An EM Algorithm for Double-Pareto-Lognormal Generalized Linear Model Applied to Heavy-Tailed Insurance Claims
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. DPLN Generalized Linear Model
3. Maximum Likelihood Estimation of Parameters
3.1. Methods of Estimation
3.2. Application of the EM Algorithm to DPLN Generalized Linear Model
3.2.1. The EM Algorithm for the DPLN GLM
3.2.2. M-Step
3.2.3. E-Step
3.2.4. Standard Errors
3.3. Gradient Ascent Method
4. Numerical Applications
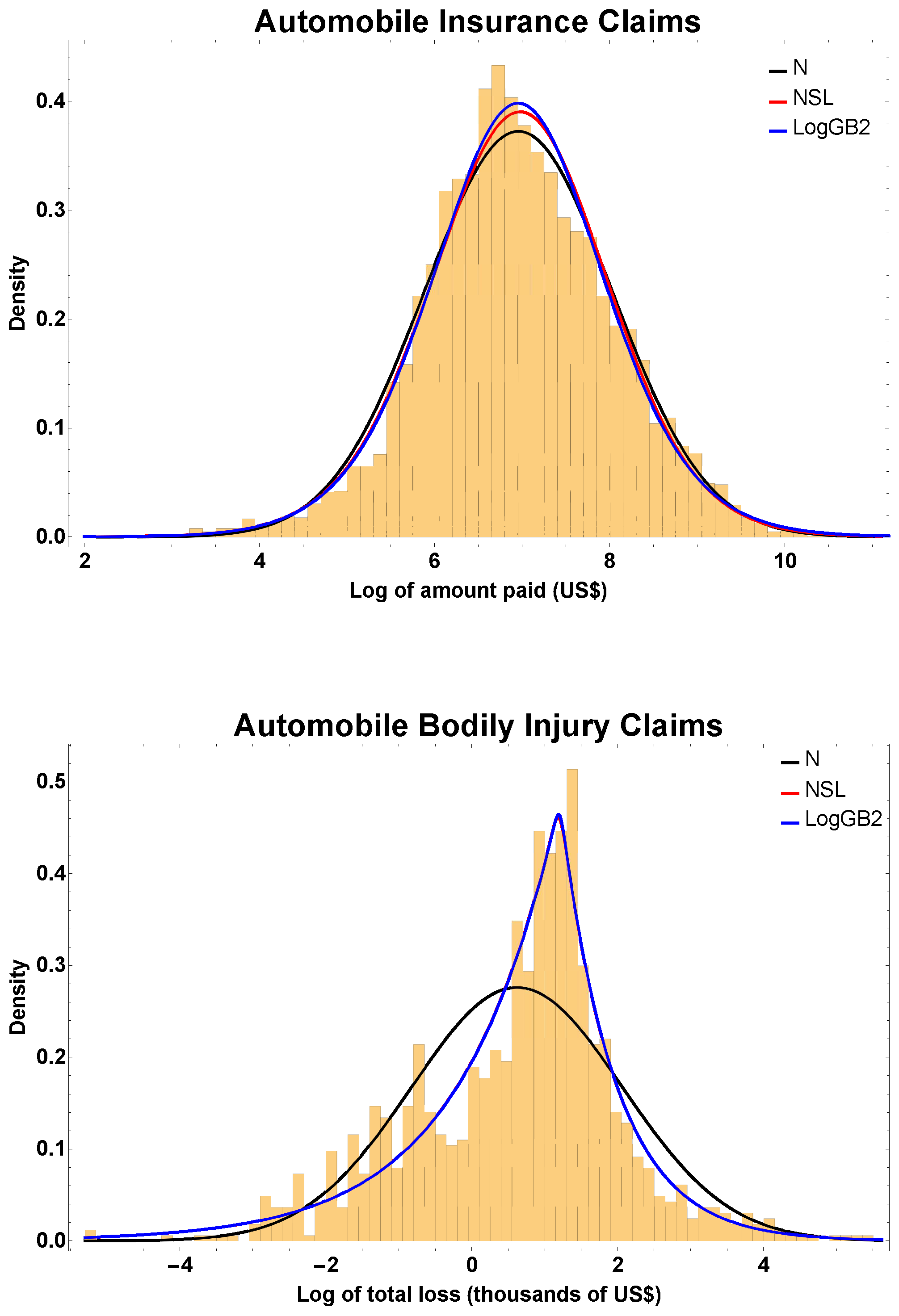
4.1. Example 1: Automobile Insurance
- GENDER, gender of operator, takes the value 1 if female and 0 otherwise;
- AGE, age of operator;
- CLASS rating class of operator as coded in Table 1.
