Design of Polymeric Membranes for Air Separation by Combining Machine Learning Tools with Computer Aided Molecular Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Rough Set Machine Learning (RSML)
1.2. Computer-Aided Molecular Design (CAMD)
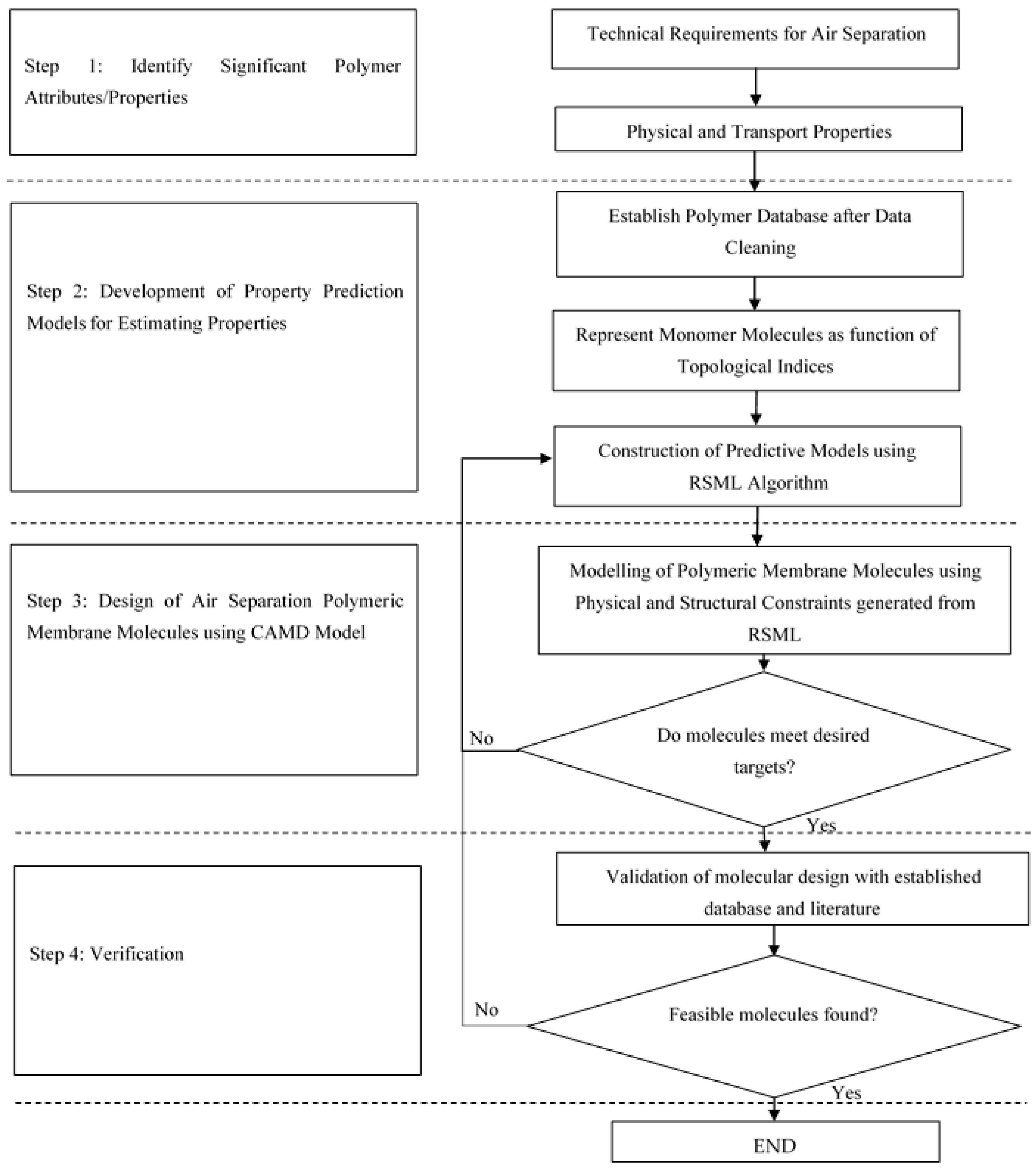
2. Methodology
- Step 1: Polymer attributes/properties identification
- Step 2: Development of property prediction models for estimating properties
- Step 2.1: Database and properties classification
- Step 2.2: Representation of monomer molecules using topological indices
- Step 2.3: Construction of predictive models using RSML
- Rule 1: (C1 < 6.8) → (D1 = 1)
- Rule 2: (C2 ≥ 6.85) → (D1 = 2)
- Rule 3: (C2 ≥ 4.15) → (D1 = 2)
- Step 3: Design of air separation polymeric membrane molecules using CAMD model
- Step 3.1: Formulation of structural constraints
- Step 3.2: Modelling of Air Separation Polymeric Membrane Molecule
- Step 3.3: Incorporation of physical constraints in CAMD modelling
- Step 4: Verification
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Development of Predictive Models Using RSML
3.1.1. Cores and Reducts Generation
3.1.2. Rules Generated from Reducts
3.1.3. Evaluation of Model Performance and Scientific Coherency of Rules Generated
3.2. Generated Air Separation Polymer Molecules
3.2.1. Non-Convexity in CAMD Modelling
3.2.2. CAMD Model with Linearised Connectivity Index Terms
3.3. Verification of Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Symbol | Description |
| 0 | Zeroth Order Connectivity (Chi) Index |
| 0 | Zeroth Order Valence Connectivity (Chi) Index |
| 1 | First Order Connectivity (Chi) Index |
| 1 | First Order Valence Connectivity (Chi) Index |
| Number of sigma electrons in the hydrogen suppressed graph | |
| Number of valence electrons | |
| Number of edges in the molecules with bond s terminates on vertices i and j | |
| 1 | First Order Kappa Shape Index |
| 2 | Second Order Kappa Shape Index |
| 3 | Third Order Kappa Shape Index |
| 1 | First Order Kappa Alpha Shape Index |
| 2 | Second Order Kappa Alpha Shape Index |
| 3 | Third Order Kappa Alpha Shape Index |
| Φ | Kappa Flexibility Index |
| Binary variable that indicates if ith position is occupied by kth group | |
| Binary variable that indicates if ith group is attached to pth group via jth site |
Appendix A. Example of Information Table
| Decision Attribute | Condition Attributes | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tag | Polymer | PO2 (Class) | E-States Index | Kappa Order 1 | Kappa Order 2 | Kappa Order 3 | Kappa Alpha Order 1 | Kappa Alpha Order 2 | Kappa Alpha Order 3 | Kappa Flexibility Index | ||||
| 1 | Poly[l-(trimethylsilyl)-1-propyne] | 2 | 5.91 | 6.50 | 3.06 | 6.00 | 13.69 | 7.00 | 2.34 | 6.00 | 7.08 | 2.40 | 6.08 | 2.43 |
| 2 | Poly(tert-butylacetylene) | 2 | 5.21 | 2.91 | 2.56 | 1.06 | 15.42 | 6.00 | 1.63 | 5.33 | 5.56 | 1.34 | 4.95 | 1.24 |
| 3 | Poly(1-n-heptyl-propyne) | 2 | 7.66 | 7.24 | 4.91 | 4.31 | 26.95 | 10.00 | 9.00 | 9.14 | 9.56 | 8.56 | 8.71 | 8.18 |
| 4 | Poly[o-(trimethylsilyl)phenylacetylene] | 2 | 9.19 | 8.89 | 5.55 | 7.62 | 24.96 | 10.08 | 3.81 | 2.49 | 9.39 | 3.35 | 2.14 | 2.62 |
| 5 | Poly(1-chloro-2-n-butylacetylene) | 2 | 5.54 | 5.26 | 3.41 | 2.88 | 15.61 | 7.00 | 6.00 | 6.00 | 6.84 | 5.84 | 5.84 | 5.71 |
