The Evolving Technological Framework and Emerging Trends in Electrical Intelligence within Nuclear Power Facilities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Nuclear Power Plant Electrical System Intelligence Demands and Challenges
2.1. Current Status of Electrical System Intelligence
- The rapid progression of artificial intelligence and big data technologies is fostering novel applications in power grid companies. These include intelligent defect recognition leveraging image recognition, intelligence-assisted inspections, and intelligent production commands, all of which offer valuable insights for the intelligent operation and maintenance of nuclear power plant electrical systems [14]. Initial successes have been achieved in areas such as computer vision, natural language processing with knowledge graphs, intelligent voice and speech recognition, and data intelligence technologies. The swift development of AI technology is poised to become a pivotal force in the realm of intelligent electrical equipment operation and maintenance [15,16];
- The research and application of intelligent equipment are currently in the nascent stages of exploration. There exists a solid foundation in the integrated design and manufacturing of conventional sensing components and equipment bodies, encompassing examples like transformer top-oil temperature monitoring and cable joint humidity monitoring [17]. However, the concept of comprehensive equipment integration design grounded in the self-awareness of states is still in its infancy, and research into sensing components and methods is in its early stages. While traditional designs for nuclear power plant construction have gained widespread adoption, there remains significant room for exploration in the standardization and modularization of equipment related to the manufacturing, operation, and maintenance professions [18];
- By enhancing the intelligence level of distribution equipment, it gains the ability to precisely perceive its actual operational status. This enables users to detect equipment defects proactively, thereby significantly improving safety, reliability, and maintenance efficiency [19]. Given the stringent reliability requirements for medium- and low-voltage distribution equipment in nuclear power plants, the application of intelligent non-safety-grade distribution equipment holds immense significance in reducing the risk of equipment failures in these facilities [20];
- Intelligent inspection technology enables the automatic transportation of inspection objects and real-time monitoring of detection data through predefined inspection methods. This facilitates the prompt resolution of issues [21]. Nuclear power plants can adopt a management model for intelligent inspection equipment, collecting data information on crucial equipment and facilities across varying environments, thus laying the groundwork for achieving their management goals [22];
- The intelligent operation and maintenance of distribution systems leverage advanced management systems to enable the real-time monitoring of diverse distribution data [23]. Operation and maintenance companies can keep a watchful eye on distribution operational data and warning notifications via a web client, seamlessly managing and dispatching personnel using mobile app platforms. Furthermore, maintenance personnel can offer timely feedback to the company through multimedia channels on the app, thereby enhancing the efficiency of electrical system management, eliminating traditional manual maintenance blind spots, and significantly reducing personnel and maintenance costs [24,25,26].
2.2. Problems with the Intelligentization of Nuclear Power Plant Electrical Systems
- The fragmented information repositories of nuclear power plant equipment constrain the degree of intelligence and impede the later-stage tracking, servicing, and design optimization of unit equipment [27];
- The traditional manual inspection process at nuclear power plants suffers from low efficiency, inconsistent detection quality, incomplete data, and a lack of real-time monitoring and accessibility [28]. This necessitates the adoption of a more scientific, comprehensive, and real-time inspection methodology;
- The absence of comprehensive intelligent design and evaluation standards for nuclear power plant electrical systems necessitates the development of reasonable designs and the establishment of robust evaluation criteria [29];
- The lack of a top-level design for information security protection in nuclear power plant electrical systems demands the exploration and implementation of a comprehensive information security system [30];
- The safety protection measures of the electrical systems in nuclear power plants need to be enhanced. The electrical systems of nuclear power plants lack effective safety strategies in “lateral isolation, vertical encryption, and comprehensive protection”, and are facing issues such as insufficient anti-virus systems, weak host security, and the absence of data encryption and authentication mechanisms, necessitating targeted measures to enhance safety protection.
3. Intelligent Electrical Equipment and Its Application in Nuclear Power Plants
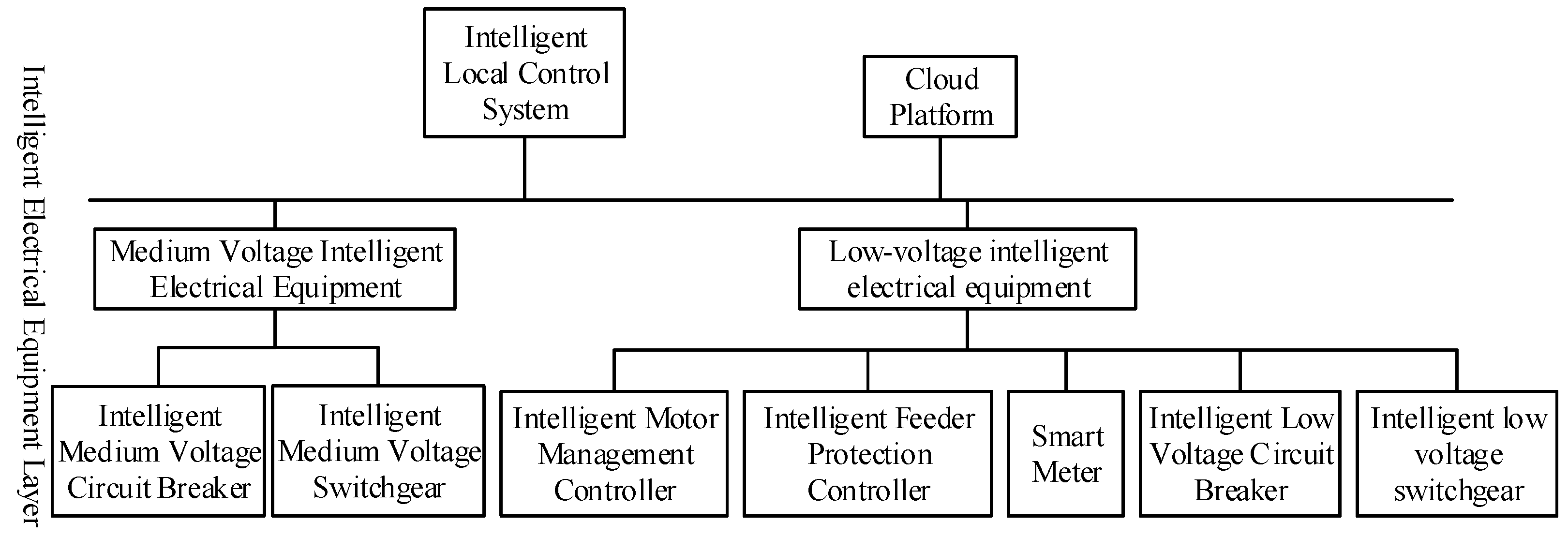
3.1. Architecture of Intelligent Electrical Equipment Technology
3.2. Smartification of Medium- and Low-Voltage Electrical Equipment
- Medium-voltage intelligent circuit breaker: Incorporating embedded temperature sensors, it gathers temperature data and facilitates the online intelligent monitoring of the opening/closing coils and energy storage motor. This expedited, visual understanding of the circuit breaker’s health status enables the dynamic diagnosis of its health trends [34];
- Medium-voltage smart switchgear: This system enables the continuous online monitoring of busbar, cable temperatures, and the coordination status between circuit breakers and switchgear [35]. It supports remote or local control of circuit breaker operations, monitors the remaining electrical life, and incorporates individual arc protection, integrated protection, and the online monitoring of leakage currents and discharge counts for surge arresters [36];
- Low-voltage distribution system: Leveraging smart motor management controllers, it controls, protects, and monitors low-voltage motors. Smart feeder protection controllers oversee feeder circuit monitoring, protection, and alarms. Smart meters measure, display, and store incoming circuit electrical parameters [37];
- Low-voltage intelligent switchgear: An integrated temperature control system within the cabinet continuously monitors the environment and temperatures of drawers and electrical equipment. It offers over-temperature warnings, the timely detection of potential fault points, and allows for drawer replacement without power interruption, enhancing operational continuity and reliability. Additionally, energy consumption data analysis aids in improving energy efficiency [41].
