Aqueous Two-Phase Systems Based on Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents as a Tool for the Recovery of Non-Protein Bioactive Compounds—A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Bioactive Compounds
3. Methods for Obtaining Bioactive Compounds and Bioseparation
4. Aqueous Two-Phase Systems (ATPS)
4.1. ATPS Phase-Forming Components
4.1.1. Ionic Liquid (IL)-Based ATPS
4.1.2. Deep Eutetic Solvent (DES)-Based ATPS
4.1.3. Organic Solvent-Based ATPS
5. Computational Modelling Related to ATPS and Applied to Bioactive Compounds
6. Application of ATPS Based on Ionic Liquids (IL) and Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES) for Bioseparation of Bioactive Compounds
| Phenolic Compounds | Raw Material | Phase-Forming | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geniposide | Gardenia fruit (Gardenia jasminoides) | PE62 (ethylene oxide-propylene oxide, 20:80) copolymer + Phosphate (KH2PO4, NaH2PO4) and sulfate ((NH4)2SO4, and MgSO4) salts + ethanol (0–10 wt%) | [184] |
| Salvianolic acid B | Salvia miltiorrhiza | Ethanol or n-propanol + (NH4)2SO4, NaCl, and K2HPO4/NaH2PO4 | [185] |
| Vanillin | Synthetic | IL (alkylmethylimidazolium cations, and Cl, Br, dicyanamide, methylsulfate, methanesulfonate, triflate, acetate anions) + K3PO4 | [186] |
| Anthocyanins | Mulberry (Morus atropurpurea) | Ethanol + (NH4)2SO4 | [187] |
| Vanillin and L-ascorbic acid | synthetic | Methanol, ethanol, 1-propanol and 2-propanol + K3PO4, K2HPO4 and KH2PO4/K2HPO4 | [159] |
| Lithospermic acid B | Salvia miltiorrhiza | Ethanol + (NH4)2SO4 | [188] |
| Gallic acid | Synthetic | IL (alkylmethylimidazolium cations, and Cl, Br, dicyanamide, methylsulfate, ethylsulfate, octylsulfate, triflate anions) + Na2SO4, K3PO4, and KH2PO4/K2HPO4 | [189] |
| Vanillin | Synthetic | Acetonitrile + carbohydrates (glucose, maltose, galactose, xylose, arabinose, fructose, sucrose and mannose) | [154] |
| Vanillin | Synthetic | Acetonitrile + dextran (6000, 40,000 and 100,000 g·mol−1) | [190] |
| Vanillin | Synthetic | Acetonitrile + polyols (glycerol, erythritol, xylitol, sorbitol and maltitol) | [155] |
| Total phenolics, flavonoids and proanthocyanidins | Grape seeds (Vitis vinifera, cultivar Riesling) | Acetone + (NH4)3Citrate | [51] |
| Rutin | Acerola waste (Malpighia glabra) | Methanol, ethanol, 1-propanol and 2-propanol + K3PO4, K2HPO4 and K2HPO4/KH2PO4 | [191] |
| Anthocyanins | Grape juice (Vitis vinifera) | Ethanol + NaH2PO4 or (NH4)2SO4 | [192] |
| Gallic, vanillic and syringic acids | Synthetic | IL (1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium cation, and Br, dicyanamide, methylsulfate, ethylsulfate, triflate anions) + Na2SO4, Na2CO3 | [193] |
| Gallic, vanillic and syringic acids | Synthetic | PEG 200–600 + Na2SO4 + IL (1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium, 1-butyl-1-methylpiperidinium, 1-butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium cations, and acetate, thiocyanate, tosylate, Cl, dicyanamide anions) | [129] |
| α-Cyclohexylmandelic acid enantiomers | Synthetic | IL (alkylmethylimidazolium cation, and dicyanamide, triflate anions) + (NH4)2SO4, Na2SO4, K2HPO4 | [194] |
| Secoisolariciresinol diglucoside | Flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum) | IL (alkylmethylimidazolium cation, and dicyanamide, BF4 anions) + (NH4)2SO4 | [54] |
| Gallic acid | Guava (Psidium guajava) | Methanol, ethanol, 1-propanol, and 2-propanol + K3PO4, K2HPO4 and K2HPO4/KH2PO4 | [195] |
| Eugenol and propyl gallate | Synthetic | IL (alkylmethylimidazolium, 1-butyl-1-methylpiperidinium, [N4444], 1-butyl-1-methyl-pyrrolidinium cation, and chloride anion) + PEG 1500 or 8000 + K3Citrate/Citric acid or K2HPO4/KH2PO4 | [196] |
| Caffeoylquinic acids | Lonicera japonica flowers | IL (1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide) + K3PO4, K2HPO4, KOH, Na2CO3, | [197] |
| Lignans | Schisandra chinensis | Ethanol + (NH4)2SO4 | [198] |
| Lithospermic acid B | Salvia miltiorrhiza | n-butyl alcohol + KH2PO4 | [199] |
| Total phenolics, and flavonoids | Aronia melanocarpa pomace | Ethanol + (NH4)2SO4 | [200] |
| Caffeoylquinic acid, parishin, and forsythoside isomers, phyllirin, salidroside, gastrodin | Synthetic | Ethanol/1-Butanol + (NH4)2SO4 and K2HPO4 | [201] |
| Hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives | Carrots (Daucus carota) | Ethanol, n-Butanol or IL ([C2mim]Acetate) + (NH4)2SO4, KH2PO4/K2KPO4 | [57] |
| Vanillic acid, vanillin, gallic acid, caffeic acid, syringaldehyde | Synthetic | PEG 8000 + Sodium Polyacrylate 8000 + Electrolyte (sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate, sodium dodecylsulfate, [N111 14]Br, [N111 16]Br, C16pyridinium chloride, C16 pyridinium bromide, [C12mim]Cl, [C14mim]Cl) | [58] |
| Chlorogenic acid | Ramie (Boehmeria nivea) | IL (1-butyl-3methylimidazolium cation, and triflate, acetate, propionate, hydrogen sulfate, dihydrogen phosphate anions) + Na2SO4, (NH4)2SO4 | [202] |
| Anthocyanins | Grape pomace | IL (1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium Acetate) + K3PO4, K2CO3 | [56] |
| Total phenolics, and xylooligosaccharides | Wheat chaff (Triticum sp.) | Ethanol + (NH4)2SO4 | [55] |
| Anthraquinones | Rheum officinalis | DES (ChCl, [N11110]Br, [N11112]Br, [N111 14]Br, as HBA, and hexafluoroisopropanol as HBD) + (NH4)2SO4, Na2SO4, K2HPO4, Na2HPO4 | [203] |
| Phloridzin | Crabapple (Malus micromalus) | Ethanol + (NH4)2SO4 | [204] |
| Chlorogenic acid | Blueberry (Vaccinium spp.) leaves | DES (ChCl as HBA, and ethylene glycol, glycerol, 1,3-butanediol, citric acid, oxalic acid, sucrose, glucose, maltose as HBD) + K2HPO4 | [53] |
| Gallic acid | Synthetic | DES (ChCl as HBA, and sucrose, glucose, fructose as HBD) + K2HPO4 | [205] |
| Flavonoids | Sophora japonica flower buds | IL (alkylimidazolium cations, and propionate, lactate anions) + K3Citrate | [206] |
| Gallic acid, caffeine, and tryptophan | Synthetic | DES ([N4444]Cl as HBA, and ethanol, n-propanol as HBD) + K3Citrate/Citric Acid | [207] |
| Vanillin | Synthetic | Acetonitrile + maltodextrins | [157] |
| Total phenolics, and lutein | Marigold (Tagetes erecta) flowers | Ethanol + (NH4)2SO4 | [208] |
| Mandelic acid enantiomers | Synthetic | IL (1-methyl quininium, N,N-dimethyl-L-proline methyl ester, N,N-diethyl-L-proline ethyl ester, N,N,N-trimethyl-L-valinolium cations, and methylsulfate, Br, I anions) + K3PO4, K2HPO4, K2CO3 | [209] |
| Psoralen | Fig (Ficus carica) leaves | IL (alkylmethylimidazolium cation, and Br, Cl, nitrate, hydrogensulfate, tetrafluoroborate anions) or Ethanol + Citric acid | [210] |
| Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside, gallic acid and quercetin. | Synthetic | Acetonitrile + polyvinylpyrrolidone (10,000, 29,000 and 40,000 g·mol−1) | [124] |
| Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside, garcinol, isogarcinol and hydroxycitric acid | Kokum (Garcinia indica) | Ethanol, and 1-propanol + (NH4)2SO4, MgSO4, Na2SO4, ZnSO4, Na3Citrate, NaH2PO4, and K2HPO4 | [171] |
| Gallic and protocatechuic acids | Synthetic | PEG (400, 1000, 1500, 4000, 6000, 8000, 10,000 and 20,000 g·mol−1) + K3PO4 + acetonitrile | [125] |
| Proanthocyanidins | Grape seeds | Ethanol + (NH4)2SO4, Na2CO3, and K2HPO4 + IL (alkylmethylimidazolium cation and [TOS], [HSO4], [CH3SO3], [NO3], [Br], [BF4] anions) | [163] |
| Paeonol | Paeonia suffruticosa root bark | Ethanol or Ethyl Acetate + NaH2PO4, (NH4)2SO4, KCl, NaCl, Na2SO4, MgSO4 | [211] |
| Rutin and quercetin | Synthetic | IL (cholinium cation, and alaninate, glycinate, serinate anions) + K2HPO4, K3PO4 | [20] |
| Lignin alkaline | - | IL (alkylmethylimidazolium cations, and Cl anion) + Na2CO3 | [212] |
| Kraft lignin | Eucalyptus globulus | PIL (2-Hydroxyethylammonium, bis(2-hydroxyethyl)ammonium, tris(2-hydroxyethyl)ammonium cations, and formate, acetate, propionate, glycolate, lactate anions) + acetone | [153] |
| Total phenolics | Peppermint leaves (Mentha × piperita) and lemon balm leaves (Melissa officinalis) | DES (ChCl as HBA, and ethylene glycol, glycerol, glucose, citric acid as HBD) + K2HPO4 | [213] |
| Lignans | Schisandra chinensis | Ethanol + (NH4)2SO4 | [67] |
| Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside, garcinol, isogarcinol and hydroxycitric acid | Kokum (Garcinia indica) rinds | 1-propanol + (NH4)2SO4 | [164] |
| Genipin | Genipap (Genipa americana) | IL (monoethanolammonium, di-ethanolammonium, triethanol-ammonium cations, and Cl, dihydrogen citrate, dihydrogen phosphate, hydrogen sulfate, nitrate anions) + Acetonitrile | [156] |
| Total phenolics, flavonoids, and chlorogenic acid | Haskap leaves (Lonicera caerulea) | Ethanol, 1-Propanol + (NH4)2SO4, NaH2PO4, glucose, and maltose | [162] |
| Vanillin and L-tryptophan | Synthetic | IL (1-decyl-3-methyl imidazolium chloride) + 2-propanol + K2HPO4 | [214] |
| Anthocyanins | Grape pomace | IL (bis(2-hydroxyethyl)ammonium hydrogen sulfate) + Acetonitrile | [215] |
| Genipin | Genipap (Genipa americana) | IL (monoethanolammonium, di-ethanolammonium, triethanol-ammonium cations, and Cl, dihydrogen phosphate, hydrogen sulfate, nitrate anions) + PEG 300–750 or PPG 400 | [216] |
| Geniposidic acid and aucubin | Eucommia ulmoides | IL (alkylmethylimidazolium cations, and Cl, Br, acetate, nitrate, dicyanamide anions) + K2CO3, K2HPO4, (NH4)2SO4 | [217] |
| Acteoside | Cistanche tubulosa | IL (alkylmethylimidazolium cations, and Cl, Br, BF4, triflate anions) + NaCl, K2HPO4, NaH2PO4, (NH4)2SO4, Na2SO4, Na3Citrate | [218] |
| Syringic and caffeic acids | Synthetic | IL (1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium triflate) + NaCl, K3PO4, K2HPO4, NaH2PO4, Na2SO4, Na2CO3 | [219] |
| Vanillic and shikimic acids | Synthetic | DES (ChCl as HBA, and sucrose, glucose, fructose, xylose as HBD) + n-propanol | [220] |
| Flavonoids | Yam (Dioscorea alata) peel. | IL (alkyl-(2-hydroxyethyl)-dimethylammonium cations, 4-sulfonatooxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethyl piperidine-1-yloxyl anion) + K3PO4 | [221] |
| Lignin derivatives | Synthetic | PEG 8000 + Sodium Polyacrylate 8000 + Electrolyte (NaCl, Na2SO4, IL ([C2mim cation, and Cl, dicyanamide, methanesulfonate, triflate, tosylate anions) | [222] |
| Gallic, ferulic, protocatechuic, caffeic and chlorogenic acids | Red apple, yellow pear, purple grape, and native banana | PEG 600 + Na2CO3 + PEG bis (methylimidazolium) ditetrachloroferrate | [223] |
| Syringic acid and eugenol | Synthetic | DES (betaine as HBA, and xylitol, tartaric acid, glycolic acid, urea as HBD) + t-butanol | [224] |
| Alkaloids | Raw Material | Phase-Forming | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Codeine and papaverine | Opium (Pericarpium papaveris) | IL (1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride) + K2HPO4 | [225] |
| Caffeine, β-carotene, and L-tryptophan | Synthetic | IL (triisobutyl(methyl)-phosphonium tosylate, tributyl-(methyl)phosphonium methylsulphate and tetrabutyl-phosphonium bromide) + K3PO4 | [226] |
| Puerarin | Pueraria lobata | IL (1-carboxymethyl-3-methylimidazolium, 1-hydroxyethyl-3-methylimidazolium and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium cations, and Br, Hydroxide, tetrafluoroborate anions) + K2HPO4 | [227] |
| Caffeine, nicotine, and xanthine | Synthetic | IL (alkylmethylimidazolium cations, and Cl, acetate, CH3SO3, HSO4, (CH3)2PO4 anions) + PEG 2000 | [228] |
| Caffeine, nicotine, theobromine, and theophylline | Synthetic | IL (alkylmethylimidazolium cations, and Cl anion) + K3Citrate/Citric Acid | [229] |
| Caffeine and nicotine | Synthetic | IL (alkylimidazolium cation, and Cl, triflate, trifluoroacetate, acetate, methanesulfonate anions) + K3PO4 | [230] |
| Matrine and oxymatrine | Sophora flavescens | Ethanol + (NH4)2SO4 or K2HPO4 | [231] |
| Glaucine | Glaucium flavum | IL (1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium acesulfamate) + Na2CO3, (NH4)2SO4, MgSO4, NaH2PO4 | [232] |
| Caffeine | Guaraná seeds (Paullinia cupana), and coffee beans (Coffea canephora, Coffea arabica) | Methanol, ethanol, 1-propanol and 2-propanol + K3PO4, K2HPO4 and K2HPO4/KH2PO4 | [233] |
| Capsaicin | Capsicum frutescens var. malagueta | Acetonitrile + IL (cholinium cation, and Cl, bitartrate, dihydrogen citrate anions) | [234] |
| Monoester- and diester-diterpenoid aconitines | Aconitum carmichaeli | IL (alkylmethylimidazolium cation, and Br, tetrafluoroborate anions) + K2HPO4 | [235] |
| Caffeine | Synthetic | IL ([C4mim]BF4) + Na2SO4, NaNO3 | [236] |
| Caffeine, theobromine, and theophylline | Synthetic | PEG 600 + IL (cholinium cation, and Cl, acetate, bicarbonate, dihydrogencitrate, dihydrogenphosphate anions) | [176] |
| Capsaicin | Capsicum chinense var. cumari-do-Pará. | Ethanol + NaH2PO4, Na2S2O3, Na2SO4, and Na2CO3 | [237] |
| Capsaicin | capsicum oleoresin | Ethanol + Na2CO3, (NH4)2SO4, NaH2PO4, Na3Citrate | [45] |
| Caffeine, nicotine, gallic acid, vanillic acid, amino acids | Synthetic | Choline chloride/Glucose + PPG 400 | [238] |
| Caffeine, codeine, and vanillin | Synthetic | Ethanol, 1-propanol, and 2-propanol + carbohydrates (xylose, L-arabinose, glucose, galactose, fructose, sucrose, maltitol, xylitol, and maltose) | [239] |
