Path Planning of Mobile Robots Based on an Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Principles of PSO and DE
3.1. Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)
3.2. Differential Evolution Algorithm (DE)
- Establish the initial population and initialize the parameters:
- 2.
- Mutation operation:
- 3.
- Cross operation:
- 4.
- Select operation.
4. Algorithm Improvement
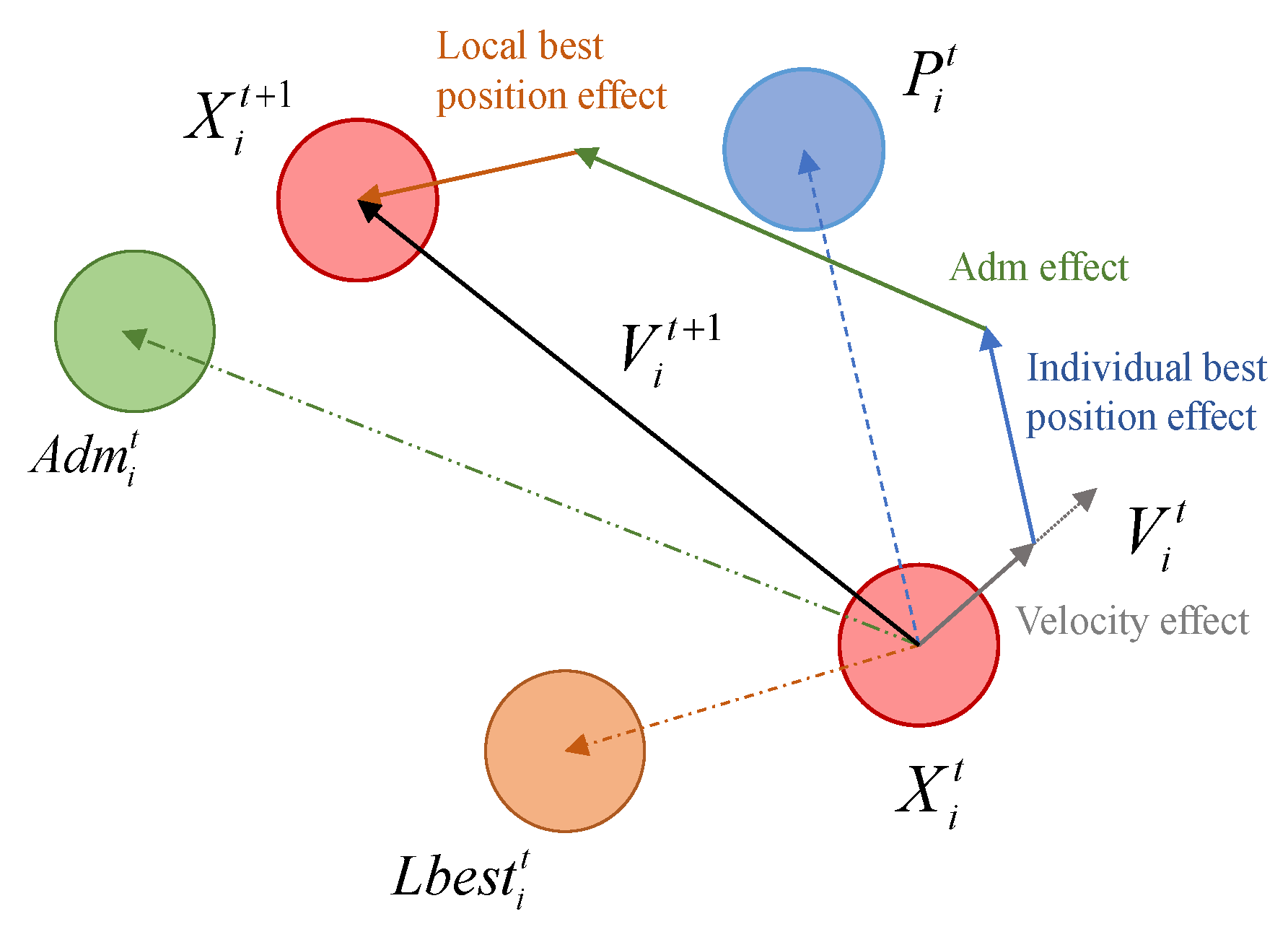
4.1. Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Based on Corporate Governance Idea (IPSO)
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- The improved mathematical formula of pos.ition update formula
4.2. Improved Differential Evolution Algorithm Based on Adaptive Parameters
- Adaptive optimization of scaling factor F
- 2.
- Adaptive optimization of cross probability factor CR
4.3. Hybrid IPSO with IDE (IPSO-IDE)
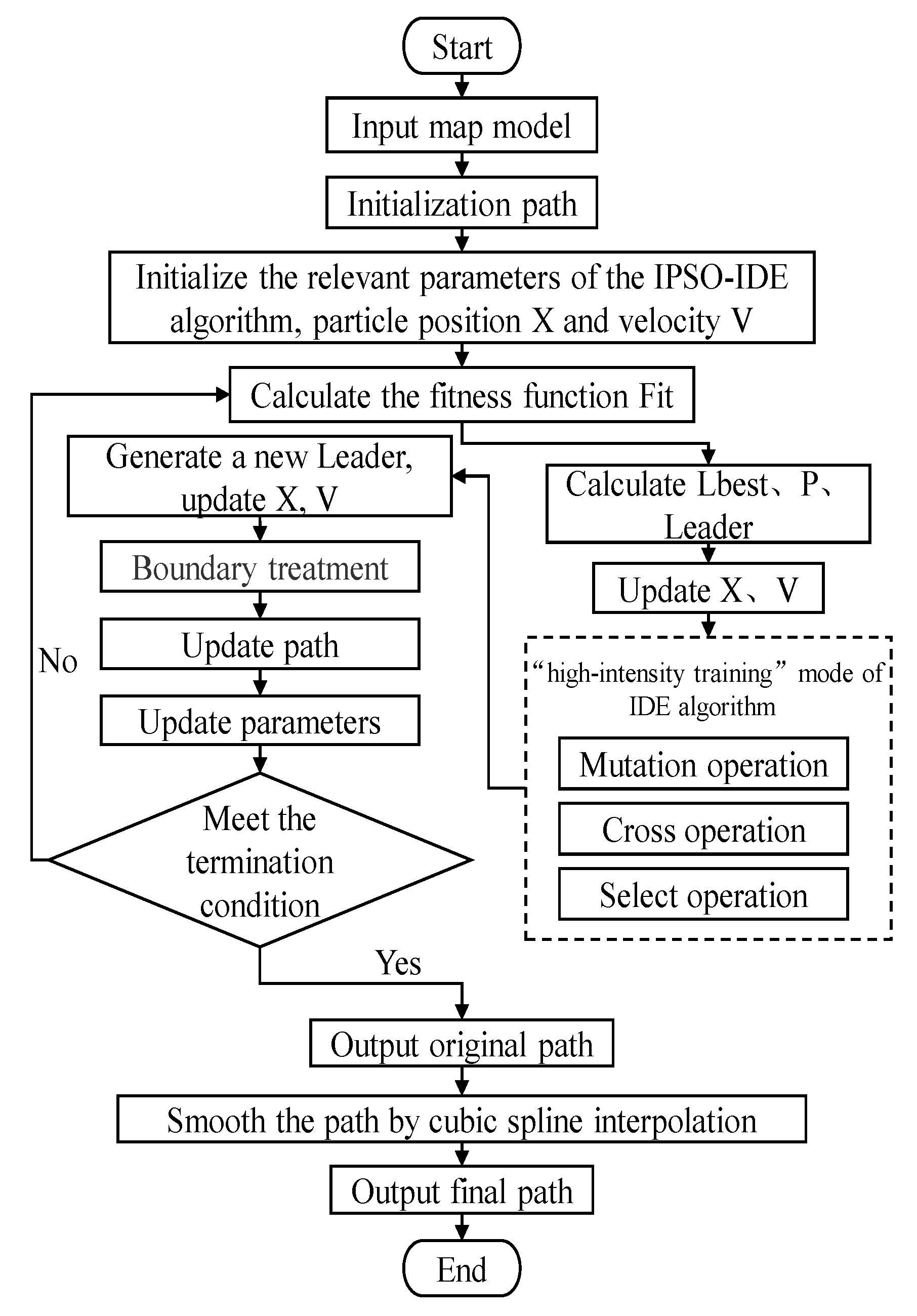
4.3.1. The Principle of IPSO-IDE Algorithm
- step1:
- Initialization parameters, including acceleration factor, number of support votes Opvote, and number of negative votes Owvote, etc.
