Physiological Signaling and Structure of the HGF Receptor MET
Abstract
:1. Background Introduction
2. HGF
3. MET
3.1. Gene and Transcript
3.2. MET Structure
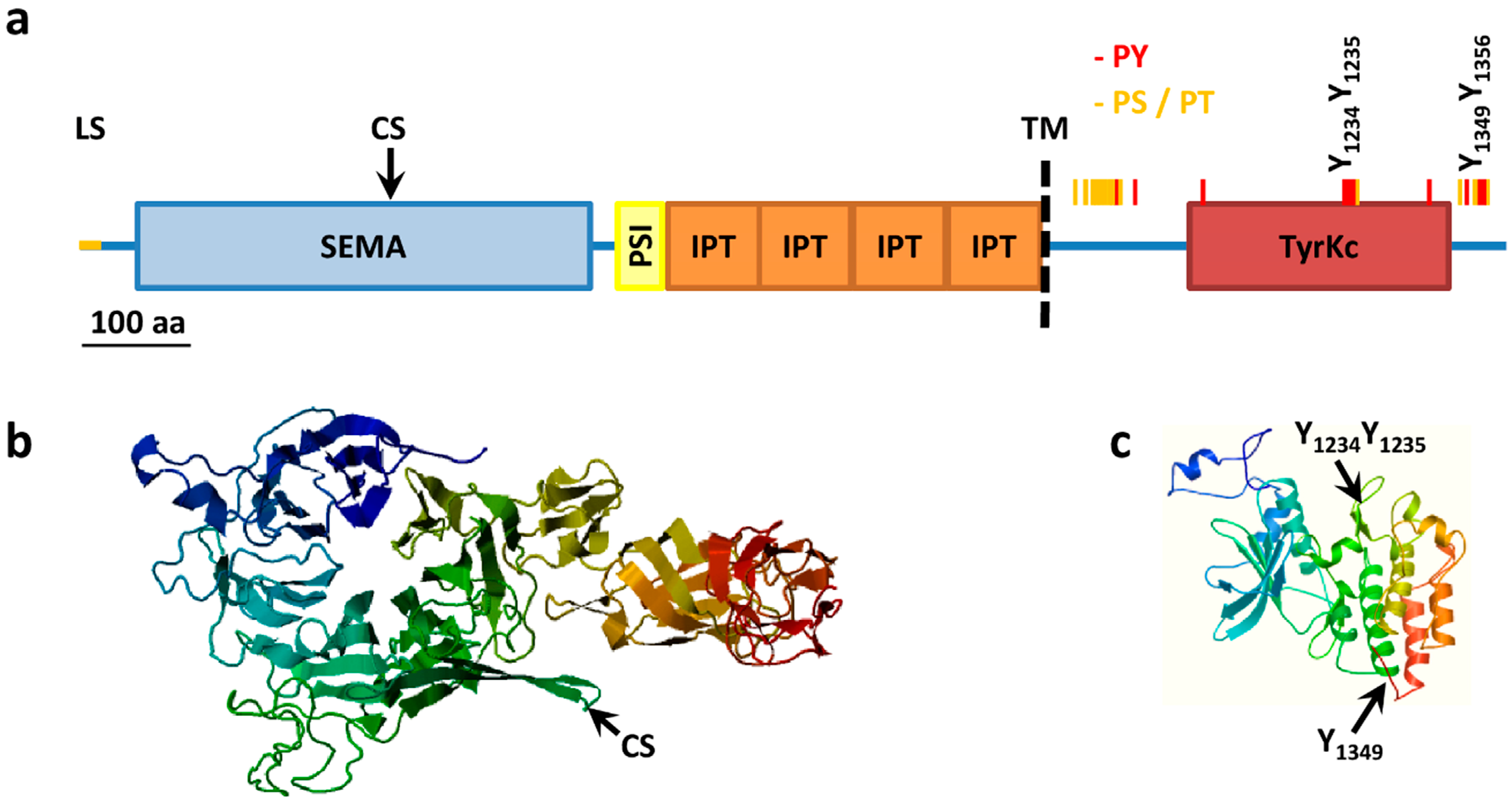
3.3. MET Activation and Signaling
- (1)
- (2)
- (3)
| SS | MS | aa | Homo sapiens | aa | Mus musculus | aa | Rattus norvegicus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 6 | S966-p | KQIkDLGsELVRyDA | S964 | RKHKDLGSELVRYDA | S967 | RKHKDLGSELVRYDA |
| 0 | 5 | Y971-p | LGsELVRyDARVHtP | Y969 | LGSELVRYDARVHtP | Y972 | LGSELVRYDARVHTP |
| 0 | 6 | T977-p | RyDARVHtPHLDRLV | T975-p | RYDARVHtPHLDRLV | T978 | RYDARVHTPHLDRLV |
| 6 | 0 | S985-p | PHLDRLVsARsVsPt | S983-p | PHLDRLVsARSVsPT | S986-p | PHLDRLVsARSVSPT |
| 0 | 19 | S988-p | DRLVsARsVsPttEM | S986 | DRLVsARSVsPTTEM | S989 | DRLVsARSVSPTTEM |
| 0 | 32 | S990-p | LVsARsVsPttEMVs | S988-p | LVsARSVsPTTEMVs | S991 | LVsARSVSPTTEMVS |
| 0 | 11 | T992-p | sARsVsPttEMVsNE | T990 | sARSVsPTTEMVsNE | T993 | sARSVSPTTEMVSNE |
| 0 | 7 | T993-p | ARsVsPttEMVsNEs | T991 | ARSVsPTTEMVsNEs | T994 | ARSVSPTTEMVSNES |
| 0 | 20 | S997-p | sPttEMVsNEsVDyR | S995-p | sPTTEMVsNEsVDyR | S998 | SPTTEMVSNESVDYR |
| 1 | 43 | S1000-p | tEMVsNEsVDyRAtF | S998-p | TEMVsNEsVDyRATF | S1001 | TEMVSNESVDYRATF |
| 11 | 361 | Y1003-p | VsNEsVDyRAtFPED | Y1001-p | VsNEsVDyRATFPED | Y1004 | VSNESVDYRATFPED |
| 0 | 9 | T1006-p | EsVDyRAtFPEDQFP | T1004 | EsVDyRATFPEDQFP | T1007 | ESVDYRATFPEDQFP |
| 0 | 15 | Y1026-p | GsCRQVQyPLTDMSP | Y1024 | GACRQVQYPLTDLSP | Y1027 | GACRQVQYLLTDLSP |
| 0 | 31 | Y1093-p | RGHFGCVyHGtLLDN | Y1091 | RGHFGCVYHGTLLDN | Y1094 | RGHFGCVYHGTLLDS |
| 4 | 112 | Y1230-p | FGLARDMyDkEyysV | Y1228-p | FGLArDMyDKEyysV | Y1231 | FGLARDMYDKEyySV |
| 39 * | 735 | Y1234-p | RDMyDkEyysVHNkt | Y1232-p | rDMyDKEyysVHNKt | Y1235-p | RDMYDKEyySVHNKT |
| 38 * | 443 | Y1235-p | DMyDkEyysVHNktG | Y1233-p | DMyDKEyysVHNKtG | Y1236-p | DMYDKEyySVHNKTG |
| 1 | 177 | S1236-p | MyDkEyysVHNktGA | S1234-p | MyDKEyysVHNKtGA | S1237 | MYDKEyySVHNKTGA |
| 0 | 5 | T1241-p | yysVHNktGAKLPVK | T1239-p | yysVHNKtGAKLPVK | T1242 | yySVHNKTGAKLPVK |
| 6 | 5 | Y1313-p | EyCPDPLyEVMLkCW | Y1311-p | EYCPDALyEVMLKCW | Y1314 | EYCPDALYEVMLKCW |
| 0 | 6 | T1343-p | RISAIFstFIGEHyV | T1341 | RISSIFSTFIGEHyV | T1344 | RISSIFSTFIGEHYV |
| 24 * | 122 | Y1349-p | stFIGEHyVHVNAty | Y1347-p | STFIGEHyVHVNATy | Y1350 | STFIGEHYVHVNATY |
| 0 | 40 | T1355-p | HyVHVNAtyVNVKCV | T1353 | HyVHVNATyVNVKCV | T1356 | HYVHVNATYVNVKCV |
| 22 * | 120 | Y1356-p | yVHVNAtyVNVKCVA | Y1354-p | yVHVNATyVNVKCVA | Y1357 | YVHVNATYVNVKCVA |
| 7 | 116 | Y1365-p | NVKCVAPyPsLLssE | Y1363-p | NVKCVAPyPSLLPSQ | Y1366 | NVKCVAPYPSLLPSQ |
| 0 | 8 | S1367-p | KCVAPyPsLLssEDN | S1365 | KCVAPyPSLLPSQDN | S1368 | KCVAPYPSLLPSQDN |
- FAK, the focal adhesion kinase, which lies at the crossroad between integrin and growth factor signaling. The FAK Y194 is also directly phosphorylated by MET contributing to activation [103]. Once activated FAK induces downstream GRB2 binding and MAPK signaling, critically controlling the cytoskeleton [104];
- αDGK (Diacylglycerol kinase alpha), which phosphorylates DG to PA. αDGK is phosphorylated by SRC on Y335 and its activity is crucial for HGF-induced cell motility by promoting PA production at ruffling sites. This drives local recruitment of PA binding proteins involved in migration such as the Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor (RhoGDI) and atypical PKC [105,106,107,108] as well as integrin recycling such as the Rab11 interactor RCP [109].
