Research on Mechanism of Surfactant Improving Wettability of Coking Coal Based on Molecular Dynamics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modeling
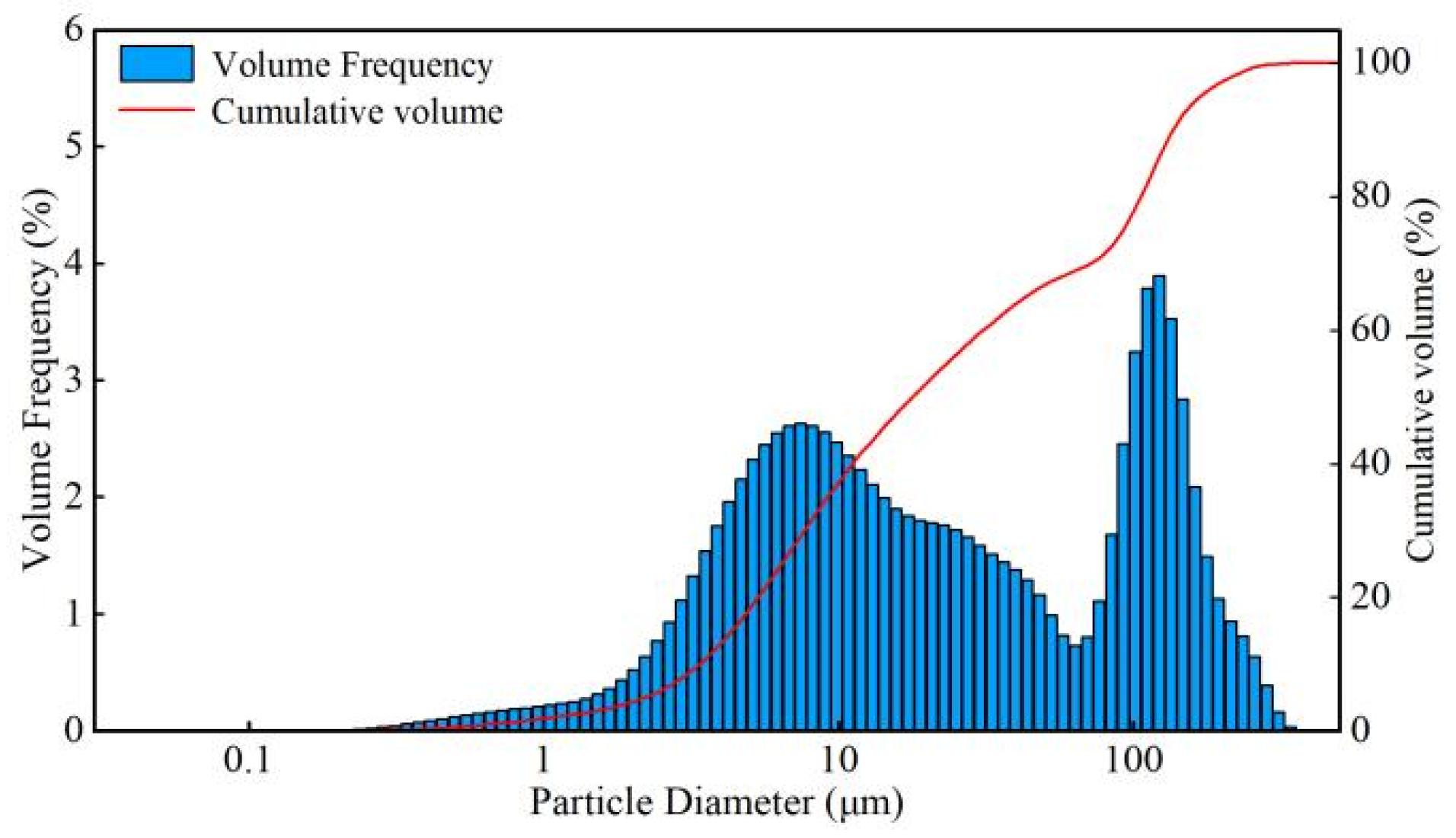
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Coking Coal Modeling
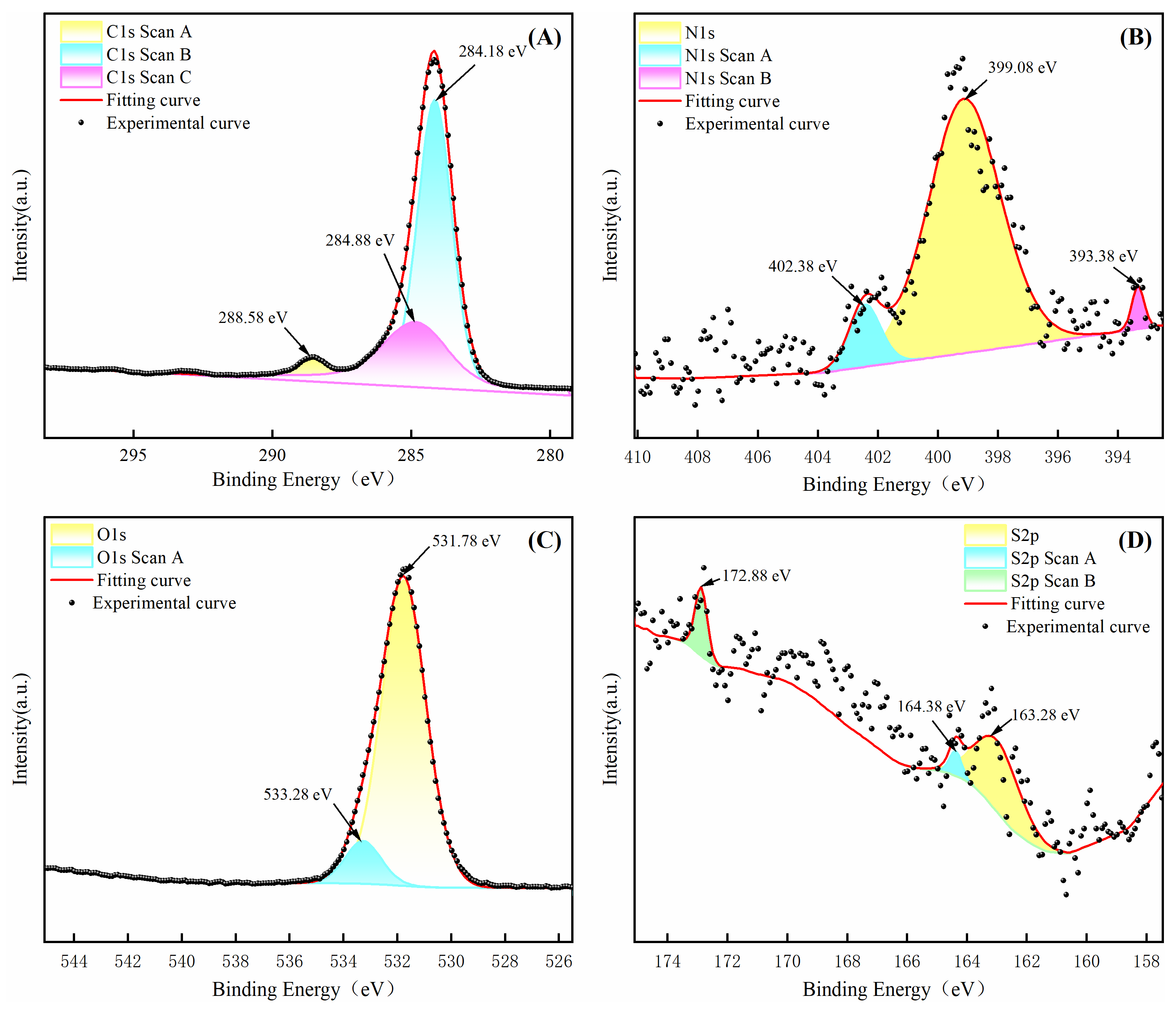
2.2.1. Carbon Atom Analysis
2.2.2. Elemental Structural Analysis
2.2.3. Comprehensive Analysis
- (1)
- Aromatic structure
- (2)
- Aliphatic carbon structure
- (3)
- Heteroatom structures
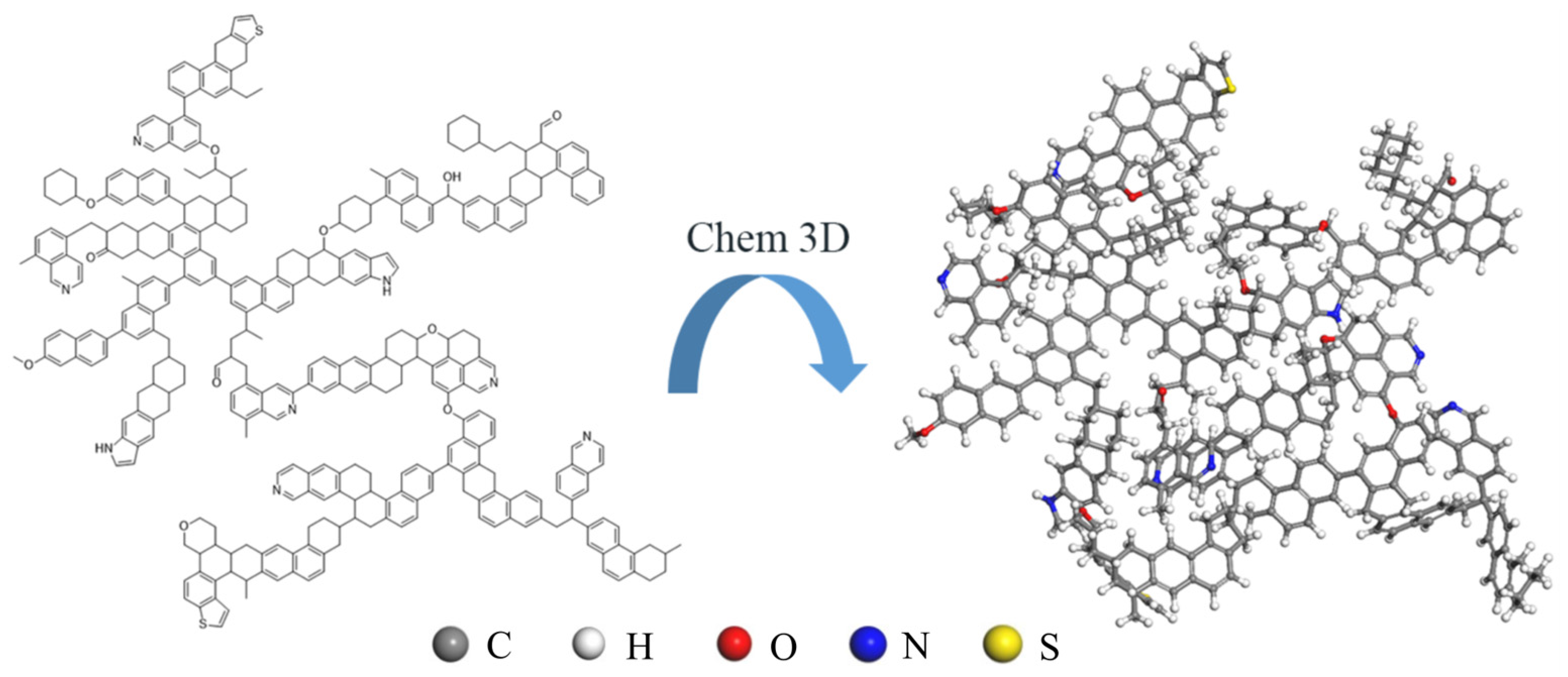
2.3. System Modeling
3. Study on Wetting Adsorption Performance of Water/Coal/Surfactant
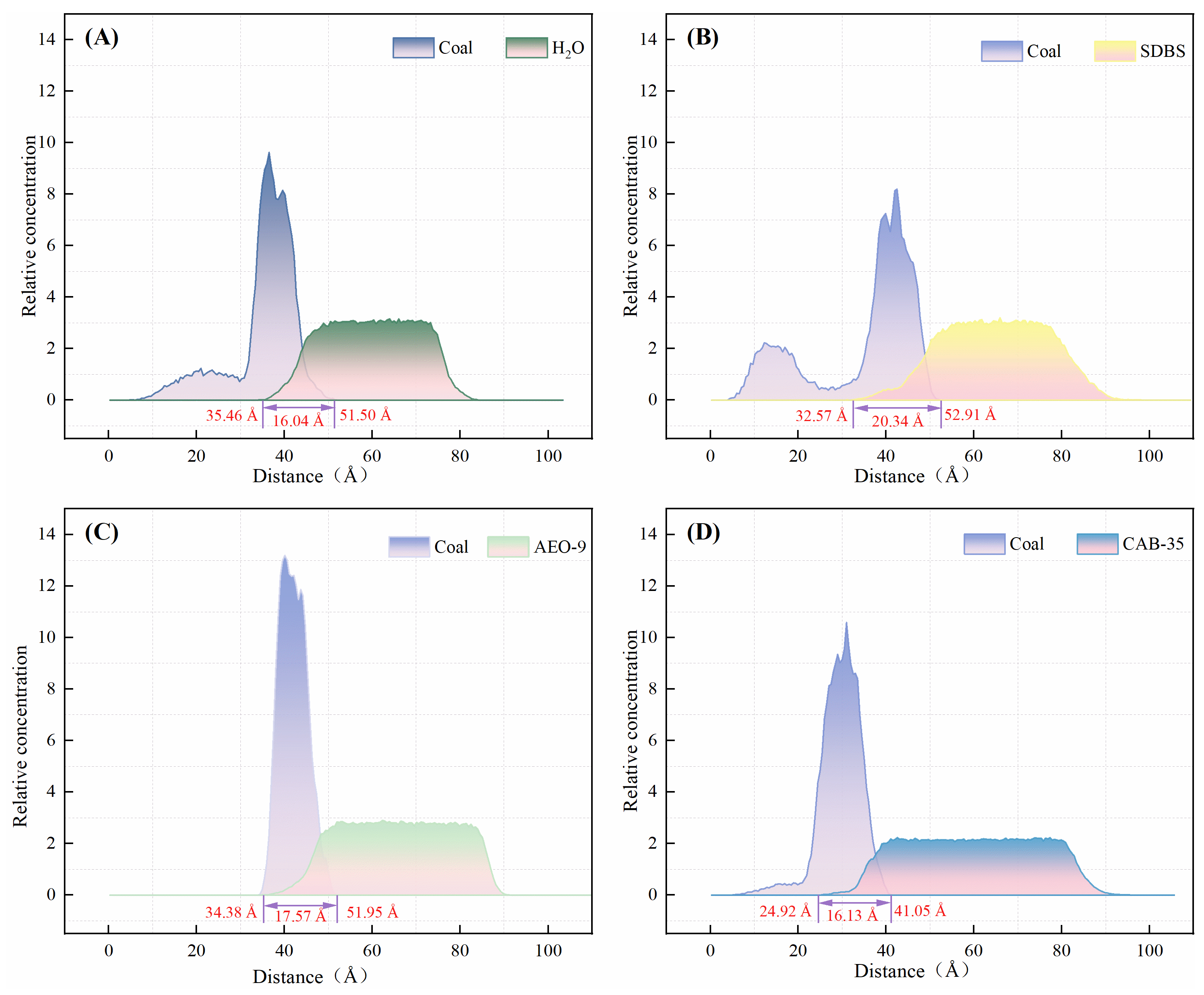
3.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics
3.2. Relative Concentration Distribution Characteristics
3.3. Analysis of Non-Bonding Interaction Energy
3.4. Diffusion Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kori, K.B.; Agrawal, H.D. Dust Monitoring Systems and Health Hazards in Coal Mining A Review. J. Trend Sci. Res. Dev. 2021, 5, 172–177. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.F.; Chen, X.; Zhao, X. Analysis of current status and development direction of coal mining technology in China. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2066, 020017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, P.; Wang, E.; Chen, D.; Li, C. Characteristics of coal resources in China and statistical analysis and preventive measures for coal mine accidents. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2023, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Yang, F.F.; Yadong Xie, Y.D.; Zhang, J.J.; Miao, Z.Q.; Ma, D.Q. Study on Dust Control of Coal Seam Shallow Hole Dynamic Pressure Water Injection Based on Prevention and Treatment of Coal Miner’s Pneumoconiosis. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 126, 274. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.B. Exploration of the Application of Green Mining Technology in Coal Mines under the New Situation. Appl. Sci. Innov. Res. 2024, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.T.; Zhou, W.; Mithal, I.J.; Wang, Z.M. Analyzing Characteristics of Particulate Matter Pollution in Open-Pit Coal Mines: Implications for Green Mining. Energies 2021, 14, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.; Mishra, P.D. Prevention and suppression of coal dust explosion in underground coal mines: Role of rock dust type, particle size, proportion, concentration, and thermal properties. Adv. Powder Technol. 2024, 35, 104343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Q.; Gao, Z.Y.; Yanying Xu, Y.Y.; Duan, G.S.; Wang, X. Research on Explosion Pressure Characteristics of Long Flame Coal Dust and the Inhibition Effect of Different Explosion Suppressants. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 35919–35928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.L.; Si, R.J.; Wang, L.; Jia, Q.S.; Xin, C.P. Explosion and explosion suppression of gas/deposited coal dust in a realistic environment. Fuel 2024, 357, 129710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.F.; Tan, X.H.; Zhang, L.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Liu, R.H. Influence of particle diameter on the wettability of coal dust and the dust suppression efficiency via spraying. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 132, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Wang, P.F.; Li, Y.J.; Liu, R.H.; Tian, C. Effect of water supply pressure on atomization characteristics and dust-reduction efficiency of internal mixing air atomizing nozzle. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 252–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.F.; Gao, R.Z.; Liu, R.H.; Yang, F.Q. CFD-based optimization of the installation location of the wall-mounted air duct in a fully mechanized excavation face. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 141, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.G.; Xu, X.Y.; Wei, J.P.; Jiang, W.; Wang, M.Y. Experimental study on the effect of cutting parameters to dust production patterns of different brittle coal. Int. J. Coal Prep. Util. 2024, 44, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Duan, J.; Sun, B.; Jing, B.