3.3. Intelligent Local Control System
- Optimize energy efficiency: Through a visual platform, it analyzes energy usage based on various load types, metering zones, and operational modes, facilitating comprehension of the system’s energy flow and pinpointing avenues for enhanced efficiency [42];
- Facilitate operation and maintenance: By showcasing system diagrams, cabinet configurations, and communication network blueprints via a maintenance management interface, it enables oversight of the electrical system’s operational standing, equipment status and parameters, and communication statuses [43]. Smart monitoring mitigates the need for manual periodic inspections, thus lessening operational manpower and time expenditure, and offering pre-emptive warnings for equipment failures, enabling proactive maintenance and minimizing unscheduled downtimes [44];
- Manage power quality: It conducts real-time surveillance of power quality parameters, governance apparatus, and electronic devices, capturing and documenting event occurrences and types, and generating comprehensive reports. This enables the remote execution of effective power management strategies [45];
- Oversee electrical equipment: It compiles and displays the operational health status, vital equipment information, and operational metrics of electrical equipment. It also assesses the condition and aging of medium-voltage switchgear, medium-voltage circuit breakers, low-voltage distribution cabinets, and low-voltage circuit breakers [46,47,48].
3.4. Cloud Platform
3.5. Electrical Main Equipment Intelligent Integration of Primary and Secondary Fusion
- Enhancing the coherence and compatibility of primary and secondary components in terms of both fundamental and intelligent functionalities;
- Establishing standardized connection protocols for primary and secondary interfaces on the grid system level to guarantee the seamless replacement and plug-and-play compatibility of equipment from diverse manufacturers;
- Boosting functional integration by incorporating capabilities like line loss management, fault distance determination, and single-phase grounding fault mitigation into primary and secondary systems, aligning with the automation demands of modern electrical systems;
- Elevating the reliability of electronic transformer and sensor devices by thoroughly investigating and addressing issues such as electromagnetic interference and life cycle matching in secondary equipment.
4. Intelligent Operation and Maintenance Technology and Application Trends in Nuclear Power Plants
4.1. Electrical Main Equipment Intelligent Integration of Primary and Secondary Fusion
- Application of power sensors in power supply scenarios: The monitoring of generator set parameters, including power, wind speed, rotation speed, vibration, angle, pressure, and temperature, alongside non-destructive testing data such as gearbox oil analysis and blade structure analysis, enables fault diagnosis and the comprehensive health monitoring of the crucial components in wind turbine transmission chains: blades, gearboxes, and generators [68];
- Application of power sensors in transmission, transformation, and distribution networks: Leveraging power optical fibers, we achieve the precise monitoring of transmission line characteristics like temperature, stress, and vibration. The optical fiber doubles as a sensing medium and communication channel, boasting an optical detection signal sampling rate of over hundreds of MHz. This allows for meter-level accuracy in localizing events on transmission lines spanning hundreds of kilometers. Integrated with sensors for video, imagery, and micro-meteorological data, we effectively monitor and pre-empt risks associated with icing, wind-induced vibrations, oscillations, and external damage [69]. Additionally, techniques and devices such as ultrahigh frequency, ultrasonic, oil chromatography, infrared detection, and optical fiber winding temperature measurement are extensively utilized in power transformers for real-time monitoring and fault diagnosis. This ensures the timely and accurate detection of latent faults, preventing their deterioration and escalation;
- Typical application scenarios on the user side: In industrial parks, sensors for environmental and energy consumption monitoring, along with intelligent devices like inverters and smart circuit breakers, gather crucial data pertaining to water, electricity, natural gas, steam, and the environment for enterprises. These data points are seamlessly integrated with production and management systems like MES and ERP, enabling efficient distributed new energy operations, maintenance, energy conservation measures, emission reduction strategies, and other business-enhancing services that ultimately boost energy utilization efficiency [70,71,72,73].
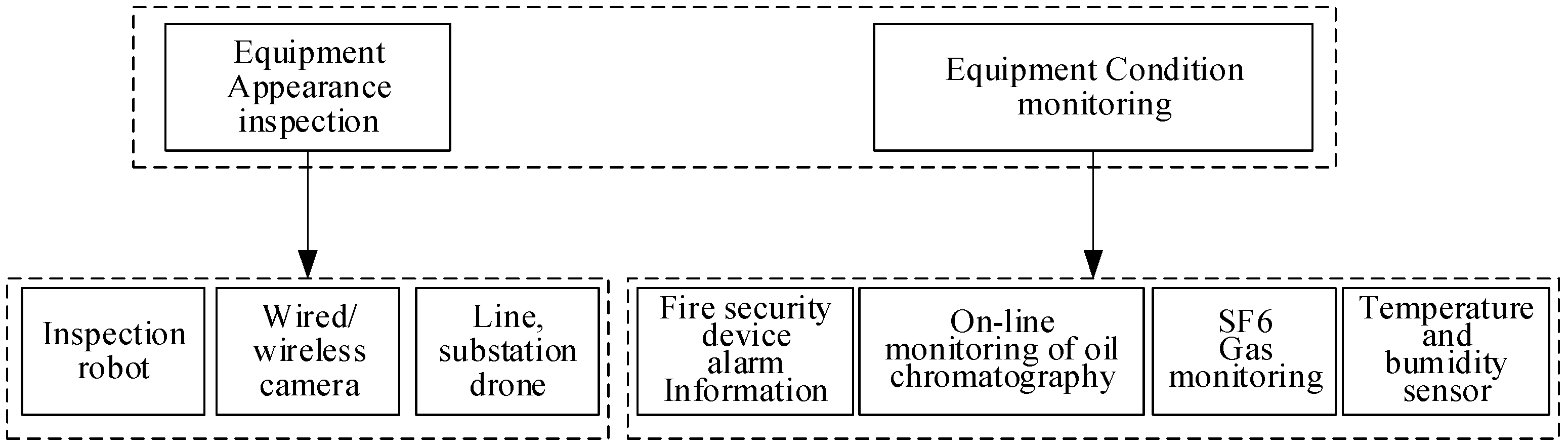
4.2. Intelligent Inspection Based on Non-Destructive Testing
4.3. Comprehensive Solution Based on Inspection Robots
- Inspection Robot Products and Capabilities
- 2.
- Essential Technologies Underpinning Intelligent Inspection Robots
- Positioning and Navigation Technologies: GPS positioning excels in accuracy and adaptability to diverse environments, yet its precision comes at a premium cost and reliance on external satellites and base stations, rendering it unsuitable for indoor applications. Magnetic track and QR code positioning methods offer precision but require significant modifications to the surroundings, thereby restricting their extensive outdoor usage. Inertial navigation provides autonomous positioning independent of the environment, yet it faces challenges due to accumulating errors and the high cost of high-precision inertial devices [85]. Laser positioning achieves high accuracy without external dependencies but relies on sophisticated algorithms. However, its reliability diminishes in dynamic environments, and multi-line laser sensors add to the overall cost. Multi-data fusion navigation positioning incorporates environmental modeling, laser radar scanning, odometer data recording, and environmental map creation. Autonomous positioning then marries real-time odometer data with pre-existing environmental maps, aligning lidar data with the maps through feature matching [86].