4.1.1. Model Without Covariates
4.1.2. Comparison of Estimation from Simulations
4.1.3. Including Explanatory Variables
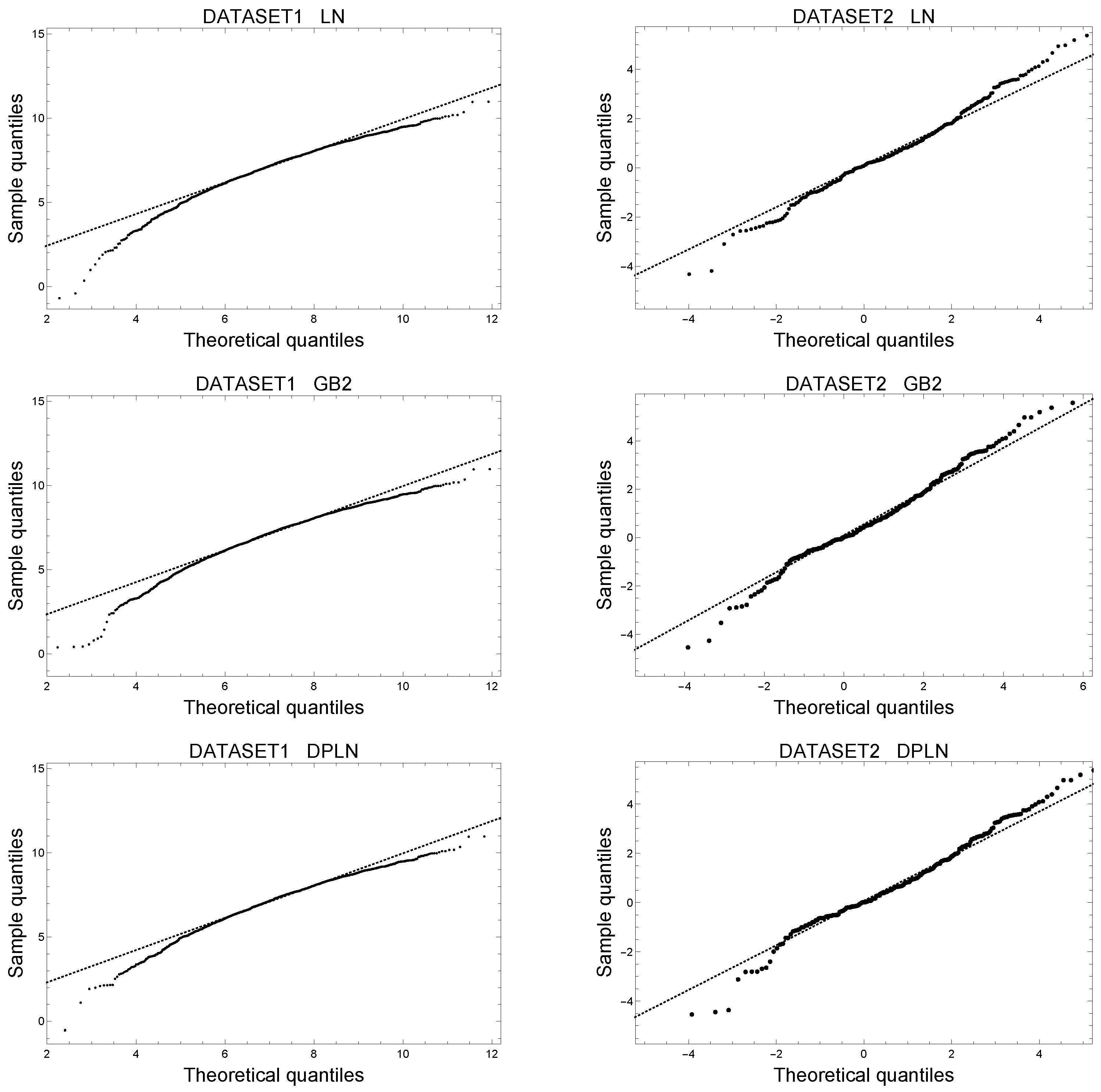
4.1.4. Model Validation
4.2. Example 2: Automobile Bodily Injury Claims
- ATTORNEY, takes the value 1 if the claimant is represented by an attorney and 0 otherwise;
- CLMSEX, takes the value 1 if the claimant is male and 0 otherwise;
- MARRIED, takes the value 1 if the claimant is married and 0 otherwise;
- SINGLE, takes the value 1 if the claimant is single and 0 otherwise;
- WIDOWED, takes the value 1 if the claimant is widowed and 0 otherwise;
- CLMINSUR, whether or not the claimant’s vehicle was uninsured ( if yes and 0 otherwise);
- SEATBELT, whether or not the claimant was wearing the seatbelt/child restraint ing belt’s vehicle was uninsured ( if yes and 0 otherwise);
- CLMAGE, claimant’s age.
