liquid electrical conductivity data from the coal samples, a comminution process was applied to the four samples required. The particles with sizes between 74 and 45 μm, employed in the coal washing using the froth flotation process, were selected to perform the solid–liquid electrical conductivity measurements; these data were compared with the coal characteristics. A flow sheet of the coal washing process and the expected coal properties obtained is presented in Figure 1.
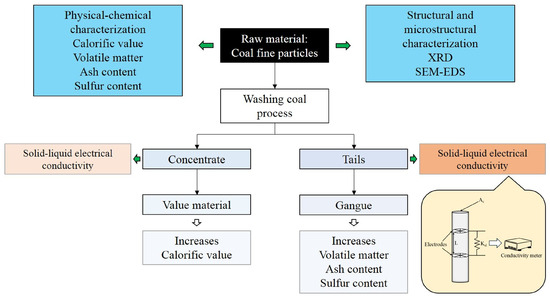
Figure 1.
Flow sheet of the coal washing process and the expected properties.
2.2.1. Batch Conductivity Measurement
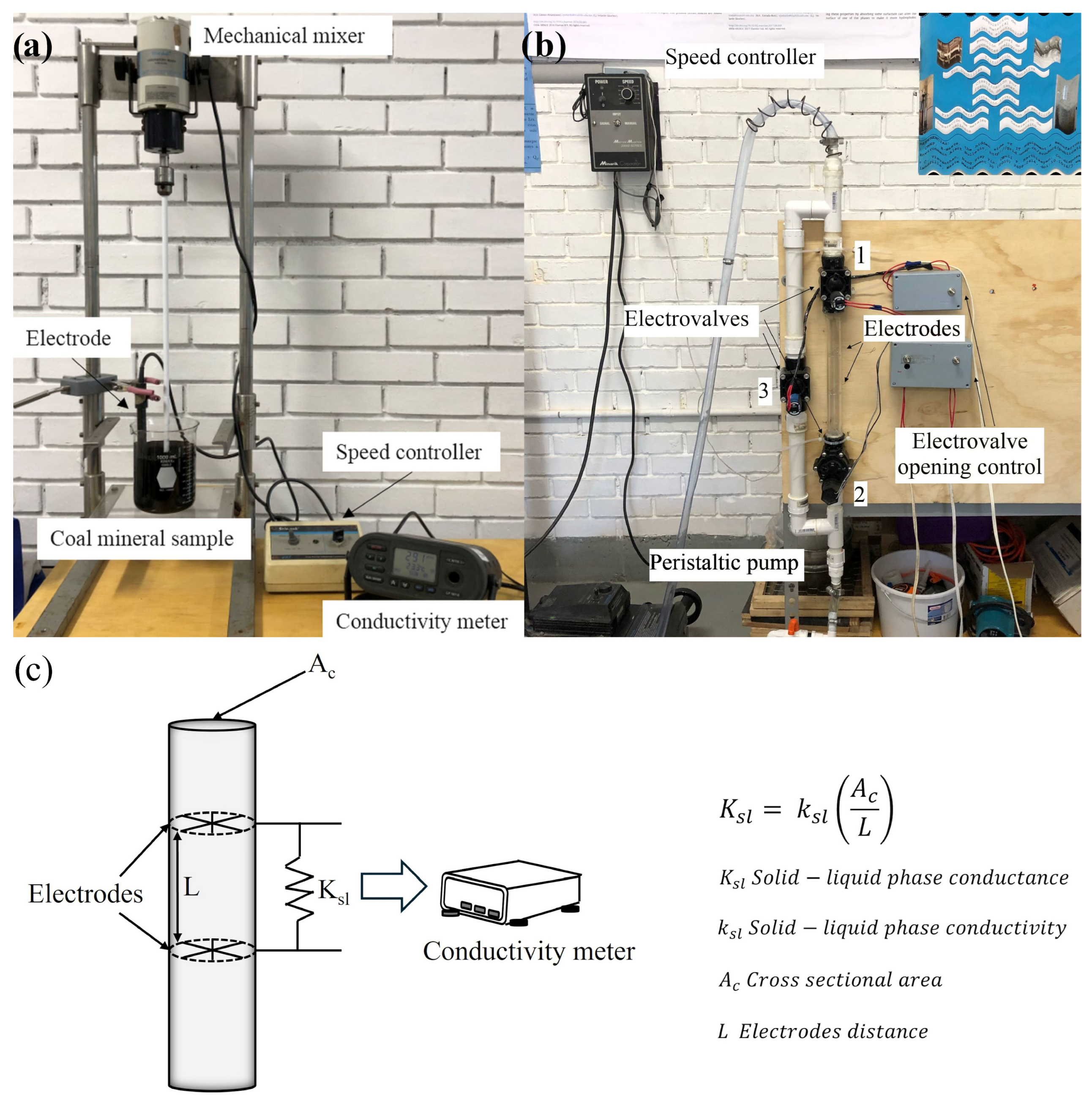
A pulp of deionized water and 1.25 wt.% of mineral coal was prepared to evaluate the solid–liquid electrical conductivity. The pulp was mixed at 300 rpm with a plastic propeller for 2 min in a laboratory mixer with a speed controller Stir-pack to ensure a homogenous pulp; afterwards, an electrode TetraCon model 325 was introduced in the pulp to measure the solid–liquid electrical conductivity in a WTW model LF-197S conductivity-meter, and records were taken for one minute. The measurements were made at room temperature, and the conductivity meter was programmed to establish the temperature compensation during the readings. Figure 2a shows the experimental apparatus employed.
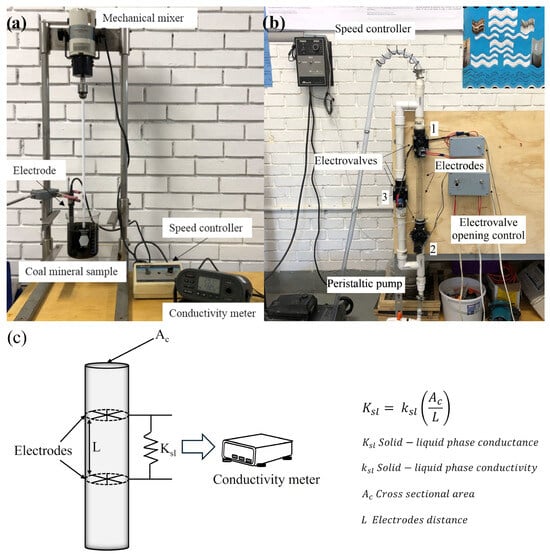
Figure 2.
Experimental apparatus employed in (a) a batch mode, (b) in a continuous mode, and (c) schematic design of the solid–liquid electrical conductivity sensor.
2.2.2. Continuous Conductivity Measurement
A prototype of the non-conventional solid–liquid electrical conductivity sensor for the acquisition of data during the coal washing process, which could be parallel-mounted in the froth flotation column, was built to obtain the data at the concentration and/or tails sections. With the help of a peristaltic pump, the pulp was introduced into a system of pipes configured as shown in Figure 2b simulating the concentration or the tails stream; as the pulp enters the system, it flows freely between two electrodes. Electrovalves 2 and 3 are initially closed so the pulp begins to accumulate at the electrode pipe; when this pipe is full of pulp, electrovalve 1 is closed to allow the measurements of solid–liquid electrical conductivity in a stationary mode to obtain accurate data from the conductivity meter; at the same time that electrovalve 1 is closed, electrovalve 3 is open to ensure the continuous flow of the pulp. When the measurements are taken, the system returns to its original configuration. In addition to the original pulp, a mixture containing 10 ppm of methyl isobutyl carbinol (MIBC) and a pulp with 10 ppm MIBC plus 1 kg/ton of diesel were measured in the continuous system. Traditionally, these conditions are employed in the industrial processes of coal washing. A deionized water run was made to ensure the correct system set up.
