Longitudinal Serum Neurofilament Levels of Multiple Sclerosis Patients Before and After Treatment with First-Line Immunomodulatory Therapies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Patients
2.2. NfL Measurements
2.3. Cytokines Measurements
2.4. MRI Scans
2.5. Cognitive Functions
2.6. Statistical Methods
2.7. Ethical Statement
3. Results
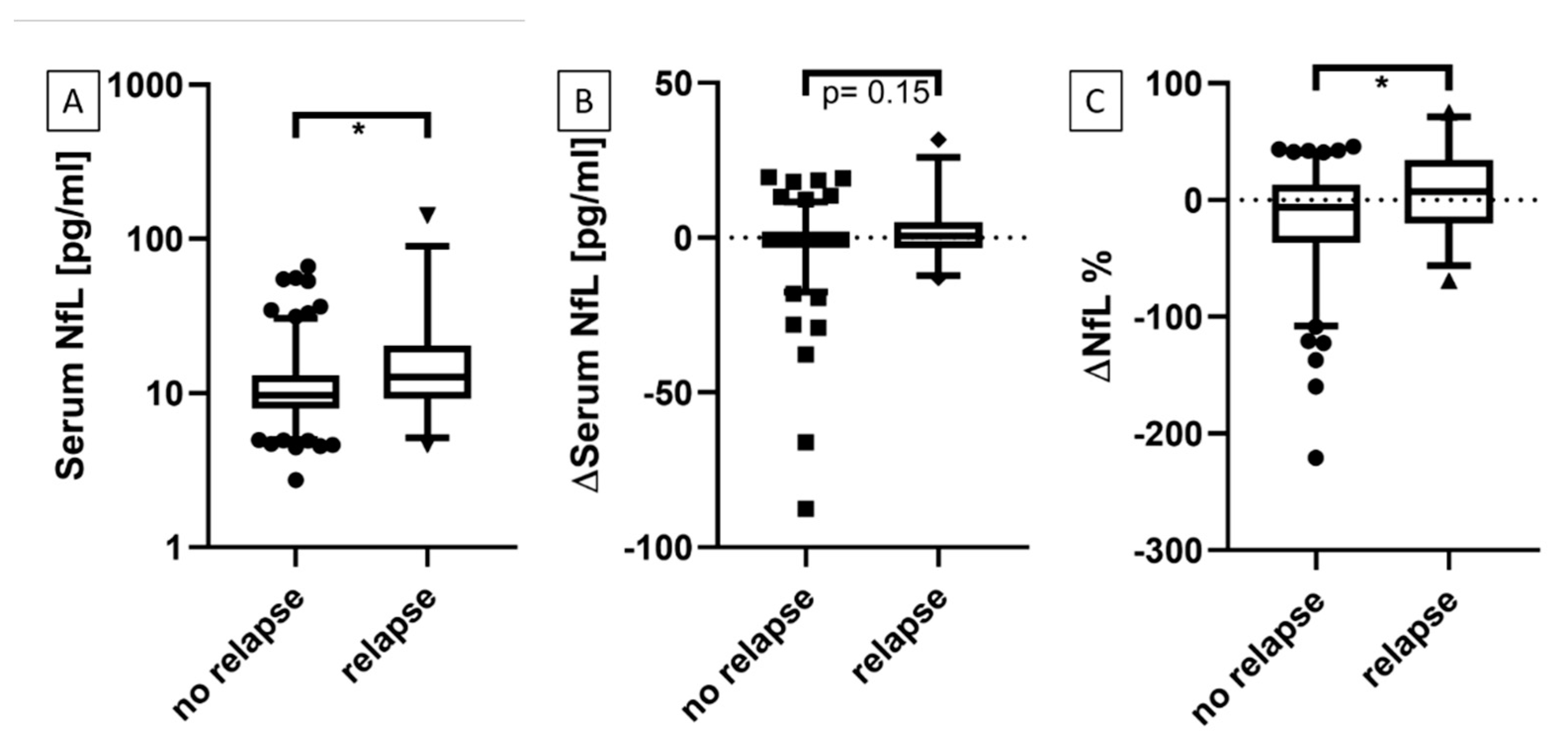
3.1. Serum NfL at Time Points With and Without Active Relapse
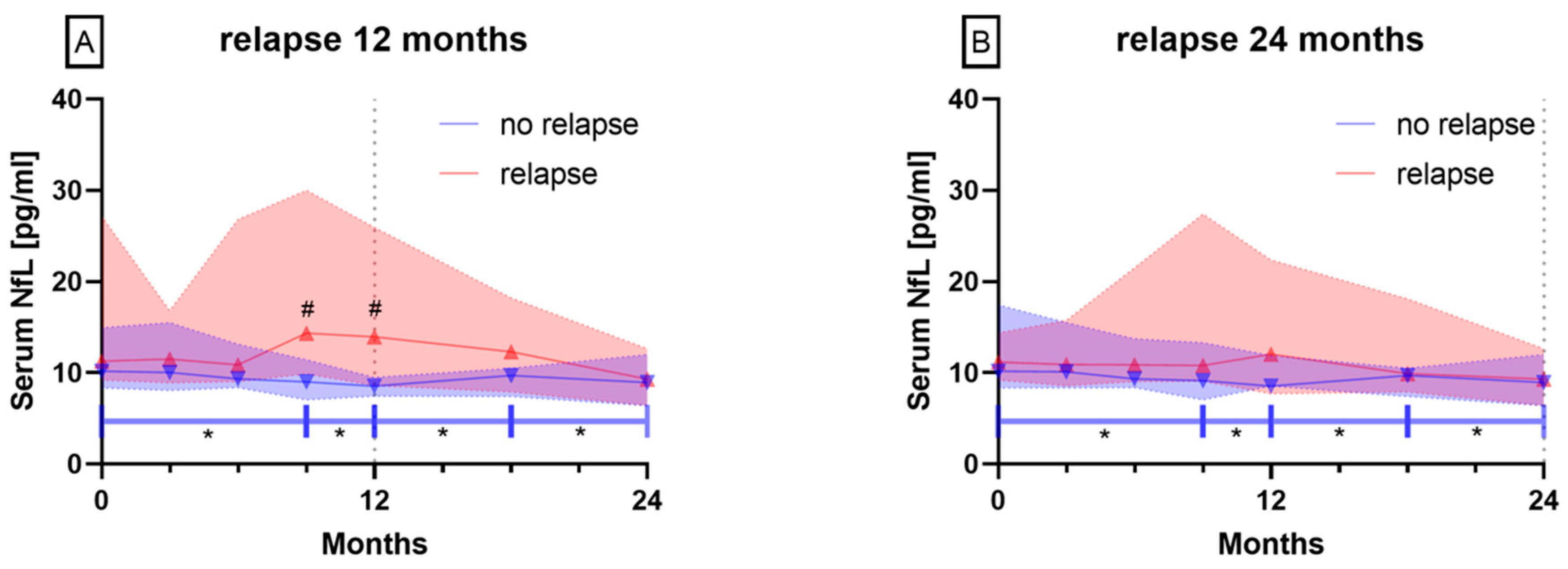
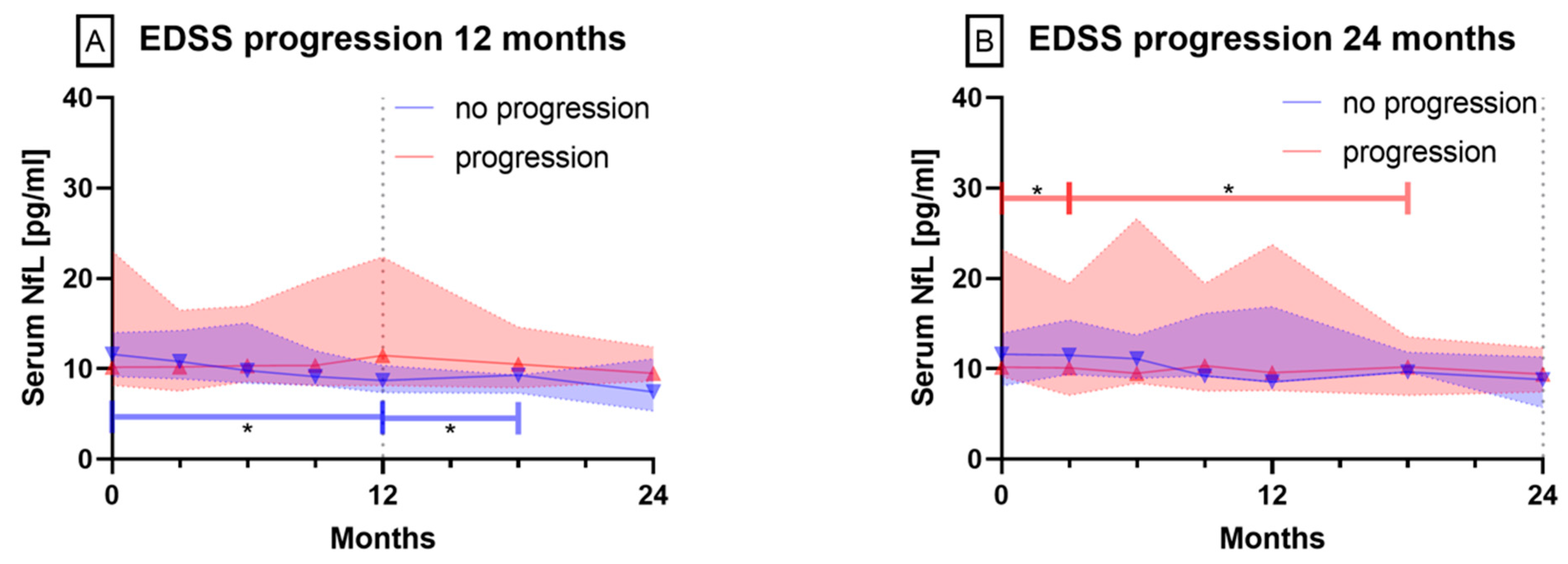
3.2. Serum NfL Levels During Follow-Up Period of 24 Months
3.2.1. Patients with Relapses vs. No Relapse
3.2.2. Patients with EDSS Progression vs. Stable or Improved EDSS
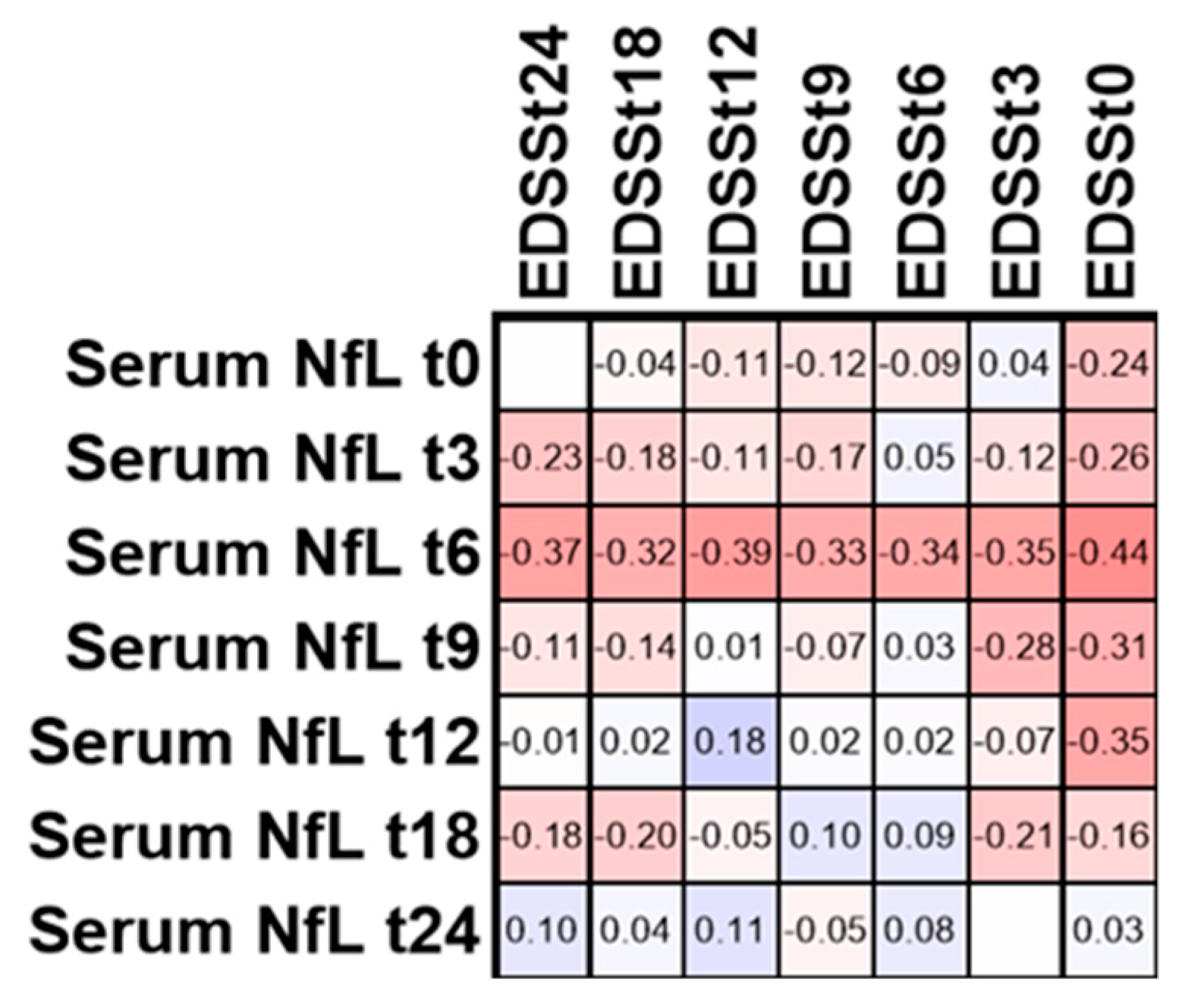
3.3. Correlation of Serum NfL with
3.3.1. Age
3.3.2. Serum Cytokine Profile in All Patients
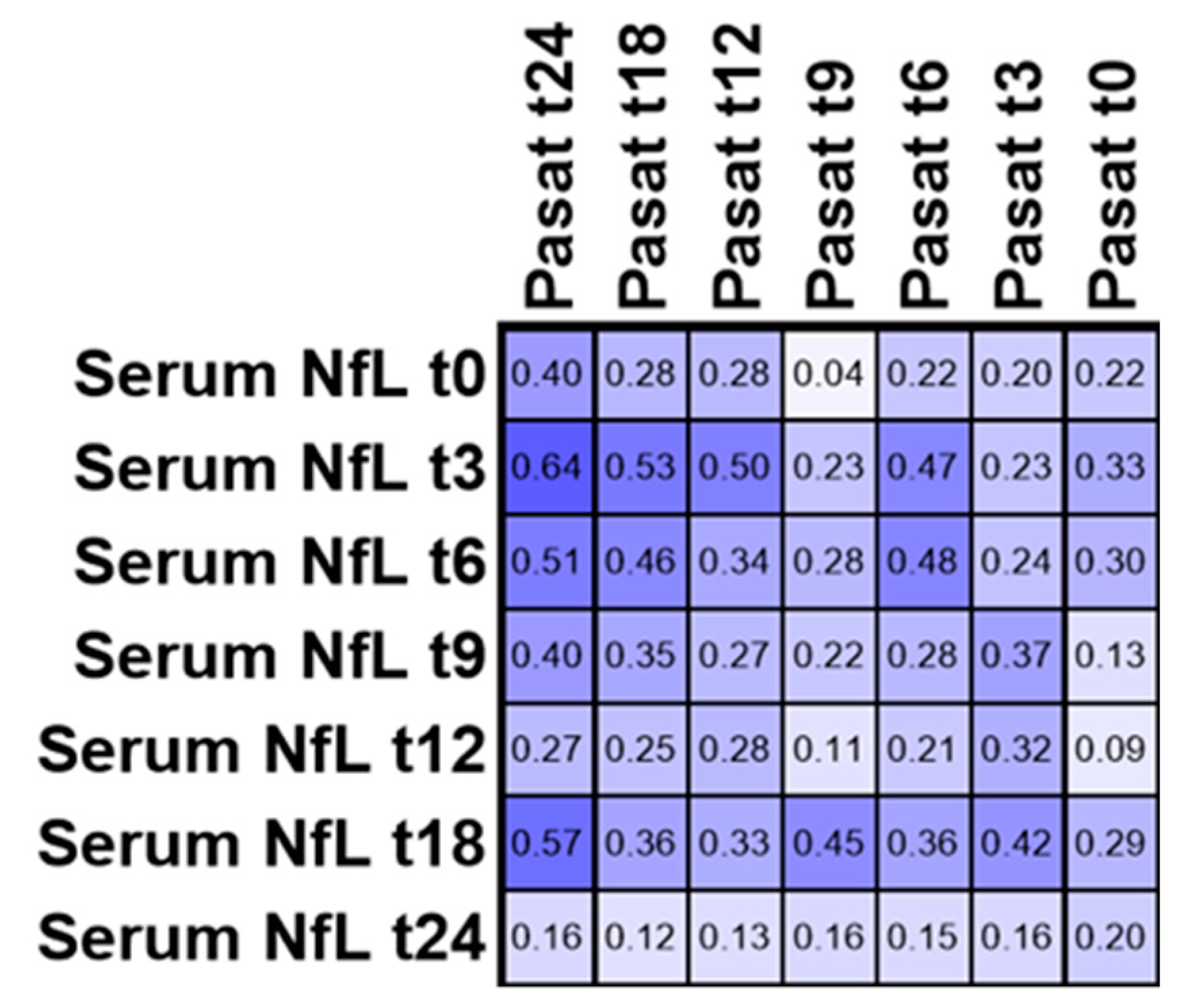
3.4. PASAT
3.5. EDSS in Patients with Active Disease within 24 Months
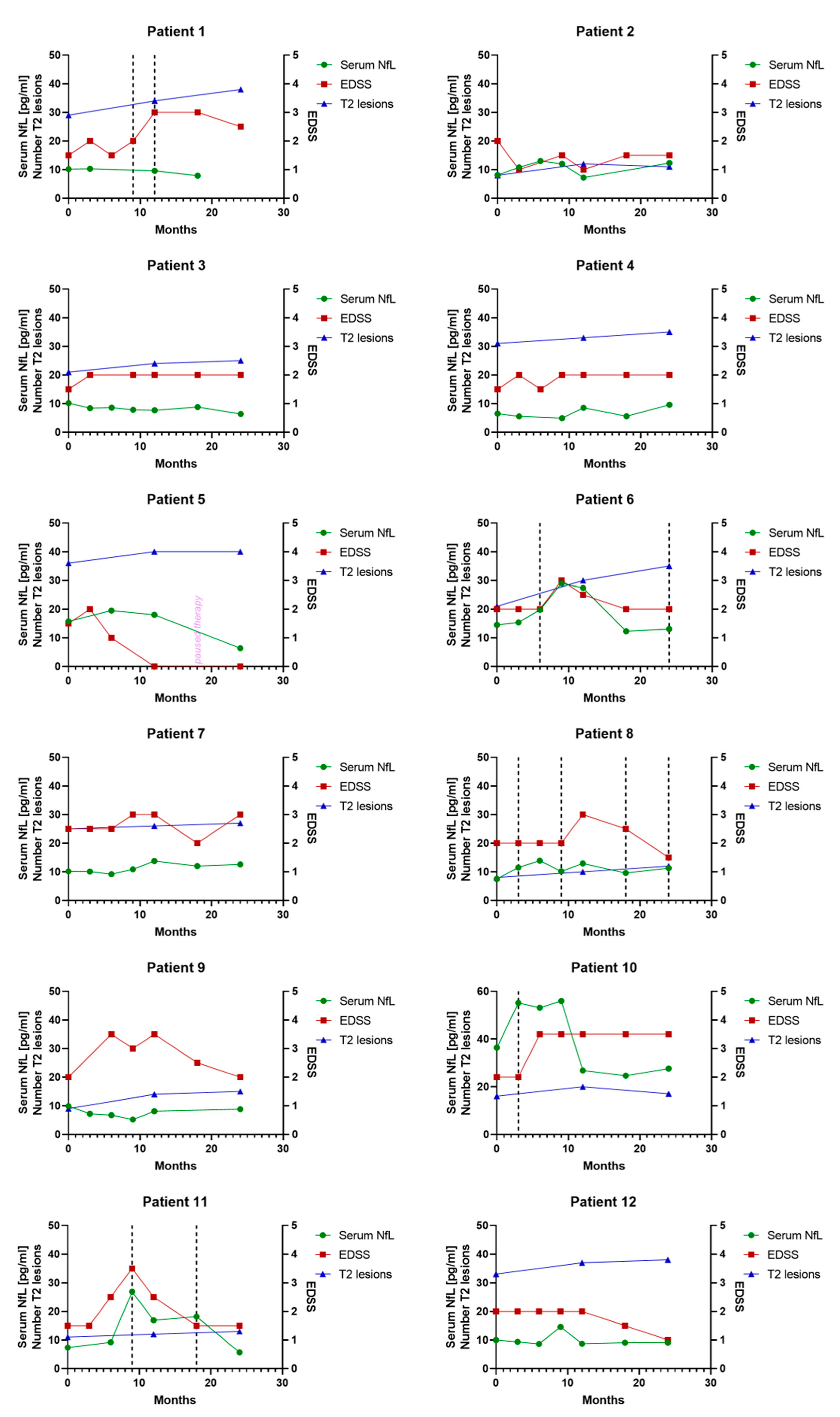
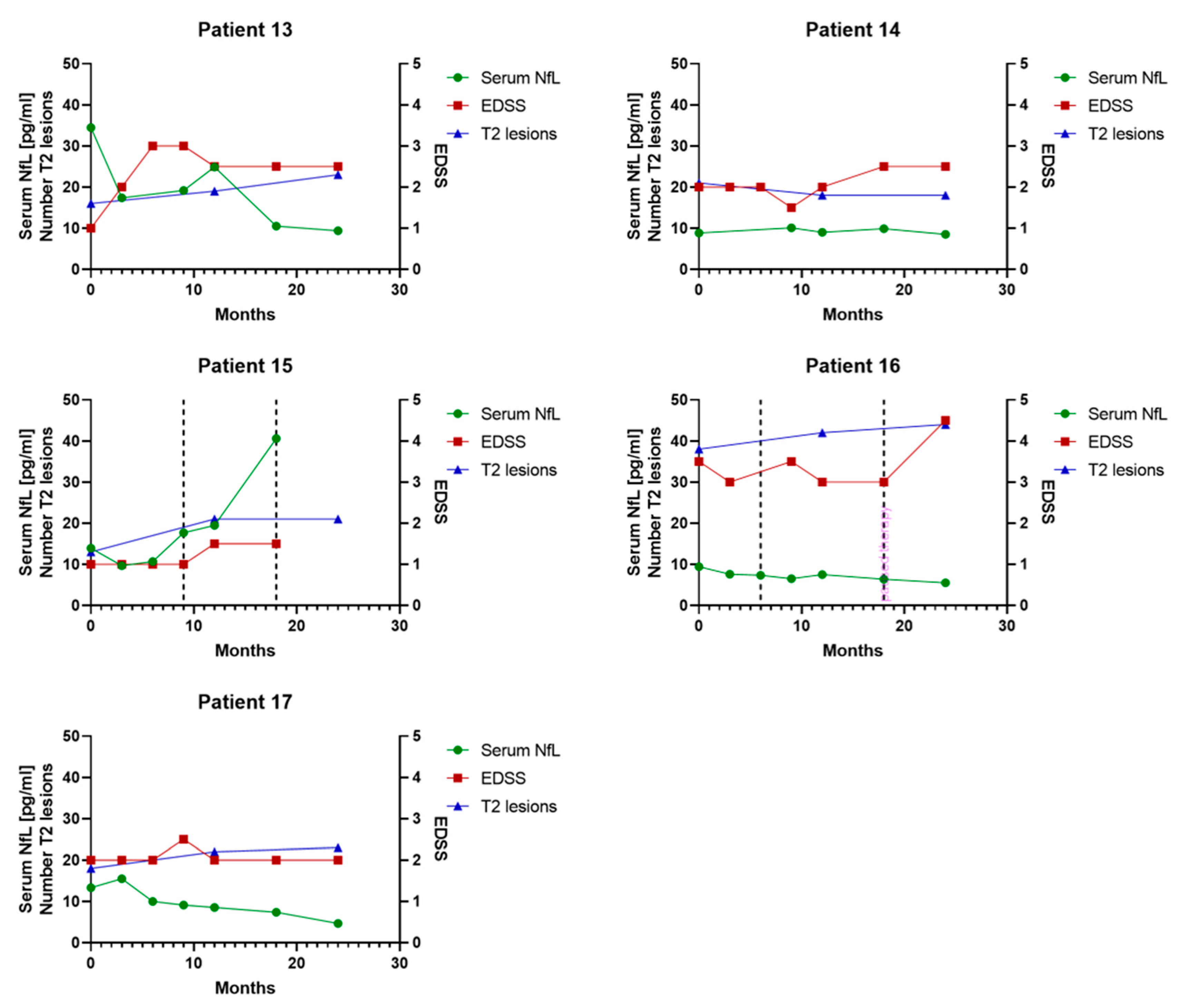
3.6. Individual Serum NfL Courses in Patients Treated with Glatiramer Acetate
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Compston, A.; Coles, A. Multiple sclerosis. Lancet 2002, 359, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compston, A.; Coles, A. Multiple Sclerosis. Lancet 2008, 372, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamm, C.P.; Uitdehaag, B.M.; Polman, C.H. Multiple sclerosis: Current knowledge and future outlook. Eur. Neurol. 