| 6 | Poly(1-chloro-2-n-hexylacetylene) | 2 | 6.95 | 6.67 | 4.41 | 3.88 | 21.51 | 9.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 8.84 | 7.84 | 7.84 | 7.71 |
| 7 | Poly(1-chloro-2-n-octylacetylene) | 2 | 8.36 | 8.08 | 5.41 | 4.88 | 27.28 | 11.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.84 | 9.84 | 9.84 | 9.70 |
| 8 | Poly[o-(trifluoromethyl)phenylacetylene] | 2 | 9.19 | 6.02 | 5.55 | 3.18 | 18.07 | 10.08 | 3.81 | 2.49 | 8.68 | 2.91 | 1.81 | 2.10 |
| 9 | Poly(1-n-hexyl-2-phenylacetylene) | 2 | 10.06 | 8.92 | 6.93 | 5.47 | 30.95 | 12.07 | 8.32 | 6.19 | 10.86 | 7.21 | 5.20 | 5.59 |
| 10 | Poly(1-ethyl-2-phenylacetylene) | 2 | 7.23 | 6.09 | 4.93 | 3.47 | 19.42 | 8.10 | 4.76 | 3.11 | 6.89 | 3.74 | 2.29 | 2.58 |
| 11 | Poly(1-phenyl-1-propyne) | 1 | 6.53 | 5.39 | 4.43 | 2.91 | 16.53 | 7.11 | 3.92 | 2.38 | 5.91 | 2.94 | 1.62 | 1.93 |
| 12 | Poly(1-chloro-2-phenylacetylene) | 1 | 6.53 | 5.52 | 4.43 | 2.98 | 13.97 | 7.11 | 3.92 | 2.38 | 6.19 | 3.16 | 1.79 | 2.17 |
| 13 | Poly(oxydimethylsilylene) | 2 | 8.41 | 9.14 | 4.27 | 9.17 | 25.28 | 10.00 | 2.94 | 5.53 | 10.70 | 3.40 | 6.20 | 3.64 |
| 14 | Hydrogenated Polybutadiene | 2 | 3.41 | 2.57 | 1.91 | 1.15 | 9.65 | 4.00 | 3.00 | 4.00 | 3.48 | 2.48 | 4.56 | 2.16 |
| 15 | Poly(1,3-butadiene) | 2 | 3.41 | 2.57 | 1.91 | 1.15 | 9.65 | 4.00 | 3.00 | 4.00 | 3.48 | 2.48 | 4.56 | 2.16 |
| 16 | Polyisoprene (NR) | 2 | 5.00 | 3.70 | 3.49 | 2.39 | 11.67 | 5.00 | 2.25 | 4.00 | 4.48 | 1.77 | 3.48 | 1.58 |
| 17 | Polychloroprene | 1 | 3.70 | 3.63 | 2.39 | 2.12 | 13.78 | 5.00 | 2.25 | 4.00 | 4.77 | 4.77 | 3.77 | 1.94 |
| 18 | Polystyrene | 1 | 5.40 | 4.67 | 3.97 | 3.02 | 16.67 | 6.13 | 3.11 | 1.80 | 5.10 | 2.31 | 1.21 | 1.48 |
Appendix B. List of First-Order Groups
| First-Order Groups | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| CH3 | CH=CH2 | COOH | CH=O |
| CF | CCl | CH2OH | C=ONH2 |
| CH3Si | COO | -O- | CH2 |
Appendix C. Rules Filtered from Validation Dataset
| Glass Transition Temperature (Tg) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rule | Decision | Strength | Coverage | Certainty |
| and Kappa Alpha Order 3 < 2.35 | Class 2 | 24% | 50% | 100% |
| and Kappa Order 3 < 2.98 | Class 2 | 24% | 50% | 100% |
| and Kappa Alpha Order 2 < 3.43 | Class 2 | 24% | 50% | 100% |
| 2.94 and Kappa Alpha Order 3 < 2.35 | Class 2 | 24% | 50% | 100% |
| 2.94 and Kappa Order 2 < 3.861 | Class 2 | 24% | 50% | 100% |
| 2.94 and Kappa Order 3 < 2.98 | Class 2 | 24% | 50% | 100% |
| E-state Index 10.17 and Kappa Flexibility Index from 1.08 to 2.32 | Class 2 | 34% | 57% | 80% |
| Molar Volume (Vm) | ||||
| Kappa Alpha Order 2 7.03 | Class 2 | 10.71% | 13.64% | 100% |
| Kappa Alpha Order 2 from 5.27 to 6.4 | Class 2 | 7.14% | 9.09% | 100% |
| Kappa Alpha Order 2 4.89 and Kappa Alpha Order 3 from 3.96 to 6.31 | Class 2 | 7.14% | 9.09% | 100% |
| Kappa Alpha Order 2 from 3.85 to 4.69 | Class 2 | 17.86% | 18.18% | 80% |
| Kappa Alpha Order 2 2.96 and Kappa Alpha Order 3 3.19 | Class 2 | 21.43% | 27.27% | 100% |
| Kappa Alpha Order 2 2.40 and Kappa Alpha Order 3 1.92 | Class 2 | 42.86% | 50% | 91.67% |
| Kappa Alpha Order 3 from 5.16 to 6.31 | Class 2 | 3.57% | 4.55% | 100% |
| Kappa Flexibility Index 6.65 | Class 2 | 10.71% | 13.64% | 100% |
| Kappa Flexibility Index from 3.66 to 4.45 | Class 2 | 17.86% | 18.18% | 80% |
