Plasma Lipoprotein(a) Levels as Determinants of Arterial Stiffening in Hypertension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Analytical Methods
2.3. Arterial Stiffness
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
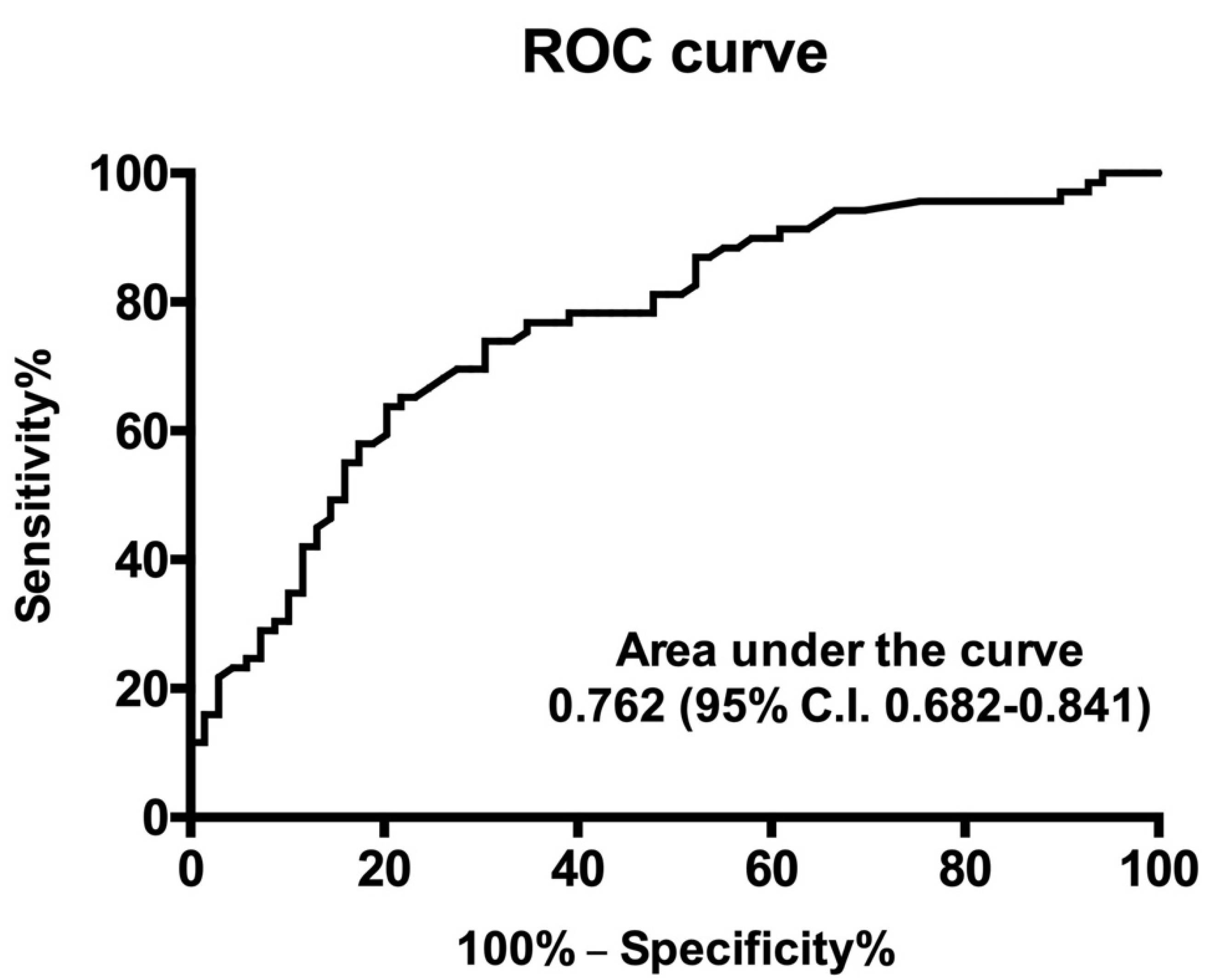
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mancia, G.; Volpe, R.; Boros, S.; Ilardi, M.; Giannattasio, C. Cardiovascular risk profile and blood pressure control in Italian hypertensive patients under specialist care. J. Hypertens. 2004, 22, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, K.; Noureen, A.; Kronenberg, F.; Utermann, G. Structure, function, and genetics of Lipoprotein(a). J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 1339–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsimikas, S. A test in context: Lipoprotein(a): Diagnosis, prognosis, controversies, and emerging therapies. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 692–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannuzzo, G.; Tripaldella, M.; Mallardo, V.; Morgillo, M.; Vitelli, N.; Iannuzzi, A.; Aliberti, E.; Giallauria, F.; Tramontano, A.; Carluccio, R.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) where do we stand? From the physiopathology to innovative therapy. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sechi, L.A.; Kronenberg, F.; De Carli, S.; Falleti, E.; Zingaro, L.; Catena, C.; Utermann, G.; Bartoli, E. Association of lipoprotein(a) levels and apolipoprotein(a) polymorphism with target-organ damage in arterial hypertension. JAMA 1997, 277, 1689–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sechi, L.A.; Catena, C.; Casaccio, D.; Zingaro, L. Lipoprotein(a), hemostatic variables, and cardiovascular damage in hypertensive patients. J. Hypertens. 2000, 18, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catena, C.; Novello, M.; Lapenna, R.; Baroselli, S.; Colussi, G.L.; Nadalini, E.; Favret, G.; Cavarape, A.; Soardo, G.; Sechi, L.A. New risk factors for atherosclerosis in hypertension: Focus on the prothrombotic state and lipoprotein(a). J. Hypertens. 2005, 23, 1617–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sechi, L.A.; Novello, M.; Colussi, G.L.; Di Fabio, A.; Chiuch, A.; Nadalini, E.; Casanova-Borca, A.; Uzzau, A.; Catena, C. Relationship of plasma renin with a prothrombotic state in hypertension: Relevance for organ damage. Am. J. Hypertens. 