Structure Investigation of Polysaccharides Extracted from Spent Coffee Grounds Using an Eco-Friendly Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Soxhlet Extraction
2.3. Recovery and Determination of Total Phenolic Content
2.4. Polysaccharides Extraction
2.5. Sugars and Nitrogen Content Analysis of SCG
2.6. Size Exclusion Chromatography of Polysaccharide Extract
2.7. Purification of Polysaccharide Extract in Gel Chromatography
2.8. FTIR Spectroscopy of Polysaccharide Fraction
2.9. NMR Spectroscopy of Polysaccharide Fraction
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Total Fat Content of SCG
3.2. Total Phenolic Content of SCG
3.3. Polysaccharides Content of SCG
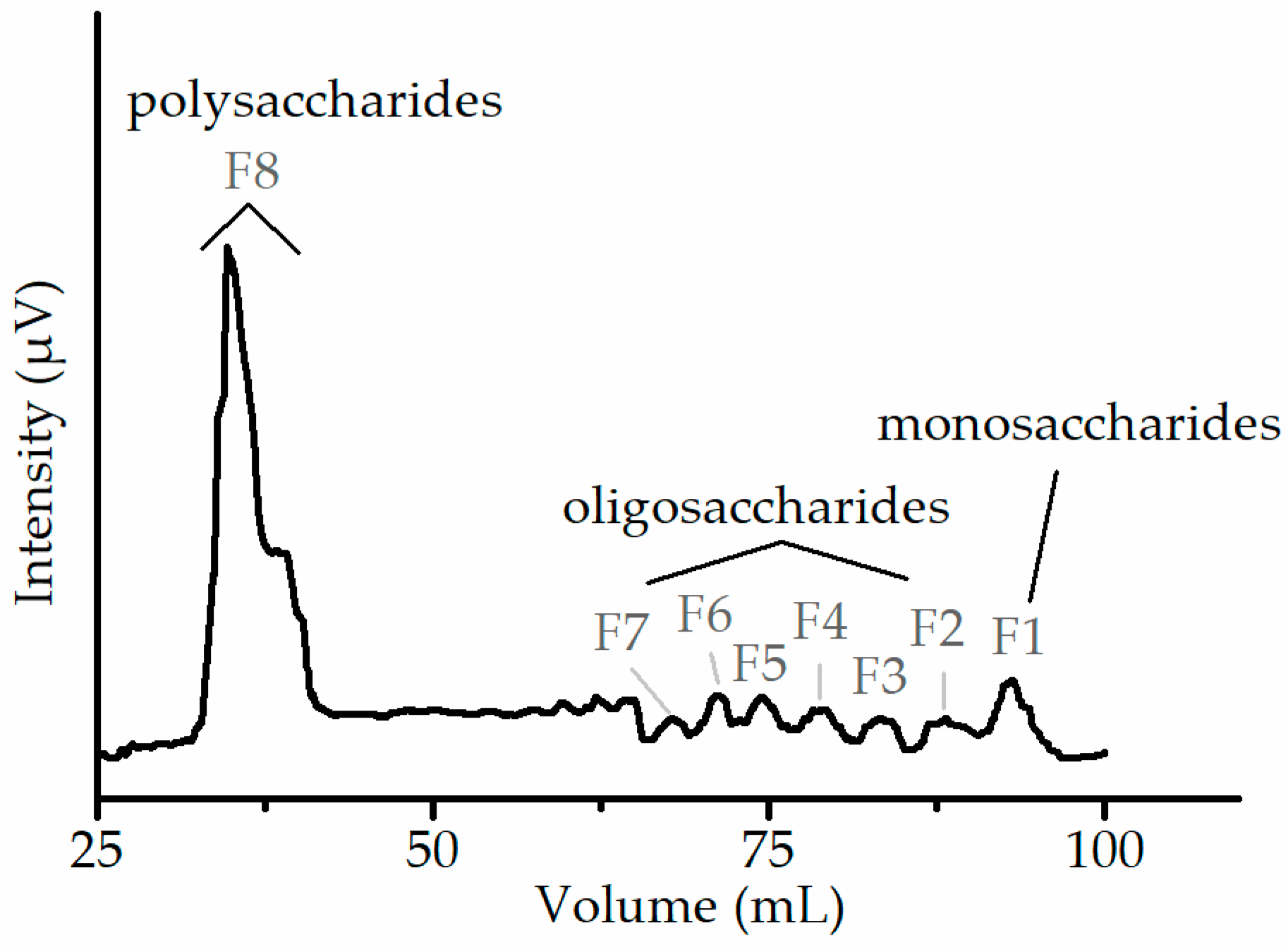
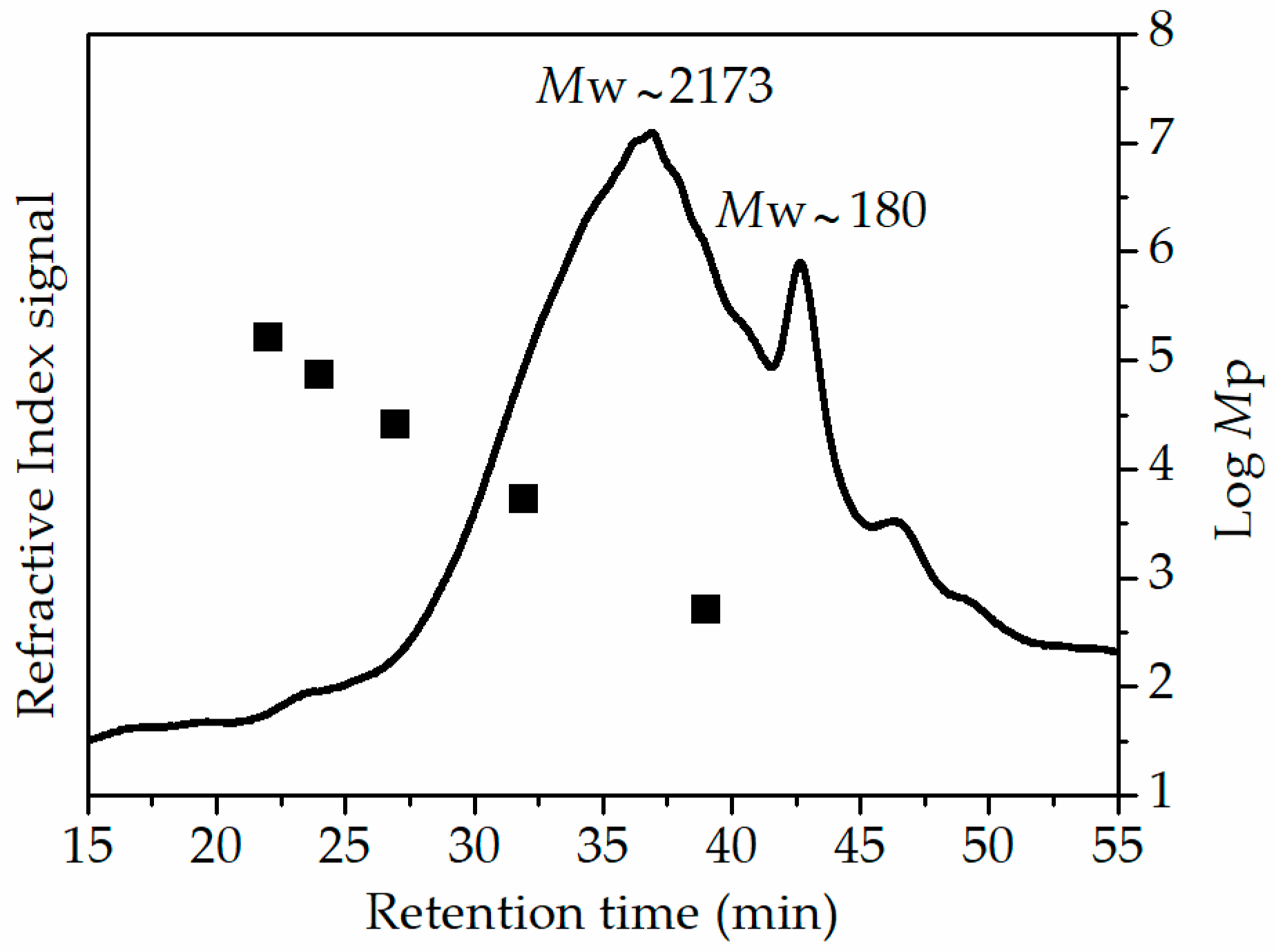
3.4. Purification of Polysaccharide Extract
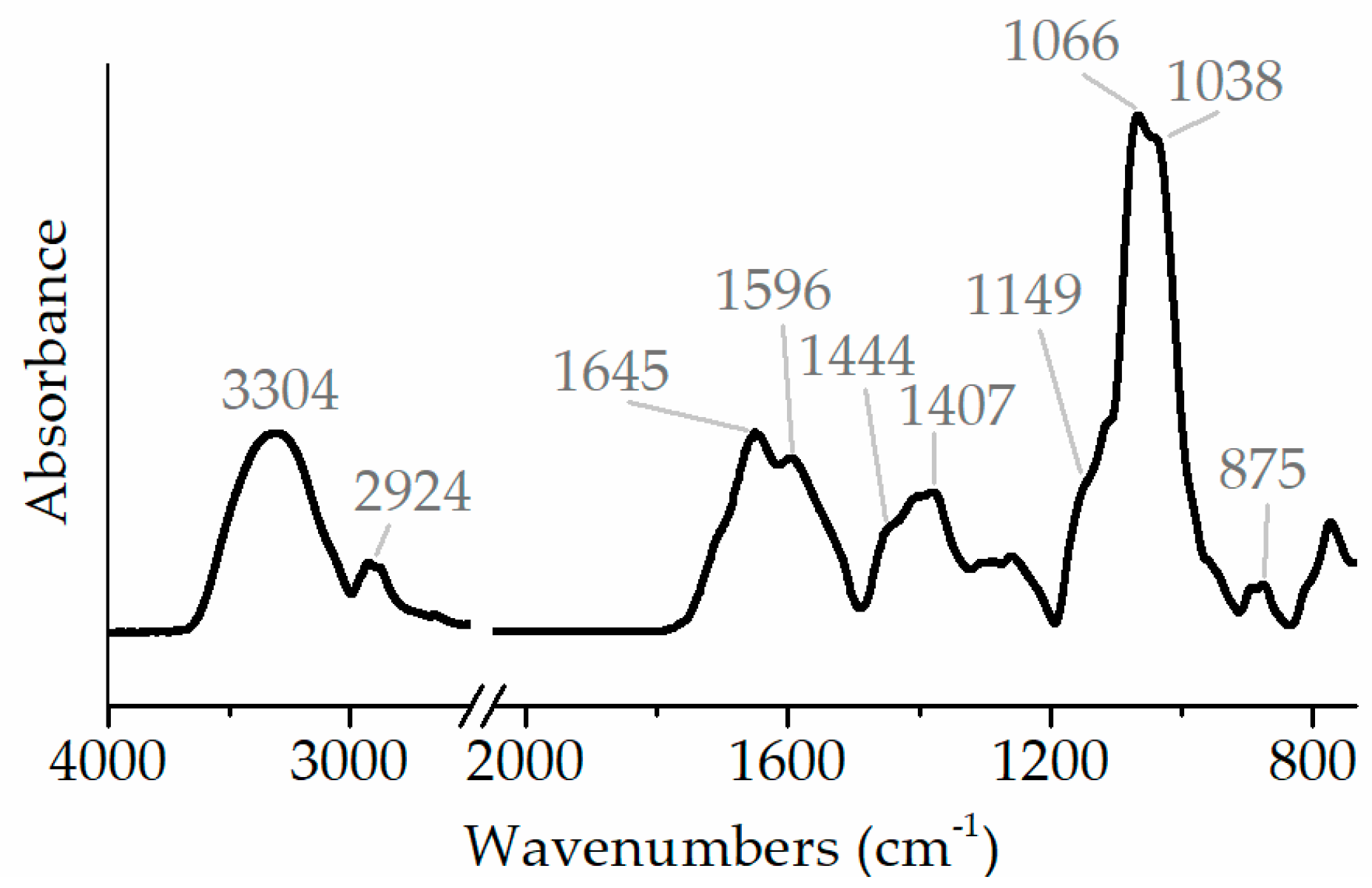
3.5. FTIR Spectroscopy of Polysaccharide Fraction
3.6. NMR Spectroscopy of Polysaccharide Fraction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campos-Vega, R.; Loarca-Piña, G.; Vergara-Castañeda, H.A.; Oomah, B.D. Spent Coffee Grounds: A Review on Current Research and Future Prospects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalcik, A.; Obruca, S.; Marova, I. Valorization of Spent Coffee Grounds: A Review. Food Bioprod. Process. 2018, 110, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janissen, B.; Huynh, T. Chemical Composition and Value-Adding Applications of Coffee Industry by-Products: A Review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 128, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Saez, N.; García, A.T.; Pérez, I.D.; Rebollo-Hernanz, M.; Mesías, M.; Morales, F.J.