| Kappa Alpha Order 3 from 3.96 to 6.31 and Kappa Flexibility Index 4.66 | Class 2 | 3.57% | 4.55% | 100% |
| Kappa Alpha Order 3 3.19 and Kappa Flexibility Index 2.54 | Class 2 | 7.14% | 9.09% | 100% |
| Kappa Alpha Order 3 from 1.19 to 1.92 and Kappa Flexibility Index 1.67 | Class 2 | 35.71% | 45.45% | 100% |
| 7.76 | Class 2 | 25% | 31.82% | 100% |
| from 5.61 to 6.56 | Class 2 | 28.56% | 36.36% | 100% |
| from 5.16 to 5.32 | Class 2 | 3.57% | 4.55% | 100% |
| from 5.56 to 5.59 | Class 2 | 7.14% | 9.09% | 100% |
| 3.98 and Kappa Alpha Order 2 < 5.17 | Class 2 | 39.29% | 45.45% | 90.9% |
| Class 2 | 32.14% | 36.36% | 88.89% | |
| from 3.98 to 5.65 and Kappa Alpha Order 3 3.96 | Class 2 | 7.14% | 9.09% | 100% |
| 3.98 and Kappa Alpha Order 3 < 3.93 | Class 2 | 57.14% | 63.64% | 87.5% |
| from 3.24 to 3.68 and Kappa Alpha Order 3 3.51 | Class 2 | 3.57% | 4.55% | 100% |
| from 3.96 to 4.71 and Kappa Alpha Order 3 1.32 | Class 2 | 21.43% | 22.72% | 83.33% |
| 3.98 and Kappa Flexibility Index < 4.85 | Class 2 | 67.86% | 77.27% | 89.47% |
| from 3.98 to 5.65 and E-state Index 25.58 | Class 2 | 17.86% | 18.18% | 80% |
| 3.98 and E-state Index < 25.42 | Class 2 | 32.14% | 36.36% | 88.89% |
| 3.24 and E-state Index from 13.25 to 15.5 | Class 2 | 3.57% | 4.55% | 100% |
| from 3.96 to 4.71 and Kappa Alpha Order 1 5.85 | Class 2 | 25% | 27.27% | 85.71% |
| from 4.76 to 5.65 | Class 2 | 10.71% | 13.64% | 100% |
| < 3.68 and Kappa Alpha Order 1 6.68 | Class 2 | 3.57% | 4.55% | 100% |
| 4.09 | Class 2 | 35.71% | 40.91% | 90% |
| from 3.05 to 3.54 | Class 2 | 28.57% | 31.82% | 87.5% |
| from 3.64 to 4.07 | Class 2 | 7.14% | 9.09% | 100% |
| E-state Index 25.58 and Kappa Alpha Order 2 from 2.96 to 6.4 | Class 2 | 32.14% | 36.36% | 88.89% |
| E-state Index from 14.42 to 25.42 and Kappa Alpha Order 2 from 2.76 to 3.46 | Class 2 | 17.86% | 18.18% | 80% |
| Kappa Alpha Order 2 from 2.4 to 2.5 | Class 2 | 3.57% | 4.55% | 100% |
| E-state Index 36.33 | Class 2 | 14.29% | 18.18% | 100% |
| E-state Index from 20.92 to 30.01 and Kappa Alpha Order 3 3.96 | Class 2 | 10.71% | 13.64% | 100% |
| E-state Index 30.42 and Kappa Alpha Order 3 5.16 | Class 2 | 3.57% | 4.55% | 100% |
| E-state Index from 14.42 to 15.08 | Class 2 | 3.57% | 4.55% | 100% |
| Kappa Alpha Order 3 from 1.32 to 1.92 | Class 2 | 35.71% | 45.45% | 100% |
| E-state Index 27.39 and Kappa Flexibility Index from 2.06 to 6.36 | Class 2 | 25% | 27.27% | 85.71% |
| E-state Index from 20.92 to 27.25 and Kappa Flexibility Index from 1.71 to 3.21 | Class 2 | 7.14% | 9.09% | 100% |
| E-state Index 13.25 and Kappa Flexibility Index from 3.66 to 4.85 | Class 2 | 17.86% | 18.18% | 80% |
| Kappa Flexibility Index from 4.86 to 6.36 | Class 2 | 3.57% | 4.55% | 100% |
| E-state Index from 13.81 to 18.63 and Kappa Flexibility Index from 1.67 to 2.17 | Class 2 | 7.14% | 9.09% | 100% |
| E-state Index from 25.58 to 30.31 and Kappa Order 1 7.06 | Class 2 | 21.43% | 22.73% | 83.33% |
| E-state Index 30.42 and Kappa Order 1 6.06 | Class 2 | 25% | 31.82% | 100% |
| E-state Index from 17.67 to 24.43 and Kappa Order 1 7.06 | Class 2 | 32.14% | 36.36% | 88.89% |
| E-state Index < 15.5 and Kappa Order 1 6.06 | Class 2 | 7.14% | 9.09% | 100% |
| E-state Index < 25.42 and Kappa Order 1 8.05 | Class 2 | 17.86% | 18.18% | 80% |