4.2.1. Model Without Covariates
4.2.2. Comparison of Estimation from Simulations
4.2.3. Including Explanatory Variables
4.2.4. Model Validation
4.3. Log-Residuals for Assessing Goodness-of-Fit
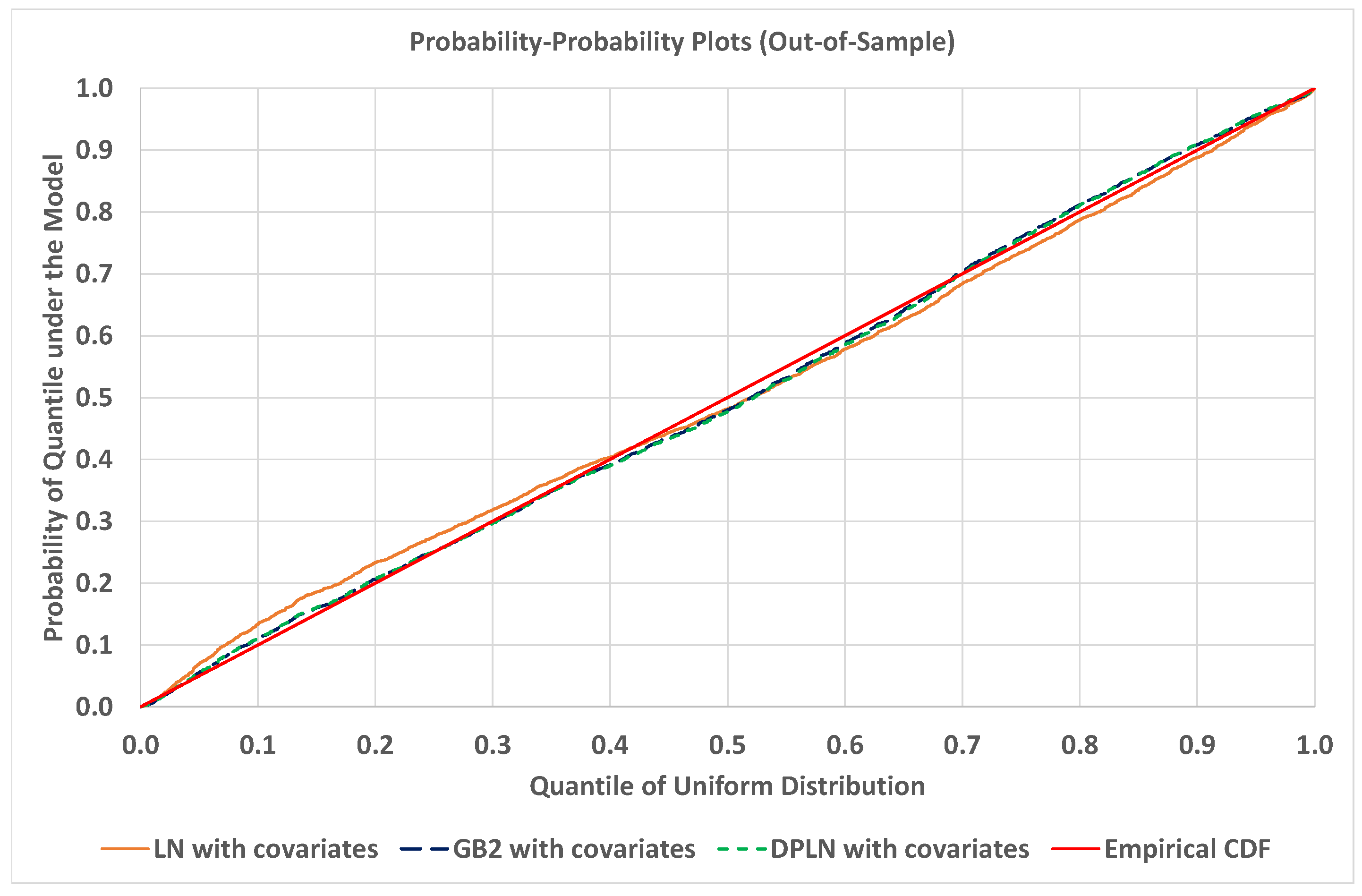
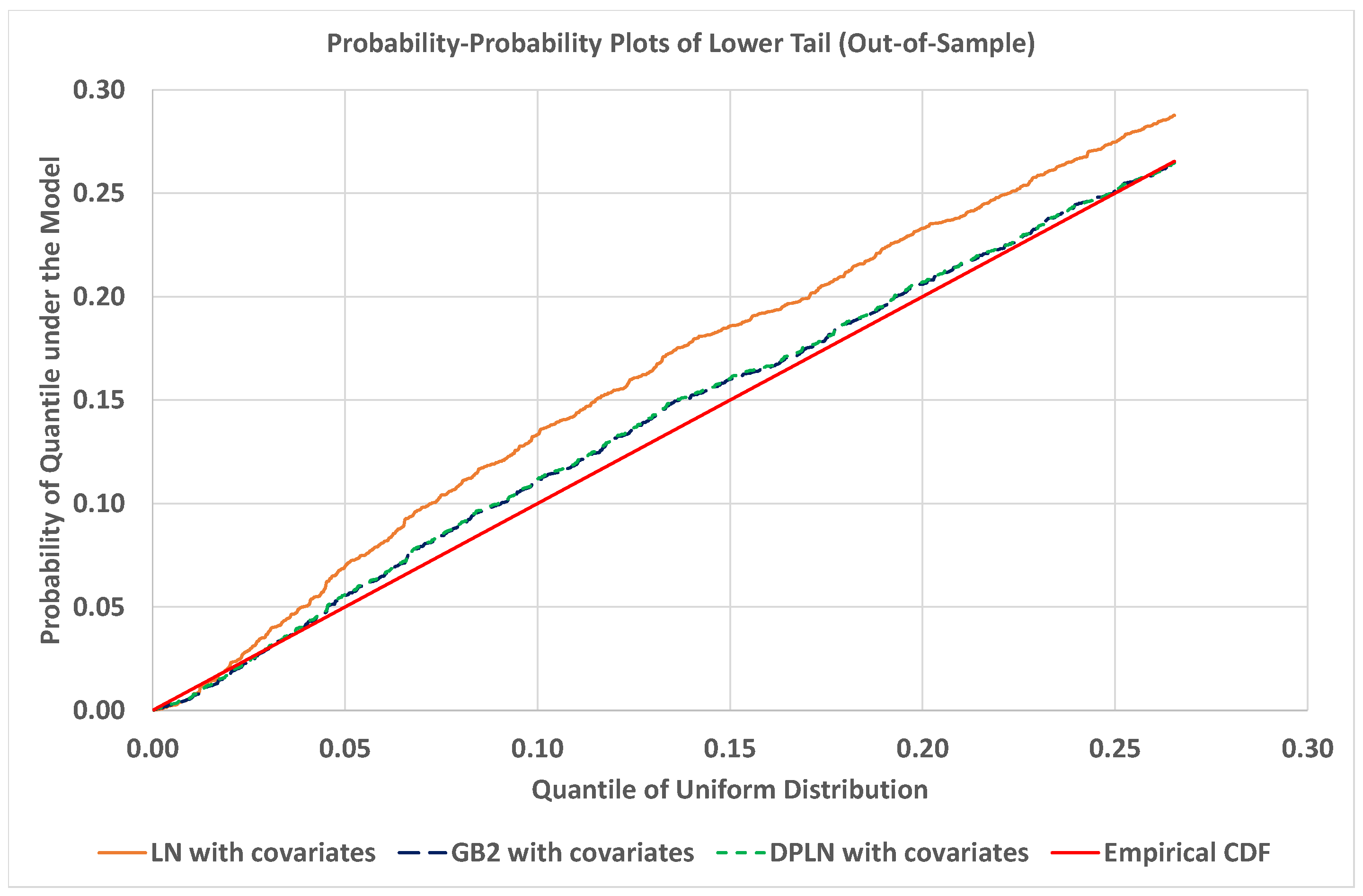
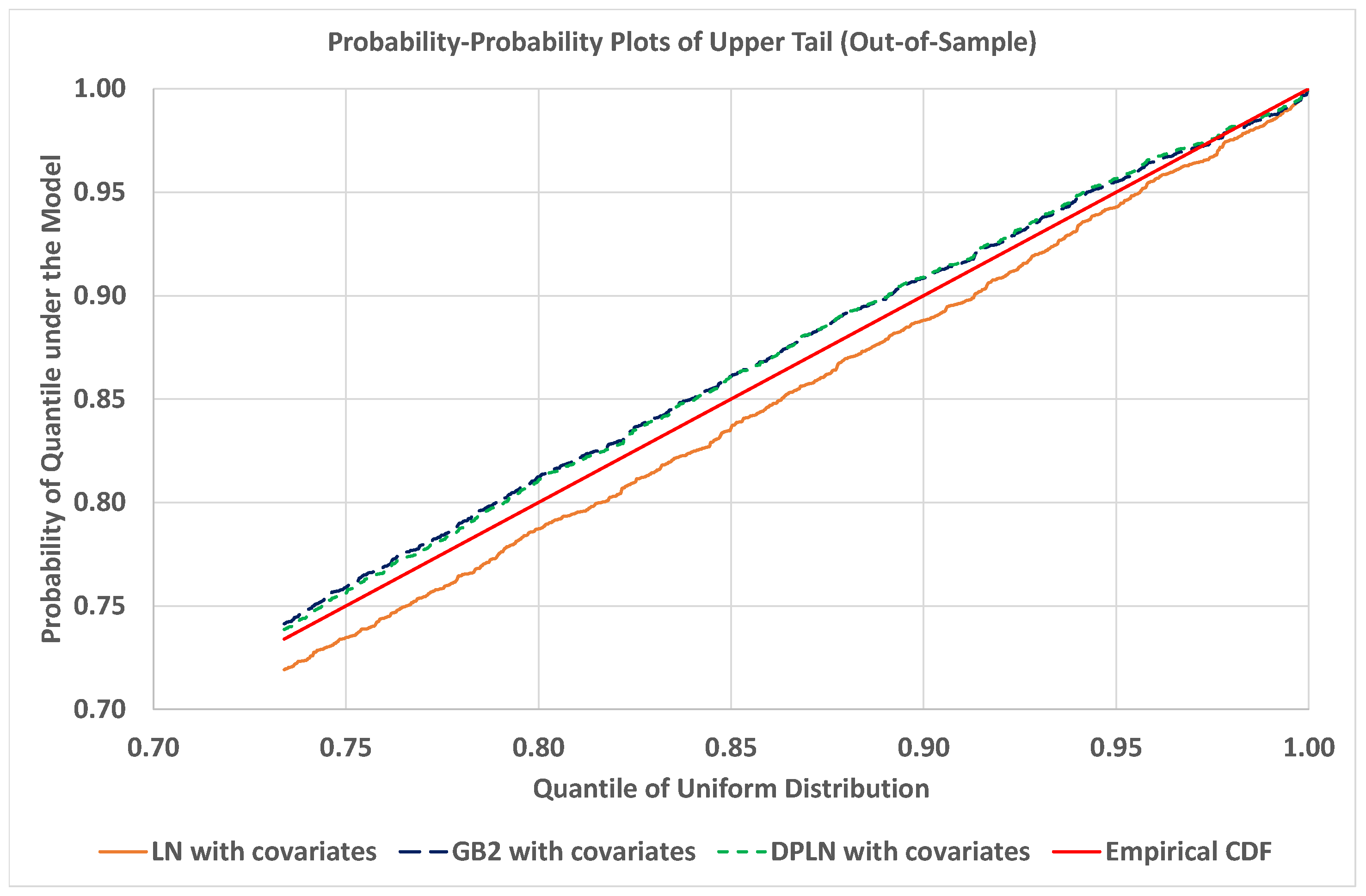
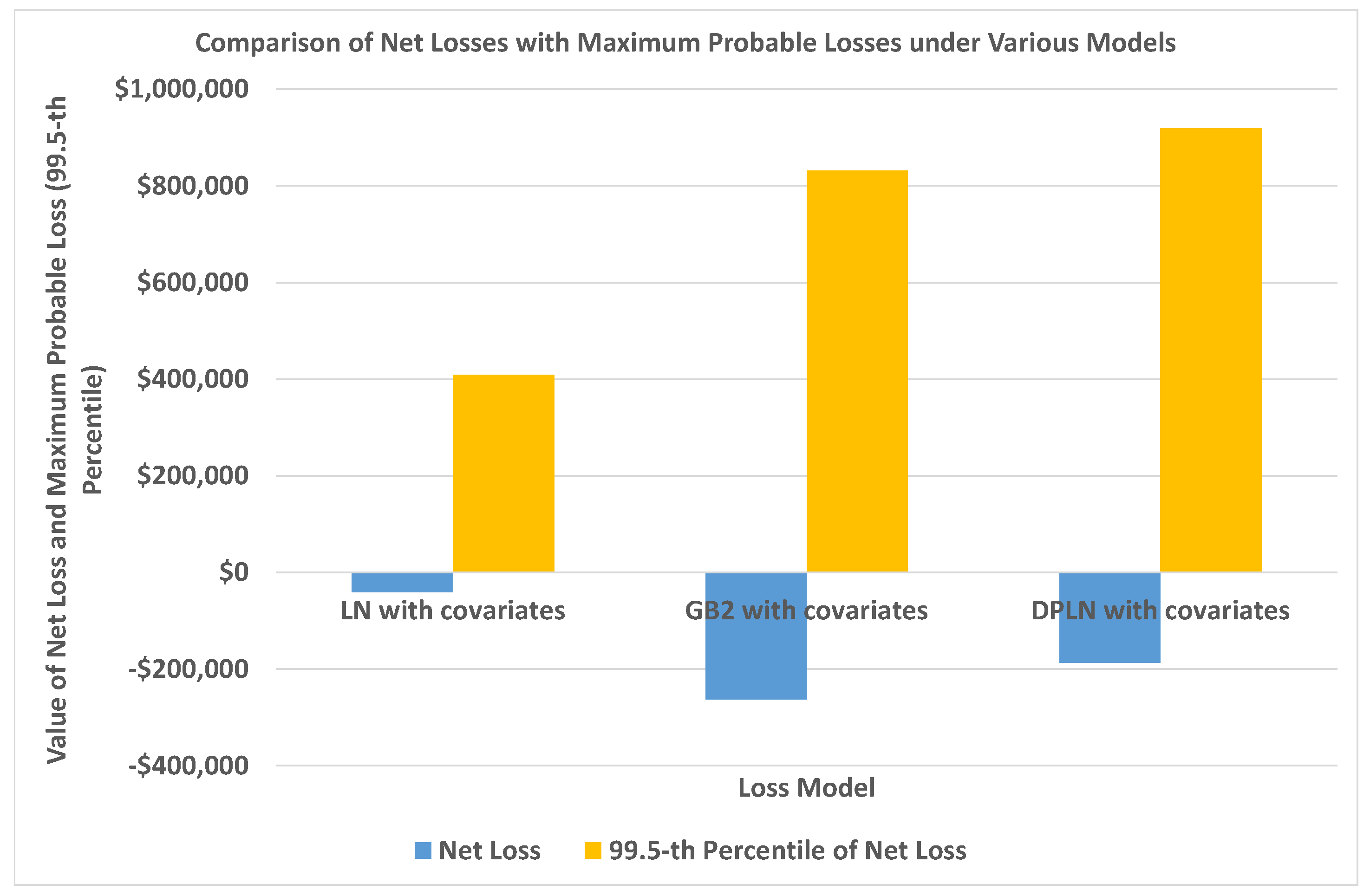
4.4. Out-of-Sample Validation of Models
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Proof of Theorem 1
Appendix A.2. Proof of Theorem 2
Appendix A.3. Score Equations
References
- Colombi, Roberto. 1990. A new model of income distribution: The Pareto lognormal distribution. In Income and Wealth Distribution, Inequality and Poverty. Edited by C. Dagum and M. Zenga. Berlin: Springer, pp. 18–32. [Google Scholar]
- Dempster, Arthur P., Nan M. Laird, and Donald B. Rubin. 1977. Maximum likelihood estimation from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B 39: 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Frees, Edward W., Richard A. Derrig, and Glenn Meyers. 2014a. Predictive Modeling Applications in Actuarial Science, Volume 1. New York: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Frees, Edward W., Richard A. Derrig, and Glenn Meyers. 2014b. Predictive Modeling Applications in Actuarial Science, Volume 2. New York: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Frees, Edward W., and Emiliano A. Valdez. 2008. Hierarchical Insurance Claims Modeling. Journal of the American Statistical Association 103: 1457–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesen, Kristian, Arndt Zimmermann, and Jens Suedekum. 2010. The size distribution across all cities—Double Pareto lognormal strikes. Journal of Urban Economics 68: 129–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajargasht, Gholamreza, and William E. Griffiths. 