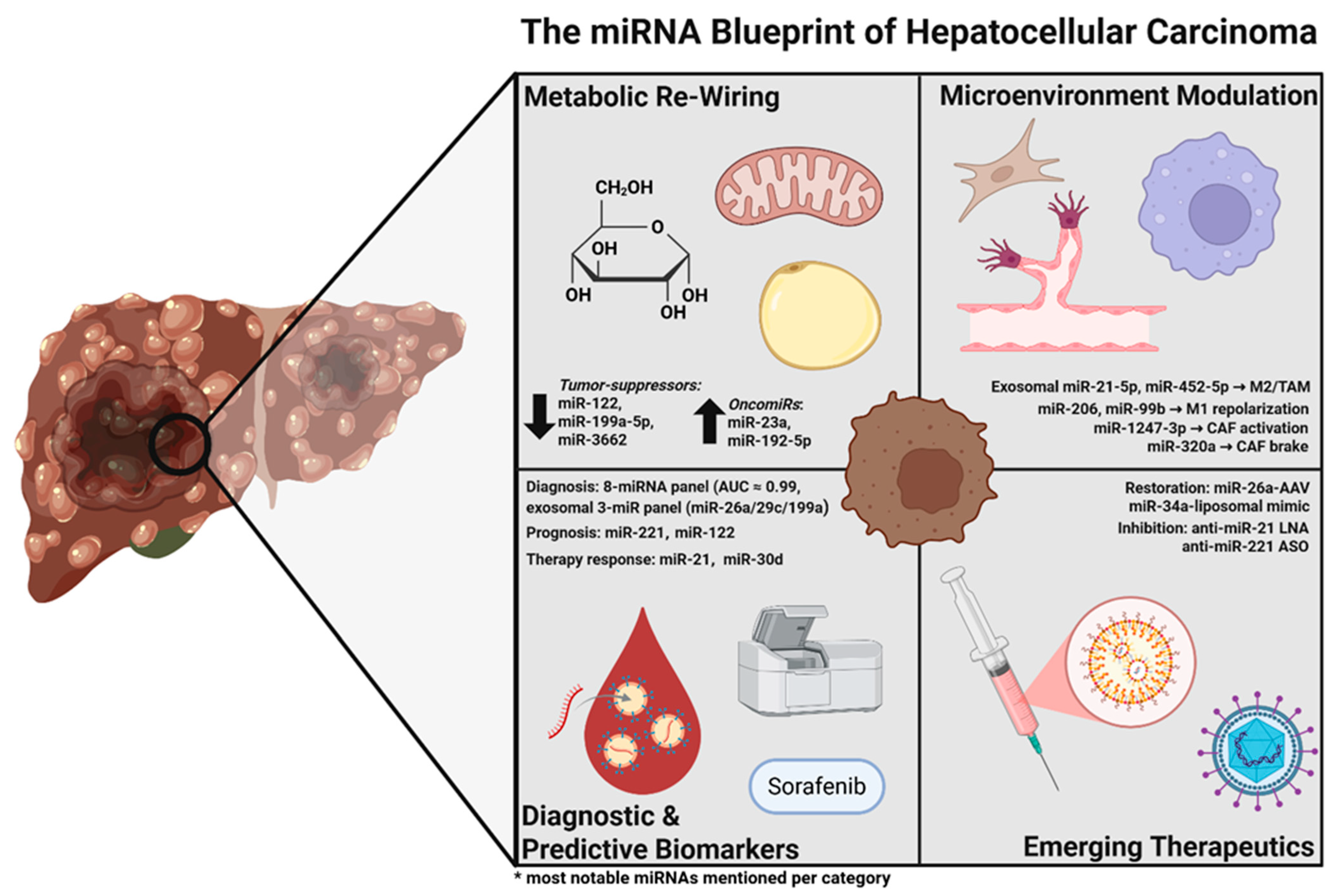
MicroRNA Landscape in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Metabolic Re-Wiring, Predictive and Diagnostic Biomarkers, and Emerging Therapeutic Targets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Main Theme
3.1. miRNA-Driven Metabolic Effects in HCC
3.1.1. Inter-Cellular Wiring of the Metabolic TME
3.1.2. Integrated Perspective
3.2. Diagnostic miRNAs in HCC
3.2.1. Early Detection of HCC via Individual miRNAs
3.2.2. Early Detection of HCC via miRNA Panels
3.2.3. Population and Etiology Considerations
3.2.4. miRNA-Based Differential Diagnosis vs. Cirrhosis
3.3. Predictive miRNAs in HCC
3.3.1. miRNAs Predictive of Recurrence After Curative Therapy
3.3.2. miRNAs Predictive of Overall and Disease-Free Survival
3.4. Therapeutic Targets in HCC
3.4.1. Restoring Tumor-Suppressor miRNAs in HCC
3.4.2. Inhibiting Oncogenic miRNAs in HCC
| miRNA (Family/Cluster) | Principal Oncogenic Targets and Pathways Repressed | Therapeutic Modality | Delivery Platform | Development Stage | Key Anti-Tumor Read-Outs (Pre-Clinical → Clinical) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A.Therapeutic Restoring of Tumor-Suppressor miRNAs in HCC | ||||||
| miR-34a (MRX34) | c-Met, BCL2, PD-L1, Cyclin D1 | Double-stranded mimic | SMARTICLE® liposomal nanoparticle | Phase I (terminated) | Target engagement and partial response in 1 HBV-HCC; immune-related SAEs ended trial | [106,107] |
| miR-199a-3p | mTOR, c-Met, PAK4, YAP1 | Mimic (2′-F/OMe modified) | Cholesterol-conjugated oligo (IV) | Orthotopic and GEMM models | ↓ nodule number/size ≈ sorafenib efficacy; mTOR ↓ | [27] |
| miR-195/15a-16 family | VEGFA/VAV2 (angiogenesis), CDK6/Cyclin D1 | Mimic | Ionisable-lipid LNP | Subcutaneous xenograft | ↓ microvessel density; G1–S blockade | [108] |
| miR-22 | Cyclin A, HDACs, SIRT1; immune and metabolic rewiring | Pri-miRNA gene cassette | AAV8 vector (liver-specific) | DEN-induced HCC mice | >lenvatinib tumor control; ↑ CD8+ T-cells; no toxicity | [111] |
| miR-124 | CDK6, Vimentin (EMT), STAT3 | Mimic | PEI-nanoplex | Cell-line and small xenografts | ↓ invasion and proliferation | [109] |
| miR-101 | EZH2, MCL1, COX-2; VM inhibition | Mimic | Lipidoid nanoparticle | Cell-line/CAM assays | Anti-proliferative; anti-vascularmimicry | [110] |
| OncomiR (cluster) | Tumor-suppressors de-repressed/pathways normalized | Inhibitor format | Delivery platform | Development stage | Key anti-tumor read-outs | Refs |
| B.Therapeutic Inhibition of Oncogenic miRNAs (OncomiRs) in HCC | ||||||
| miR-21 | PTEN, PDCD4, TP53BP1 → PI3K/AKT block; resensitises to chemo | LNA antagomir/cholesterol-ASO | GalNAc-ASO; LNP; ultrasound-microbubble | Multiple xenografts | ↓ growth, ↑ apoptosis; restores sorafenib/doxorubicin response | [115,116] |
| miR-221/miR-222 | p27Kip1, p57, PTEN; | LNA antagomir | Sub-10 kDa LNA-ASO; PLGA NP | GEMM and xenograft | Durable knock-down; ≤ 80% tumor shrinkage; restored p27/p57 | [117,119,120,127] |
| miR-155 | SOCS1, SHIP1 → STAT3 and NF-κB control; TAM repolarization | LNA antagomir | Chol-ASO | Orthotopic and immune-competent models | ↓ tumor growth and metastasis; ↑ anti-tumor immunity | [121,122] |
| miR-224 | Apaf-1, SMAD4 (apoptosis/TGFβ) | 2′-OMe antagomir | Lipidoid NP | Cell/xenograft | ↑ caspase-3 activity; ↓ invasion | [125] |
| miR-17-92 cluster | p21, E2F1, BIM | Tough-Decoy “sponge” (lentiviral) | Lentiviral | Cell/limited in vivo | Slower proliferation; partial tumor inhibition | [123,124] |
| Dual strategy (anti-miR-21 + miR-122 mimic) | Combines PTEN/PDCD4 de-repression with Cyclin G1 suppression | Co-admin antagomir + mimic | Lipoplex + ultrasound microbubbles | Rat orthotopic model | Superior tumor reduction vs. single agents; ↓ resistance | [116,126] |