- step2:
- Initialize the particle swarm randomly, including dimension D, number of population particle N, position X, velocity V, etc.
- step3:
- Calculate the particle fitness value Fit according to the set objective function.
- step4:
- Based on the fitness value Fit, calculate the individual best position Pit, the local best position Lbestit, and elect Adm according to (12) to obtain the global best position.
- step5:
- Update position X and velocity V according to the improved (9) (10) to generate the elite population with high quality.
- step6:
- Use (13) to process the boundary.
- step7:
- Use the elite population as the initial population of IDE, combine the adaptive parameters (14) (15), and use (6) (7) (8) to perform “high intensity” iterative optimization.
- step8:
- Apply the optimized result of IDE algorithm to Leader of the updated particle swarm.
- step9:
- If the termination condition is met, stop the algorithm and output the optimal results. Otherwise, go to Step2.
4.3.2. Experimental Verification of IPSO-IDE Model
5. Path Planning Based on IPSO-IDE Algorithm
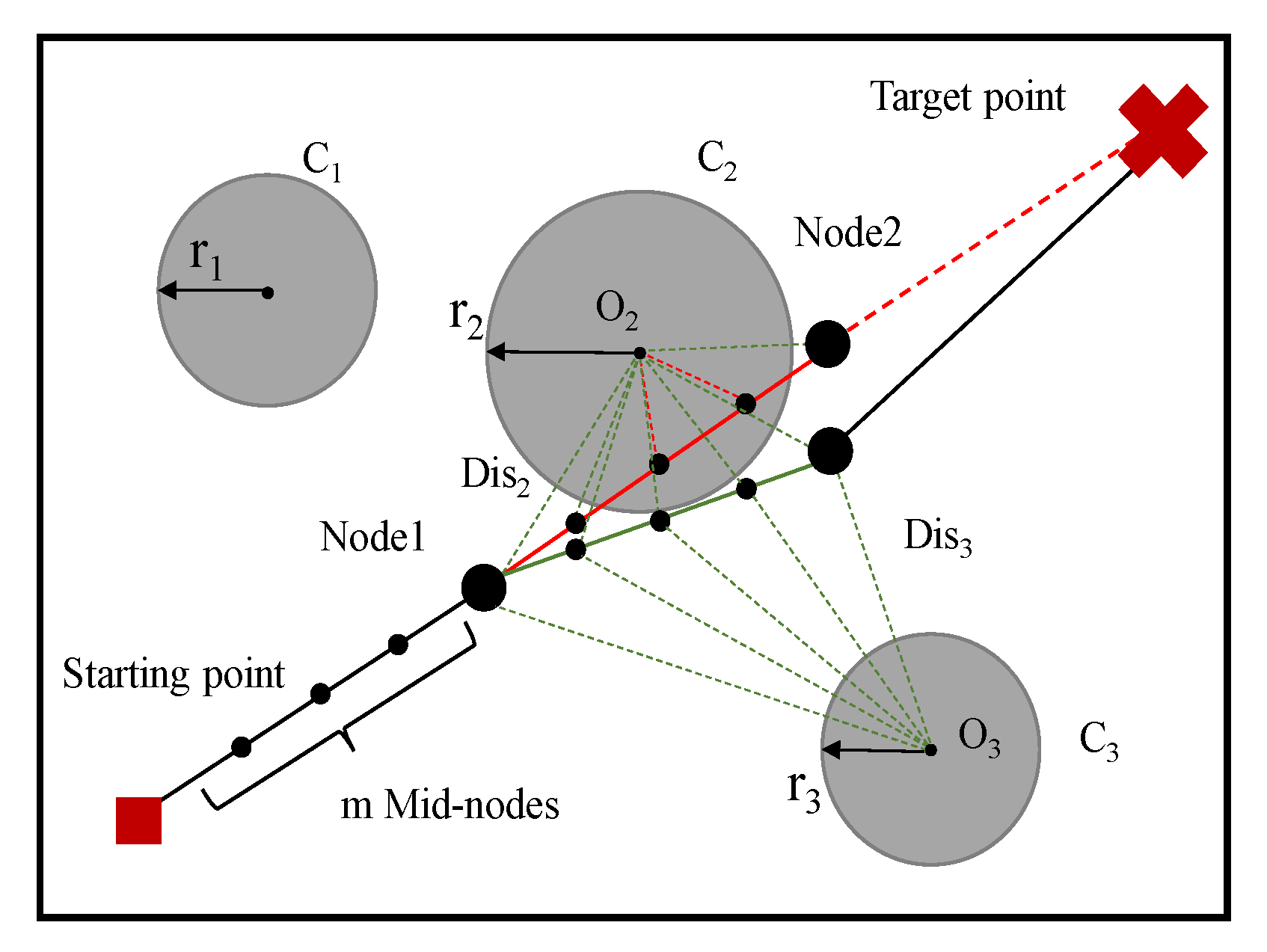
5.1. Design of Fitness Function
- Path length function
- 2.
