Biosensing Applications of Molecularly Imprinted-Polymer-Based Nanomaterials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sensors
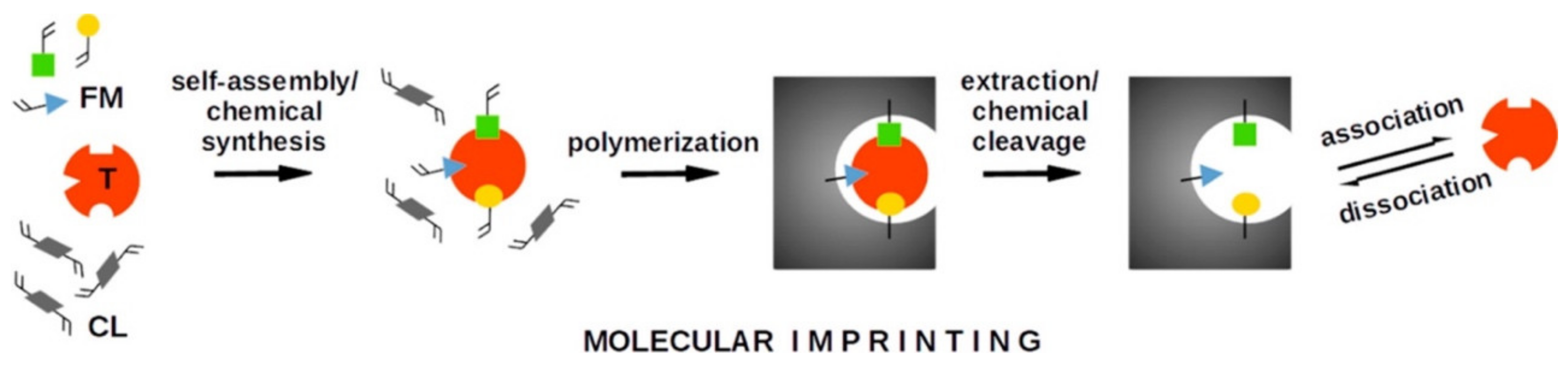
3. Molecular Imprinting Method
4. MIP-Based Sensors and Applications
4.1. Imprinted-Particle-Based Sensors
4.2. Imprinted-Nanogel-Based Sensors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Javaid, M.; Haleem, A.; Rab, S.; Singh, R.P.; Suman, R. Sensors for daily life: A review. Sens. Int. 2021, 2, 100121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhanie, E.; Salehnia, F.; Xu, G.; Hamidipanah, Y.; Arshian, S.; Firoozbakhtian, A.; Hosseini, M.; Ganjali, M.R.; Hanif, S. Recent trends and advancements in electrochemiluminescence biosensors for human virus detection. TrAC Trend. Anal. Chem. 2022, 157, 116727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, Ö.; Eş, I.; Saylan, Y.; Atabay, M.; Gungen, M.A.; Ölmez, K.; Denizli, A.; Inci, F. In situ synthesis and dynamic simulation of molecularly imprinted polymeric nanoparticles on a micro-reactor system. Nat. Comm. 2023, 14, 4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavín, Á.; de Vicente, J.; Holgado, M.; Laguna, M.F.; Casquel, R.; Santamaría, B.; Maigler, M.V.; Hernández, A.L.; Ramírez, Y. On the determination of uncertainty and limit of detection in label-free biosensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbruster, D.A.; Pry, T. Limit of blank, limit of detection and limit of quantitation. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2008, 29, S49–S52. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B.H.; Hsiao, F.C.; Lin, Y.R.; Lin, C.H.; Shen, Y.A.; Hsu, Y.Y.; Lee, P.H.; Su, Y.W.; Lu, H.R.; Lin, C.W.; et al. Highly efficient ternary near-infrared organic photodetectors for biometric monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2023, 15, 10907–10917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, K.R. Recent advances in biosensor techniques for environmental monitoring. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 568, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thévenot, D.R.; Toth, K.; Durst, R.A.; Wilson, G.S. Electrochemical biosensors: Recommended definitions and classification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Cao, M.; Du, Y.; Liu, Q.; Emran, M.Y.; Yousef, A.K.; Sun, M.; Ma, C.B.; Zhou, M. Artificial enzyme innovations in electrochemical devices: Advancing wearable and portable sensing technologies. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derin, E.; Inci, F. Advances in biosensor technologies for acute kidney injury. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 358–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapitan, L.D., Jr.; Pietrzak, M.; Krawczyk, M.; Malinowska, E. Serum biomarkers and ultrasensitive biosensors for diagnosis of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 393, 134209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akceoglu, G.A.; Saylan, Y.; Inci, F. A snapshot of microfluidics in point-of-care diagnostics: Multifaceted integrity with materials and sensors. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2100049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saylan, Y.; Erdem, Ö.; Inci, F.; Denizli, A. Advances in biomimetic systems for molecular recognition and biosensing. Biomimetics 2020, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Singh, M. Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for highly selective and sensitive determination of artificial sweetener Acesulfame-K. Talanta Open 2023, 7, 100194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaidarova, A.; Geraldi, N.R.; Wilson, R.P.; Kosel, J.; Meekan, M.G.; Eguíluz, V.M.; Hussain, M.M.; Shamim, A.; Liao, H.; Srivastava, M.; et al. Wearable sensors for monitoring marine environments and their inhabitants. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 1208–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Er, S.; Laraib, U.; Arshad, R.; Sargazi, S.; Rahdar, A.; Pandey, S.; Thakur, V.K.; Díez-Pascual, A.M. Amino acids, peptides, and proteins: Implications for nanotechnological applications in biosensing and drug/gene delivery. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goode, J.A.; Rushworth, J.V.H.; Millner, P.A. Biosensor regeneration: A review of common techniques and outcomes. Langmuir 2015, 31, 6267–6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.; Bhardwaj, A. Biosensor technology for pesticides—A review. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 175, 3093–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, Z.; Tothill, I. Biomarkers and biosensors for the early diagnosis of lung cancer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 188, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Dulta, K.; Nagraik, R.; Dua, K.; Singh, S.K.; Chellappan, D.K.; Kumar, D.; Shin, D.S. Potentialities of aptasensors in cancer diagnosis. Mater. Lett. 2022, 308, 131240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BelBruno, J.J. Molecularly imprinted polymers. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 94–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, T.; Ahmad, M.; Yu, J.; Wang, S.; Wei, T. A recyclable tetracycline imprinted polymeric SPR sensor: In synergy with itaconic acid and methacrylic acid. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 3102–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobiech, M.; Bujak, P.; Lulinski, P.; Pron, A. Semiconductor nanocrystal-polymer hybrid nanomaterials and their application in molecular imprinting. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 12030–12074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, T.P.; Sharma, P.S.; Sosnowska, M.; D’Souza, F.; Kutner, W. Functionalized polythiophenes: Recognition materials for chemosensors and biosensors of superior sensitivity, selectivity, and detectability. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 47, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Wu, X.; Li, J. Molecular imprinting: Perspectives and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2137–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodoki, A.E.; Iacob, B.C.; Bodoki, E. Perspectives of molecularly imprinted polymer-based drug delivery systems in cancer therapy. Polymers 2019, 11, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouaoui, F.; Bourouina-Bacha, S.; Bourouina, M.; Zine, N.; Errachid, A.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Mathematical modelling of glyphosate molecularly imprinted polymer-based microsensor with multiple phenomena. Molecules 2022, 27, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, N.; Kammakakam, I.; Falath, W. Nanomaterials: A review of synthesis methods, properties, recent progress, and challenges. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 1821–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekuye, B.; Abera, B. Nanomaterials: An overview of synthesis, classification, characterization, and applications. Nano Select. 2023, 4, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, H.; Pan, G. Molecularly imprinted nanomaterials with stimuli responsiveness for applications in biomedicine. Molecules 2023, 28, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saylan, Y.; Akgönüllü, S.; Denizli, A. Preparation of magnetic nanoparticles-assisted plasmonic biosensors with metal affinity for interferon-α detection. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2022, 280, 115687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dip Gandarilla, A.M.; de Souza Freire, L.; Ruzo, C.M.; Romaguera Barcelay, Y.; Brito, W.R. Electrochemical biosensors as promising methods for diagnosis of COVID-19—A minireview. Anal. Lett. 2023, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, D.; Paul, S.; Acharjee, T.; Ramachairy, S.S. Biosensors and their widespread impact on human health. Sens. Int. 2024, 5, 100257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Tang, H.; Cheng, W.; Yan, L.; Zhang, D.; Ju, H.; Ding, S.A. Sensitive electrochemical DNA biosensor for specific detection of Enterobacteriaceae bacteria by exonuclease iii-assisted signal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 48, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, J.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, F.; Ma, L.; Qin, D.; Shan, D.; Lu, X. A novel electrochemical sensor based on zirconia/ordered macroporous polyaniline for ultrasensitive detection of pesticides. Analyst 2015, 140, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Wu, J.; Ju, H. Electrochemical sensing of heavy metal ions with inorganic, organic and bio-materials. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giamblanco, N.; Conoci, S.; Russo, D.; Marletta, G. Single-step label-free hepatitis B virus detection by a piezoelectric biosensor. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 38152–38158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaseva, N.A.; Farafonova, O.V.; Ermolaeva, T.N. Highly sensitive detection of okadaic acid in seafood products via the unlabeled piezoelectric sensor. Food Anal. Method 2016, 9, 1495–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, J. Hollow molecularly imprinted polymer based quartz crystal microbalance sensor for rapid detection of methimazole in food samples. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciacca, B.; François, A.; Hoffmann, P.; Monro, T.M. Multiplexing of radiative-surface plasmon resonance for the detection of gastric cancer biomarkers in a single optical fiber. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 183, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, U.; Chandel, A.K.S.; Oleksak, P.; Mishra, A.; Krejcar, O.; Raval, I.H.; Dey, A.; Kuca, K. Recent advances in the potential applications of luminescence-based, SPR-based, and carbon-based biosensors. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 2827–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankaran, D.R.; Gobi, K.V.; Miura, N. Recent advancements in surface plasmon resonance immunosensors for detection of small molecules of biomedical, food and environmental interest. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 121, 158–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paruli, E.; Soppera, O.; Haupt, K.; Gonzato, C. Photopolymerization and photostructuring of molecularly imprinted polymers. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 4769–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.S.; Thotathil, V.; Zaidi, S.A.; Sheikh, H.; Mohamed, M.; Qureshi, A.; Sadasivuni, K.K. Picomolar or beyond limit of detection using molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensors: A review. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Li, Q.; Xu, H.X.; Zheng, Q.Y.; Zhang, Q.H.; Zhou, L.D.; Wang, C.-Z.; Yuan, C.S. Recognition and analysis of biomarkers in tumor microenvironments based on promising molecular imprinting strategies with high selectivity. TrAC Trend. Anal. Chem. 2023, 162, 117033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, M.V. Adsorption properties and structure of silica gel. Zhur. Fiz. Khim. 1931, 2, 799–805. [Google Scholar]
- Wulff, G.; Sarhan, A. The use of polymers with enzyme-analogous structures for the resolution of racemates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1972, 11, 341. [Google Scholar]
- Arshady, R.; Mosbach, K. Synthesis of substrate-selective polymers by host-guest polymerization. Makromol. Chem. 1981, 182, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K.; Verma, D.; Dalal, N.; Kumar, A.; Solanki, P.R. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based nanodiagnostics for clinically pertinent bacteria and virus detection for future pandemics. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2022, 12, 100257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Christa, J.; Deepa, J.R. Extraction of melamine from milk using a magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer. Food Chem. 2017, 227, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, C.; Ore, O.G.; Sellergren, B.; Halvorsen, T.G.; Reubsaet, L. Exploring the peptide retention mechanism in molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 5631–5643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanavicius, S.; Ramanavicius, A. Development of molecularly imprinted polymer based phase boundaries for sensors design. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 305, 102693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Wang, H.; He, K.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Gong, H.; Cai, C.A. Virus-MIPs fluorescent sensor based on FRET for highly sensitive detection of JEV. Talanta 2016, 160, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, W.; Pei, J.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Epitope imprinting technology: Progress, applications, and perspectives toward artificial antibodies. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1902048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyazit, S.; Tse Sum Bui, B.; Haupt, K.; Gonzato, C. Molecularly imprinted polymer nanomaterials and nanocomposites by controlled/living radical polymerization. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 62, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Randell, E.; Zhang, M.; Jia, Q. A review: Development and application of surface molecularly imprinted polymers toward amino acids, peptides, and proteins. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1234, 340319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saylan, Y.; Göktürk, I.; Pospiskova, K.; Safarik, I.; Denizli, A. Magnetic bacterial cellulose nanofibers for nucleoside recognition. Cellulose 2020, 27, 9479–9492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.P.; Zhang, F.Y.; Yang, X.M.; Zhang, X.H.; Cao, Y.H.; Peng, H.L. Preparation of a novel supermacroporous molecularly imprinted cryogel membrane with a specific ionic liquid for protein recognition and permselectivity. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhang, L.; Bai, S.; Yang, H.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y. Advances of molecularly imprinted polymers (MIP) and the application in drug delivery. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 143, 110179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.A. Molecular imprinted polymers as drug delivery vehicles. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 2262–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.Y.; Cao, P.P.; He, Z.Y.; He, X.W.; Li, W.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.K. Targeted imaging and targeted therapy of breast cancer cells: Via fluorescent double template-imprinted polymer coated silicon nanoparticles by an epitope approach. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 17018–17030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulou, M.; Kunath, S.; Medina-Rangel, P.X.; Haupt, K.; Tse Sum Bui, B. Fluorescent molecularly imprinted polymers as plastic antibodies for selective labeling and imaging of hyaluronan and sialic acid on fixed and living cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 88, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestora, S.; Merlier, F.; Beyazit, S.; Prost, E.; Duma, L.; Baril, B.; Greaves, A.; Haupt, K.; Tse Sum Bui, B. Plastic antibodies for cosmetics: Molecularly imprinted polymers scavenge precursors of malodors. Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 6360–6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, X.Y.; Li, J.J.; Su, X.M.; Wu, Z.Y.; Li, P.F.; Lei, F.H.; Tan, X.C.; Shi, Z.W. Synthesis of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective separation and determination of metronidazole in cosmetic samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 3875–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirata, F.; Resmini, M. Molecularly imprinted polymers for catalysis and synthesis. In Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in Biotechnology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 107–129. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, S.; Balieu, S.; Petit, E.; Galas, L.; Schapman, D.; Hardouin, J.; Baati, R.; Estour, F.A. Versatile and recyclable molecularly imprinted polymer as an oxidative catalyst of sulfur derivatives: A new possible method for mustard gas and V nerve agent decontamination. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 13243–13246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yu, S.; Liu, W.; Fu, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, L. Molecular imprinting based hybrid ratiometric fluorescence sensor for the visual determination of bovine hemoglobin. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Wang, L.; Yan, J.; Luan, D.; Wu, J.; Bian, X. Rapid, sensitive and label-free detection of pathogenic bacteria using a bacteria-imprinted conducting polymer film-based electrochemical sensor. Talanta 2021, 226, 122135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgür, E.; Saylan, Y.; Bereli, N.; Türkmen, D.; Denizli, A. Molecularly imprinted polymer integrated plasmonic nanosensor for cocaine detection. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2020, 31, 1211–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlapiano, M.; Akyol, Ç.; Foglia, A.; Pisani, M.; Astolfi, P.; Eusebi, A.L.; Fatone, F. Selective removal of contaminants of emerging concern (CECs) from urban water cycle via Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs): Potential of upscaling and enabling reclaimed water reuse. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, W.; Sun, P.; Xu, Z.; Ding, Y.; Xu, W.; Xu, W.; Gu, J. Selective extraction of myoglobin from human serum with antibody-biomimetic magnetic nanoparticles. Talanta 2020, 219, 121327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarannum, N.; Kumar, D.; Surya, S.G.; Dramou, P. Point-of-care detection assay based on biomarker-imprinted polymer for different cancers: A state-of-the-art review. Polym. Bull. 2022, 80, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.A.; Bahrani, S.; Mousavi, S.M.; Omidifar, N.; Behbahan, N.G.G.; Arjmand, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Lankarani, K.B.; Moghadami, M.; Firoozsani, M. Graphene-based femtogram-level sensitive molecularly imprinted polymer of SARS-CoV-2. Adv. Mater. Int. 2021, 8, 2101466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/search?qs=imprint (accessed on 9 January 2024).
- Alberti, G.; Zanoni, C.; Losi, V.; Magnaghi, L.R.; Biesuz, R. Current trends in polymer based sensors. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, N.; Abu Bakar, N.K.; Ekramul Mahmud, H.N.M.; Jamaludin, N.S. Molecularly imprinted polymers-based DNA biosensors. Anal. Biochem. 2021, 630, 114328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowdon, J.W.; Diliën, H.; Singla, P.; Peeters, M.; Cleij, T.J.; van Grinsven, B.; Eersels, K. MIPs for commercial application in low-cost sensors and assays–An overview of the current status quo. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 325, 128973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/search?qs=imprint%20and%20sensor (accessed on 9 January 2024).
