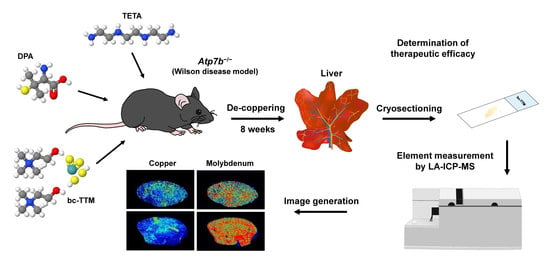
Analyzing the Therapeutic Efficacy of Bis-Choline-Tetrathiomolybdate in the Atp7b−/− Copper Overload Mouse Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Compounds
2.2. Animals
2.3. Animal Treatment
2.4. Sample Preparation for LA-ICP-MS Measurements
2.5. LA-ICP-MS Set Up and Measurements
2.6. ICP-MS Measurements
2.7. Image Generation of Bio-Metal Distribution
2.8. Electron Microscopic Analysis
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
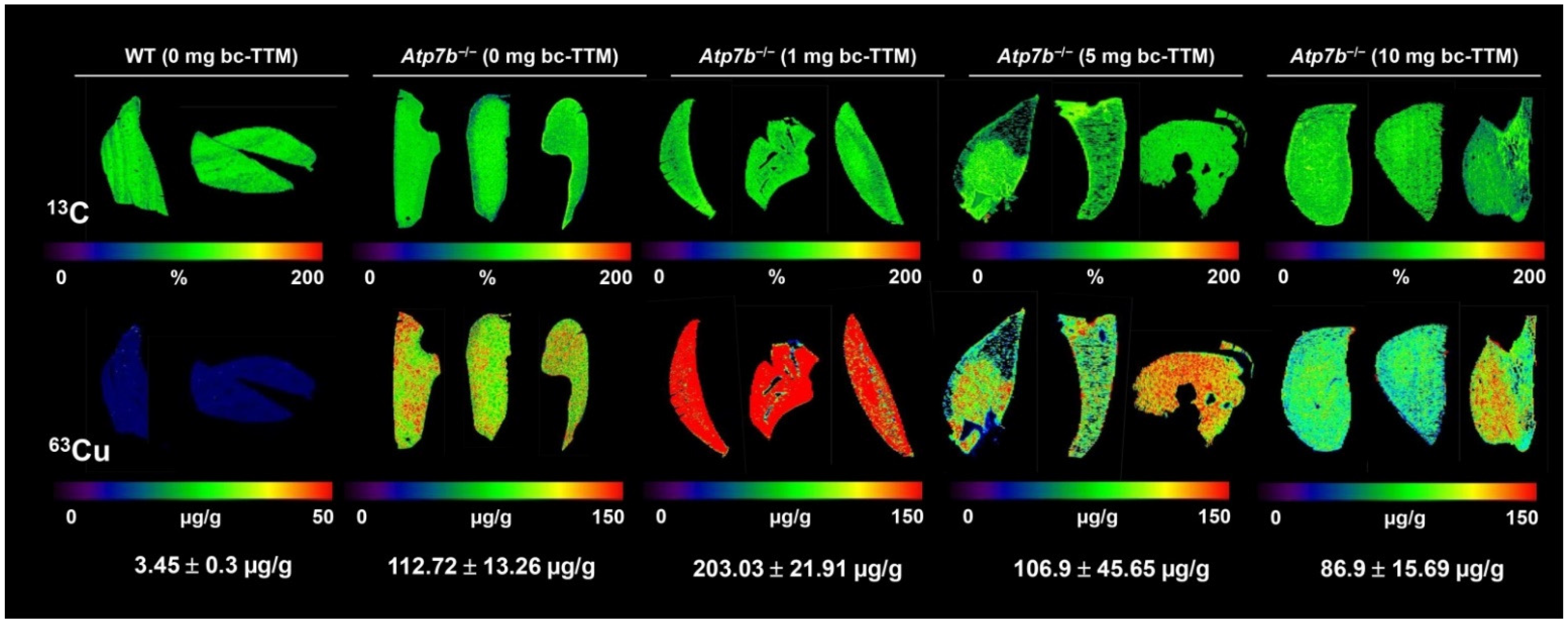
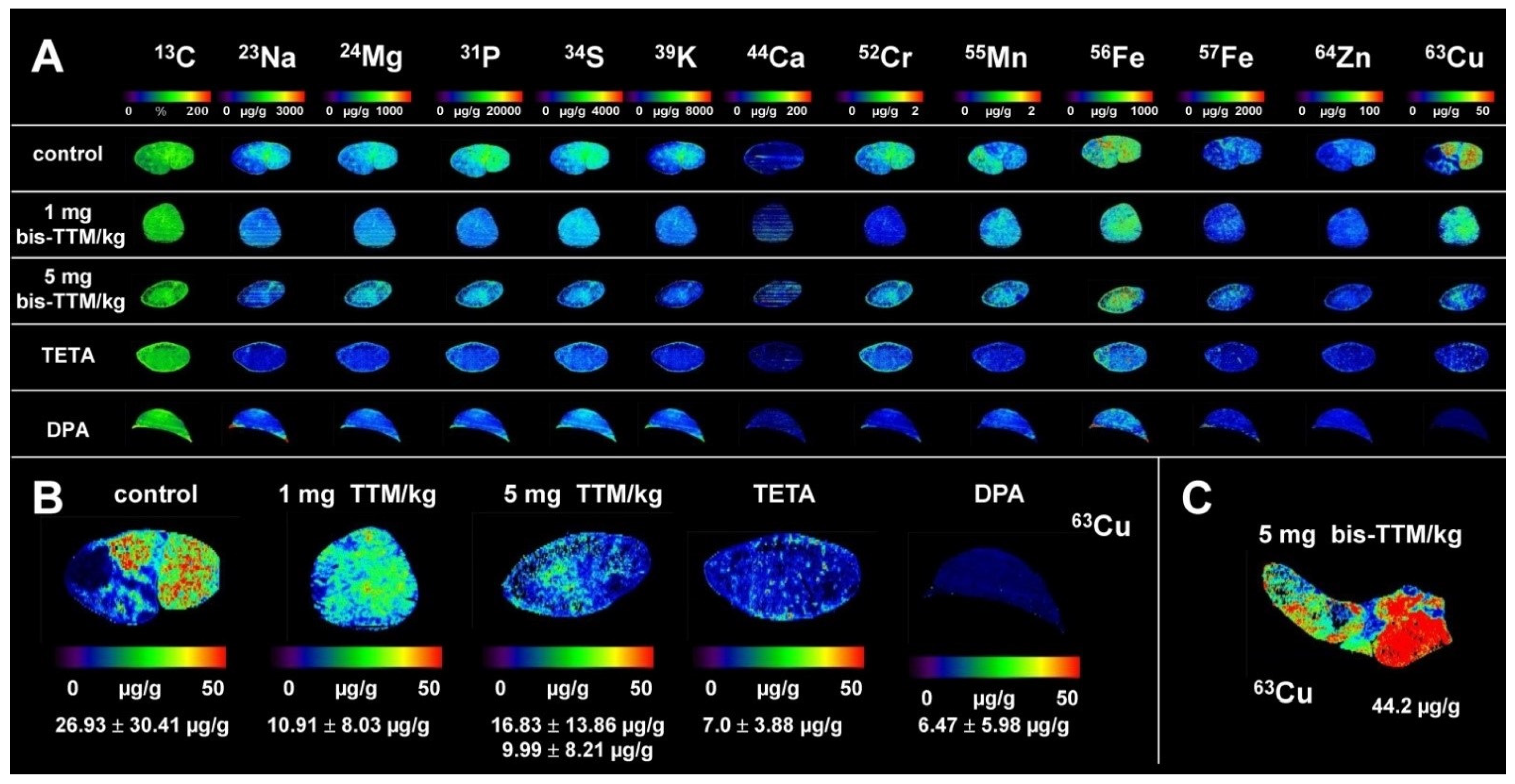
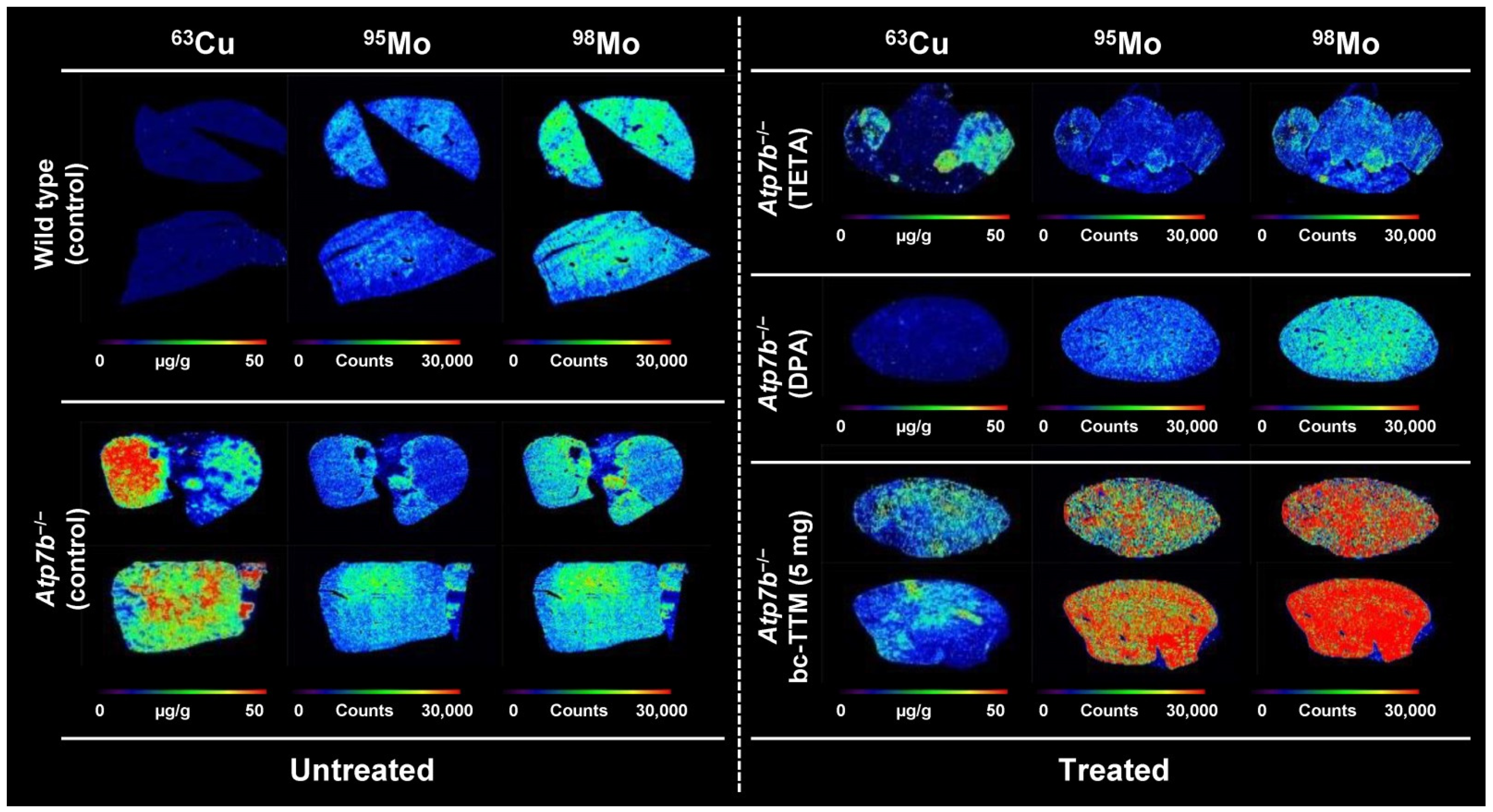
3.1. Hepatic Copper Accumulation in the Atp7b−/− Mice Model as Demonstrated by Laser Ablation Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry
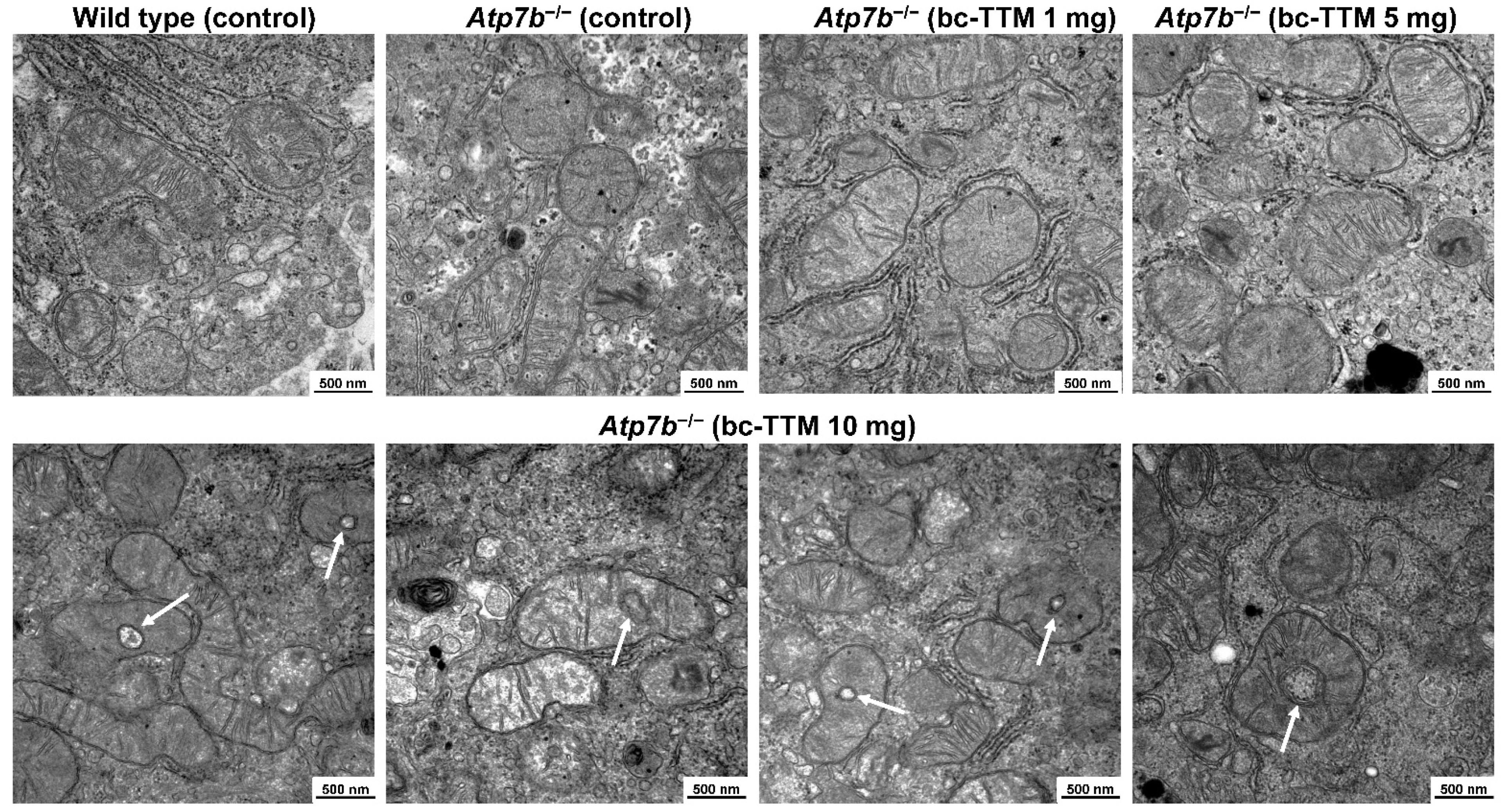
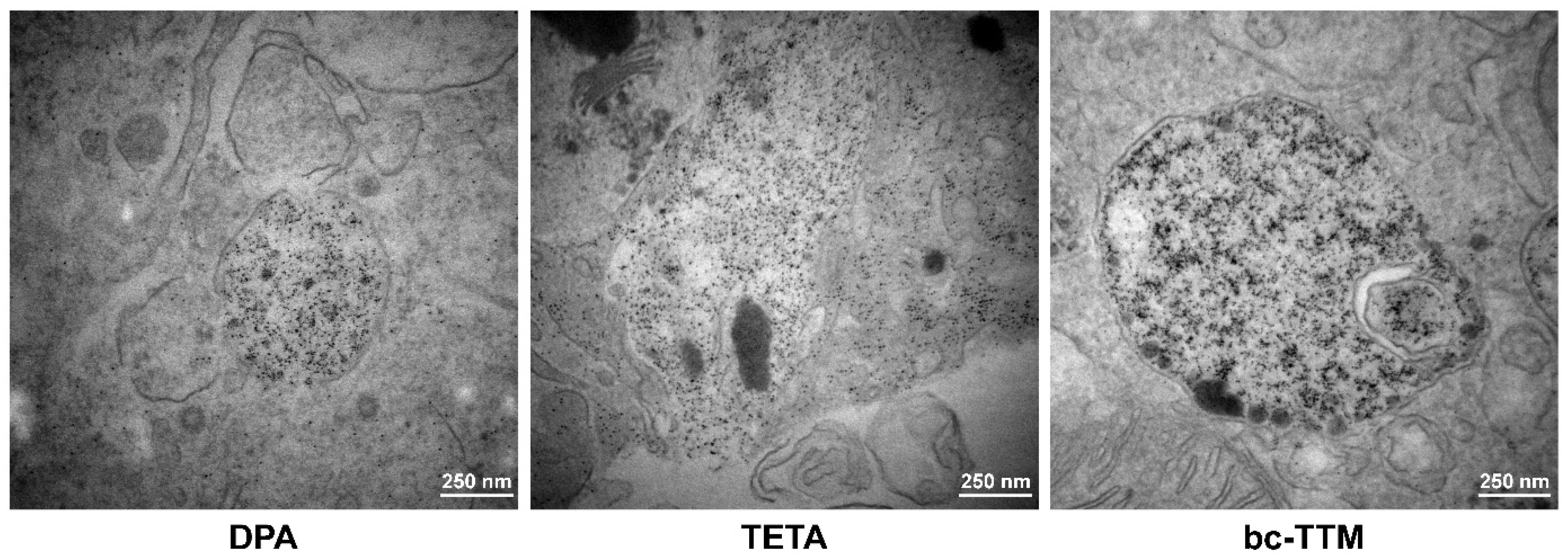
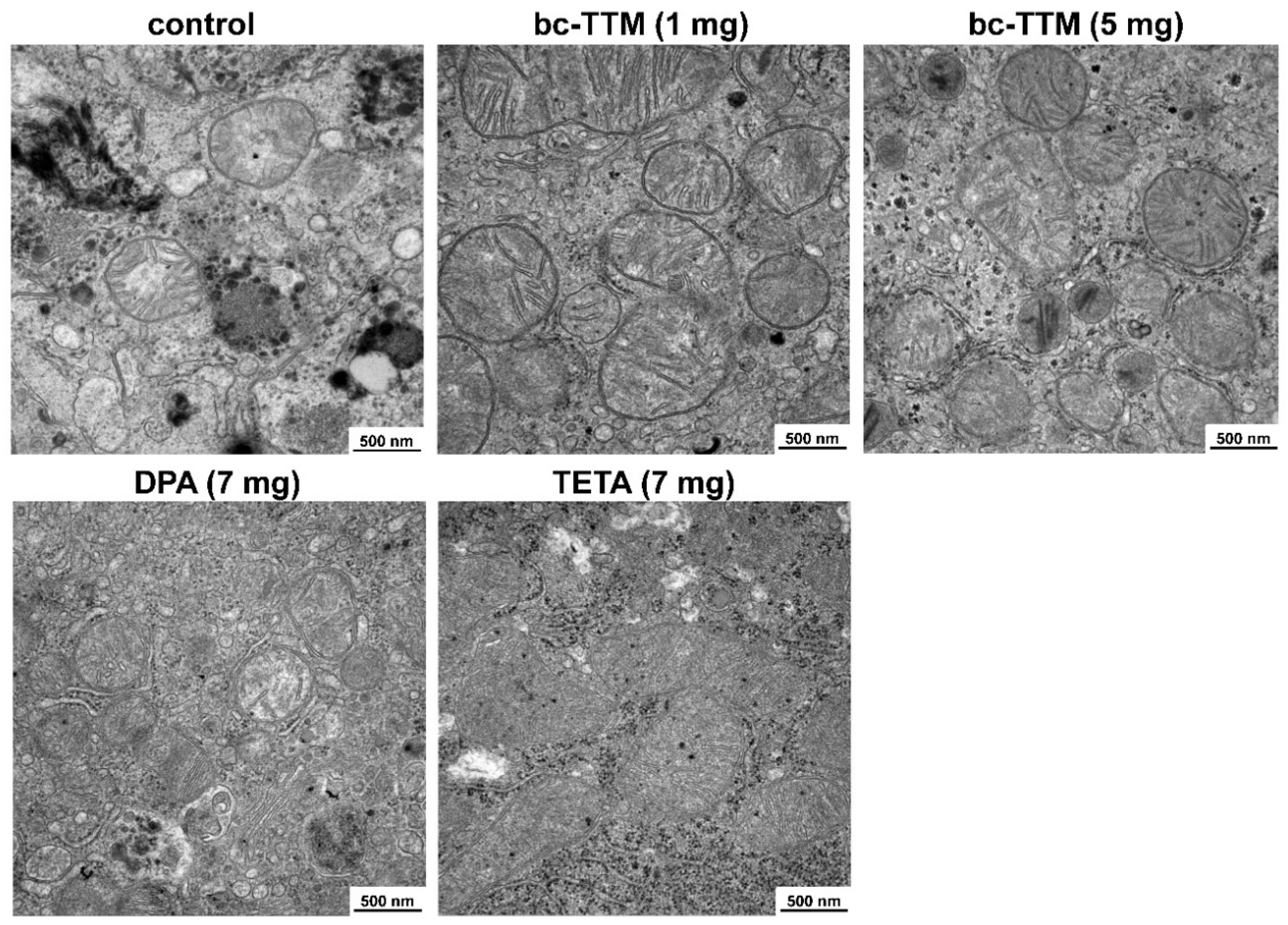
3.2. Occurrence of Granular Electron-Dense Particles in Livers of Atp7b−/− Mice Model as Demonstrated by Transmission Electron Microscopy
3.3. Therapeutic Efficacy of Different Dosages of Bis-Choline-Tetrathiomolybdate
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weiss, K.H.; Askari, F.K.; Czlonkowska, A.; Ferenci, P.; Bronstein, J.M.; Bega, D.; Ala, A.; Nicholl, D.; Flint, S.; Olsson, L.; et al. Bis-choline tetrathiomolybdate in patients with Wilson’s disease: An open-label, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, Y.; Sadakata, I.; Ogra, Y.; Suzuki, K.T. Excretion of copper complexed with thiomolybdate into the bile and blood in LEC rats. Chem. Interact. 