- Penalty function
5.2. Path Smoothing
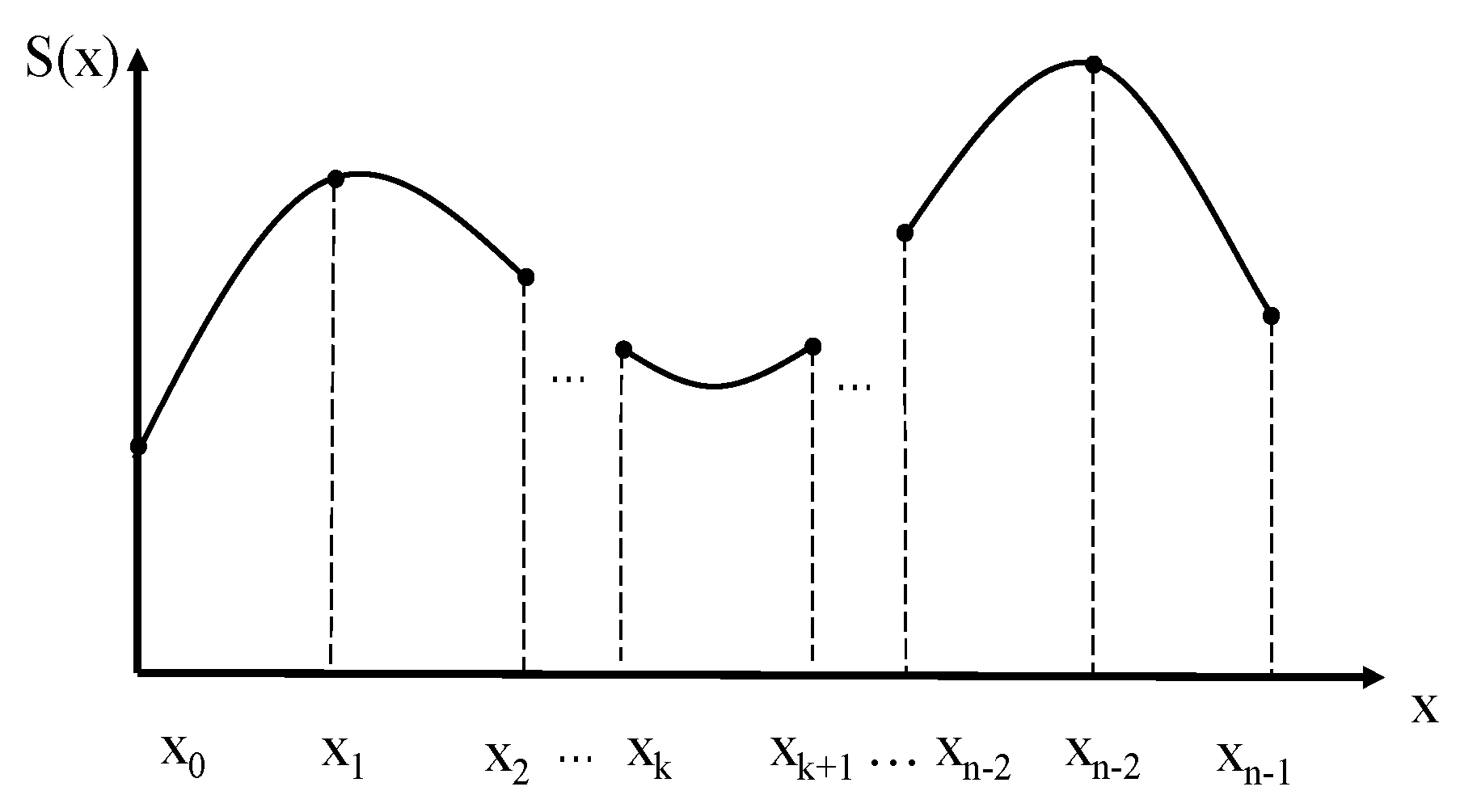
- Basic principle of cubic spline interpolation
- In n subintervals [xi, xi+1] (i = 0, 1, …, n − 1), S(x) is a cubic polynomial.
- S(xi) = yi (i = 0, 1, 2, …, n − 1).
- The first derivative and the second derivative of S(x) in the interval [xmin, xmax] are continuous.
- 2.
- Determine the equation of Spline Interpolation
- According to S(x), which is composed of n cubic polynomials, the polynomial expression can be obtained as:
- According to , it can be concluded that:
- According to the continuity of the differential, it can be concluded that:
- 3.
- Smoothing by spline interpolation
6. Simulation Experiments and Analysis
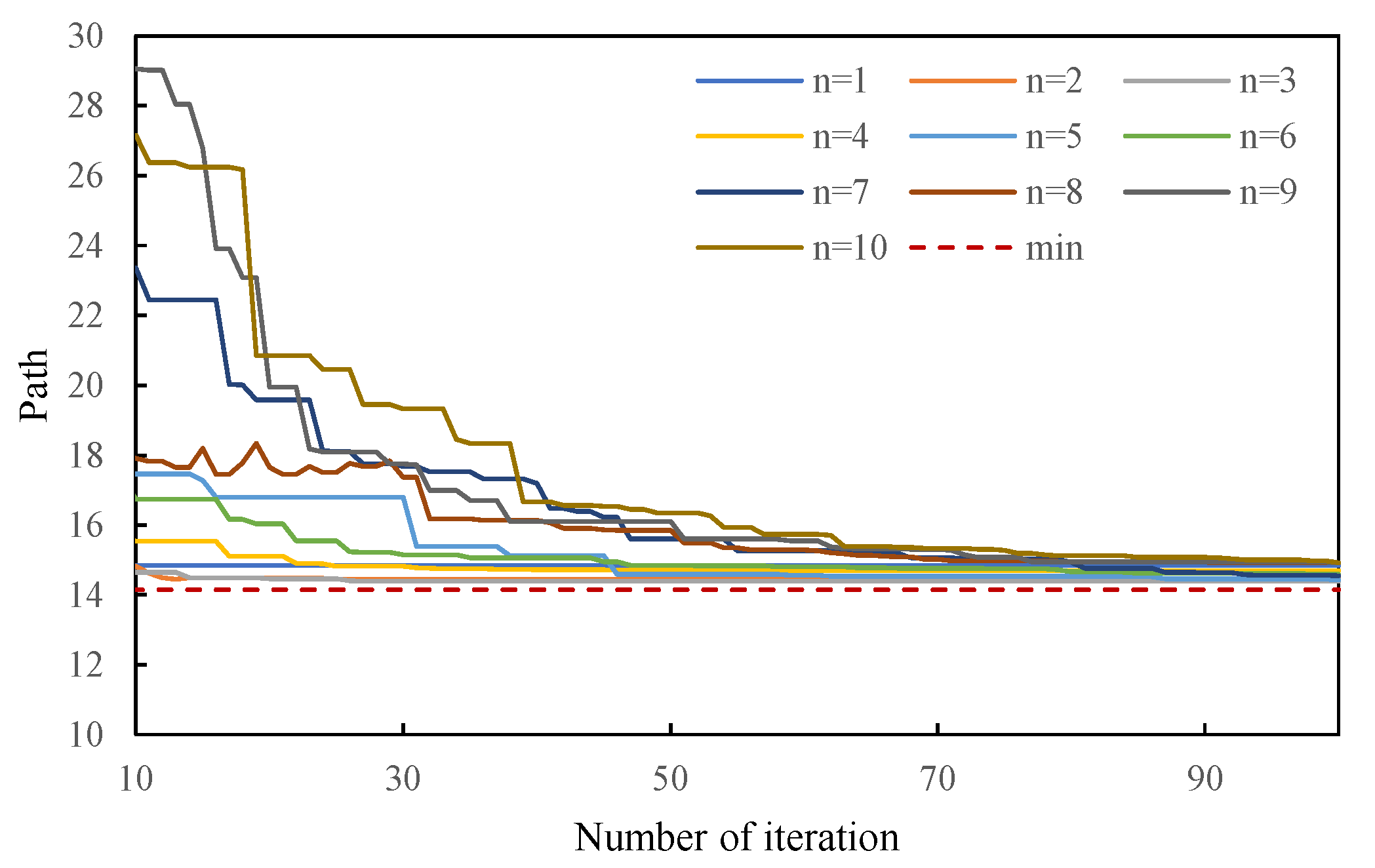
6.1. The Number of Path Nodes Experiment
6.2. Path Planning Experiment
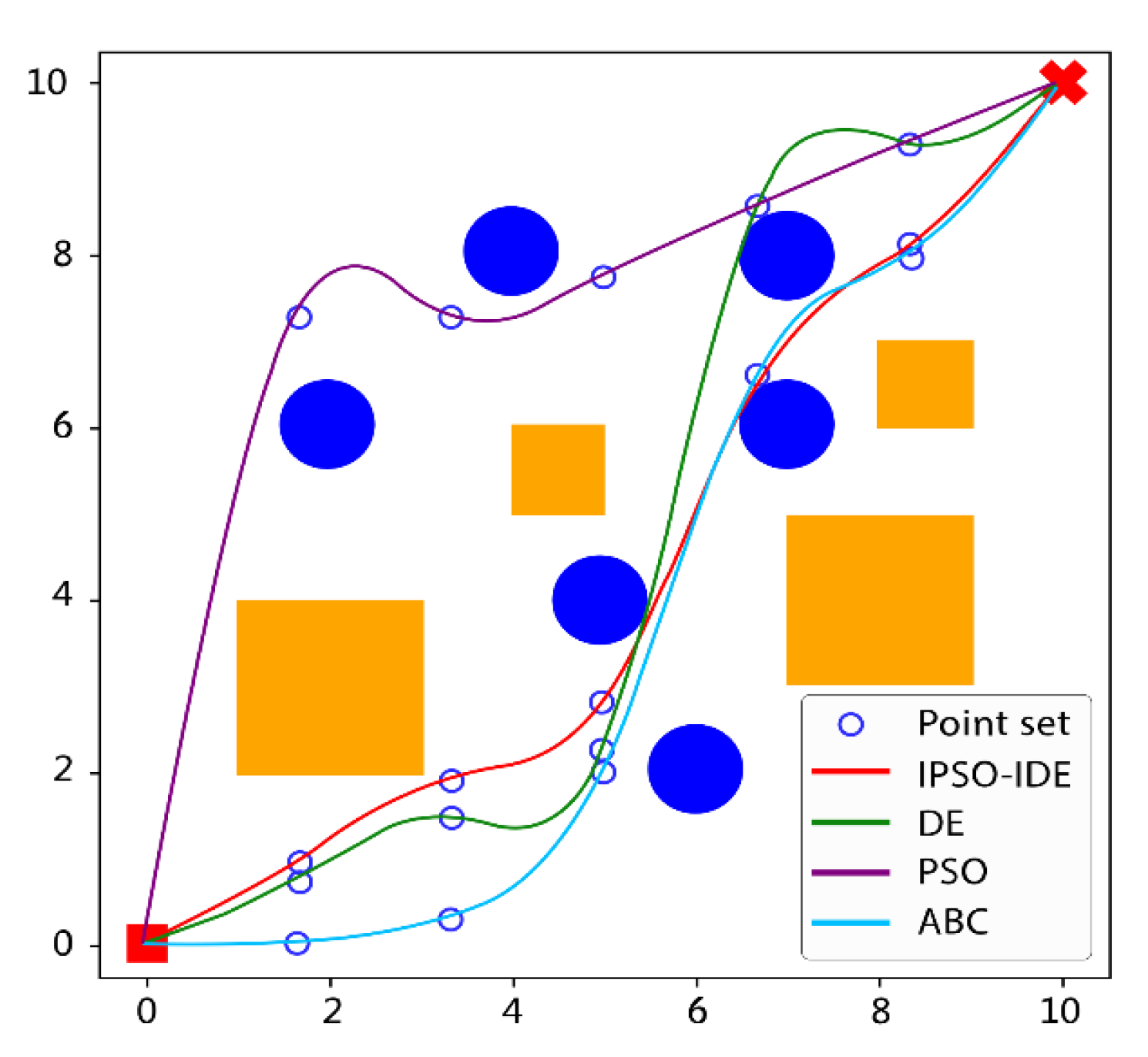
6.2.1. First Experiment: Compared with Different Traditional Heuristic Algorithms
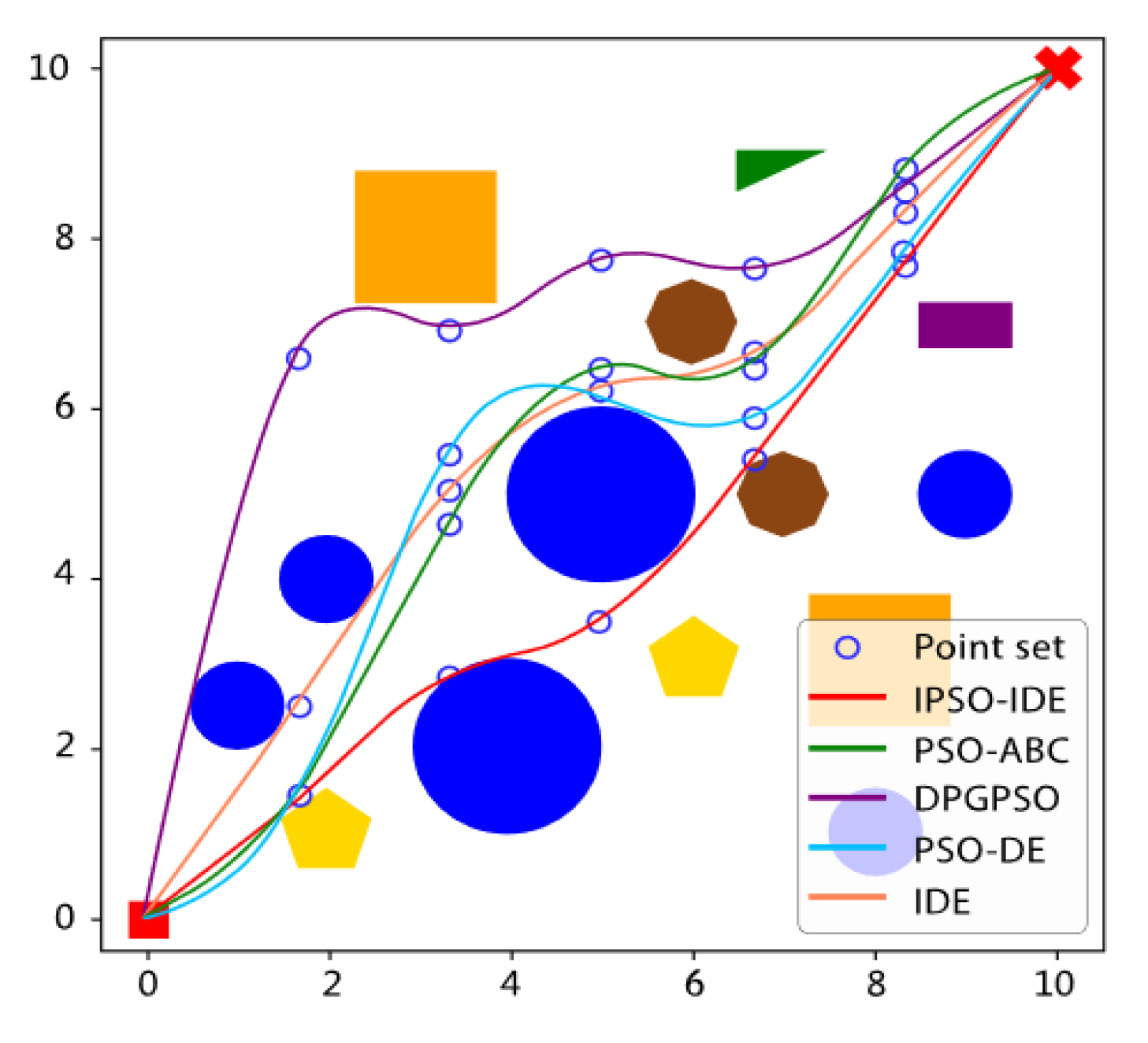
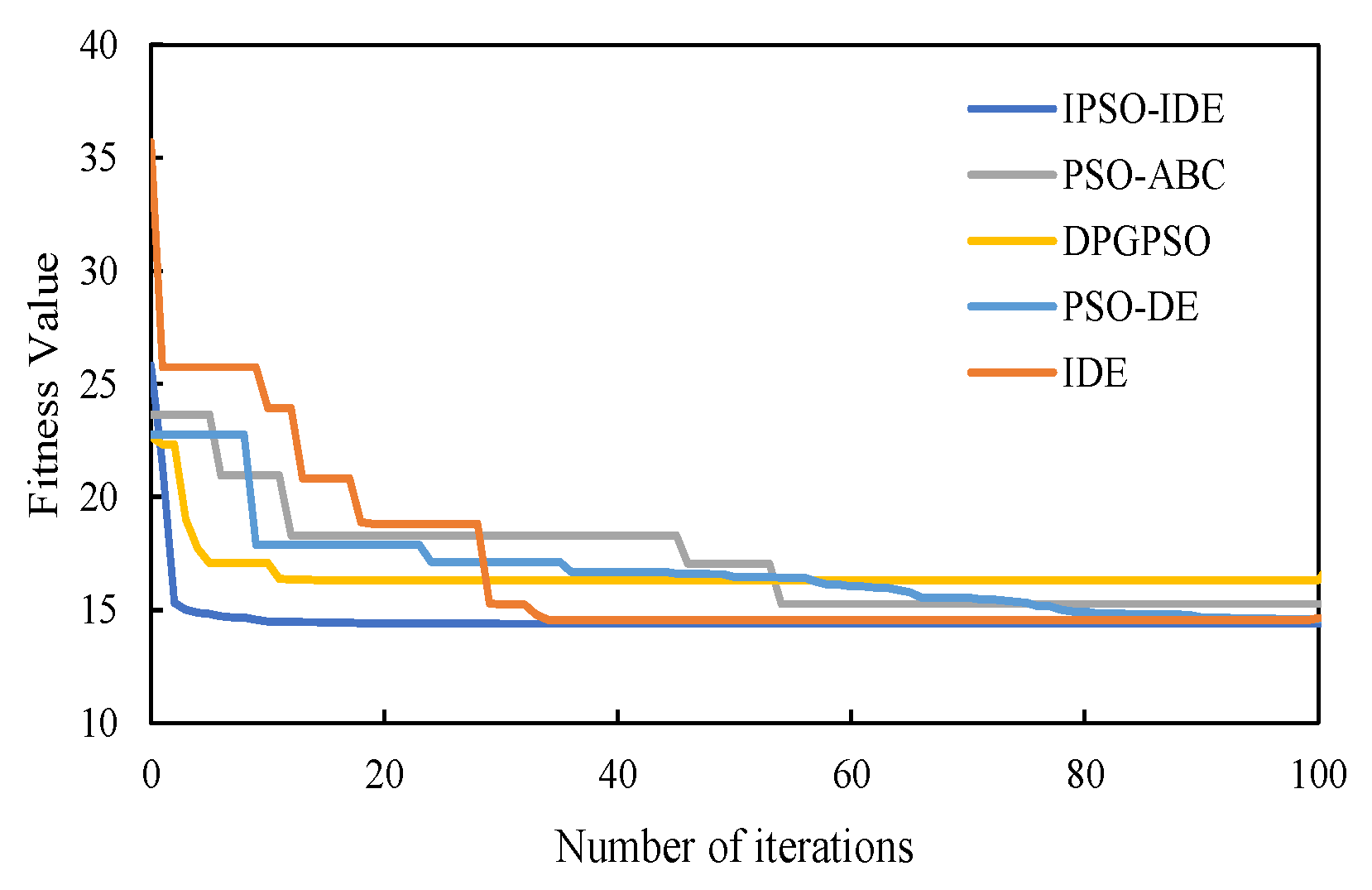
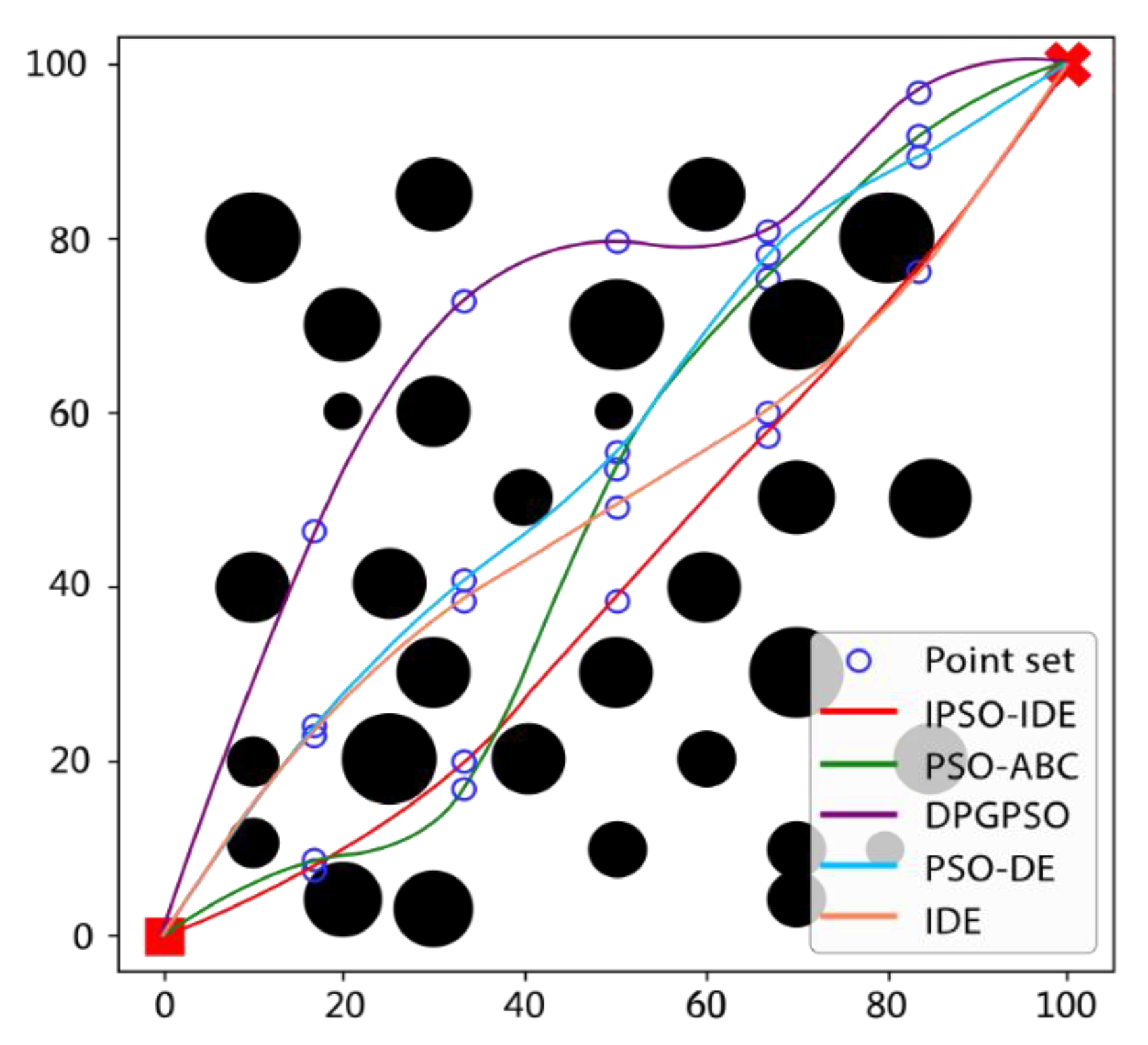
6.2.2. Second Experiment: Compared with Different Improved Algorithms
6.2.3. Third Experiment: Verification of Big Map
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | meaning |
| PSO | particle swarm optimization |
| IPSO | improved particle swarm optimization |
| DE | differential evolution |
| IDE | optimized differential evolution |
| IPSO- IDE | improved particle swarm optimization based on differential evolution |
| GA | genetic algorithm |
| CR | crossover probability factor |
| DPG-PSO | democracy-inspired particle swarm optimizer with the concept of peer groups |
| ABC | artificial bee colony |
| PSO-ABC | hybrid algorithm based on PSO and ABC |
| Algorithm 1: Code for manager selects |
| //Initialize operator, Owner, operator vote, manager vote, administrator particle. |
| ,voteid: [0,1]. |
|
1.While (fit > fitmin) 2. For t = 1 to T //T is the number of iterations. 3. For i = 1 to N //N is the number of particles in the population. 4. For d = 1 to D //D for dimension. 5. If (voteid < Opvote) 6. //If the particles vote for the operator. 7. Opvote ← Opvote + 1/(M.N) //Add up the votes. 8. Opvote ← Opvote/(Opvote+Owvote) //Standardize voting. 9. Else 10. //If the particle votes for the owner. 11. Owvote ← Owvote + 1/(M.N) //Add up the votes. 12. Owvote←Owvote/(Opvote+Owvote) //Standardize voting. 13. End if 14. expressed as follows. 15. ) 16. ←1 17. End if 18. ) 19. ←2.3 20. End if 21. and Vt 22. End for 23. End for 24.End while |
| Algorithm2: Code for IPSO-IDE |
| Initialize: pro = 1/N, ϕ ← 0.7, Opvote: = ϕ, ovote: = 1− ϕ, |
| c1 ← 0.5, c2 ← 0.5, c3 ← 1.2, c4 ← 1, X, V, Operator, Owner, Leader, Lbest, P. |
|
1. While (fit > fitmin) 2. For t = 1 to T //T is the number of iterations. 3. For i = 1 to N //N is the number of particles in the population. 4. For d = 1 to D //D for dimension. |
| //The following is the calculation of the optimal position of an individual based on the fitness value fit. |
|
5. If (fit (Xi(t)) ≤ fit (Pi(t))) 6. Pi(t) ← Xi(t) 7. Else 8. Pi(t) ← Xi(t) 9. End if |
| //The following is the calculation of the local optimal position based on the fitness value fit. |
|
10. If (fit(Xi(t)) ≤ fit(Lbesti(t))) 11. Lbesti(t) ← Xi(t) 12. Else 13. Lbesti(t) ←Lbesti(t − 1) 14. End if |
| //The following is the calculation of the global optimal position based on the fitness value fit. |
|
15. If (fit(Xi(t)) ≤ fit(Lbesti±1(t)) or (fit(Xi(t)) ≤ fit(Lbesti±2(t))) 16. Lbesti±1 (t) ← Lbesti(t) |
| //Elect an Adm according to the expression (3-15) |