2013. Pareto-lognormal distributions: Inequality, poverty, and estimation from grouped income data. Economic Modelling 33: 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hürlimann, Werner. 2014. Pareto type distributions and excess-of-loss reinsurance. International Journal of Recent Research and Applied Studies 18: 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kleiber, Christian, and Samuel Kotz. 2003. Statistical Size Distributions in Economics and Actuarial Sciences. Hoboken: Wiley. [Google Scholar]
- Kočović, Jelena, Vesna Ćojbašić Rajić, and Milan Jovanović. 2015. Estimating a tail of the mixture of log-normal and inverse gaussian distribution. Scandinavian Actuarial Journal 2015: 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, Erich Leo, and George Casella. 1998. Theory of Point Estimation, 2nd ed. New York: Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Louis, Thomas A. 1982. Finding the observed information matrix when using the EM algorithm. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B 44: 226–33. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, James B. 1990. Regression model for positive random variables. Journal of Econometrics 43: 227–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Cobo, Pepa, R. E. Lillo, S. Wilson, and M. P. Wiper. 2010. Bayesian inference for double pareto lognormal queues. The Annals of Applied Statistics 4: 1533–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, William J. 2003. The Pareto law of incomes - an explanation and an extension. Physica A 319: 469–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, William J., and Murray Jorgensen. 