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A.; Del Castillo, M.D. Use of Spent Coffee Grounds as Food Ingredient in Bakery Products. Food Chem. 2017, 216, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, P.S.; Madhava Naidu, M. Sustainable Management of Coffee Industry By-Products and Value Addition—A Review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 66, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, G.; Passos, C.P.; Ferreira, P.; Coimbra, M.A.; Gonçalves, I. Coffee By-Products and Their Suitability for Developing Active Food Packaging Materials. Foods 2021, 10, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussatto, S.I.; Carneiro, L.M.; Silva, J.P.A.; Roberto, I.C.; Teixeira, J.A. A Study on Chemical Constituents and Sugars Extraction from Spent Coffee Grounds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, L.F.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Teixeira, J.A.; Mussatto, S.I. Characterization of Polysaccharides Extracted from Spent Coffee Grounds by Alkali Pretreatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 127, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getachew, A.T.; Chun, B.S. Influence of Pretreatment and Modifiers on Subcritical Water Liquefaction of Spent Coffee Grounds: A Green Waste Valorization Approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 3719–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, C.P.; Coimbra, M.A. Microwave Superheated Water Extraction of Polysaccharides from Spent Coffee Grounds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, C.P.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Neves, J.M.M.G.C.; Lopes, G.R.; Evtuguin, D.V.; Coimbra, M.A. Structural Features of Spent Coffee Grounds Water-Soluble Polysaccharides: Towards Tailor-Made Microwave Assisted Extractions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 214, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getachew, A.T.; Cho, Y.J.; Chun, B.S. Effect of Pretreatments on Isolation of Bioactive Polysaccharides from Spent Coffee Grounds Using Subcritical Water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Pei, W.; Tang, S.; Yan, F.; Peng, Z.; Huang, C.; Yang, J.; Yong, Q. Procuring Biologically Active Galactomannans from Spent Coffee Ground (SCG) by Autohydrolysis and Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarghini, F.; Marra, F.; De Vivo, A.; Vitaglione, P.; Mauriello, G.; Maresca, D.; Troise, A.D.; Echeverria-Jaramillo, E. Acid Hydrolysis of Spent Coffee Grounds: Effects on Possible Prebiotic Activity of Oligosaccharides. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2021, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redgwell, R.J.; Curti, D.; Fischer, M.; Nicolas, P.; Fay, L.B. Coffee Bean Arabinogalactans: Acidic Polymers Covalently Linked to Protein. Carbohydr. Res. 2002, 337, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, F.M.; Reis, A.; Silva, A.M.S.; Domingues, M.R.M.; Coimbra, M.A. Rhamnoarabinosyl and Rhamnoarabinoarabinosyl Side Chains as Structural Features of Coffee Arabinogalactans. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 1573–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussatto, S.I.; Ballesteros, L.F.; Martins, S.; Teixeira, J.A. Extraction of Antioxidant Phenolic Compounds from Spent Coffee Grounds. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 83, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnous, A.; Makris, D.P.; Kefalas, P. Correlation of Pigment and Flavanol Content with Antioxidant Properties in Selected Aged Regional Wines from Greece. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2002, 15, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, C.P.; Moreira, A.S.P.; Domingues, M.R.M.; Evtuguin, D.V.; Coimbra, M.A. Sequential Microwave Superheated Water Extraction of Mannans from Spent Coffee Grounds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric Method for Determination of Sugars and Related Substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.L. Use of Dinitrosalicylic Acid Reagent for Determination of reducing Sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capek, L.; Uhliariková, I.; Košťálová, Z.; Hindáková, A.; Capek, P. Structural Properties of the Extracellular Biopolymer (β-D-Xylo-α-D-Mannan) Produced by the Green Microalga Gloeocystis vesiculosa Nägeli. Carbohydr. Res. 2023, 525, 108766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, F.; Tomé, D.; Mirand, P.P. Converting Nitrogen into Protein—Beyond 6.25 and Jones’ Factors. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loyao, A.S.; Villasica, S.L.G.; Dela Peña, P.L.L.; Go, A.W. Extraction of Lipids from Spent Coffee Grounds with Non-Polar Renewable Solvents as Alternative. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 119, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battista, F.; Zanzoni, S.; Strazzera, G.; Andreolli, M.; Bolzonella, D. The Cascade Biorefinery Approach for the Valorization of the Spent Coffee Grounds. Renew. Energy 2020, 157, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuorro, A.; Lavecchia, R. Spent Coffee Grounds as a Valuable Source of Phenolic Compounds and Bioenergy. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 34, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budryn, G.; Nebesny, E.; Podsędek, A.; Żyżelewicz, D.; Materska, M.; Jankowski, S.; Janda, B. Effect of Different Extraction Methods on the Recovery of Chlorogenic Acids, Caffeine and Maillard Reaction Products in Coffee Beans. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 228, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Petkowicz, C.L.D. Polysaccharides in Coffee and Their Relationship to Health. In Coffee in Health and Disease Prevention; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 163–172. ISBN 978-0-12-409517-5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.-L.; Wei, Y.-S.; Lin, S.-Y. Subtractive similarity method used to study the infrared spectra of proteins in aqueous solution. Vib. Spectrosc. 