3.4.3. Mechanistic Pathways Modulated by Therapeutic miRNAs
3.4.4. Preclinical Models for miRNA Studies in HCC
3.4.5. Delivery Strategies and Clinical Translation
4. Challenges and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAV | Adeno-associated virus |
| AFP | Alpha-fetoprotein |
| AKT | Protein kinase B |
| ASO | Antisense oligonucleotide |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| CAM | Chorio-allantoic membrane |
| CAF | Cancer-associated fibroblast |
| CH | Chronic hepatitis |
| CHB | Chronic hepatitis B |
| DEN | Diethylnitrosamine |
| DFS | Disease-free survival |
| DNMT1 | DNA methyltransferase 1 (gene symbol) |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| EMT | Epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| EV | Extracellular vesicle |
| FDG-PET | Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography |
| FASN | Fatty acid synthase (gene symbol) |
| GEMM | Genetically engineered mouse model |
| G6PD | Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| G6PC | Glucose-6-phosphatase |
| HDAC | Histone deacetylase |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| HK2 | Hexokinase 2 (gene symbol) |
| HIF-1α | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| LDHA | Lactate dehydrogenase A |
| LNA | Locked nucleic acid |
| LNP | Lipid nanoparticle |
| LP | Liposome (carrier) |
| miRNA | MicroRNA |
| mTOR | Mechanistic target of rapamycin |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NASH | Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis |
| NP | Nanoparticle |
| ONC | Oncogenic |
| OS | Overall survival |
| OTT | Onset To treatment |
| OXPHOS | Oxidative phosphorylation |
| PAK4 | p21-activated kinase 4 |
| PBX3 | Pre-B-cell leukemia homeobox 3 |
| PD-1 | Programmed cell death protein 1 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed death-ligand 1 |
| PDK1 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 |
| PET | Positron emission tomography |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| PKM2 | Pyruvate kinase isozyme M2 |
| PPP | Pentose–phosphate pathway |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative reverse transcription PCR |
| RFA | Radiofrequency ablation |
| RFS | Recurrence-free survival |
| SCD1 | Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 |
| SMAD4 | Small mothers against decapentaplegic 4 |
| TACE | Transarterialchemoembolisation |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| TGFβR1 | Transforming growth factor β receptor 1 |
| TKIs | Tyrosine kinase inhibitors |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| TNM | Tumor–node–metastasis staging |
| TS | Tumor-suppressor |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| VE-cadherin | Vascular endothelial cadherin |
| XPO1 | Exportin 1 (gene symbol) |
| YAP1 | Yes-associated protein 1 |
References
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Ding, C.; Cao, M.; Yang, F.; Yan, X.; He, S.; Cao, M.; Zhang, S.; Teng, Y.; Tan, N.; et al. Global Epidemiology of Liver Cancer 2022: An Emphasis on Geographic Disparities. Chin. Med. J. 2024, 137, 2334–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y. Changing Etiology and Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Asia and Worldwide. J. Liver Cancer 2024, 24, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Bao, H.; Huang, Z.; Liang, Z.; Wang, M.; Lin, N.; Ni, C.; Xu, Y. Little Things with Significant Impact: miRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1191070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma—Overview—Mayo Clinic. Available online: https://www.mayoclinicproceedings.org/article/S0025-6196(17)30480-9/fulltext (accessed on 13 April 2025).
