Extracellular Vesicles from Thapsigargin-Treated Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorated Experimental Colitis via Enhanced Immunomodulatory Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation and Culture of WJ-MSCs
2.2. Cell Viability Assay
2.3. Isolation and Characterization of EVs
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Quantitative RT-PCR
2.6. Apoptosis Assay
2.7. PBMC Isolation
2.8. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.9. The Cell Differentiation
2.10. Differentiation and Polarization of Human Macrophage
2.11. DSS-Induced Colitis Mice
2.12. Histopathologic Evaluation
2.13. Isolation of Cells from the Lamina Propria of Colons in Mice
2.14. Myeloperoxidase (MPO) Activity Assay
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
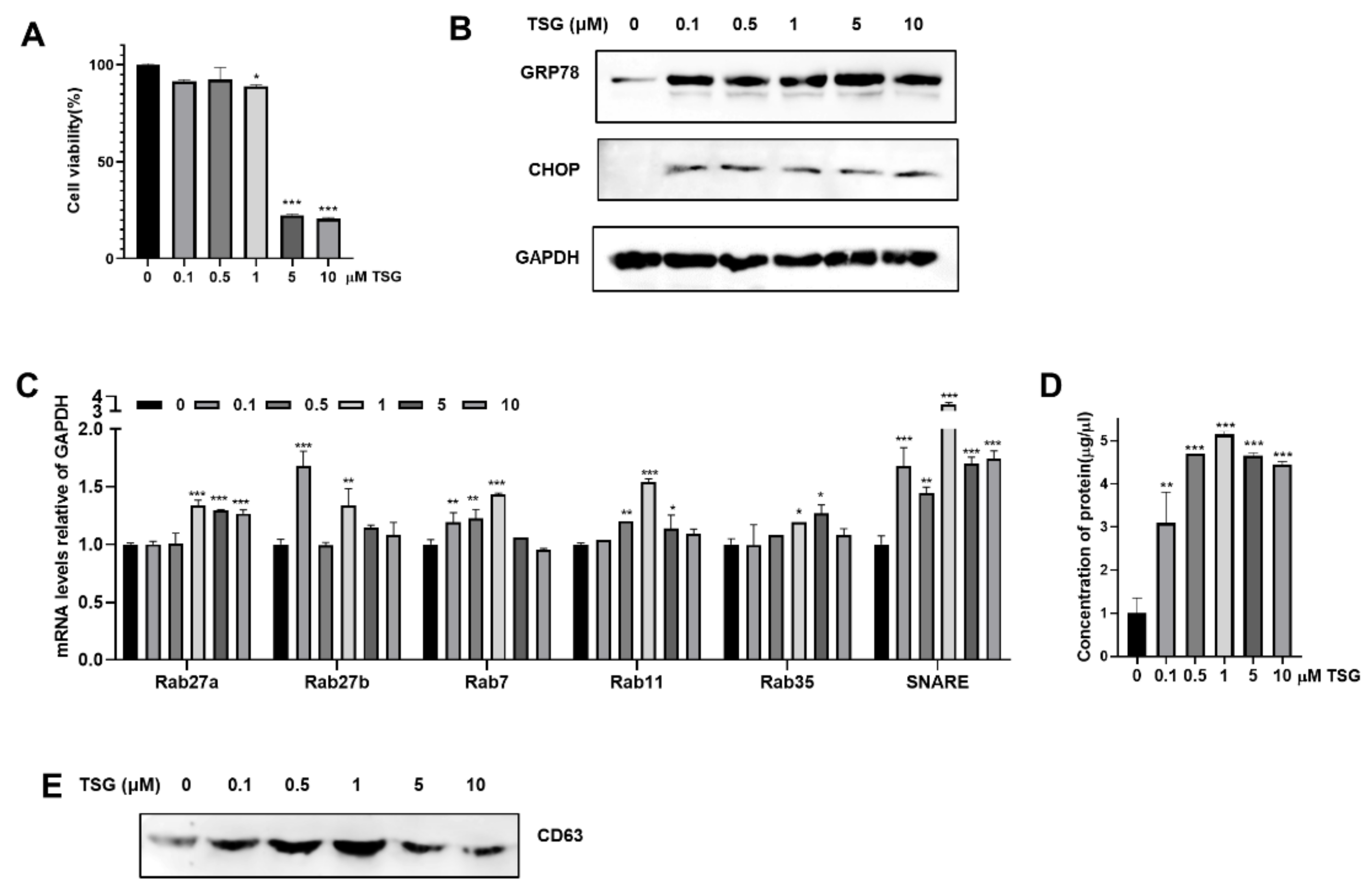
3.1. Induction of ER Stress by TSG Stimulates the Release of EV on WJ-MSCs
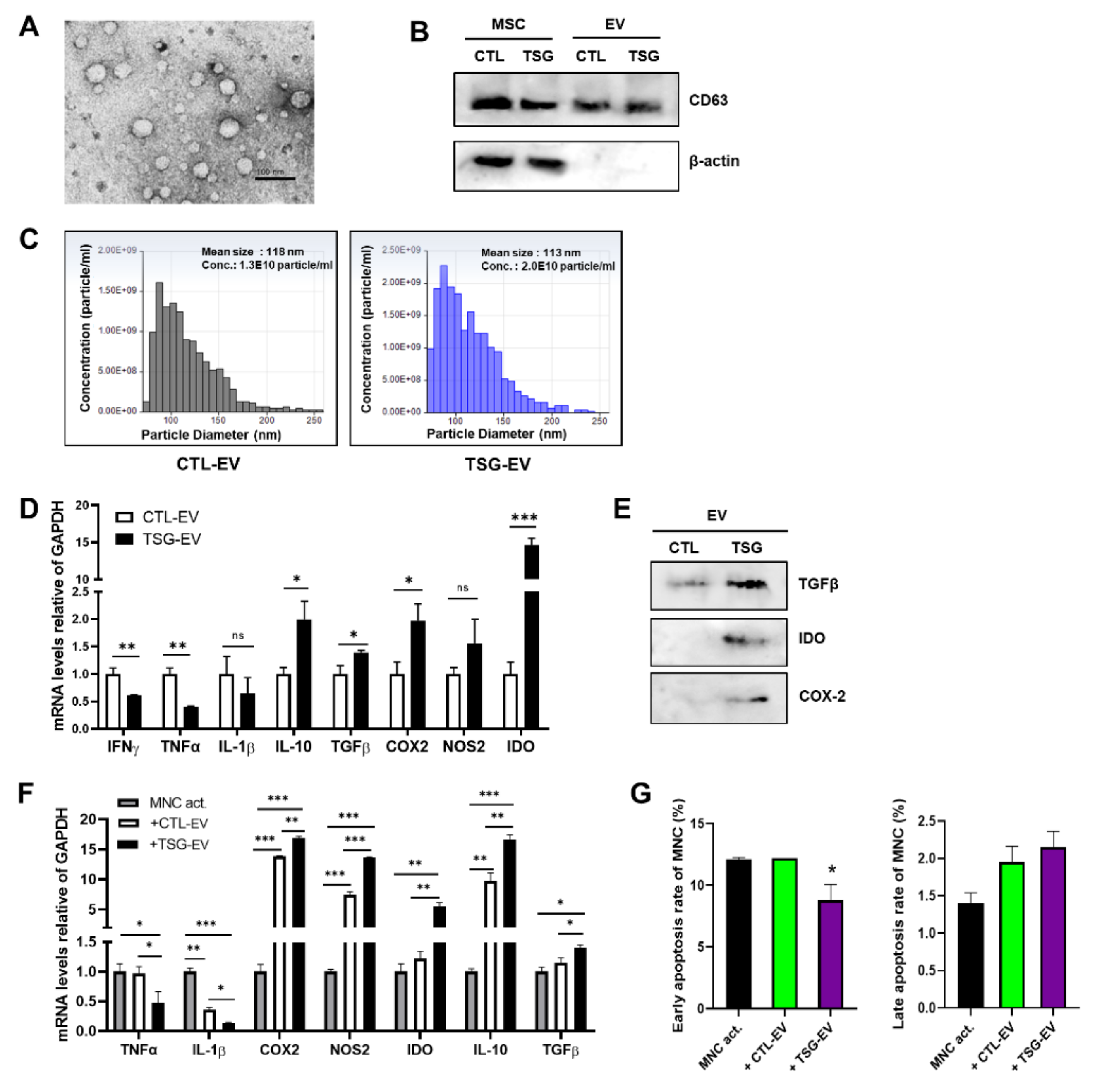
3.2. Characterization of EVs Derived from TSG Primed WJ-MSCs
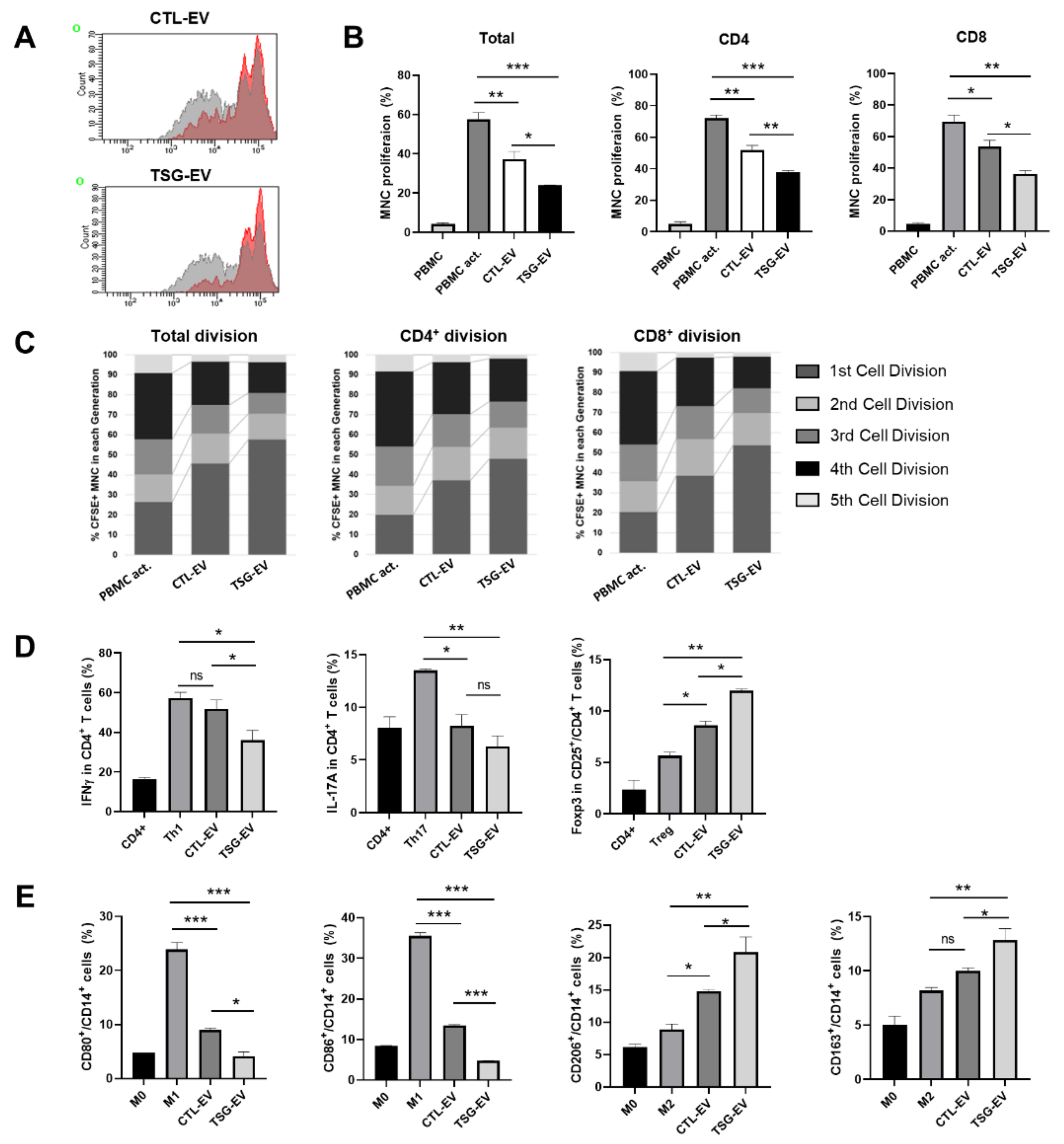
3.3. TSG-Primed EVs Inhibit T Cell Proliferation by Increasing Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Production
3.4. TSG-Primed EVs Enhance Regulatory T Cells and M2-Type Macrophage Polarization
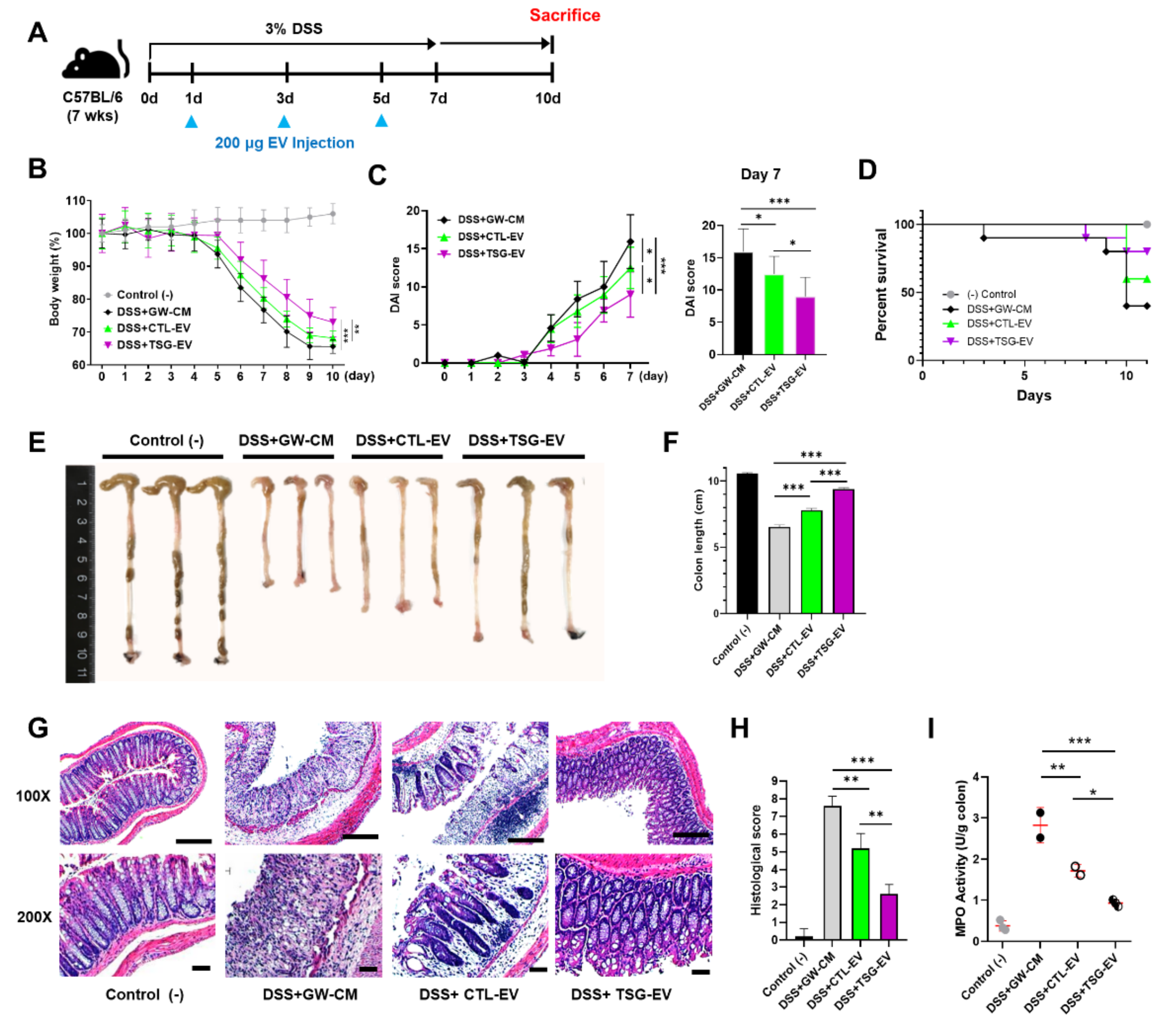
3.5. TSG-Primed EVs Significantly Alleviate DSS-Induced Colitis
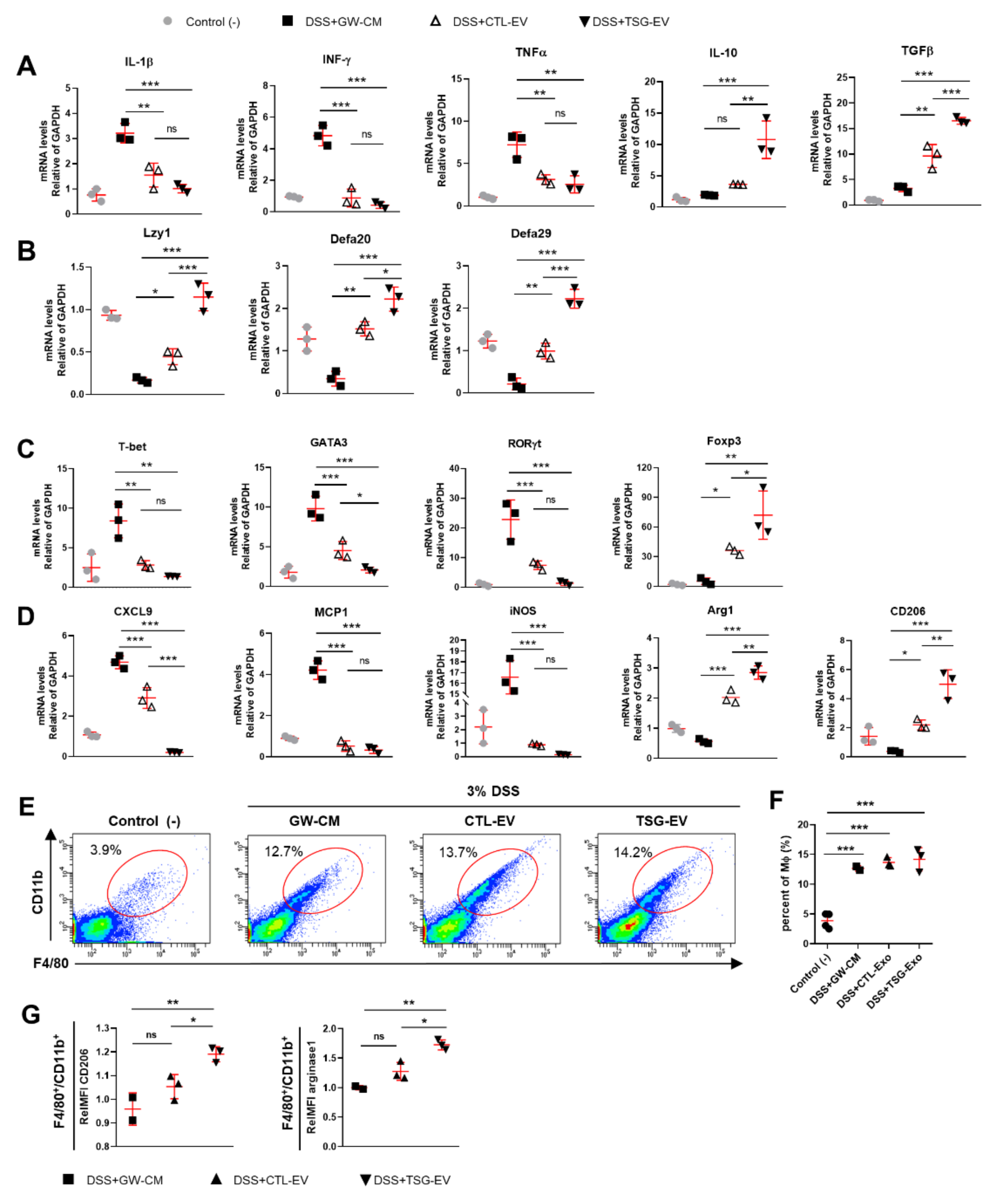
3.6. TSG-Primed EV Increase Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines in the Inflamed Colon
3.7. TSG-Primed EVs Enhance Regulatory T Cells and M2 Macrophage Polarization in the Inflamed Colon
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arno, A.I.; Amini-Nik, S.; Blit, P.H.; Al-Shehab, M.; Belo, C.; Herer, E.; Jeschke, M.G. Effect of human Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cell paracrine signaling on keloid fibroblasts. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2014, 3, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorn, J.; Moll, G.; Le Blanc, K.; van Blitterswijk, C.; de Boer, J. Therapeutic applications of mesenchymal stromal cells: Paracrine effects and potential improvements. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2012, 18, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnecchi, M.; Danieli, P.; Malpasso, G.; Ciuffreda, M.C. Paracrine Mechanisms of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Tissue Repair. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1416, 123–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.R.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Hong, I.S.; Choi, S.W.; Seo, Y.; Kang, I.; Kim, J.J.; Lee, B.C.; Lee, S.; et al. A p38 MAPK-mediated alteration of COX-2/PGE2 regulates immunomodulatory properties in human mesenchymal stem cell aging. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, N.; Scholtemeijer, M.; Shah, K. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Immunomodulation: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 41, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.Y.; Oh, M.K.; Joo, H.; Park, H.S.; Chae, D.H.; Kim, J.; Lee, H.R.; Oh, I.H.; Yu, K.R. Xeno-Free Condition Enhances Therapeutic Functions of Human Wharton’s Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells against Experimental Colitis by Upregulated Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Activity. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrello, J.; Monticone, S.; Gai, C.; Gomez, Y.; Kholia, S.; Camussi, G. Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Immune-Modulation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuda, T.; Kosaka, N.; Takeshita, F.; Ochiya, T. The therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Proteomics 2013, 13, 1637–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinney, D.G.; Pittenger, M.F. Concise Review: MSC-Derived Exosomes for Cell-Free Therapy. Stem Cells 2017, 35, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrie, A.; Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Théry, C. Exosome secretion: Molecular mechanisms and roles in immune responses. Traffic 2011, 12, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Shao, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Su, C.; Dong, L.; Yu, B.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, X. Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes on Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, Y.; Kadota, T.; Araya, J.; Ochiya, T.; Kuwano, K. Clinical Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicle-Based Therapeutics for Inflammatory Lung Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordelas, L.; Rebmann, V.; Ludwig, A.K.; Radtke, S.; Ruesing, J.; Doeppner, T.R.; Epple, M.; Horn, P.A.; Beelen, D.W.; Giebel, B. MSC-derived exosomes: A novel tool to treat therapy-refractory graft-versus-host disease. Leukemia 2014, 28, 970–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yan, Y.; Wang, B.; Qian, H.; Zhang, X.; Shen, L.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W.; Li, W.; et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate liver fibrosis. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Wu, Y.; Tang, X.; Kang, J.; Zhang, B.; Yan, Y.; Qian, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W. Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Relieve Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Mice. Biomed. Res. Int 2017, 2017, 5356760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liang, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhou, C.; Zheng, X.; Hu, T.; He, X.; Wu, X.; Lan, P. Exosomes from mesenchymal stromal cells reduce murine colonic inflammation via a macrophage-dependent mechanism. JCI Insight 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.Y.; Kang, H.J.; Hong, J.S.; Kim, C.J.; Shim, J.Y.; Lee, C.W.; Choi, J. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell extracts reduce colitis in mice by re-polarizing intestinal macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.H.; Li, Q.; Bhang, D.H.; Song, W.J.; Youn, H.Y. TNF-α and INF-γ primed canine stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles alleviate experimental murine colitis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grootjans, J.; Kaser, A.; Kaufman, R.J.; Blumberg, R.S. The unfolded protein response in immunity and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetz, C.; Chevet, E.; Harding, H.P. Targeting the unfolded protein response in disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 