- Wang, L.; Pagett, M.; Zhang, W. Molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) based electrochemical sensors and their recent advances in health applications. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2023, 5, 100153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Ji, W.; Xing, S.; Feng, Z.; Li, H.; Lu, S.; Du, K.; Li, X. Emerging trends in sensors based on molecular imprinting technology: Harnessing smartphones for portable detection and recognition. Talanta 2023, 268, 125283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Duncan, T.V. Challenges and potential solutions for nanosensors intended for use with foods. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahcen, A.A.; Surya, S.G.; Beduk, T.; Vijjapu, M.T.; Lamaoui, A.; Durmus, C.; Timur, S.; Shekhah, O.; Mani, V.; Amine, A.; et al. Metal–organic frameworks meet molecularly imprinted polymers: Insights and prospects for sensor applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Int. 2022, 14, 49399–49424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincer, C.; Bruch, R.; Costa-Rama, E.; Fernández-Abedul, M.T.; Merkoçi, A.; Manz, A.; Urban, G.A.; Güder, F. Disposable sensors in diagnostics, food, and environmental monitoring. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1806739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, O.; Saylan, Y.; Göktürk, I.; Yılmaz, F.; Denizli, A. A surface plasmon resonance sensor with synthetic receptors decorated on graphene oxide for selective detection of benzylpenicillin. Talanta 2023, 253, 123939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yılmaz, G.E.; Saylan, Y.; Göktürk, I.; Yılmaz, F.; Denizli, A. Selective amplification of plasmonic sensor signal for cortisol detection using gold nanoparticles. Biosensors 2022, 12, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.; Guo, R.; Yuan, F.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Fan, L. Red-emissive carbon quantum dots for nuclear drug delivery in cancer stem cells. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, F.; Ji, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, H.; Lu, Y.; Xu, D.; Sun, X. A novel magnetic fluorescent biosensor based on graphene quantum dots for rapid, efficient, and sensitive separation and detection of circulating tumor cells. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, J.; Ju, H. Signal amplification using functional nanomaterials for biosensing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2122–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitayama, Y.; Yoshikawa, K.; Takeuchi, T. Post-cross-linked molecular imprinting with functional polymers as a universal building block for artificial polymeric receptors. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 7526–7534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, L.; Wu, X. Rapid and reliable determination of p-nitroaniline in wastewater by molecularly imprinted fluorescent polymeric ionic liquid microspheres. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 99, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Lei, Y. Interfacial molecular imprinting in nanoparticle-stabilized emulsions. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denderz, N.; Lehotay, J. Application of the van’t Hoff dependences in the characterization of molecularly imprinted polymers for some phenolic acids. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1268, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandyarimanesh, M.; Javanbakht, M.; Dinarvand, R.; Atyabi, F. Molecularly imprinted nanoparticles prepared by miniemulsion polymerization as selective receptors and new carriers for the sustained release of carbamazepine. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2012, 23, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirhagl, R. Bioapplications for molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaseva, N.A.; Pluhar, B.; Beliaev, E.A.; Ermolaev, T.N.; Mizaikoff, B. Synthesis and application of molecularly imprinted polymers for trypsin piezoelectric sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 280, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Pan, B.; Zeng, F.; He, B.; Gao, Y.; Liu, X.; Song, Y. Magnetic colloid antibodies accelerate small extracellular vesicles isolation for point-of-care diagnostics. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 2001–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, M.; Wang, D.; Dang, Y.Y.; Ye, B.C.; Li, Y. A robust electrochemical sensing platform using carbon paste electrode modified with molecularly imprinted microsphere and its application on methyl parathion detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 106, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Q. Ratiometric fluorescent sensor with molecularly imprinted mesoporous microspheres for malachite green detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 266, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Cui, Y.; He, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, J. Synthesis of multi-mode quantum dots encoded molecularly imprinted polymers microspheres and application in quantitative detection for dopamine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 304, 127265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackerlig, J.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles in chemical sensing-Synthesis, characterisation and application. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Ragavan, K.V.; Thakur, M.S.; Raghavarao, K.S.M.S. Recent advances in nanoparticle based aptasensors for food contaminants. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 612–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Tang, X.; Zhao, L. Molecularly imprinted polymers-based novel optical biosensor for the detection of cancer marker lysozyme. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2022, 334, 113324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
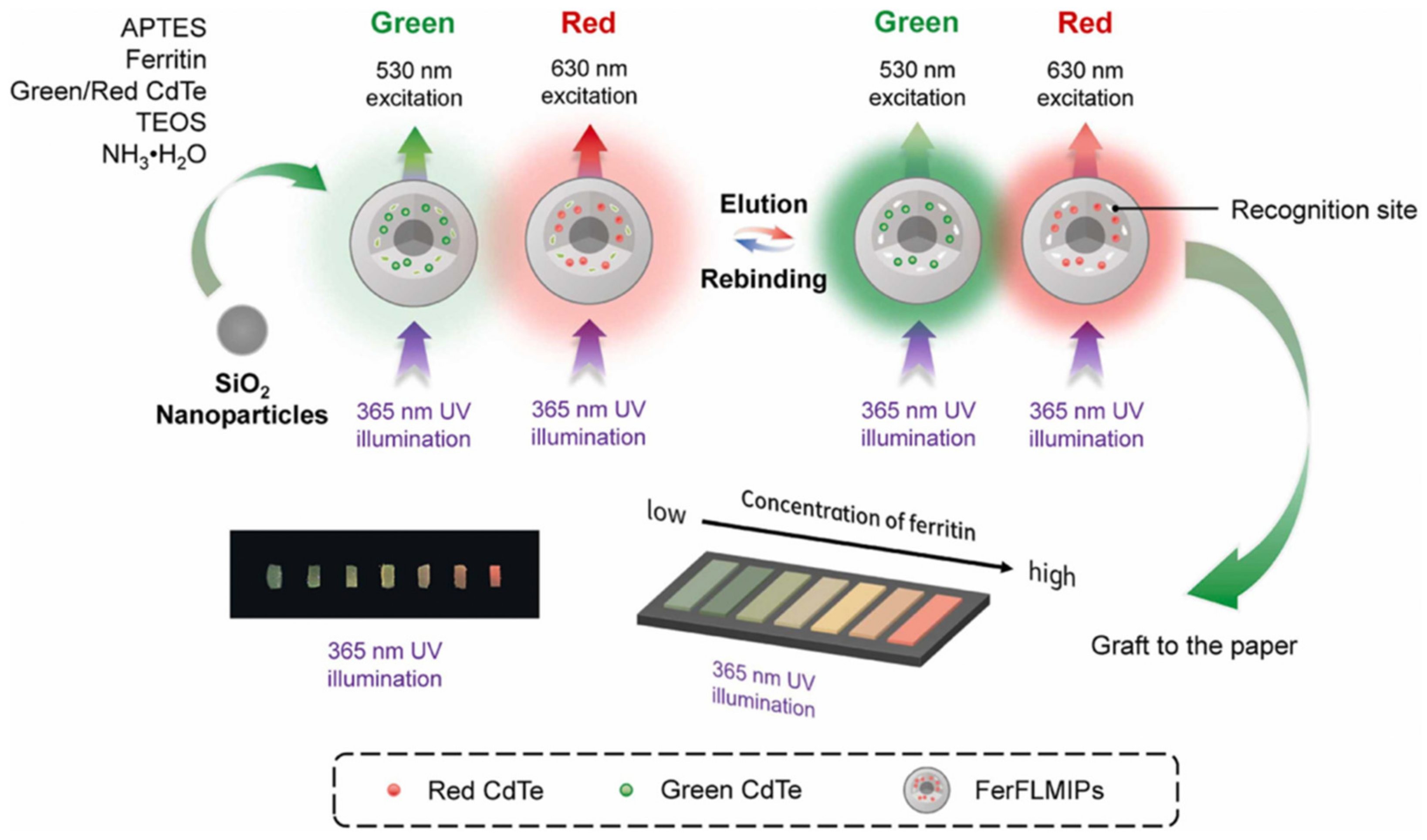
- Li, T.; Deng, Z.; Bu, J.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, S. Quantum dot based molecularly imprinted polymer test strips for fluorescence detection of ferritin. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 358, 131548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fang, M.; Tian, Y.; Bai, G.; Zhuo, K. Silanized carbon dot-based thermo-sensitive molecularly imprinted fluorescent sensor for bovine hemoglobin detection. Anal. Bioanal. 2020, 412, 5811–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahtuvanoğlu, A.; Akgönüllü, S.; Karacan, S.; Denizli, A. Biomimetic nanoparticles based surface plasmon resonance biosensors for histamine detection in foods. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 5683–5692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzato, C.; Żołek, T.; Maciejewska, D.; Kutner, A.; Merlier, F.; Haupt, K.; Sharma, P.S.; Noworyta, K.R.; Kutner, W. Molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles-based electrochemical chemosensors for selective determination of cilostazol and its pharmacologically active primary metabolite in human plasma. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 193, 113542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, A.G.; Haq, I.; Cowen, T.; Masi, S.D.; Trivedi, S.; Alanazi, K.; Piletska, E.; Mujahid, A.; Piletsky, S.A. Design and fabrication of a smart sensor using in silico epitope mapping and electro-responsive imprinted polymer nanoparticles for determination of insulin levels in human plasma. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 169, 112536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, T.; Yoshida, A.; Hayakawa, N.; Kiguchi, K.; Cheubong, C.; Sunayama, H.; Kitayama, Y.; Takeuchi, T. Molecularly imprinted nanogels possessing dansylamide interaction sites for controlling protein corona in situ by cloaking intrinsic human serum albumin. Langmuir 2020, 36, 10674–10682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Z.; Liu, L.; Li, S.L.; Wan, Y.P.; Chen, J.X.; Tian, S.; Huang, Z.M.; Xiao, Y.F.; Cui, X.; Xiang, C.Y.; et al. Biodegradable pi-conjugated oligomer nanoparticles with high photothermal conversion efficiency for cancer theranostics. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 12901–12911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.C.; Yang, Z.; Fu, X.; Yung, B.C.; Yang, J.; Mao, Z.W.; Shao, L.; Hua, B.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhang, F.W.; et al. Polyrotaxane-based supramolecular theranostics. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, T.; Kitayama, Y.; Sasao, R.; Yamada, T.; Toh, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kataoka, K. Molecularly imprinted nanogels acquire stealth in situ by cloaking themselves with native dysopsonic proteins. Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 7194–7198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheubong, C.; Yoshida, A.; Mizukawa, Y.; Hayakawa, N.; Takai, M.; Morishita, T.; Kitayama, Y.; Sunayama, H.; Takeuchi, T. Molecularly imprinted nanogels capable of porcine serum albumin detection in raw meat extract for halal food control. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 6401–6407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
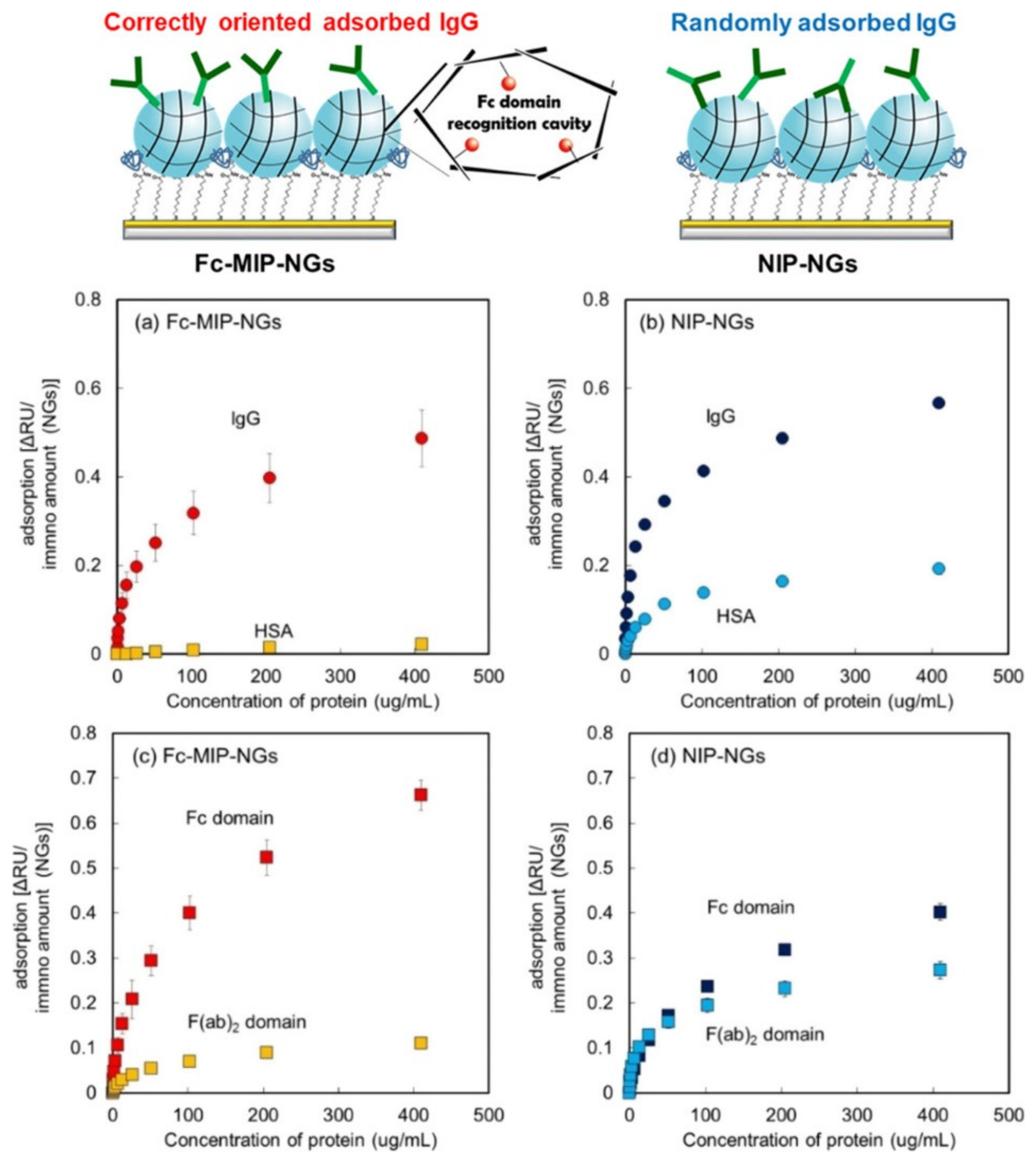
- Hayakawa, N.; Kitayama, Y.; Igarashi, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Takano, E.; Sunayama, H.; Takeuchi, T. Fc domain-imprinted stealth nanogels capable of orientational control of immunoglobulin G adsorbed in vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 16074–16081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellizzoni, E.; Tommasini, M.; Marangon, E.; Rizzolio, F.; Saito, G.; Benedetti, F.; Toffoli, G.; Resmini, M.; Berti, F. Fluorescent molecularly imprinted nanogels for the detection of anticancer drugs in human plasma. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Ref. | Material | Sensor | Target | Range | LOD | Selectivity | Real Sample |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [95] | Nanoparticle | Piezoelectric | Trypsin | 0.125–2 μg/mL | 0.07 μg/mL | Bovine serum albumin, pepsin, thermolysin, penicillin G, and salbutamol | Pharmaceutical formulations |