2004. The Double Pareto-Longnormal Distribution—A new parametric model for size distributions. Communications in Statistics - Theory and Methods 33: 1733–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, Quang H. 1989. Likelihood ratio tests for model selection and non-nested hypotheses. Econometrica: Journal of the Econometric Society 57: 307–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, M., E. Valdez, and E. Frees. 2006. GB2 regression with insurance claim severities. Paper presented at the UNSW Actuarial Research Symposium, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia, November 9. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, Kazuo. 1992. Accelerated failure-time regression models with a regression model of surviving fraction: An application to the analysis of ’permanent employment’ in Japan. Journal of the American Statistical Association 87: 284–92. [Google Scholar]
| 1. |
| Generalized Linear Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate (S.E.) | LN | GB2 | DPLN |
| INTERCEPT | 7.184 (0.150) | 7.234 (0.163) | 7.260 (0.080) |
| p-value | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| GENDER | −0.035 (0.027) | −0.012 (0.027) | −0.039 (0.014) |
| p-value | 0.1918 | 0.6604 | 0.0073 |
| AGE | −0.004 (0.002) | −0.004 (0.002) | −0.005 (0.001) |
| p-value | 0.0167 | 0.0110 | <0.0001 |
| C1 | 0.018 (0.118) | −0.002 (0.115) | 0.017 (0.063) |
| p-value | 0.8760 | 0.9877 | 0.7889 |
| C11 | 0.063 (0.116) | 0.021 (0.114) | 0.063 (0.062) |
| p-value | 0.5853 | 0.8567 | 0.3146 |
| C1A | −0.076 (0.165) | −0.047 (0.161) | −0.085 (0.088) |
| p-value | 0.6453 | 0.7687 | 0.3389 |
| C1B | 0.057 (0.122) | 0.008 (0.120) | 0.055 (0.066) |
| p-value | 0.6411 | 0.9471 | 0.4045 |
| C1C | −0.164 (0.206) | −0.154 (0.203) | −0.1392 (0.110) |
| p-value | 0.4267 | 0.4498 | 0.2075 |
| C2 | −0.134 (0.176) | 0.034 (0.170) | −0.132 (0.094) |
| p-value | 0.4450 | 0.8407 | 0.1626 |
| C6 | 0.070 (0.120) | 0.033 (0.118) | 0.086 (0.065) |