| E-state Index from 25.58 to 30.31 and Kappa Order 2 4.23 | Class 2 | 17.86% | 18.18% | 80% |
| E-state Index 30.42 and Kappa Order 2 3.22 | Class 2 | 25% | 31.82% | 100% |
| E-state Index from 15.5 to 22.64 and Kappa Order 2 from 3.22 to 4.15 | Class 2 | 21.43% | 27.27% | 100% |
| Kappa Order 2 7.82 | Class 2 | 7.14% | 9.09% | 100% |
| E-state Index 27.39 and Kappa Order 2 from 3.09 to 4.15 | Class 2 | 7.14% | 9.09% | 100% |
| E-state Index 30.42 and Kappa Order 3 3.06 | Class 2 | 17.86% | 22.72% | 100% |
| E-state Index 15.5 and Kappa Order 3 5.36 | Class 2 | 3.57% | 4.55% | 100% |
| E-state Index from 13.81 to 15.5 and Kappa Order 3 3.92 | Class 2 | 3.57% | 4.55% | 100% |
| E-state Index from 25.58 to 30.31 and Kappa Alpha Order 1 8.04 | Class 2 | 17.86% | 18.18% | 80% |
| E-state Index 30.42 and Kappa Alpha Order 1 5.85 | Class 2 | 25% | 31.82% | 100% |
| E-state Index from 18.63 to 24.43 and Kappa Alpha Order 1 6.98 | Class 2 | 17.86% | 18.18% | 80% |
| E-state Index < 18.63 and Kappa Alpha Order 1 from 5.85 to 7.52 | Class 2 | 10.71% | 13.64% | 100% |
| Kappa Order 2 from 5.16 to 6.98 and Kappa Alpha Order 3 3.96 | Class 2 | 7.14% | 9.09% | 100% |
| Kappa Order 2 3.97 and Kappa Alpha Order 3 3.19 | Class 2 | 17.86% | 22.72% | 100% |
| Kappa Order 2 from 3.16 to 3.93 and Kappa Alpha Order 3 < 2.3 | Class 2 | 28.57% | 31.82% | 87.5% |
| Kappa Order 2 4.23 and Kappa Alpha Order 3 3.93 | Class 2 | 17.86% | 18.18% | 80% |
| Kappa Order 2 7.32 and Kappa Alpha Order 3 6.82 | Class 2 | 10.71% | 13.64% | 100% |
| Kappa Order 2 from 3.09 to 3.16 and Kappa Alpha Order 3 1.32 | Class 2 | 3.57% | 4.55% | 100% |
| Kappa Order 2 <5.72 and Kappa Alpha Order 1 8.04 | Class 2 | 25% | 27.27% | 85.71% |
| Kappa Alpha Order 2 11.36 | Class 2 | 17.86% | 22.72% | 100% |
| Kappa Order 3 3.06 and Kappa Alpha Order 1 from 6.68 to 7.52 | Class 2 | 3.57% | 4.55% | 100% |
| Kappa Order 2 from 3.09 to 3.93 and Kappa Alpha Order 1 5.85 | Class 2 | 32.14% | 36.36% | 88.89% |
| Kappa Order 2 < 6.98 and Kappa Alpha Order 1 9.42 | Class 2 | 10.71% | 13.64% | 100% |
| Kappa Order 3 from 4.49 to 7.09 and Kappa Alpha Order 2 4.89 | Class 2 | 7.14% | 9.09% | 100% |
| Kappa Order 3 < 3.59 and Kappa Alpha Order 2 2.96 | Class 2 | 21.4% | 27.27% | 100% |
| Kappa Alpha Order 2 7.03 | Class 2 | 10.71% | 13.64% | 100% |
| Kappa Order 3 < 4.37 and Kappa Alpha Order 2 4.89 | Class 2 | 3.57% | 4.55% | 100% |
| Kappa Order 3 < 2.6 and Kappa Alpha Order 2 2.4 | Class 2 | 42.86% | 50% | 91.67% |
| Kappa Order 3 < 3.92 and Kappa Alpha Order 2 3.85 | Class 2 | 7.14% | 9.09% | 100% |
| Kappa Order 3 from 1.6 to 2.6 and Kappa Flexibility Index 1.67 | Class 2 | 35.71% | 45.45% | 100% |
| Kappa Order 3 from 5.36 to 7.09 | Class 2 | 7.14% | 9.09% | 100% |
| Kappa Order 3 from 3.06 to 3.59 | Class 2 | 7.14% | 9.09% | 100% |
| Cohesive Energy (Ecoh) | ||||
| and E-state Index < 13.81 | Class 1 | 23.5% | 57.14% | 100% |
| E-state Index < 10.75 | Class 1 | 23.5% | 57.14% | 100% |
| from 2.5 to 3.78 | Class 1 | 5.88% | 14.29% | 100% |
| Kappa Alpha Order 1 < 2.69 | Class 1 | 11.77% | 28.57% | 100% |
| < 4.7 and Kappa Alpha Order 2 1.73 | Class 1 | 11.77% | 28.57% | 100% |
| < 4.7 and Kappa Flexibility Index 1.57 | Class 1 | 11.77% | 28.57% | 100% |
| Kappa Order 3 3.25 and Kappa Flexibility Index from 1.52 to 2.33 | Class 1 | 11.77% | 28.57% | 100% |
