Reversal of Hyperglycemia and Suppression of Type 1 Diabetes in the NOD Mouse with Apoptotic DNA Immunotherapy™ (ADi™), ADi-100
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. ADi-100: Plasmid DNA Construct
2.2. Animals
2.3. Dendritic Cell Isolation and Characterization
2.4. GAD-Specific T Lymphocyte Proliferation
2.5. Diabetes Studies in NOD Mice
2.6. Immunohistochemistry
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
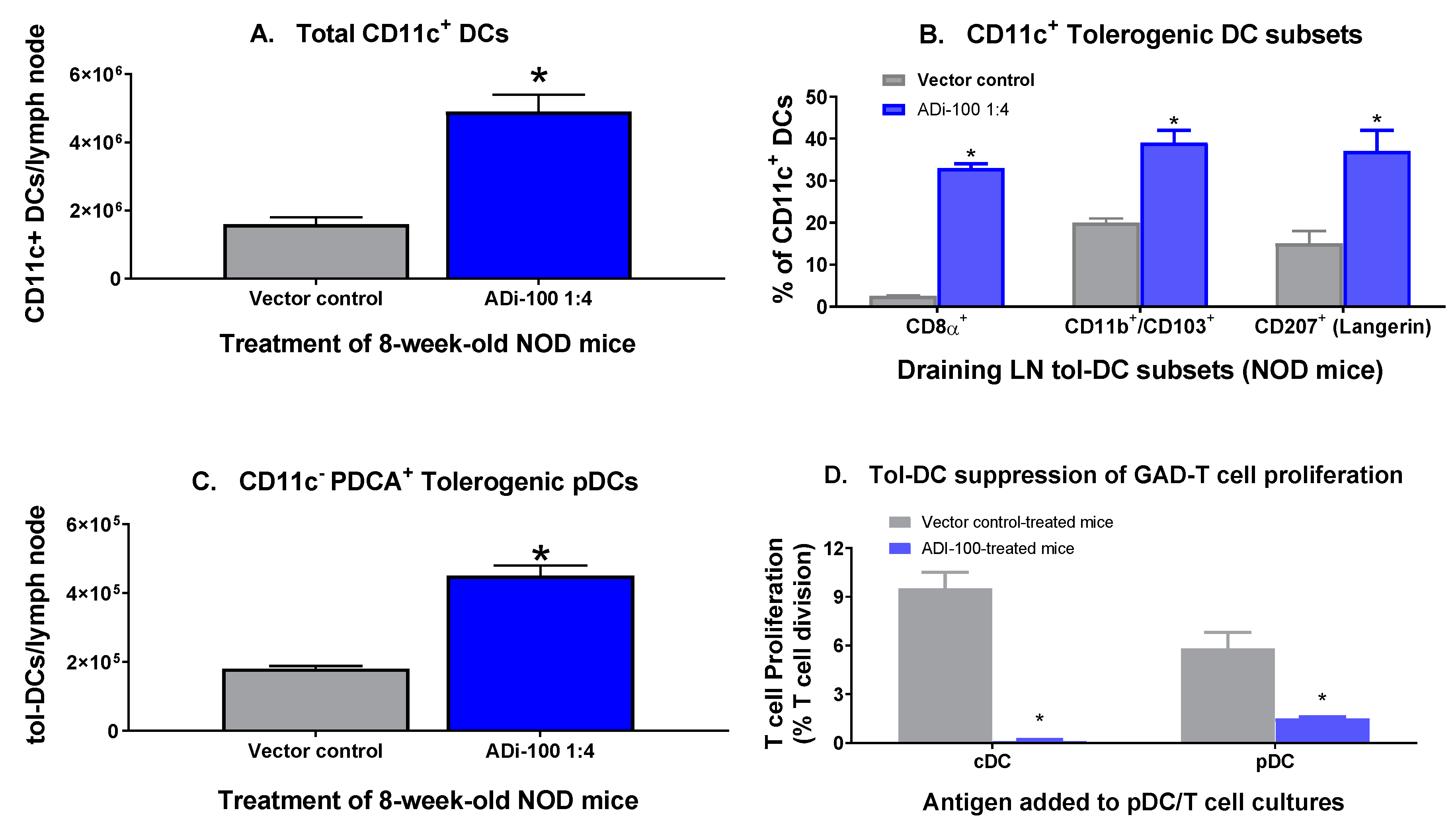
3.1. Tol-DC Subset Analysis in Draining Lymph Nodes after ADi-100 Treatment
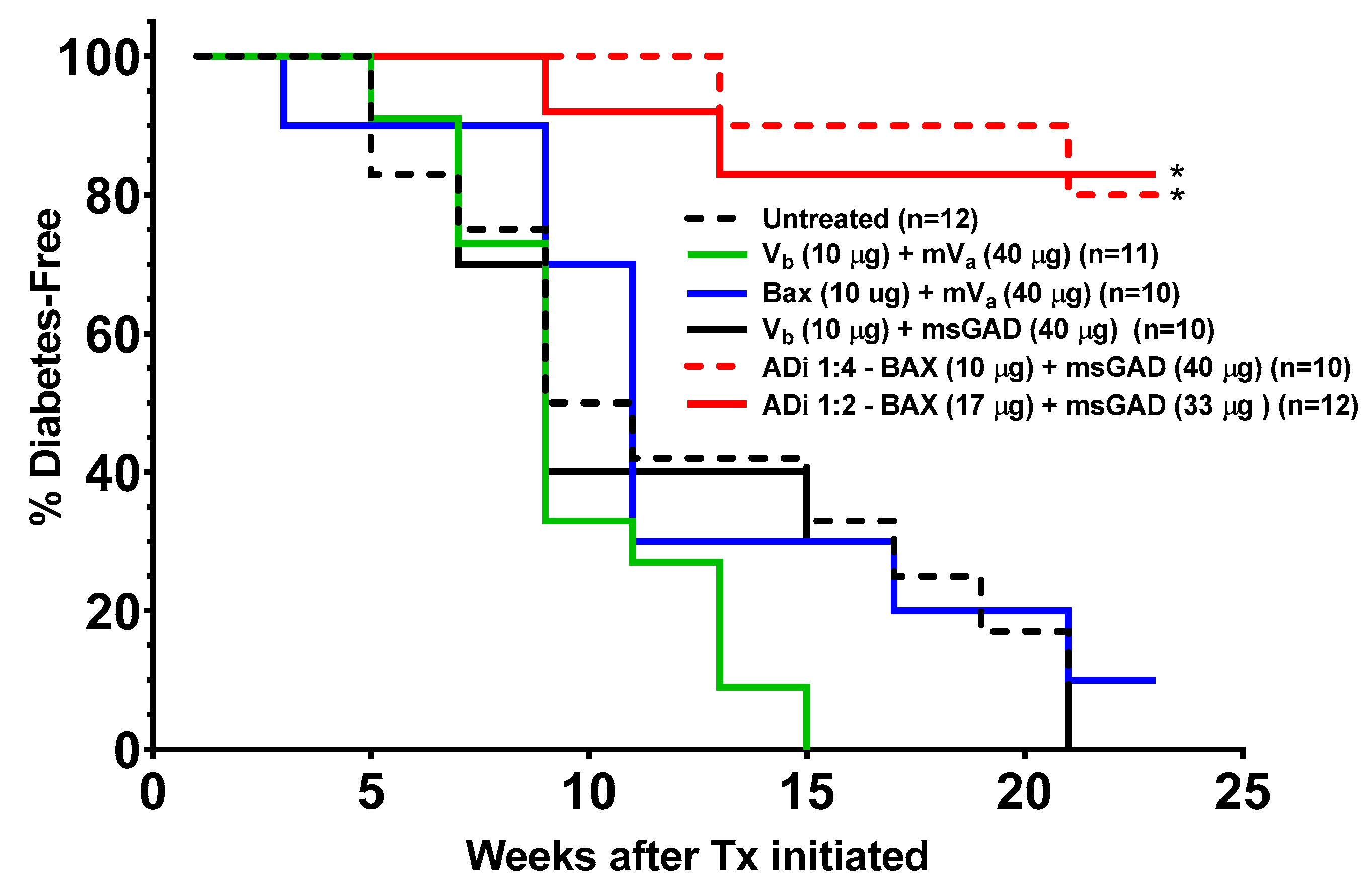
3.2. Efficacy of ADi-100 Containing Increased BAX Plasmid Content to Reverse Hyperglycemia in Mildly Hyperglycemic NOD Mice
3.3. Increased BAX Plasmid Content in the ADi-100 1:2 Formulation Resulted in Greater Efficacy in a Later Stage of Autoimmune Diabetes (i.e., Highly Hyperglycemia)
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buckner, J.H.; Nepom, G.T. Obstacles and opportunities for targeting the effector T cell response in type 1 diabetes. J. Autoimmun. 2016, 71, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hull, C.M.; Peakman, M.; Tree, T.I.M. Regulatory T cell dysfunction in type 1 diabetes: what’s broken and how can we fix it? Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1839–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.F.; Escher, A. DNA vaccines for transplantation. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2010, 10, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getts, D.R.; McCarthy, D.P.; Miller, S.D. Exploiting apoptosis for therapeutic tolerance induction. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 5341–5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, A.J.; Kontos, S.; Diaceri, G.; Quaglia-Thermes, X.; Hubbell, J.A. Memory of tolerance and induction of regulatory T cells by erythrocyte-targeted antigens. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pishesha, N.; Bilate, A.M.; Wibowo, M.C.; Huang, N.J.; Li, Z.; Dhesycka, R.; Bousbaine, D.; Li, H.; Patterson, H.C.; Dougan, S.K.; et al. Engineered erythrocytes covalently linked to antigenic peptides can protect against autoimmune disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 3157–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Ojogho, O.; Franco, E.; Baron, P.; Iwaki, Y.; Escher, A. Pro-apoptotic DNA vaccination ameliorates new onset of autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice and induces foxp3+ regulatory T cells in vitro. Vaccine 2006, 24, 