Investigation of the Antimicrobial and Physico-Mechanical Properties of Nature-Friendly Nanosilver-Loaded Pig Lining Leather Prepared Using Exhaustion Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis and Application of AgPBL to Pig Lining Leather
2.3. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activities of the Treated Pig Leather
- W: width of clear zone of inhibition, mm;
- T: total diameter of the test specimen and clear zone, mm;
- D: diameter of the test specimen, mm.
- R: the bacterial reduction percentage, %;
- Ct and Tt: the average number of colonies of three control samples and three test samples after 24 h, respectively, CFU/mL.
2.4. Characterization of the Treated Pig Leather
2.5. Physico-Mechanical Properties of the Treated Pig Leather
3. Results and Discussion
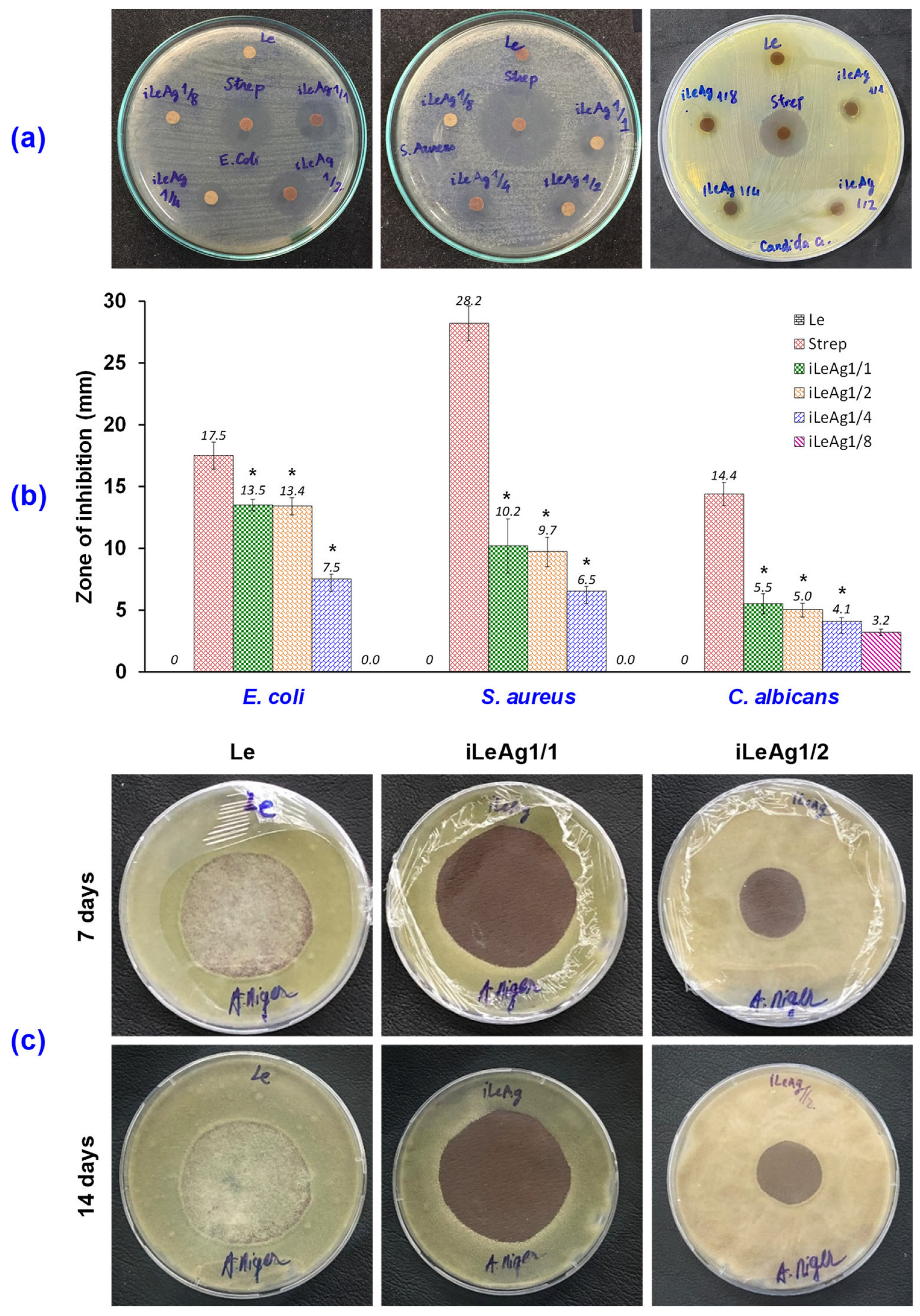
3.1. Antibacterial and Antifungal Efficacy of the AgPBL-Treated Pig Leather
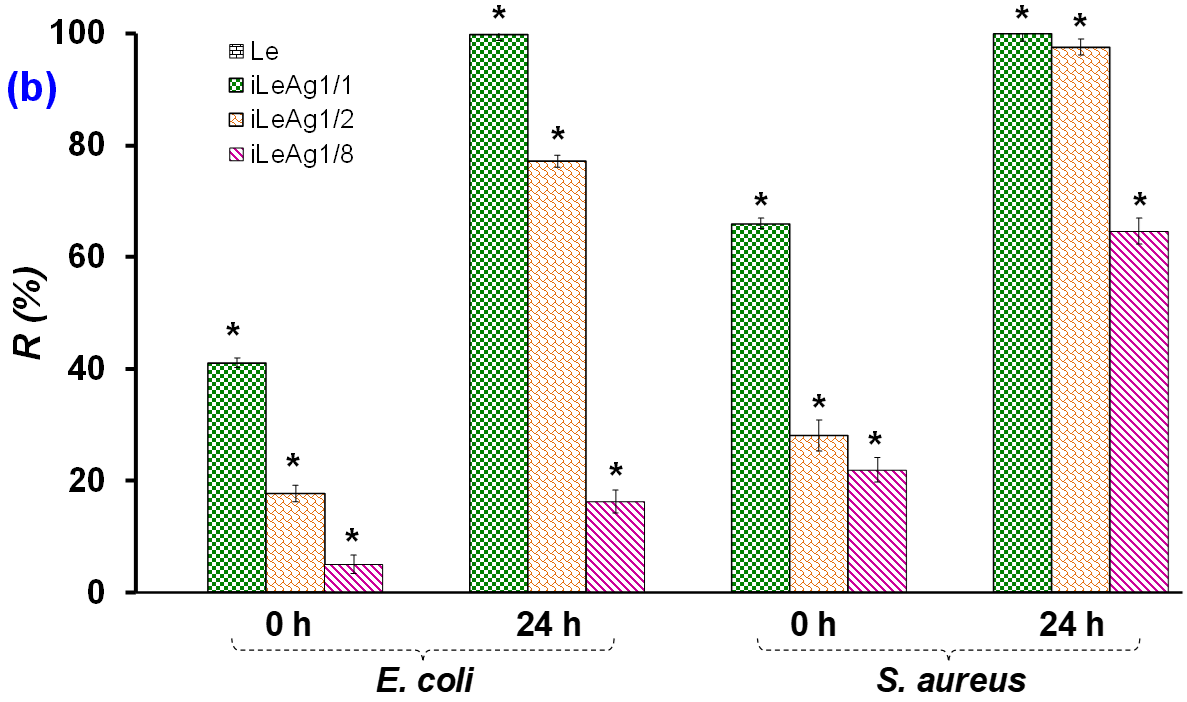
3.1.1. Antibacterial Efficacy
3.1.2. Antifungal Efficacy
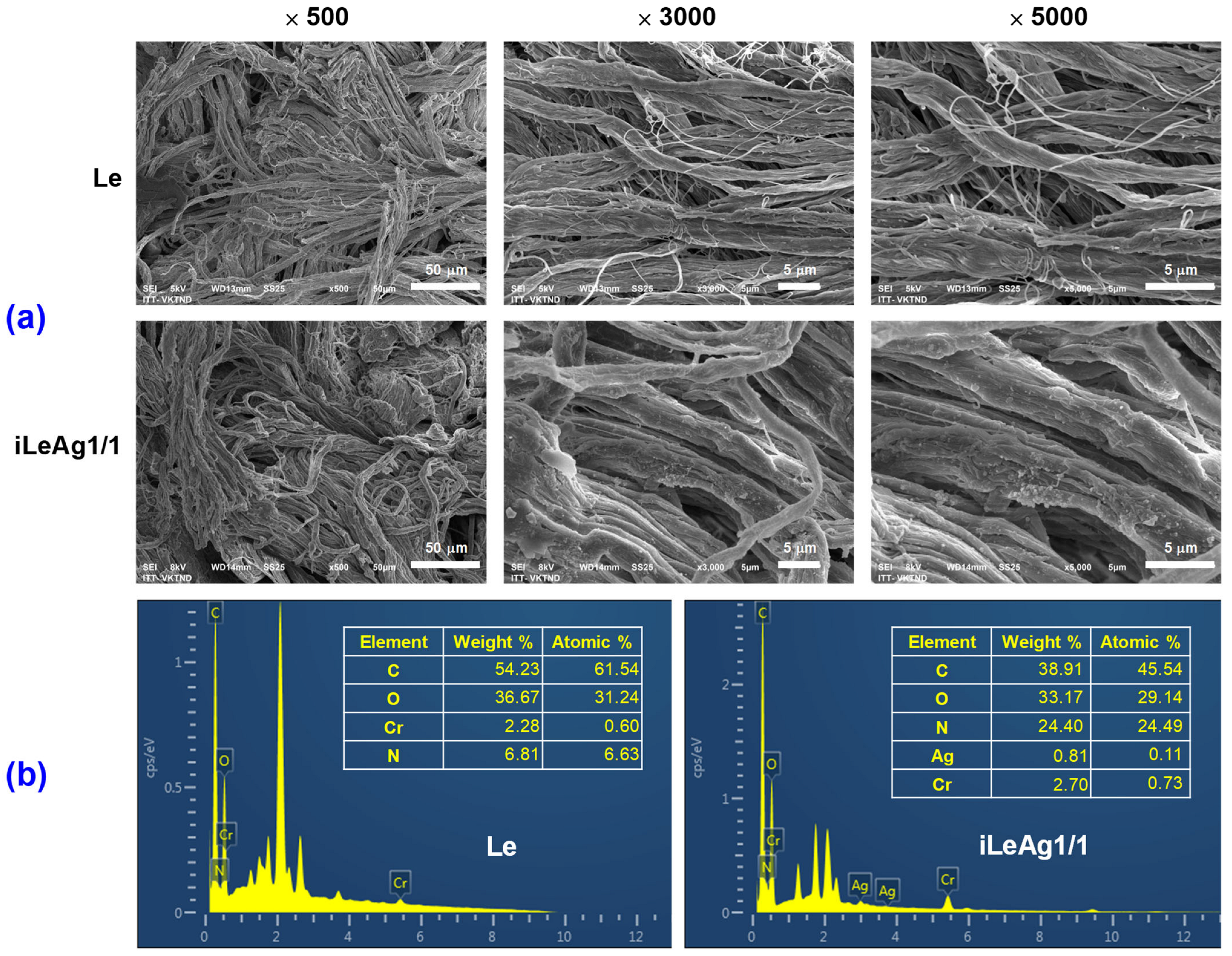
3.2. Coloration and Characteristics of the AgPBL-Treated Pig Leather
3.3. The Physico-Mechanical Properties of the AgPBL-Treated Pig Leather
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Healy, A.; Dunning, D.N.; Chockalingam, N. Materials used for footwear orthoses: A review. Footwear Sci. 2010, 2, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalyanya, K.M.; Rop, R.K.; Onyuka, A.S.; Birech, Z. A review of natural plants as sources of substances for cleaner leather tanning technologies. Text. Leather Rev. 2021, 4, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlita, A. Microbial biodeterioration of leather and its control: A review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2004, 53, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Azam, F.A.B.; Chowdhury, M. Quality assessment of shoe leather based on the properties of strength and comfort, collected from different footwear and leather industries in Bangladesh. Text. Leather Rev. 2021, 4, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Wang, X.; Zheng, M.; Yue, O.; Xie, L.; Zha, S.; Dong, S.; Li, T.; Song, Y.; Huang, M.; et al. Leather for flexible multifunctional bio-based materials: A review. J. Leather Sci. Eng. 2022, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Yang, L.; Hu, K.; Li, K.; Xiang, J.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y. Chromium Cross-Linking Based Immobilization of Silver Nanoparticle Coating on Leather Surface with Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Activity and Durability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 2352–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Wu, J.; Mu, C.; Wang, C.; Lin, W. Advances in Antimicrobial Polymer Coatings in the Leather Industry: A Comprehensive Review. J. Leather Sci. Eng. 2021, 60, 15004–15018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Ma, J.; Xu, Q. Insights into functional polymer-based organic-inorganic nanocomposites as leather finishes. J. Leather Sci. Eng. 2019, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ławińska, K.; Serweta, W.; Popovych, N.; Sieczyńska, K.; Decka, S.; Woźnicki, D.; Ogrodowczyk, D.; Rostocki, A.; Sprynskyy, M. Microbiological and chemical analysis of bamboo textile materials and leathers modified with bamboo extract at the tanning stage. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2021, 29, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Haiqi, G.; Li, K.; Xiang, J.; Lan, T.; Zhang, Z. Fabrication of silver nanoparticle sponge leather with durable antibacterial property. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 514, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lkhagvajav, N.; Koizhaiganova, M.; Yasa, I.; Çelik, E.; Sari, Ö. Characterization and antimicrobial performance of nano silver coatings on leather materials. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sportelli, M.C.; Picca, R.A.; Paladini, F.; Mangone, A.; Giannossa, L.C.; Di Franco, C.; Gallo, A.L.; Valentini, A.; Sannino, A.; Pollini, M. Spectroscopic characterization and nanosafety of Ag-modified antibacterial leather and leatherette. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou Elmaaty, T.; Sayed-Ahmed, K.; Mohamed Ali, R.; El-Khodary, K.; Abdeldayem, S.A. Simultaneous sonochemical coloration and antibacterial functionalization of leather with selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs). Polymers 2022, 14, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biškauskaitė, R.; Valeika, V. Wet Blue Enzymatic Treatment and Its Effect on Leather Properties and Post-Tanning Processes. Materials 2023, 16, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanikaivelan, P.; Rao, J.R.; Nair, B.U.; Ramasami, T. Progress and recent trends in biotechnological methods for leather processing. Trends Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, M.; Nanni, A.; Colonna, M. Recycling of Chrome-Tanned Leather and Its Utilization as Polymeric Materials and in Polymer-Based Composites: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, P.; Lee, S.-M.; Cho, M.; Park, J.-H.; Seo, S.-K.; Myung, H.; Bang, K.-S.; Oh, B.-T. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticle-coated fabric and leather against odor and skin infection causing bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 8179–8189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, H.; Hasanin, M.; Rehan, M. Enhancement of multifunctional properties of leather surface decorated with silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs). J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1234, 130130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Ma, L.; Su, H.; Xiong, J.; Li, K.; Xia, Q.; Liu, G. Layer-by-layer assembly of antibacterial composite coating for leather with cross-link enhanced durability against laundry and abrasion. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 458, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ara, K.; Hama, M.; Akiba, S.; Koike, K.; Okisaka, K.; Hagura, T.; Kamiya, T.; Tomita, F. Foot odor due to microbial metabolism and its control. Can. J. Microbiol. 2006, 52, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanlayavattanakul, M.; Lourith, N. Body malodours and their topical treatment agents. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2011, 33, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, B.; Chang, R.; Gao, D.; Ma, J. Chromium Footprint Reduction: Nanocomposites as Efficient Pretanning Agents for Cowhide Shoe Upper Leather. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5413–5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, P.; Cho, M.; Lee, S.-M.; Park, J.-H.; Bae, S.; Oh, B.-T. Antimicrobial fabrication of cotton fabric and leather using green-synthesized nanosilver. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 106, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, P.; Shim, J.; Bang, K.-S.; Oh, B.-T. Gold nanoparticles mediated coloring of fabrics and leather for antibacterial activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2016, 160, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohaeti, E.; Kasmudjiastuti, E.; Murti, R.; Dodi, I. Enhancement of antibacterial activity of suede leather through coating silver nanoparticles synthesized using Piper betle. Rasayan J. Chem. 2020, 13, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kate, S.; Sahasrabudhe, M.; Pethe, A. Biogenic Silver Nanoparticle Synthesis, Characterization and its Antibacterial activity against Leather Deteriorates. Jordan J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 13, 493–498. [Google Scholar]
- Koizhaiganova, M.; Yaşa, I.; Gülümser, G. Assessment of antibacterial activity of lining leather treated with silver doped hydroxyapatite. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 105, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelghany, T.M.; Al-Rajhi, A.M.H.; Al Abboud, M.A.; Alawlaqi, M.M.; Ganash Magdah, A.; Helmy, E.A.M.; Mabrouk, A.S. Recent Advances in Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Applications: About Future Directions. A Review. BioNanoScience 2018, 8, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadoun, S.; Arif, R.; Jangid, N.K.; Meena, R.K. Green synthesis of nanoparticles using plant extracts: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi Lan Huong, V.; Nguyen, N.T. Green synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles using Sapindus mukorossi fruit pericarp extract. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 42, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gour, A.; Jain, N.K. Advances in green synthesis of nanoparticles. Artif. Cell. Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, M.; Sadaf, I.; Rafique, M.S.; Tahir, M.B. A review on green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their applications. Artif. Cell. Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1272–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Yngard, R.A.; Lin, Y. Silver nanoparticles: Green synthesis and their antimicrobial activities. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 145, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.-T.; Liu, J.-H. A green method for in situ synthesis of poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan hydrogel thin films with entrapped silver nanoparticles. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 2827–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Munir, S.; Zeb, N.; Ullah, A.; Khan, B.; Ali, J.; Bilal, M.; Omer, M.; Alamzeb, M.; Salman, S.M.; et al. Green nanotechnology: A review on green synthesis of silver nanoparticles—An ecofriendly approach. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5087–5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.-T.; Vo, T.-L.-H. Fabrication of Silver Nanoparticles Using Cordyline fruticosa L. Leave Extract Endowing Silk Fibroin Modified Viscose Fabric with Durable Antibacterial Property. Polymers 2022, 14, 2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Kanchi, S.; Bisetty, K. Biogenic synthesis of nanoparticles: A review. Arabian J. Chem. 2019, 12, 3576–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharissova, O.V.; Dias, H.V.R.; Kharisov, B.I.; Pérez, B.O.; Pérez, V.M.J. The greener synthesis of nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alduraihem, N.S.; Bhat, R.S.; Al-Zahrani, S.A.; Elnagar, D.M.; Alobaid, H.M.; Daghestani, M.H. Anticancer and Antimicrobial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized from Pods of Acacia nilotica. Processes 2023, 11, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwana, H.; Alzahrani, T.; Alwahibi, M.S.; Aljowaie, R.M.; Aldehaish, H.A.; Alsaggabi, N.S.; Ramadan, R. Phytofabrication of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Potent Antifungal Activity against Phytopathogenic Fungi. Processes 2022, 10, 2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashiraj, K.N.; Nayaka, S.; Kumar, R.S.; Kantli, G.B.; Basavarajappa, D.S.; Gunagambhire, P.V.; Almansour, A.I.; Perumal, K. Rotheca serrata Flower Bud Extract Mediated Bio-Friendly Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles: Their Characterizations, Anticancer, and Apoptosis Inducing Ability against Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cell Line. Processes 2023, 11, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.H.; Bui, V.H.; Nguyen, N.T. Antibacterial Properties of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Piper betle L. Leaf Extract. Mater. Sci. Forum 2021, 1020, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.-T.; Vu, T.-H.; Bui, V.-H. Antibacterial and Antifungal Fabrication of Natural Lining Leather Using Bio-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles from Piper betle L. Leaf Extract. Polymers 2023, 15, 2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AATCC TM30; Test Method for Antifungal Activity, Assessment on Textile Materials: Mildew and Rot Resistance of Textile Materials. AATCC: Durham, NC, USA, 2017.
