Switch from Omalizumab to Benralizumab in Allergic Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: A Real-Life Experience from Southern Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Endpoints
2.2. Statistical Analysis
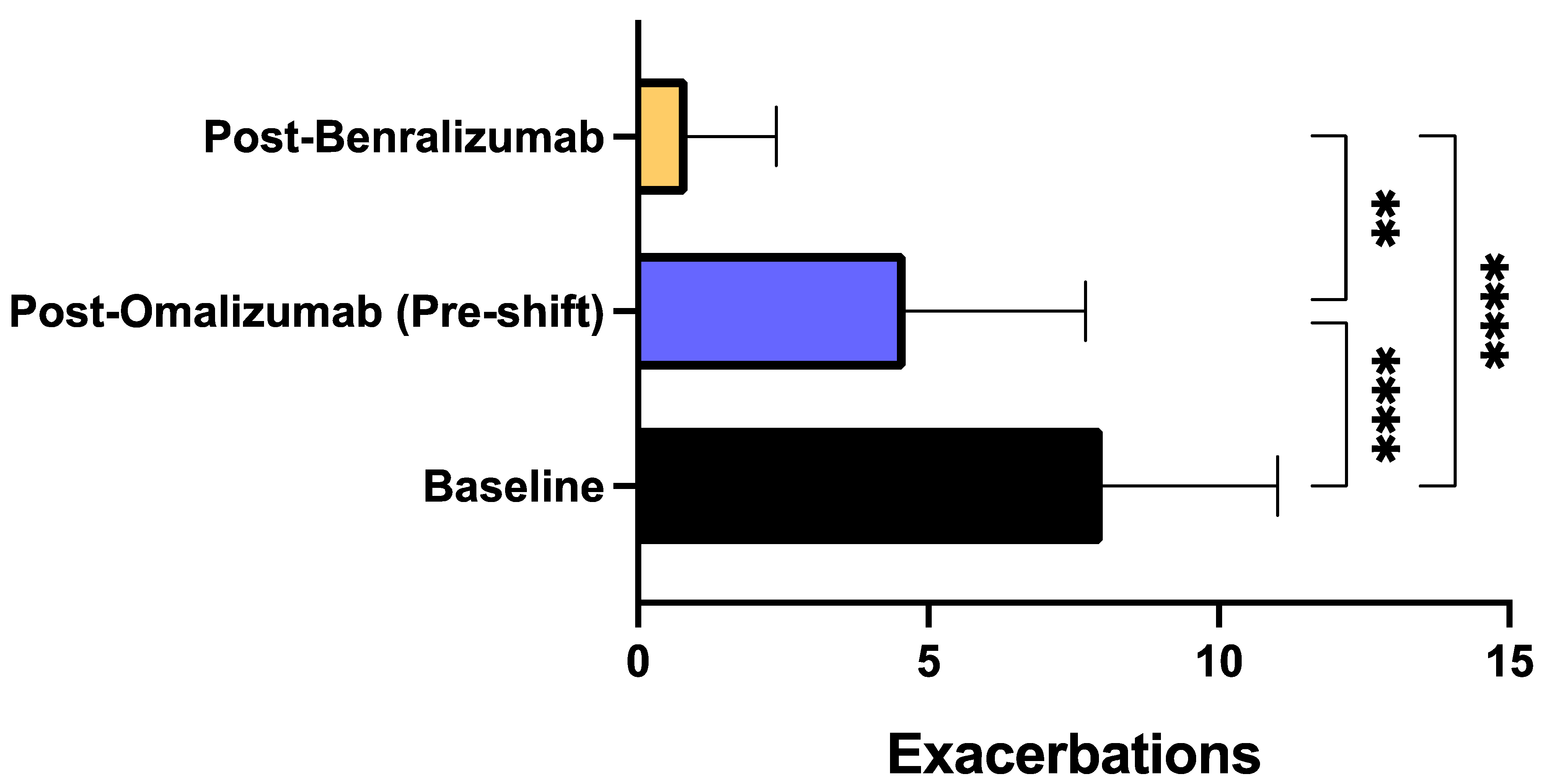
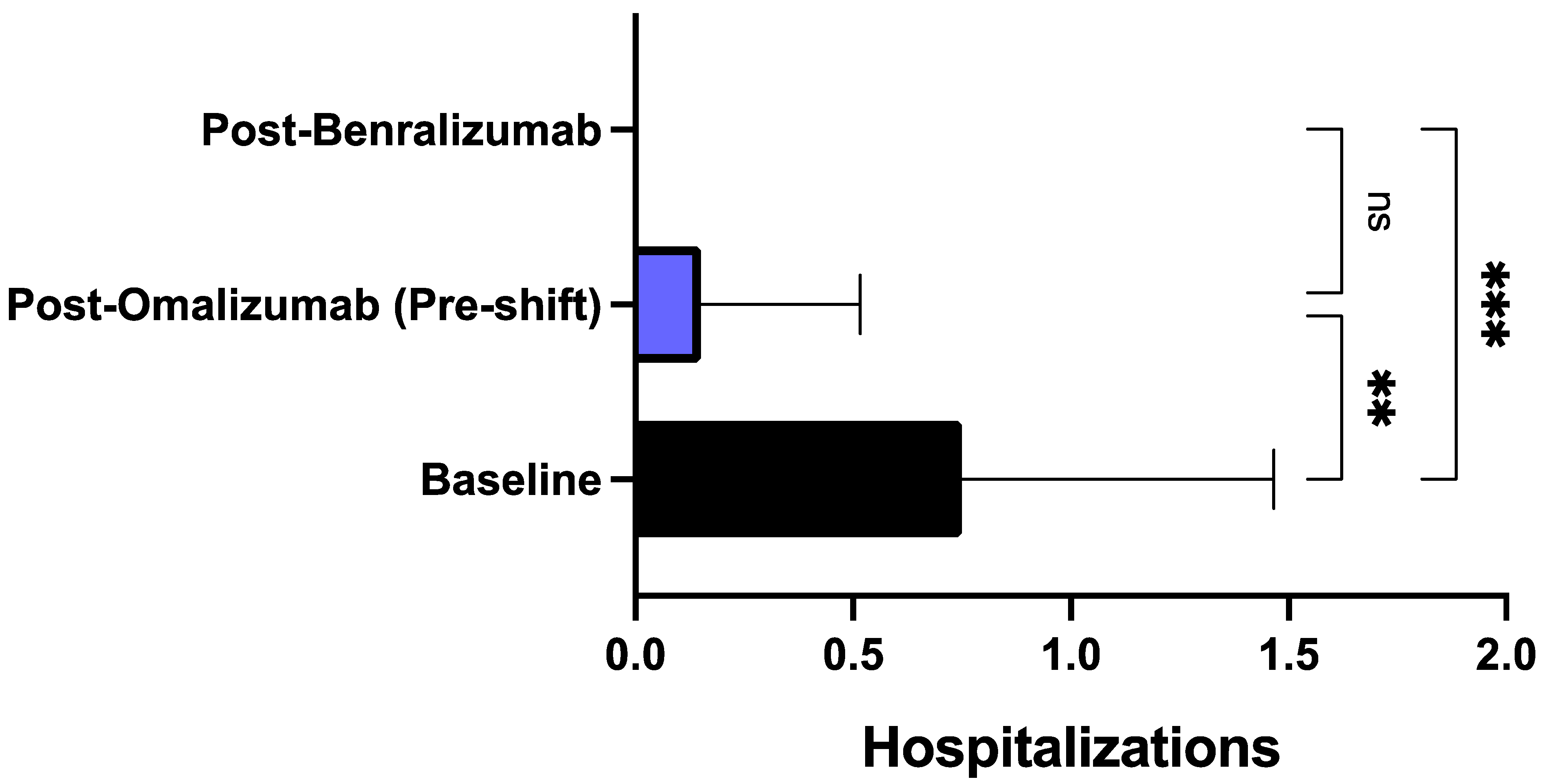
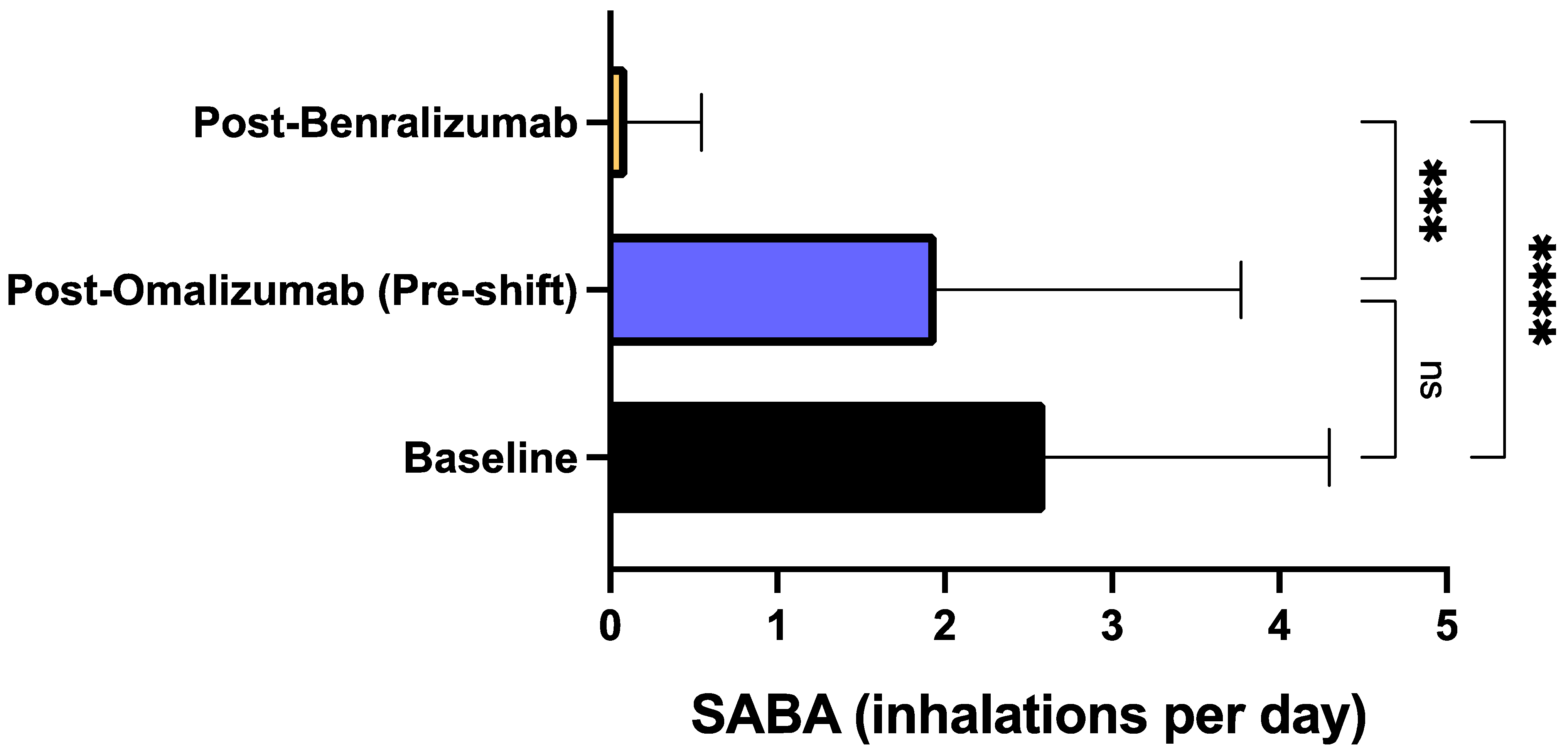
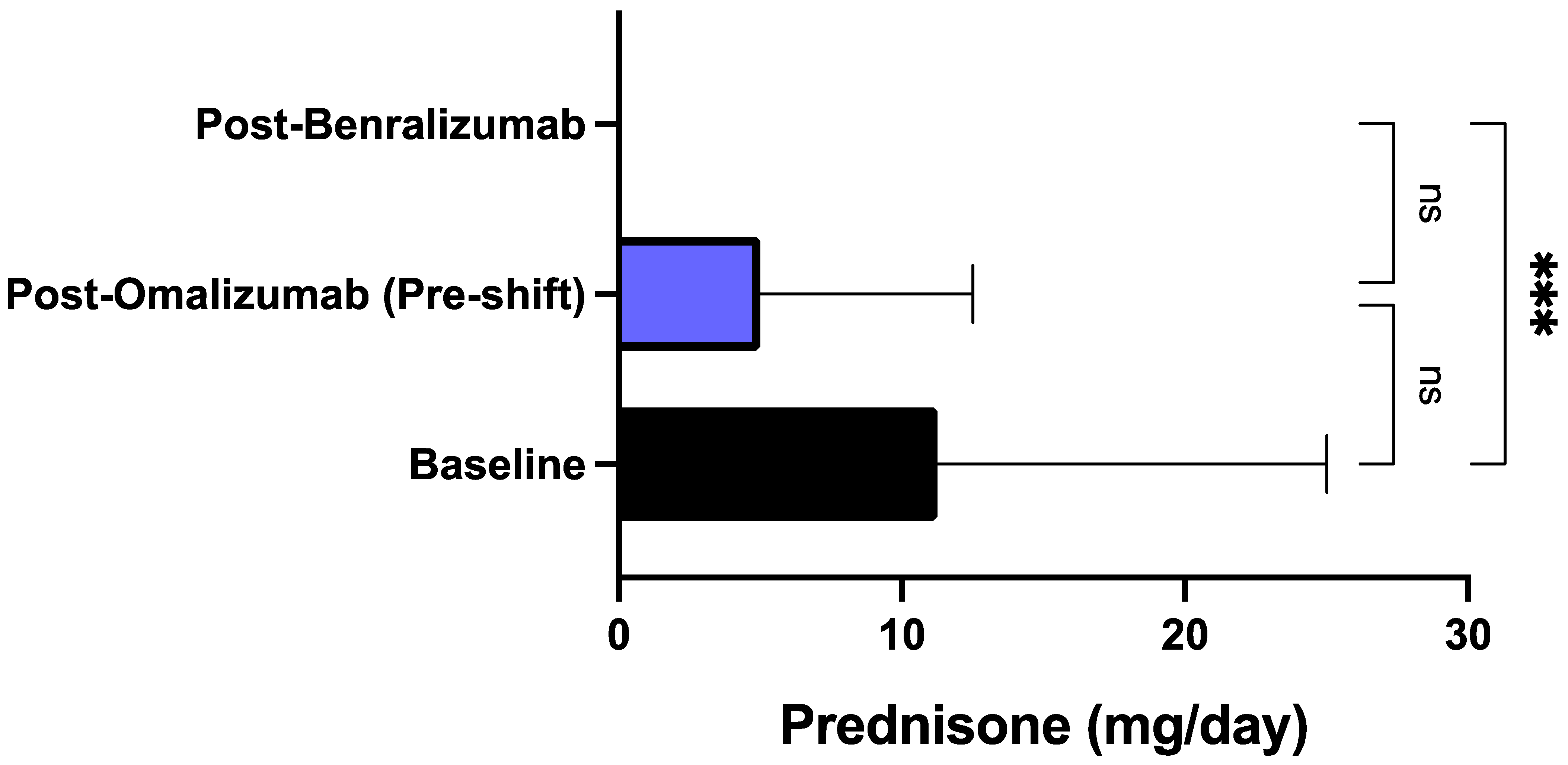
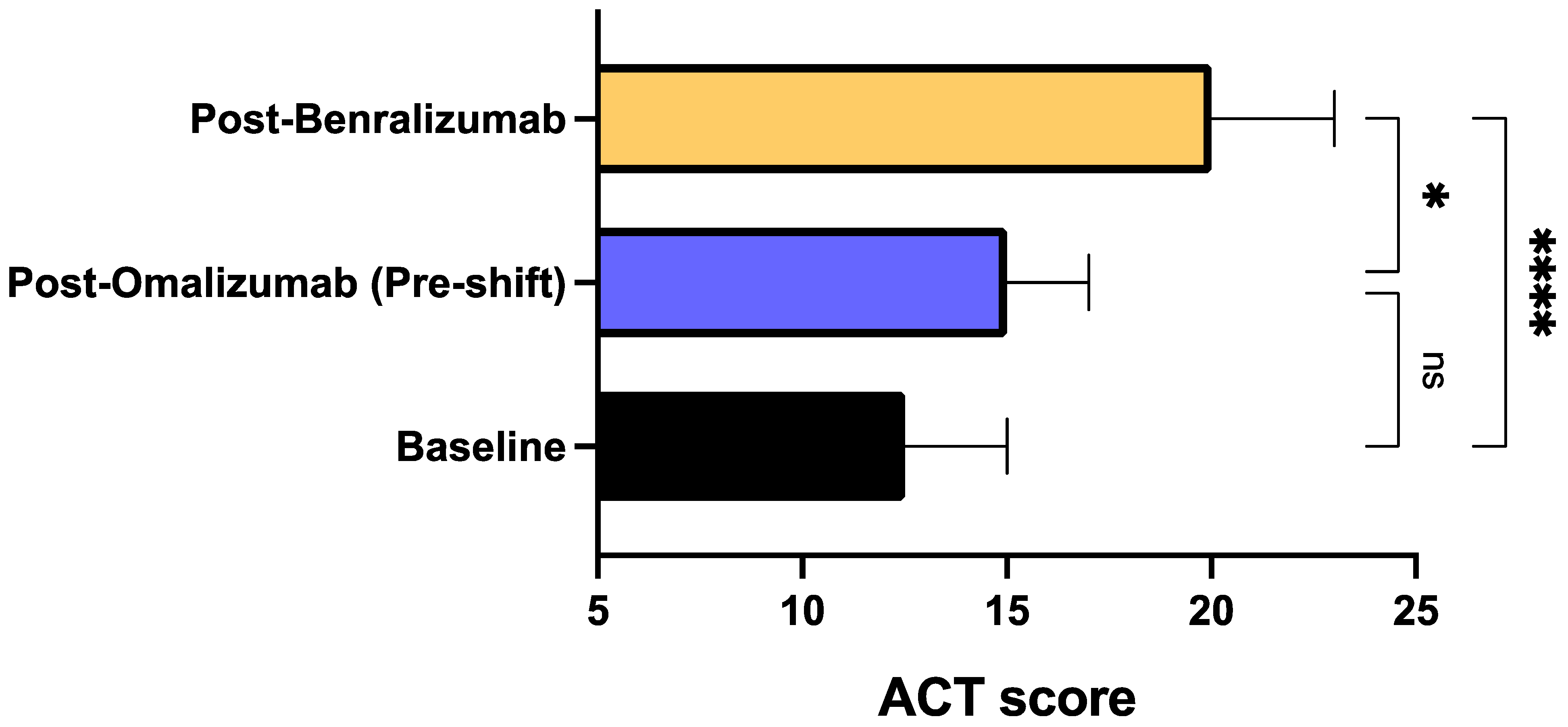
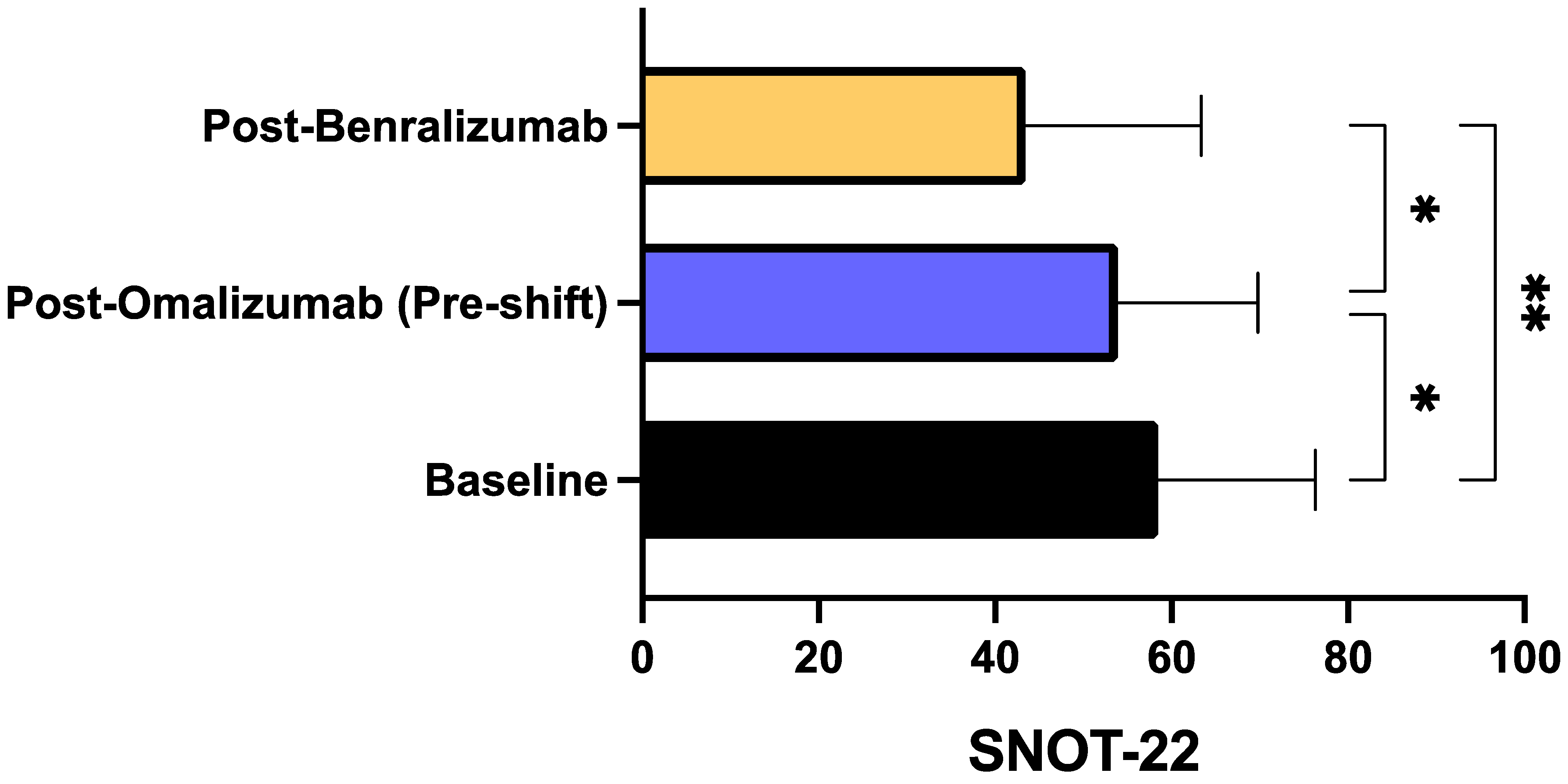
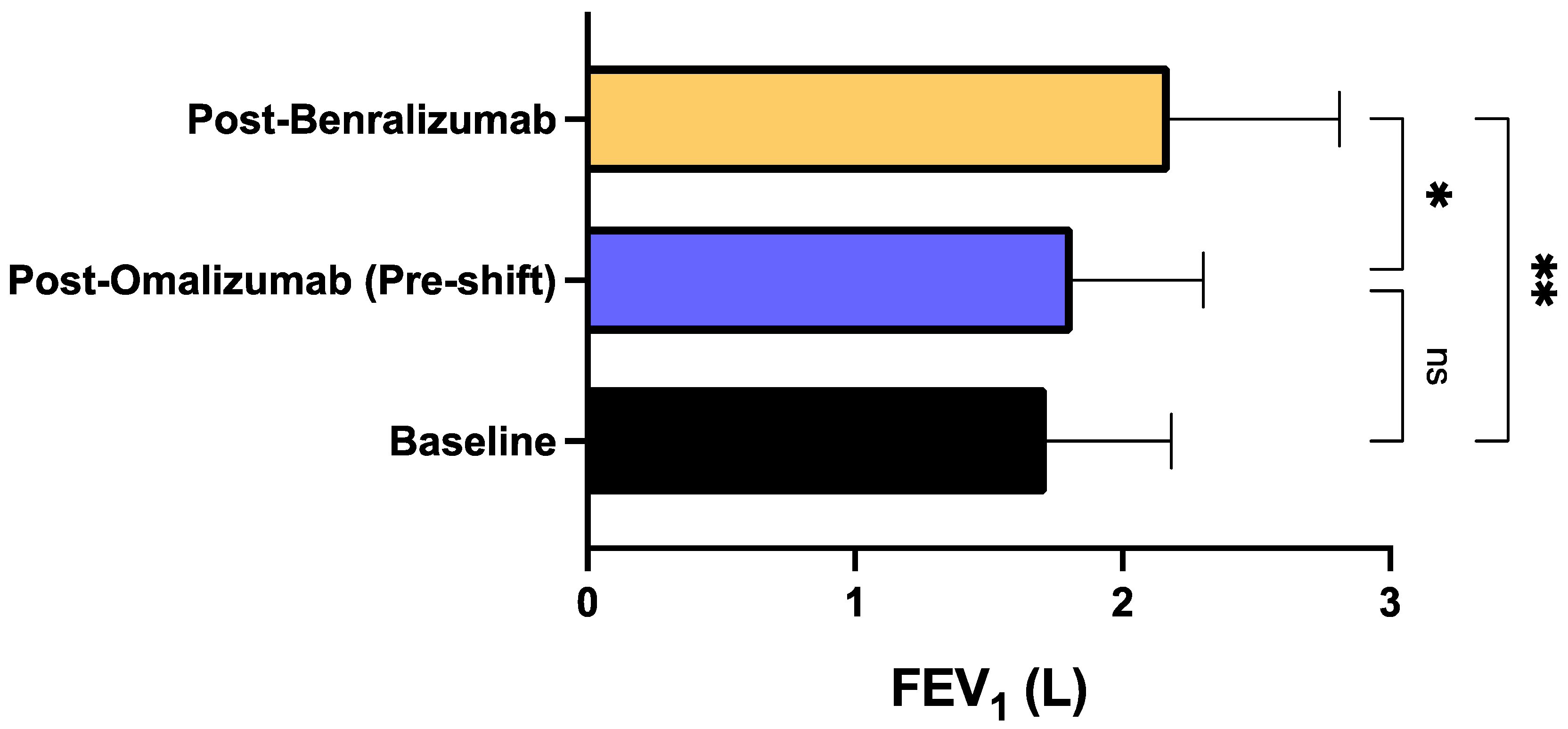
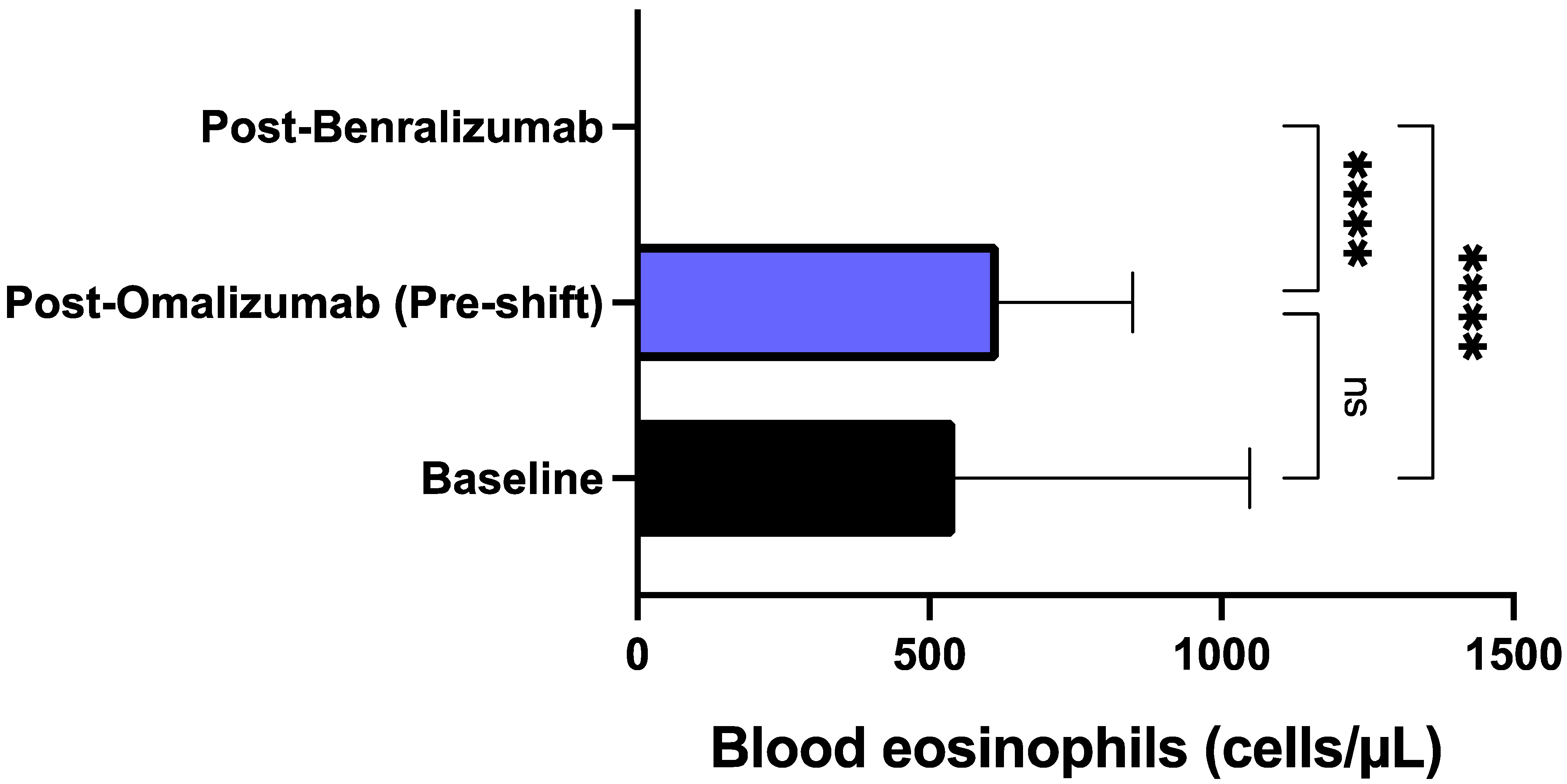
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wenzel, S.E. Severe Adult Asthmas: Integrating Clinical Features, Biology, and Therapeutics to Improve Outcomes. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camiolo, M.J.; Kale, S.L.; Oriss, T.B.; Gauthier, M.; Ray, A. Immune responses and exacerbations in severe asthma. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2021, 72, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, P.J.; Heaney, L.G. Different endotypes and phenotypes drive the heterogeneity in severe asthma. Allergy 2019, 75, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matucci, A.; Bormioli, S.; Nencini, F.; Maggi, E.; Vultaggio, A. The emerging role of type 2 inflammation in asthma. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 17, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, H.; Lambrecht, B.N. The basic immunology of asthma. Cell 2021, 184, 1469–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, T.F.; Zeki, A.A.; Kraft, M. Eosinophilic and Noneosinophilic Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R.K.; Bush, A.; Stokes, J. Eosinophilic asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol Pract. 2020, 8, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.N.; Zeiger, R.; Peters, S.P.; Colice, G.; Newbold, P.; Goldman, M.; Chipps, B.E. Overlap of atopic, eosinophilic, and TH2-high asthma phenotypes in a general population with current asthma. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016, 116, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossios, C.; Pavlidis, S.; Hoda, U.; Kuo, C.-H.; Wiegman, C.; Russell, K.; Sun, K.; Loza, M.J.; Baribaud, F.; Durham, A.L.; et al. Sputum transcriptomics reveal upregulation of IL-1 receptor family members in patients with severe asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 141, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleich, F.; Brusselle, G.; Louis, R.; Vandenplas, O.; Michils, A.; Pilette, C.; Peche, R.; Manise, M.; Joos, G. Heterogeneity of phenotypes in severe asthmatics. The Belgian Severe Asthma Registry (BSAR). Respir. Med. 2014, 108, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuruvilla, M.E.; Lee, F.E.