| from 1.4 to 3.59 and E-state Index < 15.08 | Class 1 | 23.53% | 57.14% | 100% |
| from 1.4 to 2.13 | Class 1 | 11.77% | 28.57% | 100% |
| from 2.35 to 2.6 | Class 1 | 5.88% | 14.29% | 100% |
| < 3.59 and Kappa Alpha Order 2 from 1.73 to 2.57 | Class 1 | 17.65% | 42.86% | 100% |
| E-state Index < 13.81 and Kappa Order 1 3.1 | Class 1 | 23.53% | 57.14% | 100% |
| < 2.6 and Kappa Flexibility Index 1.57 | Class 1 | 11.77% | 28.57% | 100% |
| E-state Index from 11.33 to 13.81 | Class 1 | 11.77% | 28.57% | 100% |
| E-state Index < 13.81 and Kappa Alpha Order 1 2.72 | Class 1 | 23.53% | 57.14% | 100% |
| E-state Index < 13.81 and Kappa Alpha Order 2 1.73 | Class 1 | 11.77% | 28.57% | 100% |
| E-state Index < 20.92 and Kappa Alpha Order 3 3.42 | Class 1 | 11.77% | 28.57% | 100% |
| E-state Index < 13.81 and Kappa Flexibility Index 1.57 | Class 1 | 11.77% | 28.57% | 100% |
| E-state Index < 13.81 and Kappa Flexibility Index 1.52 | Class 1 | 23.53% | 57.14% | 100% |
| from 1.85 to 2.73 | Class 1 | 17.65% | 42.86% | 100% |
| < 1.07 | Class 1 | 11.77% | 28.57% | 100% |
| O2 Permeability | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rule | Decision | Strength | Coverage | Certainty |
| from 4.63 to 5.08 | Class 2 | 5.56% | 20% | 100% |
| from 4.55 to 4.62 | Class 2 | 5.56% | 20% | 100% |
| from 2.71 to 2.78 | Class 2 | 5.56% | 20% | 100% |
| from 2.92 to 3.12 | Class 2 | 5.56% | 20% | 100% |
| from 5.84 to 6.13 | Class 2 | 5.56% | 20% | 100% |
| E-state Index < 18.24 and Kappa Order 3 4.67 | Class 2 | 11.11% | 40% | 100% |
| Kappa Order 3 from 5.43 to 6.28 | Class 2 | 5.56% | 20% | 100% |
| Kappa Alpha Order 1 from 5.52 to 5.75 | Class 2 | 5.56% | 20% | 100% |
| Kappa Alpha Order 2 from 2.94 to 3.02 | Class 2 | 5.56% | 20% | 100% |
| Kappa Alpha Order 3 from 4.87 to 5.51 | Class 2 | 5.56% | 20% | 100% |
| O2/N2 Selectivity | ||||
| 9.92 | Class 2 | 25% | 42.86% | 75% |
| from 6.26 to 6.61 and Kappa Alpha Order 2 2.94 | Class 2 | 6.25% | 14.29% | 100% |
| 9.99 | Class 2 | 6.25% | 14.29% | 100% |
| 6.16 | Class 2 | 25% | 42.86% | 75% |
| from 6.08 to 7.58 | Class 2 | 12.5% | 28.57% | 100% |
| E-state Index from 22.09 to 23.82 | Class 2 | 12.5% | 28.57% | 100% |
| E-state Index 31.88 | Class 2 | 12.5% | 28.57% | 100% |
| Kappa Order 1 12.22 | Class 2 | 12.5% | 28.57% | 100% |
| Kappa Order 2 from 6.12 to 7.84 | Class 2 | 6.25% | 14.29% | 100% |
| Kappa Order 2 from 0.67 to 1.48 | Class 2 | 6.25% | 14.29% | 100% |
| Kappa Order 3 < 2.3 and Kappa Alpha Order 2 2.38 | Class 2 | 6.25% | 14.29% | 100% |
| Kappa Order 3 < 3.83 and Kappa Alpha Order 2 from 0.67 to 1.77 | Class 2 | 6.25% | 14.29% | 100% |
| Kappa Order 3 < 3.83 and Kappa Alpha Order 2 4.03 | Class 2 | 6.25% | 14.29% | 100% |
| Kappa Alpha Order 1 11.34 | Class 2 | 12.5% | 28.57% | 100% |
| Kappa flexibility Index from 3.8 to 5.55 | Class 2 | 6.25% | 14.29% | 100% |
| Kappa flexibility Index from 1.7 to 1.85 | Class 2 | 6.25% | 14.29% | 100% |
| Kappa flexibility Index from 2.72 to 3.32 | Class 2 | 6.25% | 14.29% | 100% |
References
- Gas Separation Membrane Market (2023–2032). The Business Research Company. 2023. Available online: https://www.openpr.com/news/3068812/gas-separation-membrane-market-2023-2032-top-companies (accessed on 7 June 2023).
