Oxytocin Attenuates the Stress-Induced Reinstatement of Alcohol-Seeking in Male Rats: Role of the Central Amygdala
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Drugs
2.4. Surgery
2.5. Procedure
2.5.1. Ethanol Habituation
2.5.2. Ethanol Self-Administration
2.5.3. Experiment 1
2.5.4. Experiment 2
2.6. Tissue Collection and Histological Analysis
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
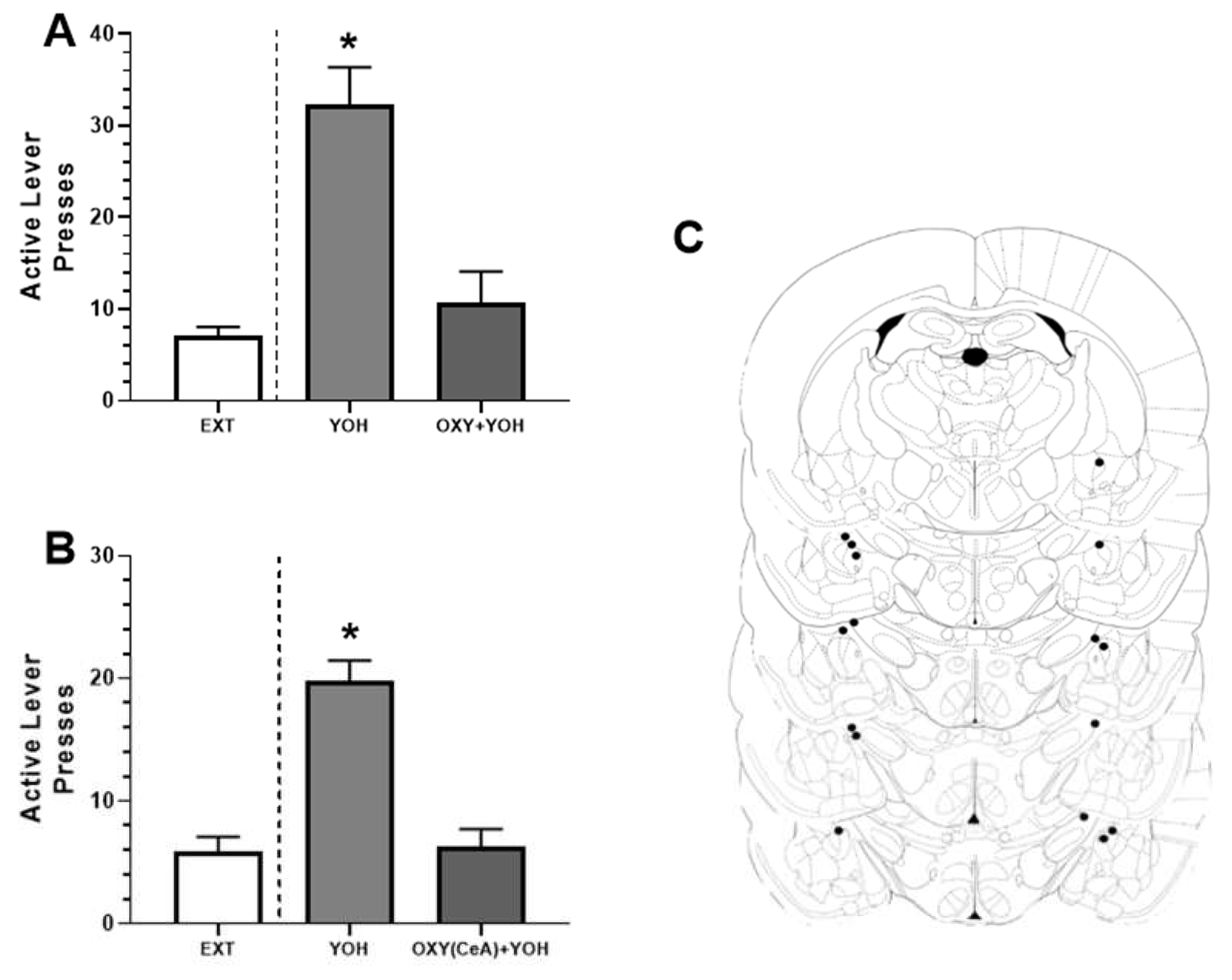
3.1. Experiment 1: Systemic OXT Attenuated Yohimbine-Induced Alcohol-Seeking Behavior
3.2. Experiment 2: Intra-CeA OXT Attenuated Yohimbine-Induced Alcohol-Seeking Behavior
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grant, B.F.; Goldstein, R.B.; Saha, T.D.; Chou, S.P.; Jung, J.; Zhang, H.; Pickering, R.P.; Ruan, W.J.; Smith, S.M.; Huang, B.; et al. Epidemiology of DSM-5 alcohol use disorder: Results from the national epidemiologic survey on alcohol and related conditions III. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brady, K.T.; Sonne, S.C. The role of stress in alcohol use, alcoholism treatment, and relapse. Alcohol Res. Health 1999, 23, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, D.C.; Zuardi, A.W.; Graeff, F.G.; Queiroz, R.H.; Crippa, J.A. Anxiolytic-like effect of oxytocin in the simulated public speaking test. J. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 26, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lancaster, K.; Goldbeck, L.; Pournajafi-Nazarloo, H.; Connelly, J.J.; Carter, S.C.; Morris, J.P. The role of endogenous oxytocin in anxiolysis: Structural and functional correlates. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2018, 3, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M.; Takayanagi, Y.; Inoue, K.; Kimura, T.; Young, L.J.; Onaka, T.; Nishimori, K. Evidence that oxytocin exerts anxiolytic effects via oxytocin receptor expressed in serotonergic neurons in mice. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 2259–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guastella, A.J.; Howard, A.L.; Dadds, M.R.; Mitchell, P.; Carson, D.S. A randomized controlled trial of intranasal oxytocin as an adjunct to exposure therapy for social anxiety disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Kim, Y.K. The Role of the Oxytocin System in Anxiety Disorders. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1191, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vinogradova, E.P.; Zhukov, D.A. The effects of intranasal administration of oxytocin on the behavior of rats with different behavioral strategies subjected to chronic mild stress. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 2018, 48, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, L.W.; Missig, G.; Schulkin, J.; Rosen, J.B. Oxytocin reduces background anxiety in a fear-potentiated startle paradigm: Peripheral vs central administration. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 2488–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windle, R.J.; Shanks, N.; Lightman, S.L.; Ingram, C.D. Central oxytocin administration reduces stress-induced corticosterone release and anxiety behavior in rats. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 2829–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ring, R.H.; Malberg, J.E.; Potestio, L.; Ping, J.; Boikess, S.; Luo, B.; Schechter, L.E.; Rizzo, S.; Rahman, Z.; Rosenzweig-Lipson, S. Anxiolytic-like activity of oxytocin in male mice: Behavioral and autonomic evidence, therapeutic implications. Psychopharmacology 2006, 185, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferland, C.L.; Reichel, C.M.; McGinty, J.F. Effects of oxytocin on methamphetamine-seeking exacerbated by predator odor pre-exposure in rats. Psychopharmacology 2016, 233, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.Y.; Du, P.; Fu, S.Y.; Wang, F.; Song, M.; Wu, C.F.; Yang, J.Y. Oxytocin via its receptor affects restraint stress-induced methamphetamine CPP reinstatement in mice: Involvement of the medial prefrontal cortex and dorsal hippocampus glutamatergic system. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2014, 119, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Nakajima, M.; Ibañez-Tallon, I.; Heintz, N. A cortical circuit for sexually dimorphic oxytocin-dependent anxiety behaviors. Cell 2016, 167, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, B.; Boyle, C.A.; Lei, S. Oxytocin receptors excite lateral nucleus of central amygdala by phospholipase Cβ- and protein kinase C-dependent depression of inwardly rectifying K+ channels. J. Physiol. 2020, 598, 3501–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viviani, D.; Charlet, A.; van den Burg, E.; Robinet, C.; Hurni, N.; Abatis, M.; Magara, F.; Stoop, R. Oxytocin selectively gates fear responses through distinct outputs from the central amygdala. Science 2011, 333, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knobloch, H.S.; Charlet, A.; Hoffmann, L.C.; Eliava, M.; Khrulev, S.; Cetin, A.H.; Osten, P.; Schwarz, M.K.; Seeburg, P.H.; Stoop, R.; et al. Evoked axonal oxytocin release in the central amygdala attenuates fear response. Neuron 2012, 73, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leri, F.; Flores, J.; Rodaros, D.; Stewart, J. Blockade of stress-induced but not cocaine-induced reinstatement by infusion of noradrenergic antagonists into the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis or the central nucleus of the amygdala. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 5713–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeichel, B.E.; Herman, M.A.; Roberto, M.; Koob, G.F. Hypocretin neurotransmission within the central amygdala mediates escalated cocaine self-administration and stress-induced reinstatement in rats. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 81, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simms, J.; Haass-Koffler, C.; Bito-Onon, J. Mifepristone in the central nucleus of the amygdala reduces yohimbine stress-induced reinstatement of ethanol-seeking. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 906–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, H.; Bruijnzeel, A.W. Stimulation of α2-adrenergic receptors in the central nucleus of the amygdala attenuates stress-induced reinstatement of nicotine seeking in rats. Neuropharmacology 2011, 60, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Wit, H.; Stewart, J. Reinstatement of cocaine-reinforced responding in the rat. Psychopharmacology 1981, 75, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaham, Y.; Shalev, U.; Lu, L.; de Wit, H.; Stewart, J. The reinstatement model of drug relapse: History, methodology and major findings. Psychopharmacology 2003, 168, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilpin, N.W.; Misra, K.; Koob, G.F. Neuropeptide Y in the central nucleus of the amygdala suppresses dependence-induced increases in alcohol drinking. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2008, 90, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leong, K.C.; Zhou, L.; Ghee, S.M.; See, R.E.; Reichel, C.M. Oxytocin decreases cocaine taking, cocaine seeking, and locomotor activity in female rats. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2016, 24, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernheim, A.; Leong, K.C.; Berini, C.; Reichel, C.M. Antagonism of mGlu2/3 receptors in the nucleus accumbens prevents oxytocin from reducing cued methamphetamine seeking in male and female rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2017, 161, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichel, C.M.; Chan, C.H.; Ghee, S.M.; See, R.E. Sex differences in escalation of methamphetamine self-administration: Cognitive and motivational consequences in rats. Psychopharmacology 2012, 223, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cox, B.M.; Young, A.B.; See, R.E.; Reichel, C.M. Sex differences in methamphetamine seeking in rats: Impact of oxytocin. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013, 10, 2343–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leong, K.C.; Freeman, L.R.; Berini, C.R.; Ghee, S.M.; See, R.E.; Reichel, C.M. Oxytocin reduces cocaine cued fos activation in a regionally specific manner. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 20, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain, in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 7th ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Baracz, S.J.; Everett, N.A.; McGregor, I.S.; Cornish, J.L. Oxytocin in the nucleus accumbens core reduces reinstatement of methamphetamine-seeking behaviour in rats. Addict. Biol. 2016, 21, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, B.M.; Bentzley, B.S.; Regen-Tuero, H.; See, R.E.; Reichel, C.M.; Aston-Jones, G. Oxytocin acts in nucleus accumbens to attenuate methamphetamine seeking and demand. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 11, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, K.C.; Cox, S.; King, C.; Becker, H.; Reichel, C.M. Oxytocin and rodent models of addiction. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2018, 140, 201–247. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.; Sundar, M.; Lorenz, E.; Leong, K.C. Oxytocin attenuates expression, but not acquisition, of sucrose conditioned place preference in rats. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 603232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baracz, S.J.; Rourke, P.I.; Pardey, M.C.; Hunt, G.E.; McGregor, I.S.; Cornish, J.L. Oxytocin directly administered into the nucleus accumbens core or subthalamic nucleus attenuates methamphetamine-induced conditioned place preference. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 228, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Che, X.; Xu, T.; Luo, Y.; Yin, M.; Lu, X.; Wu, C.; Yang, J. Repeated oxytocin treatment during abstinence inhibited context-or restraint stress-induced reinstatement of methamphetamine-conditioned place preference and promoted adult hippocampal neurogenesis in mice. Exp. Neurol. 2021, 347, 113907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.E.; Becker, H.C. Oxytocin attenuates stress-induced reinstatement of alcohol seeking behavior in male and female mice. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 2613–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, L.; Agostini, A.; Schulkin, J.; Rosen, J.B. Effects of oxytocin on background anxiety in rats with high or low baseline startle. Psychopharmacology 2016, 233, 2165–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, I.D.; Wigger, A.; Torner, L.; Holsboer, F.; Landgraf, R. Brain oxytocin inhibits basal and stress-induced activity of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis in male and female rats: Partial action within the paraventricular nucleus. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2000, 12, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bale, T.L.; Davis, A.M.; Auger, A.P.; Dorsa, D.M.; McCarthy, M.M. CNS region-specific oxytocin receptor expression: Importance in regulation of anxiety and sex behavior. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 2546–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimpl, G.; Fahrenholz, F. The oxytocin receptor system: Structure, function, and regulation. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 629–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haubensak, W.; Kunwar, P.S.; Cai, H.; Ciocchi, S.; Wall, N.R.; Ponnusamy, R.; Biag, J.; Dong, H.W.; Deisseroth, K.; Callaway, E.M.; et al. Genetic dissection of an amygdala microcircuit that gates conditioned fear. Nature 2010, 468, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gozzi, A.; Jain, A.; Giovanelli, A.; Bertollini, C.; Crestan, V.; Schwarz, A.J.; Tsetsenis, T.; Ragozzino, D.; Gross, C.T.; Bifone, A. A neural switch for active and passive fear. Neuron 2010, 67, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rickenbacher, E.; Perry, R.E.; Sullivan, R.M.; Moita, M.A. Freezing suppression by oxytocin in central amygdala allows alternate defensive behaviours and mother-pup interactions. Elife 2017, 6, 24080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, K.; Bosch, O.J.; Krömer, S.A.; Singewald, N.; Neumann, I.D. Release of oxytocin in the rat central amygdala modulates stress-coping behavior and the release of excitatory amino acids. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005, 30, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carson, D.S.; Hunt, G.E.; Guastella, A.J.; Barber, L.; Cornish, J.L.; Arnold, J.C.; Boucher, A.A.; McGregor, I.S. Systemically administered oxytocin decreases methamphetamine activation of the subthalamic nucleus and accumbens core and stimulates oxytocinergic neurons in the hypothalamus. Addict. Biol. 2010, 15, 448–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, I.D.; Maloumby, R.; Beiderbeck, D.I.; Lukas, M.; Landgraf, R. Increased brain and plasma oxytocin after nasal and peripheral administration in rats and mice. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013, 38, 1985–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, S.M.; Samineni, S.; Allen, P.C.; Stockinger, D.; Bales, K.L.; Hwa, G.G.; Roberts, J.A. Plasma and CSF oxytocin levels after intranasal and intravenous oxytocin in awake macaques. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2016, 66, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoop, R.; Hegoburu, C.; van den Burg, E. New opportunities in vasopressin and oxytocin research: A perspective from the amygdala. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 38, 369–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, D.; Veinante, P.; Stoop, R. Vasopressin and oxytocin excite distinct neuronal populations in the central amygdala. Science 2005, 308, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Ethanol Consumption (g/kg) | Experiment 1 | Experiment 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | |
| Day 1 | 2.85 | 1.67 | 4.73 | 1.49 |
| Day 2 | 4.17 | 1.87 | 5.70 | 1.96 |
| Day 3 | 3.79 | 1.88 | 5.71 | 2.11 |
| Day 4 | 5.32 | 1.45 | 5.13 | 0.84 |
| Day 5 | 6.00 | 2.10 | 6.09 | 0.94 |
| Day 6 | 6.02 | 2.20 | 6.31 | 1.05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ballas, H.S.; Wilfur, S.M.; Freker, N.A.; Leong, K.-C. Oxytocin Attenuates the Stress-Induced Reinstatement of Alcohol-Seeking in Male Rats: Role of the Central Amygdala. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121919
Ballas HS, Wilfur SM, Freker NA, Leong K-C. Oxytocin Attenuates the Stress-Induced Reinstatement of Alcohol-Seeking in Male Rats: Role of the Central Amygdala. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(12):1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121919
Chicago/Turabian StyleBallas, Hannah S., Samantha M. Wilfur, Nicole A. Freker, and Kah-Chung Leong. 2021. "Oxytocin Attenuates the Stress-Induced Reinstatement of Alcohol-Seeking in Male Rats: Role of the Central Amygdala" Biomedicines 9, no. 12: 1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121919
APA StyleBallas, H. S., Wilfur, S. M., Freker, N. A., & Leong, K.-C. (2021). Oxytocin Attenuates the Stress-Induced Reinstatement of Alcohol-Seeking in Male Rats: Role of the Central Amygdala. Biomedicines, 9(12), 1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121919