| 17. Leader, Leader_fit, Opvote, Owvote ← Choose_Leader (Operator, Owner) |
| //Update position X and speed V to generate a better elite group, and take the elite group as the initial group of IDE algorithm. |
|
18. DE_list ← X 19. h(t) ← Mutation (DE_list(t), fit(DE_list(t))) //variation. 20. v(t) ← Crossover (DE_list(t), h(t), fit(DE_list(t))) //cross. |
| //Selection. |
| 21. DE_list(t) ← Selection (v(t), DE_list(t)) (Mutation, Crossover, and Selection: |
| respectively refer to the mutation, crossover, and selection operations in the DE algorithm) |
| //Apply the optimized result of IDE algorithm to Leader of the updated particle swarm. |
|
22. DE_fitness ← fit (DE_list(t)) 23. min_f ← Minimum DE_fitness 24. min_position ← Minimum DE_fitness position 25. If (min_f ← Leader_fit) 26. Leader ← min_position 27. End if 28. Normalize Opvote and Owvote 29. If (Leaderd(t) = Opvoteid(t)) 30. ← 1 31. Else 32. ← 2.3 33. End if 34. Update Xt and Vt //Update the position and velocity of the particle. 35. End for 36. End for 37. End while |
References
- Chipade, V.S.; Panagou, D. Multiagent Planning and Control for Swarm Herding in 2-D Obstacle Environments Under Bounded Inputs. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2021, 37, 1956–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Rathinam, S.; Likhachev, M.; Choset, H. Multi-Objective Safe-Interval Path Planning With Dynamic Obstacles. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 8154–8161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, M.; An, H.; Liu, B.; Wang, C. An Improved Dyna-Q Algorithm for Mobile Robot Path Planning in Unknown Dynamic Environment. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Syst. 2022, 52, 4415–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.-L.; Hwang, R.-H.; Lin, P.-C. Controllable Path Planning and Traffic Scheduling for Emergency Services in the Internet of Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 12399–12413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaro, A.; Segato, A.; Muretti, F.; De Momi, E. An Evolutionary-Optimized Surgical Path Planner for a Programmable Bevel-Tip Needle. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2021, 37, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagale, A.; Oucheikh, R.; Bye, R.T.; Osen, O.L.; Fossen, T.I. Path planning and collision avoidance for autonomous surface vehicles I: A review. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2021, 26, 1292–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Li, Q.; Zhang, C.; Cui, J.; Zhou, H. Hybrid chaos-based particle swarm optimization-ant colony optimization algorithm with asynchro-nous pheromone updating strategy for path planning of landfill inspection robots. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2019, 16, 255795084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Chou, W. Path planning for mobile robot using self-adaptive learning particle swarm optimization. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2018, 61, 052204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, F.; Rahiman, W.; Alhady, S.S.N.; Ali, A.; Mir, I.; Jalil, A. Meta-heuristic approach for solving multi-objective path planning for autonomous guided robot using PSO–GWO optimization algorithm with evolutionary programming. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 12, 7873–7890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Hu, J.; Bhowmick, P.; Ding, Z.; Arvin, F. Distributed Motion Planning for Safe Autonomous Vehicle Overtaking via Artificial Poten-tial Field. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 21531–21547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, F.; Mir, I.; Abualigah, L.; Sumari, P.; Forestiero, A. A Consolidated Review of Path Planning and Optimization Techniques: Technical Per-spectives and Future Directions. Electronics 2021, 10, 2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Z.; Zhang, S.; Chen, S.; Nan, Z.; Zheng, N. A Global-Local Coupling Two-Stage Path Planning Method for Mobile Robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 5349–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Wang, T.; Chen, J.; Narang, D.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H. Learning-based Path Planning and Predictive Control for Autonomous Vehicles With Low-Cost Positioning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2021, early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, R.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guan, X.; Hao, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, G. A Robust Reference Path Selection Method for Path Planning Algorithm. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 4837–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, T. Path Planning for Autonomous Underwater Vehicles Under the Influence of Ocean Currents Based on a Fusion Heuristic Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 8529–8544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.; Hawash, A.; Abdalhaq, B. A Genetic Algorithm (GA) and Swarm Based Binary Decision Diagram (BDD) Reordering Optimizer Reinforced with Recent Operators. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2021, early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95-international conference on neural networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Karaboga, D.; Gorkemli, B.; Ozturk, C.; Karaboga, N. A comprehensive survey: Artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm and applications. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2014, 42, 21–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Yao, X.; Liu, M.; Jin, H. AGV path planning based on improved grey wolf optimization algorithm and its implementation prototype platform. Comput. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2018, 24, 2779–2791. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Liu, G.; Pan, Q. A Review on Representative Swarm Intelligence Algorithms for Solving Optimization Problems: Applications and Trends. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2021, 8, 1627–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storn, R.; Price, K. Differential evolution—A simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. J. Glob. Optim. 1997, 11, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-Y.; Lin, W.-M.; Chen, A.-X. Path Planning for the Mobile Robot: A Review. Symmetry 2018, 10, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, M.A.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y. Real-Time Fault-Tolerant Formation Control of Multiple WMRs Based on Hybrid GA–PSO Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2021, 18, 1263–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, M.A.; Siddique, M.D.; Mekhilef, S.; Mubin, M. Asynchronous Particle Swarm Optimization-Genetic Algorithm (APSO-GA) Based Selective Harmonic Elimination in a Cascaded H-Bridge Multilevel Inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 1477–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed Hussein, H.; Katzis, K.; Mfupe, L.P.; Bekele, E.T. Performance Optimization of High-Altitude Platform Wireless Communication Network Exploiting TVWS Spectrums Based on Modified PSO. IEEE Open J. Veh. Technol. 