High-Fat Diet Induces Pre-Diabetes and Distinct Sex-Specific Metabolic Alterations in Negr1-Deficient Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
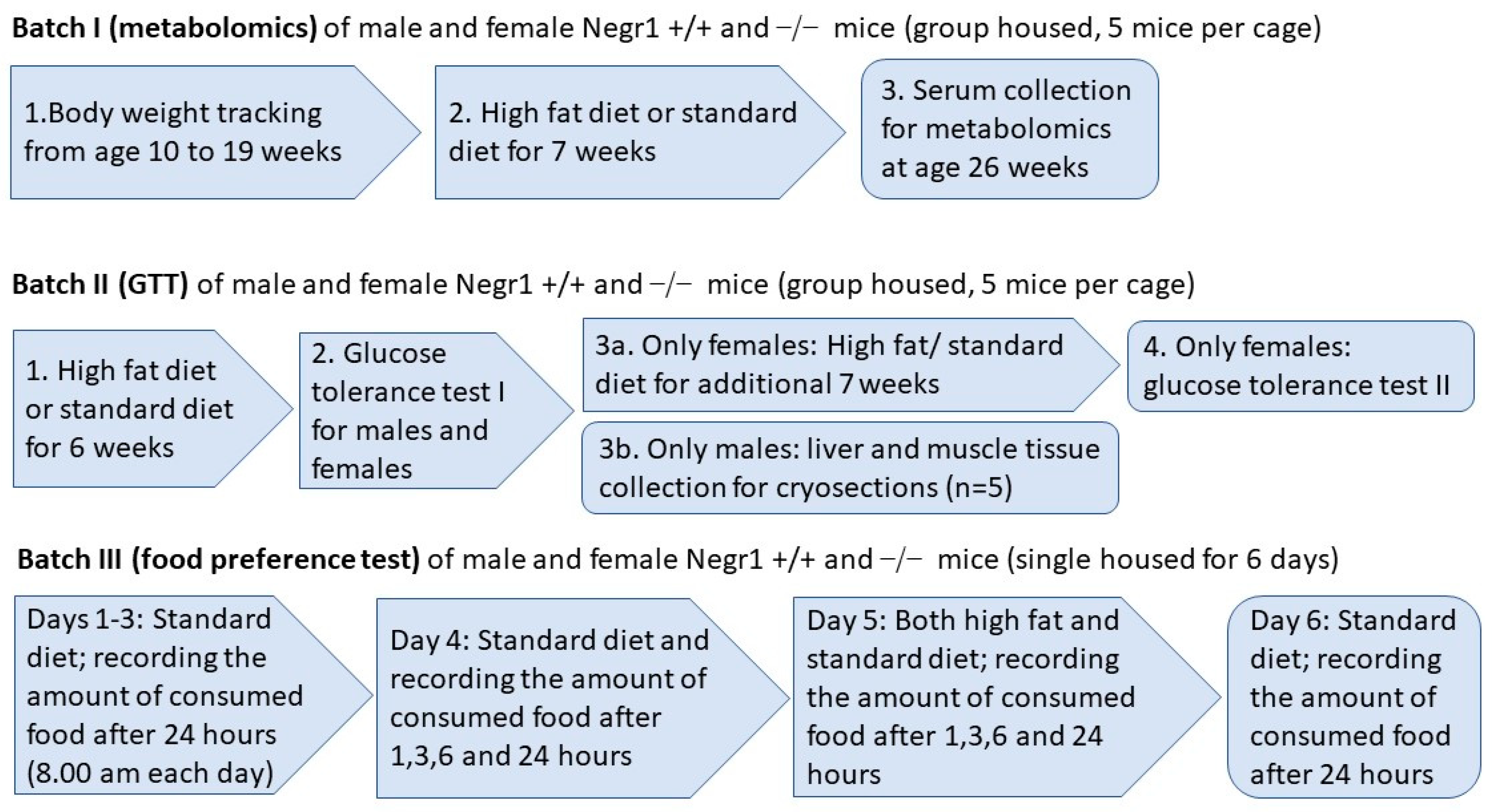
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Diet Composition
2.3. High Fat Diet
2.4. Food Preference Test (Batch III)
2.5. Sample Collection
2.6. Measurement of Metabolites
2.7. Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT, Batch II)
2.8. Neutral Lipid and Actin Staining on the Tissue Cryosections
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Negr1 Deficiency Induces Lower Intake of HF Food but Higher Body Weight Gain in Male Mice
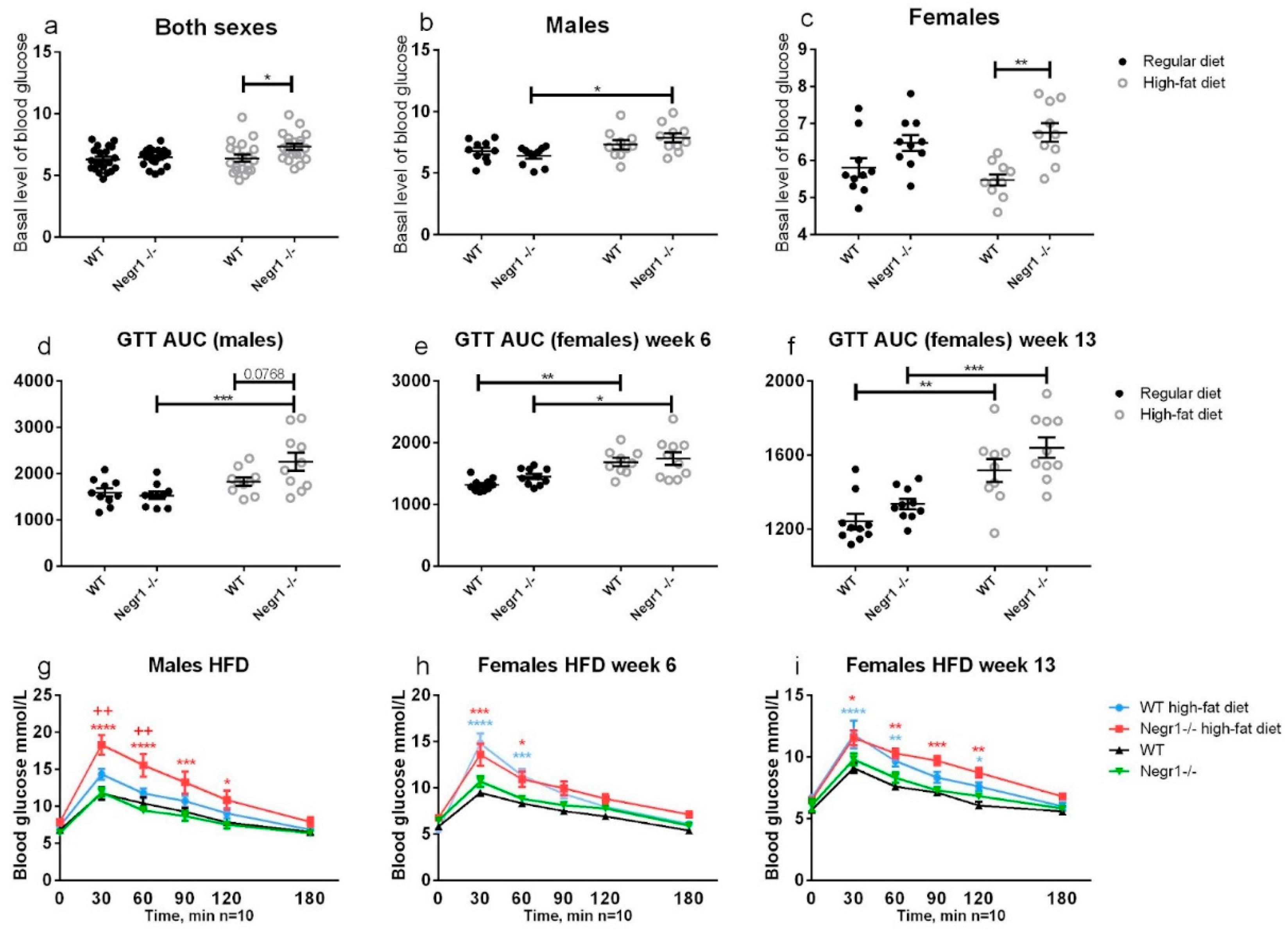
3.2. HFD Leads to Higher Levels of Blood Glucose in Negr1−/− Mice, Whereas Phenotype Difference in Glucose Tolerance Test Was Apparent Only in Males
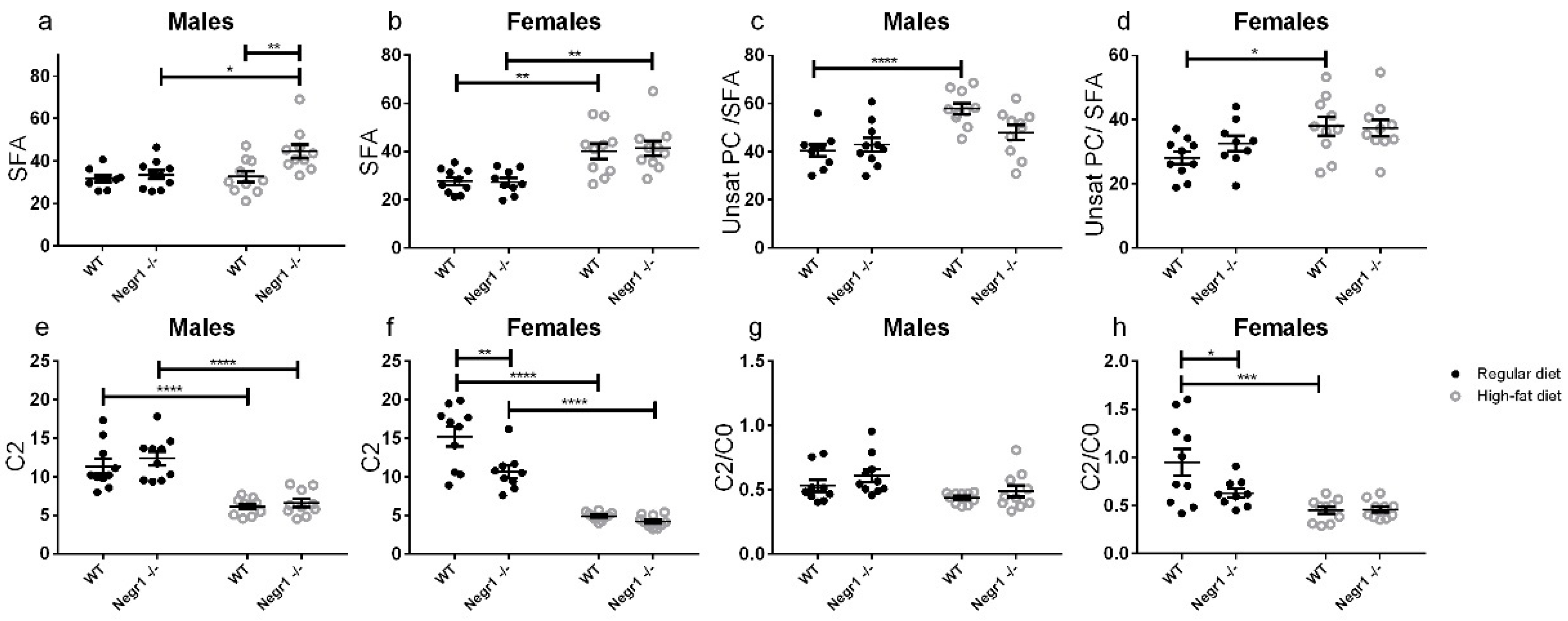
3.3. HFD Induces an Altered Profile of Circulating Lipids Sex-Specifically in Negr1−/− Mice
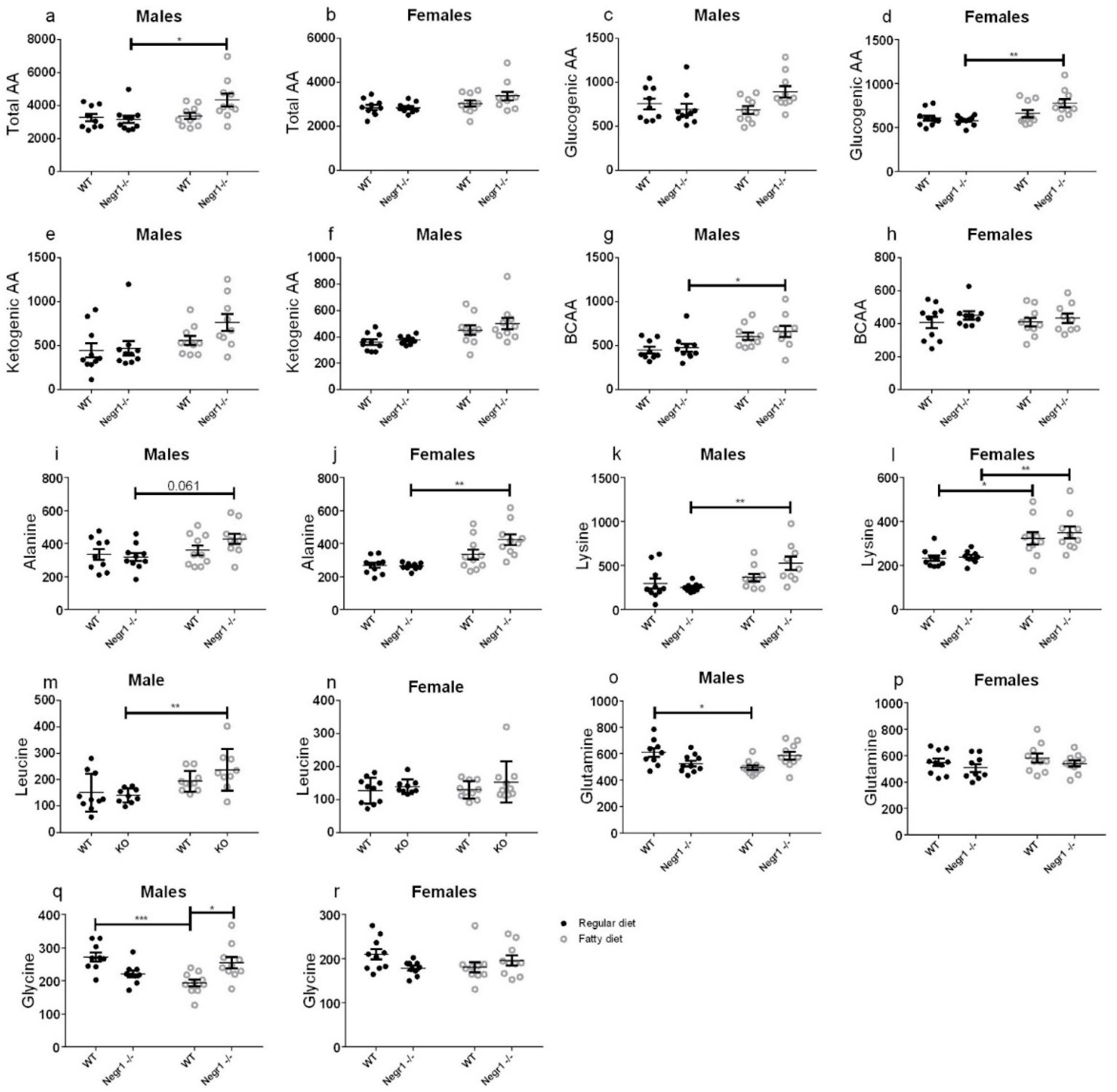
3.4. HFD Induced an Increase in Circulating Amino Acids in Negr1−/− Mice, More Prominently in Males
3.5. Altered Profile of Circulating Organic Acids in Negr1−/− Mice
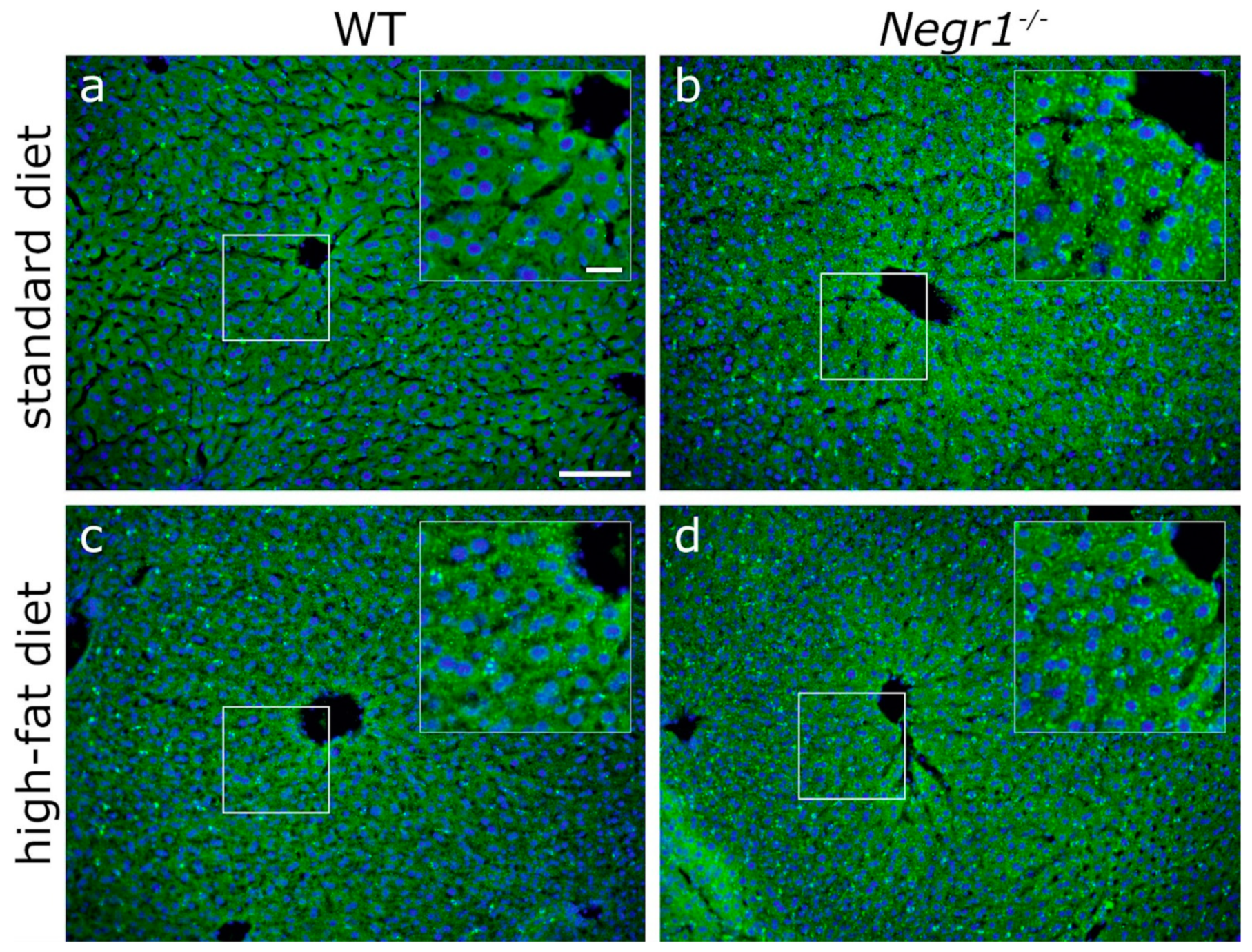
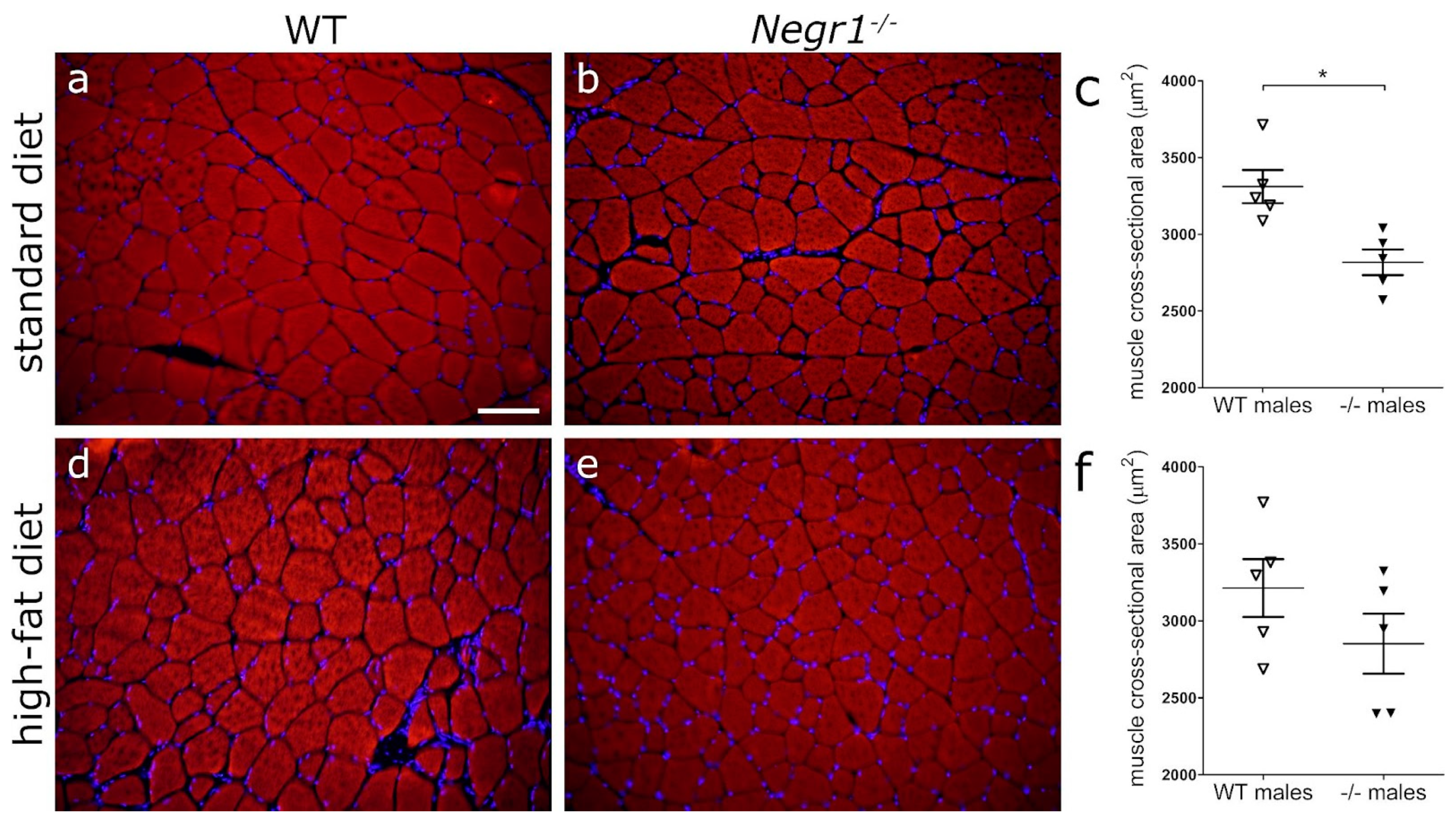
3.6. Negr1 Decifiency Induces Hepatic Fat Accumulation in Both Male and Female Mice and Reduced Skeletal Muscle Volume in Males
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marg, A.; Sirim, P.; Spaltmann, F.; Plagge, A.; Kauselmann, G.; Buck, F.; Rathjen, F.G.; Brümmendorf, T. Neurotractin, A Novel Neurite Outgrowth-promoting Ig-like Protein that Interacts with CEPU-1 and LAMP. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 145, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noh, K.; Lee, H.; Choi, T.-Y.; Joo, Y.; Kim, S.-J.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.Y.; Jahng, J.W.; Lee, S.; Choi, S.-Y.; et al. Negr1 controls adult hippocampal neurogenesis and affective behaviors. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 1189–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Loreth, D.; Pöttker, B.; Hefti, K.; Innos, J.; Schwald, K.; Hengstler, H.; Menzel, L.; Sommer, C.J.; Radyushkin, K.; et al. Neuronal Growth and Behavioral Alterations in Mice Deficient for the Psychiatric Disease-Associated Negr1 Gene. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 1662–5099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, K.; Jayaram, M.; Kaare, M.; Leidmaa, E.; Jagomäe, T.; Heinla, I.; Hickey, M.; Kaasik, A.; Schäfer, M.K.; Innos, J.; et al. Neural cell adhesion molecule Negr1 deficiency in mouse results in structural brain endophenotypes and behavioral deviations related to psychiatric disorders. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranaivoson, F.M.; Turk, L.S.; Ozgul, S.; Kakehi, S.; von Daake, S.; Lopez, N.; Trobiani, L.; DE Jaco, A.; Denissova, N.; Demeler, B.; et al. A Proteomic Screen of Neuronal Cell-Surface Molecules Reveals IgLONs as Structurally Conserved Interaction Modules at the Synapse. Structure 2019, 27, 1055–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willer, C.J.; Speliotes, E.K.; Loos, R.J.F.; Li, S.; Lindgren, C.M.; Heid, I.M.; Berndt, S.I.; Elliott, A.L.; Jackson, A.U.; Lamina, C.; et al. Six new loci associated with body mass index highlight a neuronal influence on body weight regulation. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorleifsson, G.; Walters, G.B.; Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Sulem, P.; Helgadottir, A.; Styrkarsdottir, U.; Gretarsdottir, S.; Thorlacius, S.; Jonsdottir, I.; et al. Genome-wide association yields new sequence variants at seven loci that associate with measures of obesity. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speliotes, E.K.; Willer, C.J.; Berndt, S.I.; Monda, K.L.; Thorleifsson, G.; Jackson, A.U.; Allen, H.L.; Lindgren, C.M.; Mägi, R.; Randall, J.C.; et al. Association analyses of 249,796 individuals reveal 18 new loci associated with body mass index. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Locke, A.E.; Kahali, B.; Berndt, S.I.; Justice, A.E.; Pers, T.H.; Day, F.R.; Powell, C.; Vedantam, S.; Buchkovich, M.L.; Yang, J.; et al. Genetic studies of body mass index yield new insights for obesity biology. Nature 2015, 518, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winkler, T.W.; Justice, A.E.; Graff, M.; Barata, L.; Feitosa, M.F.; Chu, S.; Czajkowski, J.; Esko, T.; Fall, T.; Kilpeläinen, T.O.; et al. The Influence of Age and Sex on Genetic Associations with Adult Body Size and Shape: A Large-Scale Genome-Wide Interaction Study. PLoS Genet. 2016, 11, e1005378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlauch, K.A.; Read, R.W.; Lombardi, V.C.; Elhanan, G.; Metcalf, W.J.; Slonim, A.D.; Twenty Three & Me Research Team; Grzymski, J.J. A Comprehensive Genome-Wide and Phenome-Wide Examination of BMI and Obesity in a Northern Nevadan Cohort. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2020, 10, 645–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wheeler, E.; Huang, N.; Bochukova, E.; Keogh, J.M.; Lindsay, S.; Garg, S.; Henning, E.; Blackburn, H.; Loos, R.; Wareham, N.J.; et al. Genome-wide SNP and CNV analysis identifies common and low-frequency variants associated with severe early-onset obesity. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino, J.; Dashti, H.S.; Sarnowski, C.; Lane, J.M.; Udler, M.S.; Todorov, P.V.; Song, Y.; Wang, H.; Kim, J.; Tucker, C.; et al. Multi-trait genome-wide association meta-analysis of dietary intake identifies new loci and genetic and functional links with metabolic traits. bioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niarchou, M.; Byrne, E.M.; Trzaskowski, M.; Sidorenko, J.; Kemper, K.; McGrath, J.J.; Donovan, M.C.O.; Owen, M.J.; Wray, N.R. Genome-wide association study of dietary intake in the UK biobank study and its associations with schizophrenia and other traits. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gamero-Villarroel, C.; González, L.M.; Gordillo, I.; Carrillo, J.A.; García-Herráiz, A.; Flores, I.; Rodríguez-López, R.; Gervasini, G. Impact of NEGR1 genetic variability on psychological traits of patients with eating disorders. Pharm. J. 2015, 15, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.H.; Anttila, V.; Won, H.; Feng, Y.