- Tzartzeva, K.; Obi, J.; Rich, N.E.; Parikh, N.D.; Marrero, J.A.; Yopp, A.; Waljee, A.K.; Singal, A.G. Surveillance Imaging and Alpha Fetoprotein for Early Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Cirrhosis: A Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1706–1718.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.-J.; Kim, Y.-J. Liquid Biopsy for Early Detection and Therapeutic Monitoring of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Liver Cancer 2022, 22, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemayehu, E.; Fasil, A.; Ebrahim, H.; Mulatie, Z.; Bambo, G.M.; Gedefie, A.; Teshome, M.; Worede, A.; Belete, M.A. Circulating microRNAs as Promising Diagnostic Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2024, 11, 1353547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Lu, H.; Wang, X.; Jin, H. MicroRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Regulation, Function, and Clinical Implications. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 924206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, A.; Oura, K.; Tadokoro, T.; Fujita, K.; Tani, J.; Masaki, T. MicroRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, K.Z.; Zhang, K.; Li, H.; Afdhal, N.H.; Albitar, M. Circulating MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 45, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuguchi, Y.; Takizawa, T.; Yoshida, H.; Uchida, E. Dysregulated miRNA in Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-T.; Liu, S.-M.; Ma, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, J. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: Circulating miRNAs for Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Xiao, X.; Han, Y.; Fan, D.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, L. MiR-3662 Suppresses Cell Growth, Invasion and Glucose Metabolism by Targeting HK2 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Neoplasma 2020, 67, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zuo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, G.; Zhang, L.; Wu, J.; Wang, X. MiR-3662 Suppresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth through Inhibition of HIF-1α-Mediated Warburg Effect. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Yan, J.-J.; Gan, Y.; Chang, Y.; Wang, H.-L.; He, X.-X.; Zhao, Q. miR-885-5p Negatively Regulates Warburg Effect by Silencing Hexokinase 2 in Liver Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 18, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, X.; Zen, K.; Li, L. The miR-125a/HK2 Axis Regulates Cancer Cell Energy Metabolism Reprogramming in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Zheng, N.; Teng, F.; Bao, L.; Liu, F.; Zhang, M.; Guo, M.; Guo, W.; Ding, G.; Wang, Q. MiR-199a/b-5p Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Post-Transcriptionally Suppressing ROCK1. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 67169–67180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Ji, F.; Liu, N.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, X.; Hu, S.; Jia, W.; Wang, X.W.; Budhu, A.; Ji, J.; et al. Loss of miR-192-5p Initiates a Hyperglycolysis and Stemness Positive Feedback in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaianni, F.; Zelli, V.; Compagnoni, C.; Miscione, M.S.; Rossi, M.; Vecchiotti, D.; Di Padova, M.; Alesse, E.; Zazzeroni, F.; Tessitore, A. Role of Circulating microRNAs in Liver Disease and HCC: Focus on miR-122. Genes 2024, 15, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Hsu, S.; Frankel, W.; Ghoshal, K.; Jacob, S.T. Stat3-Mediated Activation of miR-23a Suppresses Gluconeogenesis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Downregulating G6PC and PGC-1α. Hepatology 2012, 56, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, P.; Liu, J.; Ding, L.; Ye, Q. MiR-4310 Regulates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth and Metastasis through Lipid Synthesis. Cancer Lett. 2021, 519, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Ma, Y.; Ye, Q.; Yan, X.; Ding, L. MicroRNA-377-3p Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth and Metastasis through Negative Regulation of CPT1C-Mediated Fatty Acid Oxidation. Cancer Metab. 2022, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, K.; Bian, X.; Shi, D.; Dong, S.; Zhou, H.; Xiao, S.; Bai, J.; Wu, W. miR-612 Enhances RSL3-Induced Ferroptosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells via Mevalonate Pathway. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2023, 10, 2173–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, L.-L.; Wen, D.; Liu, D.-L.; Dong, L.-L.; Gao, D.-M.; Bian, X.-Y.; Zhou, J.; Fan, J.; Wu, W.-Z. MiR-612 Regulates Invadopodia of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by HADHA-Mediated Lipid Reprogramming. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callegari, E.; D’Abundo, L.; Guerriero, P.; Simioni, C.; Elamin, B.K.; Russo, M.; Cani, A.; Bassi, C.; Zagatti, B.; Giacomelli, L.; et al. miR-199a-3p Modulates MTOR and PAK4 Pathways and Inhibits Tumor Growth in a Hepatocellular Carcinoma Transgenic Mouse Model. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 11, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Dong, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, H.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, F.; Li, Q.; Duan, X.; Hu, Y.; Xiao, W. Exosomal microRNA Panel as a Diagnostic Biomarker in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 927251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Hemann, C.; Mahoney, C.E.; Zweier, J.L.; Loscalzo, J. MicroRNA-210 Controls Mitochondrial Metabolism during Hypoxia by Repressing the Iron-Sulfur Cluster Assembly Proteins ISCU1/2. Cell Metab. 2009, 10, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemayehu, E.; Belete, M.A.; Walle, M.; Getu, F.; Mulatie, Z.; Teshome, M.; Anley, D.T.; Weldehanna, D.G.; Gedefie, A.; Ebrahim, H. Diagnostic Accuracy of Circulating miRNAs to Discriminate Hepatocellular Carcinoma from Liver Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1359414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Friedman, J.R. miR-122 Regulates Hepatic Lipid Metabolism and Tumor Suppression. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2773–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-X.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. Preliminary Study on the Role of miR-148a and DNMT1 in the Pathogenesis of Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 2943–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, D.; Cassel, T.; Teng, K.; Aljuhani, M.; Chowdhary, V.K.; Hu, P.; Zhang, X.; Fan, T.W.-M.; Ghoshal, K. Regulation of Hepatic Glutamine Metabolism by miR-122. Mol. Metab. 2020, 34, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, D.; Zhao, Z.; Ren, P.; Li, C.; Hu, Y.; Shi, J.; Su, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; et al. Epigenetic Silencing of microRNA-137 Enhances ASCT2 Expression and Tumor Glutamine Metabolism. Oncogenesis 2017, 6, e356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, R.; Wang, H.; Liu, Q. Hypoxia-Driven miR-1307-3p Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Proliferation and Invasion by Modulating DAB2 Interacting Protein. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2022, 237, 154066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Cao, Q.; Feng, M.; Xue, F.; Wei, L.; Qin, W.; Gu, J.; Xia, Q.; et al. Mineralocorticoid Receptor Suppresses Cancer Progression and the Warburg Effect by Modulating the miR-338-3p-PKLR Axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2015, 62, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, Q.; Zou, C.; Huang, J.; Zhang, L. Crosstalk between Exosomes and Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Implication for Cancer Progression and Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1512480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Pan, J.; Zheng, S.; Cai, D.; Luo, A.; Xia, Z.; Huang, J. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell-Derived Exosomal miR-21-5p Induces Macrophage M2 Polarization by Targeting RhoB. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Wang, X.; Steer, C.J.; Song, G. MicroRNA-206 Promotes the Recruitment of CD8+ T Cells by Driving M1 Polarisation of Kupffer Cells. Gut 2022, 71, 1642–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hu, Y.-Y.; Zhao, J.-L.; Huang, F.; Liang, S.-Q.; Dong, L.; Chen, Y.; Yu, H.-C.; Bai, J.; Yang, J.-M.; et al. Targeted Delivery of miR-99b Reprograms Tumor-Associated Macrophage Phenotype Leading to Tumor Regression. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Gong, G.; Deng, Y.; Long, X.; Long, W.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, W.; Chen, R. Crosstalk between Cancer Cells and the Nervous System. Med. Adv. 2023, 1, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ren, H.; Dai, B.; Li, J.; Shang, L.; Huang, J.; Shi, X. Hepatocellular Carcinoma-Derived Exosomal miRNA-21 Contributes to Tumor Progression by Converting Hepatocyte Stellate Cells to Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Lv, H.; Lv, G.; Li, T.; Wang, C.; Han, Q.; Yu, L.; Su, B.; Guo, L.; Huang, S.; et al. Tumor-Derived Exosomal miR-1247-3p Induces Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Activation to Foster Lung Metastasis of Liver Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zongqiang, H.; Jiapeng, C.; Yingpeng, Z.; Chuntao, Y.; Yiting, W.; Jiashun, Z.; Li, L. Exosomal miR-452-5p Induce M2 Macrophage Polarization to Accelerate Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Targeting TIMP3. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 2022, 1032106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Sun, W.; Yue, S.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Ma, B.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Pu, M.; et al. Loss of Exosomal miR-320a from Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Contributes to HCC Proliferation and Metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2017, 397, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, Z.; Liu, W.; Yuan, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Qiu, Y.; et al. Dysregulated Sp1/miR-130b-3p/HOXA5 Axis Contributes to Tumor Angiogenesis and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Theranostics 2020, 10, 5209–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.O.; Youn, H.; Lee, C.-H.; Kang, K.W.; Chung, J.-K. Visualization of Exosome-Mediated miR-210 Transfer from Hypoxic Tumor Cells. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 9899–9910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orozco-García, E.; van Meurs, D.J.; Calderón, J.C.; Narvaez-Sanchez, R.; Harmsen, M.C. Endothelial Plasticity across PTEN and Hippo Pathways: A Complex Hormetic Rheostat Modulated by Extracellular Vesicles. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 31, 101633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yu, L.; Huang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, W.; Meng, N.; He, R.; Xu, Y.; Keong, T.S.; Cui, Y. Tumor-Associated Exosomes Are Involved in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tumorigenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2022, 10, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, Y.; Tan, S.M.; Karreth, F.A.; Lieberman, J.; Pandolfi, P.P. Characterization of Dual PTEN and P53-Targeting MicroRNAs Identifies MicroRNA-638/Dnm2 as a Two-Hit Oncogenic Locus. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.-H.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Shang, L.-R.; Luo, Y.-W.; Lin, Y.-F.; Yuan, Y.; Zhuang, S.-M. Hepatoma Cell-Secreted Exosomal microRNA-103 Increases Vascular Permeability and Promotes Metastasis by Targeting Junction Proteins. Hepatology 2018, 68, 1459–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tang, T.; Hu, X.; Tan, W.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Yang, M.; Zhou, M.; et al. miR-138-5p Inhibits Vascular Mimicry by Targeting the HIF-1α/VEGFA Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 2022, 7318950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; Peng, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, H.; Shan, B.; Zhang, C.; Duan, C. Vasculogenic Mimicry in Carcinogenesis and Clinical Applications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lu, Y.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Zheng, Z.-Y.; Fang, J.-H.; He, S.; Zhuang, S.-M. Vascular Mimicry Formation Is Promoted by Paracrine TGF-β and SDF1 of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Inhibited by miR-101 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2016, 383, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Wu, J.; Zhai, A.; Qian, J.; Wang, X.; Qaria, M.A.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Fang, Y.; Kao, W.; et al. HBV Triggers APOBEC2 Expression through miR-122 Regulation and Affects the Proliferation of Liver Cancer Cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 55, 1137–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.-N.; Wu, L.-N.; Liu, S.W.; Zhang, X.; Luo, X.; Nawaz, S.; Ma, Z.M.; Ding, X.-C. miR-199a/b-3p Inhibits HCC Cell Proliferation and Invasion through a Novel Compensatory Signaling Pathway DJ-1\Ras\PI3K/AKT. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanasekaran, R.; Limaye, A.; Cabrera, R. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Current Trends in Worldwide Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Diagnosis, and Therapeutics. Hepatic Med. 2012, 4, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ma, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, B.; Yu, J.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Luan, Y.; Chen, M. Diagnostic Value of Circulating microRNAs for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Results of a Meta-Analysis and Validation. Biochem. Genet. 2025. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Chen, H.; Liu, X.-P.; Wang, Y.-H.; Luo, C.-L.; Zhang, W.-W.; Xie, W.; Wang, F.-B. A miRNA Combination as Promising Biomarker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Diagnosis: A Study Based on Bioinformatics Analysis. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 3435–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Lv, X.; Lv, X.; Ma, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y. Circulating miR-21 Serves as a Serum Biomarker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Correlated with Distant Metastasis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 44050–44058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Yasuda, T.; Saigo, K.; Urashima, T.; Toyoda, H.; Okanoue, T.; Shimotohno, K. Comprehensive Analysis of microRNA Expression Patterns in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Non-Tumorous Tissues. Oncogene 2006, 25, 2537–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulouarn, C.; Factor, V.M.; Andersen, J.B.; Durkin, M.E.