5036–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Chen, J.; Hattori, M.; Franco, E.; Zuppan, C.; Ojogho, O.; Iwaki, Y.; Escher, A. A therapeutic DNA vaccination strategy for autoimmunity and transplantation. Vaccine 2010, 28, 1897–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.F.; Hough, J.; Henderson, D.; Escher, A. Co-delivery of pro-apoptotic BAX with a DNA vaccine recruits dendritic cells and promotes efficacy of autoimmune diabetes prevention in mice. Vaccine 2004, 22, 1751–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, L.; Taylor, C.; Whiting, C.C.; Fathman, C.G. Diminished adenosine A1 receptor expression in pancreatic alpha-cells may contribute to the pathology of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2013, 62, 4208–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopp, A.K.; Rupp, A.; Lukacs-Kornek, V. Self-antigen presentation by dendritic cells in autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takenaka, M.C.; Quintana, F.J. Tolerogenic dendritic cells. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathews, C.E.; Xue, S.; Posgai, A.; Lightfoot, Y.L.; Li, X.; Lin, A.; Wasserfall, C.; Haller, M.J.; Schatz, D.; Atkinson, M.A. Acute Versus Progressive Onset of Diabetes in NOD Mice: Potential Implications for Therapeutic Interventions in Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes 2015, 64, 3885–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoda, L.K.; Young, D.L.; Ramanujan, S.; Whiting, C.C.; Atkinson, M.A.; Bluestone, J.A.; Eisenbarth, G.S.; Mathis, D.; Rossini, A.A.; Campbell, S.E.; et al. A comprehensive review of interventions in the NOD mouse and implications for translation. Immunity 2005, 23, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, Y.M.; Lewis, J.S.; Carstens, M.R.; Campbell-Thompson, M.; Wasserfall, C.H.; Atkinson, M.A.; Keselowsky, B.G. A combination hydrogel microparticle-based vaccine prevents type 1 diabetes in non-obese diabetic mice. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solvason, N.; Lou, Y.P.; Peters, W.; Evans, E.; Martinez, J.; Ramirez, U.; Ocampo, A.; Yun, R.; Ahmad, S.; Liu, E.; et al. Improved efficacy of a tolerizing DNA vaccine for reversal of hyperglycemia through enhancement of gene expression and localization to intracellular sites. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 8298–8307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roep, B.O.; Solvason, N.