Study on Heat Transfer Process between High-Temperature Slag Particles and Scrap in Drum Based on DEM Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model Setup
2.1. Physical Model and Parameterization
2.2. Numerical Methods
2.2.1. Modeling of Interparticle Contact
2.2.2. Particle Temperature Update Model
2.2.3. Modeling of Inter-Particle Heat Transfer
2.3. Definition of the Evaluation Function
2.4. Validation of the Model
2.5. Verification of Grid Independence
3. Results and Discussion
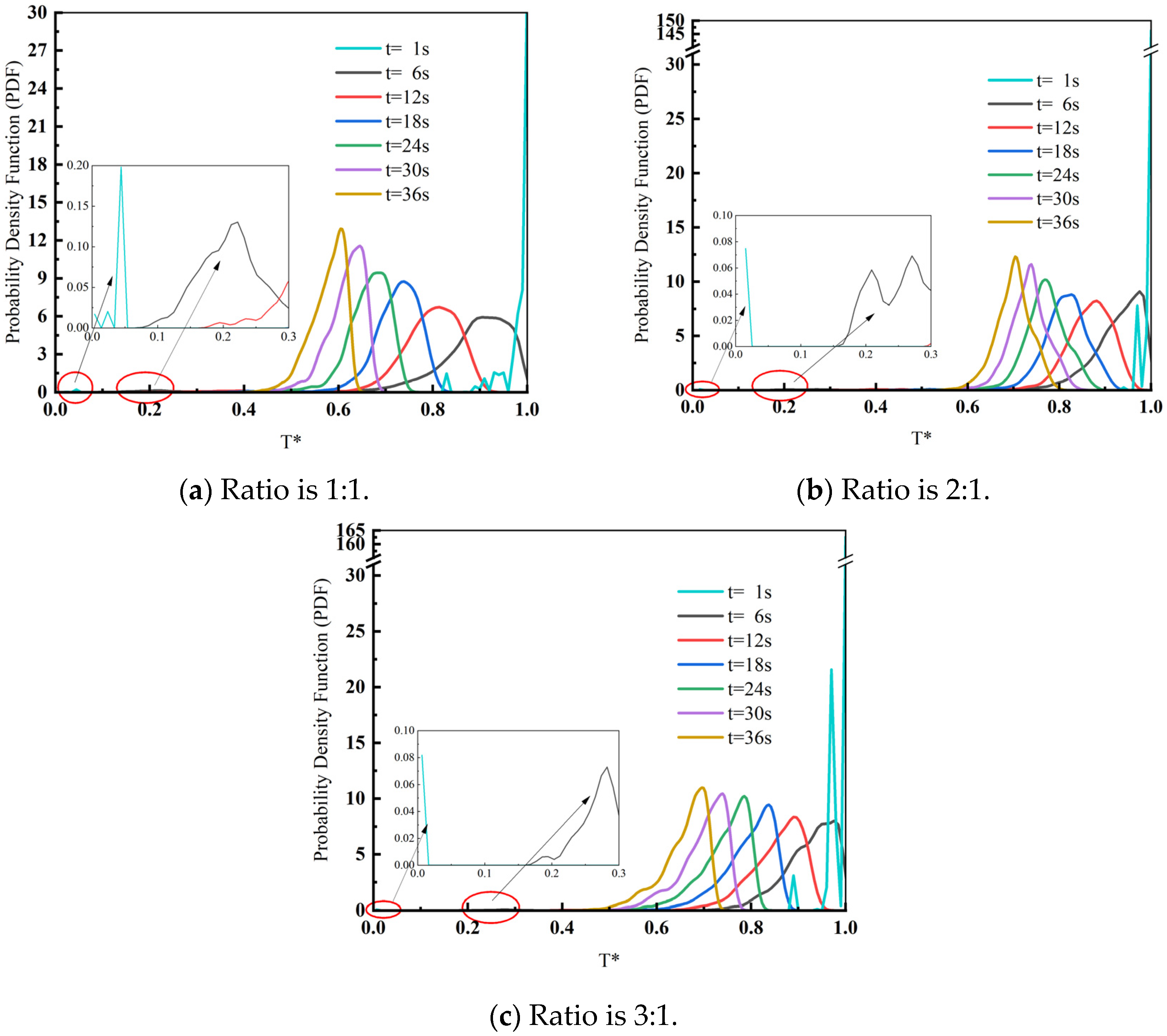
3.1. Influence of Slag–Steel Ratio on Heat Transfer Effect
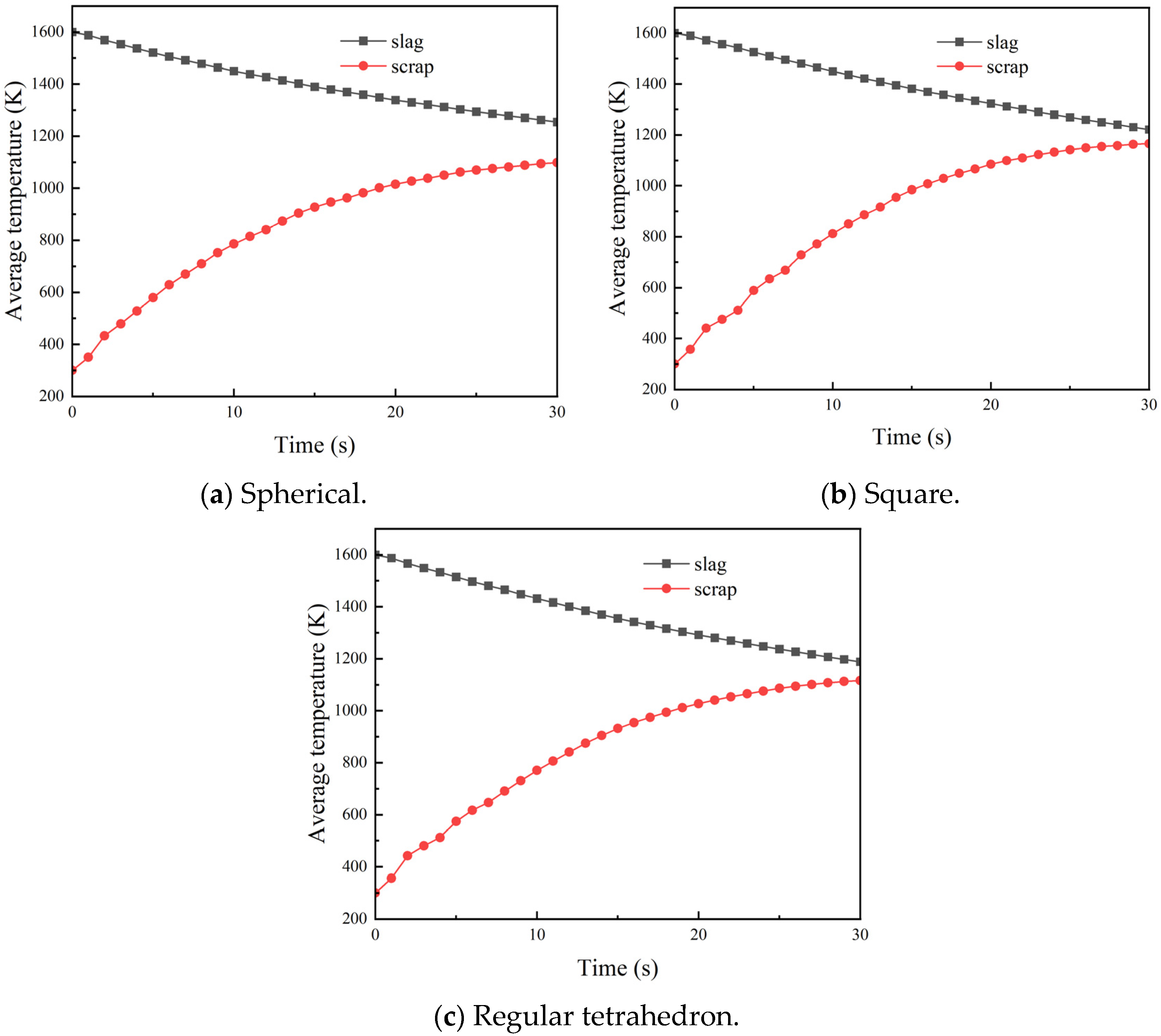
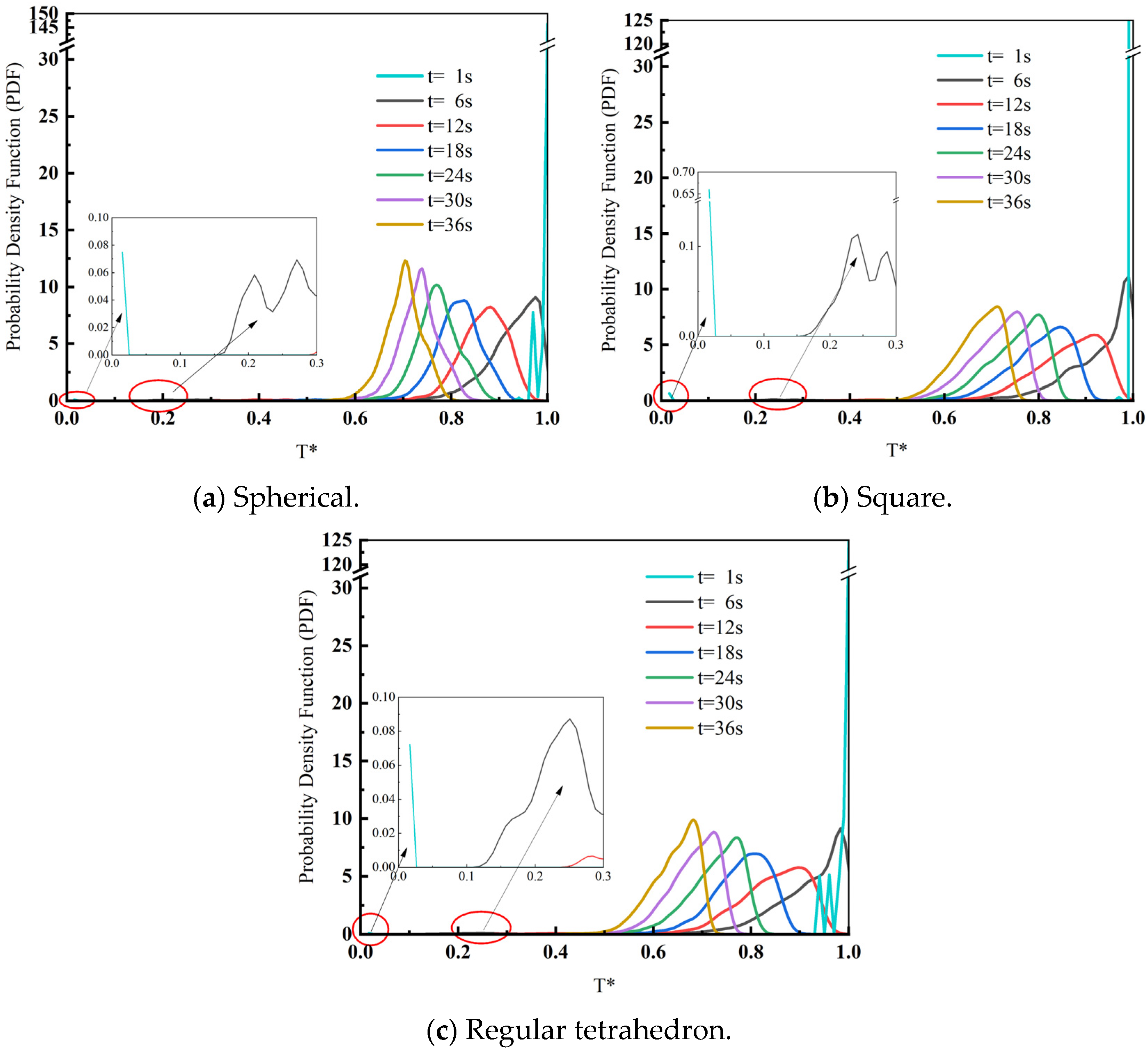
3.2. Effect of Scrap Shape on Heat Transfer Effectiveness
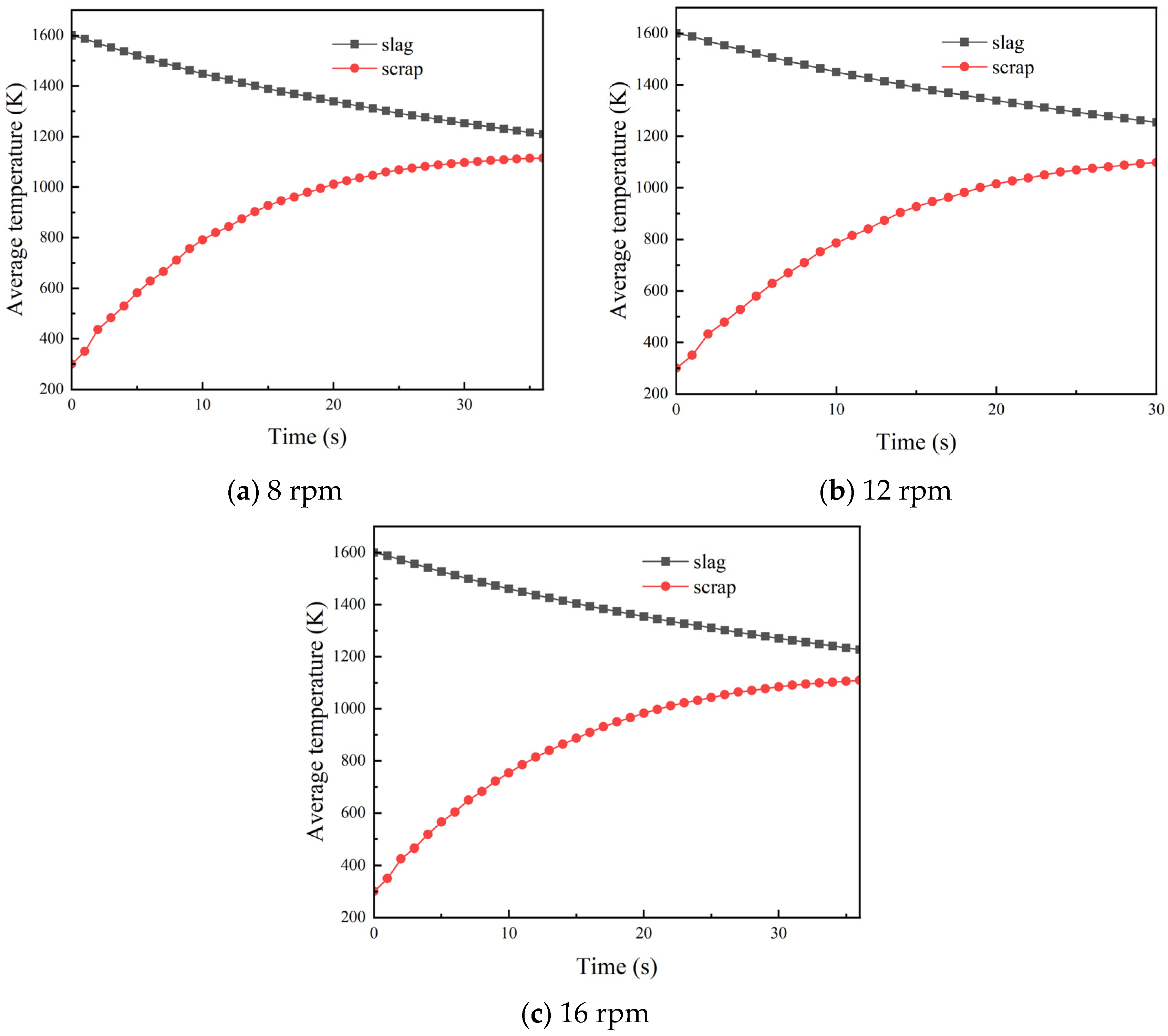
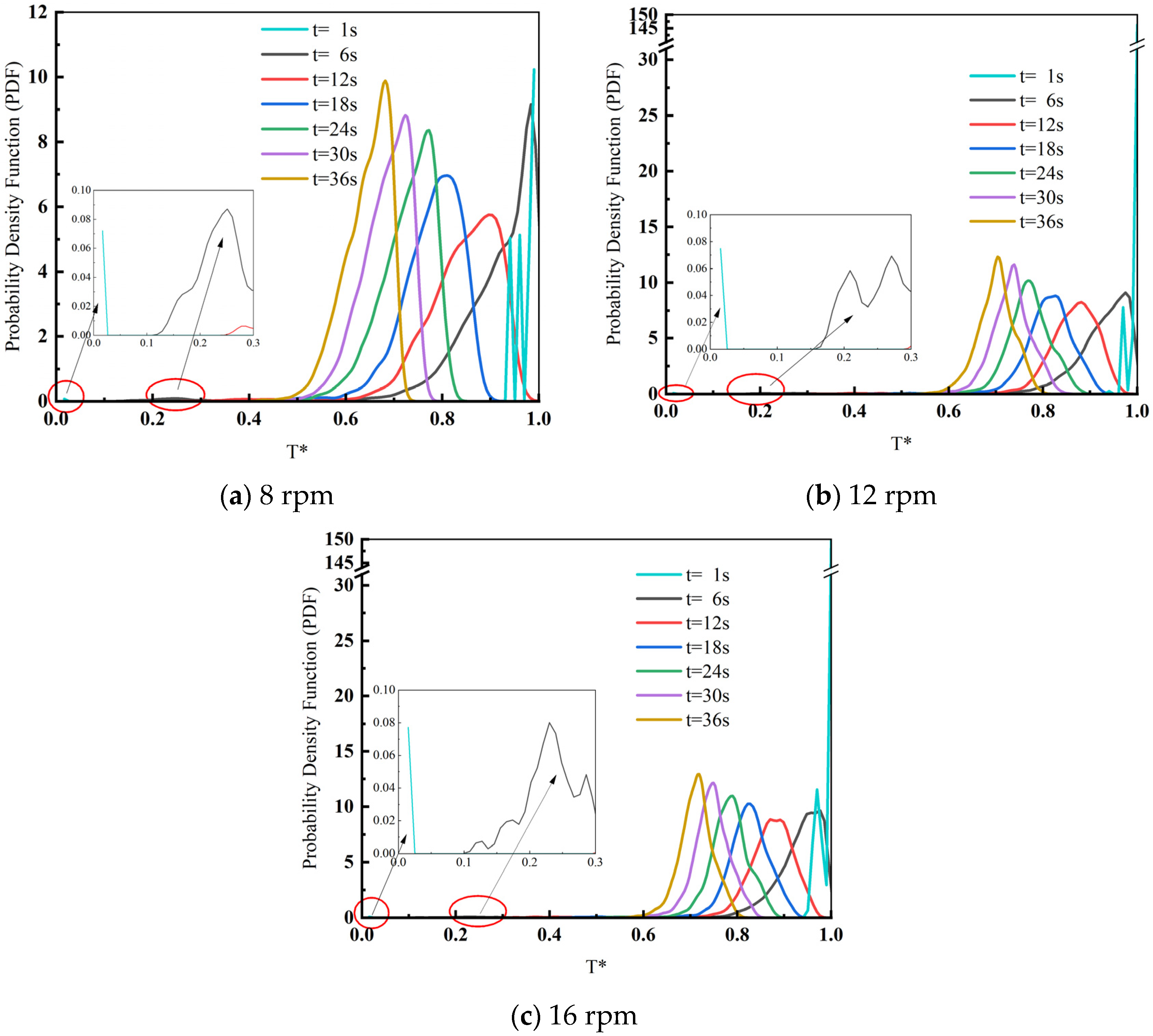
3.3. Influence of Drum Speed on the Heat Transfer Effect
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, K.; Zou, D.; Li, H. Environmental regulation and green technical efficiency: A process-level data envelopment analysis from Chinese iron and steel enterprises. Energy 2023, 277, 127662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inayat, A. Current progress of process integration for waste heat recovery in steel and iron industries. Fuel 2023, 338, 127237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Xing, H.-W.; Wu, J.-H.; Lin, W.-L.; Li, S.; Ding, G.