A schematic design of the solid–liquid electrical conductivity sensor prototype is presented in Figure 2c. As it can be seen, two electrodes with a separation L between them are located inside a circular pipe with a cross-section area Ac. When a flow is in contact with the electrodes, a signal of the conductance of the flow is generated and sent to the conductivity meter, which relates these data to the solid–liquid electrical conductivity. The solid–liquid electrical conductivity value depends on the characteristics of the flow; if a gas-solid–liquid interphase is sensed in the electrodes, the conductivity meter will present a certain value; if the sensor detects a solid–liquid interphase, a different conductivity value will be reported by the conductivity meter. Also, if the solid particles are electrical conductors, then the solid–liquid conductivity reading will be higher.
3. Results
3.1. Structural Characterization
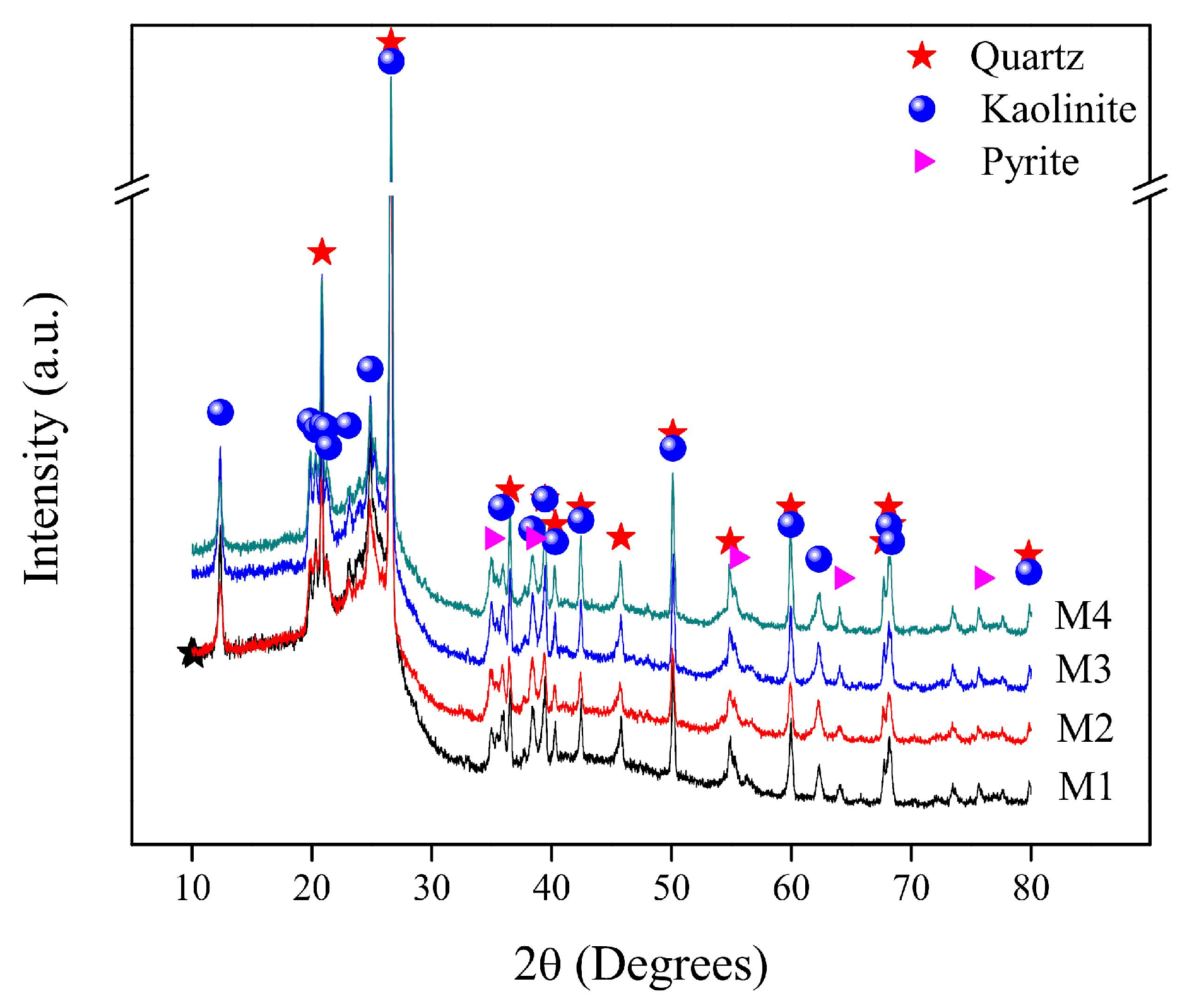
The X-ray diffraction patterns of coal samples are shown in Figure 3. As it can be seen for the four samples diffractograms, a similar behavior is present. The XRD patterns present the amorphous nature of coal as well as defined peaks of crystalline phases identified as silicium minerals: kaolinite [Al2Si2O5(OH)4], quartz (SiO2), and pyrite (FeS2). Silicon dioxide is present in bituminous coals in high quantities. The 2θ peak at 26.63 degrees, which corresponds to quartz, has the highest intensity in the X-ray diffraction patterns; this high peak intensity is typical in the bituminous coals [2,29]. Pyrite is the main carrier of sulfur in coal, and sulfur is a harmful element since it could corrode the equipment, and it also could be a hazard to the human health and ecological environment where coal is combusted [30].
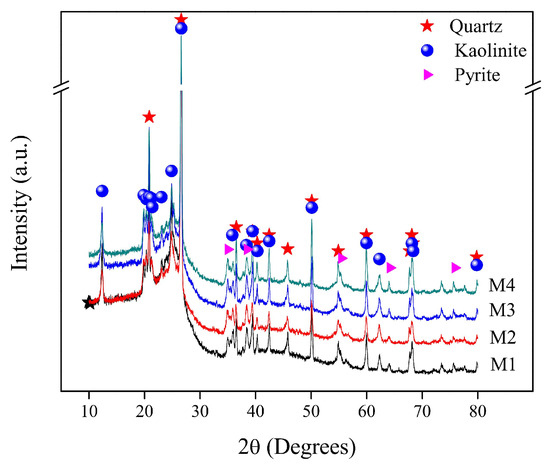
Figure 3.
X-ray diffraction patterns of coal samples.