2014, 72, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petzold, A.; Keir, G.; Green, A.J.E.; Giovannoni, G.; Thompson, E.J. A specific ELISA for measuring neurofilament heavy chain phosphoforms. J. Immunol. Methods 2003, 278, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, C.E.; Khalil, M. Neurofilaments as biomarkers in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2012, 18, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, A.; Rao, M.; Veeranna; Nixon, R.A. Neurofilaments and neurofilament proteins in health and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, a018309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaetani, L.; Blennow, K.; Calabresi, P.; Di Filippo, M.; Parnetti, L.; Zetterberg, H. Neurofilament light chain as a biomarker in neurological disorders. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhle, J.; Plattner, K.; Bestwick, J.P.; Lindberg, R.L.; Ramagopalan, S.V.; Norgren, N.; Nissim, A.; Malaspina, A.; Leppert, D.; Giovannoni, G.; et al. A comparative study of CSF neurofilament light and heavy chain protein in MS. Mult. Scler. J. 2013, 19, 1597–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Otto, M.; Piehl, F.; Sormani, M.P.; Gattringer, T.; Barro, C.; Kappos, L.; Comabella, M.; Fazekas, F.; et al. Neurofilaments as biomarkers in neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Salzer, J. CSF neurofilament light. Neurology 2016, 87, 1068–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brettschneider, J.; Petzold, A.; Junker, A.; Tumani, H. Axonal damage markers in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with clinically isolated syndrome improve predicting conversion to definite multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2006, 12, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrambide, G.; Espejo, C.; Eixarch, H.; Villar, L.M.; Alvarez-Cermeño, J.C.; Picón, C.; Kuhle, J.; Disanto, G.; Kappos, L.; Sastre-Garriga, J.; et al. Neurofilament light chain level is a weak risk factor for the development of MS. Neurology 2016, 87, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunnarsson, M.; Malmeström, C.; Axelsson, M.; Sundström, P.; Dahle, C.; Vrethem, M.; Olsson, T.P.; Piehl, F.; Norgren, N.; Rosengren, L.E.; et al. Axonal damage in relapsing multiple sclerosis is markedly reduced by natalizumab. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 69, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridel, C.; Van Wieringen, W.N.; Zetterberg, H.; Tijms, B.M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Alvarez-Cermeño, J.C.; Andreasson, U.; Axelsson, M.; Bäckström, D.C.; Bartos, A.; et al. Diagnostic value of cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light protein in neurology. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 1035–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaby, C.; Alcolea, D.; Carmona-Iragui, M.; Illán-Gala, I.; Morenas-Rodríguez, E.; Barroeta, I.; Altuna, M.; Estellés, T.; Santos-Santos, M.; Turon-Sans, J.; et al. Differential levels of Neurofilament Light protein in cerebrospinal fluid in patients with a wide range of neurodegenerative disorders. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, M.; Pirpamer, L.; Hofer, E.; Voortman, M.M.; Barro, C.; Leppert, D.; Benkert, P.; Ropele, S.; Enzinger, C.; Fazekas, F.; et al. Serum neurofilament light levels in normal aging and their association with morphologic brain changes. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissin, D.M.; Kan, C.W.; Campbell, T.G.; Howes, S.C.; Fournier, D.R.; Song, L.; Piech, T.; Patel, P.P.; Chang, L.; Rivnak, A.J.; et al. Single-molecule enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay detects serum proteins at subfemtomolar concentrations. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhle, J.; Barro, C.; Andreasson, U.; Derfuss, T.; Lindberg, R.; Sandelius, Å.; Liman, V.; Norgren, N.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H. Comparison of three analytical platforms for quantification of the neurofilament light chain in blood samples: ELISA, electrochemiluminescence immunoassay and Simoa. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2016, 54, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhle, J.; Barro, C.; Disanto, G.; Mathias, A.; Soneson, C.; Bonnier, G.; Yaldizli, Ö.; Regeniter, A.; Derfuss, T.; Canales, M.; et al. Serum neurofilament light chain in early relapsing remitting MS is increased and correlates with CSF levels and with MRI measures of disease severity. Mult. Scler. J. 2016, 22, 1550–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhle, J.; Nourbakhsh, B.; Grant, D.; Morant, S.; Barro, C.; Yaldizli, Ö.; Pelletier, D.; Giovannoni, G.; Waubant, E.; Gnanapavan, S. Serum neurofilament is associated with progression of brain atrophy and disability in early MS. Neurology 2017, 88, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siller, N.; Kuhle, J.; Muthuraman, M.; Barro, C.; Uphaus, T.; Groppa, S.; Kappos, L.; Zipp, F.; Bittner, S. Serum neurofilament light chain is a biomarker of acute and chronic neuronal damage in early multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2018, 25, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Disanto, G.; Barro, C.; Benkert, P.; Naegelin, Y.; Schädelin, S.; Giardiello, A.; Zecca, C.