- The main body platforms encompass: wheeled robots, leveraging laser-based trackless navigation for flexible path configurations and robust adaptability; track robots, operating on magnetic tracks, offering broad coverage and rapid inspection capabilities; and tracked robots, boasting excellent off-road performance and smooth operation [87];
- The automatic charging system comprises the robot body and the charging module. It determines the necessity of charging by assessing the battery level and whether the robot has completed its current inspection task;
- Control system: The centralized control framework oversees a diverse array of robots, facilitating their remote management through standardized interfaces. This allows for data collection, the issuance of control commands, and a range of functionalities, including remote control, inspection task scheduling, real-time monitoring, data analysis, and historical query capabilities [88];
- Technology outlook: We aim to comprehensively promote the standardization system for inspection robots, fostering the transition towards intelligent operation and maintenance modes. This includes strengthening technological research and development, deepening our research into the robot’s key technologies to enhance inspection effectiveness, and exploring information exchange between the robot’s backend monitoring system and production management systems to expedite system integration and interconnectivity [89].
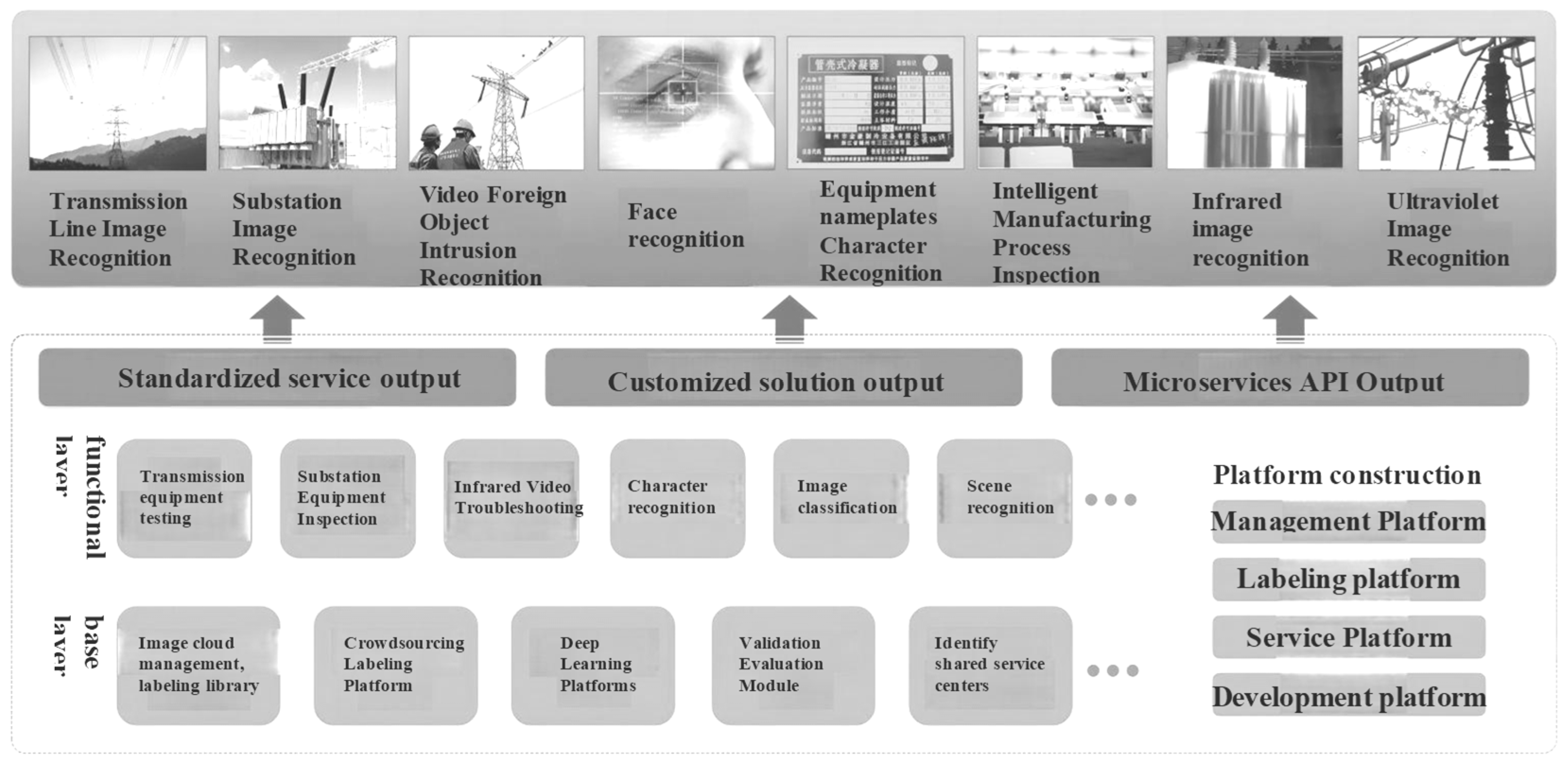
4.4. Key Technologies of Intelligent Inspection
- Artificial Intelligence Platform
- 2.
- Image recognition capabilities
- 3.
- Rapid iteration of vision applications
- 4.