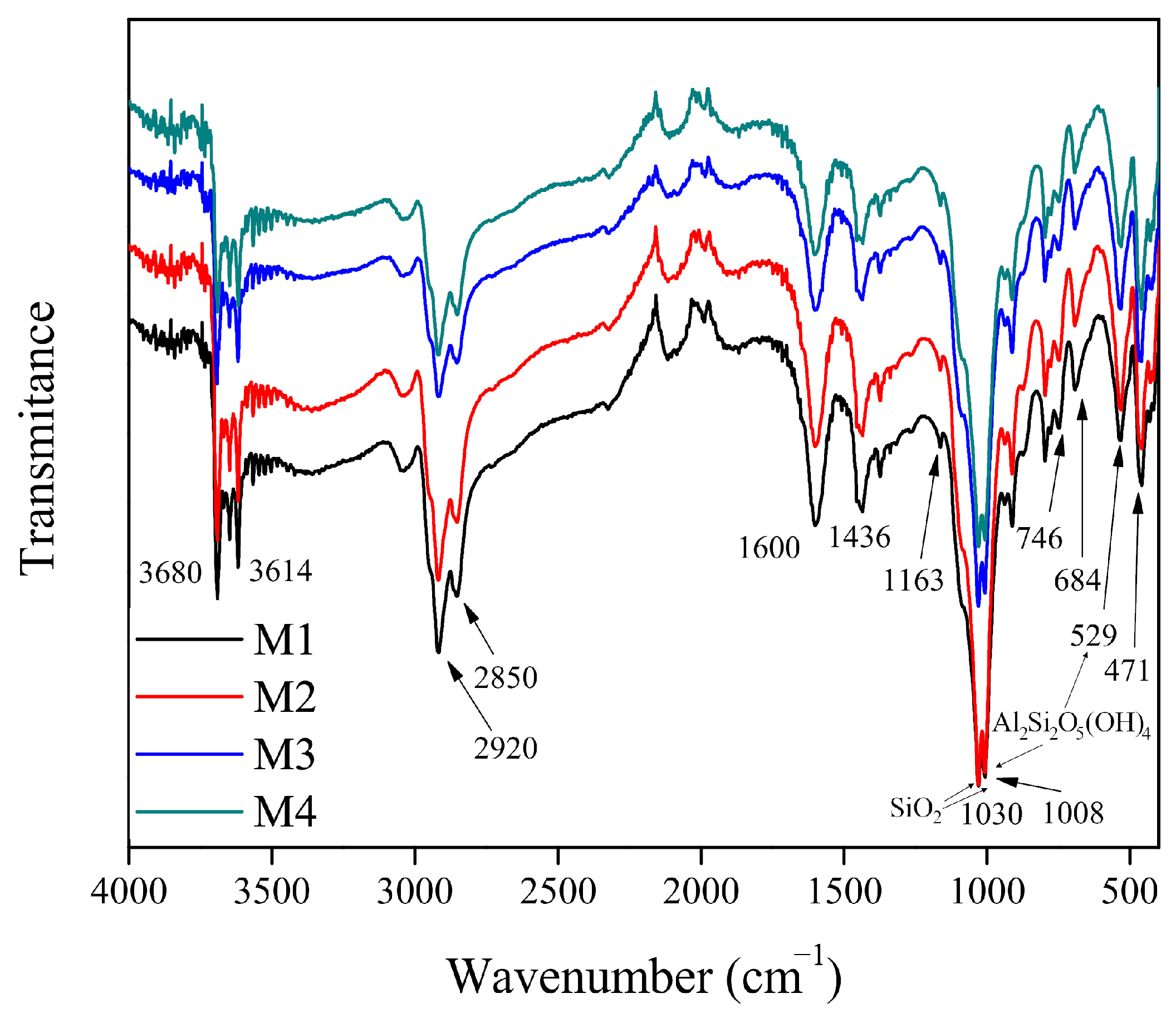
The ATR-FTIR spectrum of the coal samples is presented in Figure 4. The spectrum of the four samples analyzed is similar. The regions corresponding to the C links are presented. The one at 3600 cm−1 can be attributed to the high-frequency vibrations of the OH−. There are also aliphatic and acyclic groups CH3, CH2, and CH at 2920 and 2850 cm−1; the signal at 2920 cm−1 is higher than the signal at 2850 cm−1, which indicates a large aliphatic carbon chain [5]. Last, there are the aromatic group C=C at 1600 cm−1 and the asymmetrical deformation of CH3 at 1436 cm−1. Other regions correspond to inorganic matter. At 1163 cm−1, there is a weak absorption band, which along with the the 746 and 684 cm−1 absorption bands can be attributed to the presence of the mineral quartz. At 1030 and 1008 cm−1 are the most intense bands, which can be attributed to the stretch vibrations of the Si-O-Si. The absorption bands at 1000 and 529 cm−1 are attributed to kaolinite. Finally, the peaks at 533 and 471 cm−1 correspond to the bending vibrations of the Si-O [2,5,31,32]. Figure 4 is in accordance with the diffraction patterns analyzed in Figure 3, as both figures have the same mineral material present in the coal samples.
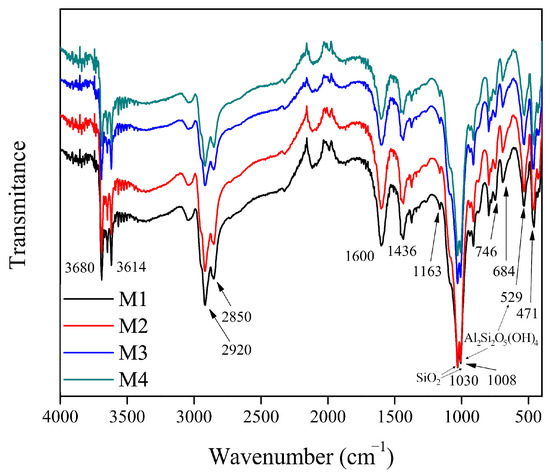
Figure 4.
FTIR spectrum of coal samples.
Images of the four different samples used for this research are shown in Figure 5. As it can be seen, the coal samples are slightly different from each other by the difference in hue or tonality; these tonalities indicate the presence of mineral matter, such as pyrite or quartz. The amount of impurities increases with the order of the photographs, indicating a reduction in the amount of carbon of the coal samples.

Figure 5.
Photographs of the four coal samples.