-H.; Lee, G.B. Understanding Asthma Phenotypes, Endotypes, and Mechanisms of Disease. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 56, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Rodriguez, N.; Gogoi, M.; McKenzie, A.N. Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells: Team Players in Regulating Asthma. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 39, 167–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, L.; Montaini, G.; Mazzoni, A.; Rossettini, B.; Capone, M.; Rossi, M.C.; Santarlasci, V.; Liotta, F.; Rossi, O.; Gallo, O.; et al. Human circulating group 2 innate lymphoid cells can express CD154 and promote IgE production. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 964–976.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froidure, A.; Mouthuy, J.; Durham, S.R.; Chanez, P.; Sibille, Y.; Pilette, C. Asthma phenotypes and IgE responses. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 304–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrecht, B.N.; Hammad, H.; Fahy, J.V. The cytokines of asthma. Immunity 2019, 50, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gour, N.; Wills-Karp, M. IL-4 and IL-13 in allergic airway disease. Cytokine 2015, 75, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardolo, F.L.M.; Silkoff, P.E. Perspectives on exhaled nitric oxide. J. Breath Res. 2017, 11, 047104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaia, C.; Paoletti, G.; Puggioni, F.; Racca, F.; Pelaia, G.; Canonica, G.W.; Heffler, E. Interleukin-5 in the Pathophysiology of Severe Asthma. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GINA. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention 2021. Available online: www.ginasthma.org (accessed on 25 August 2021).