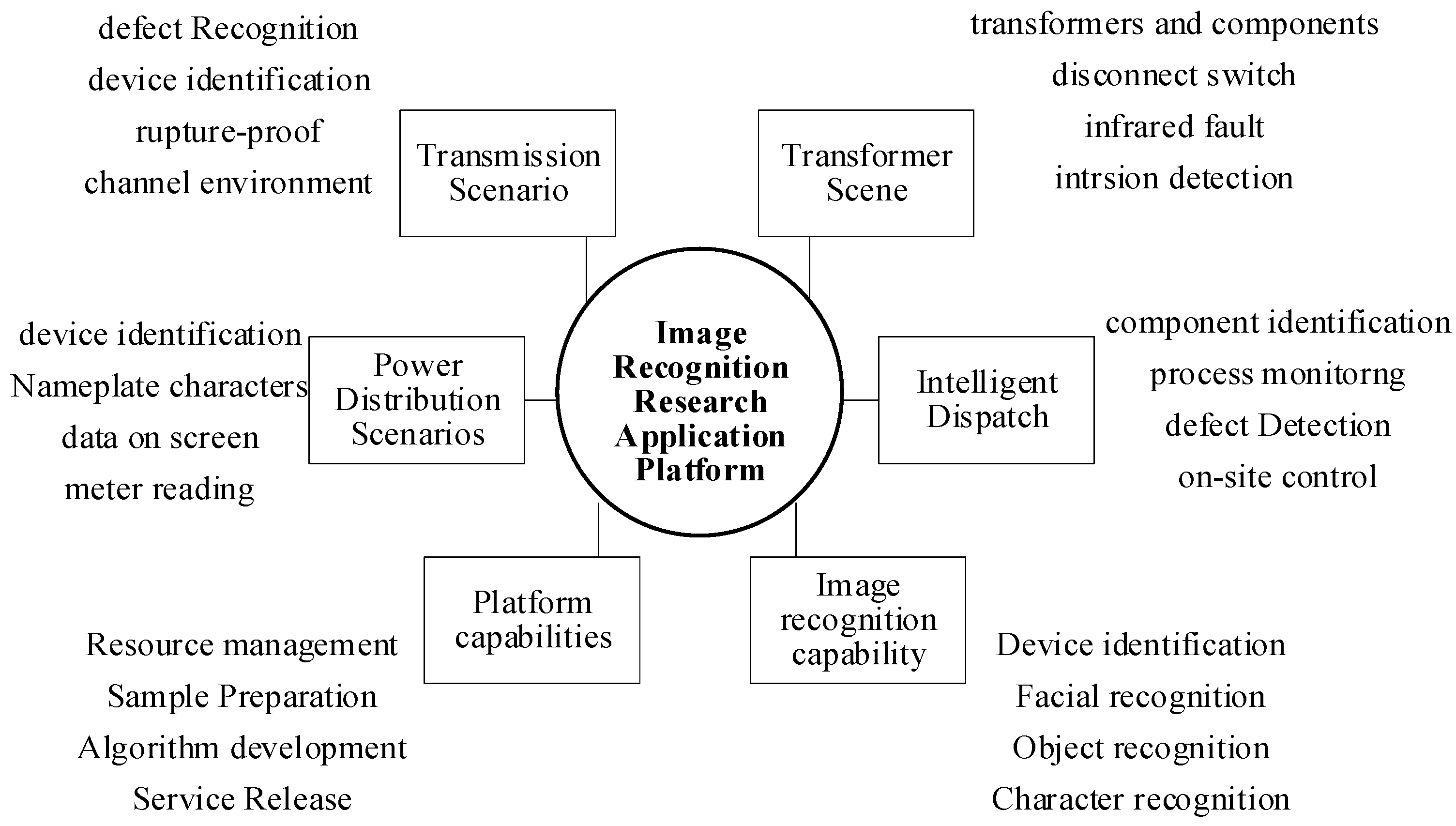
- Power Station Image Recognition
- Infrared image recognition: We possess a comprehensive fault database for substation equipment, encompassing over 200 instances of typical infrared image defects spanning 11 equipment categories and 55 fault types. This database is scalable and designed to accommodate future additions. The intelligent analysis of transformer status was shown in Table 1;
- Edge intelligence analysis technology: The edge intelligent box, integrated into the robot platform, offers miniaturized and agile computing. It enables functions such as model distribution, computational offloading, on-site analysis, and general computing capabilities, fostering a seamless collaboration between cloud and edge computing;
- External state visual perception: Leveraging deep feature learning, we have created and trained a comprehensive sample library for substation equipment. This library powers intelligent recognition and analysis of various equipment targets and faults, including transformer oil leaks, surface oil contamination, breathing apparatus defects, metal corrosion, bushing and meter damage, foreign object intrusions, and more. It further localizes, classifies, and annotates abnormalities, enhancing the accuracy of transformer status assessment and fault diagnosis to over 95%. Our recognition model boasts the capability to identify 10 subclasses within 5 major defect categories, characterized by low miss rates, high reliability, speed, and practicality, demonstrating its effectiveness in engineering applications;
- Visual multi-alignment technology: Prior to each magnification level, it precisely locates the meter position and calibrates the visible light camera’s angle to ensure the meter is centered in the frame. Leveraging high dynamic range imaging technology, it enhances crucial image features, effectively mitigates the impact of varying lighting conditions on meter readings, and ultimately elevates the accuracy of readings.
5. Nuclear Power Plant Electrical System Intelligent Development Trends
5.1. Basic Principles
- Business imperative: Maintain a focus on problem-solving, value creation, and result-driven objectives. Conduct a scientific analysis to assess the necessity of digitization requirements for various stages, targets, and operational links;
- Technical viability: Evaluate the novelty, efficacy, robustness, and universality of technologies based on factors such as application maturity, applicability, implementation ease, and problem-solving capability. Determine the optimal technical approach and implementation roadmap;
- Safety and dependability: Develop comprehensive plans for perception capture, connectivity, data storage, and shared applications across the nuclear power plant’s electrical system to guarantee utmost safety and reliability;
- Economic prudence: Strike a balance between cost and efficiency, considering benefits and adhering to a global perspective and systematic approach. Select strategies and models that are economically rational and globally optimized, tailored to local conditions.
5.2. Intelligent Architecture
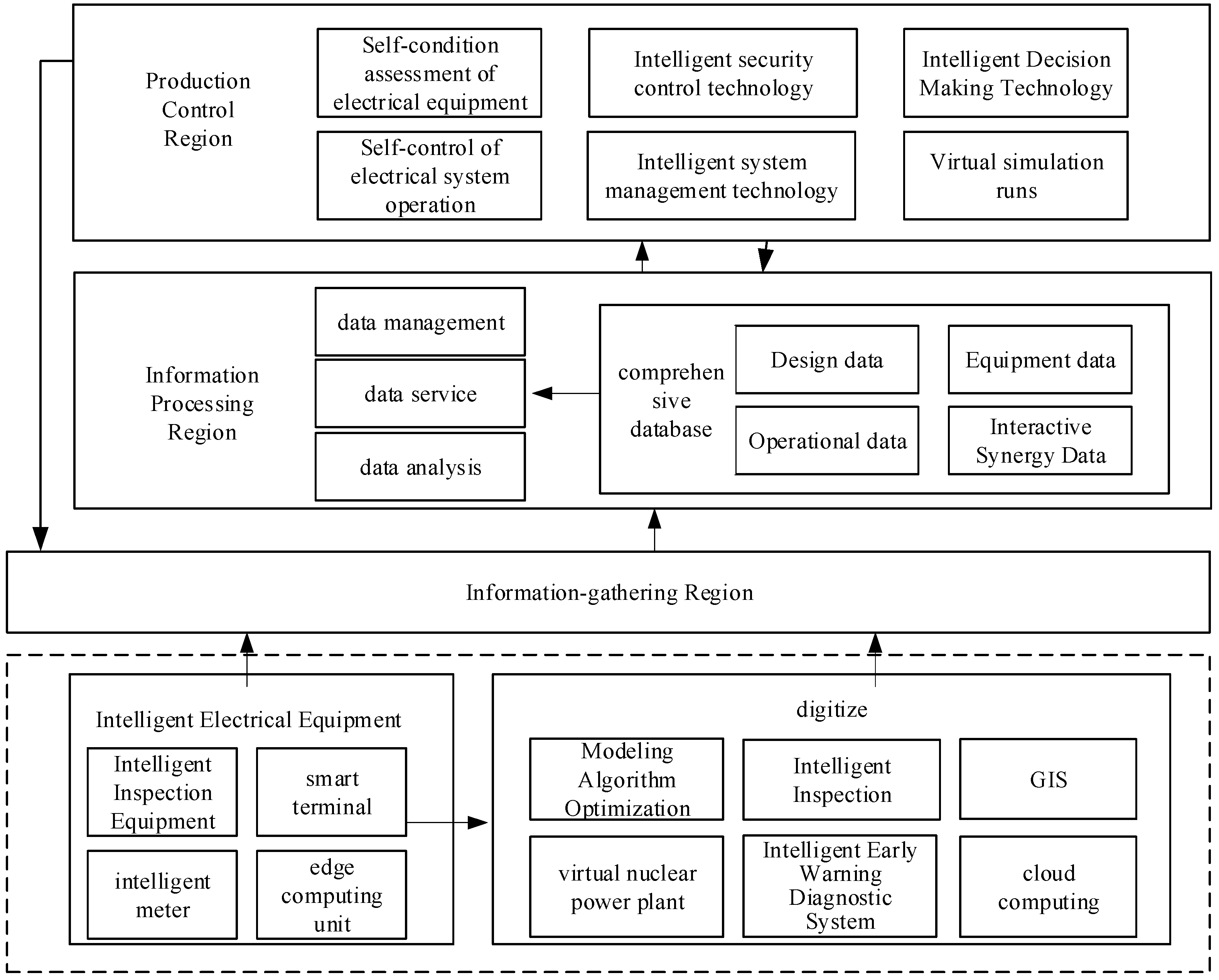
- The intelligent information architecture encompasses four key layers: production control, information processing, information acquisition, and digital intelligent electrical equipment. This architecture unfolds into four distinct stages of data management: acquisition, transmission, storage, and utilization. It harmonizes the perception and interconnectivity of various components within the intelligent electrical system, enabling shared perception devices. This fosters seamless integration and adaptive construction of diverse business applications, ultimately achieving equipment transparency, data transparency, and application transparency [94], as depicted in Figure 8.