2008, 21, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattace-Raso, F.U.S.; van der Cammen, T.J.M.; Hofman, A.; van Popele, N.M.; Bos, M.L.; Schalekamp, M.A.; Asmar, R.; Reneman, R.S.; Hoeks, A.P.G.; Bretler, M.M.B.; et al. Arterial stiffness and risk of coronary heart disease and stroke. The Rotterdam Study. Circulation 2006, 113, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willum-Hansen, T.; Staessen, J.A.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Rasmussen, S.; Thijs, L.; Ibsen, H.; Jeppesen, J. Prognostic value of aortic pulse wave velocity as index of arterial stiffness in the general population. Circulation 2006, 113, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, S.; Boutouyrie, P.; Asmar, R.; Gautier, I.; Laloux, B.; Guize, L.; Ducimetiere, P.; Benetos, A. Aortic stiffness is an independent predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in hypertensive patients. Hypertension 2001, 37, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, S.; Katsahian, S.; Fassot, C.; Tropeano, A.I.; Gautier, I.; Laloux, B.; Boutouyrie, P. Aortic stiffness is an independent predictor of fatal stroke in essential hypertension. Stroke 2003, 34, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti-Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; De Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Society of Hypertension (ESH). Eur. Heart. J. 2018, 39, 3021–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildman, R.P.; Farhat, G.N.; Patel, A.S.; Mackey, R.H.; Brockwell, S.; Thompson, T.; Sutton-Tyrrell, K. Weight change is associated with change in arterial stiffness among healthy young adults. Hypertension 2005, 45, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catena, C.; Colussi, G.L.; Frangipane, A.; Russo, A.; Verheyen, N.; Sechi, L.A. Carotid artery stiffness is related to hyperinsulinemia and insulin-resistance in middle-aged, non-diabetic hypertensive patients. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 25, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, I.B.; Prasad, K.; Hall, I.R.; Thomas, A.; MacCallum, H.; Webb, D.J.; Frenneaux, M.P.; Cockroft, J.R. Increased central pulse pressure and augmentation index in subjects with hypercholesterolemia. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 39, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatoi, N.A.; Jerrard-Dunne, P.; Feely, J.; Mahmud, A. Impact of smoking and smoking cessation on arterial stiffness and aortic wave reflection in hypertension. Hypertension 2007, 49, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catena, C.; Novello, M.; Dotto, L.; De Marchi, S.; Sechi, L.A. Serum lipoprotein(a) concentrations and alcohol consumption in hypertension: Possibile relevance for cardiovascular damage. J. Hypertens. 