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Leppert, D.; et al. Serum Neurofilament light: A biomarker of neuronal damage in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 81, 857–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sormani, M.P.; Haering, D.A.; Kropshofer, H.; Leppert, D.; Kundu, U.; Barro, C.; Kappos, L.; Tomic, D.; Kuhle, J. Blood neurofilament light as a potential endpoint in Phase 2 studies in MS. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2019, 6, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sejbæk, T.; Nielsen, H.H.; Penner, N.; Plavina, T.; Mendoza, J.P.; Martin, N.A.; Elkjaer, M.L.; Ravnborg, M.H.; Illes, Z. Dimethyl fumarate decreases neurofilament light chain in CSF and blood of treatment naïve relapsing MS patients. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 1324–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thebault, S.; Abdoli, M.; Fereshtehnejad, S.-M.; Tessier, D.; Tabard-Cossa, V.; Freedman, M.S. Serum neurofilament light chain predicts long term clinical outcomes in multiple sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akgün, K.; Kretschmann, N.; Haase, R.; Proschmann, U.; Kitzler, H.H.; Reichmann, H.; Ziemssen, T. Profiling individual clinical responses by high-frequency serum neurofilament assessment in MS. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 6, e555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, J.-W.; Kim, Y.; Kim, G.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, H.J. Longitudinal analysis of serum neurofilament light chain: A potential therapeutic monitoring biomarker for multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2019, 26, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, C.E.; Petzold, A.; Bennett, J.L.; Berven, F.S.; Brundin, L.; Comabella, M.; Franciotta, D.; Frederiksen, J.L.; Fleming, J.O.; Furlan, R.; et al. A consensus protocol for the standardization of cerebrospinal fluid collection and biobanking. Neurology 2009, 73, 1914–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumani, H.; Kassubek, J.; Hijazi, M.; Lehmensiek, V.; Unrath, A.; Süssmuth, S.; Lauda, F.; Kapfer, T.; Fang, L.; Senel, M.; et al. Patterns of TH1/TH2 cytokines predict clinical response in multiple sclerosis patients treated with glatiramer acetate. Eur. Neurol. 2011, 65, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novakova, L.; Zetterberg, H.; Sundström, P.; Axelsson, M.; Khademi, M.; Gunnarsson, M.; Malmeström, C.; Svenningsson, A.; Olsson, T.; Piehl, F.; et al. Monitoring disease activity in multiple sclerosis using serum neurofilament light protein. Neurology 2017, 89, 2230–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhak, A.; Huss, A.; Kassubek, J.; Tumani, H.; Otto, M. Serum GFAP as a biomarker for disease severity in multiple sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Högel, H.; Rissanen, E.; Barro, C.; Matilainen, M.; Nylund, M.; Kuhle, J.; Airas, L. Serum glial fibrillary acidic protein correlates with multiple sclerosis disease severity. Mult. Scler. J. 2018, 26, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnen, A.; Bürkner, P.