Membrane-Based Micro-Volume Dialysis Method for Rapid and High-Throughput Protein Crystallization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
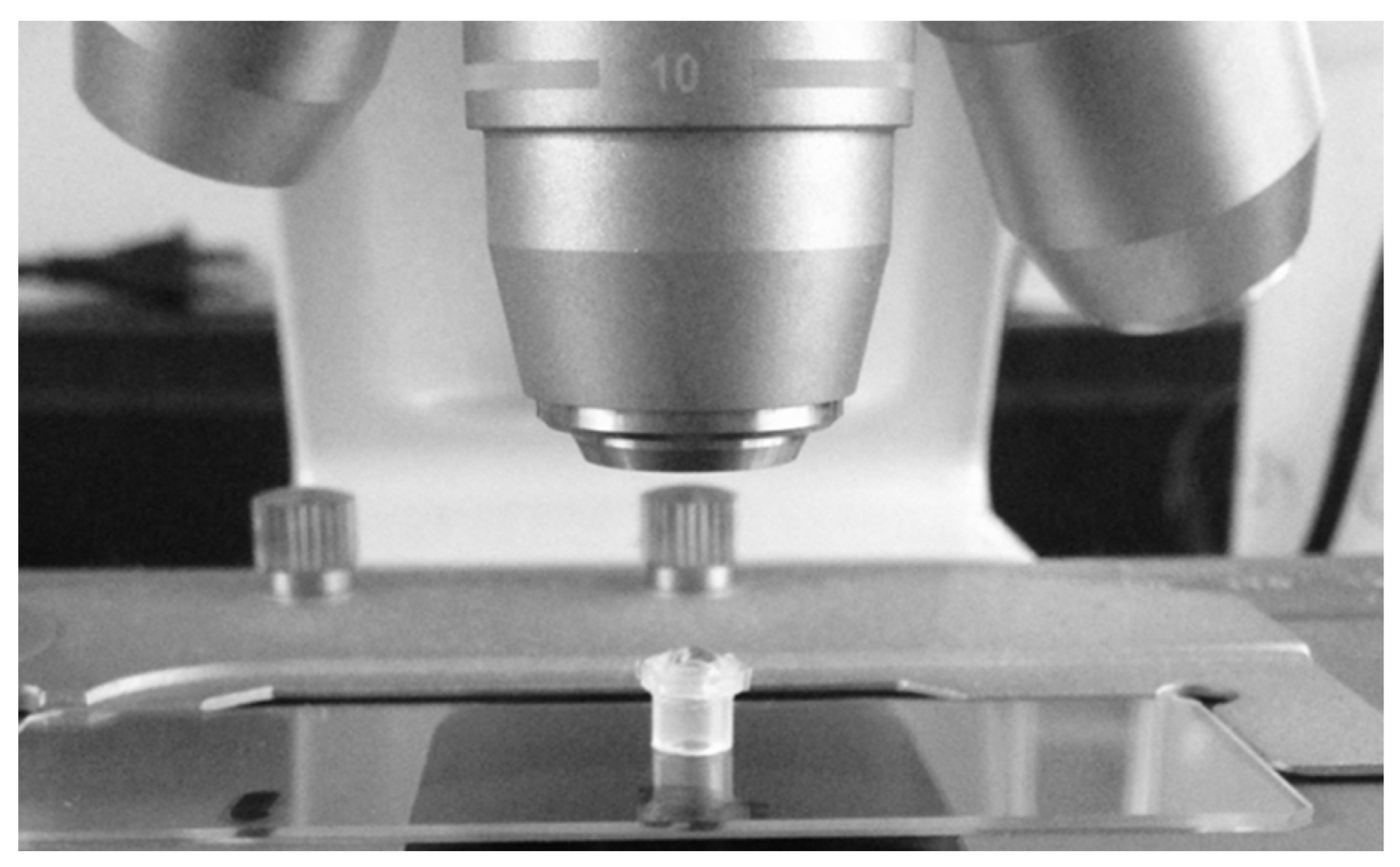
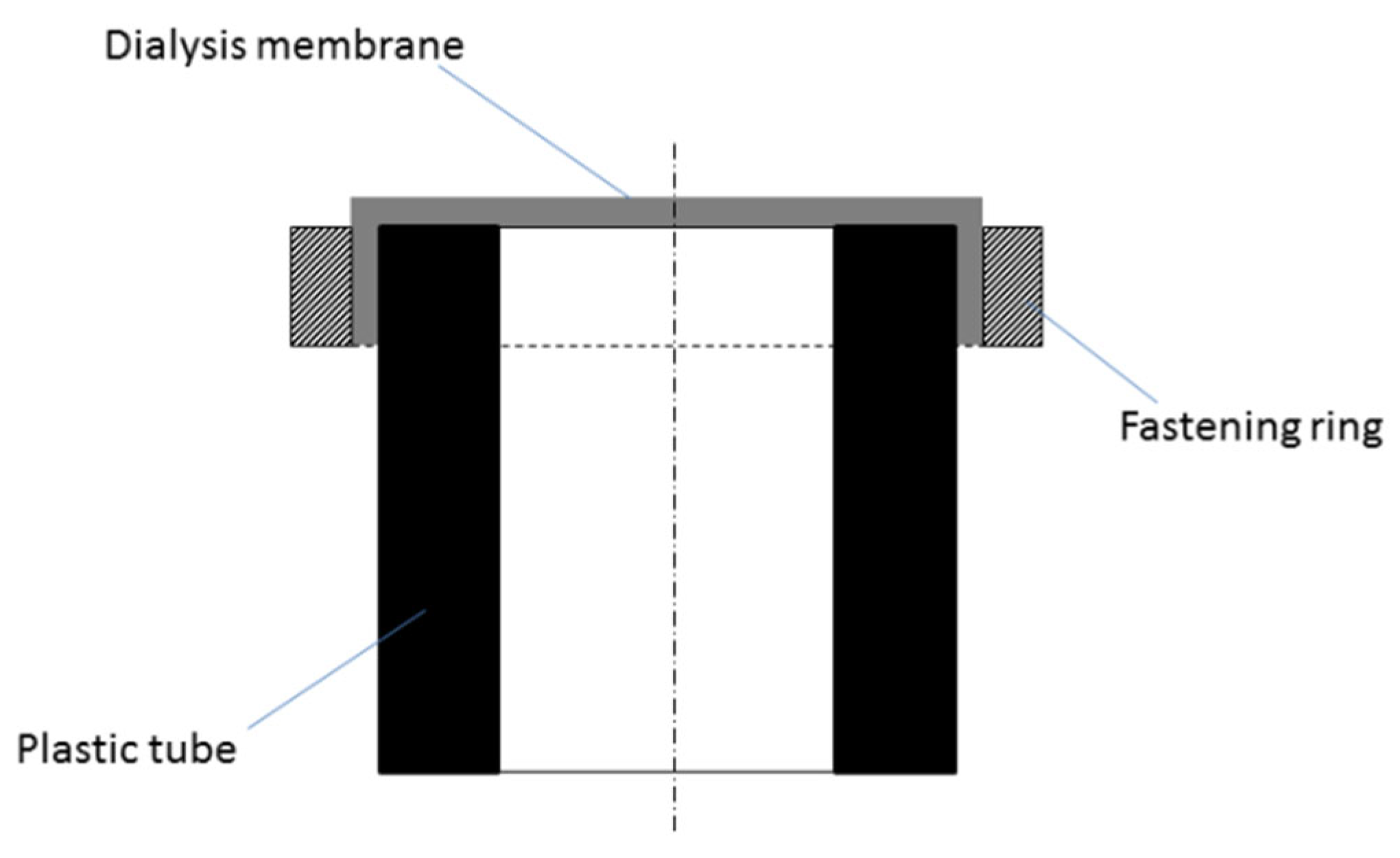
2.2. Membrane Device
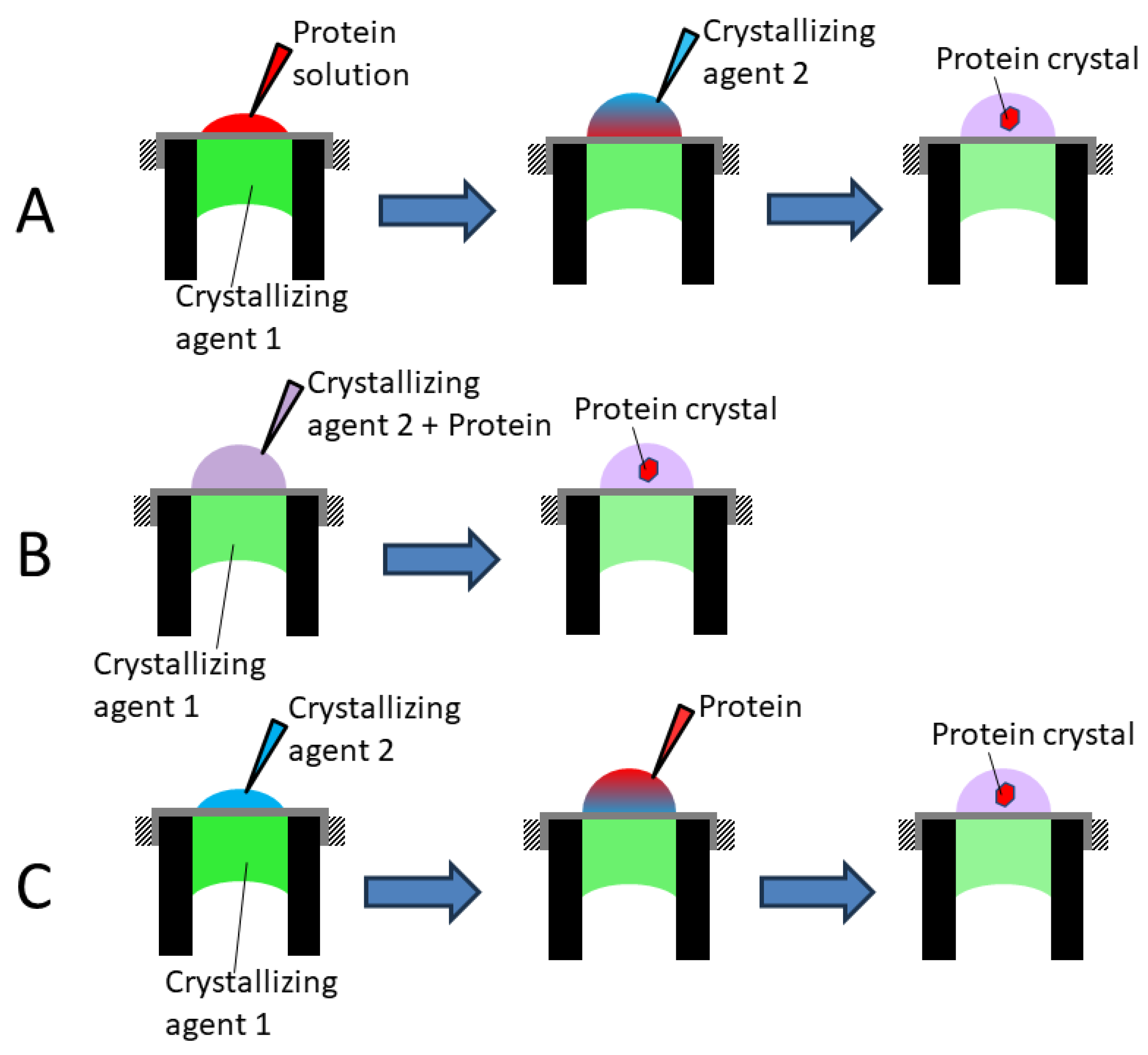
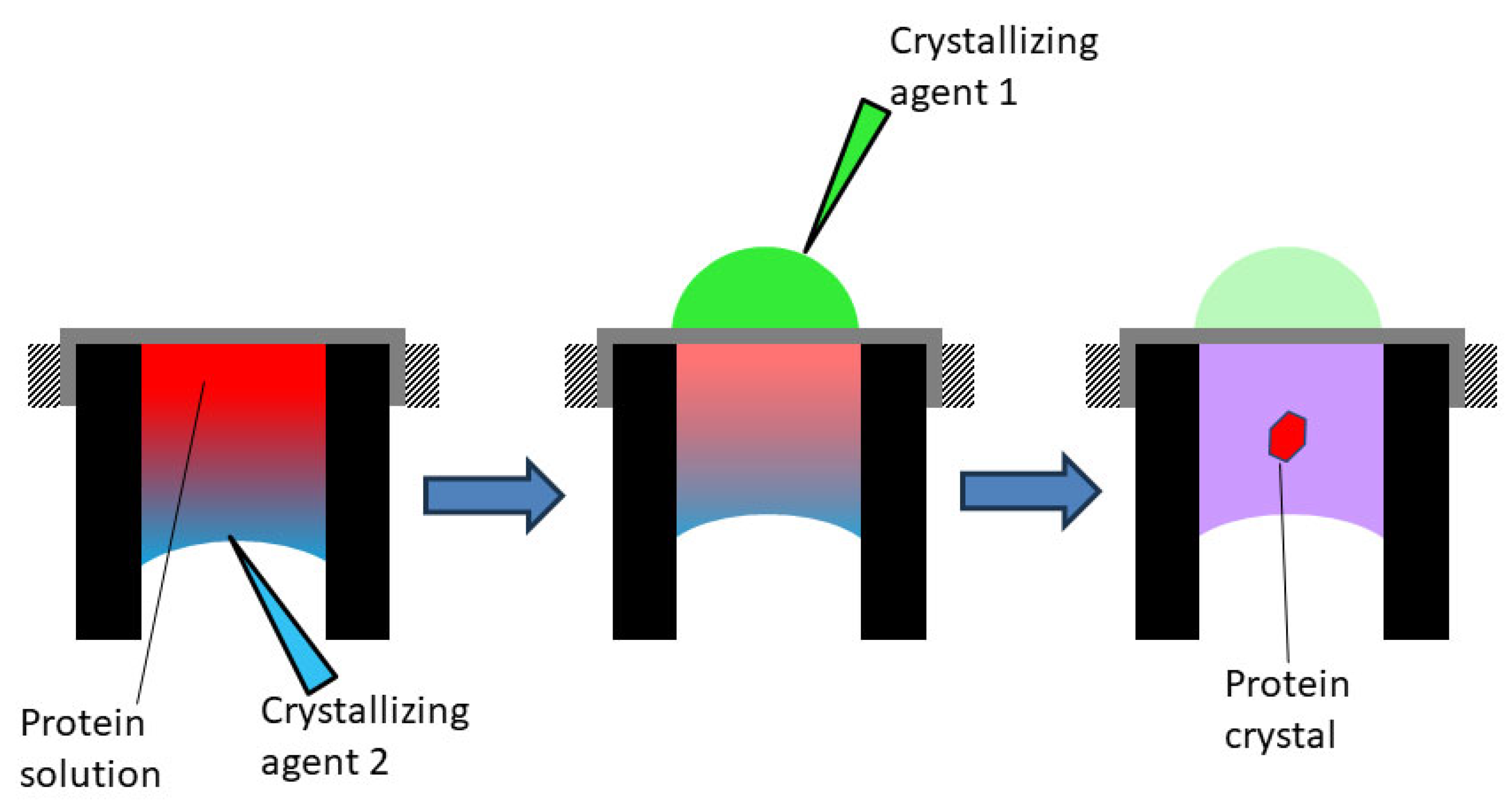
2.3. Lysozyme Crystallization
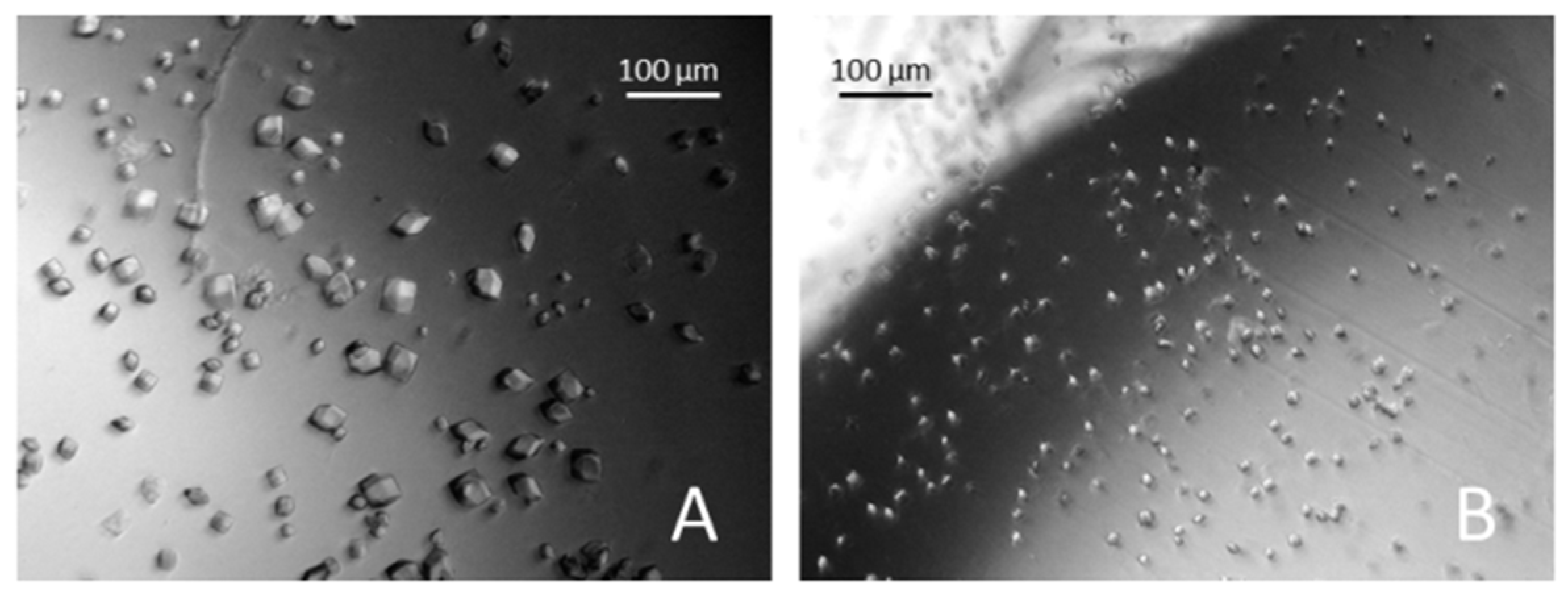
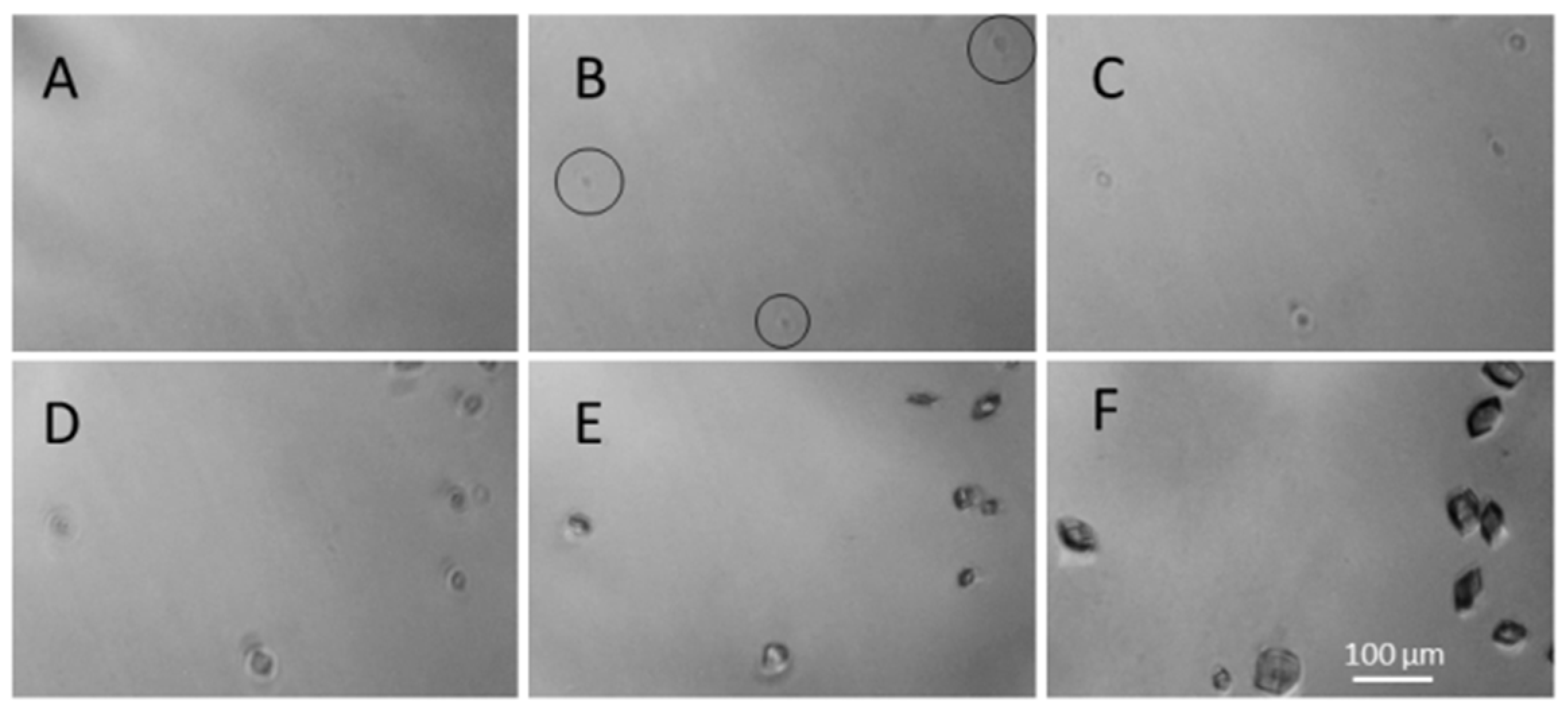
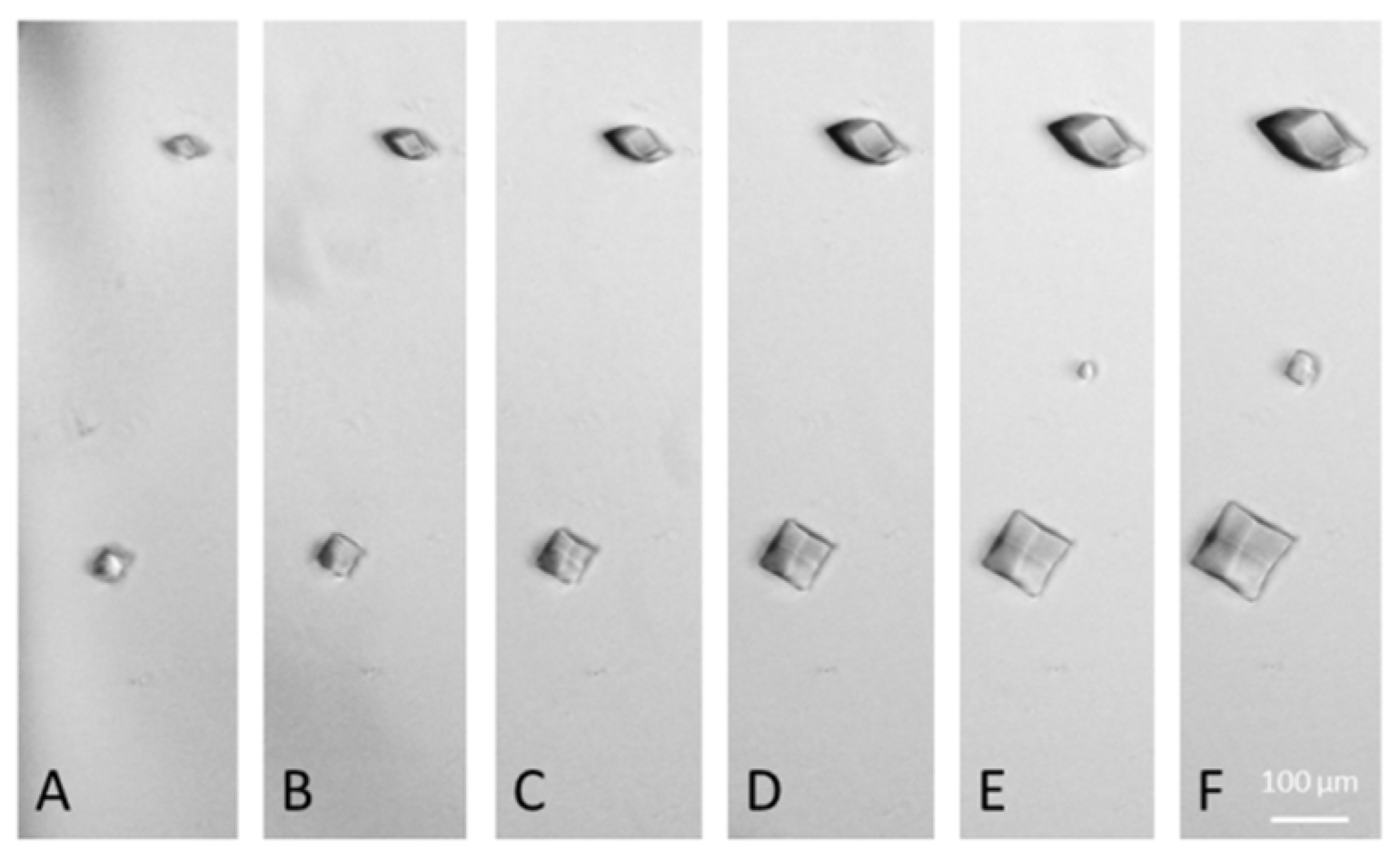
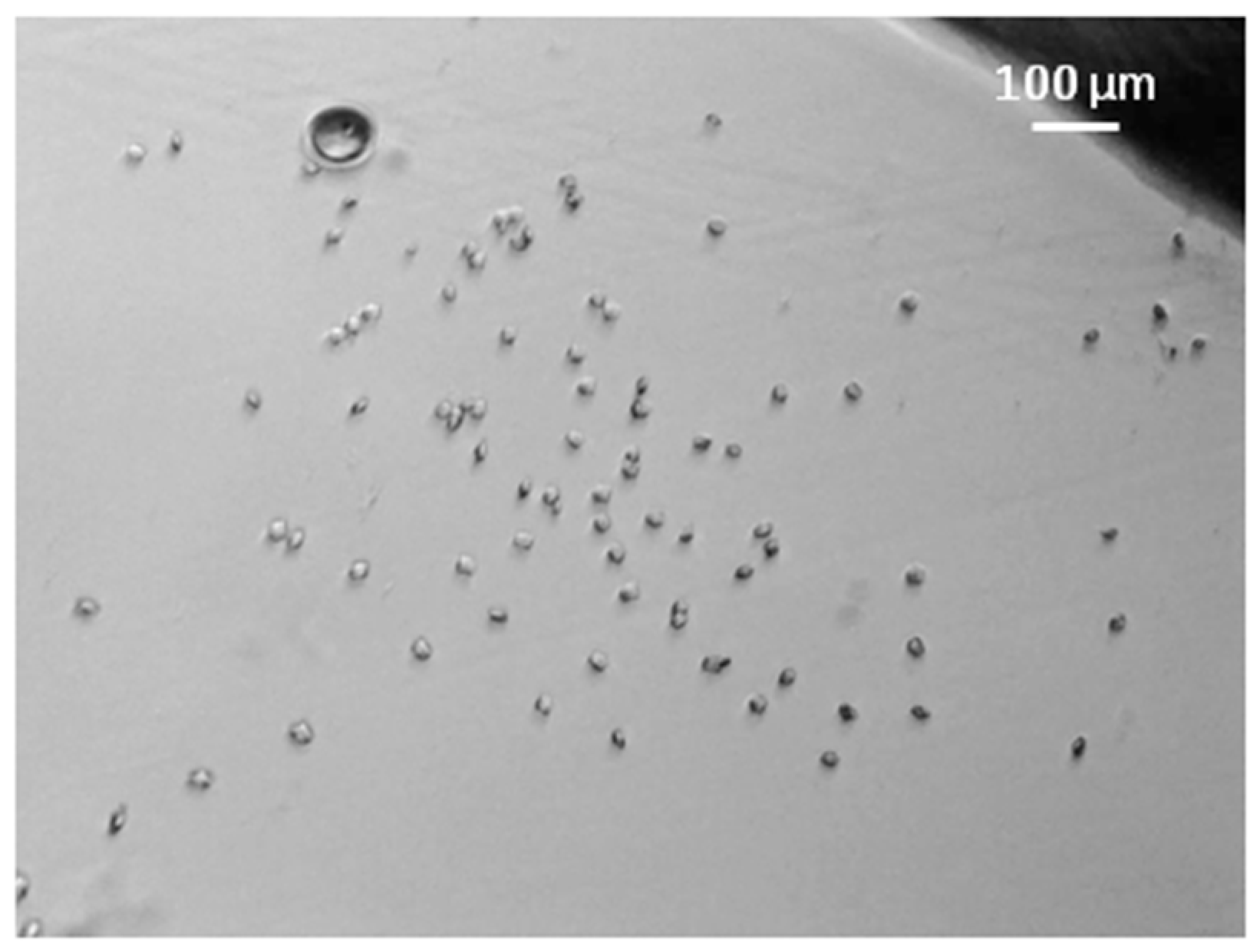
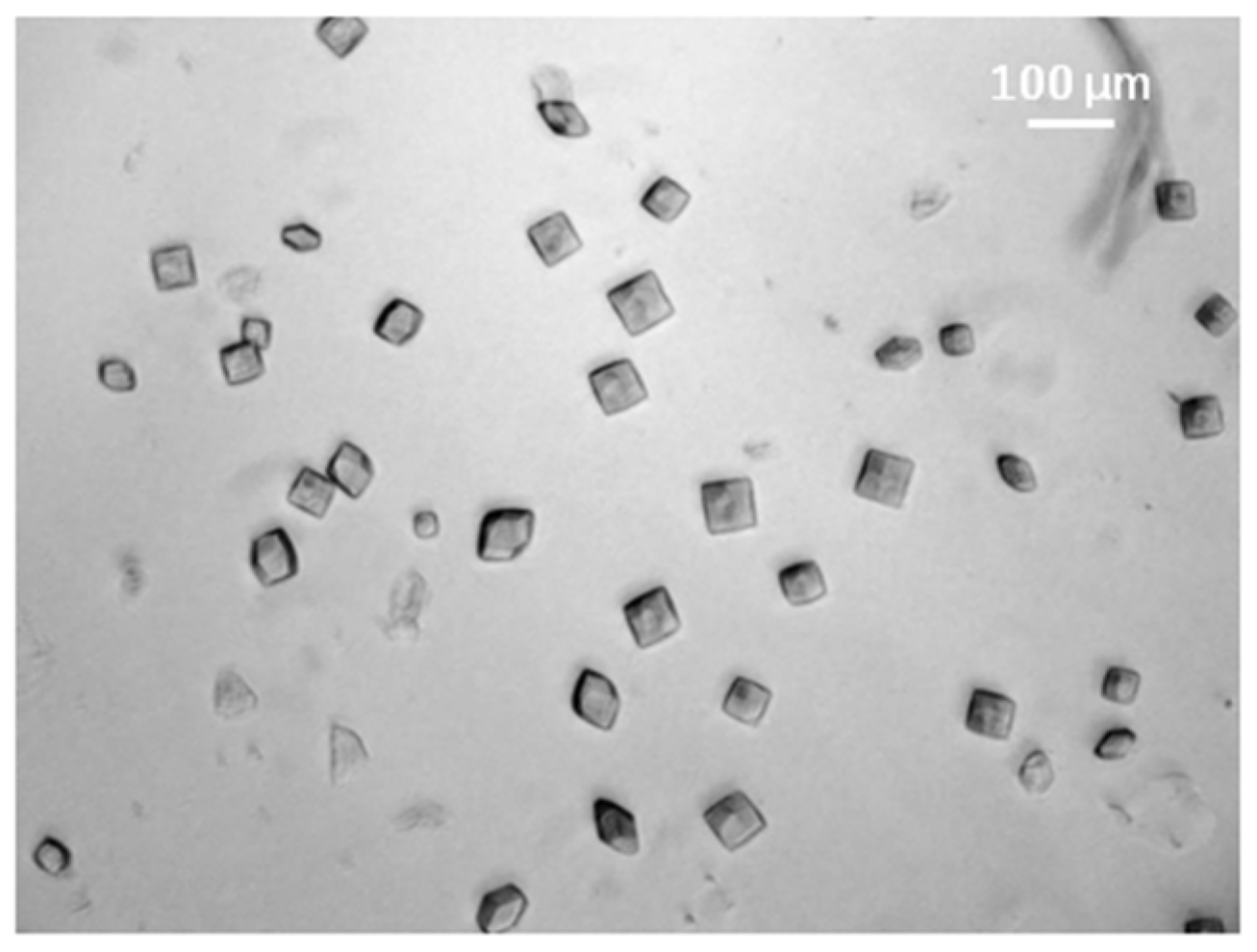
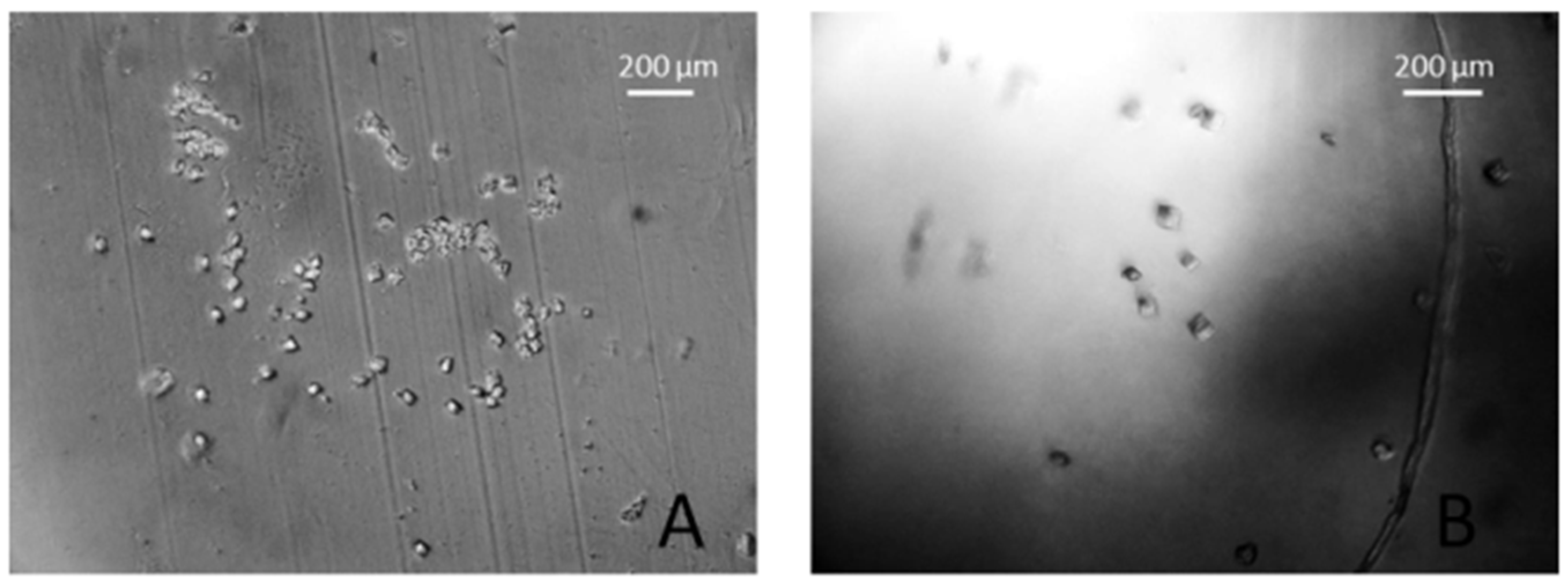
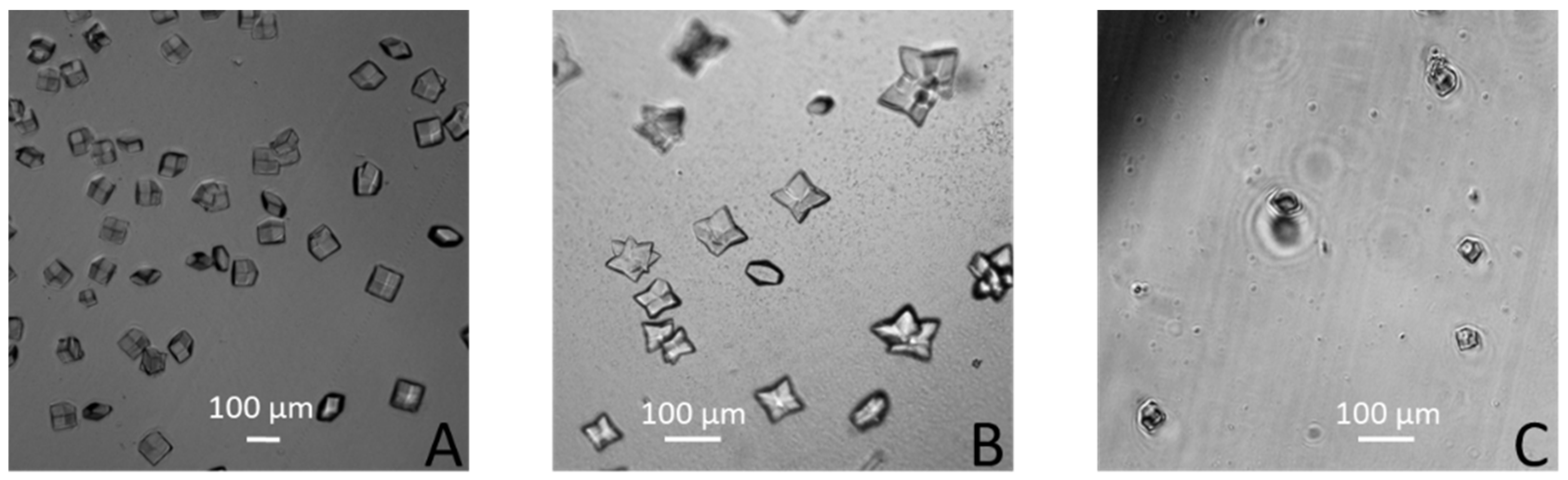
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoffman, I.D. Protein crystallization for structure-based drug design. In Structure-Based Drug Discovery; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 67–91. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, J.S.; van den Bedem, B.H.; Samelson, A.J.; Lang, P.T.; Holton, J.M.; Echols, N.; Alber, T. Accessing protein conformational ensembles using room-temperature X-ray crystallography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16247–16252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, K.A.; Kenneth, A.; Costanzi, S. New