2003, 21, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catena, C.; Colussi, G.L.; Nait, F.; Capobianco, F.; Sechi, L.A. Lipoprotein(a) levels and athrosclerotic renal artery stenosis in hypertensive patients. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2015, 40, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catena, C.; Colussi, G.L.; Url-Michitsch, M.; Nait, F.; Sechi, L.A. Subclinical carotid artery disease and plasma homocysteine levels in patients with hypertension. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2015, 9, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, W.W.; Singh, B.M. Augmentation indexas a measure of peripheral vascular disease state. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2002, 17, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Leeuwen-Segarceanu, E.M.; Tromp, W.; Bos, W.J.W.; Vogels, O.; Groothoff, J.W.; van de Lee, J.H. Comparing two instruments measuring carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity: Vicorder versus Sphygmocor. J. Hypertens. 2010, 28, 1687–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danesh, J.; Collins, R.; Peto, R. Lipoprotein(a) and coronary artery disease. Meta-analysis of prospective studies. Circulation 2000, 102, 1082–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraga, T.; Shimada, M.; Okubo, M.; Nakamishi, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Murase, T. Lipoprotein(a) is an independent risk factor for multiple cerebral infarctions. Atherosclerosis 1996, 122, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentine, R.J.; Grayburn, P.A.; Vega, G.L.; Grundy, S.M. Lp(a) lipoprotein is an independent, discriminant risk factor for premature peripheral atherosclerosis among white men. Arch. Intern. Med. 1994, 154, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shintani, S.; Kikuchi, S.; Hamaguchi, H.; Shiigai, T. High serum lipoprotein(a) levels are an independent risk factor for cerebral infarction. Stroke 1993, 24, 965–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sechi, L.A.; Zingaro, L.; Catena, C.; Perin, A.; De Marchi, S.; Bartoli, E. Lipoprotein(a) and apolipoprotein(a) isoforms and proteinuria in patients with moderate renal failure. Kidney Int. 1999, 56, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, M.; Iannuzzo, G.; Mattiello, A.; Marotta, G.; Iannuzzi, A.; Panico, S.; Rubba, P. Association between Lp(a) and atherosclerosis in menopausal women without metabolic syndrome. Biomarkers Med. 2016, 10, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colussi, G.L.; Baroselli, S.; Sechi, L. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids decrease plasma lipoprotein(a) levels in hypertensive subjects. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 23, 1246–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sechi, L.A.; Zingaro, L.; De Carli, S.; Sechi, G.; Catena, C.; Falleti, E.; Dell’Anna, E.; Bartoli, E. Increased serum lipoprotein(a) levels in patients with early renal failure. Ann. Intern. Med. 1998, 129, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzano, L.; Colussi, G.L.; Del Torre, M.; Sechi, L.A.; Catena, C. Relationships of plasma lipoprotein(a) levels with insulin resistance in hypertensive patients. Metabolism 2014, 63, 1439–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, B.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Qin, X.; Zhang, J.; Cao, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, P.; Yang, R.; et al. Association between lipid profiles and arterial stiffness in Chinese patients with hypertension: Insights from the CSPPT. Angiology 2019, 70, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luft, F.C. Molecular mechanisms of arterial stiffness: New insights. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2012, 6, 436–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumor, K.; Shoemaker-Moyle, M.; Nistala, R.; Whaley-Connell, A. Arterial stiffness in hypertension: An update. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozos, I.; Jianu, D.; Gug, C.; Stoian, D. Links between high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and pulsa wave analysis in middle-aged patients with hypertension and high normal blood pressure. Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 2568069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catena, C.; Colussi, G.L.; Brosolo, G.; Sechi, L.A. A prothrombotic state is associated with early arterial damage in hypertensive patients. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2012, 19, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buleu, F.N.; Luca, C.T.; Tudor, A.; Badalica-Petrescu, M.; Caraba, A.; Pah, A.; Georgescu, D.; Christodorescu, R.; Dragan, S. Correlations between vascular stiffness indicators, OPG, and 25-OH vitamin D3 status in heart failure patients. Medicina 2019, 55, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozos, I.; Gug, C.; Mozos, C.; Stoian, D.; Pricop, M.; Jianu, D. Associations between Intrinsic Heart Rate, P Wave and QT interval durations and pulse wave analysis in patients with hypertension and high normal blood pressure. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, R.R.; Wilkinson, I.B.; Schiffrin, E.L.; Avolio, A.P.; Chirinos, J.A.; Cockroft, J.R.; Heffernan, K.S.; Lakatta, E.G.; McEniery, C.; Mitchell, G.F.; et al. Recommendations for improving and standardizing vascular research on arterial stiffness: A scientific statment from the American Heart Association. Hypertension 2015, 66, 698–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, I.; Masuda, H. Lipoprotein(a) as a determinant of arterial stiffness in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin. Chim. Acta 2006, 373, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, A.; Kotani, K. Lipoprotein(a) and arterial stiffness parameters. Pulse 2015, 3, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morishita, R.; Ishii, J.; Kusumi, Y.; Yamada, S.; Komai, N.; Ohishi, M.; Nomura, M.; Hishida, H.; Niihashi, M.; Mitsumata, M. Association of serum oxidized lipoprotein(a) concentration with coronary artery disease: Potential role of oxidized lipoprotein(a) in the vascular wall. J. Atheroscl. Thromb. 2009, 16, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotani, K.; Yamada, S.; Yamada, T.; Kario, K.; Taniguchi, N. Oxidized lipoprotein(a) and cardio-ankle vascular index (CAVI) in hypertensive subjects. Heart Vessels 2013, 28, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, S.; Cockroft, J.; Bortel, L.V.; Boutouyrie, P.; Giannattasio, C.; Hayoz, D.; Pannier, B.; Vlachopoulos, C.; Wilkinson, I.; Struijker-Boudier, H. Expert consensus document on arterial stiffness: Methodological issues and clinical applications. Eur. Heart. J. 2006, 27, 2588–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, S.; Harpel, P.C.; Rifkin, D.B. Lipoprotein(a) inhibits the generation of transforming growth factor β: An endogenous inhibitor of smooth muscle cell migration. J. Cell. Biol. 1991, 113, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buechler, C.; Ulrich, H.; Aslanidis, C.; Bared, S.M.; Lingenhel, A.; Ritter, M.; Schmitz, G. Lipoprotein(a) downregulates lysosomal acid lipase and induces interleukine-6 in human blood monocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1642, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klezovitch, O.; Edelstein, C.; Scanu, A.M. Stimulation of interleukin-8 production in human THP-1 macrophages by apolipoprotein(a). Evidence for a critical involvement of elements in C-terminal domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 46864–46869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| All Patients (n = 138) | AIx Below Median (n = 75) | AIx Above Median (n = 63) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical characteristics | ||||