- Lasseuguette, E.; Comesaña-Gándara, B. Polymer Membranes for Gas Separation. Membranes 2022, 12, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murali, R.S.; Sankarshana, T.; Sridhar, S. Air separation by polymer-based membrane technology. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2013, 42, 130–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, K.C.; Lai, S.O.; Thiam, H.S.; Teoh, H.C.; Heng, S.L. Recent progress of oxygen/nitrogen separation using membrane technology. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2016, 11, 1016–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, J. What Is Machine Learning? In Machine Learning and the City; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Banbi, A.; Alzahabi, A.; El-Maraghi, A. Artificial Neural Network Models for PVT Properties. PVT Prop. Correl. 2018, 225–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyebi, A.; Alshami, A.S.; Yu, X.; Kolodka, E. Can machine learning methods guide gas separation membranes fabrication? J. Membr. Sci. Lett. 2022, 2, 100033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrycz, W.; Succi, G. Genetic granular classifiers in modeling software quality. J. Syst. Softw. 2005, 76, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, L.; Grzvmala-Busse, L.; Slowinski, R.; Ziarko, W. Rough Sets. Commun ACM 1995, 38, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviso, K.B.; Janairo, J.I.B.; Promentilla, M.A.B.; Tan, R.R. Prediction of CO2 storage site integrity with rough set-based machine learning. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2019, 21, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Chen, W.; Wu, B.; Chen, C.; Liu, W. A building energy consumption prediction model based on rough set theory and deep learning algorithms. Energy Build. 2021, 240, 110886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, Y.P.; Lee, H.Y.; Chong, J.W.; Tan, R.R.; Aviso, K.B.; Chemmangattuvalappil, N.G. Incorporating Machine Learning in Computer-Aided Molecular Design for Fragrance Molecules. Processes 2022, 10, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.W.; Ng, L.Y.; Aboagwa, O.A.; Thangalazhy-Gopakumar, S.; Muthoosamy, K.; Chemmangattuvalappil, N.G. Computer-Aided Framework for the Design of Optimal Bio-Oil/Solvent Blend with Economic Considerations. Processes 2021, 9, 2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, Z. Rough set approach to knowledge-based decision support. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1997, 99, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, Z. Rough sets, decision algorithms and Bayes’ theorem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 136, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churi, N.; Achenie, L.E.K. Novel Mathematical Programming Model for Computer Aided Molecular Design. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1996, 35, 3788–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Mcbride, K.; Zhang, X.; Qi, Z.; Sundmacher, K. Integrated solvent and process design exemplified for a Diels–Alder reaction. AIChE J. 2015, 61, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, P.M.; Gani, R.; Kolar, P.; Ishikawa, T. Computer-aided molecular design with combined molecular modeling and group contribution. Fluid Phase Equilib. 1999, 158–160, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Fan, T.; Sun, X.; Hao, Y.; Cui, X.; Zhao, L.; Ren, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhong, R.; Peng, Y. In Silico Prediction of O6-Methylguanine-DNA Methyltransferase Inhibitory Potency of Base Analogs with QSAR and Machine Learning Methods. Molecules 2018, 23, 2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Cheng, H. Computer-aided biocompatible solvent design for an integrated extractive fermentation–separation process. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 809–820. [Google Scholar]
- Ooi, J.; Ng, D.K.S.; Chemmangattuvalappil, N.G. Optimal molecular design towards an environmental friendly solvent recovery process. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2018, 117, 391–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffczyk, J.; Fleitmann, L.; Schwarz, A.; Lampe, M.; Bardow, A.; Leonhard, K. COSMO-CAMD: A framework for optimization-based computer-aided molecular design using COSMO-RS. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 159, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, Q.Y.; Hassim, M.H.; Chemmangattuvalappil, N.G.; Ten, J.Y.; Raslan, R. Optimization of quality, safety and health aspects in personal care product preservative design. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 157, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyanarayana, K.C.; Abildskov, J.; Gani, R.A. Computer-aided polymer design using group contribution plus property models. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2009, 33, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Chai, S.; Zhang, L.; Du, J. Computer-Aided Design of Crosslinked Polymer Membrane Using Machine Learning and Molecular Dynamics. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2022, 95, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Mao, H.; Liu, L.; Du, J.; Gani, R. A machine learning based computer- aided molecular design/screening methodology for fragrance molecules. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2018, 115, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, Y.J.; Aung, K.N.G.; Chong, J.W.; Tan, R.R.; Aviso, K.B.; Chemmangattuvalappil, N.G. Design of fragrance molecules using computer-aided molecular design with machine learning. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2022, 157, 107585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnapany, K.T.; Wong, C.Y.; Tan, F.K.; Chong, J.W.; Tan, R.R.; Aviso, K.B.; Janairo, J.I.B.; Chemmangattuvalappil, N.G. Design of fragrant molecules through the incorporation of rough sets into computer-aided molecular design. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2020, 5, 1391–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemmangattuvalappil, N.G. Development of solvent design methodologies using computer-aided molecular design tools. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2020, 27, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Mao, H.; Liu, Q.; Gani, R. Chemical product design–recent advances and perspectives. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2020, 27, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlacher, T.; Wessling, M. Gas–Gas Separation by Membranes. In Progress in Filtration and Separation; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 557–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, N.; Cui, X.; Yan, W.; Su, J.; Jin, L. A Review on the Morphology and Material Properties of the Gas Separation Membrane: Molecular Simulation. Membranes 2022, 12, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicerano, J. Prediction of Polymer Properties; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenhofer, M.; Arreguin, S.; Wong, J. Neurogastroenterology and Motility; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Van Krevelen, D.W.; Nijenhuis, K.T. Chapter 1—Polymer Properties. In Properties of Polymers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, L.; Xu, J. A simple method for prediction of gas permeability of polymers from their molecular structure. Polym. J. 1991, 23, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M. Membrane Separation of Gaseous Hydrocarbons by Semicrystalline Multiblock Copolymers: Role of Cohesive Energy Density and Crystallites of the Polyether Block. Polymers 2021, 13, 4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koros, W.J.; Mahajan, R. Pushing the limits on possibilities for large scale gas separation: Which strategies? J. Memb. Sci. 2000, 175, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanciuc, O. Electrotopological State Indices; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 85–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, L.H.; Kier, L.B. The Molecular Connectivity Chi Indexes and Kappa Shape Indexes in Structure-Property Modeling. Rev. Comput. Chem. 2007, 2, 367–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calibration, M.; Kier, L.B. I21 Index of Molecular Flexibility from Kappa Shape Attributes. Comput. Chem. 1989, 8, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T. User’s Guide for T. E. S. T. (Toxicity Estimation Software Tool) Version 5.1 A Java Application to Estimate Toxicities and Physical Properties from Molecular Structure; US Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2020.
- Prędki, B.; Słowiński, R.; Stefanowski, J.; Susmaga, R.; Wilk, S. ROSE—Software implementation of the rough set theory. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; Volume 1424, pp. 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagramanov, G.; Gurkin, V.; Farnosova, E. Physical and Mechanical Properties of Hollow Fiber Membranes and Technological Parameters of the Gas Separation Process. Membranes 2021, 11, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslick, J.C.; Ye, Q.; Park, J.; Topp, E.M.; Spencer, P.; Camarda, K.V. A computational molecular design framework for crosslinked polymer networks. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2009, 33, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E.; Martinho, A.; Matos, H.A.; Gani, R. Combined group-contribution and atom connectivity index-based methods for estimation of surface tension and viscosity. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res 2008, 47, 7940–7954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Lin, Y. Correlation between the glass transition temperatures and repeating unit structure for high molecular weight polymers. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2003, 43, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, J.R. Polymer Science and Technology, 3rd ed.; Pearson: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sulchek, T.A.; Friddle, R.W.; Noy, A. Counting and Breaking Single Bonds: Dynamic Force Spectroscopy in Tethered Single Molecule Systems. In Handbook of Molecular Force Spectroscopy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 251–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.P. Polymer Chemistry: An Introduction, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Mark, J.E. Polymer Data Polymer Data. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 655–657. [Google Scholar]