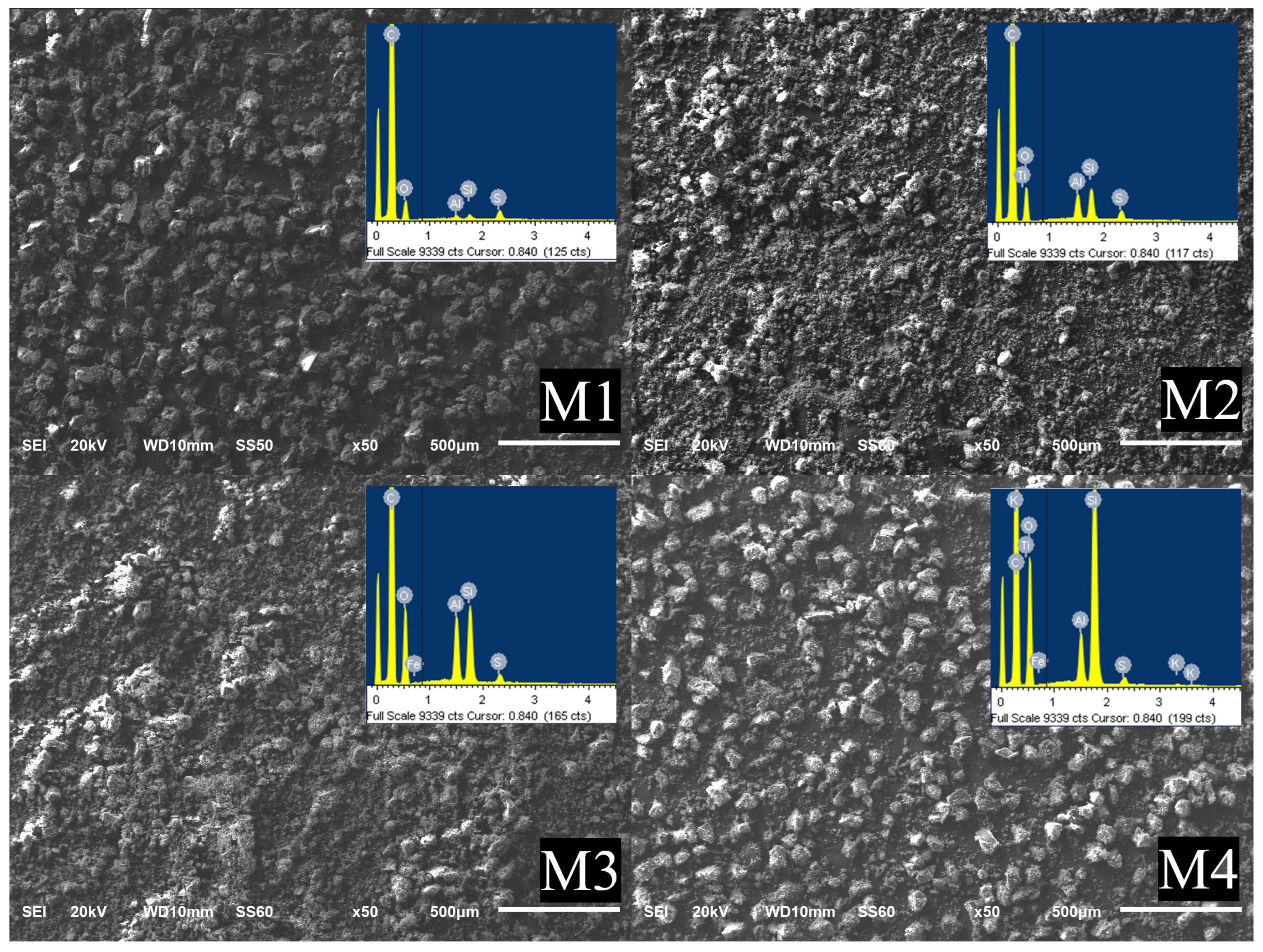
Secondary electron micrographs from coal powder samples with particle sizes of 75–63 µm are presented in Figure 6; the inserted image corresponds to general EDS analyses. Table 1 shows EDS data from the four samples. The morphology of the four samples was analyzed at a 50X magnification. Prior to the SEM analysis, the samples were grinded and screened. To avoid the oxidation of samples, the particles with a size of 75–63 μm were immediately prepared for their morphological analysis. The samples were spread out on a double-sided carbon tape, attached to an aluminum stub, and placed under the microscope. The conductive carbon tape allows the incoming electron charge to flow freely, making possible the generation of a charge-free image. The morphology of the four samples is similar: it consists of coal particles with sizes around 70 µm surrounded by finer agglomerated particles.
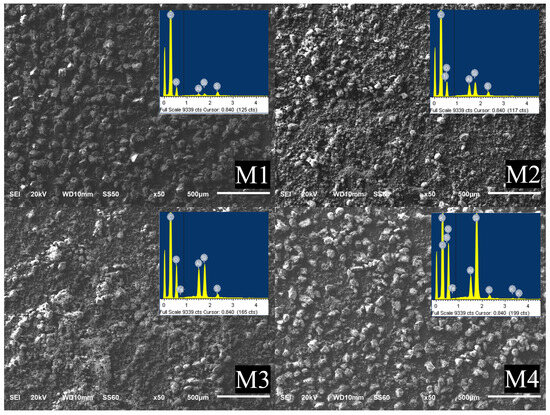
Figure 6.
Scanning electron microscopy micrographs for the four coal samples. The inserted square corresponds to the EDS analysis of the samples.

Table 1.
EDS analysis of coal samples (75–63 µm).
The EDS analysis shows that the carbon content is higher in sample 1 and it decreases from sample to sample. As the C content decreases, the content of Si and Al increases; the sulfur content remains almost constant, and iron occurs in low amounts; sulfur and iron combine to form pyrite, this compound is evident in the photographs included in Figure 5; other elements are also detected in small amounts. This increase in elements indicates a greater amount of mineral matter in the coal samples. The presence of oxygen is due to the formation of kaolinite (Al2Si2O5(OH)4) and quartz (SiO2) as well as the coal oxidation process. The elements obtained here were reported in their combined form; see Figure 3 and Figure 4. The solid–liquid electrical conductivity in the coal samples is affected by the inorganic matter. Since EDS analysis is a qualitative method, it gives an elemental composition of the samples; nevertheless, the quantitative analysis of coal samples is conducted determining the calorific value, the sulfur content, the volatile matter and the ash content.
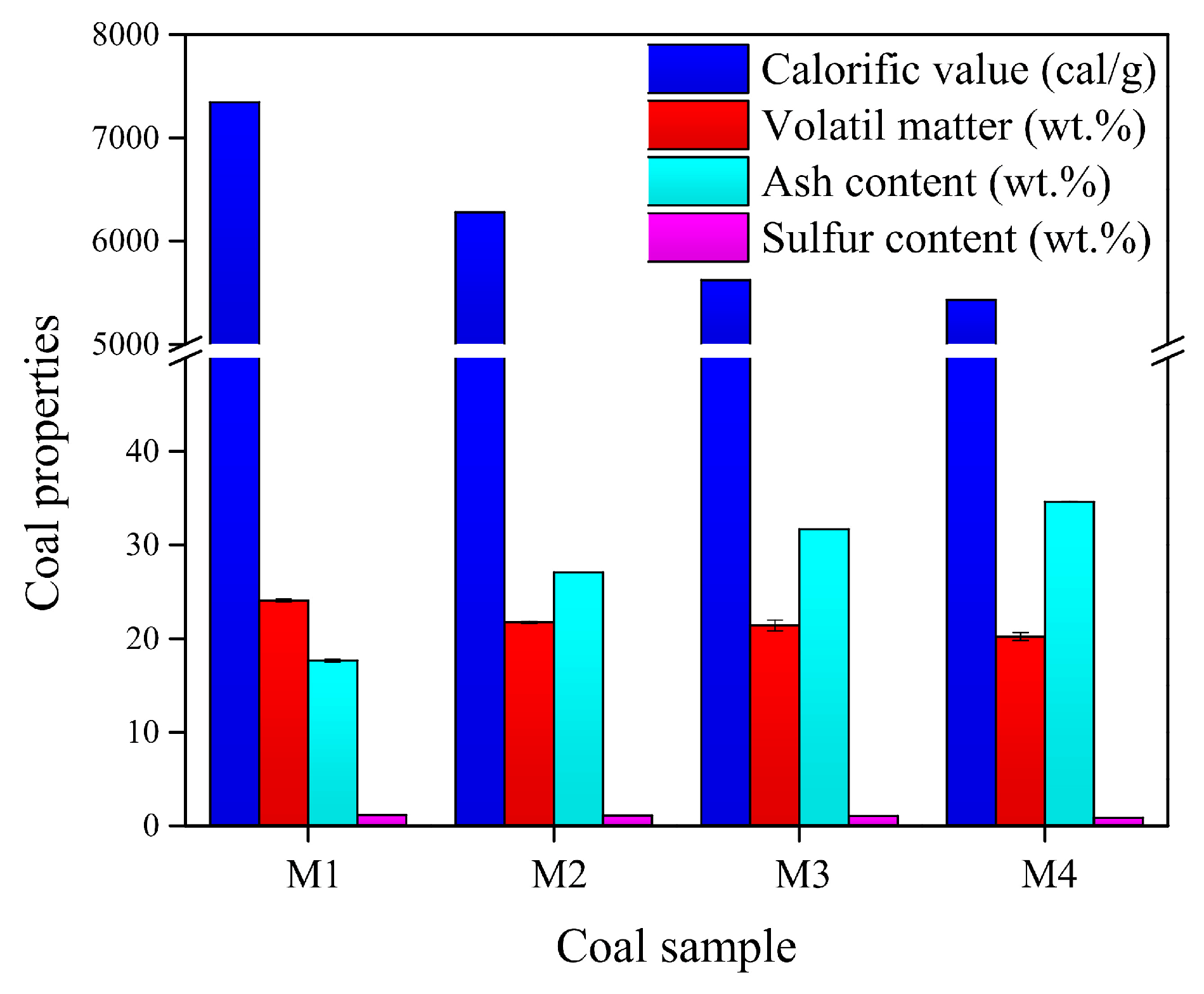
The intrinsic properties of coal samples: calorific value, volatile matter, ash content, and sulfur content for a particle size distribution of 75–63 µm are presented in Figure 7. The mentioned particle size is used in the process of washing coal by froth flotation. As it can be seen, the highest calorific value is obtained in sample M1 with a value of 7346 cal/g. This property shows a decrease in the other samples, reaching the lowest value of 5430 cal/g in sample M4. At first glance, there is a relationship between the calorific value and the amount of impurities observed in the photographs in Figure 5; the higher the impurity content, the lower the calorific value. The volatile matter tendency is similar to that of the calorific values; it has the highest value of 24.084 wt.