-C.A.; Rosenthal, J.; Zhu, Z.; Tucker-Drob, E.M.; Nivard, M.; Grotzinger, A.D.; Posthuma, D.; et al. Genomic Relationships, Novel Loci, and Pleiotropic Mechanisms across Eight Psychiatric Disorders. Cell 2019, 179, 1469–1482.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyde, C.L.; Nagle, M.; Tian, C.; Chen, X.; Paciga, S.A.; Wendland, J.R.; Tung, J.Y.; Hinds, A.; Perlis, R.H.; Winslow, A.R. Identification of 15 genetic loci associated with risk of major depression in individuals of European descent. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, D.M.; Adams, M.J.; Shirali, M.; Clarke, T.-K.; Marioni, R.E.; Davies, G.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Alloza, C.; Shen, X.; Barbu, M.C.; et al. Genome-wide association study of depression phenotypes in UK Biobank identifies variants in excitatory synaptic pathways. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Levey, D.F.; Stein, M.B.; Wendt, F.R.; Pathak, G.A.; Zhou, H.; Aslan, M.; Quaden, R.; Harrington, K.M.; Nuñez, Y.Z.; Overstreet, C.; et al. Bi-ancestral depression GWAS in the Million Veteran Program and meta-analysis in >1.2 million individuals highlight new therapeutic directions. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Aglio, L.; Lewis, C.M.; Pain, O. Delineating the Genetic Component of Gene Expression in Major Depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 89, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.W.S.; Hengstler, H.; Schwald, K.; Diaz, M.B.; Loreth, D.; Kirsch, M.; Kretz, O.; Haas, C.A.; de Angelis, M.H.; Herzig, S.; et al. Functional Inactivation of the Genome-Wide Association Study Obesity Gene Neuronal Growth Regulator 1 in Mice Causes a Body Mass Phenotype. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Chun, Y.; Che, L.