2000, 124, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, G.J. The use of copper-lowering therapy with tetrathiomolybdate in medicine. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2008, 18, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G.N. Wilson Disease. In Rosenberg’s Molecular and Genetic Basis of Neurological and Psychiatric Disease, 5th ed.; Rosenberg, R.N., Pascual, J.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 443–453. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, K.T.; Yamamoto, K.; Kanno, S.; Aoki, Y.; Takeichi, N. Selective removal of copper bound to metallothionein in the liver of LEC rats by tetrathiomolybdate. Toxicology 1993, 83, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, N.; Lai, Y.R.; Sugawara, C. Therapeutic effects of tetrathiomolybdate on hepatic dysfunction occurring naturally in Long-Evans Cinnamon (LEC) rats: A bona fide animal model for Wilson’s disease. Res. Commun. Mol. Pathol. Pharmacol. 1999, 103, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ogra, Y.; Suzuki, K.T. Removal and efflux of copper from Cu-metallothionein as Cu/tetrathiomolybdate complex in LEC rats. Res. Commun. Mol. Pathol. Pharmacol. 1995, 88, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Allen, J. Effect of molybdenum treatments on the distribution of cu and metallothionein in tissue extracts from rats and sheep. J. Inorg. Biochem. 1987, 31, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.T.; Yamamoto, K.; Ogra, Y.; Kanno, S.; Aoki, Y. Mechanisms for removal of copper from metallothionein by tetrathiomolybdate. J. Inorg. Biochem. 1994, 54, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogra, Y.; Ohmichi, M.; Suzuki, K. Systemic Dispositions of Molybdenum and Copper after Tetrathiomolybdate Injection in LEC Rats. J. Trace Elements Med. Biol. 1995, 9, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogra, Y.; Ohmichi, M.; Suzuki, K.T. Mechanisms of selective copper removal by tetrathiomolybdate from metallothionein in LEC rats. Toxicology 1996, 106, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogra, Y.; Suzuki, K.T. Targeting of tetrathiomolybdate on the copper accumulating in the liver of LEC rats. J. Inorg. Biochem. 1998, 70, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogra, Y.; Chikusa, H.; Suzuki, K.T. Metabolic fate of the insoluble copper/tetrathiomolybdate complex formed in the liver of LEC rats with excess tetrathiomolybdate. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2000, 78, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, G.N.; Pickering, I.J.; Harris, H.H.; Gailer, J.; Klein, D.; Lichtmannegger, J.; Summer, K.-H. Tetrathiomolybdate Causes Formation of Hepatic Copper−Molybdenum Clusters in an Animal Model of Wilson’s Disease. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 1704–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, D.; Arora, U.; Lichtmannegger, J.; Finckh, M.; Heinzmann, U.; Summer, K.H. Tetrathiomolybdate in the treatment of acute hepatitis in an animal model for Wilson disease. J. Hepatol. 