2022, 3, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N. An Autoselection Strategy of Multiobjective Evolutionary Algorithms Based on Performance Indicator and its Ap-plication. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2022, 19, 2422–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patle, B.K.; Ganesh Babu, L.; Anish, P.; Parhi, D.R.K. A review: On path planning strategies for navigation of mobile robot. Def. Technol. 2019, 4, 582–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burman, R.; Chakrabarti, S.; Das, S. Democracy-inspired particle swarm optimizer with the concept of peer groups. Soft Comput. 2017, 21, 3267–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Guo, D. Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm With Self-Organizing Mapping for Nash Equilibrium Strategy in Application of Multiobjective Optimization. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 5179–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Si, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Song, H. A Novel Hybrid Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Path Planning of UAVs. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 22547–22558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozna, C.; Precup, R.; Horvath, E.; Petriu, E.M. Hybrid Particle Filter-Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm and Application to Fuzzy Con-trolled Servo Systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 30, 4286–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. A new path plan method based on hybrid algorithm of reinforcement learning and particle swarm optimization. Eng. Comput. 2021, ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Xing, L.; Zheng, X.; Du, N.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q. A Self-Adaptive Differential Evolution Algorithm for Scheduling a Single Batch-Processing Machine With Arbitrary Job Sizes and Release Times. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 51, 1430–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, R.; Savvaris, A.; Tsourdos, A.; Chai, S. Multi-objective trajectory optimization of Space Manoeuvre Vehicle using adaptive differential evolution and modified game theory. Acta Astronaut. 2017, 136, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C. An adaptive-group-based differential evolution algorithm for inspecting machined workpiece path planning. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 105, 2647–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-J.; Zhou, Y.-R.; Zhang, J. Adaptive Estimation Distribution Distributed Differential Evolution for Multimodal Optimization Problems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 6059–6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, Q.; Pan, N.; Sun, Y.; An, Y.; Pan, D. UAV Stocktaking Task-Planning for Industrial Warehouses Based on the Improved Hybrid Differential Evolution Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Ind. Informatics 2022, 18, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wang, Y. Time Series Prediction Based on Improved Differential Evolution and Echo State Network. Acta Autom. Sin. 2019, 45, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Lei, T. The Relationship between Corporate Governance and Corporate Performance in China’s Civilian-Owned Listed En-terprise. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Business Intelligence and Financial Engineering, Beijing, China, 24–26 July 2009; pp. 782–785. [Google Scholar]