% in sample M1, and this value decreases in the other samples, reaching the lowest value of 20.216 wt.% in sample M4. On the other hand, the amount of ash content is small in sample M1, 17.345 wt.%, and this value increases in the other samples, reaching a value of 29.348 wt.% in sample M4; this behavior is consistent with the calorific value, as a coal ore with a high calorific value will have low ash content. Finally, the amount of sulfur shows a slight decrease from 1.15 wt.% in sample M1 to 0.84 wt. % in sample M4. Figure 3 and Figure 4 indicate the presence of different carbon matter, and these figures are in accordance with Figure 7.
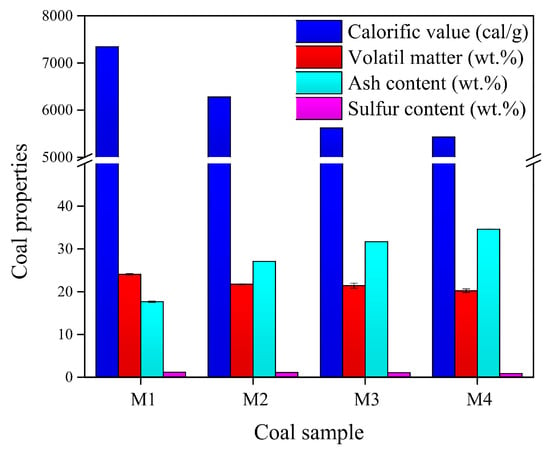
Figure 7.
Calorific value, sulfur content, volatile matter, and ash content of the four coal samples used.
3.2. Solid–Liquid Electrical Conductivity
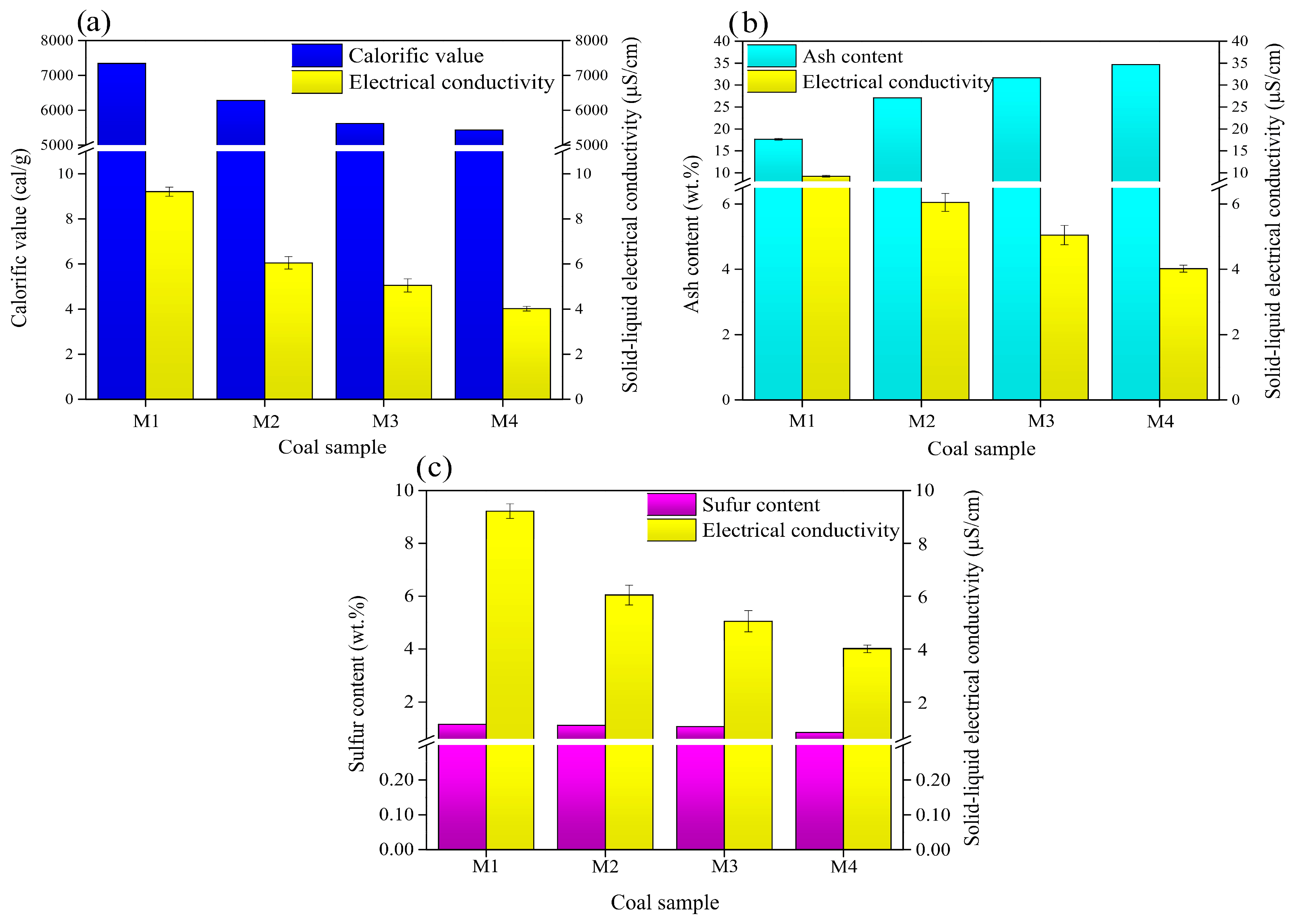
The relationship between the solid–liquid electrical conductivity and the calorific value (a), the ash content (b) and sulfur content (c) for each coal sample is illustrated in Figure 8. Solid–liquid electrical conductivity has a similar behavior to that of the calorific value for all the samples, as shown in Figure 8a. The sample with the highest calorific value, sample M1, has the largest solid–liquid electrical conductivity value of 9.2 µS/cm; in a similar way, the sample with the lowest calorific value, sample M4, has the lowest solid–liquid electrical conductivity value of 4.0 µS/cm. In Figure 8b, the ratio of solid–liquid electrical conductivity and ash content appears to be inverse to that of Figure 8a; the sample with the highest solid–liquid electrical conductivity value has the lowest ash content, while the sample with the lowest value of solid–liquid electrical conductivity has the greatest amount of ash content. Finally, as shown in Figure 8c, it appears that the sample with the highest sulfur content, sample M1, has also the highest solid–liquid electrical conductivity value, while the sample with the lowest sulfur content, sample M4, has the lowest solid–liquid electrical conductivity value. As it can be seen, the sulfur content has a very slight reduction in the different samples, but the solid–liquid electrical conductivity varies greatly from sample to sample, which is mainly due to the carbon concentration and its semiconductor properties.