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, G.; Sun, L. Numerical analysis on pollution law for dust and diesel exhaust particles in multi-ventilation parameter environment of mechanized excavation face. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 157, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.X.; Shen, C.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.Y.; Shi, G.Y.; Wang, M.Y. The spatial diffusion rule and pollution region of disorganized dust in the excavation roadway at different roadheader cutting positions. Powder Technol. 2022, 396, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Q.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, H.D.; Sun, X.; Li, T. Prevention and Treatment of Pneumoconiosis in the Context of Healthy China 2030. China CDC Wkly. 2023, 5, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shi, H.D.; Wang, P.; Wu, Y.G.; Wang, L.L.; Song, Z.L. Analysis of early diagnosis and prevention techniques for occupational pneumoconiosis based on patent perspectives in China’s coal industry. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi = Zhonghua Laodong Weisheng Zhiyebing Zazhi = Chin. J. Ind. Hyg. Occup. Dis. 2023, 41, 948–955. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, X.X.; Wang, B.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J.T.; Chu, P.; Zhu, Z.B.; Zheng, S.W. Experimental Study on the Wettability of Coal with Different Metamorphism Treated by Surfactants for Coal Dust Control. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 21925–21938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solodyankin, S.S.; Kolmakov, N.G.; Manin, N.S.; Fritslet, V.K.; Kazantsev, A.V.; Miroshnikov, A.M. Using a solution of the surfactant for increasing collection efficiency of coal dust in the exhaust system. Coke Chem. 2016, 59, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ge, S.C.; Huang, Z.H.; Jing, D.J.; Chen, X. The influence of surfactant on the wettability of coal dust and dust reduction efficiency. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.; Shah, K.; Atkin, R.; Moghtaderi, B. Physicochemical interactions of ionic liquids with coal; the viability of ionic liquids for pre-treatments in coal liquefaction. Fuel 2015, 143, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.B.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, Q.T.; Pan, H.W.; Liu, D. Experimental study on modification of physicochemical characteristics of acidified coal by surfactants and ionic liquids. Fuel 2020, 266, 116966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, G.H.; Xie, H.C.; Li, S.; Sun, Q.; Huang, D.M.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Wang, N. The effect of anionic surfactant (SDS) on pore-fracture evolution of acidified coal and its significance for coalbed methane extraction. Adv. Powder Technol. 2019, 30, 940–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S. A new method of coal fine particles humidification and agglomeration: Synergistic dust suppression with composition of soap solution. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 159, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yang, S.Y.; Hu, B.; Yuan, Z.L.; Wu, H.; Yang, L.J. Evaluating of the performance of a composite wetting dust suppressant on lignite dust. Powder Technol. 2018, 339, 882–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Y.; Wu, K.; Ren, L. Medium optimization and dust suppression performance analysis of microbial-based dust suppressant compound by response surface curve method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2024, 31, 24525–24535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Yuan, M.; Bao, Q.; Yan, J.; Zhou, W.; Guo, C.; Guo, L.; Niu, W.; Yu, F.; Hua, Y. Experimental and molecular dynamics simulation research on compound dust suppressant based on locust bean gum. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yan, D.; Yan, M.