Experimental Investigation of Cr12 Steel Under Electrostatic Minimum Quantity Lubrication During Grinding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbosa, E.L.; Brandão, L.C. The use of alternative coolant techniques to reduce the environmental impact in the use of water in through-feed centreless grinding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 91, 3417–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, S.; Kumar, S.; Roy, D.; Chakroborty, S.; Das, S. Improvement of lubrication and cooling in grinding. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2017, 33, 1459–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, M.; Dong, G. Experimental investigation on rotary ultrasonic face grinding of Sicp/Al composites. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2016, 31, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitseva, V.; Hanke, S.; Dos Santos, J.F. Influence of rotational speed on process characteristics in friction surfacing of Ti-6Al-4V. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2017, 32, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zou, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Duan, L. Investigation on diamond tool wear in ultrasonic vibration-assisted turning die steels. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2017, 32, 1505–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.L.; Xu, X. Evaluation and comparison of lubrication methods in finish machining of hardened steel mould inserts. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2017, 231, 2458–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, D.; Zhang, X.; Hou, Y.; Shen, B.; Li, R. Microscale bone grinding temperature by dynamic heat flux in nanoparticle jet mist cooling with different particle sizes. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2017, 33, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Jia, D.; Zhang, X.; Guo, S.; Li, R.; Zhai, H. Process parameter optimization and experimental evaluation for nanofluid MQL in grinding Ti-6Al-4V based on grey relational analysis. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2017, 33, 950–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.P.; Arunachalam, N.; Vijayaraghavan, L. Study on grinding of pre-sintered zirconia using diamond wheel. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2017, 33, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, M. Effect of cryogenic minimum quantity lubrication on machinability of diamond tool in ultraprecision turning 3Cr2NiMo steel. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2017, 33, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetan; Ghosh, S.; Rao, P.V. Environment Friendly Machining of Ni–Cr–Co Based Super Alloy Using Different Sustainable Techniques. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2016, 31, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveena, B.; Thaslima, S.M.; Savitha, V.; Naveen Krishna, B.; Raj, D.S.; Karunamoorthy, L. Simplified MQL System for Drilling AISI 304 SS Using Cryogenically Treated Drills. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2017, 32, 1679–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, M.K.; Madarkar, R.; Ghosh, S.; Rao, P.V. Application of eco-friendly nanofluids during grinding of inconel 718 through small quantity lubrication. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 141, 1359–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Li, B.; Jia, D. Experimental evaluation of the lubrication properties of the wheel/workpiece interface in minimum quantity lubrication (mql) grinding using different types of vegetable oils. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 127, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madarkar, R.; Agarwal, S.; Attar, P. Application of ultrasonic vibration assisted MQL in grinding of Ti–6Al–4V. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2017, 33, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dureja, J.S.; Singh, R.; Singh, T. Performance evaluation of coated carbide tool in machining of stainless steel (AISI 202) under minimum quantity lubrication (MQL). Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2015, 2, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ren, Y.; Li, T. Influence of minimum quantity lubrication parameters on grind-hardening process. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2017, 33, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, N.; Sharma, A. Development of a friction model and its application in finite element analysis of minimum quantity lubrication machining of Ti-6Al-4V. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 238, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiei, F.; Rahimi, A.R.; Hadad, M.J.; Ashrafijou, M. Performance improvement of minimum quantity lubrication (mql) technique in surface grinding by modeling and optimization. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 86, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, D.A.; Skerlos, S.J.; King, A.S.; Supekar, S.D. Rough turning inconel 750 with supercritical CO2-based minimum quantity lubrication. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2014, 214, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadad, M.J.; Tawakoli, T.; Sadeghi, M.H.; Sadeghi, B. Temperature and energy partition in minimum quantity lubrication-mql grinding process. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2012, 54–55, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.D.J.; Guermandi, L.G.; Bianchi, E.C.; Diniz, A.E.; Aguiar, P.R.D.; Canarim, R.C. Improving minimum quantity lubrication in CBN grinding using compressed air wheel cleaning. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 2559–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.H.; Haddad, M.J.; Tawakoli, T.; Emami, M. Minimal quantity lubrication-mql in grinding of Ti–6Al–4V titanium alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2009, 44, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Huang, S.; Wang, M.; Yao, W. A study on process parameters in end milling of AiSi-304 stainless steel under electrostatic minimum quantity lubrication conditions. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 90, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.F.; Wang, J.; Zheng, M.; Yu, P.; Zhang, H. A research on electroplastic effects in wire-drawing process of an austenitic stainless steel. Scr. Mater. 2001, 45, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Tang, G. The improved plasticity of niti alloy via electropulsing in rolling. Met. Sci. J. 2016, 33, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Chu, X.; Lin, S.; Gao, J. Experimental investigation on formability and microstructure of AZ31B alloy in electropulse-assisted incremental forming. Mater. Des. 2015, 87, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolovich, S.D.; Conrad, H. The effects of electric currents and fields on deformation in metals, ceramics, and ionic materials: An interpretive survey. Adv. Manuf. Process. 