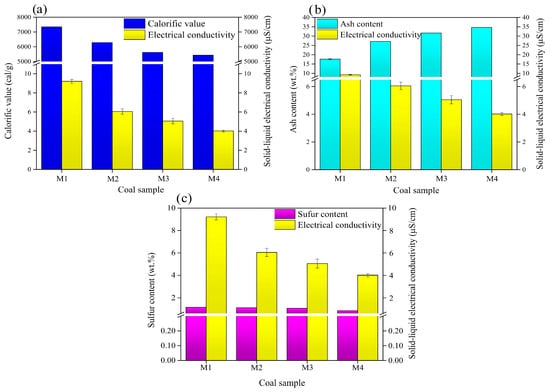
Figure 8.
Relationship between solid–liquid electrical conductivity and (a) calorific value, (b) ash content, and (c) sulfur content.
The higher carbon content in the sample presents higher solid–liquid electrical conductivity, when the amount of carbon decreases in the coal sample, due to the presence of inorganic matter, the solid–liquid electrical conductivity value will decrease, as described in Figure 8. The standard classification of coals by rank states that according to the values reported herein, coal sample M1 corresponds to medium volatile bituminous coal, and samples M2, M3, and M4 correspond to low volatile bituminous coal [33], as mentioned in the X-ray analysis; see Figure 3.
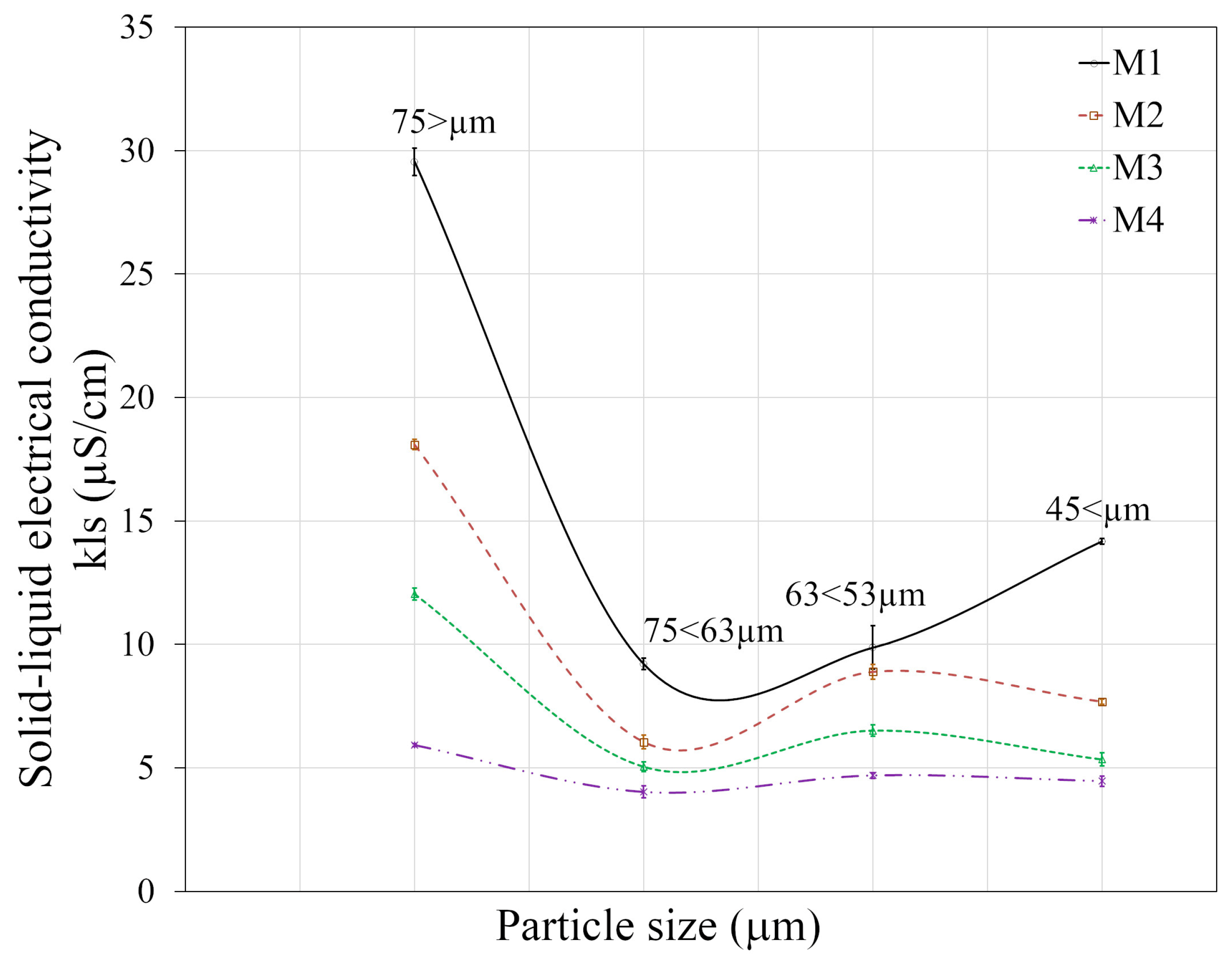
The solid–liquid electrical conductivity of the four coal samples at different powder size distributions is shown in Figure 9. As it can be seen, the value of solid–liquid electrical conductivity varies with the size of coal particles: it is apparent that the solid–liquid electrical conductivity decreases with finer particles. Sample M1 is the only sample which at smaller particle sizes presents an increase in the solid–liquid electrical conductivity. This behavior is due to the fact that large coal particles have less mineral matter on their surface and, consequently, a high solid–liquid electrical conductivity; when the particle size is small, a more inorganic matter is released and exposed to be measured, generating a reduced conductivity value, as mineral matter has a lower conductivity than coal.
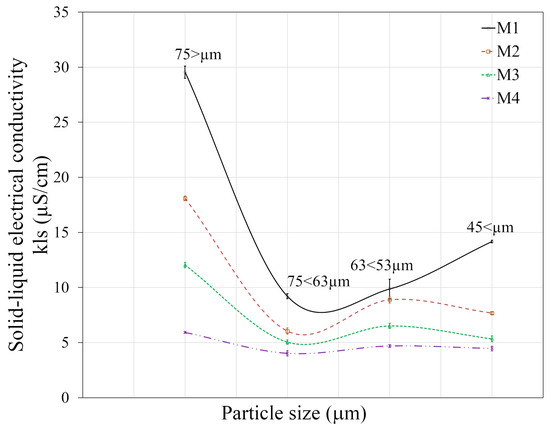
Figure 9.