703–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakes, S.A.; Papa, F.R. The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in human pathology. Annu. Rev. Pathol 2015, 10, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell 2010, 140, 900–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savina, A.; Furlán, M.; Vidal, M.; Colombo, M.I. Exosome release is regulated by a calcium-dependent mechanism in K562 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 20083–20090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collett, G.P.; Redman, C.W.; Sargent, I.L.; Vatish, M. Endoplasmic reticulum stress stimulates the release of extracellular vesicles carrying danger-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) molecules. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 6707–6717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Ouyang, X.; Tang, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, B.; Ye, Y.; Jin, M.; Al Azab, M.; Li, W.; Li, X. ER-stressed MSC displayed more effective immunomodulation in RA CD4(+)CXCR5(+)ICOS(+) follicular helper-like T cells through higher PGE2 binding with EP2/EP4. Mod. Rheumatol. 2020, 30, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Lee, S.K.; Kwon, Y.W.; Chung, S.G.; Kim, S. Pioglitazone-Primed Mesenchymal Stem Cells Stimulate Cell Proliferation, Collagen Synthesis and Matrix Gene Expression in Tenocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phinney, D.G.; Di Giuseppe, M.; Njah, J.; Sala, E.; Shiva, S.; St Croix, C.M.; Stolz, D.B.; Watkins, S.C.; Di, Y.P.; Leikauf, G.D.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells use extracellular vesicles to outsource mitophagy and shuttle microRNAs. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witwer, K.W.; Théry, C. Extracellular vesicles or exosomes? On primacy, precision, and popularity influencing a choice of nomenclature. J. Extracell Vesicles 2019, 8, 1648167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Shin, T.H.; Lee, B.C.; Yu, K.R.; Seo, Y.; Lee, S.; Seo, M.S.; Hong, I.S.; Choi, S.W.; Seo, K.W.; et al. Human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells reduce colitis in mice by activating NOD2 signaling to COX2. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 1392–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, H.L.; Makki, F.A.; Moots, R.J.; Edwards, S.W. Low-density granulocytes: Functionally distinct, immature neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis with altered properties and defective TNF signalling. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 101, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, C.R.; Jovicic, N.; Djonov, V.; Volarevic, V. Therapeutic Use of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: From Basic Science to Clinics. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Dou, H.; Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, D.; Ji, J.; Liu, F.; Ding, L.; Ni, Y.; et al. Exosomal miR-146a Contributes to the Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy of Interleukin-1beta-Primed Mesenchymal Stem Cells Against Sepsis. Stem Cells 2017, 35, 1208–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michielan, A.; D’Incà, R. Intestinal Permeability in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Pathogenesis, Clinical Evaluation, and Therapy of Leaky Gut. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 628157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, A.; Arakaki, R.; Saito, M.; Tsunematsu, T.; Kudo, Y.; Ishimaru, N. Role of regulatory T cell in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 2195–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühl, A.A.; Erben, U.; Kredel, L.I.; Siegmund, B. Diversity of Intestinal Macrophages in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Introna, M.; Lucchini, G.; Dander, E.; Galimberti, S.; Rovelli, A.; Balduzzi, A.; Longoni, D.; Pavan, F.; Masciocchi, F.; Algarotti, A.; et al. Treatment of graft versus host disease with mesenchymal stromal cells: A phase I study on 40 adult and pediatric patients. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014, 20, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, C.R.; Sadikot, R.; Pascual, J.; Fellabaum, C.; Jankovic, M.G.; Jovicic, N.; Djonov, V.; Arsenijevic, N.; Volarevic, V. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Therapy of Inflammatory Lung Diseases: Current Understanding and Future Perspectives. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 4236973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.Y.; Kim, T.W.; Jeong, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; Ryu, J.S.; Wee, W.R.; Heo, J.W.; Kim, M.K. Intraperitoneal infusion of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells prevents experimental autoimmune uveitis in mice. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 624640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, A.; Takeuchi, S.; Watanabe, T.; Yoshida, T.; Nojiri, S.; Ogawa, M.; Terai, S. Mesenchymal stem cell therapies for liver cirrhosis: MSCs as “conducting cells” for improvement of liver fibrosis and regeneration. Inflamm. Regen. 2019, 39, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanelli, L.; Buratta, S.; Sagini, K.; Ferrara, G.; Lanni, M.; Emiliani, C. Exosome-based strategies for Diagnosis and Therapy. Recent Pat. CNS drug Discov. 2015, 10, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, C.R.; Jankovic, M.G.; Fellabaum, C.; Volarevic, A.; Djonov, V.; Arsenijevic, A.; Volarevic, V. Molecular Mechanisms Responsible for Anti-inflammatory and Immunosuppressive Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Factors. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1084, 187–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, C.R.; Fellabaum, C.; Jovicic, N.; Djonov, V.; Arsenijevic, N.; Volarevic, V. Molecular Mechanisms Responsible for Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Secretome. Cells 2019, 8, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, G.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, M.; Liu, Y. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a new therapeutic strategy for liver diseases. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, F.M.; Farwell, D.G.; Nolta, J.A.; Anderson, J.D. Preclinical translation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. Stem Cells 2020, 38, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hessvik, N.P.; Llorente, A. Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2018, 75, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.C.; Yu, K.R. Impact of mesenchymal stem cell senescence on inflammaging. BMB Rep. 2020, 53, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coquerelle, C.; Oldenhove, G.; Acolty, V.; Denoeud, J.; Vansanten, G.; Verdebout, J.M.; Mellor, A.; Bluestone, J.A.; Moser, M. Anti-CTLA-4 treatment induces IL-10-producing ICOS+ regulatory T cells displaying IDO-dependent anti-inflammatory properties in a mouse model of colitis. Gut 2009, 58, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, S.W.; Wang, J.; Lee, C.J.; Liu, M.; Neelamegham, S.; Canty, J.M.; Nguyen, J. The microRNA regulatory landscape of MSC-derived exosomes: A systems view. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, M.D.; Allen, J.M.; Pence, B.D.; Wallig, M.A.; Gaskins, H.R.; White, B.A.; Woods, J.A. Exercise and gut immune function: Evidence of alterations in colon immune cell homeostasis and microbiome characteristics with exercise training. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2016, 94, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiemessen, M.M.; Jagger, A.L.; Evans, H.G.; van Herwijnen, M.J.; John, S.; Taams, L.S. CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells induce alternative activation of human monocytes/macrophages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19446–19451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Sicco, C.; Reverberi, D.; Balbi, C.; Ulivi, V.; Principi, E.; Pascucci, L.; Becherini, P.; Bosco, M.C.; Varesio, L.; Franzin, C.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Mediators of Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Endorsement of Macrophage Polarization. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogino, H.; Nakamura, K.; Ihara, E.; Akiho, H.; Takayanagi, R. CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells suppress Th17-responses in an experimental colitis model. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Kwon, J.E.; Cho, M.L. Immunological pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Intest. Res. 2018, 16, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proto, J.D.; Doran, A.C.; Gusarova, G.; Yurdagul, A., Jr.; Sozen, E.; Subramanian, M.; Islam, M.N.; Rymond, C.C.; Du, J.; Hook, J.; et al. Regulatory T Cells Promote Macrophage Efferocytosis during Inflammation Resolution. Immunity 2018, 49, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Ma, H.; Qiu, L.; Li, L.; Cao, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhao, Y. Phenotypic and functional switch of macrophages induced by regulatory CD4+CD25+ T cells in mice. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2011, 89, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Joo, H.; Oh, M.-K.; Kang, J.Y.; Park, H.S.; Chae, D.-H.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.-H.; Yoo, H.M.; Choi, U.; Kim, D.-K.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles from Thapsigargin-Treated Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorated Experimental Colitis via Enhanced Immunomodulatory Properties. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9020209
Joo H, Oh M-K, Kang JY, Park HS, Chae D-H, Kim J, Lee J-H, Yoo HM, Choi U, Kim D-K, et al. Extracellular Vesicles from Thapsigargin-Treated Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorated Experimental Colitis via Enhanced Immunomodulatory Properties. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(2):209. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9020209
Chicago/Turabian StyleJoo, Hansol, Mi-Kyung Oh, Ji Yeon Kang, Hyun Sung Park, Dong-Hoon Chae, Jieun Kim, Jong-Hee Lee, Hee Min Yoo, Uimook Choi, Do-Kyun Kim, and et al. 2021. "Extracellular Vesicles from Thapsigargin-Treated Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorated Experimental Colitis via Enhanced Immunomodulatory Properties" Biomedicines 9, no. 2: 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9020209
APA StyleJoo, H., Oh, M.-K., Kang, J. Y., Park, H. S., Chae, D.-H., Kim, J., Lee, J.-H., Yoo, H. M., Choi, U., Kim, D.-K., Lee, H., Kim, S., & Yu, K.-R. (2021). Extracellular Vesicles from Thapsigargin-Treated Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorated Experimental Colitis via Enhanced Immunomodulatory Properties. Biomedicines, 9(2), 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9020209