2004, 40, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogra, Y.; Miyayama, T.; Anan, Y. Effect of glutathione depletion on removal of copper from LEC rat livers by tetrathiomolybdate. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2010, 104, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowndes, S.A.; Adams, A.; Timms, A.; Fisher, N.; Smythe, J.; Watt, S.M.; Joel, S.; Donate, F.; Hayward, C.; Reich, S.; et al. Phase I Study of Copper-Binding Agent ATN-224 in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 7526–7534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bandmann, O.; Weiss, K.H.; Kaler, S.G. Wilson’s disease and other neurological copper disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plitz, T.; Boyling, L. Metabolic disposition of WTX101 (bis-choline tetrathiomolybdate) in a rat model of Wilson disease. Xenobiotica 2018, 49, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buiakova, O.I.; Xu, J.; Lutsenko, S.; Zeitlin, S.; Das, K.; Das, S.; Ross, B.M.; Mekios, C.; Scheinberg, I.H.; Gilliam, T.C. Null Mutation of the Murine ATP7B (Wilson Disease) Gene Results in Intracellular Copper Accumulation and Late-Onset Hepatic Nodular Transformation. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1999, 8, 1665–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uerlings, R.; Moreno, D.; Murillo, O.; Gazquez, C.; Hernández-Alcoceba, R.; González-Aseguinolaza, G.; Weiskirchen, R. Brain copper storage after genetic long-term correction in a mouse model of Wilson disease. Neurol. Genet. 