-H.; Zhang, Y.-Z. High-temperature modification and air-quenching granulation of steel slag. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2021, 29, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, S.; Hay, N.; Roylance, T.; Thomas, G. New process for dry granulation and heat recovery from molten blast-furnace slag. Ironmak. Steelmak. 1985, 12, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, D.; Pan, Y.; Flann, R.; Washington, B.; Sanetsis, S.; Donnelley, J.; Norgate, T.; Jahanshahi, S. Heat recovery from slag through dry granulation. In Proceedings of the 1st CSRP Annual Conference, Melbourne, Australia, 5 July 2007; pp. 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, H.; Nara, Y.; Nakatani, G.; Anazi, T.; Sato, H. The technology of slag heat recovery at NKK. In Proceedings of the SEAISI Conference of Energy Utilization in the Iron and Steel Industry, Singapore, 10–13 September 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, J.; Kabasawa, M.; Nagae, M.; Ono, M. Fatigue strength and strain behaviour of spot-welded joints in steels for automobiles. Nippon Kokan Tech. Rep. Overseas 1986, 47, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Rodd, L.; Koehler, T.; Walker, C.; Voermann, N. Economics of slag heat recovery from ferronickel slags. In Proceedings of the Sustainability for Profit. Conference of Metallurgists (COM2010), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3–6 October 2010; pp. 