-C.; Landmeyer, N.C.; Ambrosius, B.; Calabrese, P.; Motte, J.; Hessler, N.; Antony, G.; König, I.R.; Klotz, L.; et al. Can we predict cognitive decline after initial diagnosis of multiple sclerosis? Results from the German National early MS cohort (KKNMS). J. Neurol. 2018, 266, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Håkansson, I.; Tisell, A.; Cassel, P.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Lundberg, P.; Dahle, C.; Vrethem, M.; Ernerudh, J. Neurofilament levels, disease activity and brain volume during follow-up in multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittner, S.; Steffen, F.; Uphaus, T.; Muthuraman, M.; Fleischer, V.; Salmen, A.; Luessi, F.; Berthele, A.; Klotz, L.; Meuth, S.G.; et al. Clinical implications of serum neurofilament in newly diagnosed MS patients: A longitudinal multicentre cohort study. EBioMedicine 2020, 56, 102807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Median Values with IQR, n = 34 |
|---|---|
| Age | 33 (29–40) |
| EDSS baseline | 1.5 (1.0–2.0) |
| Serum NfL baseline (pg/mL) | 10.2 (8.4–14.7) |
| Relapse within 12 months (n) | 14 |
| Relapse within 24 months (n) | 16 |
| Treatment after baseline | |
| Glatiramer acetate | 20 |
| Interferon-beta | 12 |
| No disease-modifying therapy | 2 |
| Baseline | 3 Months | 6 Months | 9 Months | 12 Months | 18 Months | 24 Months | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical assessment | 34 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 34 |
| EDSS | 31 | 30 | 27 | 30 | 32 | 32 | 32 |
| Serum NfL | 34 | 29 | 29 | 32 | 33 | 31 | 24 |