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, B.; Long, H.; Lin, H. Molecular simulation of alkyl glycoside surfactants with different concentrations inhibiting methane diffusion in coal. Energy 2023, 263, 125771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, H.M.; Lei, J.M.; Xie, J.; Li, L.M.; Gan, Y.; Liu, Y.L. Study on the surface wetting mechanism of bituminous coal based on the microscopic molecular structure. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 5933–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.F.; Han, H.; Tian, C.; Liu, R.H.; Jiang, Y.D. Experimental study on dust reduction via spraying using surfactant solution. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, R.J.; Mainwaring, D.E. The influence of surfactant adsorption on the surface characterisation of Australian coals. Fuel 2001, 80, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.F.; Jiang, Y.D.; Liu, R.H.; Liu, L.M.; He, Y.C. Experimental study on the improvement of wetting performance of OP-10 solution by inorganic salt additives. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Coal | Mad (%) | Aad (%) | Vad (%) | FCad (%) | Cd (%) | Hd (%) | Od (%) | Nd (%) | Sd (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coking coal | 2.56 | 12.72 | 14.94 | 69.78 | 89.38 | 5.52 | 2.64 | 1.88 | 0.58 |
| Coal Samples | Number of Peaks | Chemical Shift (ppm) | Relative Area (%) | Attribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coking Coal | 1 | 18.59 | 7.93 | Aromatic Methylene Carbon |
| 2 | 34.46 | 15.09 | Methylene Carbon | |
| 3 | 49.85 | 6.20 | Quaternary and Hypomethyl Carbons | |
| 4 | 73.02 | 5.56 | Endocyclic Oxidized Fatty Carbons | |
| 5 | 107.51 | 2.18 | Protonated Aromatic Carbon | |
| 6 | 124.18 | 48.59 | Protonated Aromatic Carbon | |
| 7 | 134.38 | 12.58 | Bridged Aromatic Carbon | |
| 8 | 154.52 | 2.63 | Oxygen-Substituted Aromatic Carbons | |
| 9 | 169.62 | 4.45 | Carboxy Carbon | |
| 10 | 221.48 | 2.89 | Carboxy Carbon |