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Abreu, J.R.F.; Harrison, L.C.; Eisenbarth, G.S.; Yu, L.; Leviten, M.; Hagopian, W.A.; Buse, J.B.; et al. Plasmid-encoded proinsulin preserves C-peptide while specifically reducing proinsulin-specific CD8(+) T cells in type 1 diabetes. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 191ra182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, B.; Selck, C.; Chee, J.; Jhala, G.; Kay, T.W. Analysis of antigen specific T cells in diabetes - Lessons from pre-clinical studies and early clinical trials. J. Autoimmun. 2016, 71, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Nasr, M.; D’Addio, F.; Usuelli, V.; Tezza, S.; Abdi, R.; Fiorina, P. The rise, fall, and resurgence of immunotherapy in type 1 diabetes. Pharm. Res. 2015, 98, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takiishi, T.; Cook, D.P.; Korf, H.; Sebastiani, G.; Mancarella, F.; Cunha, J.P.; Wasserfall, C.; Casares, N.; Lasarte, J.J.; Steidler, L.; et al. Reversal of Diabetes in NOD Mice by Clinical-Grade Proinsulin and IL-10-Secreting Lactococcus lactis in Combination With Low-Dose Anti-CD3 Depends on the Induction of Foxp3-Positive T Cells. Diabetes 2017, 66, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, R.G.; Pagni, P.P.; Kupfer, T.; Wasserfall, C.H.; Deng, S.; Posgai, A.; Manenkova, Y.; Bel Hani, A.; Straub, L.; Bernstein, P.; et al. A Preclinical Consortium Approach for Assessing the Efficacy of Combined Anti-CD3 Plus IL-1 Blockade in Reversing New-Onset Autoimmune Diabetes in NOD Mice. Diabetes 2016, 65, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herold, K.C.; Bundy, B.N.; Long, S.A.; Bluestone, J.A.; DiMeglio, L.A.; Dufort, M.J.; Gitelman, S.E.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Krischer, J.P.; Linsley, P.S.; et al. An Anti-CD3 Antibody, Teplizumab, in Relatives at Risk for Type 1 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Stoica-Nazarov, C.; Surls, J.; Kehl, M.; Bona, C.; Olsen, C.; Brumeanu, T.D.; Casares, S. Reversal of type 1 diabetes by a new MHC II-peptide chimera: “Single-epitope-mediated suppression” to stabilize a polyclonal autoimmune T-cell process. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 2277–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Belle, T.L.; Coppieters, K.T.; von Herrath, M.G. Type 1 diabetes: Etiology, immunology, and therapeutic strategies. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 79–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insel, R.A.; Dunne, J.L.; Atkinson, M.A.; Chiang, J.L.; Dabelea, D.