2018, 4, e243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno, D.; Murillo, O.; Gazquez, C.; Hernandez-Alcoceba, R.; Uerlings, R.; Gonzalez-Aseguinolaza, G.; Weiskirchen, R. Visualization of the therapeutic efficacy of a gene correction approach in Wilson’s disease by laser-ablation inductively coupled mass spectrometry. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sauer, S.W.; Merle, U.; Opp, S.; Haas, D.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Stremmel, W.; Okun, J.G. Severe dysfunction of respiratory chain and cholesterol metabolism in Atp7b−/− mice as a model for Wilson disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2011, 1812, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Russell, W.M.S.; Burch, R. The Principles of Humane Experimental Technique; Methuen: London, UK, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Liedtke, C.; Luedde, T.; Sauerbruch, T.; Scholten, D.; Streetz, K.; Tacke, F.; Tolba, R.; Trautwein, C.; Trebicka, J.; Weiskirchen, R. Experimental liver fibrosis research: Update on animal models, legal issues and translational aspects. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 2013, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boaru, S.G.; Merle, U.; Uerlings, R.; Zimmermann, A.; Flechtenmacher, C.; Willheim, C.; Eder, E.; Ferenci, P.; Stremmel, W.; Weiskirchen, R. Laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry imaging of metals in experimental and clinical Wilson’s disease. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merle, U.; Tuma, S.; Herrmann, T.; Muntean, V.; Volkmann, M.; Gehrke, S.G.; Stremmel, W. Evidence for a critical role of ceruloplasmin oxidase activity in iron metabolism of Wilson disease gene knockout mice. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 25, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiskirchen, S.; Kim, P.; Weiskirchen, R. Determination of copper poisoning in Wilson’s disease using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uerlings, R.; Matusch, A.; Weiskirchen, R. Reconstruction of laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) spatial distribution images in Microsoft Excel 2007. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 395, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiskirchen, R.; Weiskirchen, S.; Kim, P.; Winkler, R. Software solutions for evaluation and visualization of laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry imaging (LA-ICP-MSI) data: A short overview. J. Chemin 2019, 11, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.; Zhang, C.; Thoröe-Boveleth, S.; Weiskirchen, S.; Gaisa, N.; Buhl, E.; Stremmel, W.; Merle, U.; Weiskirchen, R. Accurate Measurement of Copper Overload in an Experimental Model of Wilson Disease by Laser Ablation Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Kingdom. One Way ANOVA Calculator. Analysis of Variance, Tukey HSD Test. Available online: https://www.statskingdom.com/180Anova1way.html (accessed on 2 November 2021).