| p-value | 0.5594 | 0.7767 | 0.1815 |
| C7 | −0.030 (0.116) | −0.028 (0.114) | −0.033 (0.062) |
| p-value | 0.7983 | 0.8071 | 0.5960 |
| C71 | 0.018 (0.115) | −0.029 (0.113) | 0.013 (0.062) |
| p-value | 0.8725 | 0.7941 | 0.8380 |
| C72 | 0.239 (0.160) | 0.036 (0.157) | 0.226 (0.086) |
| p-value | 0.1367 | 0.8203 | 0.0087 |
| C7A | 0.127 (0.150) | 0.225 (0.147) | 0.123 (0.080) |
| p-value | 0.3965 | 0.1249 | 0.1248 |
| C7B | 0.128 (0.118) | 0.091 (0.116) | 0.129 (0.063) |
| p-value | 0.2806 | 0.4313 | 0.042 |
| C7C | 0.282 (0.162) | 0.173 (0.158) | 0.270 (0.087) |
| p-value | 0.0824 | 0.2735 | 0.0020 |
| F1 | 0.103 (0.228) | −0.134 (0.222) | 0.132 (0.122) |
| p-value | 0.6499 | 0.5462 | 0.2785 |
| F11 | −0.087 (0.203) | −0.177 (0.202) | −0.099 (0.109) |
| p-value | 0.6675 | 0.3798 | 0.3623 |
| F6 | 0.058 (0.144) | 0.069 (0.142) | 0.090 (0.077) |
| p-value | 0.6880 | 0.6300 | 0.2434 |
| F7 | −0.347 (0.178) | −0.382 (0.172) | −0.351 (0.095) |
| p-value | 0.0508 | 0.0266 | 0.0002 |
| 1.068 (0.009) | 0.968 (0.111) | 0.810 (0.006) | |
| p-value | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| p or | 2.083 (0.371) | 2.127 (0.032) | |
| p-value | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| q or | 2.109 (0.427) | 1.952 (0.029) | |
| p-value | 0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| NLL | 57,164.4 | 57,145.2 | 57,139.3 |
| AIC | 11,4370.7 | 11,4336.6 | 11,4324.6 |
| BIC | 114,513.9 | 114,493.2 | 114,481.6 |
| CT | 3.0108 | 95.4570 | 91.1358 |
| Distribution | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate (S.E.) | LN | GB2 | DPLN |
| p or | |||
| q or | 1.897 (0.316) | ||
| NLL | 57,185.1 | 57,162.5 | 57,161.5 |
| AIC | 114,374 | 114,333 | 114,331 |
| BIC | 114,390 | 114,360 | 114,358 |
| CT | 0.2340 | 3.8376 | 12.5113 |
| Distribution | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size | LN | DPLN | GB2 |