| Coal Samples | fa | fa′ | fac | faH | faN | faP | faS | faB | fal | fal* | falH | falO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coking Coal | 73.32 | 65.98 | 7.34 | 50.77 | 15.21 | 2.63 | 0 | 12.58 | 34.78 | 7.93 | 21.29 | 5.56 |
| Forms of Existence of Aromatic Structures | Coking Coal |
|---|---|
| Thiophene (C4H4S) | 2 |
| Pyridine (C5H5N) | 6 |
| Pyrrole (C4H5N) | 2 |
| Element | Quantity | Form of Existence |
|---|---|---|
| N | 8 | C5H5N, C4H5N |
| O | 11 | C-O, C=O |
| S | 2 | C4H4S |
| System | Eint/(kcal·mol−1) | Evan/(kcal·mol−1) | Eele/(kcal·mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| System A | −9416.006 | 2427.363 | −11891.369 |
| System B | −9906.651 | 2395 | −12252.468 |
| System C | −9652.390 | 2353.543 | −12005.933 |
| System D | −9857.330 | 2375.737 | −12282.388 |
| System | Diffusion Coefficient (cm2/s) |
|---|---|
| System A | 4.77383 × 10−5 |
| System B | 6.24917 × 10−5 |
| System C | 5.97467 × 10−5 |
| System D | 5.63033 × 10−5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, R.; Li, S.; Ling, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, W. Research on Mechanism of Surfactant Improving Wettability of Coking Coal Based on Molecular Dynamics. Processes 2024, 12, 1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12061271
Liu R, Li S, Ling Y, Zhao Y, Liu W. Research on Mechanism of Surfactant Improving Wettability of Coking Coal Based on Molecular Dynamics. Processes. 2024; 12(6):1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12061271
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ren, Shilin Li, Yuping Ling, Yuanpei Zhao, and Wei Liu. 2024. "Research on Mechanism of Surfactant Improving Wettability of Coking Coal Based on Molecular Dynamics" Processes 12, no. 6: 1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12061271
APA StyleLiu, R., Li, S., Ling, Y., Zhao, Y., & Liu, W. (2024). Research on Mechanism of Surfactant Improving Wettability of Coking Coal Based on Molecular Dynamics. Processes, 12(6), 1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12061271