2003, 31, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Renard, C.M.G.C.; Bureau, S.; Le Bourvellec, C. Revisiting the contribution of ATR-FTIR spectroscopy to characterize plant cell wall polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 262, 117935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogales-Bueno, J.; Baca-Bocanegra, B.; Rooney, A.; Hernández-Hierro, J.M.; Byrne, H.J.; Heredia, F.J. Study of phenolic extractability in grape seeds by means of ATR-FTIR and Raman spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripper, B.; Kaiser, C.R.; Perrone, D. Use of NMR Techniques to Investigate the Changes on the Chemical Composition of Coffee Melanoidins. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 87, 103399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, P.B.S.; Barros, W.; Santos, G.R.C.; Correia, M.T.S.; Mourão, P.A.S.; Teixeira, J.A.; Carneiro-da-Cunha, M.G. Characterization and Rheological Study of the Galactomannan Extracted from Seeds of Cassia grandis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 104, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muschin, T.; Yoshida, T. Structural Analysis of Galactomannans by NMR Spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 1893–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capek, P.; Matulová, M.; Navarini, L.; Suggi-Liverani, F. Structural Features of an Arabinogalactan-Protein Isolated from Instant Coffee Powder of Coffea arabica Beans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 80, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redgwell, R.J.; Trovato, V.; Curti, D.; Fischer, M. Effect of Roasting on Degradation and Structural Features of Polysaccharides in Arabica Coffee Beans. Carbohydr. Res. 2002, 337, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