2004, 19, 587–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Li, S.; Li, J. Study on the crystallographic orientation relationship and formation mechanism of reversed austenite in economical Cr12 super martensitic stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 2015, 109, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, M.E.; Chee, H.C.; Prasada, R.A.K. Surface hardenability studies of the die steel machined by WEDM. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2018, 33, 1745–1750. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, L.; Tang, G.; Chu, P.K. Recent advances and challenges in electroplastic manufacturing processing of metals. J. Mater. Res. 2010, 25, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontsevoi, O.Y.; Gornostyrev, Y.N.; Freeman, A.J.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Trefilov, A.V. Electronic mechanism of impurity-dislocation interactions in intermetallics: Nial. Philos. Mag. Lett. 2001, 81, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.X.; Sun, W.W.; Styles, M.J.; Arlazarov, A.; Hutchinson, C.R. Cementite coarsening during the tempering of Fe-C-Mn martensite. Acta Mater. 2018, 159, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.C.; Fang, F.; Wang, L.P.; Hu, X.J.; Xie, Z.H.; Jiang, J.Q. Torsion performance of pearlitic steel wires: Effects of morphology and crystallinity of cementite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 743, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwajka, K.; Zielińska-Szwajka, J.; Trzepieciński, T. Improving the Surface Integrity of 316L Steel in the Context of Bioimplant Applications. Materials 2023, 16, 3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Ji, H.; Yang, X.; Yang, M.; Jia, D. Analysis of grinding mechanics and improved predictive force model based on material-removal and plastic-stacking mechanisms. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2017, 122, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, Z.; Yao, W.; Xu, X. Tribological evaluation of contact-charged electrostatic spray lubrication as a new near-dry machining technique. Tribol. Int. 2015, 91, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
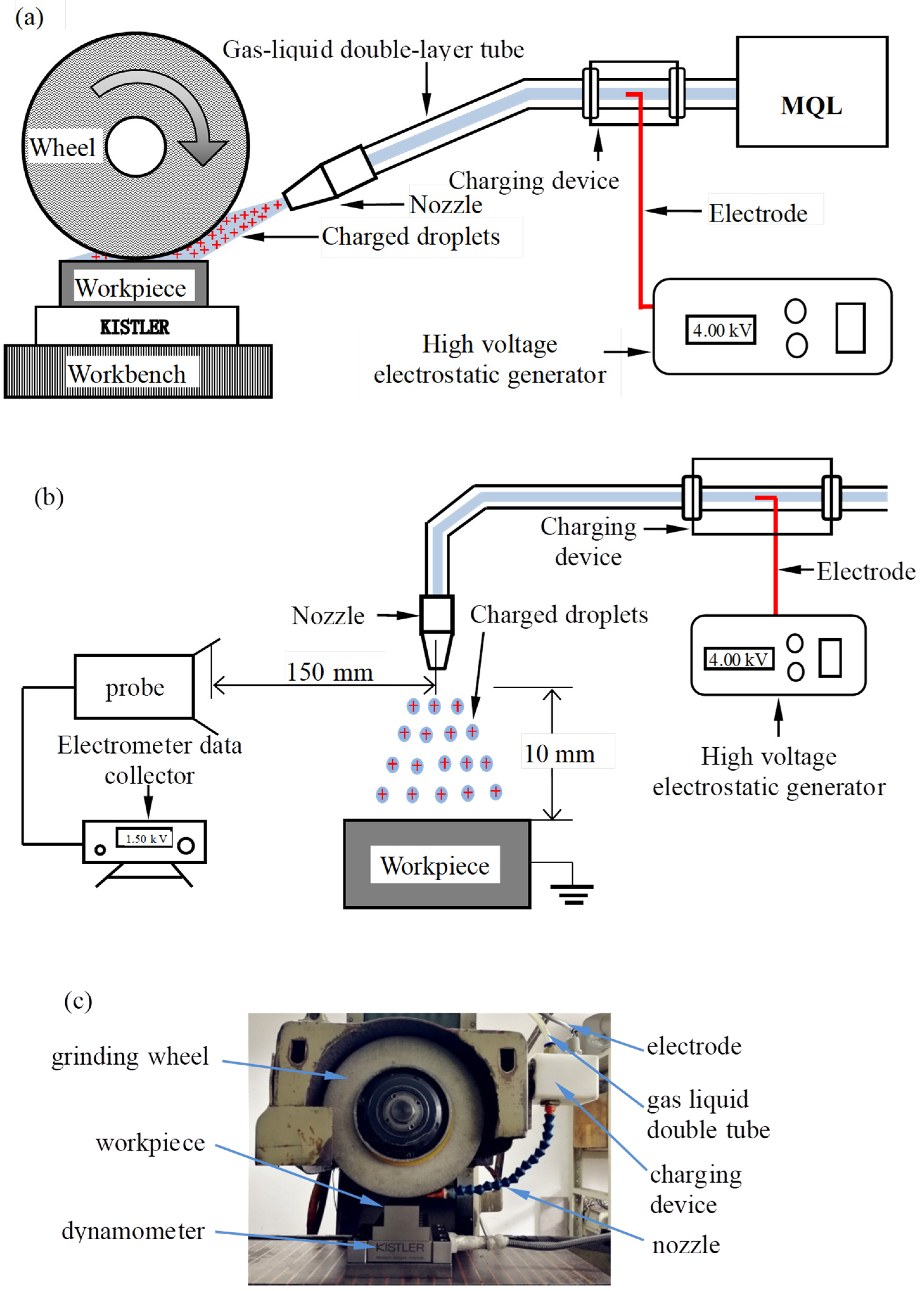
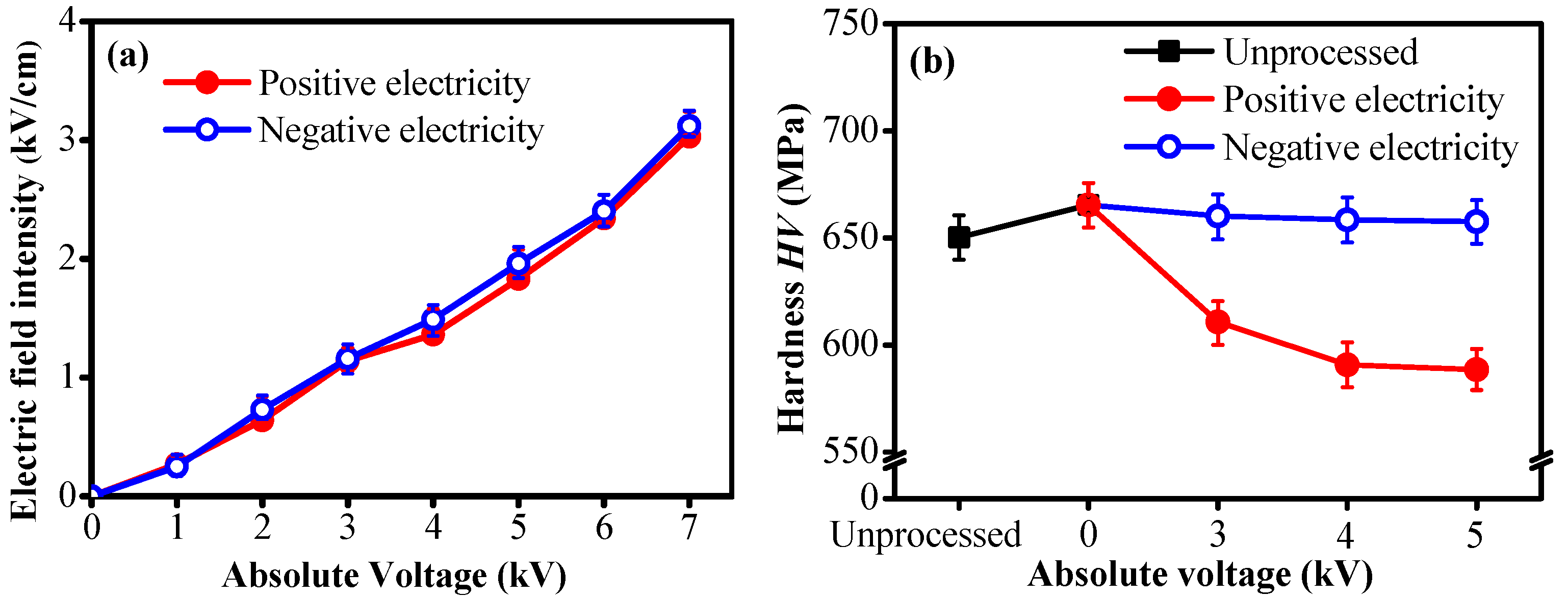


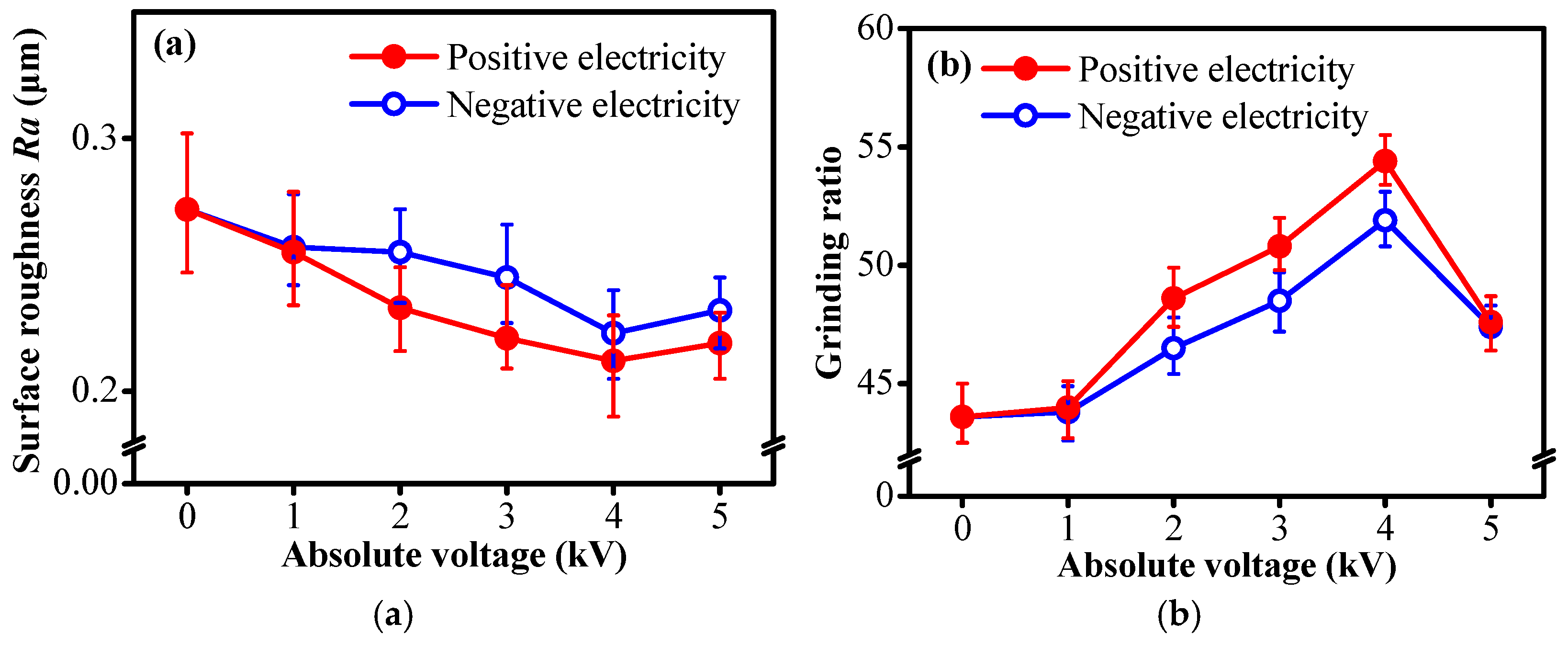
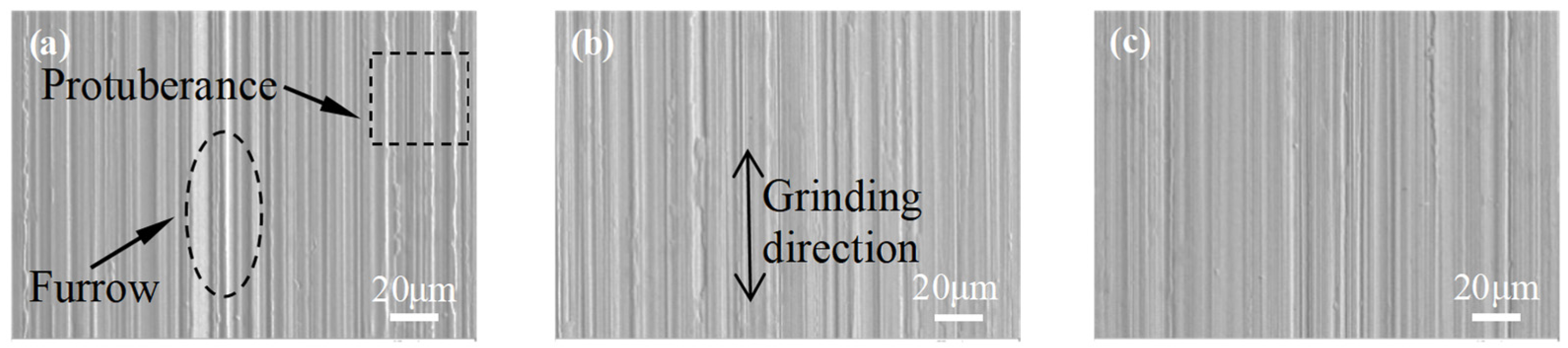