| Matrine, sophocarpine and oxymatrine | Sophora tonkinensis | Ethanol + Na2HPO4, NaH2PO4, and Na3PO4 | [240] |
| Sinomenine | Sinomenium acutum | Ethanol + (NH4)2SO4 + ionic liquids ([C4mim]Br, [C6mim]Br, [C8mim]Br, [C4mim]FeCl3Br, [C2OHmim]FeCl4, [C6mim] FeCl3Br and [C8mim] FeCl3Br) | [241] |
| Caffeine, theobromine, and theophylline | Synthetic | PIL (2-hydroxyethylammonium, bis(2-hydroxyethyl) ammonium, N-methyl-2-hydroxyethyl-ammonium cations, and acetate, propionate, butyrate, pentanoate anions) + Acetonitrile | [101] |
| Caffeine, nicotine, gallic acid, vanillic acid, amino acids, β-carotene | Synthetic | Choline chloride + alcohols (ethanol, n-propanol, ethylene glycol, 1,2-propanediol) + K2HPO4 | [242] |
| Caffeine, nicotine, gallic acid, vanillic acid, amino acids, eugenol | Synthetic | PEG 400 + IL (1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium, 1-butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium, 1-butyl-3-methylpiperidinium, tetrabutylammonium, tetrabutylphosphonium cations, and chloride anion) + K3Citrate/Citric Acid | [243] |
| Caffeine and theobromine | Synthetic | IL (N-methyl-N-alkyl-N,N-di(hydroxyethyl)ammonium cations, and Br anion) + K2CO3, K3Citrate, and K3PO4 | [244] |
| Berberine HCl | Rhizoma coptidis (Coptis chinensis, C. deltoidea, or C. teeta) | IL (alkyl-(2-hydroxyethyl)-dimethylammonium cations, 4-sulfonatooxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethyl piperidine-1-yloxyl anion) + K3PO4, K2CO3, Na3Citrate, K3Citrate, K2HPO4 | [245] |
| Caffeine and nicotine | Synthetic | Ethanol + K2CO3, K3Citrate, K2HPO4, NaH2PO4, and K3PO4 | [246] |
| Caffeine, nicotine, gallic acid, vanillic acid, amino acids, eugenol | Synthetic | PEG 400 + IL (1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium, 1-butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium, 1-butyl-3-methylpiperidinium, tetrabutylammonium, tetrabutylphosphonium, cholinium cations, and chloride anion) + (NH4)2SO4 | [247] |
| Codeine and caffeine | Synthetic | IL (1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate) + sugars (xylose, arabinose, fructose, glucose, maltose, sucrose) | [21] |
| Caffeine | Synthetic | Tetrabutylphosphonium bromide + sorbitol | [248] |
| Caffeine, nicotine, amino acids (L-tryptophan, L-phenylalanine and L-tyrosine) and phenolic compounds (gallic acid and vanillic acid) | Synthetic | Ethanol + [N111(2OH)]Cl + NaH2PO4, K2HPO4, K3PO4, K2CO3, and K3Citrate | [161] |
| Caffeine, nicotine, theobromine, and theophylline | Synthetic | Pluronic PE6200 + IL(cholinium cation, and Cl, acetate, propionate butanoate, lactate, bitaratrate, dihydrogenphosphate, dihydrogencitrate, bicarbonate anions) | [44] |
| Caffeine, nicotine, amino acids (L-tryptophan, L-phenylalanine and L-tyrosine) and phenolic compounds (gallic acid and vanillic acid) | Synthetic | Zwitterions (4-(triethylammonio)-butane-1-sulfonate, 4-(1-methylimidazolium-3-yl)butane-1-sulfonate, 4-(1-vinylimidazolium-3-yl)butane-1-sulfonate, 4-(1-methylpyrrolidinium-1-yl)butane-1-sulfonate, 4-(1-ethyl-piperidinium-1-yl))butane-1-sulfonate) + K2CO3 | [249] |
| Caffeine | Synthetic | IL (tetrabutylammonium cátion, and amino acids anions) + K3PO4, K2HPO4 and K2CO3 | [250] |
| Caffeine | Synthetic | Choline chloride/saccharose + polyethylene glycol dimethyl ether 250 | [251] |
| Pigments | Raw Material | Phase-Forming | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crocins | Crocus sativus stigmas | IL (alkylmethylimidazolium cation, acetate and BF4) or Ethanol + NaH2PO4, K2HPO4/KH2PO4 | [252] |
| Chlorophyll | silkworm excrement | Ethanol + NaOH | [253] |
| Curcuminoids | Curcuma longa powder | IL (1,3-Diethylimidazole, 1,3-dioctylimidazole, 1,3-dimethylimidazole, 1,3-dibutylimidazole cations, and Br, I anions) + K2HPO4 | [254] |
| Betanin | Opuntia ficus-indica | Tetrahydrofuran + Na2CO3 and Na3Citrate | [255] |
| C-Phycocyanin | Spirulina (Arthrospira platensis) | IL (alkylmethylimidazolium cations, and bromide anion) + K2HPO4, K2HPO4, K2CO3 | [183] |
| Curcumin | synthetic | Tetrabutylphosphonium bromide + sorbitol, fructose | [256] |
| Astaxanthin | Shrimp waste | IL (tetrabutylammonium,tetrabutylphosphonium, tributyloctylphosphonium cations, and Cl, Br anions) + K3PO4 | [22] |
| Curcumin | Curcuma longa rhizomes | Pluronic F68/McIlvaine buffer (pH 6.0; K2HPO4/Citric Acid) + IL (cholinium cation, and Cl, acetate, propanoate, butanoate, hexanoate anions) | [257] |
| R-Phycoerythrin | Porphyra yezoensis | DES (ChCl as HBA, and glycerol, ethylene glycol, sorbitol, urea, glucose, fructose as HBD) + K2HPO4 | [258] |
| C-Phycocyanin | Arthrospira platensis | DES (ChCl as HBA, and glycerol, ethylene glycol, urea, glucose, fructose as HBD) + K2HPO4 | [259] |
| Betanin | Beetroot (Beta vulgaris) | Tributylmethylammonium hexanoate + Trioctylmethylammonium adipate | [260] |
| Curcumin | synthetic | 1-ethylpiperazinium tetrafluoroborate + sodium dodecyl sulfate, and 1-phenylpiperazinium tetrafluoroborate + sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate | [261] |
| Crocin | synthetic | DES (ChCl as HBA, and urea, ethylene glycol as HBD) + Acetonitrile | [262] |
| Metabolites | Raw Material | Phase-Forming | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glycyrrhizin | Glycyrrhiza uralensis | 2-Propanol or ethanol + (NH4)2SO4 or K2HPO4 | [263] |
| DNA | Salmon testes | DES ([N4444]Br as HBA, and ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, butylene glycol, n-butanol as HBD) + Na2CO3, K2HPO4, NaH2PO4, Na2SO4 | [264] |
| Polysaccharides | Gentiana scabra | Ethanol + NaH2PO4, K2HPO4, (NH4)2SO4, Na3Citrate, and K2CO3 | [50] |
| Ginsenosides | Panax ginseng | IL (n-alkyl-tropinium and n-alkylquinolinium bromide) + Na3Citrate, K3Citrate, K2CO3, K3PO4, K2HPO4, and NaH2PO4 | [52] |
| Polysaccharides | Lilium davidii var. unicolor | Ethanol + Na2CO3, K2HPO4, (NH4)2SO4, and NaH2PO4 | [265] |
| Ginsenosides | Kang’ai injection (Astragalus membranaceus, Panax ginseng and kushenin) | DES (ChCl as HBA, and glycerol, ethylene glycol, 1,4-butanediol, glucose as HBD) + K2HPO4 | [266] |
| Carbohydrates, Proteins | Neochloris oleoabundans and Tetraselmis suecica. | IoliLyte 221 PG + K3Citrate/Citric Acid | [60] |
| Proteins, Arabinan and glucan | Isochrysis galbana | IL (alkylmethylimidazolium cations, and Cl, acetate, triflate, dicyanamide anions) + K3PO4, K2HPO4 | [267] |
| DNA | Salmon testes | [N4444]Br/PPG 400 + IL (betainium cation, and formate, acetate, propionate, butyrate anions) or DES (betaine as HBA, and glucose, xylitol, sucrose, sorbitol as HBD), or salts (Na2CO3, K2HPO4, NaH2PO4, Na3Citrate) | [268] |
| Pristimerin | Mortonia greggii | IL (1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate, 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate), or Ethanol + Sodium Phosphates | [269] |
| Ursolic acid | Cynomorium songaricum | Ethanol + DES (ChCl as HBA, and acetamide, glycerol, urea, ZnCl2, mannitol, organic acids as HBD) + K3PO4, (NH4)2SO4, Na2SO4 | [270] |
| Ursolic acid | Cynomorium songaricum | DES (ChCl as HBA, and glycerol, ethylene glycol, urea, glucose as HBD) + K2HPO4 | [271] |
| Ginsenosides | Panax quinquefolius | Ethanol + Na2CO3 | [272] |
| Ginsenoside CK | Panax notoginseng | DES (ChCl as HBA, and glycerol, ethylene glycol, urea, glucose as HBD) + K2HPO4 | [273] |
| Carbohydrates, proteins, lutein and chlorophyll | Neochloris oleoabundans | PEG 8000 + Sodium polyacrylate 8000 + electrolyte (sodium dodecyl sulfate, 1-methyl-3-tetradecylimidazolium chloride, tributyl-1-tetradecylphosphonium chloride, 1-dodecyltrimethyl-ammonium bromide) | [61] |
| Carbohydrates, proteins, lutein and chlorophyll | Neochloris oleoabundans | PPG 400 + IL (cholinium cation, and Cl, dihydrogencitrate, acetate, dihydrogenphosphate, bicarbonate, bitartrate anions) | [274] |
| Starch, glucose, proteins | Neochloris oleoabundans | PEG 400 + IL (choline dihydrogen phosphate), and IoliLyte 221 PG + K3Citrate/Citric Acid | [275] |
| α-Tocopherol and β-carotene | Tetraselmis suecica | IL (cholinium glycinate, cholinium phenylalaninate, cholinium dipeptide, 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium methylsulfate) + K3PO4 | [276] |
| DNA | Fish sperm | IL (alkylhydroxyammonium, alkylammonium cations, and bromide anion) + K2HPO4/KH2PO4 | [277] |
| Lipids, lutein | Neochloris oleoabundans | PEG 400 + IL (choline dihydrogen phosphate), and IoliLyte 221 PG + K3Citrate/Citric Acid | [278] |
| Bioproducts | Raw Material | Phase-Forming | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleic acids | Escherichia coli K-12, Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Ethanol + KH2PO4 | [279] |
| 2,3-butanediol | Klebsiella pneumoniae CICC | Ethanol + K2HPO4 | [280] |
| 2,3-butanediol | Klebsiella pneumoniae DSM2026 | Methanol, ethanol, isopropanol + NaCl, K2CO3, K3PO4, and (NH4)2SO4 | [281] |
| 1,3-propanediol | Klebsiella pneumoniae CGMCC 2028 | Ethanol + Na2CO3 | [282] |
| Red colorant | Penicillium purpurogenum DPUA 1275 | Tetraethylammonium bromide, tetrabutylammonium bromide, and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride + citric acid/K3Citrate | [62] |
| Succinic acid | Actinobacillus succinogenes CGMCC1593 | Ethanol, Isopropanol, Acetone + K2CO3, K3PO4, K2HPO4, NaH2PO4, (NH4)2SO4 | [151] |
| Succinic acid | Simulated broth | Alcohols (ethanol, 1-propanol, 2-propanol, t-butanol) or IL (alkymethylimidazolium cations, and bromide anion) + K2HPO4, Na3Citrate, Na2SO4 | [283] |
| RNA | Yeast | DES ([N4444]Cl, [N2222]Cl, [N4444]Br, [N2222]Br as HBA, and PEG 200–4000 as HBD) + Na2CO3, K2HPO4, NaH2PO4, Na3Citrate, (NH4)2SO4, MgSO4, K3PO4, K2CO3, NaCl, NH4NO3 | [284] |
| Rubropunctamine and monascorubramine | Monascus anka CICC 5013 | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride + Triton X-100 | [285] |
| sRNA | Escherichia coli | IL (cholinium cation, and amino acids anions) + PPG 400 | [286] |
| Ectoine | Halomonas salina | IL ([C4mim]BF4) + (NH4)2SO4, Na3Citrate | [287] |
| Acetoin | Bacillus subtilis CGMCC 13141 | IL (ethanolammonium, isopropanolammonium cations, and acetate, propionate, butyrate, lactate anions) + K3PO4 | [67] |
| Violacein | Yarrowia lipolytica | Tween 20 + IL (cholinium cation, Cl, acetate, dihydrogenphosphate, dihydrogencitrate, bicarbonate anions) | [65] |
| Roseoflavin | Streptomyces davaonensis | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate or Ethanol + NaH2PO4/Na2HPO4 | [59] |
| ε-Polylysine | Bacillus licheniformis | PPG-400 + IL (2-hydroxyethylammonium, cholinium cations, and formate, acetate anions) | [64] |
| Lactic acid | Microbial consortium | IL (alkylmethylimidazolium cations, and BF4, triflate anions) + glucose, xylose | [63] |
7. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
References
- MDF. Bioactive Ingredients Market. Available online: https://www.marketdataforecast.com/market-reports/global-bioactive-ingredients-market (accessed on 18 October 2022).
- Lemes, A.C.; Braga, A.R.C.; Gautério, G.V.; Fernandes, K.F.; Egea, M.B. Application of membrane technology for production of bioactive peptides. In Bioactive Peptides; John Oloche Onuh, M., Selvamuthukumaran, P.Y.V., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Poirier, P.; Burke, L.E.; Després, J.P.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Lavie, C.J.; Lear, S.A.; Ndumele, C.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Sanders, P.; et al. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, e984–e1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Noncommunicable Diseases. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/noncommunicable-diseases (accessed on 18 October 2022).
- Cazarin, C.B.B.; Bicas, J.L.; Pastore, G.M.; Marostica Junior, M.R. Chapter 1—Introduction. In Bioactive Food Components Activity in Mechanistic Approach; Cazarin, C.B.B., Bicas, J.L., Pastore, G.M., Marostica, M.R., Jr., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Kamiloglu, S.; Tomas, M.; Ozdal, T.; Yolci-Omeroglu, P.; Capanoglu, E. Chapter 2—Bioactive component analysis. In Innovative Food Analysis; Galanakis, C.M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 41–65. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, M.; Flower, D. Bioactive peptides from marine processing byproducts. In Bioactive Compounds from Marine Foods; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 57–71. [Google Scholar]