- AlMaadeed, M.A.; Ouederni, M.; Khanam, P.N. Effect of chain structure on the properties of Glass fibre/polyethylene composites. Mater. Des. 2013, 47, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.D.; Bae, C. Transition Metal-Catalyzed Functionalization of Polyolefins Containing CC, CC, and CH Bonds. In Advances in Organometallic Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 64, pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearle, J.W.S. Textile Fibers: A Comparative Overview. In Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 9100–9116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Polymer | Conditional Attributes | Decision Attribute | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | D1 | |
| P1 | 5.9 | 6.5 | 3.1 | 1 |
| P2 | 5.2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| P3 | 7.7 | 7.2 | 4.9 | 2 |
| P4 | 9.2 | 8.9 | 5.6 | 2 |
| P5 | 5.5 | 5.3 | 3.4 | 1 |
| Rule | Kappa Order 3 | Kappa Alpha Order 2 | Decision | Strength | Coverage (Recall) | Certainty (Precision) | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 5.432 to 11.545 | - | Class 1 (Selectivity < 4) | 13.51% | 29.41% | 100% | 83% |
| 10 | <3.828 | 0.671 to 1.773 | 4) | 10.81% | 20% | 100% | 60% |
| Rule | Decision | Strength | Coverage (Recall) | Certainty (Precision) | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.94 and Kappa Order 3 < 2.98 | Tg = Class 2 | 31% | 44% | 89% | 83% |
| 7.03, or Kappa Alpha Order 3 from 5.16 to 6.31 | Vm = Class 2 | 42.3% | 50% | 100% | 85% |
| 2.5 and E-state Index < 13.81, or from 1.404 to 3.59 and E-state Index < 15.08, or 2.72 and E-state Index < 15.08 | Ecoh = Class 1 | 29.4% | 100% | 100% | 86% |
| 4.67, or from 4.63 to 5.08 | Permeability = Class 2 | 11.1% | 40% | 100% | 83% |
| Kappa Order 3 < 3.83 and Kappa Alpha Order 2 from 0.67 to 1.77, or Kappa Flexibility Index from 2.72 to 3.32 | Selectivity = Class 2 | 12.5% | 28.57% | 100% | 89% |
| Polymer Name | Poly(1-Hexene) | Poly(4-Methyl-1-Pentene) | Poly (5-Methyl-Hexene-1) | Poly(3-Chlorohexene) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monomer Molecular Structure | 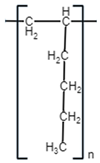 | 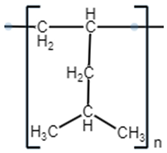 | 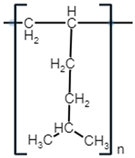 |  |
| Formula | C6H12 | C6H12 | C7H14 | C6H11Cl |
| CAS number | 592-41-6 | 691-37-2 | 3524-73-0 | 53101-38-5 |
| Structural Assumptions |
|
|
|
|
| TS [1] | 3 | 4 | 5 | 2 |
| O2 Permeability (Barrers) | 10 | 32.3 | 20 | Not available |
| O2 Selectivity | 2.6 | 4.225 | 2.5 | Not available |
| 4.406 | 4.992 | 5.698 | 5.698 | |
| 2.932 | 2.770 | 3.270 | 3.3081 | |
| 2.932 | 2.379 | 2.879 | 3.011 | |
| E-state index | 11.5 | 11.833 | 13.333 | 15.4444 |
| 1 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 7 |
| 2 | 5 | 3.2 | 4.167 | 4.167 |
| 3 | 5.333 | 5.333 | 6 | 3.840 |
| 1 | 5.740 | 5.740 | 6.740 | 7.026 |
| 2 | 4.740 | 2.951 | 3.915 | 4.192 |
| 3 | 5.105 | 5.105 | 5.740 | 3.867 |
| Φ | 4.535 | 2.824 | 3.769 | 4.208 |
| Tg (K) | 223 | 302 | 259 | Not available |
| Vm (cm3/mol) | 97.9 | 235 | 139.6 | Not available |
| Ecoh (J/mol) | 13,000 | 26,160 | 7900 | Not available |
| Literature TS (MPa) | 39 | 28 | 40 | Not available |
| Polymer Name | Polycarbonate | Polyphenylene Oxide | Polymethyl Methacrylate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monomer Molecular Structure | 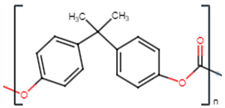 | 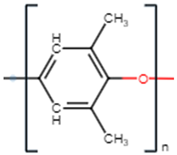 |  |
| Formula | C15H16O2 | C8H8O | C5O2H8 |
| CAS number | 25037-45-0 | 25134-01-4 | 9011-14-7 |
| Structural Assumptions |
|
|
|
| TS * | 1 | 7 | 6 |
| O2 Permeability (Barrers) | 1.5 | 16.8 | 20 |
| O2 Selectivity | 5.769 | 4.421 | 3.71 |
| 3.577 | 4.690 | 5.492 | |
| 1.732 | 3.450 | 3.189 | |
| 1.354 | 2.230 | 2.274 | |
| E-state index | 8.667 | 11.095 | 20.833 |
| 1 | 4 | 3.938 | 7 |
| 2 | 3.740 | 1.240 | 3.061 |
| 3 | 1.333 | 0.490 | 2.667 |
| 1 | 1.105 | 3.218 | 6.377 |
| 2 | 0 | 0.874 | 2.533 |
| 3 | 0 | 0.302 | 2.121 |
| Φ | 1.033 | 0.402 | 2.307 |
| Tg (K) | 423 | 488 | 378 |
| Vm (cm3/mol) | 320 | 76.6 | 89.3 |
| Ecoh (J/mol) | 14,400 | 33,300 | 27,700 |
| Literature TS (MPa) | 62.1 | 75 | 50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheun, J.-Y.; Liew, J.-Y.-L.; Tan, Q.-Y.; Chong, J.-W.; Ooi, J.; Chemmangattuvalappil, N.G. Design of Polymeric Membranes for Air Separation by Combining Machine Learning Tools with Computer Aided Molecular Design. Processes 2023, 11, 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072004
Cheun J-Y, Liew J-Y-L, Tan Q-Y, Chong J-W, Ooi J, Chemmangattuvalappil NG. Design of Polymeric Membranes for Air Separation by Combining Machine Learning Tools with Computer Aided Molecular Design. Processes. 2023; 11(7):2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072004
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheun, Jie-Ying, Joshua-Yeh-Loong Liew, Qian-Ying Tan, Jia-Wen Chong, Jecksin Ooi, and Nishanth G. Chemmangattuvalappil. 2023. "Design of Polymeric Membranes for Air Separation by Combining Machine Learning Tools with Computer Aided Molecular Design" Processes 11, no. 7: 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072004
APA StyleCheun, J.-Y., Liew, J.-Y.-L., Tan, Q.-Y., Chong, J.-W., Ooi, J., & Chemmangattuvalappil, N. G. (2023). Design of Polymeric Membranes for Air Separation by Combining Machine Learning Tools with Computer Aided Molecular Design. Processes, 11(7), 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11072004