| Age, years | 51 ± 14 | 48 ± 14 | 55 ± 12 | 0.002 |
| Males, n (%) | 66 (48) | 46 (61) | 20 (32) | 0.001 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 26.8 ± 4.7 | 26.6 ± 5.2 | 27.1 ± 4.0 | 0.563 |
| Heart rate, bpm | 68 ± 13 | 70 ± 12 | 67 ± 13 | 0.192 |
| Systolic blood pressure, mmHg | 145 ± 18 | 144 ± 16 | 146 ± 21 | 0.435 |
| Diastolic BP, mmHg | 89 ± 12 | 89 ± 10 | 89 ± 14 | 0.993 |
| Duration of hypertension, years | 8 ± 9 | 7 ± 9 | 9 ± 8 | 0.179 |
| Smokers, n (%) | 30 (22) | 10 (13) | 20 (32) | 0.044 |
| Alcohol intake, gr/day | 8 ± 12 | 8 ± 13 | 8 ± 11 | 0.924 |
| Physically active, n (%) | 36 (26) | 22 (29) | 14 (22) | 0.343 |
| Anti-hypertensive drugs, n (%) | 87 (63) | 43 (57) | 44 (70) | 0.129 |
| Biochemical variables | ||||
| Creatinine cl., ml/min/1.73 m2 | 101 ± 25 | 99 ± 25 | 104 ± 25 | 0.325 |
| Fasting glucose, mg/dl | 90 ± 13 | 90 ± 11 | 91 ± 14 | 0.417 |
| Triglycerides, mg/dl | 106 ± 56 | 103 ± 62 | 111 ± 48 | 0.397 |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dl | 197 ± 45 | 189 ± 42 | 205 ± 47 | 0.040 |
| HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl | 57 ± 18 | 60 ± 19 | 57 ± 16 | 0.339 |
| LDL-cholesterol, mg/dl | 117 ± 40 | 110 ± 38 | 126 ± 40 | 0.018 |
| C-reactive protein, mg/l | 1.16 [0.58–2.10] | 0.94 [0.42–1.61] | 1.30 [0.76–2.85] | 0.003 |
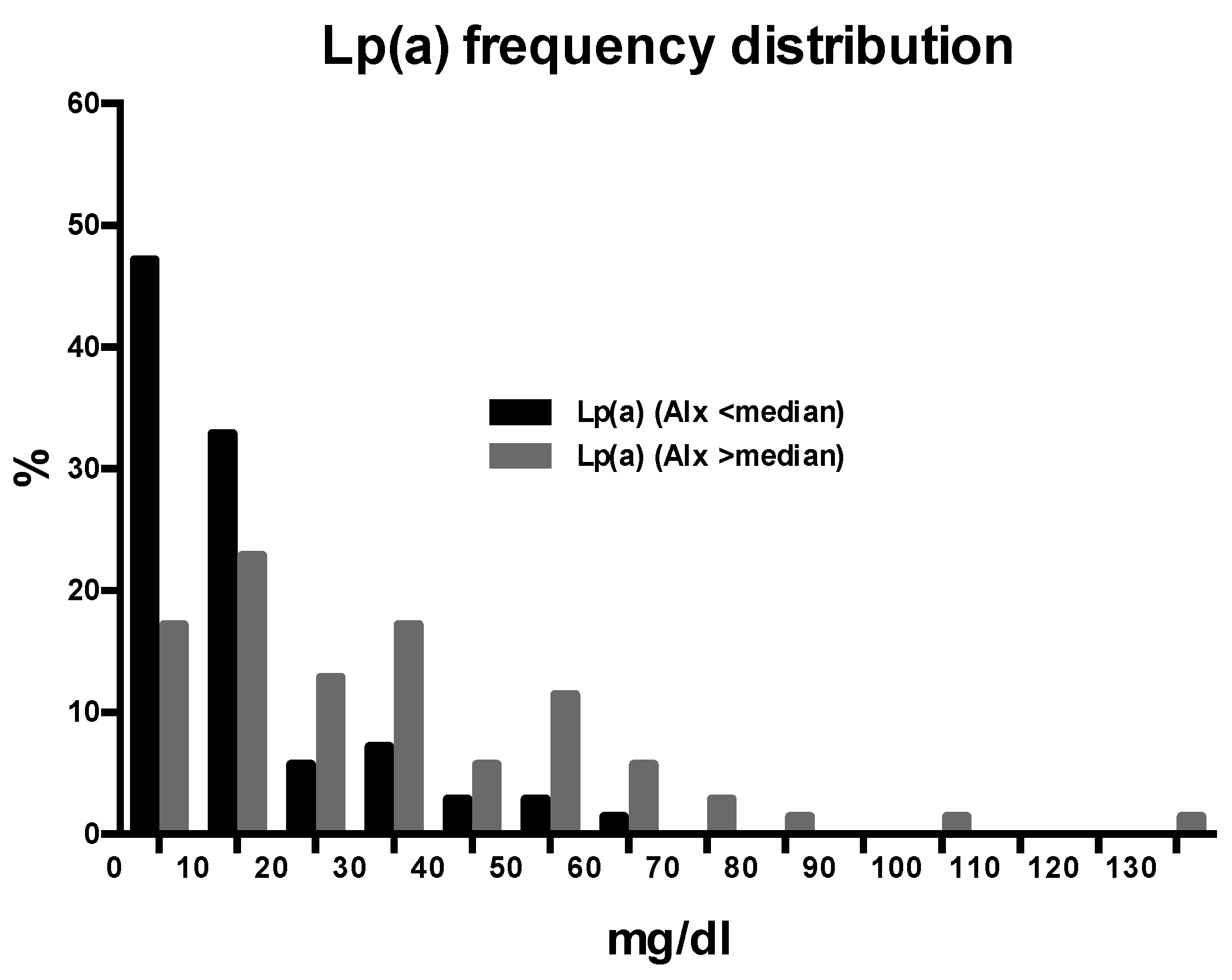
| Lipoprotein(a), mg/dl | 10.4 [3.0–31.2] | 7.2 [3.0–13.0] | 22.4 [8.8–41.2] | <0.001 |
| Instrumental variables | ||||
| Augmentation index | 27 ± 8 | 18 ± 8 | 38 ± 7 | <0.001 |
| Pulse wave velocity, m/s | 7.7 ± 1.9 | 7.2 ± 1.8 | 8.3 ± 1.9 | <0.001 |
| Variables | Augmentation Index | Pulse Wave Velocity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical characteristics | r | p | r | p |
| Age | 0.311 | <0.001 | 0.501 | <0.001 |
| Body mass index | 0.101 | 0.237 | 0.230 | 0.007 |
| Heart rate | −0.167 | 0.055 | −0.115 | 0.187 |
| Systolic blood pressure | −0.018 | 0.834 | 0.296 | <0.001 |
| Diastolic blood pressure | −0.030 | 0.795 | 0.006 | 0.949 |
| Duration of hypertension | 0.043 | 0.618 | 0.354 | <0.001 |
| Alcohol consumption | 0.010 | 0.912 | 0.137 | 0.117 |
| Biochemical variables | ||||
| Creatinine clearance | 0.036 | 0.677 | −0.118 | 0.170 |