| MRI (T2 lesion load) | 17 | 17 | 17 | ||||
| Serum cytokine profile | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 |
| PASAT | 32 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 32 | 30 | 31 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huss, A.; Senel, M.; Abdelhak, A.; Mayer, B.; Kassubek, J.; Ludolph, A.C.; Otto, M.; Tumani, H. Longitudinal Serum Neurofilament Levels of Multiple Sclerosis Patients Before and After Treatment with First-Line Immunomodulatory Therapies. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8090312
Huss A, Senel M, Abdelhak A, Mayer B, Kassubek J, Ludolph AC, Otto M, Tumani H. Longitudinal Serum Neurofilament Levels of Multiple Sclerosis Patients Before and After Treatment with First-Line Immunomodulatory Therapies. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(9):312. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8090312
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuss, André, Makbule Senel, Ahmed Abdelhak, Benjamin Mayer, Jan Kassubek, Albert C. Ludolph, Markus Otto, and Hayrettin Tumani. 2020. "Longitudinal Serum Neurofilament Levels of Multiple Sclerosis Patients Before and After Treatment with First-Line Immunomodulatory Therapies" Biomedicines 8, no. 9: 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8090312
APA StyleHuss, A., Senel, M., Abdelhak, A., Mayer, B., Kassubek, J., Ludolph, A. C., Otto, M., & Tumani, H. (2020). Longitudinal Serum Neurofilament Levels of Multiple Sclerosis Patients Before and After Treatment with First-Line Immunomodulatory Therapies. Biomedicines, 8(9), 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8090312