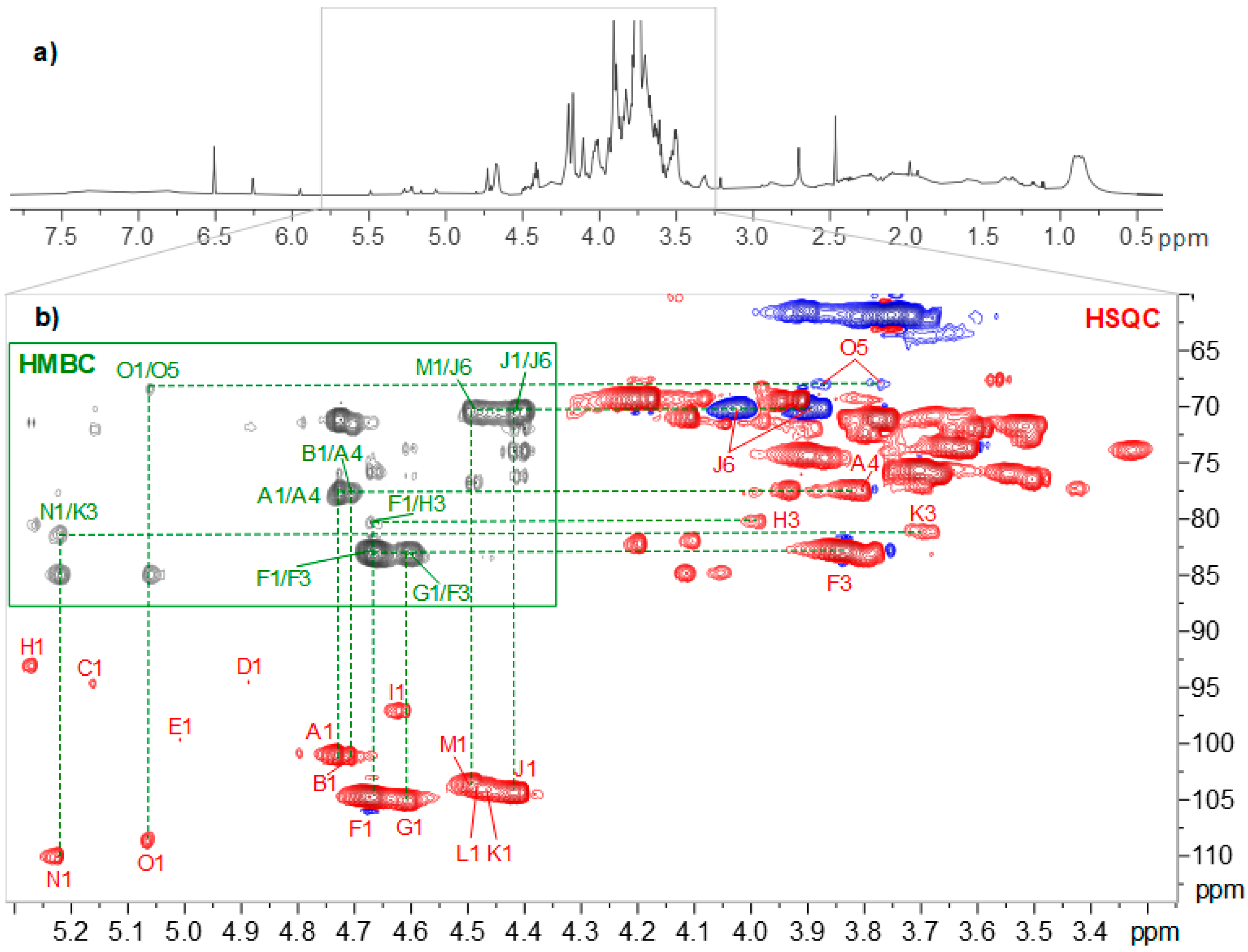
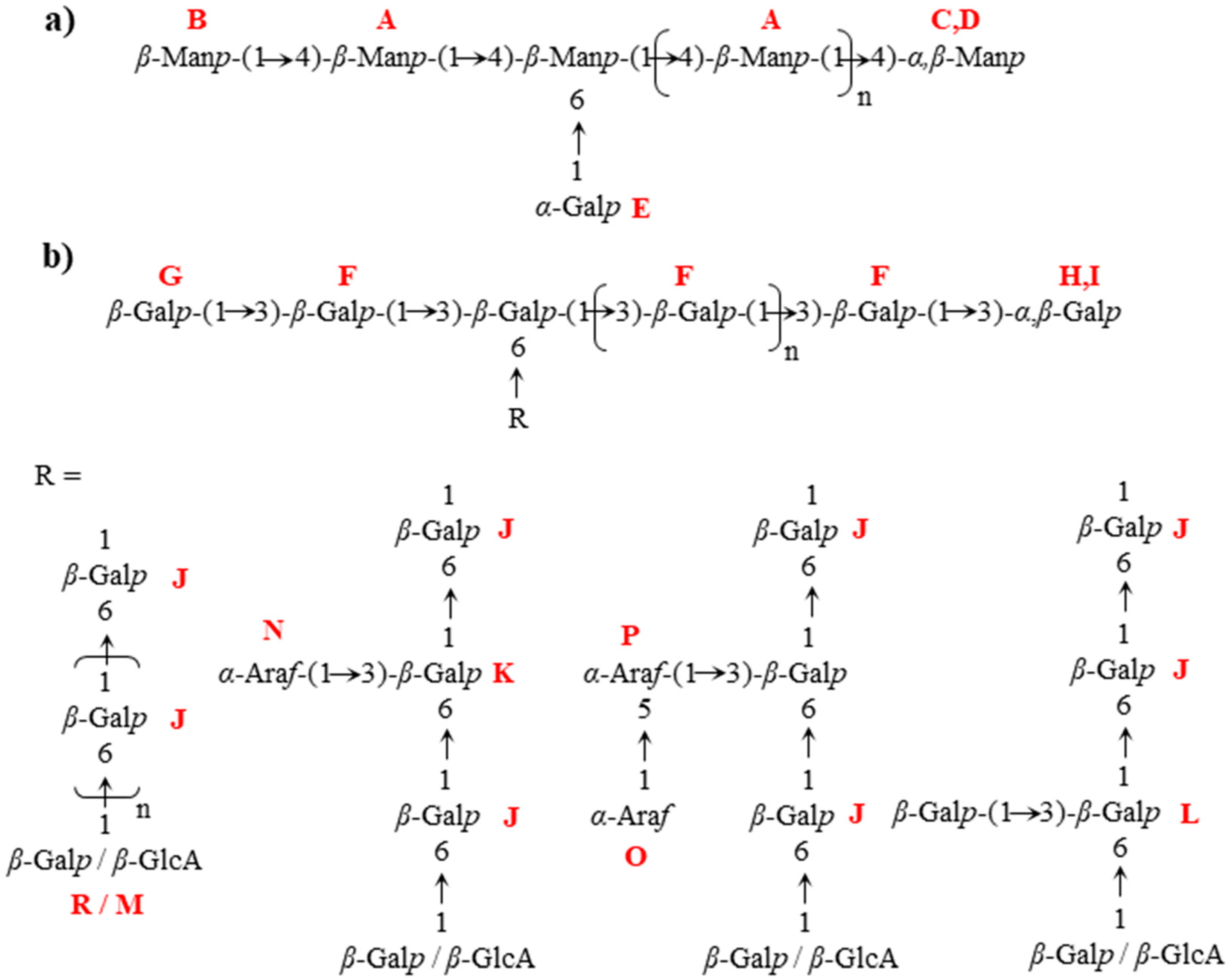
| Chemical Shifts (ppm) | Interconnectivity H and C (ppm) from HMBC | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | Residue | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| A | → 4)-β-D-Manp-(1 → | 4.73 101.0 | 4.10 70.8 | 3.7972.3 | 3.8177.3 | 3.5475.8 | 61.5 | AH1/AC4, BH1/AC4 |
| B | β-D-Manp-(1 → | 4.71 101.0 | 4.04 71.3 | 3.6373.7 | 3.5667.6 | 3.4177.3 | 61.9 | BH1/AC4 |
| C | → 4)-α-D-Manp | 5.16 94.7 | 3.97 71.2 | |||||
| D | → 4)-β-D-Manp | 4.88 94.5 | 71.5 | |||||
| E | α-D-Galp-(1 → | 5.00 99.7 | ||||||
| F | → 3)-β-D-Galp-(1 → | 4.67 104.8 | 3.78 71.1 | 3.8482.8 | 4.2069.3 | 3.7075.6 | 61.7 | FH1/FC3, FH1/HC3, GH1/FC3, IH1/FC3 |
| G | β-D-Galp-(1 → 3 | 4.61 105.1 | 3.59 71.9 | 3.6773.5 | 3.9169.4 | 3.6576.0 | GH1/FC3 | |
| H | → 3)-α-D-Galp | 5.27 93.0 | 3.98 68.2 | 3.9880.2 | 4.2370.0 | FH1/HC3 | ||
| I | → 6)-β-D-Galp | 4.62 97.1 | 83.2 | 4.1769.3 | IH1/FC3 | |||
| J | → 6)-β-D-Galp-(1 → | 4.41 104.4 | 3.52 71.7 | 3.6273.7 | 3.9469.5 | 3.8974.3 | 3.89–4.0370.1 | JH1/JC6, MH1/JC6 |
| K | → 3, 6)-β-D-Galp-(1 → subs. α-Araf-(1 → | 4.47 104.1 | 3.6981.1 | NH1/KC3 | ||||
| L | → 3, 6)-β-D-Galp-(1 → subs. β-D-Galp-(1 → | 4.48 103.7 | 3.7883.0 | |||||
| M | β-D-GlcAp-(1 → | 4.50 103.6 | 3.33 73.8 | 3.5076.4 | 3.5172.7 | 3.6976.6 | MH1/JC6 | |