| 100 | () | () | () |
| () | () | () | |
| () | () | ||
| () | () | ||
| 200 | () | () | () |
| () | () | () | |
| () | () | ||
| () | () | ||
| 300 | () | () | () |
| () | () | () | |
| () | () | ||
| () | () | ||
| 400 | () | () | () |
| () | () | () | |
| () | () | ||
| () | () | ||
| 500 | () | () | () |
| () | () | () | |
| () | () | ||
| () | () | ||
| 1000 | () | () | () |
| () | () | () | |
| () | () | ||
| () | () | ||
| Distribution | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate (S.E.) | LN | GB2 | DPLN |
| p or | |||
| q or | |||
| NLL | 2626.74 | 2573.47 | 2573.47 |
| AIC | 5257.48 | 5154.94 | 5154.94 |
| BIC | 5267.47 | 5174.92 | 5174.92 |
| CT | 0.1716 | 3.4476 | 3.0888 |
| Distribution | ||
|---|---|---|
| Sample Size | LN | DPLN |
| 100 | () | () |
| () | () | |
| () | ||
| () | ||
| 200 | () | () |
| () | () | |
| () | ||
| () | ||
| 300 | () | () |
| () | () | |
| () | ||
| () | ||
| 400 | () | () |
| () | () | |
| () | ||
| () | ||
| 500 | () | () |
| () | () | |
| () | ||
| () | ||
| 1000 | () | () |
| () | () | |
| () | ||
| () | ||
| Generalized Linear Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate (S.E.) | LN | GB2 | DPLN |
| INTERCEPT | 0.764 (0.382) | 1.083 (0.383) | 1.023 (0.376) |
| p-value | 0.0458 | 0.0048 | 0.0067 |
| ATTORNEY | 1.368 (0.075) | 1.215 (0.079) | 1.213 (0.075) |
| p-value | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| CLMSEX | −0.103 (0.076) | −0.135 (0.070) | −0.135 (0.069) |
| p-value | 0.1757 | 0.0524 | 0.0516 |
| MARRIED | −0.221 (0.235) | −0.350 (0.233) | −0.352 (0.234) |
| p-value | 0.3464 | 0.1340 | 0.1320 |
| SINGLE | −0.378 (0.241) | −0.494 (0.237) | −0.498 (0.237) |
| p-value | 0.1171 | 0.0374 | 0.0360 |
| WIDOWED | −0.887 (0.430) | −0.748 (0.417) | −0.744 (0.419) |