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Loss of miR-122 Expression in Liver Cancer Correlates with Suppression of the Hepatic Phenotype and Gain of Metastatic Properties. Oncogene 2009, 28, 3526–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramantieri, L.; Ferracin, M.; Fornari, F.; Veronese, A.; Sabbioni, S.; Liu, C.-G.; Calin, G.A.; Giovannini, C.; Ferrazzi, E.; Grazi, G.L.; et al. Cyclin G1 Is a Target of miR-122a, a MicroRNA Frequently Down-Regulated in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6092–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Kondo, S.; Matsuzaki, J.; Esaki, M.; Okusaka, T.; Shimada, K.; Murakami, Y.; Enomoto, M.; Tamori, A.; Kato, K.; et al. Highly Sensitive Circulating MicroRNA Panel for Accurate Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Liver Disease. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Hao, K.; Li, M.; Wang, A.; Tang, H.; Xu, L.; Ma, C.; Du, W.; Sun, L.; Hou, X.; et al. Five miRNAs Identified in Fucosylated Extracellular Vesicles as Non-Invasive Diagnostic Signatures for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Liao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. The Diagnostic Value of Circulating microRNAs as Biomarkers for Coronary Artery Disease: A Meta-analysis. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2020, 24, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wong, Y.S.; Goh, B.K.P.; Chan, C.Y.; Cheow, P.C.; Chow, P.K.H.; Lim, T.K.H.; Goh, G.B.B.; Krishnamoorthy, T.L.; Kumar, R.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cermelli, S.; Ruggieri, A.; Marrero, J.A.; Ioannou, G.N.; Beretta, L. Circulating MicroRNAs in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tu, S.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, Y.; Yu, W. Diagnostic Accuracy of Circulating microRNAs for Hepatitis C Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, K.K.K.; Lu, Y.; Qiu, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Xie, H.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, M. Establishing a miRNA Panel for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Screening through a Multicenter Study. iScience 2025, 28, 112986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Wan, R.; Ren, L.; Yang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wang, W. Circulating MicroRNA Panel as a Diagnostic Marker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 33, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelkhalek, Z.S.; Abdalla, M.S.; Fathy, M.M.; Elbaz, T.M.; Abdelaziz, A.O.; Nabeel, M.M.; Shousha, H.I.; Kamel, A.H.; Kamel, M.H. Role of Circulating microRNA-21 and microRNA-215 in the Diagnosis of Hepatitis C Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2021, 15, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, A.I.; Khan, S.A.; Leen, E.L.; Waked, I.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D. Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayob, N.; Kanwal, F.; Alsarraj, A.; Hernaez, R.; El-Serag, H.B. The Performance of AFP, AFP-3, DCP as Biomarkers for Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): A Phase 3 Biomarker Study in the United States. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 415–423.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Dong, X.; Zhai, B.; Jiang, X.; Dong, D.; Li, B.; Jiang, H.; Xu, S.; Sun, X. MiR-21 Mediates Sorafenib Resistance of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Inhibiting Autophagy via the PTEN/Akt Pathway. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 28867–28881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohno, T.; Morishita, A.; Iwama, H.; Fujita, K.; Tani, J.; Takuma, K.; Nakahara, M.; Oura, K.; Tadokoro, T.; Nomura, T.; et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Circulating microRNAs as Predictive Biomarkers for Sorafenib Therapy Outcome in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 1727–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Lin, Z.; Wan, Z.; Xia, S.; Jiang, S.; Cen, D.; Cai, L.; Xu, J.; Cai, X. miR-486-3p Mediates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Sorafenib Resistance by Targeting FGFR4 and EGFR. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koustas, E.; Trifylli, E.-M.; Sarantis, P.; Papadopoulos, N.; Papanikolopoulos, K.; Aloizos, G.; Damaskos, C.; Garmpis, N.; Garmpi, A.; Matthaios, D.; et al. An Insight into the Arising Role of MicroRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Future Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Lu, C. Diagnostic Performance of microRNAs for Predicting Response to Transarterial Chemoembolization in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2025, 14, 1483196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, A.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X.; Zeng, D.; Gu, M.; Lv, C. MicroRNA-1271 Inhibits Cellular Proliferation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 6783–6788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tork, A.S.E.-D.; Kamel, A.A.F.; Zaki, M.A.; Abo El-Wafa, R.A.H.; El-Assar, O.S.; Ibrahim Abdelkarem, O.A. Circulating MiRNA-373 as a Predictor of Response to Super-Selective Transarterial Chemoembolization Bridging Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Awaiting Liver Transplantation. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2023, 24, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratama, M.Y.; Visintin, A.; Crocè, L.S.; Tiribelli, C.; Pascut, D. Circulatory miRNA as a Biomarker for Therapy Response and Disease-Free Survival in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H.E.A.; Emam, A.A.; Zeeneldin, A.A.; Srour, R.; Tabashy, R.; El-Desouky, E.D.; Abd Elmageed, Z.Y.; Abdel-Wahab, A.-H.A. Circulating miR-26a, miR-106b, miR-107 and miR-133b Stratify Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients According to Their Response to Transarterial Chemoembolization. Clin. Biochem. 2019, 65, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; Cho, H.J.; Nam, J.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, D.R.; Won, J.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, B.H.; et al. Plasma MicroRNA-21, 26a, and 29a-3p as Predictive Markers for Treatment Response Following Transarterial Chemoembolization in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2018, 33, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabeti Touchaei, A.; Vahidi, S. MicroRNAs as Regulators of Immune Checkpoints in Cancer Immunotherapy: Targeting PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 Pathways. Cancer Cell Int. 2024, 24, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.Y.; Yu, J.I.; Choi, C.; Kang, S.Y.; Joh, J.-W.; Paik, S.W.; Kim, S.; Kim, M.; Park, H.C.; Park, C.-K. Prognostic Significance of miR-122 Expression after Curative Resection in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, G.E.; Yoon, J.-H.; Myung, S.J.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, S.-M.; Kim, S.-J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Lee, H.-S.; Kim, C.Y. High Expression of microRNA-15b Predicts a Low Risk of Tumor Recurrence Following Curative Resection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 23, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Qin, C. MicroRNA-34a Expression Is Predictive of Recurrence after Radiofrequency Ablation in Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 3887–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasuri, F.; Fittipaldi, S.; De Pace, V.; Gramantieri, L.; Bertuzzo, V.; Cescon, M.; Pinna, A.D.; Fiorentino, M.; D’Errico, A.; Ravaioli, M. Tissue miRNA 483-3p Expression Predicts Tumor Recurrence after Surgical Resection in Histologically Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinomas. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 17895–17905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisetti, L.; Võ, N.V.T.; Nguyễn, N.N.Q.; Crocè, L.S.; Visintin, A.; Tiribelli, C.; Pascut, D. MiR-3201 as a Prognostic Blood Biomarker for Curative Treatments in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 21, 15330338221132924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, L.K.; Yang, Y.T.; Ma, X.; Han, B.; Wang, Z.S.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Wu, L.Q.; Qu, Z.Q. MicroRNA-92b Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Targeting Smad7 and Is Mediated by Long Non-Coding RNA XIST. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Chen, I.-H.; Wang, C.-C.; Chen, P.-J.; Tseng, H.-P.; Huang, K.-T.; Hu, T.-H.; Li, L.-C.; Goto, S.; Cheng, Y.-F.; et al. Circulating Exosomal miR-92b: Its Role for Cancer Immunoediting and Clinical Value for Prediction of Posttransplant Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence. Am. J. Transplant. 2019, 19, 3250–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khare, S.; Khare, T.; Ramanathan, R.; Ibdah, J.A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Role of MicroRNAs. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hu, K.; Zhang, F.; Lu, S.; Chen, R.; Ren, Z.; Yin, X. The Prognostic Significance of microRNA-221 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Updated Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2021, 36, 17246008211032689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, L.; Zhai, L.; Chen, D.; Li, Y.; Shang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, Y.; et al. Construction and Validation of a Three-microRNA Signature as Prognostic Biomarker in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 984–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.J.; Eun, J.W.; Baek, G.O.; Seo, C.W.; Ahn, H.R.; Kim, S.S.; Cho, S.W.; Cheong, J.Y. Serum Exosomal MicroRNA, miR-10b-5p, as a Potential Diagnostic Biomarker for Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zou, B.; Nan, T.; Zheng, X.; Zheng, L.; Lan, J.; Chen, W.; Yu, J. MiR-25 Enhances Autophagy and Promotes Sorafenib Resistance of Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Targeting FBXW7. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 19, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiuso, P.; Potenza, N.; Lombardi, A.; Ferrandino, I.; Monaco, A.; Zappavigna, S.; Vanacore, D.; Mosca, N.; Castiello, F.; Porto, S.; et al. MicroRNA-423-5p Promotes Autophagy in Cancer Cells and Is Increased in Serum from Hepatocarcinoma Patients Treated With Sorafenib. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2015, 4, e233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Evert, M.; Calvisi, D.F.; Chen, X. β-Catenin Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e154515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Hu, Y.; Bai, B.; Zhang, S. Serum miR-335 Level Is Associated with the Treatment Response to Trans-Arterial Chemoembolization and Prognosis in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA: Trends in Clinical Trials of Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy Strategies. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; He, X. The Role of microRNAs in Liver Cancer Progression. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, J.; Chivukula, R.R.; O’Donnell, K.A.; Wentzel, E.A.; Montgomery, C.L.; Hwang, H.-W.; Chang, T.-C.; Vivekanandan, P.; Torbenson, M.; Clark, K.R.; et al. Therapeutic microRNA Delivery Suppresses Tumorigenesis in a Murine Liver Cancer Model. Cell 2009, 137, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; Nasser, M.W.; Wang, B.; Hsu, S.-H.; Datta, J.; Kutay, H.; Yadav, A.; Nuovo, G.; Kumar, P.; Ghoshal, K. MicroRNA-122 Inhibits Tumorigenic Properties of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells and Sensitizes These Cells to Sorafenib. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 32015–32027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltier, H.J.; Kelnar, K.; Bader, A.G. Effects of MRX34, a Liposomal miR-34 Mimic, on Target Gene Expression in Human White Blood Cells (hWBCs): qRT-PCR Results from a First-in-Human Trial of microRNA Cancer Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, e14090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirna Therapeutics, Inc. A Multicenter Phase I Study of MRX34, MicroRNA miR-RX34 Liposomal Injection; Mirna Therapeutics, Inc.: Austin, TX, USA, 2016. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Hong, D.S.; Kang, Y.-K.; Borad, M.; Sachdev, J.; Ejadi, S.; Lim, H.Y.; Brenner, A.J.; Park, K.; Lee, J.-L.; Kim, T.-Y.; et al. Phase 1 Study of MRX34, a Liposomal miR-34a Mimic, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhu, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Ge, Y.-Y.; Yun, J.-P.; Zhuang, S.-M. MicroRNA-195 Suppresses Tumorigenicity and Regulates G1/S Transition of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Hepatology 2009, 50, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, M.; Kozaki, K.; Tanaka, S.; Arii, S.; Imoto, I.; Inazawa, J. miR-124 and miR-203 Are Epigenetically Silenced Tumor-Suppressive microRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Z.; Deng, F.; Li, H.; Wang, D.-D.; Zhang, W.; Ding, L.; Tang, J.-H. MiR-101: A Potential Therapeutic Target of Cancers. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 3310–3321. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Setayesh, T.; Vaziri, F.; Wu, X.; Hwang, S.T.; Chen, X.; Wan, Y.-J.Y. miR-22 Gene Therapy Treats HCC by Promoting Anti-Tumor Immunity and Enhancing Metabolism. Mol. Ther. 2023, 31, 1829–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhuri, K.; Gaddam, R.R.; Vikram, A.; Slack, F.J.; Bahal, R. Therapeutic Potential of Chemically Modified, Synthetic, Triplex Peptide Nucleic Acid–Based Oncomir Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 5613–5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otmani, K.; Rouas, R.; Lewalle, P. OncomiRs as Noncoding RNAs Having Functions in Cancer: Their Role in Immune Suppression and Clinical Implications. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 913951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Ali, D.J.; Tian, T.; Xu, H.; Si, K.; Sun, B.; Chen, B.; Xiao, Z. Engineered Exosomes for Targeted Co-Delivery of miR-21 Inhibitor and Chemotherapeutics to Reverse Drug Resistance in Colon Cancer. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenaar, T.R.; Zabludoff, S.; Ahn, S.-M.; Allerson, C.; Arlt, H.; Baffa, R.; Cao, H.; Davis, S.; Garcia-Echeverria, C.; Gaur, R.; et al. Anti-miR-21 Suppresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth via Broad Transcriptional Network Deregulation. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullick Chowdhury, S.; Wang, T.-Y.; Bachawal, S.; Devulapally, R.; Choe, J.W.; Abou Elkacem, L.; Yakub, B.K.; Wang, D.S.; Tian, L.; Paulmurugan, R.; et al. Ultrasound-Guided Therapeutic Modulation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Complementary microRNAs. J. Control. Release 2016, 238, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineau, P.; Volinia, S.; McJunkin, K.; Marchio, A.; Battiston, C.; Terris, B.; Mazzaferro, V.; Lowe, S.W.; Croce, C.M.; Dejean, A. miR-221 Overexpression Contributes to Liver Tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- le Sage, C.; Nagel, R.; Egan, D.A.; Schrier, M.; Mesman, E.; Mangiola, A.; Anile, C.; Maira, G.; Mercatelli, N.; Ciafrè, S.A.; et al. Regulation of the p27Kip1 Tumor Suppressor by miR-221 and miR-222 Promotes Cancer Cell Proliferation. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 3699–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornari, F.; Gramantieri, L.; Ferracin, M.; Veronese, A.; Sabbioni, S.; Calin, G.A.; Grazi, G.L.; Giovannini, C.; Croce, C.M.; Bolondi, L.; et al. MiR-221 Controls CDKN1C/P57 and CDKN1B/P27 Expression in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5651–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ren, Z.; Lü, J.; Mo, X.; Lin, J.; Li, Y.; Ma, W.; Liu, P.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Nanoparticles Carrying Paclitaxel and Anti-miR-221 for Breast Cancer Therapy Triggered by Ultrasound. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, S.; Zhuang, Y.; Nagesh, P.T.; Catalano, D.; Zivny, A.; Wang, Y.; Xie, J.; Gao, G.; Szabo, G. Therapeutic Inhibition of miR-155 Attenuates Liver Fibrosis via STAT3 Signaling. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2023, 33, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.-X.; Yin, M.; Liu, H.-L.; Chen, J.-P.; Han, J.-Q.; Wang, W.-B. MiRNA-155 Mediates TAM Resistance by Modulating SOCS6-STAT3 Signalling Pathway in Breast Cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2015, 7, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ji, H.; Lu, X.; Xia, J.; Li, L.; Chen, F.; Bu, H.; Shi, Y. MiR-17 92 Ablation Impairs Liver Regeneration in an Estrogen-Dependent Manner. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Han, C.; Wu, T. MiR-17-92 Cluster Promotes Hepatocarcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Fan, X.; Mao, L.; Zhang, J.; LI, J.; Wu, J.; Tang, J. MicroRNA-224: As a Potential Target for miR-Based Therapy of Cancer. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 6645–6652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischhusen, J.C.; Chowdhury, S.M.; Lee, T.; Wang, H.; Bachawal, S.; Devulapally, R.; Afjei, R.; Sukumar, U.K.; Paulmurugan, R. Ultrasound-Mediated Delivery of miRNA-122 and Anti-miRNA-21 Therapeutically Immunomodulates Murine Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Vivo. J. Control. Release 2020, 321, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Grillone, K.; Ascrizzi, S.; Caridà, G.; Fiorillo, L.; Ciliberto, D.; Staropoli, N.; Tagliaferri, P.; Tassone, P.; Martino, M.T.D. LNA-i-miR-221 Activity in Colorectal Cancer: A Reverse Translational Investigation. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2024, 35, 102221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Li, H.; Zhao, S.; Wang, E.; Zhu, J.; Feng, D.; Zhu, Y.; Dou, W.; Fan, Q.; Hu, J.; et al. Epigenetic Silencing of miR-144/451a Cluster Contributes to HCC Progression via Paracrine HGF/MIF-Mediated TAM Remodeling. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X. Liver Organoids: An in Vitro 3D Model for Liver Cancer Study. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broutier, L.; Mastrogiovanni, G.; Verstegen, M.M.; Francies, H.E.; Gavarró, L.M.; Bradshaw, C.R.; Allen, G.E.; Arnes-Benito, R.; Sidorova, O.; Gaspersz, M.P.; et al. Human Primary Liver Cancer–Derived Organoid Cultures for Disease Modeling and Drug Screening. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami Nejad, A.; Najafgholian, S.; Rostami, A.; Sistani, A.; Shojaeifar, S.; Esparvarinha, M.; Nedaeinia, R.; Haghjooy Javanmard, S.; Taherian, M.; Ahmadlou, M.; et al. The Role of Hypoxia in the Tumor Microenvironment and Development of Cancer Stem Cell: A Novel Approach to Developing Treatment. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakiri, L.; Wagner, E.F. Mouse Models for Liver Cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2013, 7, 206–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Xue, H.; Yun, W.-J. An Overview of Mouse Models of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Infect. Agents Cancer 2023, 18, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiberger, T.; Chen, Y.; Ramjiwan, R.R.; Hato, T.; Fan, C.; Samuel, R.; Roberge, S.; Huang, P.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Zhu, A.; et al. An Orthotopic Mouse Model of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Underlying Liver Cirrhosis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 1264–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigliano, A.; Liao, W.; Deiana, G.A.; Rizzo, D.; Chen, X.; Calvisi, D.F. Preclinical Models of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Current Utility, Limitations, and Challenges. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manganelli, M.; Grossi, I.; Ferracin, M.; Guerriero, P.; Negrini, M.; Ghidini, M.; Senti, C.; Ratti, M.; Pizzo, C.; Passalacqua, R.; et al. Longitudinal Circulating Levels of miR-23b-3p, miR-126-3p and lncRNA GAS5 in HCC Patients Treated with Sorafenib. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Ren, L.; Li, J.; Lin, W.; Lou, L.; Wang, M.; Li, C.; Jiang, Y. Proteomic Analysis of DEN and CCl4-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Mouse Model. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganguly, S.; Muench, G.A.; Shang, L.; Rosenthal, S.B.; Rahman, G.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Kwon, H.C.; Diomino, A.M.; Kisseleva, T.; et al. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and HCC in a Hyperphagic Mouse Accelerated by Western Diet. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 12, 891–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehara, T.; Pogribny, I.P.; Rusyn, I. The DEN and CCl4-Induced Mouse Model of Fibrosis and Inflammation-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Hu, Y.-W.; Zhao, J.-Y.; Hu, X.-M.; Li, S.-F.; Wang, Y.-C.; Gao, J.-J.; Sha, Y.-H.; Kang, C.-M.; Lin, L.; et al. MicroRNA-195-5p Acts as an Anti-Oncogene by Targeting PHF19 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-K.; Kogure, T.; Nuovo, G.J.; Jiang, J.; He, L.; Kim, J.H.; Phelps, M.A.; Papenfuss, T.L.; Croce, C.M.; Patel, T.; et al. miR-221 Silencing Blocks Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Promotes Survival. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 7608–7616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callegari, E.; Elamin, B.K.; Giannone, F.; Milazzo, M.; Altavilla, G.; Fornari, F.; Giacomelli, L.; D’Abundo, L.; Ferracin, M.; Bassi, C.; et al. Liver Tumorigenicity Promoted by microRNA-221 in a Mouse Transgenic Model. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gu, A.; Tang, N.; Zengin, G.; Li, M.-Y.; Liu, Y. Patient-Derived Xenograft Models in Pan-Cancer: From Bench to Clinic. Interdiscip. Med. 2025, e20250016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shuen, T.W.H.; Toh, T.B.; Chan, X.Y.; Liu, M.; Tan, S.Y.; Fan, Y.; Yang, H.; Lyer, S.G.; Bonney, G.K.; et al. Development of a New Patient-Derived Xenograft Humanised Mouse Model to Study Human-Specific Tumour Microenvironment and Immunotherapy. Gut 2018, 67, 1845–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, D.; Ren, B.