| N | α-L-Araf-(1 → | 5.22 110.0 | 4.19 82.2 | 3.9377.5 | 4.1184.78 | 62.1 | NH1/KC3 | |
| O | α-L-Araf-(1 → 5 | 5.06 108.7 | 4.10 81.9 | 3.9377.4 | 4.0584.8 | 62.1 | OH1/PC5 | |
| P | → 5)-α-L-Araf-(1 → | 5.04 108.7 | 3.76–3.8768.1 | OH1/PC5 | ||||
| R | β-D-Galp-(1 → 6 | 4.42 104.4 | 75.9 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Košťálová, Z.; Manavaki, M.; Christaki, S.; Papadakis, E.-N.; Mourtzinos, I. Structure Investigation of Polysaccharides Extracted from Spent Coffee Grounds Using an Eco-Friendly Technique. Processes 2024, 12, 2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122869
Košťálová Z, Manavaki M, Christaki S, Papadakis E-N, Mourtzinos I. Structure Investigation of Polysaccharides Extracted from Spent Coffee Grounds Using an Eco-Friendly Technique. Processes. 2024; 12(12):2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122869
Chicago/Turabian StyleKošťálová, Zuzana, Malamatenia Manavaki, Stamatia Christaki, Emmanouil-Nikolaos Papadakis, and Ioannis Mourtzinos. 2024. "Structure Investigation of Polysaccharides Extracted from Spent Coffee Grounds Using an Eco-Friendly Technique" Processes 12, no. 12: 2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122869
APA StyleKošťálová, Z., Manavaki, M., Christaki, S., Papadakis, E.-N., & Mourtzinos, I. (2024). Structure Investigation of Polysaccharides Extracted from Spent Coffee Grounds Using an Eco-Friendly Technique. Processes, 12(12), 2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122869