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, S. The new obesity-associated protein, neuronal growth regulator 1 (NEGR1), is implicated in Niemann-Pick disease Type C (NPC2)-mediated cholesterol trafficking. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkannagari, H.; Kasper, J.; Misra, A.; Rush, S.; Fan, S.; Lee, H.; Sun, H.; Seshadrinathan, S.; Machius, M.; Hommel, J.D.; et al. Highly Conserved Molecular Features in IgLONs Contrast Their Distinct Structural and Biological Outcomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 5287–5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boender, A.J.; van Gestel, M.A.; Garner, K.M.; Luijendijk, M.C.M.; Adan, R.A.H. The obesity-associated gene Negr1 regulates aspects of energy balance in rat hypothalamic areas. Physiol. Rep. 2012, 2, e12083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boender, A.J.; Van Rozen, A.J.; Adan, R.A. Nutritional State Affects the Expression of the Obesity-Associated GenesEtv5, Faim2, Fto, and Negr1. Obesity 2019, 20, 2420–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yi, J.; Ray, W.K.; Vu, L.; Helm, R.F.; Siegel, P.B.; Cline, M.A.; Gilbert, E.R. Fasting differentially alters the hypothalamic proteome of chickens from lines with the propensity to be anorexic or obese. Nutr. Diabetes 2011, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sandholt, C.H.; Vestmar, M.A.; Bille, D.S.; Borglykke, A.; Almind, K.; Hansen, L.; Sandbæk, A.; Lauritzen, T.; Witte, D.; Jørgensen, T.; et al. Studies of Metabolic Phenotypic Correlates of 15 Obesity Associated Gene Variants. PLoS ONE 2005, 6, e23531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, M.; Bräuer, A.U.; Savaskan, N.E.; Rathjen, F.G.; Brümmendorf, T. Neurotractin/kilon promotes neurite outgrowth and is expressed on reactive astrocytes after entorhinal cortex lesion. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2012, 29, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walley, A.J.; Jacobson, P.; Falchi, M.; Bottolo, L.; Andersson-Assarsson, J.; Petretto, E.; Bonnefond, A.; Vaillant, E.; Lecoeur, C.; Vatin, V.; et al. Differential coexpression analysis of obesity-associated networks in human subcutaneous adipose tissue. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 36, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanaveski, T.; Singh, K.; Narvik, J.; Eskla, K.-L.; Visnapuu, T.; Heinla, I.; Jayaram, M.; Innos, J.; Lilleväli, K.; Philips, M.-A.; et al. Promoter-Specific Expression and Genomic Structure of IgLON Family Genes in Mouse. Front. Neurosci. 2012, 11, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernhard, F.; Landgraf, K.; Klöting, N.; Berthold, A.; Büttner, P.; Friebe, D.; Kiess, W.; Kovacs, P.; Blüher, M.; Körner, A. Functional relevance of genes implicated by obesity genome-wide association study signals for human adipocyte biology. Diabetol. 2020, 56, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, D.; Joo, Y.; Kim, H. The role of NEGR1 in the formation of lipid droplets. FASEB J. 2019, 34, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, Y.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.; Lee, S. Neuronal growth regulator 1-deficient mice show increased adiposity and decreased muscle mass. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 43, 1769–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leidmaa, E.; Gazea, M.; Patchev, A.V.; Pissioti, A.; Gassen, N.C.; Kimura, M.; Liposits, Z.; Kallo, I.; Almeida, O.F.X. Blunted leptin sensitivity during hedonic overeating can be reinstated by activating galanin 2 receptors (Gal2R) in the lateral hypothalamus. Acta Physiol. 2012, 228, e13345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2008, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farmer, A.; Korszun, A.; Owen, M.J.; Craddock, N.; Jones, L.; Jones, I.; Gray, J.; Williamson, R.J.; McGuffin, P. Medical disorders in people with recurrent depression. Br. J. Psychiatry 2020, 192, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tramunt, B.; Smati, S.; Grandgeorge, N.; Lenfant, F.; Arnal, J.