Pristine and UV-Weathered PET Microplastics as Water Contaminants: Appraising the Potential of the Fenton Process for Effective Remediation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of PET MP Samples
2.3. MP Removal by Fenton Process
2.4. Quantification of the PET MP Removal
2.5. X-ray Photoemission Spectroscopy Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Removal of PET MPs by the Fenton Process
3.2. X-ray Photoemission Spectroscopy Analysis of the PET MPs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plastics—The Facts. 2022. Available online: https://plasticseurope.org/knowledge-hub/plastics-the-facts-2022/ (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- Revel, M.; Châtel, A.; Mouneyrac, C. Micro(nano)plastics: A threat to human health? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 1, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, M.S. Effects of Microplastics on Fish and in Human Health. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 827289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Xie, C.; Liang, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, Z. Accumulation of microplastics in fish guts and gills from a large natural lake: Selective or non-selective? Environ. Pollut. 2022, 309, 119785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.L.; Kelly, F.J. Plastic and Human Health: A Micro Issue? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6634–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.L.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chang, X.; Hu, M.; Fang, J.K.-H.; Sokolova, I.M.; Huang, W.; Xu, E.G.; Wang, Y. Is microplastic an oxidative stressor? Evidence from a meta-analysis on bivalves. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adediran, G.A.; Cox, R.; Jürgens, M.D.; Morel, E.; Cross, R.; Carter, H.; Pereira, M.G.; Read, D.S.; Johnson, A.C. Fate and behaviour of Microplastics (>25 µm) within the water distribution network, from water treatment works to service reservoirs and customer taps. Water Res. 2024, 255, 121508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visentin, E.; Manuelian, C.L.; Niero, G.; Benetti, F.; Perini, A.; Zanella, M.; Pozza, M.; De Marchi, M. Characterization of microplastics in skim-milk powders. J. Dairy Sci. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.M.; Almeida, C.M.R.; Guardiola, F.A.; Pereira, R.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Ramos, S. Uncovering microplastics contamination in canned seafood. Food Chem. 2024, 448, 139049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syamsu, D.A.; Deswati, D.; Syafrizayanti, S.; Putra, A.; Suteja, Y. Presence of microplastics contamination in table salt and estimated exposure in humans. Glob. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2024, 10, 205–224. [Google Scholar]
- Espiritu, E.Q.; Pauco, J.L.R.; Bareo, R.S.; Palaypayon, G.B.; Capistrano, H.A.M.; Jabar, S.R.; Coronel, A.S.O.; Rodolfo, R.S.; Enriquez, E.P. Microplastics contamination in selected staple consumer food products. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Hoh, E.; Kurobe, T.; Teh, S.J. Ingested plastic transfers hazardous chemicals to fish and induces hepatic stress. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuten, E.L.; Saquing, J.M.; Knappe, D.R.U.; Barlaz, M.A.; Jonsson, S.; Björn, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S.; Yamashita, R.; et al. Transport and release of chemicals from plastics to the environment and to wildlife. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2027–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettler, E.R.; Mincer, T.J.; Amaral-Zettler, L.A. Life in the “Plastisphere”: Microbial Communities on Plastic Marine Debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7137–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, W.K.; Law, J.C.F.; Zhang, T.; Leung, K.S.Y. Effects of Weathering on the Sorption Behavior and Toxicity of Polystyrene Microplastics in Multi-solute Systems. Water Res. 2020, 187, 116419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, S.A.; Liu, J.; Tesoro, A.G. Transport and fate of microplastic particles in wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2016, 91, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, N.d.O.; Busquets, R.; Campos, L.C. Insights into the removal of microplastics and microfibres by Advanced Oxidation Processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 861, 160665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bule Možar, K.; Miloloža, M.; Martinjak, V.; Cvetnić, M.; Kušić, H.; Bolanča, T.; Kučić Grgić, D.; Ukić, Š. Potential of Advanced Oxidation as Pretreatment for Microplastics Biodegradation. Separations 2023, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babuponnusami, A.; Muthukumar, K. A review on Fenton and improvements to the Fenton process for wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusic, H.; Koprivanac, N.; Srsan, L. Azo dye degradation using Fenton type processes assisted by UV irradiation: A kinetic study. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2006, 181, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papac Zjačić, J.; Tonković, S.; Pulitika, A.; Katančić, Z.; Kovačić, M.; Kušić, H.; Hrnjak Murgić, Z.; Lončarić Božić, A. Effect of Aging on Physicochemical Properties and Size Distribution of PET Microplastic: Influence on Adsorption of Diclofenac and Toxicity Assessment. Toxics 2023, 11, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopar, M.; Kusic, H.; Koprivanac, N. Treatment of simulated industrial wastewater by photo-Fenton process. Part I: The optimization of process parameters using design of experiments (DOE). Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 173, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacic, M.; Salaeh, S.; Kusic, H.; Suligoj, A.; Kete, M.; Fanetti, M.; Stangar, U.L.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Bozic, A.L. Solar-driven photocatalytic treatment of diclofenac using immobilized TiO2-based zeolite composites. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17982–17994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomic, A.; Cvetnic, M.; Kovacic, M.; Kusic, H.; Karamanis, P.; Bozic, A.L. Structural features promoting adsorption of contaminants of emerging concern onto TiO2 P25: Experimental and computational approaches. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 87628–87644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, M.N.; Jin, B.; Chow, C.W.K.; Saint, C. Recent developments in photocatalytic water treatment technology: A review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2997–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edge, M.; Wiles, R.; Allen, N.S.; McDonald, W.A.; Mortlock, S.V. Characterisation of the species responsible for yellowing in melt degraded aromatic polyesters—I: Yellowing of poly(ethylene terephthalate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1996, 53, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, J.; Alfè, D.; Tkatchenko, A. Nanoscale π–π stacked molecules are bound by collective charge fluctuations. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Zhou, P.; Yang, Y.; Hall, T.; Nie, G.; Yao, Y.; Duan, X.; Wang, S. Degradation of Microplastics by a Thermal Fenton Reaction. ACS ES&T Eng. 2022, 2, 110–120. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.-M.; Zheng, J.-C.; Lei, N.-Y.; Yu, L.; Kong, K.H.-K.; Yu, H.-Q.; Lau, T.-C.; Lam, M.H.W. Photoassisted Fenton Degradation of Polystyrene. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Ding, J.; Song, Z.; Yang, B.; Zhang, C.; Guan, B. Degradation of nano-sized polystyrene plastics by ozonation or chlorination in drinking water disinfection processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 131690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, D.; Munoz, M.; Nieto-Sandoval, J.; Romera-Castillo, C.; de Pedro, Z.M.; Casas, J.A. Insights into the degradation of microplastics by Fenton oxidation: From surface modification to mineralization. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allé, P.H.; Garcia-Muñoz, P.; Adouby, K.; Keller, N.; Robert, D. Efficient photocatalytic mineralization of polymethylmethacrylate and polystyrene nanoplastics by TiO2/β-SiC alveolar foams. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 1803–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Wang, L.; Zhang, F.; Wu, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, J. Feasible Degradation of Polyethylene Terephthalate Fiber-Based Microplastics in Alkaline Media with Bi2O3@N-TiO2 Z-Scheme Photocatalytic System. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2022, 6, 2100516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Song, X.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, J.; Huo, P. Enhanced degradation of polyethylene terephthalate plastics by CdS/CeO2 heterojunction photocatalyst activated peroxymonosulfate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Song, X.; Wang, H.; Huo, P. Removal of polyethylene terephthalate plastics waste via Co–CeO2 photocatalyst–activated peroxymonosulfate strategy. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 479, 147781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshnikov, V.A.; Kobzeva, T.V.; Polyakov, N.E.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Inhibition of Fe2+- and Fe3+- induced hydroxyl radical production by the iron-chelating drug deferiprone. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 78, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovac, N.; Juretic, D.; Kusic, H.; Dermadi, J.; Bozic, A.L. Photooxidative degradation of aromatic carboxylic acids in water: Influence of hydroxyl substituents. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 10590–10598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
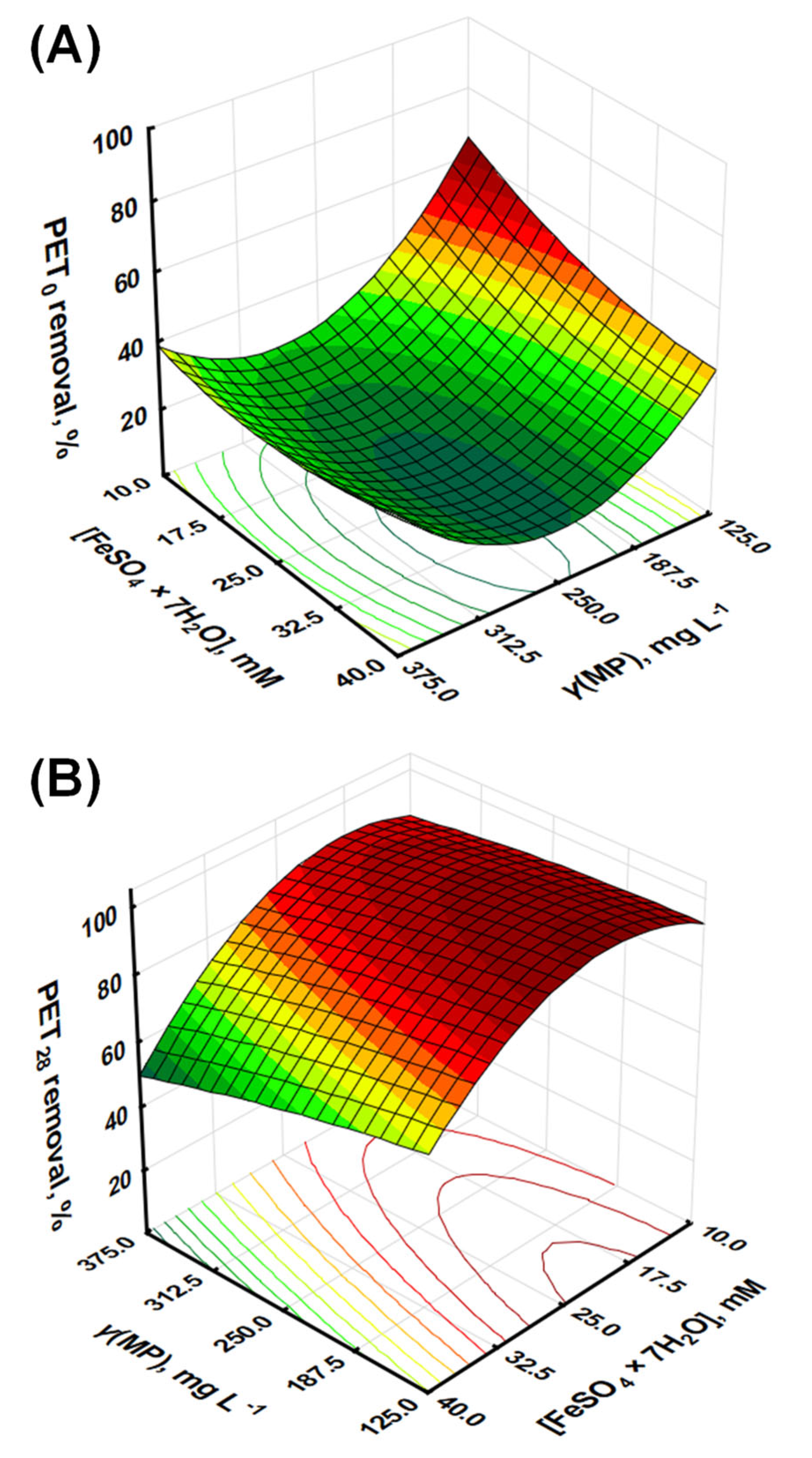
| Parameters | Model Variables/Coded Values | Level/Range | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| γ (MP), mg L−1 | X1 | 5 | 20 | 35 |
| [Fe2+], mM | X2 | 10 | 25 | 40 |
| Factor (Coded) | Statistical Analysis | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SS | df | MSS | F | p | ||||||
| Y1 | Y2 | Y1 | Y2 | Y1 | Y2 | Y1 | Y2 | Y1 | Y2 | |
| Model | 2023.89 | 2241.41 | 5 | 5 | 404.78 | 448.28 | 56.80 | 44.72 | 0.0036 * | 0.0051 * |
| X1 | 319.89 | 312.19 | 1 | 1 | 319.89 | 312.19 | 44.89 | 31.14 | 0.0068 * | 0.0114 * |
| X12 | 1307.48 | 4.87 | 1 | 1 | 1307.48 | 4.87 | 183.46 | 0.49 | 0.0009 * | 0.5361 |