| [96] | Magnetic nanoparticle | Microfluidic chip | Extracellular vesicles | 5 × 102–109 sEVs/mL | 400 sEVs/mL | EpCAM and CD24 | Mouse and human plasma |
| [97] | Microsphere | Electrochemical | Methyl parathion | 1 × 10−12–8 × 10−9 mol/L | 3.4 × 10−13 mol/L | Methamidophos and parathion | Soil and vegetables |
| [98] | Microsphere | Fluorescence | Malachite green | 27.4 nM–137 μM | 17 nM | Atrazine, glufosinate, ametroyn, trifiuralin, and pendimethalin | River water and lake water |
| [99] | Microsphere | Fluorescence | Dopamine | 5–300 μg/L and 1–100 μg/L | 2 μg/L and 0.5 μg/L | Ions, amino acids, sugars, structural analogues, and other co-existing substances | Human urine, pork kidney, and rabbit serum |
| [102] | Quantum dot | Fluorescence | Lysozyme | 10–120 μg/mL | 3.2 μg/mL | Cytochrome c, bovine serum albumin, bovine hemoglobin, and ovalbumin | Human serum and chicken egg white |
| [103] | Quantum dot | Fluorescence | Ferritin | 1–6 μM | 0.1868 μM | Bovine serum albumin, lysozyme, and bovine hemoglobin | Human urine |
| [104] | Carbon dot | Fluorescence | Bovine hemoglobin | 0.31–1.55 μM | 1.55 μM | Bovine serum albumin, ovalbumin, and lipase | Urine |
| [105] | Nanoparticle | Optic | Histamine | 0.001–10 μg/mL | 0.58 ng/mL | Histidine, tryptophan, and dopamine | Fish and cheese |
| [106] | Nanoparticle | Electrochemical | Cilostazol | 134 nM–2.58 μM | 86.5 nM | Cholesterol, glucose, and dehydroaripiprazole | Human plasma |
| [107] | Nanoparticle | Electrochemical | Insulin | 50–2000 pM | 26 fM | Human proinsulin C-peptide and insulin-like growth factor 1 | Human plasma |
| [111] | Nanogel | Fluorescence | Human serum albumin | 35–55 mg/mL | Not available | Fibrinogen and immunoglobulin G | Liver cells |
| [112] | Nanogel | Piezoelectric | Porcine serum albumin | 10–2000 μg/mL | 12 μg/mL | Bovine, human, goat, sheep, and rabbit serum albumin | Pork and beef |
| [113] | Nanogel | Optic | Immunoglobulin G | 0.4–410 μg/mL | Not available | Human serum albumin | Mice blood |
| [114] | Nanogel | Fluorescence | Sunitinib | 0–4.5 μM | 400 nM | SN38 and paclitaxel | Human plasma |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saylan, Y.; Kılıç, S.; Denizli, A. Biosensing Applications of Molecularly Imprinted-Polymer-Based Nanomaterials. Processes 2024, 12, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12010177
Saylan Y, Kılıç S, Denizli A. Biosensing Applications of Molecularly Imprinted-Polymer-Based Nanomaterials. Processes. 2024; 12(1):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12010177
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaylan, Yeşeren, Seçkin Kılıç, and Adil Denizli. 2024. "Biosensing Applications of Molecularly Imprinted-Polymer-Based Nanomaterials" Processes 12, no. 1: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12010177
APA StyleSaylan, Y., Kılıç, S., & Denizli, A. (2024). Biosensing Applications of Molecularly Imprinted-Polymer-Based Nanomaterials. Processes, 12(1), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12010177