insights for drug design from the X-ray crystallographic structures of G-protein-coupled receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 82, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPherson, A. Introduction to protein crystallization. Methods 2004, 34, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPherson, A.; Gavira, J.A. Introduction to protein crystallization. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Commun. 2014, 70, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, S.; Saridakis, E.; Govada, L.; Chayen, N.E. Porous nucleating agents for protein crystallization. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 1621–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garman, E.F. Developments in X-ray crystallographic structure determination of biological macromolecules. Science 2014, 343, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, A. Crystallization of Biological Macromolecules; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Santarsiero, B.D.; Yegian, D.T.; Lee, C.C.; Spraggon, G.; Gu, J.; Scheibe, D.; Uber, D.C.; Cornell, E.W.; Nordmeyer, R.A.; Kolbe, W.F.; et al. An approach to rapid protein crystallization using nanodroplets. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2002, 35, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, R.C. High-throughput protein crystallization. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2000, 10, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chayen, N.E. High-throughput protein crystallization. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2009, 77, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, B.; Roach, L.S.; Ismagilov, R.F. Screening of protein crystallization conditions on a microfluidic chip using nanoliter-size droplets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 11170–11171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, J.; Salmon, J.B. Microfluidic crystallization. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhouib, K.; Malek, C.K.; Pfleging, W.; Gauthier-Manuel, B.; Duffait, R.; Thuillier, G.; Ferrigno, R.; Jacquamet, L.; Ohana, J.; Ferrer, J.L.; et al. Microfluidic chips for the crystallization of biomacromolecules by counter-diffusion and on-chip crystal X-ray analysis. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Sun, K.; Hu, X.; Li, G.; Jin, Q.; Zhao, J. A Centrifugal Microfluidic Device for Screening Protein Crystallization Conditions by Vapor Diffusion. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 219, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, P.; Pissis, C.; Navaza, R.; Mechaly, A.E.; Saul, F.; Alzari, P.M.; Haouz, A. High-throughput crystallization pipeline at the crystallography core facility of the institut Pasteur. Molecules 2019, 24, 4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutanto, F.; Shaabani, S.; Oerlemans, R.; Eris, D.; Patil, P.; Hadian, M.; Wang, M.; Sharpe, M.E.; Groves, M.R.; Dömling, A. Combining High-Throughput Synthesis and High-Throughput Protein Crystallography for Accelerated Hit Identification. Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 18379–18387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blay, V.; Tolani, B.; Ho, S.P.; Arkin, M.R. High-throughput screening: Today’s biochemical and cell-based approaches. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1807–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, K.; Yamashita, K.; Ueno, G.; Kawano, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Kumasaka, T.; Yamamoto, M. ZOO: An automatic data-collection system for high-throughput structure analysis in protein microcrystallography. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Struct. Biol. 2019, 75, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Jedrzejczak, R.; Maltseva, N.I.; Wilamowski, M.; Endres, M.; Godzik, A.; Michalska, M.; Joachimiak, A. Crystal structure of Nsp15 endoribonuclease NendoU from SARS-CoV-2. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, A.R.; Ragbirsingh, R.; McMonagle, C.J.; Waddell, P.G.; Heaps, S.E.; Steed, J.W.; Thaw, P.; Hall, M.J.; Probert, M.R. Encapsulated nanodroplet crystallization of organic-soluble small molecules. Chem 2020, 6, 1755–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junius, N.; Jaho, S.; Sallaz-Damaz, Y.; Borel, F.; Salmon, J.B.; Budayova-Spano, M. A microfluidic device for both on-chip dialysis protein crystallization and in situ X-ray diffraction. Lab. Chip 2020, 20, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhou, J.; Dong, J.; Su, Z.; Huang, L. Revealing the effects of microwell sizes on the crystal growth kinetics of active pharmaceutical ingredients by deep learning. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, W.; Peczulis, P.; Heng, J.Y.Y. Development and workflow of a continuous protein crystallization process: A case of lysozyme. Cryst. Growth Des. 2019, 19, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieske, J.; Cerv, M.; Kreida, S.; Komadina, D.; Fischer, J.; Barthelmess, M.; Fischer, P. On-chip crystallization for serial crystallography experiments and on-chip ligand-binding studies. IUCrJ 2019, 6, 714–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aherne, M.; Lyons, J.A.; Caffrey, M. A fast, simple and robust protocol for growing crystals in the lipidic cubic phase. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 1330–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Ito, K.; Hayakawa, R.; Ataka, M. Size and number density of precrystalline aggregates in lysozyme crystallization process. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 111, 10330–10337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.G.; Liu, Y.H.; Di, Y.D.; Xu, Z.R. Generation of two-dimensional concentration-gradient droplet arrays on a two-layer chip for screening of protein crystallization conditions. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2015, 18, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Maruyama, M.; Yoshimura, M.; Okada, S.; Yoshikawa, H.Y.; Sugiyama, S.; Adachi, H.; Matsumura, H.; Inoue, T.; Takano, K.; et al. Spiral growth can enhance both the normal growth rate and quality of tetragonal lysozyme crystals grown under a forced solution flow. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 2137–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Ching, C.B. Toward further understanding of lysozyme crystallization: Phase diagram, protein–protein interaction, nucleation kinetics, and growth kinetics. Cryst. Growth Des. 2010, 10, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikumar, M.V.; Glatz, C.E.; Larson, M.A. Lysozyme crystal growth and nucleation kinetics. J. Cryst. Growth 1998, 187, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielasi, F.S.; Hirtz, M.; Sekula-Neuner, S.; Laue, T.; Fuchs, H.; Willaert, R.G. Dip-Pen Nanolithography-Assisted Protein Crystallization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 137, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akella, S.V.; Mowitz, A.; Heymann, M.; Fraden, S. Emulsion-Based Technique To Measure Protein Crystal Nucleation Rates of Lysozyme. Cryst. Growth Des. 2014, 14, 4487–4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugebauer, P.; Khinast, J.G. Continuous Crystallization of Proteins in a Tubular Plug-Flow Crystallizer. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, R. An osmolyte-based micro-volume ultrafiltration technique. Lab. Chip 2014, 14, 4559–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Görisch, H. Drop dialysis: Time course of salt and protein exchange. Anal. Biochem. 1988, 173, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghosh, R. Membrane-Based Micro-Volume Dialysis Method for Rapid and High-Throughput Protein Crystallization. Processes 2023, 11, 2148. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072148
Ghosh R. Membrane-Based Micro-Volume Dialysis Method for Rapid and High-Throughput Protein Crystallization. Processes. 2023; 11(7):2148. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072148
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhosh, Raja. 2023. "Membrane-Based Micro-Volume Dialysis Method for Rapid and High-Throughput Protein Crystallization" Processes 11, no. 7: 2148. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072148
APA StyleGhosh, R. (2023). Membrane-Based Micro-Volume Dialysis Method for Rapid and High-Throughput Protein Crystallization. Processes, 11(7), 2148. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072148