Solid–liquid electrical conductivity for different distributions of powder sizes for each coal sample.
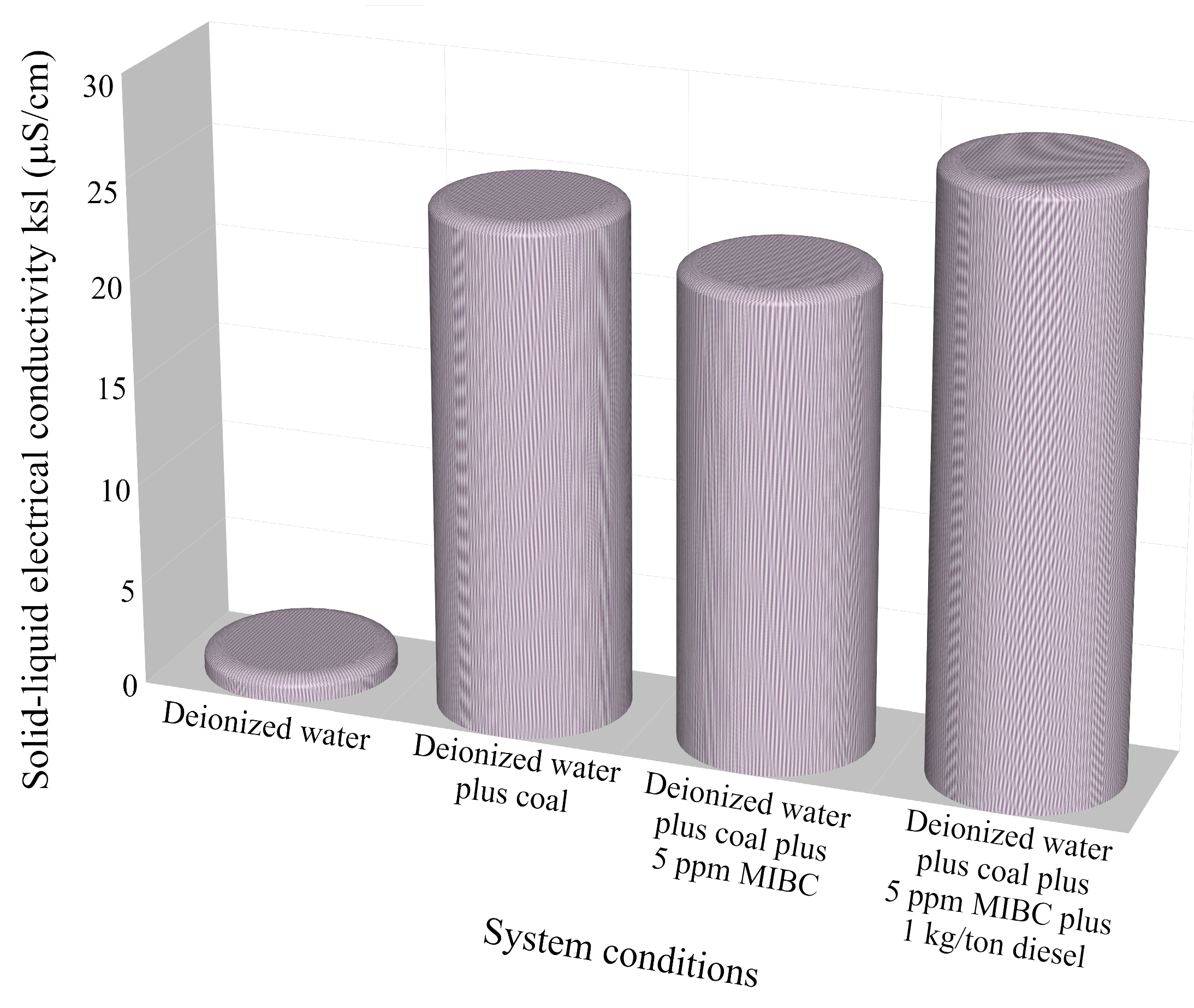
The effect of solid–liquid electrical conductivity with the additions of methyl isobutyl carbinol (MIBC) and diesel as a frother in sample M1 is illustrated in Figure 10; this sample showed the best values in its properties. The solid–liquid electrical conductivity in the continuous system shows different values for the different pulps used. With deionized water, the conductivity value is almost zero (1.2 µS/cm); when coal is added to the deionized water, the value is drastically increased (almost 25 µS/cm); with the addition of MIBC, the value drops a little (23 µS/cm); and, finally, with the addition of MIBC plus diesel, the solid–liquid electrical conductivity is increased to the highest value obtained (almost 30 µS/cm). It is important to note that because another type of electrode was used in continuous testing, the solid–liquid electrical conductivity value is slightly different. The addition of surfactants in the flotation process of coal is used to facilitate the generation of smaller bubbles, improve the adhesion of hydrophobic particles to bubbles, improve the flotation of very fine particles, and prevent the coalescence of air bubbles within the froth or bubble burst on the surface, preventing the previously attached coal particles into the plateau borders and vertices to be release and drop back into the tails zone [10,34].
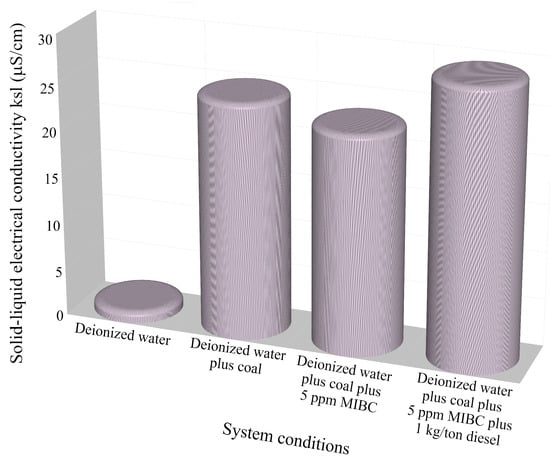
Figure 10.
Effect of the chemical condition of coal pulp in solid–liquid electric conductivity.
The results mentioned before allow relating the solid–liquid electrical conductivity with the intrinsic properties of coal. Non-conventional sensors for the measurement of the solid–liquid electrical conductivity could be connected to the flotation column, parallel to the concentrate and tails pipes, and monitor, in situ, the coal grade. A value of solid–liquid electrical conductivity could be defined as a value which ensures the correct performance of the washing process, any different value could be interpreted as a disturbance of the pulp; an adjustment process to the pulp should be required in order to return to the expected solid–liquid electrical conductivity value. Any change in the coal composition in the pulp could be corrected in shorter times when compared with the conventional heuristic procedure, which implies longer times of sampling and a non-efficient control of surfactant dosage in the pulp, improving the efficiency and profitability of the coal washing process. Also, the tails stream generated will not contain carbon, helping the sustainability of the environment.
Currently, the authors are working on evaluating solid–liquid electrical conductivity in a laboratory froth flotation column, taking readings of its value in the concentrate as well as in the tails streams, to analyze them in relation to the quality of the coal washing process.