- Kashyap, S.; Jeyasekar, A. A Competent and Accurate BlockChain based E-Voting System on Liquid Democracy. In Proceedings of the 2020 2nd Conference on Blockchain Research & Applications for Innovative Networks and Services (BRAINS), Paris, France, 28–30 September 2020; pp. 202–203. [Google Scholar]
- Sadikin, R.; Swardiana, I.W.A.; Wirahman, T. Cubic spline interpolation for large regular 3D grid in cylindrical coordinate: (Invited pa-per). In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Computer, Control, Informatics and its Applications (IC3INA), Jakarta, Indonesia, 23–26 October 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bogdanov, V.V.; Volkov, Y.S. Near-optimal tension parameters in convexity preserving interpolation by generalized cubic splines. Numer. Algorithms 2021, 86, 833–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Xiang, K.; Pang, M. An integrated particle swarm optimization approach hybridizing a new self-adaptive particle swarm optimization with a modified differential evolution. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 4849–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Test Function | Expression | Value Range | Min | Dim |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sphere | [−100,100] | 0 | 30 | |
| Step | [−10,10] | 0 | 30 | |
| H14 | [−1.28,1.28] | 0 | 30 | |
| Schwefel’s P2.22 | [−10,10] | 0 | 30 | |
| Alpine | [−10,10] | 0 | 30 | |
| Quadric | [−100,100] | 0 | 30 | |
| Rastrigin | [−5.12,5.12] | 0 | 30 | |
| Ackley | [−32,32] | 0 | 30 | |
| Griewank | [−600,600] | 0 | 30 |
| Algorithm | Parameter |
|---|---|
| IPSO-IDE | c1 = 0.5, c2 = 0.5, c3 = 1.2, c4 = 1; ω = 0.4–0.2; ϕ = 0.7; β = 1–1.5; Vmax = 0.6 × Range; F = 0.6; CR = 0.9–0.1 |
| PSO | c1 = 2; c2 = 2; ω = 1; Vmax = 0.5 × Range; Vmax = 0.1 × Range |
| DPG-PSO | c1 = 2, c2 = 1.5, c3 = 0.5, c4 = 0.8; ω = 0.2; ϕ = 0.7; Vmax = 0.5 × Range |
| PSO-ABC | c1 = 2, c2 = 2; ω = 0.95–0.4; Vmax = Range |
| IDE | F = 0.6; CR = 0.9–0.1; Vmax = Range |
| Algorithm | Evaluation Index | IPSO-IDE | PSO | DPG-PSO | PSO-ABC | IDE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| f1 | Mean | 0 | 1.539 | 0.075 | 2.9 × 10−5 | 1.7 × 10−27 |
| Best | 0 | 1.330 | 0.002 | 2.83 × 10−5 | 1.12 × 10−30 | |
| Worst | 0 | 1.86 | 0.236 | 3.0 × 10−5 | 1.6 × 10−26 | |
| Std | 0 | 0.1809 | 0.0573 | 4.29 × 10−7 | 3.93 × 10−27 | |
| M-iters | 332 | 1180 | 214 | 425 | 1993 | |
| f2 | Mean | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Best | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Worst | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Std | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| M-iters | 15 | 1118 | 21 | 100 | 384 | |
| f3 | Mean | 0 | 1.1045 | 2.79 × 10−6 | 5.36 × 10−6 | 0 |
| Best | 0 | 0.88 | 1.36 × 10−8 | 3.82 × 10−6 | 0 | |
| Worst | 0 | 1.15 | 1.21 × 10−5 | 6.84 × 10−6 | 0 | |
| Std | 0 | 0.1067 | 4.06 × 10−6 | 9.82 × 10−7 | 0 | |
| M-iters | 16 | 286 | 279 | 1065 | 1173 | |
| f4 | Mean | 0 | 5.36 | 0.362 | 0.029 | 1.01 × 10−21 |
| Best | 0 | 5.04 | 0.19 | 0.029 | 1.94 × 10−22 | |
| Worst | 0 | 5.83 | 0.7 | 0.029 | 2.04 × 10−21 | |
| Std | 0 | 0.2892 | 0.1968 | 3.88 × 10−18 | 7.3 × 10−22 | |
| M-iters | 19 | 1248 | 135 | 186 | 1997 | |
| f5 | Mean | 0 | 3.6045 | 0.0116 | 1.7435 | 2.88 × 10-19 |
| Best | 0 | 1.99 | 0.002 | 0.039 | 8.01 × 10−28 | |
| Worst | 0 | 4.8 | 0.04 | 2.41 | 6.73 × 10−19 | |
| Std | 0 | 1.1845 | 0.0123 | 1.1265 | 6.73 × 10−19 | |
| M-iters | 18 | 335 | 126 | 2000 | 2000 | |
| f6 | Mean | 0 | 9.582 | 0.923 | 4.11 × 10−4 | 3.98 × 10−29 |
| Best | 0 | 7.5 | 0.105 | 4 × 10−4 | 3.14 × 10−29 | |