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Greenbaum, C.J.; Herold, K.C.; Krischer, J.P.; Lernmark, A.; et al. Staging presymptomatic type 1 diabetes: A scientific statement of JDRF, the Endocrine Society, and the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1964–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skyler, J.S. Prevention and reversal of type 1 diabetes-past challenges and future opportunities. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agardh, C.D.; Cilio, C.M.; Lethagen, A.; Lynch, K.; Leslie, R.D.; Palmer, M.; Harris, R.A.; Robertson, J.A.; Lernmark, A. Clinical evidence for the safety of GAD65 immunomodulation in adult-onset autoimmune diabetes. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2005, 19, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryden, A.K.; Wesley, J.D.; Coppieters, K.T.; Von Herrath, M.G. Non-antigenic and antigenic interventions in type 1 diabetes. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2014, 10, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Casares, X.; Tsai, S.; Huang, C.; Santamaria, P. Antigen-specific therapeutic approaches in Type 1 diabetes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a007773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Herrath, M.; Peakman, M.; Roep, B. Progress in immune-based therapies for type 1 diabetes. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 172, 186–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keijzer, C.; van der Zee, R.; van Eden, W.; Broere, F. Treg inducing adjuvants for therapeutic vaccination against chronic inflammatory diseases. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludvigsson, J.; Krisky, D.; Casas, R.; Battelino, T.; Castano, L.; Greening, J.; Kordonouri, O.; Otonkoski, T.; Pozzilli, P.; Robert, J.J.; et al. GAD65 antigen therapy in recently diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wherrett, D.K.; Bundy, B.; Becker, D.J.; DiMeglio, L.A.; Gitelman, S.E.; Goland, R.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Greenbaum, C.J.; Herold, K.C.; Marks, J.B.; et al. Antigen-based therapy with glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) vaccine in patients with recent-onset type 1 diabetes: A randomised double-blind trial. Lancet 2011, 378, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, P.; Santamaria, P. Nanoparticle-based autoimmune disease therapy. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 160, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannoukakis, N.; Trucco, M. Dendritic cell therapy for Type 1 diabetes suppression. Immunotherapy 2012, 4, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seay, H.R.; Putnam, A.L.; Cserny, J.; Posgai, A.L.; Rosenau, E.H.; Wingard, J.R.; Girard, K.F.; Kraus, M.; Lares, A.P.; Brown, H.L.; et al. Expansion of Human Tregs from Cryopreserved Umbilical Cord Blood for GMP-Compliant Autologous Adoptive Cell Transfer Therapy. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2017, 4, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, S.; Gysemans, C.; Takiishi, T.; Korf, H.; Spagnuolo, I.; Sebastiani, G.; Van Huynegem, K.; Steidler, L.; Caluwaerts, S.; Demetter, P.; et al. Oral delivery of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD)-65 and IL10 by Lactococcus lactis reverses diabetes in recent-onset NOD mice. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2876–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwell, B.L.; Antunez, L.; Sullivan, B.P.; Thati, S.; Sestak, J.O.; Berkland, C. Multivalent nanomaterials: Learning from vaccines and progressing to antigen-specific immunotherapies. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 346–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontos, S.; Kourtis, I.C.; Dane, K.Y.; Hubbell, J.A. Engineering antigens for in situ erythrocyte binding induces T-cell deletion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E60–E68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutterotti, A.; Yousef, S.; Sputtek, A.; Sturner, K.H.; Stellmann, J.P.; Breiden, P.; Reinhardt, S.; Schulze, C.; Bester, M.; Heesen, C.; et al. Antigen-specific tolerance by autologous myelin peptide-coupled cells: A phase 1 trial in multiple sclerosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 188ra175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Fernandez, S.; Pujol-Autonell, I.; Brianso, F.; Perna-Barrull, D.; Cano-Sarabia, M.; Garcia-Jimeno, S.; Villalba, A.; Sanchez, A.; Aguilera, E.; Vazquez, F.; et al. Phosphatidylserine-Liposomes Promote Tolerogenic Features on Dendritic Cells in Human Type 1 Diabetes by Apoptotic Mimicry. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Mouse ID | mBG on Tx Day 0 (mg/dL) | Age (Days) on Day 0 | Occurrences ≥ 180 mg/dL Prior to Day 0 | Occurrences ≥ 180 mg/dL from Day 1–35 | Age (days) at T1D a | Days from Day 0 to T1D | Islet Insulin Staining c | mBG at Day 35 (Study Termination) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADi-100 1:4 Tx group | ||||||||
| 1 | 245 | 175 | 1 | 35 | 186 | 11 | negative | ≥600 |
| 2 | 230 | 91 | 0 | 35 | 93 | 2 | n/a | ≥600 |