- MET (Y1003/Y1230/Y1234/Y1235);
- phosphoproteins that regulate transcriptional control: STAT3 (S727) and CREB (S133);
- cell cycle G1/S checkpoint: RB (S612), RB1 (S780);
- cell survival and apoptosis: AKT1 (S473/T308), JNK (T183/Y185);
- cell proliferation and differentiation: MEK1/2 (S221/S225), ERK1/2 (T185/Y187), ERK1/2 (T202/Y204);
- stress and inflammatory response to cytokines and growth factors: MEK3/6 (S189/S207), p38α (T180/Y182); JNK (T183/Y185);
- Cytoskeletal functions: FAK (Y576/S722/S910), adducin-α (S724) and adducin-γ (S662).
3.4. Biological Effects of MET Triggering
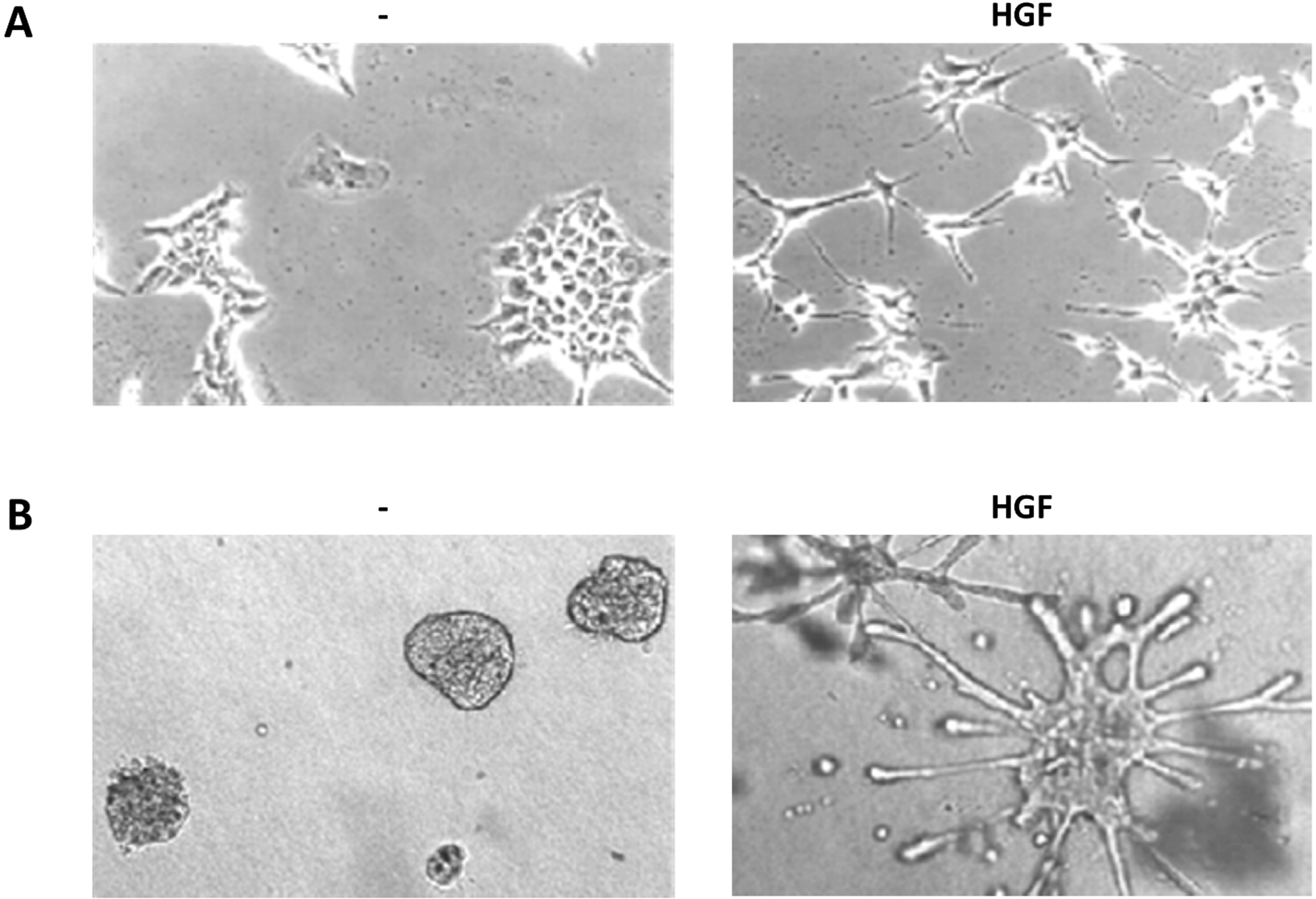
3.4.1. Scattering
3.4.2. Branching Morphogenesis
3.4.3. Balance between Proliferation and Apoptosis
3.5. Negative Regulation of MET Signaling
4. Signaling Integration by Met Multi-Receptor Complexes
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Abbreviations
| Short name (used in the manuscript) | Full name (Uniprot) |
| HGF | Hepatocyte growth factor |
| MET | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor |
| MSP | Hepatocyte growth factor-like protein |
| RON | Macrophage-stimulating protein receptor |
| CD44v3 | CD44 antigen including variant exon 3 |
| CD44v6 | CD44 antigen including variant exon 6 |
| InlB | Internalin B |
| GRB2 | growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 |
| PLCγ | 1-phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate phosphodiesterase gamma |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase |
| SHP-2 | tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 11 |
| SHC | SHC-transforming protein |
| GAB1 | GRB2-associated binding protein |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| SOS | Son of sevenless homolog |
| NCK | cytoplasmic protein NCK |
| CRK-I and CRK-II | adapter molecule crk |
| C3G | Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor 1 |
| N-WASP | Neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein |
| PKD | Serine/threonine-protein kinase D |
| AKT | RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase |
| PKC | Protein kinase C |
| PLD | Phospholipase D |
| PAP | Phosphatidic acid phosphohydrolase |
| JUN | Transcription factor AP-1 |
| FOS | Proto-oncogene c-Fos |
| SRC | proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase SRC |
| FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn |
| FAK | Focal adhesion kinase |
| αDGK | Diacylglycerol kinase alpha |
| RhoGDI | Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor |
| RCP | Rab11 family-interacting protein 1 |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| SHIP-1 | SH2 domain-containing inositol 5-phosphatases 1 |
| SHIP-2 | SH2 domain-containing inositol 5-phosphatases 2 |
| PLA2 | Phospholipase A2 |
| COX-2 | Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 |
| CREB | Cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein |
| RB | Retinoblastoma-associated protein |
| JNK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 |
| MEK-1 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 |
| MEK-2 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 |
| ERK1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 |
| ERK2 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 |
| MEK3 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3 |
| MEK6 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 |
| PKR | Protein kinase R |
| p38α | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 |
| CDK1 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 |
| Snail | Zinc finger protein SNAI1 |
| Slug | Zinc finger protein SNAI2 |
| Egr1 | early growth response protein 1 |
| Elk-1 | ETS domain-containing protein Elk-1 |
| S6K | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase beta |
| GSK3 | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 |
| Lef | Lymphoid enhancer-binding factor |
| PAK | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 1 |
| ROCK | Rho-associated protein kinase |
| MT1-MMP | Matrix metalloproteinase-14 |
| BAD | Bcl2-associated agonist of cell death |
| Bcl-xL | Bcl-2-like protein 1 (long isoform) |
| Mcl-1 | Induced myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein Mcl-1 |
| mTOR | Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR |
| Mdm2 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Mdm2 |
| TP53 | Cellular tumor antigen p53 |
| MYC | Myc proto-oncogene protein |
| 4E-BP1 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 |
| p16-INK4a | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A |
| p21 | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 |
| PTP-1B | Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 1 |
| RPTP-β | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase B |
| LAR | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase F |
| CD148 | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase eta |
| Cbl | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CBL |
| CIN85 | SH3 domain-containing kinase-binding protein 1 |
| Hrs | Hepatocyte growth factor-regulated tyrosine kinase substrate |
| Stam | Signal transducing adapter molecule |
| IRS1 | Insulin receptor substrate 1 |
| IRS2 | Insulin receptor substrate 2 |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| HER2 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 |
| HER3 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-3 |
| RET | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret |
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nakamura, T.; Teramoto, H.; Ichihara, A. Purification and characterization of a growth factor from rat platelets for mature parenchymal hepatocytes in primary cultures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 6489–6493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoker, M.; Perryman, M. An epithelial scatter factor released by embryo fibroblasts. J. Cell Sci. 1985, 77, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naldini, L.; Weidner, K.M.; Vigna, E.; Gaudino, G.; Bardelli, A.; Ponzetto, C.; Narsimhan, R.P.; Hartmann, G.; Zarnegar, R.; Michalopoulos, G.K. Scatter factor and hepatocyte growth factor are indistinguishable ligands for the met receptor. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 2867–2878. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sonnenberg, E.; Meyer, D.; Weidner, K.M.; Birchmeier, C. Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor and its receptor, the c-met tyrosine kinase, can mediate a signal exchange between mesenchyme and epithelia during mouse development. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 123, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Nishizawa, T.; Hagiya, M.; Seki, T.; Shimonishi, M.; Sugimura, A.; Tashiro, K.; Shimizu, S. Molecular cloning and expression of human hepatocyte growth factor. Nature 1989, 342, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, T.; Hagiya, M.; Shimonishi, M.; Nakamura, T.; Shimizu, S. Organization of the human hepatocyte growth factor-encoding gene. Gene 1991, 102, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchhofer, D.; Yao, X.; Peek, M.; Eigenbrot, C.; Lipari, M.T.; Billeci, K.L.; Maun, H.R.; Moran, P.; Santell, L.; Wiesmann, C.; et al. Structural and functional basis of the serine protease-like hepatocyte growth factor beta-chain in met binding and signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 39915–39924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamos, J.; Lazarus, R.A.; Yao, X.; Kirchhofer, D.; Wiesmann, C. Crystal structure of the HGF beta-chain in complex with the sema domain of the met receptor. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 2325–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazawa, K.; Tsubouchi, H.; Naka, D.; Takahashi, K.; Okigaki, M.; Arakaki, N.; Nakayama, H.; Hirono, S.; Sakiyama, O. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of cdna for human hepatocyte growth factor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989, 163, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashiro, K.; Hagiya, M.; Nishizawa, T.; Seki, T.; Shimonishi, M.; Shimizu, S.; Nakamura, T. Deduced primary structure of rat hepatocyte growth factor and expression of the mrna in rat tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 3200–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, T.; Yuhki, N.; Wang, M.H.; Skeel, A.; Leonard, E.J. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of human macrophage stimulating protein (msp, mst1) confirms msp as a member of the family of kringle proteins and locates the MSP gene on chromosome 3. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 15461–15468. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stahl, S.J.; Wingfield, P.T.; Kaufman, J.D.; Pannell, L.K.; Cioce, V.; Sakata, H.; Taylor, W.G.; Rubin, J.S.; Bottaro, D.P. Functional and biophysical characterization of recombinant human hepatocyte growth factor isoforms produced in Escherichia coli. Biochem. J. 1997, 326, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cioce, V.; Csaky, K.G.; Chan, A.M.; Bottaro, D.P.; Taylor, W.G.; Jensen, R.; Aaronson, S.A.; Rubin, J.S. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)/nk1 is a naturally occurring hgf/scatter factor variant with partial agonist/antagonist activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 13110–13115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montesano, R.; Soriano, J.V.; Malinda, K.M.; Ponce, M.L.; Bafico, A.; Kleinman, H.K.; Bottaro, D.P.; Aaronson, S.A. Differential effects of hepatocyte growth factor isoforms on epithelial and endothelial tubulogenesis. Cell Growth Differ. 