- 2.
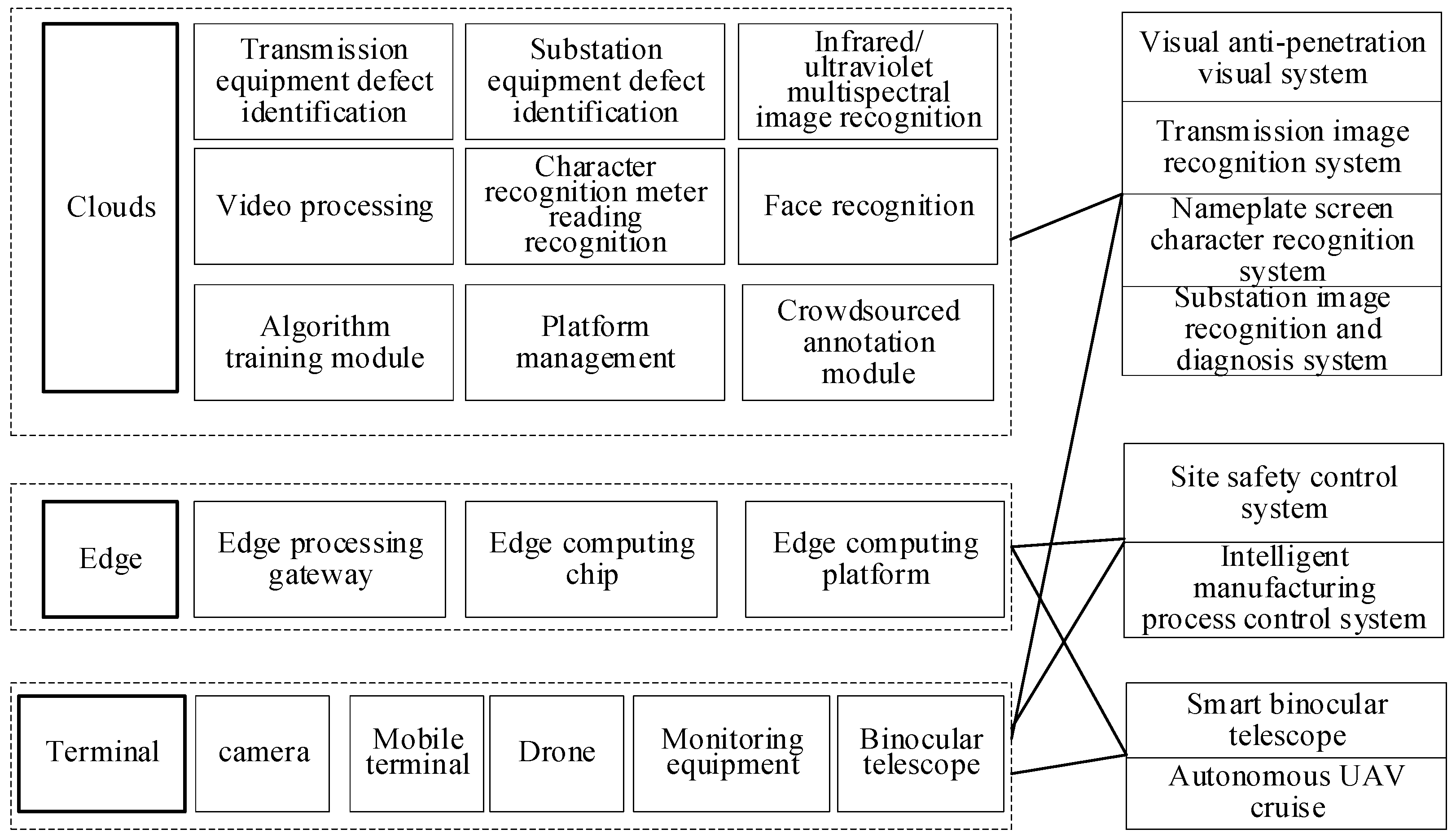
- The equipment management layer architecture comprehensively encompasses several key aspects such as intelligent video management, three-dimensional scene management, equipment status monitoring, equipment analysis, operational and maintenance business administration, as well as specialized technical management. A detailed breakdown of these components is presented in Figure 9.
- 3.
- Data Layer Model Architecture: Figure 10 illustrates the model architecture of the data layer that underpins the intelligence of the electrical system in nuclear power plants. This architecture comprises primary and secondary equipment models, data models, equipment analysis models, operational and maintenance business models, as well as professional management models, drawing from references [95].
5.3. Evolutionary Path of Development
5.4. Stage Goals and Key Technologies
- Recent past: For operational nuclear power plants, cost-effective and reliable upgrades and transformations are carried out on electrical system equipment, encompassing the renewal of sensors, primary and secondary fusion switchgear, ring main units, and distribution transformers. This involves implementing intelligent system modifications or constructions at the operational and maintenance levels to enhance the electrical system’s intelligence level. By advancing the digitization of the electrical system’s foundation through smart sensing, data collection technology, and primary and secondary fusion intelligentization, we empower primary equipment with greater intelligence, enabling status visualization, networked control, and automation. This serves as the fundamental functional backbone for the electrical system’s intelligentization [97].
- Mid-term: For newly built or refurbished nuclear power plants, a holistic approach to electrical intelligentization is implemented. This methodology involves the design of multifaceted applications and platform systems encompassing intelligent operation, inspection, communication, monitoring, information security, and electrical system protection. This approach systematically elevates the level of electrical intelligence. By leveraging secure and efficient computing platforms, along with robust foundational data, advanced numerical algorithms, benchmark modeling, 3D simulation models, and visualization techniques, we gradually establish digital and intelligent applications tailored specifically for nuclear power plant electrical systems. This allows for a comprehensive, accurate, and intuitive representation, calculation, and prediction of the primary performance, parameters, and behaviors of real-world electrical system components within nuclear power plants. Additionally, through the efficient iteration and precise restoration of production data, we achieve comprehensive optimization and enhancement of nuclear power plant electrical system performance, providing valuable feedback and assistance [98].
- Forwards:We aim to establish interdisciplinary, cross-domain, and cross-regional data information platforms that facilitate intelligent development practices spanning the entire plant and across all specialties. Leveraging existing industrial internet or Internet of Things (IoT) frameworks, our efforts within the nuclear power plant’s internal electrical systems focus on exploring and accessing data beyond local constraints. Through collaborative exploration and practice, we gradually establish cross-disciplinary, cross-domain, and cross-regional digital models and operational platforms. Ultimately, within this digital platform, a collaborative comprehensive application system and its corresponding development improvement mechanism are forged.
6. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, C.; Lyu, J.; Zhang, L.; Gong, A.; Fan, Y.; Yan, J.; Li, X. Nuclear Power Plants With Artificial Intelligence in Industry 4.0 Era: Top-Level Design and Current Applications—A Systemic Review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 194315–194332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Ping, J.; Xie, H.; Wang, C.; Li, S. Power and Temperature Control of Nuclear Power Plant Based on Transfer Function Matrix Method. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 33922–33928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Song, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Z. Module Coordination Control of MHTGR-Based Multi-Modular Nuclear Plants. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2016, 63, 1889–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leake, H.C.; Kozo, E.; Attarian, G.E. A Simplified Method to Predict Post-Trip Switchyard Voltage at Nuclear Generating Stations. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2014, 29, 1964–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xue, Y.; Cai, B. Pathway Planning of Nuclear Power Development Incorporating Assessment of Nuclear Event Risk. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2024, 12, 500–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramana, M.V. Small Modular and Advanced Nuclear Reactors: A Reality Check. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 42090–42099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogita, D.; Toshniwal, P.K.; Gupta, V.; Khurana, P. ADQ—Anomaly Detection and Quantification from Delayed Neutron Monitoring Data of Nuclear Power Plants. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 7207–7216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, J.; Jeong, C.; Choo, J. Transverse Electric Scattering of Open Cabinet in Nuclear Power Plants. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2016, 15, 1204–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George-Williams, H.; Lee, M.; Patelli, E. Probabilistic Risk Assessment of Station Blackouts in Nuclear Power Plants. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2018, 67, 494–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boghdady, T.A.; Mahmoud, M.; Zahab, E.A.; Tag-Eldin, E.; Sayed, M. Power Level Control of Nuclear Power Plants During Load Following Operation Using Fractional Order Controller Based on a Modified Algorithm. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 134382–134403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Lu, R.; Xie, H.; Ping, J.; Lu, C.; Zhou, X.; Gao, J.; Li, J. Fault Diagnosis of Air Compressor in Nuclear Power Plant Based on Vibration Observation Window. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 222274–222284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, S.; Sakurai, S.; Kasada, R.; Konishi, S. Plasma Control Requirements for Commercial Fusion Power Plants: A Quantitative Scenario Analysis With a Dynamic Fusion Power Plant Model. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2018, 46, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Buttles, J.W.; Beaty, L.H.; Naser, J.; Hallbert, B.P. Wireless Online Position Monitoring of Manual Valve Types for Plant Configuration Management in Nuclear Power Plants. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Q.; Cao, X. Stochastic-Distributionally Robust Frequency-Constrained Optimal Planning for an Isolated Microgrid. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy, 2024; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkawi, M.; Jiang, J. An Inverse Control-Based Set-Point Function for Steam Generator Level Control in Nuclear Power Plants. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2011, 58, 3291–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Klein, J.; Wu, Y.; Xing, S.; Flammang, R.; Heibel, M.; Zuo, L. A Thermoelectric Energy Harvesting System for Powering Wireless Sensors in Nuclear Power Plants. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2016, 63, 2738–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, L.; Filtz, J.R.; DeFelice, P.; Sadli, M.; Plompen, A.; Heyse, J.; Hay, B.; Dinsdale, A.; Pommé, S.; Cassette, P.; et al. Metrology for New Generation Nuclear Power Plants–MetroFission. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2014, 61, 2017–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.; Shin, J.; Lee, C.; Kwon, K.; Seo, J.T. Cyber Security Controls in Nuclear Power Plant by Technical Assessment Methodology. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 15229–15241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.; Pereira, R.C.; Sousa, J.; Carvalho, P.F.; Correia, M.; Rodrigues, A.P.; Carvalho, B.B.; Correia, C.M.; Gonçalves, B. FPGA Remote Update for Nuclear Environments. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2016, 63, 1645–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Chang, J.; Hu, L.; Wang, X.; Zong, W.; Gui, L. Analysis of the Interturn Short Circuits of Stator Field Windings in Multiphase Angular Brushless Exciter at Nuclear Power Plant. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 2126–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, B.; Joshi, K.; Gokaraju, R. A Dynamic Model of Small Modular Reactor Based Nuclear Plant for Power System Studies. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiei, M.; Ansarifar, G.R.; Hadad, K. Core Power Control of a Nuclear Research Reactor During Power Maneuvering Transients Using Optimized PID-Controller Based on the Fractional Neutron Point Kinetics Model With Reactivity Feedback Effects. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2019, 66, 1804–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.; Akhtar, N.; Rashid, T.; Ansari, S.A. Evaluation of Fast Neutron Fluence for Reactor Pressure Vessel Surveillance of Chashma Nuclear Power Plants Units 1 and 2. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2017, 64, 2661–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Guo, Y.; Sarkar, S.; Ray, A.; Edwards, R.M. Anomaly Detection in Nuclear Power Plants via Symbolic Dynamic Filtering. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2011, 58, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Megias, P.; Hidalgo-Salaverri, J.; Chacartegui, R.; Ayllon-Guerola, J.; Becerra-Villanueva, J.A.; Viezzer, E. Boosting the Efficiency of Future Fusion Power Plants Combining Energy and Heat Production. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2022, 50, 4430–4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.J.; Yun, J.H. Integrated Response Time Evaluation Methodology for the Nuclear Safety Instrumentation System. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2017, 64, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.; Choi, J.; Yoon, H. New Complementary Points of Cyber Security Schemes for Critical Digital Assets at Nuclear Power Plants. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 78379–78390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W. Allocating Ex-post Deviation Cost of Virtual Power Plants in Distribution Networks. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2023, 11, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.-S.; Chung, W.-H.; Kuo, S.-Y. Cyberphysical Security and Dependability Analysis of Digital Control Systems in Nuclear Power Plants. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2016, 46, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.K.; Vinod, G.; Tripathi, A.K. Design Verification of Instrumentation and Control Systems of Nuclear Power Plants. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2014, 61, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Chen, B.-K.; Chen, N.-M.; Liu, C.-W. Lessons Learned From the Blackout Accident at a Nuclear Power Plant in Taiwan. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2010, 25, 2726–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Song, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Z. Coordination Control of SMR-Based NSSS Modules Integrated by Feedwater Distribution. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2016, 63, 2682–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Shen, S.; Fan, S.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Lou, J. A Novel Detection Method for Valve Damage of Nuclear Power Using Attention-Based U-Net (ABUNet). IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 21562–21573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, H.; Imamura, K.; Hirota, N.; Ando, T.; Shibatani, S.; Mizuno, N.; Nakanishi, M.; Mishima, F.; Akiyama, Y.; Nishijima, S.; et al. Development of a Magnetic Separation System of Boiler Feedwater Scale in Thermal Power Plants. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2016, 26, 3701505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Singh, L.K. Modeling and Measuring Common Cause Failures in Measurement of Reliability of Nuclear Power Plant Systems. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 3001608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z. Physically-Based Power-Level Control for Modular High Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactors. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2012, 59, 2531–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ding, T.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, Z.; Siano, P.; Shahidehpour, M. A Two-Stage Stochastic Unit Commitment With Mixed-Integer Recourses for Nuclear Power Plants to Accommodate Renewable Energy. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2024, 15, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Cai, B.; Xue, Y. Review on Optimization of Nuclear Power Development: A Cyber-Physical-Social System in Energy Perspective. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2022, 10, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nodari, C.J.; da Cruz Saladanha, P.L.; Fontes, G.S. Safety Aspects in Dry Storage of Spent Nuclear Fuel in Long Term Operation for Brazilian Nuclear Power Plants. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2020, 18, 1807–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Liu, G.; Li, J.; Yang, J. A Reliability-Based Mapping Scheme for Assessing System Operational Performance With Erroneous Human Behavior at NPPs. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 123416–123429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Jung, W. A Study on the Validity of a Task Complexity Measure for Emergency Operating Procedures of Nuclear Power Plants—Comparing With a Subjective Workload. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2006, 53, 2962–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhou, Z.; Jing, X. Safety implementation of hydrogen igniters and recombiners for nuclear power plant severe accident management. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2006, 11, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, X.; Xu, W.; Qiao, J.; Tan, L. Active Arc Suppression Algorithm for Generator Stator Winding Ground Fault in the Floating Nuclear Power Plant. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2022, 37, 5356–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z. Nonlinear Coordinated Control for MHTGR-Based Nuclear Steam Supply Systems. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2014, 61, 2643–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, A.R.W.; Gibbins, J.; Harrison, G.P.; Chalmers, H. Operational Flexibility of Future Generation Portfolios Using High Spatial- and Temporal-Resolution Wind Data. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2016, 7, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perillo, S.R.P.; Upadhyaya, B.R.; Li, F. Control and Instrumentation Strategies for Multi-Modular Integral Nuclear Reactor Systems. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2011, 58, 2442–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.; Kwon, I.; Je, M. Radiation-Hardened Sensor Interface Circuit for Monitoring Severe Accidents in Nuclear Power Plants. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2020, 67, 1738–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.A.; Haroon, M.; Rashid, A.; Kazmi, Z. Measurement and Analysis of Structural Integrity of Reactor Core Support Structure in Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) Plant. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2017, 64, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, K.; Neda, T.; Suto, O.; Kaneda, M.; Kawamura, A. Application of Hierarchical Computer Complex Concept for Nuclear Power Plants. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1983, 30, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshkbar-Bakhshayesh, K.; Ghofrani, M.B. Development of an Efficient Identifier for Nuclear Power Plant Transients Based on Latest Advances of Error Back-Propagation Learning Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2014, 61, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, D.; Lee, K.Y. Decentralized Fuzzy MPC on Spatial Power Control of a Large PHWR. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2016, 63, 2343–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.G.; Hyun, J.H.; Choi, J.H.; Bhang, B.G.; Ahn, H.-K. Quality Analysis of Photovoltaic System Using Descriptive Statistics of Power Performance Index. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 28427–28438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magne, S.; Nehr, S.; Buet, X.; Bentaïb, A.; Porcheron, E.; Grosseuvres, R.; Studer, E.; Scarpa, R.; Abdo, D.; Widloecher, J.L.; et al. In Situ Gas Monitoring by Fiber-Coupled Raman Spectrometry for H₂-Risk Management in Nuclear Containment During a Severe Nuclear Accident. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2020, 67, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshkbar-Bakhshayesh, K.; Ghofrani, M.B. Development of a New Method for Forecasting Future States of NPPs Parameters in Transients. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2014, 61, 2636–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunatha, K.A.; Agarwal, V.; Mack, A.L.; Koester, D.; Adams, D.E. Total Unwrapped Phase-Based Diagnosis of Wall Thinning in Nuclear Power Plants Secondary Piping Structures. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 113726–113740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; He, P.; Xiong, G.; Wei, Y.; Yang, D.; Wang, X.; Duan, X.; et al. Diagnosis of Rotor Winding Short-Circuit Fault in Multi-Phase Annular Brushless Exciter Through Stator Field Current Harmonics. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 1808–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Lee, S.W.; Na, M.G. Prediction of Axial DNBR Distribution in a Hot Fuel Rod Using Support Vector Regression Models. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2011, 58, 2084–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, P.; Wu, H.; Xu, J.; Wei, L.; Zhu, H.; Ni, L. Thermal Pollution Monitoring of Tianwan Nuclear Power Plant for the Past 20 Years Based on Landsat Remote Sensed Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 6146–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spangler, R.M.; Agarwal, V.; Cole, D.G. A Hybrid Reliability Model Using Generalized Renewal Processes for Predictive Maintenance in Nuclear Power Plant Circulating Water Systems. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 136726–136740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, Y.; Huang, X. Cascaded HTGR Power-Level Control Only by Regulating Primary Helium Flow Rate. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2020, 67, 1780–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroze, Y.; Yamada, M.; Shintani, H.; Nunoko, A.; Murakami, R. Continuous measurement of iodine concentration in the primary coolant of a nuclear power plant. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1997, 44, 760–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-E.; Choo, J.; Choo, H. Electromagnetic Scattering of Periodic Cabinets in Nuclear Power Plants: Parallel Polarization. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 16487–16493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tong, J.; Mao, D. Influence of DC supply systems on unplanned reactor trips in nuclear power plants. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2001, 6, 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Giuliani, U.; Agostini, M.; Bustreo, C.; Zollino, G. The Fusion to Hydrogen Option in a Carbon Free Energy System. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 131178–131190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Hsu, S.-C.; Hsi, P.-H.; Chen, S.-L. Transferring of VFTO From an EHV to MV System as Observed in Taiwan’s No. 3 Nuclear Power Plant. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2011, 26, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno, N.; Mishima, F.; Akiyama, Y.; Okada, H.; Hirota, N.; Matsuura, H.; Maeda, T.; Shigemoto, N.; Nishijima, S. Removal of Iron Oxide With Superconducting Magnet High Gradient Magnetic Separation From Feed-Water in Thermal Plant. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2015, 25, 3700804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Gu, H.; Shen, X.; You, D. Bayesian Long Short-Term Memory Model for Fault Early Warning of Nuclear Power Turbine. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 50801–50813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čerňan, M.; Halaška, J.; Müller, Z.; Tlustý, J. The Impact of Distributed Autonomous PV Installations on Critical Infrastructure in Crisis Situations. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 97520–97530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiani, D.; Mazzanti, G.; Suraci, S.V.; Diban, B. Innovative Development and Application of a Stress-Strength Model for Reliability Estimation of Aged LV Cables for Nuclear Power Plants. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2021, 28, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, M.; Soler, E.; Llopis, L.; Trillo, J. Integrating Blockchain in Safety-Critical Systems: An Application to the Nuclear Industry. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 190605–190619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Almási, I.; Hlavathy, Z.; Zsigrai, J.; Lakosi, L.; Nagy, P.; Parkó, T.; Pós, I. Monitoring Burn-Up of Spent Fuel Assemblies by Gamma Spectrometry. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2013, 60, 1107–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preble, D.W. Collapsing Power Grid Reliability and Economics. IEEE J. Radio Freq. Identif. 2022, 6, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabi, K.; Safarzadeh, O.; Rahimi-Moghaddam, A. Robust Control of the PWR Core Power Using Quantitative Feedback Theory. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2011, 58, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, R.D.; Srivastava, G.D.; Rautela, P. Design Implementation and Parallel Operation of High-Current High-Power Multipulse Converters Feeding Nuclear Fuel Simulators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 1598–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajpayee, V.; Becerra, V.; Bausch, N.; Deng, J.; Shimjith, S.R.; Arul, A.J. L₁-Adaptive Robust Control Design for a Pressurized Water-Type Nuclear Power Plant. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2021, 68, 1381–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matveev, I.B. Plasma or Retirement. Alternatives to the Coal-Fired Power Plants. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2011, 39, 3259–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Shimjith, S.R.; Tiwari, A.P. Adaptive Unscented Kalman Filtering for Reactivity Estimation in Nuclear Power Plants. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2019, 66, 2388–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.H.; Thai, V.X.; Lee, E.S.; Kim, J.H.; Rim, C.T. Dipole-Coil-Based Wide-Range Inductive Power Transfer Systems for Wireless Sensors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 3158–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, S.; Tanaka, K.; Maki, K.-I. Microwave Power Transmission Technologies for Solar Power Satellites. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Xiong, Y. Event-Driven-Based Water Level Control for Nuclear Steam Generators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 5480–5489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Huang, X.; Hao, Y.; Li, C.-W. Linear Representation and Sparse Solution for Transient Identification in Nuclear Power Plants. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2013, 60, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Youn, S.; Park, J.-E.; Choo, J.; Choo, H. Electromagnetic Field Propagation and Indoor Exclusion Zone Analysis in a Nuclear Power Plant. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2020, 62, 2386–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.M.; Lee, H.J.; Ji, Y.H.; Kim, T.H.; Ryu, S.Y.; Kim, S.R.; Jo, S.K.; Kim, J.C.; Kim, S.H. A Cytogenetic Study of Korean Native Goat Bred in the Nuclear Power Plant using the Micronucleus Assay. J. Radiat. Res. 2005, 46, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dong, Z. Model-Free Power-Level Control of MHTGRs Against Input Saturation and Dead-Zone. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2015, 62, 3297–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, A. Nuclear Power Plant Control beyond the 1980s. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1980, 27, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Uhrig, R.E. Nuclear power plant performance study by using neural networks. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1992, 39, 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.P.; Correia, M.; Batista, A.; Sousa, J.; Goncalves, B.; Correia, C.M.; Varandas, C.A. Intelligent Platform Management Controller for Nuclear Fusion Fast Plant System Controllers. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2011, 58, 1733–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.-X.; Liu, L.-G.; Pirjola, R.J.; Wang, K.-R.; Dong, B. Impact of the EHV Power System on Geomagnetically Induced Currents in the UHV Power System. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2015, 30, 2163–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, W.; Furse, C. Spread Spectrum Techniques for Measurement of Dielectric Aging on Low Voltage Cables for Nuclear Power Plants. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2021, 28, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Arigi, A.M.; Kim, J. Algorithm for Autonomous Power-Increase Operation Using Deep Reinforcement Learning and a Rule-Based System. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 196727–196746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, D.; Lee, C.W.; Kim, H.R.; Lee, S.J. Safety Assessment Framework for Nuclear Power Plant Decommissioning Workers. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 76305–76316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Shin, J.; Kim, B.-S.; Nah, W.; Lim, C.; Chai, J. Electrical and mechanical diagnosis of aging 600 V rated STP cables in a nuclear power plant. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2017, 24, 1574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.-J.; Shen, Q.-Q.; Wang, S.; Lu, J.-Y.; Meng, Q.-X. Generation Scheduling of a Hydrothermal System Considering Multiple Provincial Peak-Shaving Demands. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 46225–46239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, B.; Gokaraju, R. Optimal Operation of SMR-RES Hybrid Energy System for Electricity & District Heating. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 3146–3155. [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta, S.; Murphy, J.J. Degraded or Loss of Voltage Protection of Class 1E Auxiliary Power Systems in a Nuclear Power Plant. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1979, 26, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z. Nonlinear Adaptive Power-Level Control for Modular High Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactors. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2013, 60, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, C.A.; Cline, J.E.; Keller, J.H. Measurement of Sources of Iodine-131 Releases to the Atmosphere from Nuclear Power Plants. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1974, 21, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, D.; Lee, K.Y. Quasi-min-max Fuzzy MPC of UTSG Water Level Based on Off-Line Invariant Set. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2015, 62, 2266–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Serial Number | Transformer Location | Type of Exception |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | High-pressure side casing | Cracks and discoloration on casing surface, metal corrosion |
| 2 | Low-voltage side casing | Cracked and discolored casing, rusted metal |
| 3 | Oil pillow | Component surface oil, metal corrosion |
| 4 | Oil temperature | Meter identification, meter breakage |
| 5 | Oil level | Meter identification, meter breakage |
| 6 | Operational data | Meter identification, meter breakage |
| 7 | All sides | Rusting |
| 8 | Top of transformer | Component surface oil, metal corrosion |
| 9 | Transformer perimeter | Foreign object |
| 10 | Surrounding ground | Ground oil stains |
| 11 | Ventilator | Discoloration of silicone, damage to oil seal |
| Step | Evolutionary Path | Time Series | Objectives and Performance Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Automatization | Recent past | Utilizing advanced sensing technology, we aim to elevate the automation level of the electrical equipment system, enabling the miniaturization and integration of equipment. This involves the profound integration of diverse sensing units, intelligent self-testing of equipment health status, electromagnetic compatibility, and data transmission anti-interference measures. Furthermore, we leverage computer network technology to effectively manage and monitor the electrical system, ensuring its optimal performance and reliability. |
| 2 | Digitalization 1.0 | Recent past | While still relatively basic in terms of software application, the system is capable of achieving data acquisition, structured processing, and analysis for a single electrical component. This functionality provides foundational support for professional data handling and feedback mechanisms. |
| 3 | Digitalization 2.0 | Mid-term | The implementation of data acquisition, structured processing, and analysis for small electrical systems has been achieved, accompanied by significant advancements and improvements in the hardware platform and model level. |
| 4 | Meshing | Mid-term | From the perspective of the local plant electrical system, we aim to accomplish the mining and interfacing of data beyond the local area, gradually exploring the establishment of cross-disciplinary, cross-field, and cross-regional data flow within our platform. By connecting structured data, upgrading our hardware platform and modeling capabilities, we comprehensively enrich nuclear power-related applications and services. |
| 5 | Intelligent 1.0 | Forwards | From the perspective of the electrical system spanning the entire plant, we can leverage intelligent technology to construct a smart brain within the new frontier. This brain will enable self-learning and self-optimization capabilities, thereby assisting in decision-making processes. |
| 6 | Intelligent 2.0 | Forwards | We have achieved breakthroughs in the development of complex integrated models and nuclear power global situational awareness and perception models, addressing challenging issues. This enables nuclear power systems to achieve networked and intelligent self-adaptation to cyclic processes, allowing for customized intelligent recommendations to assist in decision-making. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, B.; Dong, X.; Wang, C. The Evolving Technological Framework and Emerging Trends in Electrical Intelligence within Nuclear Power Facilities. Processes 2024, 12, 1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071374
Sun Y, Wang Z, Huang Y, Zhao J, Wang B, Dong X, Wang C. The Evolving Technological Framework and Emerging Trends in Electrical Intelligence within Nuclear Power Facilities. Processes. 2024; 12(7):1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071374
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yao, Zhijian Wang, Yao Huang, Jie Zhao, Bo Wang, Xuzhu Dong, and Chenhao Wang. 2024. "The Evolving Technological Framework and Emerging Trends in Electrical Intelligence within Nuclear Power Facilities" Processes 12, no. 7: 1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071374
APA StyleSun, Y., Wang, Z., Huang, Y., Zhao, J., Wang, B., Dong, X., & Wang, C. (2024). The Evolving Technological Framework and Emerging Trends in Electrical Intelligence within Nuclear Power Facilities. Processes, 12(7), 1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071374