- Bousquet, J.; Brusselle, G.; Buhl, R.; Busse, W.W.; Cruz, A.A.; Djukanovic, R.; Domingo, C.; Hanania, N.A.; Humbert, M.; Gow, A.M.; et al. Care pathways for the selection of a biologic in severe asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1701782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakakos, A.; Loukides, S.; Usmani, O.S.; Bakakos, P. Biologics in severe asthma: The overlap endotype—Opportunities and challenges. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2020, 20, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, S. Severe asthma: From characteristics to phenotypes to endotypes. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2012, 42, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suraya, R.; Nagano, T.; Katsurada, M.; Sekiya, R.; Kobayashi, K.; Nishimura, Y. Molecular mechanism of asthma and its novel molecular target therapeutic agent. Respir. Investig. 2021, 59, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, F.C.; Müllerová, H.; Gunsoy, N.B.; Shin, J.-Y.; Nelsen, L.M.; Bradford, E.S.; Cockle, S.M.; Suruki, R.Y. Biologic treatment eligibility for real-world patients with severe asthma: The IDEAL study. J. Asthma 2017, 55, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaia, G.; Canonica, G.W.; Matucci, A.; Paolini, R.; Triggiani, M.; Paggiaro, P. Targeted therapy in severe asthma today: Focus on immunoglobulin E. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, ume 11, 1979–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pelaia, C.; Calabrese, C.; Terracciano, R.; De Blasio, F.; Vatrella, A.; Pelaia, G. Omalizumab, the first available antibody for biological treatment of severe asthma: More than a decade of real-life effectiveness. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, G.J.; Neffen, H.; Castro-Rodriguez, J.A. Efficacy and safety of subcutaneous omalizumab vs placebo as add-on therapy to corticosteroids for children and adults with asthma: A systematic review. Chest 2011, 139, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrejos, S.; Moreira, A.; Ramirez, A.; Quirce, S.; Campos, G.S.; Dávila, I.; Campo, P. FENOMA Study: Achieving Full Control in Patients with Severe Allergic Asthma. J. Asthma Allergy 2020, 13, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaia, G.; Gallelli, L.; Romeo, P.; Renda, T.; Busceti, M.; Proietto, A.; Grembiale, R.; Marsico, S.; Maselli, R.; Vatrella, A. Omalizumab decreases exacerbation frequency, oral intake of corticosteroids and peripheral blood eosinophils in atopic patients with uncontrolled asthma. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 49, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Calabrese, C.; Barbuto, S.; Busceti, M.T.; Preianò, M.; Gallelli, L.; Savino, R.; Vatrella, A.; Pelaia, G. Omalizumab lowers asthma exacerbations, oral cor-ticosteroid intake and blood eosinophils: Results of a 5-year single centre observational study. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 54, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, E.; Ferraro, M.; Bruno, A.; Chiappara, G.; Bousquet, J.; Gjomarkaj, M. Clinical Benefits of 7 Years of Treatment with Omalizumab in Severe Uncontrolled Asthmatics. J. Asthma 2011, 48, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzella, F.; Galeone, C.; Formisano, D.; Castagnetti, C.; Ruggiero, P.; Simonazzi, A.; Zucchi, L. Real-life Efficacy of Omalizumab After 9 Years of Follow-up. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2017, 9, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Leru, P.M.; Anton, V.F. Real-Life Benefit of Omalizumab in Improving Control of Bronchial Asthma During COVID-19 Pandemic. Cureus 2021, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, K.R.; Albers, F.C.; Chipps, B.; Muñoz, X.; Devouassoux, G.; Bergna, M.; Galkin, D.; Azmi, J.; Mouneimne, D.; Price, R.G.; et al. The clinical benefit of mepolizumab replacing omalizumab in uncontrolled severe eosinophilic asthma. Allergy 2019, 74, 1716–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpagnano, G.E.; Pelaia, C.; D’Amato, M.; Crimi, N.; Scichilone, N.; Scioscia, G.; Resta, O.; Calabrese, C.; Pelaia, G.; Quarato, C.M.I.; et al. Switching from omalizumab to mepolizumab: Real-life experience from Southern Italy. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2020, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpagnano, G.E.; Resta, E.; Povero, M.; Pelaia, C.; D’Amato, M.; Crimi, N.; Scichilone, N.; Scioscia, G.; Resta, O.; Calabrese, C.; et al. Clinical and economic consequences of switching from omalizumab to mepolizumab in uncontrolled severe eosinophilic asthma. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnasco, D.; Menzella, F.; Caminati, M.; Caruso, C.; Guida, G.; Bonavia, M.; Riccio, A.; Milanese, M.; Manfredi, A.; Senna, G.; et al. Efficacy of mepolizumab in patients with previous omalizumab treatment failure: Real-life observation. Allergy 2019, 74, 2539–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.C.; Chipps, B.; Munoz, X.; Devouassoux, G.; Bergna, M.; Smith, S.G.; Price, R.G.; Galkin, D.V.; Azmi, J.; Mouneimne, D.; et al. Benefit of switching to mepolizumab from omalizumab in severe eosinophilic asthma based on patient characteristics. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Vatrella, A.; Busceti, M.T.; Gallelli, L.; Terracciano, R.; Savino, R.; Pelaia, G. Severe eosinophilic asthma: From the pathogenic role of interleukin-5 to the therapeutic action of mepolizumab. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 3137–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Busceti, M.T.; Solinas, S.; Terracciano, R.; Pelaia, G. Real-life evaluation of the clinical, functional, and hematological effects of mepolizumab in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma: Results of a single-centre observational study. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 53, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnasco, D.; Milanese, M.; Rolla, G.; Lombardi, C.; Bucca, C.; Heffler, E.; Canonica, G.W.; Passalacqua, G. The North-Western Italian experience with anti IL-5 therapy amd comparison with regulatory trials. World Allergy Organ. J. 2018, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Crimi, C.; Pelaia, G.; Nolasco, S.; Campisi, R.; Heffler, E.; Valenti, G.; Crimi, N. Real-life evaluation of mepolizumab efficacy in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma, according to atopic trait and allergic phenotype. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2020, 50, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaia, C.; Crimi, C.; Vatrella, A.; Tinello, C.; Terracciano, R.; Pelaia, G. Molecular Targets for Biological Therapies of Severe Asthma. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaia, C.; Calabrese, C.; Vatrella, A.; Busceti, M.T.; Garofalo, E.; Lombardo, N.; Terracciano, R.; Pelaia, G. Benralizumab: From the Basic Mechanism of Action to the Potential Use in the Biological Therapy of Severe Eosinophilic Asthma. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Vatrella, A.; Bruni, A.; Terracciano, R.; Pelaia, G. Benralizumab in the treatment of severe asthma: Design, development and potential place in therapy. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, ume 12, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Busceti, M.T.; Vatrella, A.; Rago, G.F.; Crimi, C.; Terracciano, R.; Pelaia, G. Real-life rapidity of benralizumab effects in patients with severe allergic asthma: Assessment of blood eosinophils, symptom control, lung function and oral corticosteroid intake after the first drug dose. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 58, 101830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Busceti, M.T.; Crimi, C.; Carpagnano, G.E.; Lombardo, N.; Terracciano, R.; Vatrella, A.; Pelaia, G. Real-Life effects of benralizumab on exacerbation number and lung hyperinflation in atopic patients with severe eosinophilic asthma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaia, C.; Busceti, M.T.; Vatrella, A.; Ciriolo, M.; Garofalo, E.; Crimi, C.; Terracciano, R.; Lombardo, N.; Pelaia, G. Effects of the first three doses of benralizumab on symptom control, lung function, blood eosinophils, oral corticosteroid intake, and nasal polyps in a patient with severe allergic asthma. SAGE Open Med. Case Rep. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, N.; Pelaia, C.; Ciriolo, M.; Della Corte, M.; Piazzetta, G.; LoBello, N.; Viola, P.; Pelaia, G. Real-life effects of benralizumab on allergic chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyposis associated with severe asthma. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2020, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavanagh, J.E.; Hearn, A.P.; Dhariwal, J.; D’Ancona, G.; Douiri, A.; Roxas, C.; Fernandes, M.; Green, L.; Thomson, L.; Nanzer, A.M.; et al. Real-World Effectiveness of Benralizumab in Severe Eosinophilic Asthma. Chest 2020, 159, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Crimi, C.; Benfante, A.; Caiaffa, M.F.; Calabrese, C.; Carpagnano, G.E.; Ciotta, D.; D’Amato, M.; Macchia, L.; Nolasco, S.; et al. Therapeutic Effects of Benralizumab Assessed in Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: Real-Life Evaluation Correlated with Allergic and Non-Allergic Phenotype Expression. J. Asthma Allergy 2021, 14, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.F.; Wenzel, S.E.; Brozek, J.L.; Bush, A.; Castro, M.; Sterk, P.J.; Adcock, I.M.; Bateman, E.D.; Bel, E.H.; Bleecker, E.R.; et al. International ERS/ATS guidelines on definition, evaluation and treatment of severe asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 43, 343–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzella, F.; Facciolongo, N.; Castagnetti, C.; Simonazzi, A.; Zucchi, L. Omalizumab: When the non-responder is a late-responder. Eur. Ann. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, B.L.; Steenbruggen, I.; Miller, M.R.; Barjaktarevic, I.Z.; Cooper, B.G.; Hall, G.L.; Hallstrand, T.S.; Kaminsky, D.A.; McCarthy, K.; McCormack, M.C.; et al. Standardization of Spirometry 2019 Update. An Official American Thoracic Society and European Respiratory Society Technical Statement. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, e70–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Pelaia, G.; Crimi, C. Biologics in severe asthma. Minerva Med. 2021. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardolo, F.L.; Bertolini, F.; Carriero, V.; Sprio, A.E. Asthma phenotypes and endotypes. Minerva Med. 2021, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numata, T.; Araya, J.; Miyagawa, H.; Okuda, K.; Fujita, Y.; Utsumi, H.; Takekoshi, D.; Hashimoto, M.; Minagawa, S.; Ishikawa, T.; et al. Effectiveness of Switching Biologics for Severe Asthma Patients in Japan: A Single-Center Retrospective Study. J. Asthma Allergy 2021, 14, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sposato, B.; Scalese, M.; Latorre, M.; Scichilone, N.; Matucci, A.; Milanese, M.; Masieri, S.; Rolla, G.; Steinhilber, G.; Rosati, Y.; et al. Effects of omalizumab in severe asthmatics across ages: A real life Italian experience. Respir. Med. 2016, 119, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drick, N.; Seeliger, B.; Welte, T.; Fuge, J.; Suhling, H. Anti-IL-5 therapy in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma—Clinical efficacy and possible criteria for treatment response. BMC Pulm. Med. 2018, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.B.; Rigazio, A.; Campbell, J.D.; Bleecker, E.R.; Corrigan, C.; Thomas, M.; Wenzel, S.; Wilson, A.M.; Small, M.B.; Gopalan, G.; et al. Blood eosinophil count and prospective annual asthma disease burden: A UK cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2015, 3, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiger, R.S.; Schatz, M.; Li, Q.; Chen, W.; Khatry, D.; Gossage, D.; Tran, T.N. High Blood Eosinophil Count Is a Risk Factor for Future Asthma Exacerbations in Adult Persistent Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 2, 741–750.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiger, R.S.; Schatz, M.; Dalal, A.A.; Chen, W.; Sadikova, E.; Suruki, R.Y.; Kawatkar, A.A.; Qian, L. Blood Eosinophil Count and Outcomes in Severe Uncontrolled Asthma: A Prospective Study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 5, 144–153.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, R.A.; Sorkness, C.A.; Kosinski, M.; Schatz, M.; Li, J.T.; Marcus, P.; Murray, J.J.; Pendergraft, T.B. Development of the asthma control test: A survey for assessing asthma control. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.E.; Zhang, H.P.; Lv, Y.; Liang, R.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Powell, H.; Fu, J.-J.; Wang, L.; Gibson, P.; Wang, G. The Asthma Control Test and Asthma Control Questionnaire for assessing asthma control: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, T.W.; Chanez, P.; Menzella, F.; Canonica, G.W.; Louis, R.; Cosio, B.G.; Lugogo, N.L.; Mohan, A.; Burden, A.; McDermott, L.; et al. Onset of effect and impact on health-related quality of life, exacerbation rate, lung function, and nasal polyposis symptoms for patients with severe eosinophilic asthma treated with benralizumab (ANDHI): A randomized, controlled, phase 3b trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2021, 9, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolasco, S.; Crimi, C.; Pelaia, C.; Benfante, A.; Caiaffa, M.F.; Calabrese, C.; Carpagnano, G.E.; Ciotta, D.; D’Amato, M.; Macchia, L.; et al. Benralizumab effectiveness in severe eosinophilic asthma patients with and without chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: A real-world multicentre study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol Pract. 2021. Online ahead of print 19:S2213-2198(21)00903-X. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaert, P.; Omachi, T.A.; Corren, J.; Mullol, J.; Han, J.; Lee, S.E.; Kaufman, D.; Ligueros-Saylan, M.; Howard, M.; Zhu, R.; et al. Efficacy and safety of omalizumab in nasal polyposis: 2 randomized phase 3 trials. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matucci, A.; Bormioli, S.; Nencini, F.; Chiccoli, F.; Vivarelli, E.; Maggi, E.; Vultaggio, A. Asthma and chronic rhinosinusitis: How similar are they in pathogenesis and treatment responses? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scadding, G.K.; Scadding, G.W. Innate and adaptive immunity: ILC2 and Th2 cells in upper and lower airway allergic diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol Pract. 2021, 9, 1851–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Wu, F. Association between fractional exhaled nitric oxide, sputum induction and peripheral blood eosinophil in un-controlled asthma. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Oliver, B.G.; Zhang, H.P.; Kang, D.Y.; Wang, L.; Qiu, Z.X.; Li, W.M. Multidimensional Assessment of Asthma Identifies Clinically Relevant Phenotype Overlap: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 9, 349–362.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacwik, P.; Kupczyk, M. Asthma Phenotype Overlap: More May Be Less. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 9, 363–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zervas, E.; Samitas, K.; Papaioannou, A.I.; Bakakos, P.; Loukides, S.; Gaga, M. An algorithmic approach for the treatment of severe uncontrolled asthma. ERJ Open Res. 2018, 4, 00125–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, D.J.; Humbert, M.; Hirsch, I.; Newbold, P.; Gil, E.G. Ability of serum IgE concentration to predict exacerbation risk and benralizumab ef-ficacy for patients with severe eosinophilic asthma. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahn, U.; Martin, C.; Freeman, P.; Blogg, M.; Jimenez, P. Relationship between pretreatment specific IgE and the response to omalizumab therapy. Allergy 2009, 64, 1780–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleecker, E.R.; Wechsler, M.E.; Fitzgerald, J.M.; Menzies-Gow, A.; Wu, Y.; Hirsch, I.; Goldman, M.; Newbold, P.; Zangrilli, J.G. Baseline patient factors impact on the clinical efficacy of benralizumab for severe asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1800936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Total Population (N = 20) |
|---|---|
| Female gender, N (%) | 13 (65) |
| Male gender, N (%) | 7 (35) |
| Age, mean (±SD), years | 52.85 ± 9.39 |
| Asthma onset age, mean (±SD), years | 31.40 ± 14.34 |
| Duration of asthma, mean (±SD), years | 21.85 ± 15.90 |
| BMI, mean (±SD), % predicted | 23.47 ± 3.54 |
| FEV1, mean (±SD), % predicted | 62.47 ± 13.84 |
| FEV1/FVC, mean (±SD), % | 61.15 ± 11.65 |
| Blood eosinophils, median value (IQR), cells/μL | 543.5 (360.0–1048) |
| Total serum IgE, median value (IQR), IU/mL | 274.5 (198.8–412.8) |
| Gastro-esophageal reflux disease, N (%) | 11 (55) |
| Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps, N (%) | 9 (45) |
| Bronchiectasis, N (%) | 7 (35) |
| Atopic dermatitis, N (%) | 3 (15) |
| Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, N (%) | 2 (10) |
| On treatment with ICS/LABA, N (%) | 20 (100) |
| On treatment with LAMA, N (%) | 15 (75) |
| On treatment with LTRA drugs, N (%) | 14 (70) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pelaia, C.; Crimi, C.; Nolasco, S.; Carpagnano, G.E.; Brancaccio, R.; Buonamico, E.; Campisi, R.; Gagliani, C.; Patella, V.; Pelaia, G.; et al. Switch from Omalizumab to Benralizumab in Allergic Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: A Real-Life Experience from Southern Italy. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121822
Pelaia C, Crimi C, Nolasco S, Carpagnano GE, Brancaccio R, Buonamico E, Campisi R, Gagliani C, Patella V, Pelaia G, et al. Switch from Omalizumab to Benralizumab in Allergic Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: A Real-Life Experience from Southern Italy. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(12):1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121822
Chicago/Turabian StylePelaia, Corrado, Claudia Crimi, Santi Nolasco, Giovanna Elisiana Carpagnano, Raffaele Brancaccio, Enrico Buonamico, Raffaele Campisi, Claudia Gagliani, Vincenzo Patella, Girolamo Pelaia, and et al. 2021. "Switch from Omalizumab to Benralizumab in Allergic Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: A Real-Life Experience from Southern Italy" Biomedicines 9, no. 12: 1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121822
APA StylePelaia, C., Crimi, C., Nolasco, S., Carpagnano, G. E., Brancaccio, R., Buonamico, E., Campisi, R., Gagliani, C., Patella, V., Pelaia, G., Valenti, G., & Crimi, N. (2021). Switch from Omalizumab to Benralizumab in Allergic Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: A Real-Life Experience from Southern Italy. Biomedicines, 9(12), 1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121822