- Boaru, S.G.; Merle, U.; Uerlings, R.; Zimmermann, A.; Weiskirchen, S.; Matusch, A.; Stremmel, W.; Weiskirchen, R. Simultaneous monitoring of cerebral metal accumulation in an experimental model of Wilson’s disease by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. BMC Neurosci. 2014, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.C.; Volkmann, M.; Tuma, S.; Stremmel, W.; Merle, U. Metallothionein is elevated in liver and duodenum of Atp7b(−/−) mice. BioMetals 2018, 31, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamilton, J.P.; Koganti, L.; Muchenditsi, A.; Pendyala, V.S.; Huso, D.; Hankin, J.; Murphy, R.C.; Huster, D.; Merle, U.; Mangels, C.; et al. Activation of liver X receptor/retinoid X receptor pathway ameliorates liver disease in Atp7B−/− (Wilson disease) mice. Hepatology 2015, 63, 1828–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uerlings, R.; Weiskirchen, R. An At-A-Glance Visualization of Regional Metal Accretion in Tissue Samples by Image Overlay in Laser Ablation Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. In Laser Ablation: Advances in Research and Applications in Approaching; Bellucci, C., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 87–113. [Google Scholar]
- Fanni, D.; Fanos, V.; Gerosa, C.; Piras, M.; Dessì, A.; Atzei, A.; Van, E.P.; Gibo, Y.; Faa, G. Effects of Iron and Copper Overload on the Human Liver: An Ultrastructural Study. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 3768–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iancu, T.C.; Manov, I. Electron Microscopy of Liver Biopsies. In Liver Biopsy; Takahashi, H., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iancu, T.C.; Manov, I.; Shaoul, R.; Haimi, M.; Lerner, A. What’s in a Name?—“Lipolysosome”: Ultrastructural Features of a Lipid-containing Organelle. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2013, 37, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, G.J. Description of the Anticopper Drugs Which Are Used in Wilson’s Disease Therapy. In Wilson’s Disease: A Clinician’s Guide to Recognition, Diagnosis, and Management; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 49–68. ISBN 978-1-4615-1645-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, G.J.; Askari, F.; Dick, R.B.; Sitterly, J.; Fink, J.K.; Carlson, M.; Kluin, K.J.; Lorincz, M.T. Treatment of Wilson’s disease with tetrathiomolybdate: V. control of free copper by tetrathiomolybdate and a comparison with trientine. Transl. Res. 2009, 154, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medici, V.; Sturniolo, G.C. Tetrathiomolybdate, a copper chelator for the treatment of Wilson disease, pulmonary fibrosis and other indications. IDrugs Investig. Drugs J. 2008, 11, 592–606. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer, R.F. Wilson’s disease. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2011, 100, 681–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.-B.; Feng, L.; Lin, X.-P.; Zhang, W.; Li, F.-R.; Liang, X.-L.; Li, X.-H. Penicillamine Increases Free Copper and Enhances Oxidative Stress in the Brain of Toxic Milk Mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zischka, H.; Lichtmannegger, J.; Schmitt, S.; Jägemann, N.; Schulz, S.; Wartini, D.; Jennen, L.; Rust, C.; Larochette, N.; Galluzzi, L.; et al. Liver mitochondrial membrane crosslinking and destruction in a rat model of Wilson disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1508–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smirnova, J.; Kabin, E.; Järving, I.; Bragina, O.; Tõugu, V.; Plitz, T.; Palumaa, P. Copper(I)-binding properties of de-coppering drugs for the treatment of Wilson disease. α-Lipoic acid as a potential anti-copper agent. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhardsson, L.; Kazantzis, G. Diagnosis and Treatment of Metal Poisoning: General Aspects. In Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 487–505. [Google Scholar]
- Członkowska, A.; Litwin, T.; Chabik, G. Wilson disease: Neurologic features. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2017, 142, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camarata, M.; Ala, A.; Schilsky, M. Update on Wilson disease: Focus on WTX-101. Drugs Futur. 2018, 43, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, G.J.; Dick, R.D.; Yuzbasiyan-Gurkin, V.; Tankanow, R.; Young, A.B.; Kluin, K.J. Initial Therapy of Patients with Wilson’s Disease with Tetrathiomolybdate. Arch. Neurol. 1991, 48, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewer, G.J.; Johnson, V.; Dick, R.D.; Kluin, K.J.; Fink, J.K.; Brunberg, J.A. Treatment of Wilson Disease with Ammonium Tetrathiomolybdate. II. Initial therapy in 33 neurologically affected patients and follow-up with zinc therapy. Arch. Neurol. 1996, 53, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haywood, S.; Dincer, Z.; Holding, J.; Parry, N.M. Metal (molybdenum, copper) accumulation and retention in brain, pituitary and other organs of ammonium tetrathiomolybdate-treated sheep. Br. J. Nutr. 1998, 79, 329–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haywood, S.; Dincer, Z.; Jasani, B.; Loughran, M. Molybdenum-associated Pituitary Endocrinopathy in Sheep Treated with Ammonium Tetrathiomolybdate. J. Comp. Pathol. 