| p-value | 0.0393 | 0.0730 | 0.0763 |
| CLMINSUR | −0.009 (0.127) | −0.043 (0.116) | −0.041 (0.115) |
| p-value | 0.9448 | 0.7091 | 0.7218 |
| SEATBELT | −0.996 (0.278) | −0.785 (0.272) | −0.768 (0.272) |
| p-value | 0.0015 | 0.0040 | 0.0048 |
| CLMAGE | 0.014 (0.003) | 0.013 (0.003) | 0.013 (0.003) |
| p-value | 0.0010 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| 1.230 (0.026) | 0.448 (0.129) | 0.538 (0.110) | |
| p-value | <0.0001 | 0.0006 | <0.0001 |
| p or | 0.513 (0.185) | 1.458 (0.139) | |
| p-value | 0.0055 | <0.0001 | |
| q or | 0.670 (0.252) | 1.112 (0.085) | |
| p-value | 0.0079 | <0.0001 | |
| NLL | 2450.54 | 2429.59 | 2430.02 |
| AIC | 4921.09 | 4883.18 | 4884.05 |
| BIC | 4971.04 | 4943.12 | 4943.98 |
| CT | 0.4524 | 6.2556 | 3.2488 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Calderín-Ojeda, E.; Fergusson, K.; Wu, X. An EM Algorithm for Double-Pareto-Lognormal Generalized Linear Model Applied to Heavy-Tailed Insurance Claims. Risks 2017, 5, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks5040060
Calderín-Ojeda E, Fergusson K, Wu X. An EM Algorithm for Double-Pareto-Lognormal Generalized Linear Model Applied to Heavy-Tailed Insurance Claims. Risks. 2017; 5(4):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks5040060
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalderín-Ojeda, Enrique, Kevin Fergusson, and Xueyuan Wu. 2017. "An EM Algorithm for Double-Pareto-Lognormal Generalized Linear Model Applied to Heavy-Tailed Insurance Claims" Risks 5, no. 4: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks5040060
APA StyleCalderín-Ojeda, E., Fergusson, K., & Wu, X. (2017). An EM Algorithm for Double-Pareto-Lognormal Generalized Linear Model Applied to Heavy-Tailed Insurance Claims. Risks, 5(4), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks5040060