| Worst | 0 | 10.27 | 2.56 | 4.2 × 10−4 | 4.76 × 10−29 | |
| Std | 0 | 1.0278 | 1.2421 | 1.15 × 10−5 | 1.13 × 10−29 | |
| M-iters | 400 | 1432 | 463 | 765 | 2000 | |
| f7 | Mean | 0 | 38.066 | 26.629 | 0.0051 | 15.17 |
| Best | 0 | 27.98 | 19.14 | 0.004 | 10.94 | |
| Worst | 0 | 59.34 | 35.63 | 0.0058 | 19.9 | |
| Std | 0 | 12.1852 | 7.5275 | 0.001 | 4.4048 | |
| M-iters | 25 | 503 | 208 | 665 | 738 | |
| f8 | Mean | 3.09 × 10−16 | 8.432 | 9 × 10−4 | 0.004 | 0.4575 |
| Best | 4.4 × 10−17 | 7.18 | 6.58 × 10−5 | 0.004 | 7.55 × 10−15 | |
| Worst | 4.44 × 10−16 | 9.51 | 1.8 × 10−3 | 0.004 | 1.34 | |
| Std | 2.31 × 10−16 | 0.8422 | 8.26 × 10−4 | 0 | 0.6338 | |
| M-iters | 51 | 430 | 182 | 548 | 1831 | |
| Grade | N | - | - | - | - | |
| f9 | Mean | 0 | 35.96 | 0.0664 | 2.01 × 10−6 | 0.0147 |
| Best | 0 | 31.05 | 0.037 | 2.01 × 10−6 | 0 | |
| Worst | 0 | 41.02 | 0.147 | 2.01 × 10−6 | 0.0172 | |
| Std | 0 | 3.97 | 0.0495 | 0 | 0.0218 | |
| M-iters | 21 | 2000 | 341 | 112 | 1222 |
| Algorithm | Parameter |
|---|---|
| IPSO-IDE | c1 = 0.5, c2 = 0.5, c3 = 1.2, c4 = 1; ω = 0.4–0.2; ϕ = 0.7; β = 1–1.5; Vmax = 0.6 × Range; F = 0.9–0.1; CR = 0.9–0.1 |
| DE | F = 0.6; CR = 0.7; Vmax = Range |
| PSO | c1 = 2, c2= 2; ω = 1; Vmax = 0.5 × Range;Vmax = 0.1 × Range |
| ABC | nOnLooker = 10; φ = 1.2; P = 0.5; Vmax = Range |
| PSO-ABC | c1 = 2, c2 = 2; ω = 0.95–0.4; Vmax = Range |
| DPG-PSO | c1 = 2, c2 = 1.5, c3 = 0.5, c4 = 0.8; ω = 0.2; ϕ = 0.7; Vmax = 0.5 × Range |
| PSO-DE | c1 = 2, c2 = 2; F = 0.7; CR = 0.7; Vmax = 0.6 × Range |
| IDE | F = 0.9–0.1; CR = 0.9–0.1; Vmax = Range |
| Algorithm | Mean | Best | Worst | Std | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPSO-IDE | 15.273 | 14.562 | 18.311 | 1.255 | 5.83 |
| DE | 16.461 | 15.514 | 18.317 | 1.359 | 7.52 |
| PSO | 22.735 | 18.919 | 33.489 | 4.833 | 6.53 |
| ABC | 16.865 | 15.557 | 18.356 | 1.330 | 7.90 |
| Algorithm | Mean | Best | Worst | Std | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPSO-IDE | 14.656 | 14.374 | 15.487 | 0.376 | 7.08 |
| PSO-ABC | 15.896 | 15.257 | 16.364 | 0.463 | 9.13 |
| DPG-PSO | 17.636 | 16.325 | 18.689 | 0.971 | 7.52 |
| PSO-DE | 15.147 | 14.572 | 15.793 | 0.547 | 11.13 |
| IDE | 14.843 | 14.534 | 15.635 | 0.426 | 9.74 |
| Algorithm | Mean | Best | Worst | Std | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPSO-IDE | 143.982 | 143.362 | 144.527 | 0.738 | 16.51 |
| PSO-ABC | 158.504 | 157.924 | 151.457 | 1.120 | 43.02 |
| DPG-PSO | 157.771 | 157.158 | 159.090 | 0.819 | 35.21 |
| PSO-DE | 145.137 | 144.443 | 146.481 | 0.781 | 43.12 |
| IDE | 145.703 | 145.180 | 147.504 | 1.021 | 45.34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, Q.; Sun, R.; Du, X. Path Planning of Mobile Robots Based on an Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. Processes 2023, 11, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11010026
Yuan Q, Sun R, Du X. Path Planning of Mobile Robots Based on an Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. Processes. 2023; 11(1):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11010026
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Qingni, Ruitong Sun, and Xiaoying Du. 2023. "Path Planning of Mobile Robots Based on an Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm" Processes 11, no. 1: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11010026
APA StyleYuan, Q., Sun, R., & Du, X. (2023). Path Planning of Mobile Robots Based on an Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. Processes, 11(1), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11010026