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Arink, T.; Hassan, M.I. Metal scrap preheating using flue gas waste heat. Energy Procedia 2017, 105, 4788–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Sohn, I. Review of innovative energy savings technology for the electric arc furnace. JOM 2014, 66, 1581–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ryan, S.; Silaen, A.K.; Zhou, C.Q. An Investigation into EAF Burner Preheating and Melting Characteristics: CFD Model Development and Experimental Validation. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2023, 54, 1068–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Lee, E.; Noh, D. Development of an oxygen-enhanced combustor for scrap preheating in an electric arc furnace. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 91, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, J.; Varun, V.; Vishwam, V. Waste heat recovery from metal casting and scrap preheating using recovered heat. Procedia Eng. 2014, 97, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Si, X.D.; Lu, J.F.; Wang, W.; Li, J.J. Research on Heat Transfer Model of Cylindrical Slag Cooler. J. Power Eng. 2011, 31, 342–346. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.Z.; Lai, J.A.; Wang, J.; Liao, B.Q.; Peng, T. Axial Diffusion Motion of Particles in Cylindrical Slag Cooler Based on EDEM-FLUENT Coupling. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2022, 22, 1004–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, Y.; Chen, H.P.; Yang, H.P.; Wang, X.H.; Zhang, S.H. One-Dimensional Heat Transfer Simulation of Cylindrical Slag Cooler. J. Power Eng. 2011, 31, 497–501+529. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Gao, J.; Feng, D.; Zhang, X. Modeling of the molten blast furnace slag particle deposition on the wall including phase change and heat transfer. Appl. Energy 2019, 248, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, F.; Chai, H.; Ma, L.; Luo, G.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Z. Simulation of dynamic transport of flexible ribbon particles in a rotary dryer. Powder Technol. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Wet Dry Part. Syst. 2016, 297, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, B.K.; Jensen, R.P. Discrete Element Methods: Numerical Modeling of Discontinua; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Luding, S. Introduction to discrete element methods: Basic of contact force models and how to perform the micro-macro transition to continuum theory. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2008, 12, 785–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cundall, P.A. A computer model for simulating progressive, large-scale movement in blocky rock system. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Rock Mechanics, Nancy, France, 4–6 October 1971; pp. 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Cundall, P.A. Computer simulations of dense sphere assemblies. Stud. Appl. Mech. 1988, 20, 113–123. [Google Scholar]
- Cundall, P.A.; Strack, O.D. A discrete numerical model for granular assemblies. Géotechnique 1979, 29, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruggel-Emden, H.; Wirtz, S.; Simsek, E.; Scherer, V. Modeling of granular flow and combined heat transfer in hoppers by the discrete element method (DEM). J. Press. Vessel. Technol. 2006, 128, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindlin, R.D. Compliance of Elastic Bodies in Contact. J. Appl. Mech. 1949, 16, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, W.L.; McCarthy, J.J. Heat conduction in granular materials. Aiche J. 2001, 47, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, N.; Fan, J. Numerical study of heat conduction of granular particles in rotating wavy drums. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 84, 740–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, R.; Muniandy, S.V.; San Wong, C.; Singh, J. Discrete element method study of shear-driven granular segregation in a slowly rotating horizontal drum. Particuology 2017, 32, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Wen, Z.; Su, F.; Wang, Z.; Lou, G.; Liu, X.; Dou, R. Radial mixing of metallurgical slag particles and steel balls in a horizontally rotating drum: A discussion of particle size distribution and mixing time. Powder Technol. 