| Experimental Contents | Experimental Conditions |
|---|---|
| Grinding machine | MM7120A type plane grinder |
| Grinding wheel | Corundum grinding wheel: grain size. 60#; maximum linear speed. 35 m/s; size: 250 mm × 16 mm × 75 mm |
| Grinding parameters | The linear speed of the grinding wheel was 20 m/s; the workpiece speed was 150 mm/s; the grinding depth was 10 μm; and the total grindingdepth was 100 μm |
| Workpiece material | Cr12 die steel; workpiece size: 65 mm × 55 mm × 48 mm |
| Lubricating fluid | Calteche SYN 40 total synthetic liquid: water = 1:9 (mass ratio) |
| Charging voltages | 0 kV. ±1 kV. ±2 kV. ±3 kV. ±4 kV. ±5 kV |
| Air pressure | 0.4 MPa |
| Flow rate | 50 mL/h |
| Dressing condition | Using a single point diamond trimmer; the dressing depth was 100 μm; the dressing speed was 20 m/s |
| Absolute Voltage (kV) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wetting angle on the Cr12 surface (°) | Positive electricity | 51 | 47 | 45 | 43 | 39 | 38 | 34 | 29 |
| Negative electricity | 48 | 46 | 43 | 41 | 39 | 35 | 30 | ||
| Surface tension (N·m−1) | Positive electricity | 0.047 | 0.044 | 0.043 | 0.042 | 0.040 | 0.037 | 0.033 | 0.028 |
| Negative electricity | 0.045 | 0.044 | 0.042 | 0.041 | 0.038 | 0.033 | 0.029 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, B.; Guo, X.; Guo, P.; Tong, Z.; Xu, X. Experimental Investigation of Cr12 Steel Under Electrostatic Minimum Quantity Lubrication During Grinding. Processes 2024, 12, 2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112551
Feng B, Guo X, Guo P, Tong Z, Xu X. Experimental Investigation of Cr12 Steel Under Electrostatic Minimum Quantity Lubrication During Grinding. Processes. 2024; 12(11):2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112551
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Bohua, Xiaomei Guo, Pengcheng Guo, Zeqi Tong, and Xuefeng Xu. 2024. "Experimental Investigation of Cr12 Steel Under Electrostatic Minimum Quantity Lubrication During Grinding" Processes 12, no. 11: 2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112551
APA StyleFeng, B., Guo, X., Guo, P., Tong, Z., & Xu, X. (2024). Experimental Investigation of Cr12 Steel Under Electrostatic Minimum Quantity Lubrication During Grinding. Processes, 12(11), 2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12112551