1998, 9, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.M.; Rubin, J.S.; Bottaro, D.P.; Hirschfield, D.W.; Chedid, M.; Aaronson, S.A. Identification of a competitive HGF antagonist encoded by an alternative transcript. Science 1991, 254, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, T.; Jakubczak, J.; Vieira, W.; Bottaro, D.P.; Breckenridge, D.; Larochelle, W.J.; Merlino, G. Disassociation of met-mediated biological responses in vivo: The natural hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor splice variant nk2 antagonizes growth but facilitates metastasis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 2055–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, H.; Nakae, Y.; Sogabe, T.; Ihara, I.; Ueno, S.; Sakai, H.; Inoue, H.; Shimizu, S.; Nakamura, T.; Shimizu, N. Structural study of the n-linked oligosaccharides of hepatocyte growth factor by two-dimensional sugar mapping. J. Biochem. 1993, 114, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fukuta, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Nakamura, T. Multiple biological responses are induced by glycosylation-deficient hepatocyte growth factor. Biochem. J. 2005, 388, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Nawa, K.; Ichihara, A.; Kaise, N.; Nishino, T. Purification and subunit structure of hepatocyte growth factor from rat platelets. FEBS Lett. 1987, 224, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naka, D.; Ishii, T.; Yoshiyama, Y.; Miyazawa, K.; Hara, H.; Hishida, T.; Kidamura, N. Activation of hepatocyte growth factor by proteolytic conversion of a single chain form to a heterodimer. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 20114–20119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weidner, K.M.; Behrens, J.; Vandekerckhove, J.; Birchmeier, W. Scatter factor: Molecular characteristics and effect on the invasiveness of epithelial cells. J. Cell. Biol. 1990, 111, 2097–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mars, W.M.; Zarnegar, R.; Michalopoulos, G.K. Activation of hepatocyte growth factor by the plasminogen activators upa and tpa. Am. J. Pathol. 1993, 143, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miyazawa, K.; Shimomura, T.; Kitamura, A.; Kondo, J.; Morimoto, Y.; Kitamura, N. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the cdna for a human serine protease reponsible for activation of hepatocyte growth factor. Structural similarity of the protease precursor to blood coagulation factor XII. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 10024–10028. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shimomura, T.; Miyazawa, K.; Komiyama, Y.; Hiraoka, H.; Naka, D.; Morimoto, Y.; Kitamura, N. Activation of hepatocyte growth factor by two homologous proteases, blood-coagulation factor XIIa and hepatocyte growth factor activator. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 229, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.L.; Huang, P.Y.; Roller, P.; Cho, E.G.; Park, D.; Dickson, R.B. Matriptase/epithin participates in mammary epithelial cell growth and morphogenesis through hgf activation. Mech. Dev. 2010, 127, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchhofer, D.; Peek, M.; Lipari, M.T.; Billeci, K.; Fan, B.; Moran, P. Hepsin activates pro-hepatocyte growth factor and is inhibited by hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor-1b (hai-1b) and hai-2. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 1945–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazawa, K.; Shimomura, T.; Kitamura, N. Activation of hepatocyte growth factor in the injured tissues is mediated by hepatocyte growth factor activator. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 3615–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, K.; Inoue, H.; Hagiya, M.; Shimizu, S.; Nose, T.; Shimohigashi, Y.; Nakamura, T. Hairpin loop and second kringle domain are essential sites for heparin binding and biological activity of hepatocyte growth factor. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 1131–1136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tajima, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Nakamura, T. Regulation of cell growth and motility by hepatocyte growth factor and receptor expression in various cell species. Exp. Cell Res. 1992, 202, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, M.; Deakin, J.A.; Gallagher, J.T. The mode of action of heparan and dermatan sulfates in the regulation of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 1040–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, M.; Deakin, J.A.; Rahmoune, H.; Fernig, D.G.; Nakamura, T.; Gallagher, J.T. Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor binds with high affinity to dermatan sulfate. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Honke, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Nakamura, T.; Ishizuka, I.; Makita, A. Hepatocyte growth factor specifically binds to sulfoglycolipids. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 9817–9821. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chirgadze, D.Y.; Hepple, J.P.; Zhou, H.; Byrd, R.A.; Blundell, T.L.; Gherardi, E. Crystal structure of the nk1 fragment of HGF/SF suggests a novel mode for growth factor dimerization and receptor binding. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1999, 6, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata, H.; Stahl, S.J.; Taylor, W.G.; Rosenberg, J.M.; Sakaguchi, K.; Wingfield, P.T.; Rubin, J.S. Heparin binding and oligomerization of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor isoforms. Heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycan requirement for met binding and signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 9457–9463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolbert, W.D.; Daugherty, J.; Gao, C.; Xie, Q.; Miranti, C.; Gherardi, E.; Vande Woude, G.; Xu, H.E. A mechanistic basis for converting a receptor tyrosine kinase agonist to an antagonist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14592–14597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Voort, R.; Taher, T.E.; Wielenga, V.J.; Spaargaren, M.; Prevo, R.; Smit, L.; David, G.; Hartmann, G.; Gherardi, E.; Pals, S.T. Heparan sulfate-modified cd44 promotes hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor-induced signal transduction through the receptor tyrosine kinase c-met. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 6499–6506. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, J.S.; Day, R.M.; Breckenridge, D.; Atabey, N.; Taylor, W.G.; Stahl, S.J.; Wingfield, P.T.; Kaufman, J.D.; Schwall, R.; Bottaro, D.P. Dissociation of heparan sulfate and receptor binding domains of hepatocyte growth factor reveals that heparan sulfate-c-met interaction facilitates signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 32977–32983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherardi, E.; Youles, M.E.; Miguel, R.N.; Blundell, T.L.; Iamele, L.; Gough, J.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Hartmann, G.; Butler, P.J. Functional map and domain structure of met, the product of the c-met protooncogene and receptor for hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12039–12044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, L.; Goldschneider, I. Cutting edge: Identification of a hybrid cytokine consisting of il-7 and the beta-chain of the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 3550–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, G.A.; Naujokas, M.A.; Park, M. Alternative splicing generates isoforms of the met receptor tyrosine kinase which undergo differential processing. Mol. Cell Biol. 1991, 11, 2962–2970. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C.; Yamada, K.M. Identification of a novel type of alternative splicing of a tyrosine kinase receptor. Juxtamembrane deletion of the c-met protein kinase c serine phosphorylation regulatory site. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 19457–19461. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prat, M.; Crepaldi, T.; Gandino, L.; Giordano, S.; Longati, P.; Comoglio, P. C-terminal truncated forms of met, the hepatocyte growth factor receptor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1991, 11, 5954–5962. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Crepaldi, T.; Prat, M.; Giordano, S.; Medico, E.; Comoglio, P.M. Generation of a truncated hepatocyte growth factor receptor in the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 1750–1755. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wajih, N.; Walter, J.; Sane, D.C. Vascular origin of a soluble truncated form of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor (c-met). Circ. Res. 2002, 90, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlin, S.; Pietronave, S.; Locarno, D.; Valente, G.; Follenzi, A.; Prat, M. Deletion of the ectodomain unleashes the transforming, invasive, and tumorigenic potential of the met oncogene. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deheuninck, J.; Goormachtigh, G.; Foveau, B.; Ji, Z.; Leroy, C.; Ancot, F.; Villeret, V.; Tulasne, D.; Fafeur, V. Phosphorylation of the met receptor on juxtamembrane tyrosine residue 1001 inhibits its caspase-dependent cleavage. Cell Signal 2009, 21, 1455–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prat, M.; Narsimhan, R.P.; Crepaldi, T.; Nicotra, M.R.; Natali, P.G.; Comoglio, P.M. The receptor encoded by the human c-met oncogene is expressed in hepatocytes, epithelial cells and solid tumors. Int. J. Cancer 1991, 49, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Renzo, M.F.; Narsimhan, R.P.; Olivero, M.; Bretti, S.; Giordano, S.; Medico, E.; Gaglia, P.; Zara, P.; Comoglio, P.M. Expression of the met/hgf receptor in normal and neoplastic human tissues. Oncogene 1991, 6, 1997–2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bussolino, F.; Di Renzo, M.F.; Ziche, M.; Bocchietto, E.; Olivero, M.; Naldini, L.; Gaudino, G.; Tamagnone, L.; Coffer, A.; Comoglio, P.M. Hepatocyte growth factor is a potent angiogenic factor which stimulates endothelial cell motility and growth. J. Cell. Biol. 1992, 119, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishino, T.; Hisha, H.; Nishino, N.; Adachi, M.; Ikehara, S. Hepatocyte growth factor as a hematopoietic regulator. Blood 1995, 85, 3093–3100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taher, T.E.; Tjin, E.P.; Beuling, E.A.; Borst, J.; Spaargaren, M.; Pals, S.T. C-cbl is involved in met signaling in b cells and mediates hepatocyte growth factor-induced receptor ubiquitination. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 3793–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoker, M.; Gherardi, E.; Perryman, M.; Gray, J. Scatter factor is a fibroblast-derived modulator of epithelial cell mobility. Nature 1987, 327, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Shen, C.; Wang, H.; Shen, H.; Chen, Y.; Nie, A.; Yan, G.; Lu, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, P. Identification of n-glycosylation sites on secreted proteins of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells with a complementary proteomics approach. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlov, G.; Perreault, A.; Schrag, J.D.; Park, M.; Cygler, M.; Gehring, K.; Ekiel, I. Insights into function of PSI domains from structure of the met receptor psi domain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 321, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemann, H.H.; Jäger, V.; Butler, P.J.; van den Heuvel, J.; Schmidt, S.; Ferraris, D.; Gherardi, E.; Heinz, D.W. Structure of the human receptor tyrosine kinase met in complex with the listeria invasion protein inlb. Cell 2007, 130, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komada, M.; Hatsuzawa, K.; Shibamoto, S.; Ito, F.; Nakayama, K.; Kitamura, N. Proteolytic processing of the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor receptor by furin. FEBS Lett. 1993, 328, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronsin, C.; Muscatelli, F.; Mattei, M.G.; Breathnach, R. A novel putative receptor protein tyrosine kinase of the met family. Oncogene 1993, 8, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bottaro, D.P.; Rubin, J.S.; Faletto, D.L.; Chan, A.M.; Kmiecik, T.E.; Vande Woude, G.F.; Aaronson, S.A. Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-met proto-oncogene product. Science 1991, 251, 802–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naldini, L.; Vigna, E.; Narsimhan, R.P.; Gaudino, G.; Zarnegar, R.; Michalopoulos, G.K.; Comoglio, P.M. Hepatocyte growth factor (hgf) stimulates the tyrosine kinase activity of the receptor encoded by the proto-oncogene c-met. Oncogene 1991, 6, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Naujokas, M.; Park, M.; Ireton, K. Inib-dependent internalization of listeria is mediated by the met receptor tyrosine kinase. Cell 2000, 103, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youles, M.; Holmes, O.; Petoukhov, M.V.; Nessen, M.A.; Stivala, S.; Svergun, D.I.; Gherardi, E. Engineering the nk1 fragment of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor as a met receptor antagonist. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 377, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basilico, C.; Arnesano, A.; Galluzzo, M.; Comoglio, P.M.; Michieli, P. A high affinity hepatocyte growth factor-binding site in the immunoglobulin-like region of met. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 21267–21277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong-Beltran, M.; Stamos, J.; Wickramasinghe, D. The sema domain of met is necessary for receptor dimerization and activation. Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komada, M.; Kitamura, N. Regulatory role of major tyrosine autophosphorylation site of kinase domain of c-met receptor (scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor receptor). J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 16131–16136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhen, Z.; Giordano, S.; Longati, P.; Medico, E.; Campiglio, M.; Comoglio, P.M. Structural and functional domains critical for constitutive activation of the HGF-receptor (met). Oncogene 1994, 9, 1691–1697. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Longati, P.; Bardelli, A.; Ponzetto, C.; Naldini, L.; Comoglio, P.M. Tyrosines1234–1235 are critical for activation of the tyrosine kinase encoded by the met proto-oncogene (HGF receptor). Oncogene 1994, 9, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferracini, R.; Longati, P.; Naldini, L.; Vigna, E.; Comoglio, P.M. Identification of the major autophosphorylation site of the met/hepatocyte growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 19558–19564. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ponzetto, C.; Bardelli, A.; Zhen, Z.; Maina, F.; dalla Zonca, P.; Giordano, S.; Graziani, A.; Panayotou, G.; Comoglio, P.M. A multifunctional docking site mediates signaling and transformation by the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor receptor family. Cell 1994, 77, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardelli, A.; Longati, P.; Williams, T.A.; Benvenuti, S.; Comoglio, P.M. A peptide representing the carboxyl-terminal tail of the met receptor inhibits kinase activity and invasive growth. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 29274–29281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, T.M.; Kamikura, D.; Teng, K.; Park, M. Branching tubulogenesis but not scatter of madin-darby canine kidney cells requires a functional grb2 binding site in the met receptor tyrosine kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 22211–22217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royal, I.; Park, M. Hepatocyte growth factor-induced scatter of madin-darby canine kidney cells requires phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 27780–27787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Naujokas, M.A.; Fixman, E.D.; Torossian, K.; Park, M. Tyrosine 1356 in the carboxyl-terminal tail of the hgf/sf receptor is essential for the transduction of signals for cell motility and morphogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 29943–29948. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pelicci, G.; Giordano, S.; Zhen, Z.; Salcini, A.E.; Lanfrancone, L.; Bardelli, A.; Panayotou, G.; Waterfield, M.D.; Ponzetto, C.; Pelicci, P.G. The motogenic and mitogenic responses to HGF are amplified by the shc adaptor protein. Oncogene 1995, 10, 1631–1638. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maina, F.; Casagranda, F.; Audero, E.; Simeone, A.; Comoglio, P.M.; Klein, R.; Ponzetto, C. Uncoupling of grb2 from the met receptor in vivo reveals complex roles in muscle development. Cell 1996, 87, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponzetto, C.; Zhen, Z.; Audero, E.; Maina, F.; Bardelli, A.; Basile, M.L.; Giordano, S.; Narsimhan, R.; Comoglio, P. Specific uncoupling of grb2 from the met receptor. Differential effects on transformation and motility. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 14119–14123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, S.; Bardelli, A.; Zhen, Z.; Menard, S.; Ponzetto, C.; Comoglio, P.M. A point mutation in the met oncogene abrogates metastasis without affecting transformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 13868–13872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardelli, A.; Longati, P.; Gramaglia, D.; Stella, M.C.; Comoglio, P.M. Gab1 coupling to the hgf/met receptor multifunctional docking site requires binding of grb2 and correlates with the transforming potential. Oncogene 1997, 15, 3103–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidner, K.M.; Di Cesare, S.; Sachs, M.; Brinkmann, V.; Behrens, J.; Birchmeier, W. Interaction between gab1 and the c-met receptor tyrosine kinase is responsible for epithelial morphogenesis. Nature 1996, 384, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.; Holgado-Madruga, M.; Maroun, C.; Fixman, E.D.; Kamikura, D.; Fournier, T.; Charest, A.; Tremblay, M.L.; Wong, A.J.; Park, M. Association of the multisubstrate docking protein gab1 with the hepatocyte growth factor receptor requires a functional grb2 binding site involving tyrosine 1356. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 20811–20819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroun, C.R.; Holgado-Madruga, M.; Royal, I.; Naujokas, M.A.; Fournier, T.M.; Wong, A.J.; Park, M. The gab1 ph domain is required for localization of gab1 at sites of cell-cell contact and epithelial morphogenesis downstream from the met receptor tyrosine kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 1784–1799. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gual, P.; Giordano, S.; Williams, T.A.; Rocchi, S.; van Obberghen, E.; Comoglio, P.M. Sustained recruitment of phospholipase c-gamma to gab1 is required for hgf-induced branching tubulogenesis. Oncogene 2000, 19, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaeper, U.; Gehring, N.H.; Fuchs, K.P.; Sachs, M.; Kempkes, B.; Birchmeier, W. Coupling of gab1 to c-met, grb2, and shp2 mediates biological responses. J. Cell. Biol. 2000, 149, 1419–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakkab, D.; Lewitzky, M.; Posern, G.; Schaeper, U.; Sachs, M.; Birchmeier, W.; Feller, S.M. Signaling of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor (HGF) to the small gtpase rap1 via the large docking protein gab1 and the adapter protein crkl. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 10772–10778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamorte, L.; Royal, I.; Naujokas, M.; Park, M. Crk adapter proteins promote an epithelial-mesenchymal-like transition and are required for hgf-mediated cell spreading and breakdown of epithelial adherens junctions. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 1449–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroun, C.R.; Naujokas, M.A.; Holgado-Madruga, M.; Wong, A.J.; Park, M. The tyrosine phosphatase shp-2 is required for sustained activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and epithelial morphogenesis downstream from the met receptor tyrosine kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 8513–8525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, A.; Matozaki, T.; Fukuhara, A.; Kikyo, M.; Ichihashi, M.; Takai, Y. Involvement of an shp-2-rho small G protein pathway in hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor-induced cell scattering. Mol. Biol. Cell 2000, 11, 2565–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.; Kochhar, K.; Nakamura, T.; Iyer, A. Hepatocyte growth factor-induced signal transduction in two normal mouse epithelial cell lines. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1995, 36, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kochhar, K.S.; Iyer, A.P. Hepatocyte growth factor induces activation of nck and phospholipase c-gamma in lung carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 1996, 104, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buday, L.; Wunderlich, L.; Tamás, P. The nck family of adapter proteins: Regulators of actin cytoskeleton. Cell Signal 2002, 14, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abella, J.V.; Vaillancourt, R.; Frigault, M.M.; Ponzo, M.G.; Zuo, D.; Sangwan, V.; Larose, L.; Park, M. The gab1 scaffold regulates rtk-dependent dorsal ruffle formation through the adaptor nck. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 1306–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graziani, A.; Gramaglia, D.; Cantley, L.C.; Comoglio, P.M. The tyrosine-phosphorylated hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor receptor associates with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 22087–22090. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bardelli, A.; Maina, F.; Gout, I.; Fry, M.J.; Waterfield, M.D.; Comoglio, P.M.; Ponzetto, C. Autophosphorylation promotes complex formation of recombinant hepatocyte growth factor receptor with cytoplasmic effectors containing sh2 domains. Oncogene 1992, 7, 1973–1978. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ponzetto, C.; Bardelli, A.; Maina, F.; Longati, P.; Panayotou, G.; Dhand, R.; Waterfield, M.D.; Comoglio, P.M. A novel recognition motif for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding mediates its association with the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor receptor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 4600–4608. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Derman, M.P.; Cunha, M.J.; Barros, E.J.; Nigam, S.K.; Cantley, L.G. Hgf-mediated chemotaxis and tubulogenesis require activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Am. J. Physiol. 1995, 268, F1211–F1217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Skouteris, G.G.; Georgakopoulos, E. Hepatocyte growth factor-induced proliferation of primary hepatocytes is mediated by activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 218, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osada, S.; Nakashima, S.; Saji, S.; Nakamura, T.; Nozawa, Y. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) mediates the sustained formation of 1,2-diacylglycerol via phosphatidylcholine-phospholipase c in cultured rat hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1992, 297, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, A.; Hayashi, N.; Tsubouchi, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Ito, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Fusamoto, H.; Daikuhara, Y.; Kamada, T. Intracellular calcium as a second messenger for human hepatocyte growth factor in hepatocytes. Hepatology 1992, 15, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machide, M.; Kamitori, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Kohsaka, S. Selective activation of phospholipase c gamma1 and distinct protein kinase c subspecies in intracellular signaling by hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor in primary cultured rat neocortical cells. J. Neurochem. 1998, 71, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awasthi, V.; King, R.J. Pkc, p42/p44 mapk, and p38 mapk are required for hgf-induced proliferation of h441 cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2000, 279, L942–L949. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adachi, T.; Nakashima, S.; Saji, S.; Nakamura, T.; Nozawa, Y. Phospholipase d activation in hepatocyte growth factor-stimulated rat hepatocytes mediates the expressions of c-jun and c-fos: Involvement of protein tyrosine kinase, protein kinase c, and Ca2+. Hepatology 1996, 24, 1274–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, N.; Hung, W.; Tremblay, E.; Saulnier, R.; Elliott, B. C-src kinase activity is required for hepatocyte growth factor-induced motility and anchorage-independent growth of mammary carcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 33714–33721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, P.C.; Chen, Y.L.; Cheng, C.H.; Yu, K.C.; Cary, L.A.; Shu, K.H.; Ho, W.L.; Chen, H.C. Src phosphorylates grb2-associated binder 1 upon hepatocyte growth factor stimulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 44075–44082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.H.; Chan, P.C.; Chen, C.L.; Chen, H.C. Phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase on tyrosine 194 by met leads to its activation through relief of autoinhibition. Oncogene 2011, 30, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.C.; Chan, P.C.; Tang, M.J.; Cheng, C.H.; Chang, T.J. Tyrosine phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase stimulated by hepatocyte growth factor leads to mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 25777–25782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldanzi, G.; Cutrupi, S.; Chianale, F.; Gnocchi, V.; Rainero, E.; Porporato, P.; Filigheddu, N.; van Blitterswijk, W.J.; Parolini, O.; Bussolino, F.; et al. Diacylglycerol kinase-alpha phosphorylation by src on y335 is required for activation, membrane recruitment and hgf-induced cell motility. Oncogene 2008, 27, 942–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutrupi, S.; Baldanzi, G.; Gramaglia, D.; Maffè, A.; Schaap, D.; Giraudo, E.; van Blitterswijk, W.; Bussolino, F.; Comoglio, P.M.; Graziani, A. Src-mediated activation of alpha-diacylglycerol kinase is required for hepatocyte growth factor-induced cell motility. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 4614–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chianale, F.; Rainero, E.; Cianflone, C.; Bettio, V.; Pighini, A.; Porporato, P.E.; Filigheddu, N.; Serini, G.; Sinigaglia, F.; Baldanzi, G.; et al. Diacylglycerol kinase alpha mediates hgf-induced rac activation and membrane ruffling by regulating atypical pkc and rhogdi. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4182–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chianale, F.; Cutrupi, S.; Rainero, E.; Baldanzi, G.; Porporato, P.E.; Traini, S.; Filigheddu, N.; Gnocchi, V.F.; Santoro, M.M.; Parolini, O.; et al. Diacylglycerol kinase-alpha mediates hepatocyte growth factor-induced epithelial cell scatter by regulating rac activation and membrane ruffling. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 4859–4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainero, E.; Caswell, P.T.; Muller, P.A.; Grindlay, J.; McCaffrey, M.W.; Zhang, Q.; Wakelam, M.J.; Vousden, K.H.; Graziani, A.; Norman, J.C. Diacylglycerol kinase α controls rcp-dependent integrin trafficking to promote invasive migration. J. Cell. Biol. 2012, 196, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccaccio, C.; Andò, M.; Tamagnone, L.; Bardelli, A.; Michieli, P.; Battistini, C.; Comoglio, P.M. Induction of epithelial tubules by growth factor hgf depends on the stat pathway. Nature 1998, 391, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaper, F.; Siewert, E.; Gómez-Lechon, M.J.; Gatsios, P.; Sachs, M.; Birchmeier, W.; Heinrich, P.C.; Castell, J. Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor (hgf/sf) signals via the stat3/aprf transcription factor in human hepatoma cells and hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1997, 405, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, M.; Koch, A.; Mancini, A.; Mohr, A.; Weidner, K.M.; Niemann, H.; Tamura, T. Src homology 2-containing inositol 5-phosphatase 1 binds to the multifunctional docking site of c-met and potentiates hepatocyte growth factor-induced branching tubulogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 3017–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, A.; Mancini, A.; El Bounkari, O.; Tamura, T. The sh2-domian-containing inositol 5-phosphatase (ship)-2 binds to c-met directly via tyrosine residue 1356 and involves hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-induced lamellipodium formation, cell scattering and cell spreading. Oncogene 2005, 24, 3436–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.K.; Sasaki, E.; Halter, F.; Pai, R.; Nakamura, T.; Arakawa, T.; Kuroki, T.; Tarnawski, A.S. Hgf triggers activation of the cox-2 gene in rat gastric epithelial cells: Action mediated through the erk2 signaling pathway. FASEB J. 1999, 13, 2186–2194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Skouteris, G.G.; Schröder, C.H. Cytosolic phospholipase a2 is activated by the hepatocyte growth factor receptor-kinase in madin darby canine kidney cells. J. Cell. Sci. 1997, 110, 1655–1663. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, P.C.; Tretiakova, M.S.; Nallasura, V.; Jagadeeswaran, R.; Husain, A.N.; Salgia, R. Downstream signalling and specific inhibition of c-met/hgf pathway in small cell lung cancer: Implications for tumour invasion. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 97, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaposi-Novak, P.; Lee, J.S.; Gòmez-Quiroz, L.; Coulouarn, C.; Factor, V.M.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Met-regulated expression signature defines a subset of human hepatocellular carcinomas with poor prognosis and aggressive phenotype. J. Clin. Invest. 2006, 116, 1582–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiery, J.P. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grotegut, S.; von Schweinitz, D.; Christofori, G.; Lehembre, F. Hepatocyte growth factor induces cell scattering through mapk/egr-1-mediated upregulation of snail. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 3534–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy, P.; Mostov, K.E. Slug is required for cell survival during partial epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hgf-induced tubulogenesis. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2007, 18, 1943–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Leenders, G.J.; Sookhlall, R.; Teubel, W.J.; de Ridder, C.M.; Reneman, S.; Sacchetti, A.; Vissers, K.J.; van Weerden, W.; Jenster, G. Activation of c-met induces a stem-like phenotype in human prostate cancer. PLoS One 2011, 6, e26753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodgers, J.T.; King, K.Y.; Brett, J.O.; Cromie, M.J.; Charville, G.W.; Maguire, K.K.; Brunson, C.; Mastey, N.; Liu, L.; Tsai, C.R.; et al. Mtorc1 controls the adaptive transition of quiescent stem cells from g0 to g(alert). Nature 2014, 510, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Medico, E.; Mongiovi, A.M.; Huff, J.; Jelinek, M.A.; Follenzi, A.; Gaudino, G.; Parsons, J.T.; Comoglio, P.M. The tyrosine kinase receptors ron and sea control “scattering” and morphogenesis of liver progenitor cells in vitro. Mol. Biol. Cell 1996, 7, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisendi, S.; Arpin, M.; Crepaldi, T. Effect of hepatocyte growth factor on assembly of zonula occludens-1 protein at the plasma membrane. J. Cell. Physiol. 1998, 176, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, E.D.; Zuk, A. Transformations between epithelium and mesenchyme: Normal, pathological, and experimentally induced. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1995, 26, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potempa, S.; Ridley, A.J. Activation of both map kinase and phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase by ras is required for hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor-induced adherens junction disassembly. Mol. Biol. Cell. 1998, 9, 2185–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khwaja, A.; Lehmann, K.; Marte, B.M.; Downward, J. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase induces scattering and tubulogenesis in epithelial cells through a novel pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 18793–18801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridley, A.J.; Comoglio, P.M.; Hall, A. Regulation of scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor responses by ras, rac, and rho in mdck cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1995, 15, 1110–1122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Royal, I.; Fournier, T.M.; Park, M. Differential requirement of grb2 and pi3-kinase in HGF/SF-induced cell motility and tubulogenesis. J. Cell. Physiol. 1997, 173, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.X.; Yu, C.F.; Nickel, C.; Thomas, S.; Cantley, L.G. Hepatocyte growth factor induces ERK-dependent paxillin phosphorylation and regulates paxillin-focal adhesion kinase association. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 10452–10458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graziani, A.; Gramaglia, D.; dalla Zonca, P.; Comoglio, P.M. Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor stimulates the ras-guanine nucleotide exchanger. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 9165–9168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, G.; Weidner, K.M.; Schwarz, H.; Birchmeier, W. The motility signal of scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor mediated through the receptor tyrosine kinase met requires intracellular action of ras. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 21936–21939. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tanimura, S.; Nomura, K.; Ozaki, K.; Tsujimoto, M.; Kondo, T.; Kohno, M. Prolonged nuclear retention of activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 is required for hepatocyte growth factor-induced cell motility. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 28256–28264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.Y.; Wong, A.S. Activation of p70s6k induces expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 associated with hepatocyte growth factor-mediated invasion in human ovarian cancer cells. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 2557–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monga, S.P.; Mars, W.M.; Pediaditakis, P.; Bell, A.; Mulé, K.; Bowen, W.C.; Wang, X.; Zarnegar, R.; Michalopoulos, G.K. Hepatocyte growth factor induces wnt-independent nuclear translocation of beta-catenin after met-beta-catenin dissociation in hepatocytes. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 2064–2071. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Papkoff, J.; Aikawa, M. Wnt-1 and hgf regulate gsk3 beta activity and beta-catenin signaling in mammary epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 247, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abella, J.V.; Parachoniak, C.A.; Sangwan, V.; Park, M. Dorsal ruffle microdomains potentiate met receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and down-regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 24956–24967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, C.M.; Ahmed, T.; Masters, J.R.; Jones, G.E. Rho family gtpases are activated during HGF-stimulated prostate cancer-cell scattering. Cell. Motil. Cytoskeleton 2005, 62, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royal, I.; Lamarche-Vane, N.; Lamorte, L.; Kaibuchi, K.; Park, M. Activation of cdc42, rac, pak, and rho-kinase in response to hepatocyte growth factor differentially regulates epithelial cell colony spreading and dissociation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2000, 11, 1709–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobes, C.D.; Hall, A. Rho, rac, and cdc42 gtpases regulate the assembly of multimolecular focal complexes associated with actin stress fibers, lamellipodia, and filopodia. Cell 1995, 81, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, T.; Sasaki, T.; Takaishi, K.; Kato, M.; Yaku, H.; Araki, K.; Matsuura, Y.; Takai, Y. Rac p21 is involved in insulin-induced membrane ruffling and rho p21 is involved in hepatocyte growth factor- and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (tpa)-induced membrane ruffling in kb cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994, 14, 2447–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaishi, K.; Sasaki, T.; Kato, M.; Yamochi, W.; Kuroda, S.; Nakamura, T.; Takeichi, M.; Takai, Y. Involvement of rho p21 small gtp-binding protein and its regulator in the HGF-induced cell motility. Oncogene 1994, 9, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cozzolino, M.; Stagni, V.; Spinardi, L.; Campioni, N.; Fiorentini, C.; Salvati, E.; Alemà, S.; Salvatore, A.M. P120 catenin is required for growth factor-dependent cell motility and scattering in epithelial cells. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2003, 14, 1964–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, H.; Nickel, C.H.; Cantley, L.G.; Bruggeman, L.A.; Bennardo, L.N.; Wang, B. Epha kinase activation regulates HGF-induced epithelial branching morphogenesis. J. Cell. Biol. 2003, 162, 1281–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukata, Y.; Oshiro, N.; Kinoshita, N.; Kawano, Y.; Matsuoka, Y.; Bennett, V.; Matsuura, Y.; Kaibuchi, K. Phosphorylation of adducin by rho-kinase plays a crucial role in cell motility. J. Cell. Biol. 1999, 145, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, K.; Nakamura, T.; Kramer, R.H. Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor induces tyrosine phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase (p125fak) and promotes migration and invasion by oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 31807–31813. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Hiscox, S.; Nakamura, T.; Hallett, M.; Puntis, M.; Mansel, R. Hepatocyte growth factor induces tyrosine phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase (fak) and paxillin and enhances cell-matrix interactions. Oncol. Rep. 1996, 3, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trusolino, L.; Cavassa, S.; Angelini, P.; Andó, M.; Bertotti, A.; Comoglio, P.M.; Boccaccio, C. Hgf/scatter factor selectively promotes cell invasion by increasing integrin avidity. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trusolino, L.; Serini, G.; Cecchini, G.; Besati, C.; Ambesi-Impiombato, F.S.; Marchisio, P.C.; De Filippi, R. Growth factor-dependent activation of alphavbeta3 integrin in normal epithelial cells: Implications for tumor invasion. J. Cell. Biol. 1998, 142, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nusrat, A.; Parkos, C.A.; Bacarra, A.E.; Godowski, P.J.; Delp-Archer, C.; Rosen, E.M.; Madara, J.L. Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor effects on epithelia. Regulation of intercellular junctions in transformed and nontransformed cell lines, basolateral polarization of c-met receptor in transformed and natural intestinal epithelia, and induction of rapid wound repair in a transformed model epithelium. J. Clin. Invest. 1994, 93, 2056–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crepaldi, T.; Pollack, A.L.; Prat, M.; Zborek, A.; Mostov, K.; Comoglio, P.M. Targeting of the sf/hgf receptor to the basolateral domain of polarized epithelial cells. J. Cell. Biol. 1994, 125, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korhan, P.; Erdal, E.; Kandemiş, E.; Cokaklı, M.; Nart, D.; Yılmaz, F.; Can, A.; Atabey, N. Reciprocal activating crosstalk between c-met and caveolin 1 promotes invasive phenotype in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One 2014, 9, e105278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; O’Brien, L.E.; Wang, F.; Bourne, H.; Mostov, K.E.; Zegers, M.M. Hepatocyte growth factor switches orientation of polarity and mode of movement during morphogenesis of multicellular epithelial structures. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2003, 14, 748–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollack, A.L.; Runyan, R.B.; Mostov, K.E. Morphogenetic mechanisms of epithelial tubulogenesis: Mdck cell polarity is transiently rearranged without loss of cell–cell contact during scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor-induced tubulogenesis. Dev. Biol. 1998, 204, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, L.E.; Tang, K.; Kats, E.S.; Schutz-Geschwender, A.; Lipschutz, J.H.; Mostov, K.E. Erk and mmps sequentially regulate distinct stages of epithelial tubule development. Dev. Cell 2004, 7, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamasuna, R.; Kataoka, H.; Moriyama, T.; Itoh, H.; Seiki, M.; Koono, M. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (mmp-2) by hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor (hgf/sf) in human glioma cells: HGF/SF enhances mmp-2 expression and activation accompanying up-regulation of membrane type-1 mmp. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 82, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Keiser, J.A. Hepatocyte growth factor enhances mmp activity in human endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 272, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCawley, L.J.; Li, S.; Wattenberg, E.V.; Hudson, L.G. Sustained activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. A mechanism underlying receptor tyrosine kinase specificity for matrix metalloproteinase-9 induction and cell migration. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 4347–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tushir, J.S.; D’Souza-Schorey, C. Arf6-dependent activation of erk and rac1 modulates epithelial tubule development. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 1806–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.H.; Jeffers, M.; Bellacosa, A.; Mitsuuchi, Y.; Vande Woude, G.F.; Testa, J.R. Anti-apoptotic signaling by hepatocyte growth factor/met via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.; Chen, S.; You, Z.; Yang, F.; Carey, T.E.; Saims, D.; Wang, C.Y. Hepatocyte growth factor inhibits anoikis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells by activation of ERK and AKT signaling independent of nfkappa b. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 25203–25208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y. Hepatocyte growth factor promotes renal epithelial cell survival by dual mechanisms. Am J. Physiol. 1999, 277, F624–F633. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schulze-Bergkamen, H.; Brenner, D.; Krueger, A.; Suess, D.; Fas, S.C.; Frey, C.R.; Dax, A.; Zink, D.; Büchler, P.; Müller, M.; et al. Hepatocyte growth factor induces mcl-1 in primary human hepatocytes and inhibits cd95-mediated apoptosis via AKT. Hepatology 2004, 39, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moumen, A.; Patané, S.; Porras, A.; Dono, R.; Maina, F. Met acts on mdm2 via mtor to signal cell survival during development. Development 2007, 134, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassetta, M.; D’Alessandro, L.; Coltella, N.; di Renzo, M.F.; Rasola, A. Hepatocyte growth factor installs a survival platform for colorectal cancer cell invasive growth and overcomes p38 mapk-mediated apoptosis. Cell Signal 2006, 18, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabregat, I.; de Juan, C.; Nakamura, T.; Benito, M. Growth stimulation of rat fetal hepatocytes in response to hepatocyte growth factor: Modulation of c-myc and c-fos expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992, 189, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Lechón, M.J.; Guillén, I.; Ponsoda, X.; Fabra, R.; Trullenque, R.; Nakamura, T.; Castell, J.V. Cell cycle progression proteins (cyclins), oncogene expression, and signal transduction during the proliferative response of human hepatocytes to hepatocyte growth factor. Hepatology 1996, 23, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, K.; Shibamoto, S.; Nagamine, K.; Shigemori, I.; Omura, S.; Kitamura, N.; Ito, F. Signaling pathways leading to transcription and translation cooperatively regulate the transient increase in expression of c-fos protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 26077–26083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Meng, Q.; Laterra, J.J.; Rosen, E.M. Ras effector pathways modulate scatter factor-stimulated nf-kappab signaling and protection against DNA damage. Oncogene 2007, 26, 4774–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, M.; Morotti, A.; Ponzetto, C. Activation of nf-kappab is essential for hepatocyte growth factor-mediated proliferation and tubulogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Tsukada, Y.; Hara, E.; Kitamura, N.; Tanaka, T. Hepatocyte growth factor induces redistribution of p21(cip1) and p27(kip1) through ERK-dependent p16(ink4a) up-regulation, leading to cell cycle arrest at g1 in hepg2 hepatoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 31548–31556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shima, N.; Stolz, D.B.; Miyazaki, M.; Gohda, E.; Higashio, K.; Michalopoulos, G.K. Possible involvement of p21/waf1 in the growth inhibition of hepg2 cells induced by hepatocyte growth factor. J. Cell. Physiol. 1998, 177, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangwan, V.; Paliouras, G.N.; Abella, J.V.; Dubé, N.; Monast, A.; Tremblay, M.L.; Park, M. Regulation of the met receptor-tyrosine kinase by the protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1b and t-cell phosphatase. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 34374–34383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa-Moruzzi, E.; Puntoni, F.; Bardelli, A.; Vigna, E.; de Rosa, S.; Comoglio, P.M. Protein tyrosine phosphatase ptp-s binds to the juxtamembrane region of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor met. Biochem. J. 1998, 336, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Xia, W.; Baker, D.; Zhou, J.; Cha, H.C.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. Receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase beta (rptp-beta) directly dephosphorylates and regulates hepatocyte growth factor receptor (hgfr/met) function. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 15980–15988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Carey, T.E.; McHugh, J.B.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. Receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase β regulates met phosphorylation and function in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Neoplasia 2012, 14, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kulas, D.T.; Goldstein, B.J.; Mooney, R.A. The transmembrane protein-tyrosine phosphatase lar modulates signaling by multiple receptor tyrosine kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machide, M.; Hashigasako, A.; Matsumoto, K.; Nakamura, T. Contact inhibition of hepatocyte growth regulated by functional association of the c-met/hepatocyte growth factor receptor and lar protein-tyrosine phosphatase. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 8765–8772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palka, H.L.; Park, M.; Tonks, N.K. Hepatocyte growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase met is a substrate of the receptor protein-tyrosine phosphatase dep-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 5728–5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashigasako, A.; Machide, M.; Nakamura, T.; Matsumoto, K. Bi-directional regulation of ser-985 phosphorylation of c-met via protein kinase c and protein phosphatase 2a involves c-met activation and cellular responsiveness to hepatocyte growth factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 26445–26452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandino, L.; Longati, P.; Medico, E.; Prat, M.; Comoglio, P.M. Phosphorylation of serine 985 negatively regulates the hepatocyte growth factor receptor kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 1815–1820. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Gao, C.F.; Lee, C.C.; Kim, M.D.; vande Woude, G.F. An alternatively spliced form of met receptor is tumorigenic. Exp. Mol. Med. 2006, 38, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joffre, C.; Barrow, R.; Ménard, L.; Calleja, V.; Hart, I.R.; Kermorgant, S. A direct role for met endocytosis in tumorigenesis. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2011, 13, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Guzman, M.; Larsen, E.; Vuori, K. The proto-oncogene c-cbl is a positive regulator of met-induced map kinase activation: A role for the adaptor protein crk. Oncogene 2000, 19, 4058–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrelli, A.; Gilestro, G.F.; Lanzardo, S.; Comoglio, P.M.; Migone, N.; Giordano, S. The endophilin-cin85-cbl complex mediates ligand-dependent downregulation of c-met. Nature 2002, 416, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peschard, P.; Ishiyama, N.; Lin, T.; Lipkowitz, S.; Park, M. A conserved dpyr motif in the juxtamembrane domain of the met receptor family forms an atypical c-cbl/cbl-b tyrosine kinase binding domain binding site required for suppression of oncogenic activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 29565–29571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raiborg, C.; Bache, K.G.; Gillooly, D.J.; Madshus, I.H.; Stang, E.; Stenmark, H. Hrs sorts ubiquitinated proteins into clathrin-coated microdomains of early endosomes. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, D.E.; Carter, S.; McCullough, J.; Urbé, S.; vande Woude, G.; Clague, M.J. Endosomal dynamics of met determine signaling output. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2003, 14, 1346–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, D.E.; Urbé, S.; vande Woude, G.F.; Clague, M.J. Down-regulation of met, the receptor for hepatocyte growth factor. Oncogene 2001, 20, 2761–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, M.; Muratori, C.; Corso, S.; Tenaglia, E.; Bertotti, A.; Capparuccia, L.; Trusolino, L.; Comoglio, P.M.; Tamagnone, L. The tetraspanin cd151 is required for met-dependent signaling and tumor cell growth. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 38756–38764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trusolino, L.; Bertotti, A.; Comoglio, P.M. A signaling adapter function for alpha6beta4 integrin in the control of HGF-dependent invasive growth. Cell 2001, 107, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertotti, A.; Comoglio, P.M.; Trusolino, L. Beta4 integrin is a transforming molecule that unleashes met tyrosine kinase tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 10674–10679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertotti, A.; Comoglio, P.M.; Trusolino, L. Beta4 integrin activates a shp2-src signaling pathway that sustains hgf-induced anchorage-independent growth. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 175, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, A.K.; Sawada, K.; Tiwari, P.; Mui, K.; Gwin, K.; Lengyel, E. Ligand-independent activation of c-met by fibronectin and α(5)β(1)-integrin regulates ovarian cancer invasion and metastasis. Oncogene 2011, 30, 1566–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antipenko, A.; Himanen, J.P.; van Leyen, K.; Nardi-Dei, V.; Lesniak, J.; Barton, W.A.; Rajashankar, K.R.; Lu, M.; Hoemme, C.; Püschel, A.W.; et al. Structure of the semaphorin-3a receptor binding module. Neuron 2003, 39, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, S.; Corso, S.; Conrotto, P.; Artigiani, S.; Gilestro, G.; Barberis, D.; Tamagnone, L.; Comoglio, P.M. The semaphorin 4d receptor controls invasive growth by coupling with met. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2002, 4, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conrotto, P.; Corso, S.; Gamberini, S.; Comoglio, P.M.; Giordano, S. Interplay between scatter factor receptors and b plexins controls invasive growth. Oncogene 2004, 23, 5131–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conrotto, P.; Valdembri, D.; Corso, S.; Serini, G.; Tamagnone, L.; Comoglio, P.M.; Bussolino, F.; Giordano, S. Sema4d induces angiogenesis through met recruitment by plexin b1. Blood 2005, 105, 4321–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, A.; Götze, T.; Korc, M. Hepatocyte growth factor-mediated cell invasion in pancreatic cancer cells is dependent on neuropilin-1. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 10309–10316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulpice, E.; Plouët, J.; Bergé, M.; Allanic, D.; Tobelem, G.; Merkulova-Rainon, T. Neuropilin-1 and neuropilin-2 act as coreceptors, potentiating proangiogenic activity. Blood 2008, 111, 2036–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orian-Rousseau, V.; Chen, L.; Sleeman, J.P.; Herrlich, P.; Ponta, H. Cd44 is required for two consecutive steps in HGF/c-met signaling. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 3074–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crepaldi, T.; Gautreau, A.; Comoglio, P.M.; Louvard, D.; Arpin, M. Ezrin is an effector of hepatocyte growth factor-mediated migration and morphogenesis in epithelial cells. J. Cell. Biol. 1997, 138, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orian-Rousseau, V.; Morrison, H.; Matzke, A.; Kastilan, T.; Pace, G.; Herrlich, P.; Ponta, H. Hepatocyte growth factor-induced ras activation requires erm proteins linked to both cd44v6 and f-actin. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasenauer, S.; Malinger, D.; Koschut, D.; Pace, G.; Matzke, A.; von Au, A.; Orian-Rousseau, V. Internalization of met requires the co-receptor cd44v6 and its link to erm proteins. PLoS One 2013, 8, e62357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todaro, M.; Gaggianesi, M.; Catalano, V.; Benfante, A.; Iovino, F.; Biffoni, M.; Apuzzo, T.; Sperduti, I.; Volpe, S.; Cocorullo, G.; et al. Cd44v6 is a marker of constitutive and reprogrammed cancer stem cells driving colon cancer metastasis. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fafalios, A.; Ma, J.; Tan, X.; Stoops, J.; Luo, J.; Defrances, M.C.; Zarnegar, R. A hepatocyte growth factor receptor (met)-insulin receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertola, A.; Bonnafous, S.; Cormont, M.; Anty, R.; Tanti, J.F.; Tran, A.; Le Marchand-Brustel, Y.; Gual, P. Hepatocyte growth factor induces glucose uptake in 3t3-l1 adipocytes through a gab1/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/glut4 pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 10325–10332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdomo, G.; Martinez-Brocca, M.A.; Bhatt, B.A.; Brown, N.F.; O’Doherty, R.M.; Garcia-Ocaña, A. Hepatocyte growth factor is a novel stimulator of glucose uptake and metabolism in skeletal muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 13700–13706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Follenzi, A.; Bakovic, S.; Gual, P.; Stella, M.C.; Longati, P.; Comoglio, P.M. Cross-talk between the proto-oncogenes met and ron. Oncogene 2000, 19, 3041–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benvenuti, S.; Lazzari, L.; Arnesano, A.; Li Chiavi, G.; Gentile, A.; Comoglio, P.M. Ron kinase transphosphorylation sustains met oncogene addiction. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1945–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, M.; Stolz, D.B.; Esplen, J.E.; Dorko, K.; Michalopoulos, G.K.; Strom, S.C. Cross-talk between epidermal growth factor receptor and c-met signal pathways in transformed cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 8806–8811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanizaki, J.; Okamoto, I.; Sakai, K.; Nakagawa, K. Differential roles of trans-phosphorylated egfr, her2, her3, and ret as heterodimerisation partners of met in lung cancer with met amplification. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baldanzi, G.; Graziani, A. Physiological Signaling and Structure of the HGF Receptor MET. Biomedicines 2015, 3, 1-31. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines3010001
Baldanzi G, Graziani A. Physiological Signaling and Structure of the HGF Receptor MET. Biomedicines. 2015; 3(1):1-31. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines3010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaldanzi, Gianluca, and Andrea Graziani. 2015. "Physiological Signaling and Structure of the HGF Receptor MET" Biomedicines 3, no. 1: 1-31. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines3010001
APA StyleBaldanzi, G., & Graziani, A. (2015). Physiological Signaling and Structure of the HGF Receptor MET. Biomedicines, 3(1), 1-31. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines3010001