2020, 378, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herz, F.; Mitov, I.; Specht, E.; Stanev, R. Experimental study of the contact heat transfer coefficient between the covered wall and solid bed in rotary drums. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 82, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafsun, A.; Herz, F.; Specht, E.; Komossa, H.; Wirtz, S.; Scherer, V. Experimental investigation of thermal bed mixing in rotary drums. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics, Skukuza, South Africa, 20–23 July 2015. [Google Scholar]







| Physical Properties | Unit | Slag | Scrap |
|---|---|---|---|
| Densities, ρ | Kg/m3 | 2800 | 7800 |
| Poisson’s ratio, ν | 0.25 | 0.3 | |
| Shear modulus, E | Pa | 1 × 108 | 8 × 1010 |
| Specific heat capacity, Cp | J/(Kg·K) | 1105 | 460 |
| Influencing Factors | Values |
|---|---|
| The ratio of slag to steel | 3:1, 2:1, 1:1 |
| The shape of scrap steel | Spherical, cube, tetrahedral |
| Drum speed | 8 rpm, 12 rpm, 16 rpm |
| Physical Properties | Unit | Quartz Sand | Fiberglass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Densities, ρ | Kg/m3 | 2650 | 1680 |
| Poisson’s ratio, ν | 0.25 | 0.2 | |