-F.; Montagner, A.; Gourdy, P. Sex differences in metabolic regulation and diabetes susceptibility. Diabetologia 2018, 63, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mauvais-Jarvis, F. Gender differences in glucose homeostasis and diabetes. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 187, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauschert, S.; Uhl, O.; Koletzko, B.; Mori, T.A.; Beilin, L.J.; Oddy, W.H.; Hellmuth, C. Sex differences in the association of phospholipids with components of the metabolic syndrome in young adults. Biol. Sex Differ. 2018, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cochran, J.; Taufalele, P.V.; Lin, K.D.; Zhang, Y.; Abel, E.D. Sex Differences in the Response of C57BL/6 Mice to Ketogenic Diets. Diabetes 2011, 67, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.J.; Larson, M.; Vasan, R.S.; Cheng, S.; Rhee, E.P.; McCabe, E.; Lewis, G.D.; Fox, C.S.; Jacques, P.F.; Fernandez, C.; et al. Metabolite profiles and the risk of developing diabetes. Nat. Med. 2014, 17, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, R.; Xiong, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Guo, H.; Hao, L.; Yao, P.; Liu, L.; et al. Leucine facilitates the insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and insulin signaling in skeletal muscle cells: Involving mTORC1 and mTORC2. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 1971–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, C.J.; Adams, S. Branched-chain amino acids in metabolic signalling and insulin resistance. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 1965, 10, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kornacker, M.S.; Lowenstein, J.M. Citrate and the conversion of carbohydrate into fat. The activities of citrate-cleavage enzyme and acetate thiokinase in livers of starved and re-fed rats. Biochem. J. 2002, 94, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munday, M.R. Regulation of mammalian acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2014, 30, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, E.; Jansson, P.A.; Perfilyev, A.; Volkov, P.; Pedersen, M.; Svensson, M.K.; Poulsen, P.; Ribel-Madsen, R.; Pedersen, N.L.; Almgren, P.; et