| 3 | 255 | 111 | 0 | 35 | 116 | 5 | negative | ≥600 |
| 4 | 245 | 109 | 0 | 29 | 126 | 2 | negative | ≥600 |
| 5 | 301 | 279 | 3 | 35 | 279 | 0 | negative | ≥600 |
| mean | 255b | 153 | 34 b | 160 | 4 | |||
| SEM | 12 | 35 | 1 | 34 | 2 | |||
| 6 | 217 | 181 | 2 | 15 | n.d. | n/a | ||
| 7 | 197 | 270 | 0 | 15 | n.d. | negative | 184 | |
| 8 | 192 | 231 | 6 | 16 | n.d. | negative | 199 | |
| 9 | 180 | 222 | 1 | 11 | n.d. | negative | 183 | |
| 10 | 213 | 146 | 2 | 4 | n.d. | n/a | ||
| mean | 200 | 210 | 12 | |||||
| SEM | 7 | 21 | 2 | |||||
| ADi-100 1:2 Tx group | ||||||||
| 1 | 284 | 191 | 1 | 27 | 209 | 18 | negative | 511 |
| 2 | 214 | 139 | 2 | 27 | 168 | 29 | negative | 351 |
| 3 | 211 | 243 | 2 | 20 | n.d. | + | 150 | |
| 4 | 185 | 179 | 1 | 7 | n.d. | + | 133 | |
| 5 | 286 | 192 | 0 | 6 | n.d. | + | 139 | |
| 6 | 212 | 159 | 0 | 13 | n.d. | + | 174 | |
| 7 | 202 | 197 | 0 | 3 | n.d. | n/a | 135 | |
| 8 | 202 | 180 | 1 | 3 | n.d. | + | 130 | |
| 9 | 196 | 188 | 0 | 0 | n.d. | n/a | 151 | |
| mean | 213 | 191 | 7.4 | |||||
| SEM | 13 | 10 | 2.6 | |||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alleva, D.G.; Rezaee, M.; Yip, L.; Ren, G.; Rosenberg, J.; Concepcion, W.; Escher, A.; Shabahang, S.; Thakor, A.S. Reversal of Hyperglycemia and Suppression of Type 1 Diabetes in the NOD Mouse with Apoptotic DNA Immunotherapy™ (ADi™), ADi-100. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8030053
Alleva DG, Rezaee M, Yip L, Ren G, Rosenberg J, Concepcion W, Escher A, Shabahang S, Thakor AS. Reversal of Hyperglycemia and Suppression of Type 1 Diabetes in the NOD Mouse with Apoptotic DNA Immunotherapy™ (ADi™), ADi-100. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(3):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8030053
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlleva, David G., Melika Rezaee, Linda Yip, Gang Ren, Jarrett Rosenberg, Waldo Concepcion, Alan Escher, Shahrokh Shabahang, and Avnesh S. Thakor. 2020. "Reversal of Hyperglycemia and Suppression of Type 1 Diabetes in the NOD Mouse with Apoptotic DNA Immunotherapy™ (ADi™), ADi-100" Biomedicines 8, no. 3: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8030053
APA StyleAlleva, D. G., Rezaee, M., Yip, L., Ren, G., Rosenberg, J., Concepcion, W., Escher, A., Shabahang, S., & Thakor, A. S. (2020). Reversal of Hyperglycemia and Suppression of Type 1 Diabetes in the NOD Mouse with Apoptotic DNA Immunotherapy™ (ADi™), ADi-100. Biomedicines, 8(3), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8030053