| Shear modulus, E | Pa | 5 × 108 | 5 × 1010 |
| Specific heat capacity, Cp | J/(Kg·K) | 1080 | 800 |
| Mesh Size | 0.1 R | 1 R | 2.5 R | 5 R | 10 R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average temperature of scrap/K | 990 | 995 | 998 | 950 | 1056 |
| deviation | — | 0.51 | 0.82 | 4.04 | 6.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, G.; Su, F.; Zhao, Q.; Li, C.; Li, B. Study on Heat Transfer Process between High-Temperature Slag Particles and Scrap in Drum Based on DEM Method. Processes 2024, 12, 815. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12040815
Fan G, Su F, Zhao Q, Li C, Li B. Study on Heat Transfer Process between High-Temperature Slag Particles and Scrap in Drum Based on DEM Method. Processes. 2024; 12(4):815. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12040815
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Guangyan, Fuyong Su, Qianlong Zhao, Cunwang Li, and Bin Li. 2024. "Study on Heat Transfer Process between High-Temperature Slag Particles and Scrap in Drum Based on DEM Method" Processes 12, no. 4: 815. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12040815
APA StyleFan, G., Su, F., Zhao, Q., Li, C., & Li, B. (2024). Study on Heat Transfer Process between High-Temperature Slag Particles and Scrap in Drum Based on DEM Method. Processes, 12(4), 815. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12040815