- AATCC TM90; Test Method for Antibacterial Activity of Textile Materials: Agar Plate. AATCC: Durham, NC, USA, 2016.
- ISO 16187:2013; Footwear and Footwear Components—Test Method to Assess Antibacterial Activity. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- ISO 20882:2007; Footwear—Performance Requirements for Components for Footwear—Lining and Insocks. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Yu, D. Synthesis of waterborne polyurethane–silver nanoparticle antibacterial coating for synthetic leather. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2018, 15, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, T.I.; Abd El Aty, A.A. In-situ green myco-synthesis of silver nanoparticles onto cotton fabrics for broad spectrum antimicrobial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 2121–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, I.; Lima, M.J.; Nobre, D.; Marques, S.M.; Castro, D.; Leite, T.R.; Henriques, M.; Duarte, F.; Ramalho, A.; Carvalho, S. Silver oxide coatings deposited on leathers to prevent diabetic foot infections. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 442, 128338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese Alex, K.; Tamil Pavai, P.; Rugmini, R.; Shiva Prasad, M.; Kamakshi, K.; Sekhar, K.C. Green Synthesized Ag Nanoparticles for Bio-Sensing and Photocatalytic Applications. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 13123–13129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Lim, B.; Skrabalak, S.E. Shape-Controlled Synthesis of Metal Nanocrystals: Simple Chemistry Meets Complex Physics? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 60–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almansob, A.; Bahkali, A.H.; Albarrag, A.; Alshomrani, M.; Binjomah, A.; Hailan, W.A.; Ameen, F. Effective treatment of resistant opportunistic fungi associated with immuno-compromised individuals using silver biosynthesized nanoparticles. Appl. Nanosci. 2022, 12, 3871–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Lu, J.; Liu, N.; Lu, W.; Li, Y.; Shang, C.; Li, X.; Hu, L.; Jiang, G. Antiviral Properties of Silver Nanoparticles against SARS-CoV-2: Effects of Surface Coating and Particle Size. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | AgPBL (μg/mL) | L* | a* | b* | ΔE* | Real Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Le | 0 | 62.42 | 9.77 | 23.86 | 0 |  |
| iLeAg1/1 | 160 | 57.28 | 9.6 | 22.08 | 2.39 |  |
| iLeAg1/2 | 80 | 57.72 | 9.78 | 22.22 | 2.23 |  |
| iLeAg1/4 | 40 | 59.28 | 9.73 | 22.74 | 1.51 |  |
| iLeAg1/8 | 20 | 59.75 | 9.65 | 23.31 | 1.19 |  |