4. Conclusions
A non-conventional sensor for the measurement of the solid–liquid conductivity was assembled to obtain data from the different flows of a coal washing process.
The intrinsic properties of coal, obtained from samples conditioned by qualified personnel, are related with the solid–liquid electrical conductivity, which could be obtained directly during the washing process.
X-ray diffraction patterns and FTIR spectra show the presence of inorganic matter in coal samples, which decreases the calorific value of coal as well as increases ash content.
The solid–liquid electrical conductivity decreases as the calorific value and sulfur content decrease and the ash content increases.
The solid–liquid electrical conductivity of coal at different particle sizes has the same trend for the four samples analyzed here. For a defined particle size, solid–liquid electrical conductivity is increased when the pulp is conditioned with MIBC plus diesel, which are agents used in fine coal froth flotation.
The solid–liquid electrical conductivity from the natural pulp is 25 µS/cm; when the MIBC is added to the pulp, the value drops to 23 µS/cm, and the pulp conditioned with MIBC plus diesel has a value of 30 µS/cm.
Solid–liquid electrical conductivity is an easy-to-use tool for assessing pulp quality in coal froth flotation, creating a sustainable process.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.H.E.-R. and R.F.-C.; Formal analysis, R.H.E.-R., G.T.R.-E., A.M.-L. and Z.M.-V.; Investigation, R.F.-C., M.R.-R. and Z.M.-V.; Methodology, R.H.E.-R., R.F.-C., G.T.R.-E. and M.R.-R.; Project administration, R.H.E.-R.; Writing—original draft, R.H.E.-R. and R.F.-C.; Writing—review and editing, R.H.E.-R. and A.M.-L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Datasets related to this article can be found at doi:10.17632/4s825d7cy3.1, an open-source online data repository hosted at Mendeley Data. Created on 10 October 2019.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to D. Vazquez and G. Flores-Campos for their technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- ASTM D 121-00; Standard Terminology of Coal and Coke. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2000.
- Mohamad, N.F.; Hidayu, A.R.; Sherif, A.A.; Sharifah, A.S.A.K. Characteristics of bituminous coal, sub-bituminous coal and bottom ash from a coal-fired power plant. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Business Engineering and Industrial Applications Colloquium (BEIAC), Langkawi, Malaysia, 7–9 April 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, P.S.; Kumar, S.S.; Banerjee, P.K.; Ganguly, S. Chemical leaching of high-ash Indian coals for production of low-ash clean coal. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2013, 34, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, K.F.; Sampaio, C.H.; Kussler, J.A.T. Washability curves for the lower coal seams in Candiota Mine—Brazil. Fuel Process. Technol. 2012, 96, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, B.K.; Boruah, R.K.; Gogoi, P.K. FT-IR and XRD analysis of coal from Makum coalfield of Assam. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 116, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speight, J.G. Handbook of Coal Analysis, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, C.; Xia, W.; Xie, G. Effect of low-temperature pyrolysis on surface properties of sub-bituminous coal sample and its relationship to flotation response. Fuel 2017, 208, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, J.; Li, Z.; Sun, X.; Wang, G. Coal Gangue Target Detection Based on Improved YOLOv5s. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morar, S.H.; Harris, M.C.; Bradshaw, D.J. The use of machine vision to predict flotation performance. Miner. Eng. 2012, 36–38, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, J.S. Coal Flotation and Fine Coal Utilization; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Riquelme, A.; Desbiens, A.; Del Villar, R.; Maldonado, M. A device for measuring conductivity of dispersions. Measurement 2014, 53, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, B.A.; Finch, J.A. Wills’ Mineral Processing Technology: An Introduction to the Practical Aspects of Ore Treatment and Mineral Recovery, 8th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Liang, L.; Tan, J.; Sha, J.; Xie, G. Effect of flotation reagent adsorption by different ultra-fine coal particles on coal flotation. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 142, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Li, Z.; Peng, Y.; Tan, J.; Xie, G. Influence of coal particles on froth stability and flotation performance. Miner. Eng. 2015, 81, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrich, C.; Marais, C.; Shean, B.J.; Cilliers, J.J. Online monitoring and control of froth flotation systems with machine vision: A review. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2010, 96, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtham, P.; Nguyen, K. On-line analysis of froth surface in coal and mineral flotation using JKFrothCam. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2002, 64, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Peng, T.; Zhao, L.; Song, Y.; Gui, W. Working condition recognition based on an improved NGLDM and interval data-based classifier for the antimony roughing process. Miner. Eng. 2016, 86, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, Z.; Liu, J.; Tan, Z.; Xu, P. Recognition of flotation working conditions through froth image statistical modeling for performance monitoring. Miner. Eng. 2016, 86, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaartinen, J.; Hätönen, J.; Hyötyniemi, H.; Miettunen, J. Machine-vision-based control of zinc flotation—A case study. Control Eng. Pract. 2006, 14, 1455–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Ruiz, R.H.; Pérez-Garibay, R. Análisis de imágenes de espumas de flotación: Cálculo de la velocidad de la espuma empleando la técnica de correlación cruzada normalizada. Supl. Rev. Latinoam. Metal. Mater. 2009, 2, 811–817. [Google Scholar]
- Jahedsaravani, A.; Massinaei, M.; Marhaban, M. An image segmentation algorithm for measurement of flotation froth bubble size distributions. Measurement 2017, 111, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahedsaravani, A.; Massinaei, M.; Marhaban, M. Development of a machine vision system for real-time monitoring and control of batch flotation process. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2017, 167, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moolman, D.W.; Aldrich, C.; Schmitz, G.P.J.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. The interrelationship between surface froth characteristics and industrial flotation performance. Miner. Eng. 1996, 9, 837–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moolman, D.W.; Eksteen, J.J.; Aldrich, C.; van Deventer, J.S.J. The significance of flotation froth appearance for machine vision control. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1996, 48, 135–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahedsaravani, A.; Marhaban, M.H.; Massinaei, M. Prediction of the metallurgical performances of a batch flotation system by image analysis and neural networks. Miner. Eng. 2014, 69, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, C.O.; Finch, J.A. Gas dispersion measurements in flotation cells. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2007, 84, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shean, B.J.; Cilliers, J.J. A review of froth flotation control. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2011, 100, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, J.A.; Dobby, G.S. Column Flotation; Pergamon Press: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, K.; Zou, W.; Kou, J.; Sun, C.; Xu, H.; Dong, H.; Rao, B.; Sun, T. Utilization of low metamorphic degree bituminous coal in direct reduction of high-phosphorus oolitic hematite and its mechanism. Fuel 2024, 375, 132497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Wang, W.; Zhang, K. Occurrence Characteristics of Fine-Grained Pyrite in Coal and Its Scaling Effect on Flotation Desulfurization. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 42467–42481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinyemi, S.A.; Gitari, W.M.; Akinlua, A.; Petrik, L.F. Mineralogy and Geochemistry of Sub-Bituminous Coal and Its Combustion Products from Mpumalanga Province, South Africa. In Analytical Chemistry; Krull, I.S., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 47–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.T.; Li, H.J.; Hou, Q.L.; Li, X.S.; Yu, L.Y. The effect of different deformation mechanisms on the chemical structure of anthracite coals. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D 388-99; Standard Classification of Coals by Rank. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2002.
- Fuerstenau, M.C.; Jameson, G.J.; Yoon, R.H. Froth Flotation: A Century of Innovation; SME: Englewood, CO, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).