| Fasting glucose | 0.064 | 0.460 | 0.366 | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides | 0.175 | 0.042 | 0.173 | 0.044 |
| Total cholesterol | 0.268 | 0.002 | 0.075 | 0.387 |
| HDL-cholesterol | −0.135 | 0.117 | −0.334 | <0.001 |
| LDL-cholesterol | 0.314 | <0.001 | 0.197 | 0.022 |
| Log C-reactive protein | 0.334 | <0.001 | 0.326 | 0.001 |
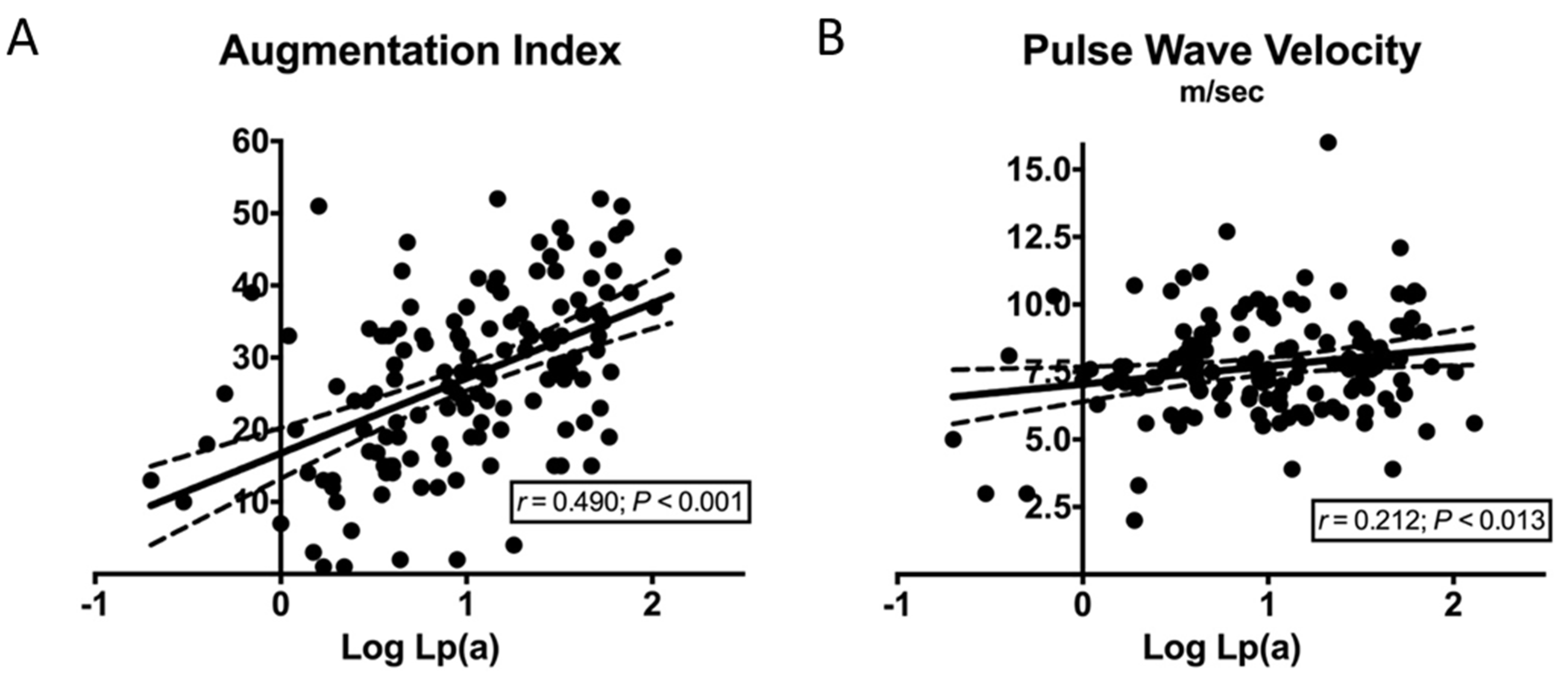
| Log Lipoprotein(a) | 0.490 | <0.001 | 0.212 | 0.013 |
| Variables | β | p |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.281 | 0.002 |
| Gender | −0.078 | 0.360 |
| Triglycerides | −0.050 | 0.588 |
| LDL-cholesterol | 0.162 | 0.066 |
| Log C-reactive protein | 0.253 | 0.005 |
| Log Lipoprotein(a) | 0.326 | <0.001 |
| Diuretics | 0.092 | 0.371 |
| Beta blockers | −0.193 | 0.072 |
| Variables | β | p |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.328 | 0.001 |
| Body mass index | −0.034 | 0.705 |
| Systolic blood pressure | 0.104 | 0.211 |
| Duration of hypertension | 0.107 | 0.283 |
| Antihypertensive therapy | −0.140 | 0.233 |
| Triglycerides | −0.117 | 0.197 |
| HDL-cholesterol | −0.331 | 0.001 |
| LDL-cholesterol | 0.139 | 0.100 |
| Fasting glucose | 0.137 | 0.143 |
| Log C-reactive protein | 0.142 | 0.113 |
| Log Lipoprotein(a) | 0.018 | 0.838 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brosolo, G.; Da Porto, A.; Bulfone, L.; Vacca, A.; Bertin, N.; Colussi, G.; Cavarape, A.; Sechi, L.A.; Catena, C. Plasma Lipoprotein(a) Levels as Determinants of Arterial Stiffening in Hypertension. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9111510
Brosolo G, Da Porto A, Bulfone L, Vacca A, Bertin N, Colussi G, Cavarape A, Sechi LA, Catena C. Plasma Lipoprotein(a) Levels as Determinants of Arterial Stiffening in Hypertension. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(11):1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9111510
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrosolo, Gabriele, Andrea Da Porto, Luca Bulfone, Antonio Vacca, Nicole Bertin, Gianluca Colussi, Alessandro Cavarape, Leonardo A. Sechi, and Cristiana Catena. 2021. "Plasma Lipoprotein(a) Levels as Determinants of Arterial Stiffening in Hypertension" Biomedicines 9, no. 11: 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9111510
APA StyleBrosolo, G., Da Porto, A., Bulfone, L., Vacca, A., Bertin, N., Colussi, G., Cavarape, A., Sechi, L. A., & Catena, C. (2021). Plasma Lipoprotein(a) Levels as Determinants of Arterial Stiffening in Hypertension. Biomedicines, 9(11), 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9111510