| Sample | AgPBL (μg/mL) | Total Silver Content (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| Le | 0 | 0 |
| iLeAg1/1 | 160 | 513.3 ± 7.2 |
| No | Properties | Unit | Le | iLeAg1/1 | ISO 20882:2007 Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tear strength (ISO 17696) | N | 32 | 31.9 | lining ≥ 15 N |
| Compared to the pristine leather (Le) | % | 100.0 | 99.7 | ||
| Compared to ISO 20882:2007 | % | 213.3 | 212.7 | ||
| 2 | Abrasion resistance (ISO 17704) | cycles | Without hole through the thickness of the material component | 25,600 cycles dry 12,800 cycles wet | |
| 3 | Flex resistance (ISO 17694) | cycles | 15,000 cycles dry without visible damage | Dry 15,000 cycles without visible damage | |
| 4 | Lining water vapour permeability (ISO 17699) | mg/cm2·h | 3.13 | 3.56 | WVP of lining ≥ 2.0 mg/cm2·h |
| Compared to the pristine leather (Le) | % | 100.0 | 113.7 | ||
| Compared to ISO 20882:2007 | % | 156.0 | 178.0 | ||
| 5 | Lining water vapour absorption (ISO 17699) | mg/cm2 | 21.0 | 20.6 | WVA of lining ≥ 8.0 mg/cm2 |
| Compared to the pristine leather (Le) | % | 100.0 | 98.1 | ||
| Compared to ISO 20882:2007 | % | 263.0 | 257.5 | ||
| 6 | Lining water absorption (ISO 22649) | mg/cm2 | 54.1 | 53.6 | absorption ≥ 70 mg/cm2 |
| Compared to the pristine leather (Le) | % | 100.0 | 99.1 | ||
| Compared to ISO 20882:2007 | % | 90.1 | 89.0 | ||
| 7 | Lining water desorption (ISO 22649) | % | 97.1 | 96.8 | desorption ≥ 60% |
| Compared to the pristine leather (Le) | % | 100.0 | 99.7 | ||
| Compared to ISO 20882:2007 | % | 161.8 | 161.3 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, N.-T.; Vu, T.-H.; Bui, V.-H.; Phan, D.-N.; Nguyen, T.-H.; Nguyen, T.-M.-L. Investigation of the Antimicrobial and Physico-Mechanical Properties of Nature-Friendly Nanosilver-Loaded Pig Lining Leather Prepared Using Exhaustion Method. Processes 2023, 11, 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11071891
Nguyen N-T, Vu T-H, Bui V-H, Phan D-N, Nguyen T-H, Nguyen T-M-L. Investigation of the Antimicrobial and Physico-Mechanical Properties of Nature-Friendly Nanosilver-Loaded Pig Lining Leather Prepared Using Exhaustion Method. Processes. 2023; 11(7):1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11071891
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Ngoc-Thang, Tien-Hieu Vu, Van-Huan Bui, Duy-Nam Phan, Thi-Hang Nguyen, and Thi-My-Linh Nguyen. 2023. "Investigation of the Antimicrobial and Physico-Mechanical Properties of Nature-Friendly Nanosilver-Loaded Pig Lining Leather Prepared Using Exhaustion Method" Processes 11, no. 7: 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11071891
APA StyleNguyen, N.-T., Vu, T.-H., Bui, V.-H., Phan, D.-N., Nguyen, T.-H., & Nguyen, T.-M.-L. (2023). Investigation of the Antimicrobial and Physico-Mechanical Properties of Nature-Friendly Nanosilver-Loaded Pig Lining Leather Prepared Using Exhaustion Method. Processes, 11(7), 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11071891