- Lemes, A.C.; Egea, M.B.; Oliveira Filho, J.G.d.; Gautério, G.V.; Ribeiro, B.D.; Coelho, M.A.Z. Biological Approaches for Extraction of Bioactive Compounds From Agro-industrial By-products: A Review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 9, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanakis, C.M.; Drago, S.R. Chapter 1—Introduction. In Nutraceutical and Functional Food Components, 2nd ed.; Galanakis, C.M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Egea, M.B.; Bolanho, B.C.; Lemes, A.C.; Bragatto, M.M.; Silva, M.R.; Carvalho, J.C.M.; Danesi, E.D.G. Low cost cassava, peach palm and soy by-products for the nutritional enrichment of cookies: Physical, chemical and sensorial characteristics. Int. Food Res. J. 2018, 25, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Guimarães, R.M.; Pimentel, T.C.; de Rezende, T.A.M.; Silva, J.d.S.; Falcão, H.G.; Ida, E.I.; Egea, M.B. Gluten-free bread: Effect of soy and corn co-products on the quality parameters. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madureira, J.; Margaça, F.M.A.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Ferreira, I.; Verde, S.C.; Barros, L. Applications of bioactive compounds extracted from olive industry wastes: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 453–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, I.d.A.A.; Maciel, G.M.; Maroldi, W.V.; Bortolini, D.G.; Pedro, A.C.; Haminiuk, C.W.I. Bioactive compounds, health-promotion properties and technological applications of Jabuticaba: A literature overview. Meas. Food 2022, 8, 100057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemes, A.C.; Gautério, G.V.; Folador, G.O.; Sora, G.T.S.; Paula, L.C. Reintrodução de resíduos agroindustriais na produção de alimentos. In Realidades e Perspectivas em Ciência Dos Alimentos; Nogueira, W.V., Ed.; Pantanal Editora: Nova Xavantina, Brazil, 2020; Volume II, pp. 67–79. [Google Scholar]
- Makowski, B.; Rosicka-Kaczmarek, J.; Nebesny, E. Bioactive compounds in cereals. In Biotechnology of Bioactive Compounds; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 103–122. [Google Scholar]
- Dinis, T.B.V.; Passos, H.; Lima, D.L.D.; Esteves, V.I.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. One-step extraction and concentration of estrogens for an adequate monitoring of wastewater using ionic-liquid-based aqueous biphasic systems. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 2570–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.G.; Cláudio, A.F.M.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Marrucho, I.M.; Lopes, J.N.C.; Rebelo, L.P.N. Aqueous biphasic systems: A boost brought about by using ionic liquids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4966–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemes, A.C.; Machado, J.R.; Brites, M.L.; Luccio, M.D.; Kalil, S.J. Design Strategies for Integrated β-Galactosidase Purification Processes. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2014, 37, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, Y.K.; Ooi, C.W.; Ng, E.-P.; Lan, J.C.-W.; Ling, T.C.; Show, P.L. Current applications of different type of aqueous two-phase systems. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2015, 2, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, E.; Requejo, P.F.; Tojo, E.; Macedo, E.A. Recovery of flavonoids using novel biodegradable choline amino acids ionic liquids based ATPS. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2019, 493, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamehbozorg, B.; Sadeghi, R. Extractions of Alkaloids Codeine and Caffeine with [Bmim][BF4]/Carbohydrate Aqueous Biphasic Systems as a Novel Class of Liquid–Liquid Extraction Systems. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Fang, C.; Lin, Y.; Nie, F.; Ji, H.; Liu, S. Enhanced extraction of astaxanthin using aqueous biphasic systems composed of ionic liquids and potassiumphosphate. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, C.A.M.; Crespo, J.G. Green Separation Processes: Fundamentals and Applications; Wiley-VCH Verlag: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; p. 363. [Google Scholar]
- García-Serna, J.; Pérez-Barrigón, L.; Cocero, M.J. New trends for design towards sustainability in chemical engineering: Green engineering. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 133, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.A.; Kazlauskas, R. Biocatalysis for Green Chemistry and Chemical Process Development; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; p. 496. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Kayal, A.; Gong, Z.; Zheng, L.; He, Q. Molecular modelling of ionic liquids: Physical properties of species with extremely long aliphatic chains from a near-optimal regime. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 367, 120492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulczyński, B.; Sidor, A.; Gramza-Michałowska, A. Characteristics of Selected Antioxidative and Bioactive Compounds in Meat and Animal Origin Products. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, H.; Wilfred, C.D.; Shaharun, M.S. Ionic liquid-based extraction and separation trends of bioactive compounds from plant biomass. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 559–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemes, A.C.; Álvares, G.T.; Egea, M.B.; Brandelli, A.; Kalil, S.J. Simultaneous production of proteases and antioxidant compounds from agro-industrial by-products. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 222, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Macias, P.; Hernandez de Jesus, M.d.L.; Barragan-Huerta, B.E. The production of biomaterials from agro-industrial waste. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2017, 26, 4128–4152. [Google Scholar]
- Baiano, A. Recovery of biomolecules from food wastes—A review. Molecules 2014, 19, 14821–14842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, D.; Nörnberg, J.; Ritt, L.; Scheibler, R.; Antunes Rizzo, F.; Milani, M. Potencialidades funcionais e nutracêuticas das proteínas do leite bovino. Rev. Eletrônica Em Gestão Educ. E Tecnol. Ambient. 2014, 18, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clare, D.A.; Swaisgood, H.E. Bioactive milk peptides: A prospectus. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, C.M. Bioactive foods and ingredients for health. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 306s–311s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva Pinto, M.; Kwon, Y.I.; Apostolidis, E.; Lajolo, F.M.; Genovese, M.I.; Shetty, K. Functionality of bioactive compounds in Brazilian strawberry (Fragaria x ananassa Duch.) cultivars: Evaluation of hyperglycemia and hypertension potential using in vitro models. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 4386–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Filho, J.G.; Rodrigues, J.M.; Valadares, A.C.F.; Almeida, A.B.; Valencia-Mejia, E.; Fernandes, K.F.; Lemes, A.C.; Alves, C.C.F.; Sousa, H.A.d.F.; Silva, E.R.; et al. Bioactive Properties of Protein Hydrolysate of Cottonseed Byproduct: Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Activities. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul, G.M.; Shama, M. Phenolic compounds. In Bioactive Compounds; Leila Queiroz, Z., Tatiele Casagrande do, N., Eduardo, J.-L., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2021; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Swanson, B.G. Tanninsand and polyphenols. In Encyclopedia of Food Sciences and Nutrition, 2nd ed.; Caballero, B., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2003; pp. 5729–5733. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, D.; Xiao, M.; Zhao, J.; Li, Z.; Xing, B.; Li, X.; Kong, M.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; et al. An Overview of Plant Phenolic Compounds and Their Importance in Human Nutrition and Management of Type 2 Diabetes. Molecules 2016, 21, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzio, V. Phenolic compounds: Introduction. In Natural Products: Phytochemistry, Botany and Metabolism of Alkaloids, Phenolics and Terpenes; Ramawat, K.G., Mérillon, J.-M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 1543–1580. [Google Scholar]
- Joanna, K. Introductory chapter: Alkaloids—Their importance in nature and for human life. In Alkaloids; Joanna, K., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2019; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Waller, G.R.; Nowacki, E.K. The role of alkaloids in plants. In Alkaloid Biology and Metabolism in Plants; Waller, G.R., Nowacki, E.K., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 1978; pp. 143–181. [Google Scholar]
- Debnath, B.; Singh, W.S.; Das, M.; Goswami, S.; Singh, M.K.; Maiti, D.; Manna, K. Role of plant alkaloids on human health: A review of biological activities. Mater. Today Chem. 2018, 9, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrijević, A.; Tavares, A.P.M.; Jocić, A.; Marić, S.; Trtić-Petrović, T.; Gadžurić, S.; Freire, M.G. Aqueous biphasic systems comprising copolymers and cholinium-based salts or ionic liquids: Insights on the mechanisms responsible for their creation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 248, 117050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Lu, Y.M.; Yu, B.; Tan, C.P.; Cui, B. Extraction and purification of capsaicin from capsicum oleoresin using an aqueous two-phase system combined with chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1063, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemes, A.C.; Reis, D.F.; Ores, J.C.; Braga, A.R.C. Microalgas como fontes de pigmentos naturais para aplicação industrial. In A Biodiversidade Como Fonte de Compostos Bioativos: Moléculas e Aplicações, 1st ed.; Egea, M.B., Marcionilio, S.M.L.O., Eds.; Editora IF Goiano: Rio Verde, Brasil, 2022; pp. 47–63. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, N.; Roriz, C.; Morales, P.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I. Food colorants: Challenges, opportunities and current desires of agro-industries to ensure consumer expectations and regulatory practices. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 52, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberoumand, A. A Review Article on Edible Pigments Properties and Sources as Natural Biocolorants in Foodstuff and Food Industry. World J. Dairy Food Sci. 2011, 6, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, V.S.; Sant’Anna, C. Impact of culture conditions on the chlorophyll content of microalgae for biotechnological applications. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Song, H.; Cao, X.; Shen, Q.; Han, D.; Zhong, F.; Hu, H.; Yang, Y. Simultaneous extraction and purification of polysaccharides from Gentiana scabra Bunge by microwave-assisted ethanol-salt aqueous two-phase system. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 102, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Xiu, Z.-L. Microwave-assisted aqueous two-phase extraction of phenolics from grape (Vitis vinifera) seed. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 89, 1576–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Dong, B.; Feng, X.; Yao, S. Extraction of bioactive ginseng saponins using aqueous two-phase systems of ionic liquids and salts. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 196, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xu, W.-J.; Wang, S.-X.; Kou, P.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.-Q.; Fu, Y.-J. Integrated and sustainable separation of chlorogenic acid from blueberry leaves by deep eutectic solvents coupled with aqueous two-phase system. Food Bioprod. Process. 2017, 105, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.J.; Wang, C.Y.; Yang, Z.Z.; Yi, Y.J.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhou, W.L.; Li, F.F. Ionic Liquid-Based Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction of Secoisolariciresinol Diglucoside from Flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) with Further Purification by an Aqueous Two-Phase System. Molecules 2015, 20, 17929–17943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đorđević, T.; Antov, M. Ultrasound assisted extraction in aqueous two-phase system for the integrated extraction and separation of antioxidants from wheat chaff. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 182, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, Á.S.; Soares, C.M.F.; Paltram, R.; Halbwirth, H.; Bica, K. Extraction and consecutive purification of anthocyanins from grape pomace using ionic liquid solutions. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2017, 451, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Rangel, J.C.; Jacobo-Velázquez, D.A.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Benavides, J. Primary recovery of bioactive compounds from stressed carrot tissue using aqueous two-phase systems strategies. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 91, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.H.P.M.; Martins, M.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Ventura, S.P.M. Fractionation of phenolic compounds from lignin depolymerisation using polymeric aqueous biphasic systems with ionic surfactants as electrolytes. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 5569–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra-Herrera, C.C.; Meza-Dorantes, A.; Mora-Lugo, R.; González-Valdez, J.; Mack, M.; Mata-Gómez, M.A. Recovery of roseoflavin from a recombinant Streptomyces davaonensis strain by using biphasic aqueous systems. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 2529–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, E.S.; Suarez Ruiz, C.A.; Tilaye, T.; Eppink, M.H.M.; Wijffels, R.H.; van den Berg, C. Fractionation of proteins and carbohydrates from crude microalgae extracts using an ionic liquid based-aqueous two phase system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 204, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, C.A.S.; Martins, M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Wijffels, R.H.; Eppink, M.H.M.; Berg, C.v.d.; Ventura, S.P.M. Neochloris oleoabundans biorefinery: Integration of cell disruption and purification steps using aqueous biphasic systems-based in surface-active ionic liquids. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 399, 125683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, S.P.; Santos-Ebinuma, V.C.; Pereira, J.F.; Teixeira, M.F.; Pessoa, A.; Coutinho, J.A. Isolation of natural red colorants from fermented broth using ionic liquid-based aqueous two-phase systems. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 40, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhan, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xiu, Z.; Tong, Y. Ionic liquid-based multi-stage sugaring-out extraction of lactic acid from simulated broth and actual lignocellulosic fermentation broth. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2021, 8, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira, R.A.; Sharma, M.; Pereira, M.M.; Singh, N.; Bhattacharya, S.; Chudasama, N.A.; Prasad, K. One step selective partition of ε-polylysine present in broth cultures in ionic liquid-based aqueous biphasic systems. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholany, M.; Trébulle, P.; Martins, M.; Ventura, S.P.; Nicaud, J.-M.; Coutinho, J.A. Extraction and purification of violacein from Yarrowia lipolytica cells using aqueous solutions of surfactants. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 1126–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, O.S.; Gomes, M.H.G.; Oliveira, R.L.; Porto, A.L.F.; Converti, A.; Porto, T.S. Partitioning and extraction protease from Aspergillus tamarii URM4634 using PEG-citrate aqueous two-phase systems. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017, 9, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dai, J.-Y.; Xiu, Z.-L. Salting-out extraction of acetoin from fermentation broths using hydroxylammonium ionic liquids as extractants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 240, 116584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarante, M.C.A.d.; Braga, A.R.C.; Sala, L.; Moraes, C.C.; Kalil, S.J. Design strategies for C-phycocyanin purification: Process influence on purity grade. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 252, 117453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.W.; Ju, X.Y.; Li, X.W.; Gong, Y.; Xu, M.J.; Zhang, C.M.; Yuan, B.; Lv, Z.P.; Qin, S. Fermentation conditions optimization, purification, and antioxidant activity of exopolysaccharides obtained from the plant growth-promoting endophytic actinobacterium Glutamicibacter halophytocola KLBMP 5180. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafarani-Moattar, M.T.; Nasiri, S. (Liquid + liquid) and (liquid + solid) equilibrium of aqueous two-phase systems containing poly ethylene glycol di-methyl ether 2000 and di-sodium hydrogen phosphate. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2010, 42, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertsson, P.E.R.Å. Partition of Proteins in Liquid Polymer–Polymer Two-Phase Systems. Nature 1958, 182, 709–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaslavsky, B.Y. Aqueous Two-Phase Partitioning—Physical Chemistry and Bioanalytical Applications. Ber. Der Bunsenges. Für Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, S.; Murty, R.; Thivaharan, V.; Rajasekar, V.; Ramesh, V. Aqueous Two Phase Systems for the Recovery of Biomolecules –A Review. Sci. Technol. 2012, 1, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, R.R.; Azevedo, A.M.; Van Alstine, J.M.; Aires-Barros, M.R. Partitioning in aqueous two-phase systems: Analysis of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 10, 1158–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phong, W.N.; Show, P.L.; Chow, Y.H.; Ling, T.C. Recovery of biotechnological products using aqueous two phase systems. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2018, 126, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, A.W.; da Cruz Silva, K.; Mageste, A.B.; Rodrigues, G.D.; de Lemos, L.R. Lycopene partition in new aqueous two-phase systems. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 339, 116755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides, J.; Rito-Palomares, M.; Asenjo, J. Aqueous two-phase systems. In Comprehensive Biotechnology, 2nd ed.; Moo-Young, M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 2, pp. 697–713. [Google Scholar]
- Albertsson, P.-Å.; Cajarville, A.; Brooks, D.E.; Tjerneld, F. Partition of proteins in aqueous polymer two-phase systems and the effect of molecular weight of the polymer. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 1987, 926, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, R.D.; Bond, A.H.; Bauer, C.B.; Zhang, J.; Griffin, S.T. Metal ion separations in polyethylene glycol-based aqueous biphasic systems: Correlation of partitioning behavior with available thermodynamic hydration data. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1996, 680, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.M.; Van Ness, H.C.; Abbott, M.M. Introdução à Termodinâmica da Engenharia Química, 7th ed.; LTC: New York, NY, USA, 2007; p. 584. [Google Scholar]
- Albertsson, P.A. Partition of Cell Particles and Macromolecules, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1986; p. 346. [Google Scholar]
- Tubio, G.; Nerli, B.B.; Picó, G.A.; Venâncio, A.; Teixeira, J. Liquid–liquid equilibrium of the Ucon 50-HB5100/sodium citrate aqueous two-phase systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 65, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchuk, J.C.; Andrews, B.A.; Asenjo, J.A. Aqueous two-phase systems for protein separation: Studies on phase inversion. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1998, 711, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutowski, K.E.; Broker, G.A.; Willauer, H.D.; Huddleston, J.G.; Swatloski, R.P.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Controlling the Aqueous Miscibility of Ionic Liquids: Aqueous Biphasic Systems of Water-Miscible Ionic Liquids and Water-Structuring Salts for Recycle, Metathesis, and Separations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 6632–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molino, J.V.; Viana Marques Dde, A.; Júnior, A.P.; Mazzola, P.G.; Gatti, M.S. Different types of aqueous two-phase systems for biomolecule and bioparticle extraction and purification. Biotechnol. Prog. 2013, 29, 1343–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, A.M.; Rosa, P.A.J.; Ferreira, I.F.; Pisco, A.M.M.O.; de Vries, J.; Korporaal, R.; Visser, T.J.; Aires-Barros, M.R. Affinity-enhanced purification of human antibodies by aqueous two-phase extraction. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 65, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rito-Palomares, M. Practical application of aqueous two-phase partition to process development for the recovery of biological products. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2004, 807, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, R.L.; Barbosa, J.M.; Zanin, G.M.; Lobão, M.W.; Soares, C.M.; Lima, A.S. Partitioning of porcine pancreatic lipase in a two-phase systems of polyethylene glycol/potassium phosphate aqueous. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 161, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biazus, J.P.M.; Santana, J.; Souza, R.; Jordão, E.; Tambourgi, E. Continuous extraction of α- and β-amylases from Zea mays malt in a PEG4000/CaCl2 ATPS. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2007, 858, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.A.S.; Coimbra, J.S.R.; Rojas, E.E.G.; Teixeira, J.A.C. Partitioning of glycomacropeptide in aqueous two-phase systems. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 1213–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Tao, Y.; Xie, S.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Peng, D.; Sattar, A.; Shabbir, M.A.B.; et al. Aqueous two-phase system (ATPS): An overview and advances in its applications. Biol. Proc. Online 2016, 18, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, K.M.; Maciel, G.E.L.O.; Buarque, F.S.; Santos, A.J.; Marques, M.N.; Cavalcanti, E.B.; Soares, C.M.F.; Lima, Á.S. Novel phase diagrams of aqueous two-phase systems based on tetrahydrofuran + carbohydrates + water: Equilibrium data and partitioning experiments. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2017, 433, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, K.M.; Merlo, L.H.Z.; Marques, M.N.; Cavalcanti, E.B.; Souza, R.L.; Soares, C.M.F.; Lima, A.S. Partitioning of diuron in a novel aqueous two-phase system based on polyols and tetrahydrofuran. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2016, 429, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buarque, F.S.; Soares, C.M.F.; de Souza, R.L.; Pereira, M.M.; Lima, Á.S. Development of an ethanolic two-phase system (ETPS) based on polypropylene glycol 2000 + ethylene glycol + ethanol for separation of hydrophobic compounds. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 2156–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buarque, F.S.; Soares, C.M.F.; Marques, M.N.; Miranda, R.d.C.M.; Cavalcanti, E.B.; Souza, R.L.; Lima, Á.S. Simultaneous concentration and chromatographic detection of water pesticides traces using aqueous two-phase system composed of tetrahydrofuran and fructose. Microchem. J. 2019, 147, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Sha, X.; Chao, Y.; Chen, G.; Han, C.; Zhu, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q. Green aqueous biphasic systems containing deep eutectic solvents and sodium salts for the extraction of protein. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 49361–49367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, H.; Tavares, D.J.P.; Ferreira, A.M.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Are Aqueous Biphasic Systems Composed of Deep Eutectic Solvents Ternary or Quaternary Systems? ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2881–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y. Conductivities, Volumes, Fluorescence, and Aggregation Behavior of Ionic Liquids [C4mim][BF4] and [Cnmim]Br (n = 4, 6, 8, 10, 12) in Aqueous Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 6181–6188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, M.J.; Esperança, J.M.S.S.; Gilea, M.A.; Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Magee, J.W.; Seddon, K.R.; Widegren, J.A. The distillation and volatility of ionic liquids. Nature 2006, 439, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, R.D.; Seddon, K.R. Chemistry. Ionic liquids—Solvents of the future? Science 2003, 302, 792–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plácido, N.S.O.; Carlos, A.L.S.; Galvão, J.U.S.; Souza, R.L.; Soares, C.M.F.; Mattedi, S.; Fricks, A.T.; Lima, Á.S. Protic ionic liquids as a constituent of biphasic systems based on acetonitrile: Phase diagram and alkaloid partitioning. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 200, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.-J.; Li, S.-N.; Zhai, Q.-G.; Jiang, Y.-C.; Hu, M.-C. Physicochemical Properties for the Binary Systems of Ionic Liquids [Cnmim]Cl + N,N-Dimethylformamide. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2014, 59, 1411–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, V.H.; Dosil, N.; Gonzalez-Cabaleiro, R.; Mattedi, S.; Martin-Pastor, M.; Iglesias, M.; Navaza, J.M. Brønsted Ionic Liquids for Sustainable Processes: Synthesis and Physical Properties. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, V.H.; Mattedi, S.; Martin-Pastor, M.; Aznar, M.; Iglesias, M. Synthesis and thermophysical properties of two new protic long-chain ionic liquids with the oleate anion. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2010, 299, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deetlefs, M.; Seddon, K.R. Assessing the greenness of some typical laboratory ionic liquid preparations. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Pérez, M.; Tomé, L.I.N.; Freire, M.G.; Marrucho, I.M.; Cabeza, O.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Extraction of biomolecules using aqueous biphasic systems formed by ionic liquids and aminoacids. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 72, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quental, M.V.; Pereira, M.M.; Ferreira, A.M.; Pedro, S.N.; Shahriari, S.; Mohamadou, A.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Enhanced separation performance of aqueous biphasic systems formed by carbohydrates and tetraalkylphosphonium- or tetraalkylammonium-based ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 2978–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.G.; Pereira, J.F.; Francisco, M.; Rodríguez, H.; Rebelo, L.P.; Rogers, R.D.; Coutinho, J.A. Insight into the interactions that control the phase behaviour of new aqueous biphasic systems composed of polyethylene glycol polymers and ionic liquids. Chemistry 2012, 18, 1831–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, S.P.M.; Neves, C.M.S.S.; Freire, M.G.; Marrucho, I.M.; Oliveira, J.