| X2 | 171.31 | 1232.09 | 1 | 1 | 171.31 | 1232.09 | 24.04 | 122.91 | 0.0162 * | 0.0016 * |
| X22 | 66.20 | 632.97 | 1 | 1 | 66.20 | 632.97 | 9.29 | 63.14 | 0.0555 | 0.0042 * |
| X1 × X2 | 159.01 | 59.29 | 1 | 1 | 159.01 | 59.29 | 22.31 | 5.91 | 0.0180 * | 0.0932 |
| Residual | 21.38 | 30.07 | 3 | 3 | 7.13 | 10.02 | ||||
| Total | 2045.27 | 2271.49 | 8 | 8 | ||||||
| Type of MPs Studied | Treatment Method | Treatment Conditions | MPs Removal Extent | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | Fenton process | [Fe2+] = 4 mM, [H2O2] = 200 mM, acidic pH, 140 °C, 12 h | 75.6% mineralization | [30] |
| Polystyrene (PS) | Fenton process | [Fe3+] = 0–0.63 mM, [H2O2] = 0–176 mM, pH 2, 250 W Xe lamp, 250 min | 99% mineralization | [31] |
| Polystyrene (PS) | Ozonation | [O3] = 4.1 mg L−1, 240 min | 42.7% mineralization | [32] |
| Polystyrene (PS) | Fenton process | [Fe3+] = 10 mgL−1, [H2O2] =1000 mgL−1, pH 3; T = 80 °C, 7.5 h | 70% mineralization | [33] |
| Polystyrene (PS) | Photocatalysis | UV-A (354 nm), TiO2@SiC foam, natural pH, 7 h | 35% mineralization | [34] |
| Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) | Photocatalysis | 300 W Xe lamp, Bi2O3@N–TiO2, pH 9, 48 h | 10.23% mass loss | [35] |
| Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) | Photocatalysis | CdS/CeO2 (wt. CdS 10%), [HSO5-] = 3 mM, 6 h | ~94% mass loss | [36] |
| Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) | Photocatalysis | Co–CeO2, [HSO5-] = 3 mM, [H2O2] = 3 mM, 6 h | ~92% mass loss | [37] |
| Identified Functional Groups and Interactions | PET0, % | PET28, % |
|---|---|---|
| C=C | 38.80 | 40.64 |
| C-O-C, C-OH | 21.73 | 19.73 |
| O-C=O | 17.38 | 16.48 |
| π-π | 2.70 | 2.83 |
| C-C, C-H | 19.40 | 20.32 |
| Identified Functional Groups and Interactions | PET0, % | PET28, % |
|---|---|---|
| C=C | 35.80 | 15.80 |
| C-O-C, C-OH | 8.70 | 46.48 |
| O-C=O | 30.5 | 8.81 |
| π-π | 2.49 | 1.10 |
| C-C, C-H | 43.57 | 21.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kovačić, M.; Tomić, A.; Tonković, S.; Pulitika, A.; Papac Zjačić, J.; Katančić, Z.; Genorio, B.; Kušić, H.; Lončarić Božić, A. Pristine and UV-Weathered PET Microplastics as Water Contaminants: Appraising the Potential of the Fenton Process for Effective Remediation. Processes 2024, 12, 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12040844
Kovačić M, Tomić A, Tonković S, Pulitika A, Papac Zjačić J, Katančić Z, Genorio B, Kušić H, Lončarić Božić A. Pristine and UV-Weathered PET Microplastics as Water Contaminants: Appraising the Potential of the Fenton Process for Effective Remediation. Processes. 2024; 12(4):844. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12040844
Chicago/Turabian StyleKovačić, Marin, Antonija Tomić, Stefani Tonković, Anamarija Pulitika, Josipa Papac Zjačić, Zvonimir Katančić, Boštjan Genorio, Hrvoje Kušić, and Ana Lončarić Božić. 2024. "Pristine and UV-Weathered PET Microplastics as Water Contaminants: Appraising the Potential of the Fenton Process for Effective Remediation" Processes 12, no. 4: 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12040844
APA StyleKovačić, M., Tomić, A., Tonković, S., Pulitika, A., Papac Zjačić, J., Katančić, Z., Genorio, B., Kušić, H., & Lončarić Božić, A. (2024). Pristine and UV-Weathered PET Microplastics as Water Contaminants: Appraising the Potential of the Fenton Process for Effective Remediation. Processes, 12(4), 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12040844