2004, 130, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fabregues, O.; Viñas, J.; Palasí, A.; Quintana, M.; Cardona, I.; Auger, C.; Vargas, V. Ammonium tetrathiomolybdate in the decoppering phase treatment of Wilson’s disease with neurological symptoms: A case series. Brain Behav. 2020, 10, e01596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barceloux, D.G. Molybdenum. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeannin, Y.; Sécheresse, F.; Bernès, S.; Robert, F. Molecular architecture of copper (I) thiometallate complexes. Example of a cubane with an extra face, (NPr4)3[MS4Cu4Cl5] M = Mo, W. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1992, 198, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, H.M.; Xue, Y.; Robinson, C.D.; Canalizo-Hernández, M.A.; Marvin, R.G.; Kelly, R.A.; Mondragón, A.; Penner-Hahn, J.E.; O’Halloran, T.V. Tetrathiomolybdate Inhibits Copper Trafficking Proteins Through Metal Cluster Formation. Science 2010, 327, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clayton, G.D.; Clayton, F.E. Patty’s Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology, 3rd ed.; John Wiley Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, C.F.; Davis, G.K. Molybdenum. In Trace Elements in Human and Animal Nutrition, 5th ed.; Mertz, W., Ed.; Academic Press Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 1987; Volume 1, pp. 429–463. ISBN 9780124912519. [Google Scholar]
- Parry, N.M.A.; Phillippo, M.; Reid, M.D.; McGaw, B.A.; Flint, D.J.; Loveridge, N. Molybdenum-induced changes in the epiphyseal growth plate. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1993, 53, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyubimov, A.V.; Smith, J.A.; Rousselle, S.D.; Mercieca, M.D.; Tomaszewski, J.E.; Smith, A.C.; Levine, B.S. The effects of tetrathiomolybdate (TTM, NSC-714598) and copper supplementation on fertility and early embryonic development in rats. Reprod. Toxicol. 2004, 19, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Yang, C.-T.; Meng, F.-H.; Pacheco, A.; Chen, L.; Xian, M. Ammonium tetrathiomolybdate as a water-soluble and slow-release hydrogen sulfide donor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 1585–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.; Chan, A.; Ali, S.S.; Saha, A.; Haushalter, K.J.; Lam, W.-L.M.; Glasheen, M.; Parker, J.; Brenner, M.; Mahon, S.B.; et al. Hydrogen Sulfide—Mechanisms of Toxicity and Development of an Antidote. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stremmel, W. Bis-choline Tetrathiomolybdate as Old Drug in a New Design for Wilson’s Disease: Good for Brain and Liver? Hepatology 2018, 69, 901–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapp, R. Molybdenum. Encyclopedia 2014, 3, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moini, M.; To, U.; Schilsky, M.L. Recent advances in Wilson disease. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldari, S.; Di Rocco, G.; Toietta, G. Current Biomedical Use of Copper Chelation Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baldari, S.; Di Rocco, G.; Heffern, M.C.; Su, T.A.; Chang, C.J.; Toietta, G. Effects of Copper Chelation on BRAFV600E Positive Colon Carcinoma Cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brady, D.C.; Crowe, M.; Greenberg, D.N.; Counter, C.M. Copper Chelation Inhibits BRAFV600E-Driven Melanomagenesis and Counters Resistance to BRAFV600E and MEK1/2 Inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 6240–6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, P.; Zhang, C.C.; Thoröe-Boveleth, S.; Buhl, E.M.; Weiskirchen, S.; Stremmel, W.; Merle, U.; Weiskirchen, R. Analyzing the Therapeutic Efficacy of Bis-Choline-Tetrathiomolybdate in the Atp7b−/− Copper Overload Mouse Model. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1861. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121861
Kim P, Zhang CC, Thoröe-Boveleth S, Buhl EM, Weiskirchen S, Stremmel W, Merle U, Weiskirchen R. Analyzing the Therapeutic Efficacy of Bis-Choline-Tetrathiomolybdate in the Atp7b−/− Copper Overload Mouse Model. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(12):1861. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121861
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Philipp, Chengcheng Christine Zhang, Sven Thoröe-Boveleth, Eva Miriam Buhl, Sabine Weiskirchen, Wolfgang Stremmel, Uta Merle, and Ralf Weiskirchen. 2021. "Analyzing the Therapeutic Efficacy of Bis-Choline-Tetrathiomolybdate in the Atp7b−/− Copper Overload Mouse Model" Biomedicines 9, no. 12: 1861. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121861
APA StyleKim, P., Zhang, C. C., Thoröe-Boveleth, S., Buhl, E. M., Weiskirchen, S., Stremmel, W., Merle, U., & Weiskirchen, R. (2021). Analyzing the Therapeutic Efficacy of Bis-Choline-Tetrathiomolybdate in the Atp7b−/− Copper Overload Mouse Model. Biomedicines, 9(12), 1861. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121861