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Evaluation of Anion Influence on the Formation and Extraction Capacity of Ionic-Liquid-Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 9304–9310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, J. Partitioning behavior of amino acids in aqueous two-phase systems formed by imidazolium ionic liquid and dipotassium hydrogen phosphate. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1231, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchel, M.; João, K.G.; Marrucho, I.M. On the use of ionic liquids as adjuvants in PEG-(NH4)2SO4 aqueous biphasic systems: Phase diagrams behavior and the effect of IL concentration on myoglobin partition. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 210, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourão, T.; Cláudio, A.F.M.; Boal-Palheiros, I.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Evaluation of the impact of phosphate salts on the formation of ionic-liquid-based aqueous biphasic systems. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2012, 54, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patinha, D.J.S.; Alves, F.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Marrucho, I.M. Ionic liquids based aqueous biphasic systems: Effect of the alkyl chains in the cation versus in the anion. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2013, 65, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.; Kurnia, K.; Cojocaru, O.; Gurau, G.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Rogers, R.; Freire, M. Molecular interactions in aqueous biphasic systems composed of polyethylene glycol and crystalline vs. liquid cholinium-based salts. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 5723–5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, A.; Arce, A.; Khoshkbarchi, M.K. Partitioning of antibiotics in a two-liquid phase system formed by water and a room temperature ionic liquid. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 44, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, H.F.D.; Marrucho, I.M.; Freire, M.G. Removal of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs from Aqueous Environments with Reusable Ionic-Liquid-based Systems. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2428–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.A.; Caban, M.; Kholany, M.; Stepnowski, P.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Ventura, S.P.M. Recovery of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs from Wastes Using Ionic-Liquid-Based Three-Phase Partitioning Systems. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4574–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buarque, F.S.; Barreto, V.S.; Soares, C.M.F.; Souza, R.L.; Pereira, M.M.; Lima, Á.S. Selective extraction of female hormones using aqueous two-phase system composed of double protic ionic liquid + acetonitrile. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2020, 508, 112443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quental, M.V.; Caban, M.; Pereira, M.M.; Stepnowski, P.; Coutinho, J.A.; Freire, M.G. Enhanced extraction of proteins using cholinium-based ionic liquids as phase-forming components of aqueous biphasic systems. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 10, 1457–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.M.; Cruz, R.A.P.; Almeida, M.R.; Lima, Á.S.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Single-step purification of ovalbumin from egg white using aqueous biphasic systems. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Khoiroh, I.; Ling, T.C.; Show, P.L. Aqueous Two-Phase Flotation for the Recovery of Biomolecules. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2016, 45, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akama, Y.; Ito, M.; Tanaka, S. Selective separation of cadmium from cobalt, copper, iron (III) and zinc by water-based two-phase system of tetrabutylammonium bromide. Talanta 2000, 53, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akama, Y.; Sali, A. Extraction mechanism of Cr(VI) on the aqueous two-phase system of tetrabutylammonium bromide and (NH(4))(2)SO(4) mixture. Talanta 2002, 57, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, B.S.; D’Anzicourt, C.M.d.S.; Soares, C.M.F.; Souza, R.L.; Lima, Á.S. Liquid-Liquid extraction of phenolic compounds in systems based on acetonitrile + water + polyvinylpyrrolidone at 298.15 K. Data Brief 2018, 20, 2045–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosário, R.; Souza, R.; Farias, F.; Mafra, M.; Soares, C.; Passos, H.; Coutinho, J.; Lima, Á. Acetonitrile as adjuvant to tune polyethylene glycol + K3PO4 aqueous two-phase systems and its effect on phenolic compounds partition. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 223, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.F.B.; Lima, Á.S.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Ionic liquids as adjuvants for the tailored extraction of biomolecules in aqueous biphasic systems. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, R.L.; Campos, V.C.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Soares, C.M.F.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Lima, Á.S. Effect of ionic liquids as adjuvants on PEG-based ABS formation and the extraction of two probe dyes. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2014, 375, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Zhou, C.; Yu, X.; Yagoub, A.E.-G.A.; Ma, H. Effect of ionic liquid based imidazolium as an additive on the formation of polymer/salt aqueous biphasic systems. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 256, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.R.; Passos, H.; Pereira, M.M.; Lima, Á.S.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Ionic liquids as additives to enhance the extraction of antioxidants in aqueous two-phase systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 128, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, J.P.; Welton, T. Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids: Solvents for Synthesis and Catalysis. 2. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3508–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.B.; Domínguez-Pérez, M.; Cabeza, O.; Lopes-da-Silva, J.A.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Surface tensions of binary mixtures of ionic liquids with bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide as the common anion. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2013, 64, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buarque, F.S.; Camêlo, L.C.A.; Soares, C.M.F.; Mattedi, S.; Ferreira, A.F.B.; Feitosa, F.X.; Souza, R.L.; de Sant’Ana, H.B.; Lima, Á.S. Binary Mixture of Double Protic Ionic Liquid: Density, Viscosity, Refractive Index, Surface Tension, and Derivative Properties. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2021, 66, 4309–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 1, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, M.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; Kroon, M.C. Low-transition-temperature mixtures (LTTMs): A new generation of designer solvents. Angew. Chem. (Int. Ed. Engl.) 2013, 52, 3074–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Boothby, D.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K. Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed between Choline Chloride and Carboxylic Acids: Versatile Alternatives to Ionic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9142–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, M.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; Kroon, M.C. New natural and renewable low transition temperature mixtures (LTTMs): Screening as solvents for lignocellulosic biomass processing. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 2153–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Witkamp, G.-J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents as a New Extraction Media for Phenolic Metabolites in Carthamus tinctorius L. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6272–6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. Green solvents for the extraction of bioactive compounds from natural products using ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 26, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvjetko Bubalo, M.; Vidović, S.; Radojčić Redovniković, I.; Jokić, S. New perspective in extraction of plant biologically active compounds by green solvents. Food Bioprod. Process. 2018, 109, 52–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanda, H.; Dai, Y.; Wilson, E.G.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Green solvents from ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents to natural deep eutectic solvents. Comptes. Rendus Chim. 2018, 21, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Pertiwi, A.S.; Kembaren, Y.H.; Rahman, A.; Munâim, A. Application of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Ultrasonic Assisted Extraction of Total Polyphenolic and Caffeine Content from Coffe Beans (Coffea Beans L.) For Instant Food Products. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 8, 138–143. [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri, J.B.; Goltz, C.; Batistão Cavalheiro, F.; Theodoro Toci, A.; Igarashi-Mafra, L.; Mafra, M.R. Deep eutectic solvents applied in the extraction and stabilization of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) phenolic compounds. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 144, 112049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kantar, S.; Rajha, H.N.; Boussetta, N.; Vorobiev, E.; Maroun, R.G.; Louka, N. Green extraction of polyphenols from grapefruit peels using high voltage electrical discharges, deep eutectic solvents and aqueous glycerol. Food Chem. 2019, 295, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Cai, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Tan, Z. Extraction and preliminary purification of polysaccharides from Camellia oleifera Abel. seed cake using a thermoseparating aqueous two-phase system based on EOPO copolymer and deep eutectic solvents. Food Chem. 2020, 313, 126164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ding, X.; Chen, J.; Xu, K. Deep eutectic solvents as novel extraction media for protein partitioning. Analyst 2014, 139, 2565–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, M.A.R.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Insights into the Nature of Eutectic and Deep Eutectic Mixtures. J. Solut. Chem. 2019, 48, 962–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, C.F. Chapter 2—Solvent selection for liquid-phase extraction. In Liquid-Phase Extraction; Poole, C.F., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 45–89. [Google Scholar]
- Grundtvig, I.P.R.; Heintz, S.; Krühne, U.; Gernaey, K.V.; Adlercreutz, P.; Hayler, J.D.; Wells, A.S.; Woodley, J.M. Screening of organic solvents for bioprocesses using aqueous-organic two-phase systems. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1801–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grecco, C.; Miranda, L.; Cruz, J.; Queiroz, M.E. Extração líquido-líquido assistida pelo efeito salting out para análise de amostras biológicas. Sci. Chromatogr. 2018, 10, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.H.; Zheng, P.; Yan, Q.; Liu, W. Aqueous two-phase system: An alternative process for recovery of succinic acid from fermentation broth. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 138, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Song, W.; Fu, C.; Yi, C.; Qiu, X. Separation of acetone: From a water miscible system to an efficient aqueous two-phase system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 192, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, R.M.; Netto, G.C.A.; Petrin, L.C.G.; Pelaquim, F.P.; Sosa, F.H.B.; Costa, M.C.D. Aqueous two-phase system formed by alkanolammonium-based Protic Ionic Liquids and acetone: Experimental data, thermodynamic modeling, and Kraft lignin partition. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 250, 117207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, G.B.; Mourão, T.; Pereira, F.M.; Freire, M.G.; Fricks, A.T.; Soares, C.M.F.; Lima, Á.S. Aqueous two-phase systems based on acetonitrile and carbohydrates and their application to the extraction of vanillin. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 104, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, G.B.; Souza, I.N.; Mourão, T.; Freire, M.G.; Soares, C.M.F.; Lima, Á.S. Novel aqueous two-phase systems composed of acetonitrile and polyols: Phase diagrams and extractive performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 124, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camêlo, L.C.A.; Souza Dias Santos, G.; Lucena de Souza, R.; Faria Soares, C.M.; Brandão Pereira, J.F.; Lima, Á.S. Protic ionic liquids as constituent of aqueous two-phase system based on acetonitrile: Synthesis, phase diagrams and genipin pre-purification. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2020, 507, 112425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, I.N.; Soares, C.M.F.; Souza, R.L.; Freire, M.G.; Lima, A.S. Aqueous two-phase systems formed by maltodextrin and acetonitrile: Phase diagrams and partitioning studies. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2018, 476, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, C.W.; Tey, B.T.; Hii, S.L.; Kamal, S.M.M.; Lan, J.C.W.; Ariff, A.; Ling, T.C. Purification of lipase derived from Burkholderia pseudomallei with alcohol/salt-based aqueous two-phase systems. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, I.A.O.; Santos, S.B.; Santos, L.A.; Oliveira, N.; Freire, M.G.; Pereira, J.F.B.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Soares, C.M.F.; Lima, Á.S. Increased significance of food wastes: Selective recovery of added-value compounds. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2453–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.C.; Ramanan, R.N.; Tey, B.T.; Tan, W.S.; Show, P.L.; Ling, T.C.; Ooi, C.W. Purification of the recombinant enhanced green fluorescent protein from Escherichia coli using alcohol+salt aqueous two-phase systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 192, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, F.O.; Oliveira, G.; Leal, F.C.; Wojeicchowski, J.P.; Yamamoto, C.I.; Igarashi-Mafra, L.; Mafra, M.R. Cholinium chloride effect on ethanol-based aqueous biphasic systems: Liquid-liquid equilibrium and biomolecules partition behavior. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2020, 505, 112363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, K.Y.; Brooks, M.S.-L. Effects of recycling on the aqueous two-phase extraction of bioactives from haskap leaves. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 255, 117755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.; Yang, C.; Xu, M.; Yi, Z.; Ren, D.; Yi, L. Enhanced aqueous two-phase extraction of proanthocyanidins from grape seeds by using ionic liquids as adjuvants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 226, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nainegali, B.S.; Iyyaswami, R.D.; Belur, P. Partitioning of bio-active compounds from rinds of Garcinia indica using aqueous two-phase system: Process evaluation and optimization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 253, 117520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wu, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Hu, Y. Liquid–liquid equilibria of hydrophilic alcohol+sodium hydroxide+water systems: Experimental and correlation. Thermochim. Acta 2013, 566, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Zhai, Q.; Liu, Z. Phase Diagram of the Cesium Carbonate + Ethanol + Water Ternary System at (0, 20, and 40) °C. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2004, 49, 717–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, J.; Xu, X.; Hu, S.; Yan, Y. Partition behavior and partition mechanism of antibiotics in ethanol/2-propanol–ammonium sulfate aqueous two-phase systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 75, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati-Kande, E.; Shekaari, H.; Jafari, S.A. Liquid–liquid equilibrium of 1-propanol, 2-propanol, 2-methyl-2-propanol or 2-butanol+sodium sulfite+water aqueous two phase systems. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2012, 329, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekaari, H.; Sadeghi, R.; Jafari, S.A. Liquid−Liquid Equilibria for Aliphatic Alcohols + Dipotassium Oxalate + Water. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 4586–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, P.A.; Lourenço, N.I.; Igarashi, E.M.S.; Sousa, M.N.; Arce, P.F. Thermodynamic Behavior of the Phase Equilibrium of Ethyl Acetate + Ethanol + Water Systems at Atmospheric Pressure: Experiment and Modeling. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2020, 65, 1402–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nainegali, B.S.; Iyyaswami, R.; Belur, P.D. Simultaneous extraction of four different bioactive compounds from Garcinia indica and their enrichment using Aqueous Two-Phase Systems. Food Bioprod. Process. 2019, 114, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buarque, F.S.; Guimarães, D.E.M.; Soares, C.M.F.; Souza, R.L.; Pereira, M.M.; Lima, Á.S. Ethanolic two-phase system formed by polypropylene glycol, ethylene glycol and/or ionic liquid (phase-forming or adjuvant) as a platform to phase separation and partitioning study. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 344, 117702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klamt, A.; Eckert, F. COSMO-RS: A novel and efficient method for the a priori prediction of thermophysical data of liquids. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2000, 172, 43–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klamt, A. Conductor-like Screening Model for Real Solvents: A New Approach to the Quantitative Calculation of Solvation Phenomena. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 2224–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojeicchowski, J.P.; Ferreira, A.M.; Abranches, D.O.; Mafra, M.R.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Using COSMO-RS in the Design of Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Extraction of Antioxidants from Rosemary. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 12132–12141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.F.B.; Magri, A.; Quental, M.V.; Gonzalez-Miquel, M.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Alkaloids as Alternative Probes To Characterize the Relative Hydrophobicity of Aqueous Biphasic Systems. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Taha, M.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Interactions of pyridinium, pyrrolidinium or piperidinium based ionic liquids with water: Measurements and COSMO-RS modelling. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2016, 414, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Kurnia, K.A.; Sintra, T.E.; Saraiva, J.A.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Assessing the activity coefficients of water in cholinium-based ionic liquids: Experimental measurements and COSMO-RS modeling. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2014, 361, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Gong, Z.; Zheng, L.; Kalhor, P.; Huai, Z.; Liu, Z. Molecular modelling of ionic liquids: General guidelines on fixed-charge force fields for balanced descriptions. J. Ion. Liq. 2022, 2, 100043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wang, M.; He, Q.; Liu, Z. Molecular Modeling of Ionic Liquids: Force-Field Validation and Thermodynamic Perspective from Large-Scale Fast-Growth Solvation Free Energy Calculations. Adv. Theory Simul. 2022, 5, 2200274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, K.Y.; Stefanova, R.; Zhang, J.; Brooks, M.S.-L. Aqueous two-phase extraction of bioactive compounds from haskap leaves (Lonicera caerulea): Comparison of salt/ethanol and sugar/propanol systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 252, 117399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, P.G.C. Processo Integrativo de Extração e Purificação de Compostos Bioativos Presentes No Alecrim (Rosmarinus Officinalis); Universidade Tiradentes—UNIT: Aracajú, Brasil, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.-K.; Show, P.-L.; Lan, J.C.-W.; Tsai, J.-C.; Huang, C.-R. Isolation of C-phycocyanin from Spirulina platensis microalga using Ionic liquid based aqueous two-phase system. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 270, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, I.H.; Chiu, H.H.; Lu, C.H.; Lee, L.T.; Li, Y.K. Aqueous two-phase extraction as an effective tool for isolation of geniposide from gardenia fruit. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 977, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, W.; Deng, Q. Purification of salvianolic acid B from the crude extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza with hydrophilic organic/salt-containing aqueous two-phase system by counter-current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1116, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cláudio, A.F.M.; Freire, M.G.; Freire, C.S.R.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Extraction of vanillin using ionic-liquid-based aqueous two-phase systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 75, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liang, L.; Zou, Y.; Zhao, T.; Zhao, J.; Li, F.; Yang, L. Aqueous two-phase extraction, identification and antioxidant activity of anthocyanins from mulberry (Morus atropurpurea Roxb.). Food Chem. 2011, 129, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.X.; Han, J.; Zhang, D.Y.; Wang, L.H.; Zhou, L.L. An ammonium sulfate/ethanol aqueous two-phase system combined with ultrasonication for the separation and purification of lithospermic acid B from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2012, 19, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cláudio, A.F.M.; Ferreira, A.M.; Freire, C.S.R.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Optimization of the gallic acid extraction using ionic-liquid-based aqueous two-phase systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 97, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, G.d.B.; Souza, I.N.; Pereira, M.M.; Freire, M.G.; Soares, C.M.F.; Lima, Á.S. Aqueous two-phase systems formed by biocompatible and biodegradable polysaccharides and acetonitrile. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 136, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, I.A.O.; Santos, S.B.; Pereira, F.D.S.; Sobral, C.R.S.; Freire, M.G.; Freitas, L.S.; Soares, C.M.F.; Lima, Á.S. Extraction and Recovery of Rutin from Acerola Waste using Alcohol-Salt-Based Aqueous Two-Phase Systems. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Han, J.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Ni, L. Extraction and preliminary purification of anthocyanins from grape juice in aqueous two-phase system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 124, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cláudio, A.F.M.; Marques, C.F.C.; Boal-Palheiros, I.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Development of back-extraction and recyclability routes for ionic-liquid-based aqueous two-phase systems. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-L.; Li, F.-F.; Tan, Z.-J. Chiral separation of α-cyclohexylmandelic acid enantiomers using ionic liquid/salt aqueous two-phase system. Chem. Pap. 2015, 69, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, I.A.O.; Campos, A.F.; Santos, P.H.S.; Santos, S.B.; Soares, C.M.F.; Lima, Á.S. Potassium Phosphate Salts-Based Aqueous Two-Phase Systems Applied in the Extraction of Gallic Acid from Guava. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.H.; e Silva, F.A.; Ventura, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.; de Souza, R.L.; Soares, C.M.; Lima, Á.S. Ionic liquid-based aqueous biphasic systems as a versatile tool for the recovery of antioxidant compounds. Biotechnol. Prog. 2015, 31, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.; Lai, C.J.; OuYang, H.; He, M.Z.; Feng, Y. Ionic liquid-based ultrasound-assisted extraction and aqueous two-phase system for analysis of caffeoylquinic acids from Flos Lonicerae Japonicae. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 120, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Cheng, L.; Song, H.; Yu, L.; Zhong, F.; Shen, Q.; Hu, H. Aqueous two-phase system for preliminary purification of lignans from fruits of Schisandra chinensis Baill. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 166, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.X.; Shi, C.Z.; Zhang, L.; Lv, L.; Zhang, Y.Y. Extraction and isolation of lithospermic acid B from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge using aqueous two-phase extraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 3624–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Y.; Qiu, Y.; Ren, H.; Ju, D.H.; Jia, H.L. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted aqueous two-phase system extraction of polyphenolic compounds from Aronia melanocarpa pomace by response surface methodology. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 47, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Hong, Z.; Gao, M.; Wang, Z.; Gu, M.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, H. Polarity, selectivity and performance of hydrophilic organic/salt-containing aqueous two-phase system on counter-current chromatography for polar compounds. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1448, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Tan, Z.; Li, F.; Li, X. An effective method for the extraction and purification of chlorogenic acid from ramie (Boehmeria nivea L.) leaves using acidic ionic liquids. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 89, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.-W.; Zong, Y.; Xiao, Y.-X. Hexafluoroisopropanol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent/Salt Aqueous Two-Phase Systems for Extraction of Anthraquinones from Rhei Radix et Rhizoma Samples. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4267–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, F.; He, C.; Yu, Y.; Wang, M. Optimization of Ultrasonic-Assisted Aqueous Two-Phase Extraction of Phloridzin from Malus Micromalus Makino with Ethanol/Ammonia Sulfate System. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2944–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farias, F.O.; Sosa, F.H.B.; Igarashi-Mafra, L.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Mafra, M.R. Study of the pseudo-ternary aqueous two-phase systems of deep eutectic solvent (choline chloride:sugars) + K2HPO4 + water. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2017, 448, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Chang, Y.; Tan, Z.; Li, F. A novel combined process for extracting, separating and recovering flavonoids from flos sophorae immaturus. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 172, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, F.O.; Passos, H.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Mafra, M.R. pH Effect on the Formation of Deep-Eutectic-Solvent-Based Aqueous Two-Phase Systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 16917–16924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.-Q.; Ma, N.; Sun, W.-P.; Dang, Y.-Y. Microwave and enzyme co-assisted aqueous two-phase extraction of polyphenol and lutein from marigold (Tagetes erecta L.) flower. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 123, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.A.; Kholany, M.; Sintra, T.E.; Caban, M.; Stepnowski, P.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Aqueous Biphasic Systems Using Chiral Ionic Liquids for the Enantioseparation of Mandelic Acid Enantiomers. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2018, 36, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Gu, C.-B.; Wang, S.-X.; Kou, P.; Jiao, J.; Fu, Y.-J. Simultaneous extraction, transformation and purification of psoralen from fig leaves using pH-dependent ionic liquid solvent based aqueous two-phase system. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Mu, X.; Chen, G.; Gou, Y.; Wang, C.; Yuan, X. Water-insoluble cosolvent in aqueous two-phase system improved the extraction of paeonol from cortex moutan. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 2229–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, G.; Hazarika, S. Ionic liquid-mediated aqueous two-phase system to enhance the partitioning of lignin. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 2527–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miličević, N.; Panić, M.; Valinger, D.; Cvjetko Bubalo, M.; Benković, M.; Jurina, T.; Gajdoš Kljusurić, J.; Radojčić Redovniković, I.; Jurinjak Tušek, A. Development of continuously operated aqueous two-phase microextraction process using natural deep eutectic solvents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 244, 116746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzideh, S.M.; Movagharnejad, K.; Pirdashti, M. Ion-solvent interaction of 1-decyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride and isopropanol in a quaternary aqueous two phase system for the efficient partitioning of vanillin and L-tryptophan. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 332, 115860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, Á.S.; Oliveira, B.S.d.; Shabudin, S.V.; Almeida, M.; Freire, M.G.; Bica, K. Purification of anthocyanins from grape pomace by centrifugal partition chromatography. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 326, 115324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristina Alves Camêlo, L.; de Souza Dias Santos, G.; Lucena de Souza, R.; Faria Soares, C.M.; Brandão Pereira, J.F.; Silva Lima, Á. Pre-purification of genipin from genipap using aqueous-two-phase systems composed of protic ionic liquids + polymers + water at 298 K and atmospheric pressure. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 256, 117843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, L. Extraction of geniposidic acid and aucubin employing aqueous two-phase systems comprising ionic liquids and salts. Microchem. J. 2021, 169, 106592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, X.; Hao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, J. Highly selective separation of acteoside from Cistanche tubulosa using an ionic liquid based aqueous two–phase system. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 333, 115982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yu, X.; Zhou, C.; Yagoub, A.E.A.; Sun, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, L. Development of back-extraction recyclability of IL-ATPS for the efficient recovery of syringic and caffeic acid. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 328, 115390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Chen, L.; Yin, K.; Fan, T.; Yan, Z. Sugars as hydrogen-bond donors tune the phase behavior in a novel liquid–liquid biphasic system formed by hydrophilic deep eutectic solvents and n-propanol. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2022, 556, 113393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Jia, M.; Huang, L.; He, Y.; Dong, S. Rapid Extraction of Yam Peel Total Flavonoids in A Cholinium-Based Magnetic Ionic Liquid Aqueous Biphasic System. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2022, 21, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, I.L.D.; da Costa Lopes, A.M.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Selective Separation of Vanillic Acid from Other Lignin-Derived Monomers Using Centrifugal Partition Chromatography: The Effect of pH. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 4913–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumcu, T.; Seyhan Bozkurt, S. Simultaneous extraction of five phenolic acids in fruits using ultrasound assisted aqueous two phase system based on polyethylene glycol-ionic liquid-sodium carbonate. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Chen, L.; Liu, F.; Fan, T.; Yan, Z. Pseudoternary Systems of Deep Eutectic Solvents + tert-Butanol + Water at T = 288.15 K, 298.15 K, and 308.15 K: Liquid–Liquid Equilibrium and Ability for Syringic Acid/Eugenol Separation. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2022, 67, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; He, C.; Liu, H.; Li, K.; Liu, F. Ionic liquid-based aqueous two-phase system, a sample pretreatment procedure prior to high-performance liquid chromatography of opium alkaloids. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2005, 826, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louros, C.L.; Cláudio, A.F.; Neves, C.M.; Freire, M.G.; Marrucho, I.M.; Pauly, J.; Coutinho, J.A. Extraction of biomolecules using phosphonium-based ionic liquids + K(3)PO(4) aqueous biphasic systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 1777–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.-P.; Cao, J.; Zhang, X.-H.; Huang, J.-Z.; Kong, T.; Tong, S.; Tian, Z.-Y.; Zhu, J.-H.; Ouyang, X.-K. Extraction of Puerarin using Ionic Liquid Based Aqueous Two-Phase Systems. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 1740–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.F.B.; Ventura, S.P.M.; e Silva, F.A.; Shahriari, S.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Aqueous biphasic systems composed of ionic liquids and polymers: A platform for the purification of biomolecules. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 113, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, H.; Trindade, M.P.; Vaz, T.S.M.; da Costa, L.P.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. The impact of self-aggregation on the extraction of biomolecules in ionic-liquid-based aqueous two-phase systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 108, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolrahimi, S.; Nasernejad, B.; Pazuki, G. Prediction of partition coefficients of alkaloids in ionic liquids based aqueous biphasic systems using hybrid group method of data handling (GMDH) neural network. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 191, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, D.; Fan, H.; Liu, X.; Wan, Q.; Wu, X.; Liu, P.; Tang, J.Z. Simultaneous extraction and purification of alkaloids from Sophora flavescens Ait. by microwave-assisted aqueous two-phase extraction with ethanol/ammonia sulfate system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 141, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keremedchieva, R.; Svinyarov, I.; Bogdanov, M.G. Ionic Liquid-Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems—A Facile Approach for Ionic Liquid Regeneration from Crude Plant Extracts. Processes 2015, 3, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.B.; Reis, I.A.O.; Silva, C.P.C.; Campos, A.F.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Soares, C.M.F.; Lima, Á.S. Selective partition of caffeine from coffee bean and guaraná seed extracts using alcohol–salt aqueous two-phase systems. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 2008–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.L.; Santos, L.N.S.; Ventura, S.P.M.; de Souza, R.L.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Soares, C.M.F.; Lima, Á.S. Recovery of capsaicin from Capsicum frutescens by applying aqueous two-phase systems based on acetonitrile and cholinium-based ionic liquids. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2016, 112, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Jin, Y. Green determination of aconitum alkaloids in Aconitum carmichaeli (Fuzi) by an ionic liquid aqueous two-phase system and recovery of the ionic liquid coupled with in situ liquid–liquid microextraction. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 6566–6572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, D.A.; Sosa, F.H.B.; Martins, A.D.; Igarashi-Mafra, L.; Yamamoto, C.I.; Souza, M.O.; Castilhos, F.; Mafra, M.R. Assessment of Sodium Salt Anions (SO42- and NO3-) Influence on Caffeine Partitioning in Polyethylene Glycol and 1-Butyl-3-Methylimidazolium Tetrafluoroborate Based ATPS. J. Solut. Chem. 2016, 45, 1857–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cienfuegos, N.E.C.; Santos, P.L.; García, A.R.; Soares, C.M.F.; Lima, A.S.; Souza, R.L. Integrated process for purification of capsaicin using aqueous two-phase systems based on ethanol. Food Bioprod. Process. 2017, 106, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, F.O.; Passos, H.; Lima, Á.S.; Mafra, M.R.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Is It Possible to Create Ternary-like Aqueous Biphasic Systems with Deep Eutectic Solvents? ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 9402–9411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, N.; Sadeghi, R. Propanol—Sugar aqueous biphasic systems as a suitable platform for biomolecules extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1581–1582, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wu, X.; Huang, Y.; Xie, X.; Lin, Y.; Fan, H.; Luo, L.; Zhang, W.; Tang, J.Z. Microwave-assisted aqueous two-phase extraction of alkaloids from Radix Sophorae Tonkinensis with an ethanol/Na2HPO4 system: Process optimization, composition identification and quantification analysis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 122, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, Q.; Wu, S.; Sun, D.; Tan, Z. Salting-out extraction of sinomenine from Sinomenium acutum by an alcohol/salt aqueous two-phase system using ionic liquids as additives. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 1925–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, F.O.; Passos, H.; Sanglard, M.G.; Igarashi-Mafra, L.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Mafra, M.R. Designer solvent ability of alcohols in aqueous biphasic systems composed of deep eutectic solvents and potassium phosphate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 200, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.d.C.S.; Pereira, M.M.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Evaluation of the effect of ionic liquids as adjuvants in polymer-based aqueous biphasic systems using biomolecules as molecular probes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 196, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Pei, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, J. Choline derivative ionic liquids-based aqueous two-phase systems: Phase diagrams and partition of purine alkaloids. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2018, 118, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.-r.; Song, H.; Yohannes, A.; Liang, S.; Yao, S. Extraction in cholinium-based magnetic ionic liquid aqueous two-phase system for the determination of berberine hydrochloride in Rhizoma coptidis. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 25201–25209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo, M.O.; Farias, F.O.; Igarashi-Mafra, L.; Mafra, M.R. Salt Effect on Ethanol-Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems Applied to Alkaloids Partition: An Experimental and Theoretical Approach. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 2018–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, C.; Sousa, R.C.S.; Pereira, M.M.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Understanding the Effect of Ionic Liquids as Adjuvants in the Partition of Biomolecules in Aqueous Two-Phase Systems Formed by Polymers and Weak Salting-Out Agents. Biochem. Eng. J. 2019, 141, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdabadi, A.; Shahriari, S.; Salehifar, M. Extraction of caffeine using aqueous two-phase systems containing ionic liquid and sorbitol. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2019, 502, 112287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaiahgari, A.; Passos, H.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Gardas, R.L. The influence of zwitterions on the partition of biomolecules in aqueous biphasic systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 253, 117537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaiahgari, A.; Priyanka, V.P.; Ijardar, S.P.; Gardas, R.L. Aqueous biphasic systems of amino acid-based ionic liquids: Evaluation of phase behavior and extraction capability for caffeine. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2020, 506, 112373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, P.; Jouyban, A. Partitioning behavior of caffeine, lamotrigine, clonazepam and oxcarbazepine in a biodegradable aqueous two-phase system comprising of polyethylene glycol dimethyl ether 250 and choline chloride/saccharose deep eutectic solvent. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 323, 115055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalvo-Hernández, B.; Rito-Palomares, M.; Benavides, J. Recovery of crocins from saffron stigmas (Crocus sativus) in aqueous two-phase systems. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1236, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Wu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Ni, L.; Li, Y. Simultaneous aqueous two-phase extraction and saponification reaction of chlorophyll from silkworm excrement. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 115, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Gao, M.; Wang, X.; Song, R.; Lu, J.; Chen, X. Separation of curcuminoids using ionic liquid based aqueous two-phase system coupled with in situ dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. Talanta 2016, 149, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, R.P.; Souza, L.M.; Balieiro, A.L.; Soares, C.M.F.; Lima, Á.S.; Souza, R.L. Integrated process of extraction and purification of betanin from Opuntia ficus-indica using aqueous two-phase systems based on THF and sodium salts. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemzadeh, B.; Shahriari, S.; Pazuki, G. Efficient separation of curcumin using tetra butyl phosphonium bromide / carbohydrates (sorbitol, fructose) aqueous two-phase system. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2019, 498, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnik, I.S.; Noronha, M.A.; Câmara, M.C.C.; Mazzola, P.G.; Vicente, A.A.; Pereira, J.F.B.; Lopes, A.M. Separation and purification of curcumin using novel aqueous two-phase micellar systems composed of amphiphilic copolymer and cholinium ionic liquids. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 250, 117262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Hou, Y. Efficient Purification of R-phycoerythrin from Marine Algae (Porphyra yezoensis) Based on a Deep Eutectic Solvents Aqueous Two-Phase System. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wei, N.; Wang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Ren, X.; Wei, Q. Single-step purification of C-phycocyanin from Arthrospira platensis using aqueous two-phase system based on natural deep eutectic solvents. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 3873–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-García, P.; Calvillo-Muñoz, E.Y.; Lijanova, I.V.; Likhanova, N.V.; Olivares-Xometl, O.; Arellanes-Lozada, P. Synthesis of Ammonium-Based Ionic Liquids for the Extraction Process of a Natural Pigment (Betanin). Molecules 2021, 26, 5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, L.; Xie, H. Distribution of pigments in the aqueous two-phase system formed with piperazinium-based ionic liquid and anionic surfactant. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 330, 115677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Mohammadian, M.; Pazuki, G.; Shahriari, S. Partitioning of Crocin in a Novel Aqueous Two-Phase System Composed of a Deep Eutectic Solvent and Acetonitrile. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2022, 67, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tianwei, T.; Qing, H.; Qiang, L. Purification of glycyrrhizin from Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch with ethanol/phosphate aqueous two phase system. Biotechnol. Lett. 2002, 24, 1417–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Xu, K.; Wen, Q.; Ding, X.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Q. High-performance of deep eutectic solvent based aqueous bi-phasic systems for the extraction of DNA. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 84406–84414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Teng, G.; Zhang, J. Ethanol/salt aqueous two-phase system based ultrasonically assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Lilium davidiivar. unicolor Salisb: Physicochemical characterization and antiglycation properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 256, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhao, P.; Liu, W.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, W.; Bao, L.; Jin, Y.; Li, X. Determination of common ginsenosides in Kang’ai injection by aqueous two-phase extraction with deep eutectic solvents and HPLC-UV/DAD. Microchem. J. 2018, 137, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.H.P.M.; Trigo, J.P.; Maricato, É.; Nunes, C.; Coimbra, M.A.; Ventura, S.P.M. Fractionation of Isochrysis galbana Proteins, Arabinans, and Glucans Using Ionic-Liquid-Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 14042–14053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Wei, X.; Xu, W.; Ni, R.; Meng, J.; Zhou, Y. A novel aqueous biphasic system formed by deep eutectic solvent and ionic liquid for DNA partitioning. Talanta 2018, 189, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía-Manzano, L.A.; Barba-Dávila, B.A.; Vázquez-Villegas, P.; Serna-Saldívar, S.O.; González-Valdez, J. Improved extraction of the natural anticancerigen pristimerin from Mortonia greggii root bark using green solvents and aqueous two-phase systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 211, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Wu, S.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Sun, D.; Li, F.; Tan, Z. Deep eutectic solvents used as adjuvants for improving the salting-out extraction of ursolic acid from Cynomorium songaricum Rupr. in aqueous two-phase system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 209, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Teng, G.; Zhang, J. Deep eutectic solvents aqueous two-phase system based ultrasonically assisted extraction of ursolic acid (UA) from Cynomorium songaricum Rupr. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2019, 206, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Hou, B.; Fang, H.; Sun, X.; Ma, F. Salting-out extraction of ginsenosides from the enzymatic hydrolysates of Panax quinquefolium based on ethanol/sodium carbonate system. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Li, W.; Ma, X.; Fan, D. Enzymatic hydrolysis and extraction of ginsenoside recovered from deep eutectic solvent-salt aqueous two-phase system. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2020, 130, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, C.A.S.; Kwaijtaal, J.; Peinado, O.C.; van den Berg, C.; Wijffels, R.H.; Eppink, M.H.M. Multistep Fractionation of Microalgal Biomolecules Using Selective Aqueous Two-Phase Systems. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 2441–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, C.A.S.; Baca, S.Z.; van den Broek, L.A.M.; van den Berg, C.; Wijffels, R.H.; Eppink, M.H.M. Selective fractionation of free glucose and starch from microalgae using aqueous two-phase systems. Algal Res. 2020, 46, 101801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandeira, L.; Sanromán, M.Á.; Deive, F.J.; Rodríguez, A. Cholinium dipeptide as the cornerstone to build promising separation processes: A simultaneous recovery strategy for microalgae biorefineries. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 250, 117288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athira, K.K.; Gardas, R.L. Insights into the Partitioning of DNA in Aqueous Biphasic System Containing Ammonium-based Ionic Liquid and Phosphate Buffer. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2022, 558, 113463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, C.A.S.; Cabau-Peinado, O.; van den Berg, C.; Wijffels, R.H.; Eppink, M.H.M. Efficient Fractionation of Lipids in a Multiproduct Microalgal Biorefinery by Polymers and Ionic Liquid-Based Aqueous Two-Phase Systems. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louwrier, A. Model isolations of nucleic acids from prokaryotic and eukaryotic sources using an organic/aqueous biphasic system. Biotechnol. Tech. 1999, 13, 329–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Li, Z.-G.; Dai, J.-Y.; Zhang, D.-J.; Xiu, Z.-L. Aqueous two-phase extraction of 2,3-butanediol from fermentation broths using an ethanol/phosphate system. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Teng, H.; Xiu, Z. Aqueous two-phase extraction of 2,3-butanediol from fermentation broths using an ethanol/ammonium sulfate system. Process Biochem. 2010, 45, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-G.; Sun, Y.-Q.; Zheng, W.-L.; Teng, H.; Xiu, Z.-L. A novel and environment-friendly bioprocess of 1,3-propanediol fermentation integrated with aqueous two-phase extraction by ethanol/sodium carbonate system. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 80, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratiwi, A.I.; Yokouchi, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Kondo, K. Extraction of succinic acid by aqueous two-phase system using alcohols/salts and ionic liquids/salts. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 155, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, K.; Li, N.; Wen, Q.; Yang, Q. Aqueous biphasic systems containing PEG-based deep eutectic solvents for high-performance partitioning of RNA. Talanta 2017, 170, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Lu, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z. Isolation of ionizable red Monascus pigments after extractive fermentation in nonionic surfactant micelle aqueous solution. Process Biochem. 2017, 61, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quental, M.V.; Pedro, A.Q.; Pereira, P.; Sharma, M.; Queiroz, J.A.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Sousa, F.; Freire, M.G. Integrated Extraction-Preservation Strategies for RNA Using Biobased Ionic Liquids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 9439–9448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.S.; Wan, P.K.; Ng, T.-C.; Lan, J.C.-W. Primary purification of intracellular Halomonas salina ectoine using ionic liquids-based aqueous biphasic system. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2020, 130, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
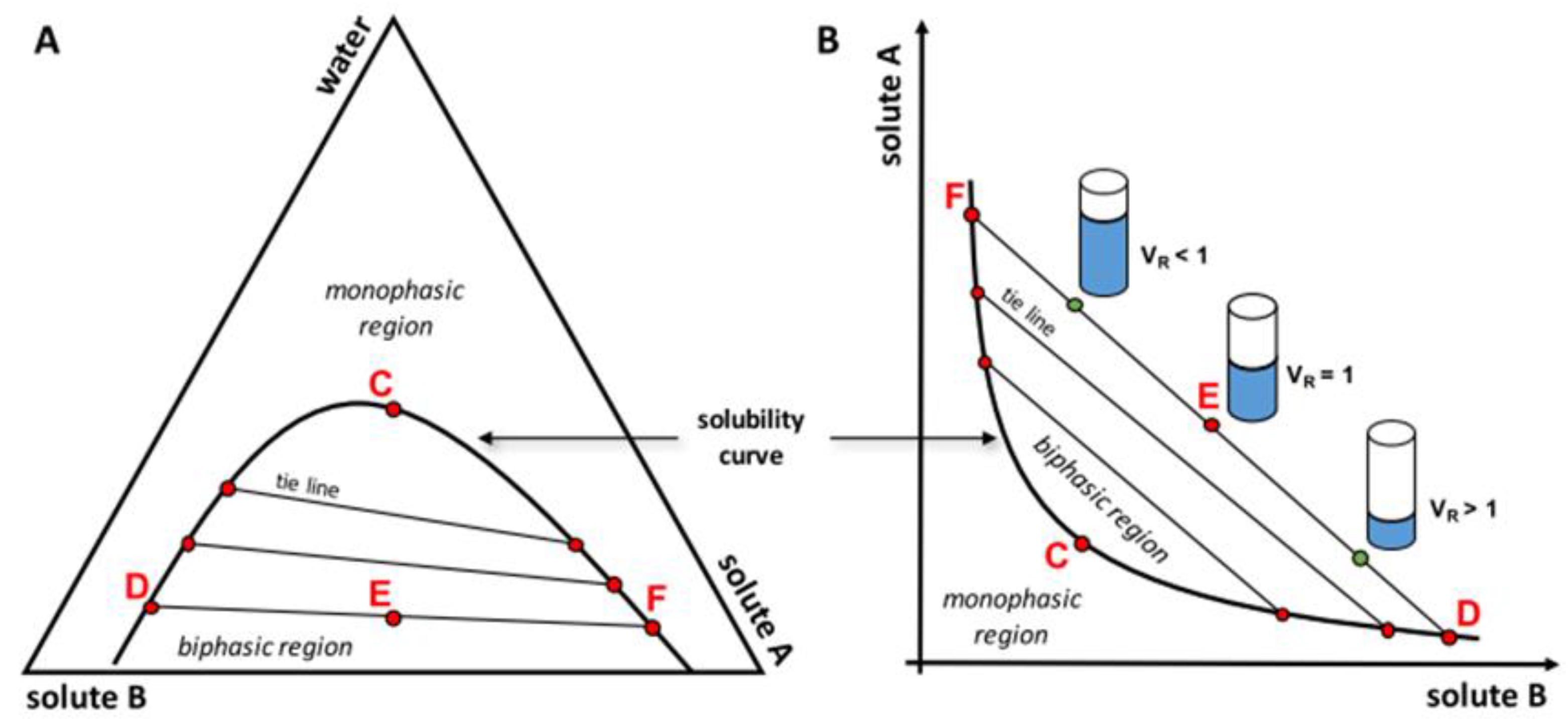

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buarque, F.S.; Gautério, G.V.; Coelho, M.A.Z.; Lemes, A.C.; Ribeiro, B.D. Aqueous Two-Phase Systems Based on Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents as a Tool for the Recovery of Non-Protein Bioactive Compounds—A Review. Processes 2023, 11, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11010031
Buarque FS, Gautério GV, Coelho MAZ, Lemes AC, Ribeiro BD. Aqueous Two-Phase Systems Based on Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents as a Tool for the Recovery of Non-Protein Bioactive Compounds—A Review. Processes. 2023; 11(1):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11010031
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuarque, Filipe Smith, Gabrielle Victoria Gautério, Maria Alice Zarur Coelho, Ailton Cesar Lemes, and Bernardo Dias Ribeiro. 2023. "Aqueous Two-Phase Systems Based on Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents as a Tool for the Recovery of Non-Protein Bioactive Compounds—A Review" Processes 11, no. 1: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11010031
APA StyleBuarque, F. S., Gautério, G. V., Coelho, M. A. Z., Lemes, A. C., & Ribeiro, B. D. (2023). Aqueous Two-Phase Systems Based on Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents as a Tool for the Recovery of Non-Protein Bioactive Compounds—A Review. Processes, 11(1), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11010031