al. Altered DNA Methylation and Differential Expression of Genes Influencing Metabolism and Inflammation in Adipose Tissue from Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2019, 63, 2962–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jana, B.A.; Chintamaneni, P.K.; Krishnamurthy, P.T.; Wadhwani, A.; Mohankumar, S.K. Cytosolic lipid excess-induced mitochondrial dysfunction is the cause or effect of high fat diet-induced skeletal muscle insulin resistance: A molecular insight. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaare, M.; Mikheim, K.; Lilleväli, K.; Kilk, K.; Jagomäe, T.; Leidmaa, E.; Piirsalu, M.; Porosk, R.; Singh, K.; Reimets, R.; et al. High-Fat Diet Induces Pre-Diabetes and Distinct Sex-Specific Metabolic Alterations in Negr1-Deficient Mice. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091148
Kaare M, Mikheim K, Lilleväli K, Kilk K, Jagomäe T, Leidmaa E, Piirsalu M, Porosk R, Singh K, Reimets R, et al. High-Fat Diet Induces Pre-Diabetes and Distinct Sex-Specific Metabolic Alterations in Negr1-Deficient Mice. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(9):1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091148
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaare, Maria, Kaie Mikheim, Kersti Lilleväli, Kalle Kilk, Toomas Jagomäe, Este Leidmaa, Maria Piirsalu, Rando Porosk, Katyayani Singh, Riin Reimets, and et al. 2021. "High-Fat Diet Induces Pre-Diabetes and Distinct Sex-Specific Metabolic Alterations in Negr1-Deficient Mice" Biomedicines 9, no. 9: 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091148
APA StyleKaare, M., Mikheim, K., Lilleväli, K., Kilk, K., Jagomäe, T., Leidmaa, E., Piirsalu, M., Porosk, R., Singh, K., Reimets, R., Taalberg, E., Schäfer, M. K. E., Plaas, M., Vasar, E., & Philips, M.-A. (2021). High-Fat Diet Induces Pre-Diabetes and Distinct Sex-Specific Metabolic Alterations in Negr1-Deficient Mice. Biomedicines, 9(9), 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091148