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z. Upregulation of miR-501-5p Activates the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway and Enhances Stem Cell-like Phenotype in Gastric Cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Wang, G.; Men, K.; Li, C.; Gao, N.; Li, L. Advances in Clinical Application of Nanoparticle-Based Therapy for Cancer Treatment: A Systematic Review. Nano TransMed 2024, 3, 100036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravalli, R.N. Development of MicroRNA Therapeutics for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Diagnostics 2013, 3, 170–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.; Yu, B.; Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; Schmidt, C.R.; Lee, R.J.; Lee, L.J.; Jacob, S.T.; Ghoshal, K. Cationic Lipid Nanoparticles for Therapeutic Delivery of siRNA and miRNA to Murine Liver Tumor. Nanomedicine 2013, 9, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, D.P.; Gross, O.; Wang, F.; Esteban de la Rosa, R.J.; Hall, M.; Sayer, J.A.; Appel, G.; Hariri, A.; Liu, S.; Maski, M.; et al. A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial Testing Effects of Lademirsen on Kidney Function Decline in Adults with Alport Syndrome. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2024, 19, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querfeld, C.; Pacheco, T.; Foss, F.M.; Halwani, A.S.; Porcu, P.; Seto, A.G.; Ruckman, J.; Landry, M.L.; Jackson, A.L.; Pestano, L.A.; et al. Preliminary Results of a Phase 1 Trial Evaluating MRG-106, a Synthetic microRNA Antagonist (LNA antimiR) of microRNA-155, in Patients with CTCL. Blood 2016, 128, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Yang, Y.; Peng, F.; Liu, Y.; Fu, X.; Ji, B. Gold Nanoparticles-Loaded Anti-miR221 Enhances Antitumor Effect of Sorafenib in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 16, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornari, F.; Pollutri, D.; Patrizi, C.; La Bella, T.; Marinelli, S.; CasadeiGardini, A.; Marisi, G.; BaronToaldo, M.; Baglioni, M.; Salvatore, V.; et al. In Hepatocellular Carcinoma miR-221 Modulates Sorafenib Resistance through Inhibition of Caspase-3-Mediated Apoptosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3953–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| miRNA | Primary Target(s) | Pathway/Cell Type Affected | Net Effect on HCC Biology | Dys-Reg. | Mode of Action | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. Cancer-Cell-Intrinsic Metabolic Regulation | ||||||
| Glycolysis and Glutaminolysis | ||||||
| miR-122 | PKM2, GLS1, SLC1A5/ASCT2, G6PD | Warburg glycolysis, glutaminolysis, PPP in tumor cells | Restores oxidative metabolism; ↓ lactate and glutamine use → growth restraint | ↓ | TS | [31,33] |
| miR-3662 | HIF-1α | HIF-driven glycolytic programming | ↓ GLUT1/HK2/PKM2/LDHA → curtailed glycolysis and tumor growth | ↓ | TS | [15,16] |
| miR-199a-5p | HIF-1α | Warburg glycolysis | ↓ glucose uptake and lactate → slower proliferation | ↓ | TS | [19,56] |
| miR-885-5p | HK2 | Glycolysis | Blunts aerobic glycolysis under hypoxia | ↓ | TS | [17] |
| miR-125a | HK2 | Glycolysis and ROS balance | ↓ glucose consumption, lactate and ROS | ↓ | TS | [18,40] |
| miR-192-5p | c-Myc axis (GLUT1, PFKFB3) | Glycolysis | Loss fuels glycolysis; re-expression dampens invasiveness | ↓ | TS | [20] |
| miR-23a | PPARGC1A/PGC-1α, G6PC | Gluconeogenesis ↔ glycolysis switch | IL-6/STAT3-induced Warburg enhancement | ↑ | ONC | [22] |
| Lipid Metabolism and β-Oxidation | ||||||
| miR-148a | c-Myc, DNMT1, PGC-1α, SIRT7 | Lipogenesis, FAO, OXPHOS | Restoring curbs lipid accumulation and tumor growth | TS | [32] | |
| miR-4310 | FASN, SCD1 | De novo fatty-acid synthesis | ↓ lipogenesis → ↓ proliferation/metastasis | ↓ | TS | [23] |
| miR-377-3p | CPT1C | Mitochondrial FA β-oxidation | Impairs FA import; suppresses growth and metastasis | ↓ | TS | [24] |
| miR-612 | HADHA | Terminal FA β-oxidation | Re-expression limits metastasis; low levels mark aggressiveness | ↓ | TS | [15,25] |
| Amino-Acid Transport/Glutamine Axis | ||||||
| miR-137 | SLC1A5/ASCT2 | Glutamine uptake and anaplerosis | Restored miR-137 ↓ glutamine flux → tumor inhibition | ↓ | TS | [34] |
| B. Tumor-Micro-Environment Modulation | ||||||
| Immune-Cell Reprogramming (TAM-centric) | ||||||
| miR-21-5p | RhoB (also PTEN) | Macrophage M2 polarization | Immunosuppression; supports growth and poor prognosis | ↑ | ONC | [38] |
| miR-452-5p | TIMP3 | TAM M2 shift, ECM remodeling | ↑ M2 TAMs and metastasis | ↑ | ONC | [44] |
| miR-23a-3p | PTEN | PI3K/AKT → PD-L1 on TAMs | T-cell suppression/immune escape | ↑ | ONC | [22] |
| miR-206 | KLF4/NF-κB axis | Macrophage M1 activation | ↑ CD8+ T-cell recruitment; anti-tumor immunity | ↓ | TS | [39] |
| miR-99b | κB-Ras2, mTOR, IRF4 | TAM re-programming to M1 | ↑ phagocytosis and antigen presentation | ↓ | TS | [40] |
| Fibroblast/CAF Activation | ||||||
| miR-1307-3p | DAB2IP | Hypoxia-AKT/mTOR loop in CAF-like milieu | Promotes survival, invasion and HIF-1α feed-back | ↑ | ONC | [35] |
| miR-1247-3p | B4GALT3 | β1-integrin/NF-κB in fibroblasts | Converts fibroblasts to IL-6/8-secreting CAFs → EMT/metastasis | ↑ | ONC | [43,50] |
| miR-130b-3p | HOXA5 | PI3K/AKT/mTOR and VEGF | Drives angiogenic CAF phenotype | ↑ | ONC | [46] |
| miR-320a | PBX3 | MAPK signaling in HCC cells | Paradoxical growth restraint; tumor-suppressive | ↓ | TS | [45] |
| miR-101 | TGFβR1, SMAD2 (HCC); SDF1 (CAF) | CAF-induced vascular mimicry | Blocks VM and neovascularization | ↓ | TS | [54] |
| Angiogenesis and Vascular Permeability | ||||||
| miR-210 | SMAD4, STAT6 | Hypoxia-driven angiogenesis (endothelium) | Abnormal vessel formation; pro-tumor | ↑ | ONC | [29,47] |
| miR-103 | VE-cadherin, p120-catenin, ZO-1 | Endothelial junction integrity | ↑ vascular permeability → intravasation | ↑ | ONC | [51] |
| miRNA | Sample Source | Comparison Group(s) | Diagnostic Context | Performance (AUC, Sens, Spec) | Dysregulation in HCC | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-21 (single) | Serum | Healthy vs. HCC | General HCC detection (all stages) | AUC 0.849, 82% sens, 84% spec vs. healthy, also AUC ~0.81 vs. LC | ↑ | [60] |
| miR-122 (single) | Serum | Chronic hepatitis vs. HCC | HCC vs. chronic liver disease | AUC 0.892 (95% CI 0.84–0.93) vs. chronic hepatitis | ↓ | [58] |
| miR-221 (single) | Serum | Chronic hepatitis vs. HCC | HCC vs. chronic liver disease | AUC ~0.806 (95% CI 0.75–0.86) vs. chronic hepatitis | ↑ | [58] |
| miR-1246 (single) | Plasma | Cirrhotic/healthy vs. HCC | HCC detection (mixed controls) | AUC ~0.812 in meta-analysis; elevated in HCC plasma vs. both cirrhosis and healthy | ↑ | [58] |
| miR-26a (single) | Serum | Chronic hepatitis vs. HCC | HCC vs. chronic liver disease | AUC ~0.867 (95% CI 0.81–0.91) vs. chronic hepatitis | ↓ | [58] |
| 8-miRNA panel (e.g., Yamamoto et al.) | Serum | At-risk (LC + CH) vs. HCC | Early HCC detection (Stage I/II) | AUC 0.99, 98% sensitivity for Stage I HCC | (panel of ↑/↓) | [64] |
| 3-miRNAexosomalpanel(miR-26a/29c/199a) | Exosomes (plasma) | LC and healthy vs. HCC | Early detection and differential | AUC 0.994 (100% sens, 96% spec) vs. healthy; 0.965 vs. LC | ↓ | [28] |
| 5-miRNA EV panel (miR-183/19a/148b/34a/215) | Extracellular vesicles | Non-HCC controls vs. HCC | General HCC detection | ~90% sensitivity, 92% specificity in mixed cohort | ↑ | [65] |
| miR-221 + miR-29c (two-miRNA combo) | Serum | Healthy vs. early HCC | Early HCC vs. non-cancer | AUC ~0.97 for Stage I–II HCC vs. normal; detected ~85% of early HCC vs. 46% by AFP | ↑ (miR-221); ↓ (miR-29c) | [59] |
| 3-miRNA plasma panel (miR-126/206/222) + AFP | Plasma + AFP | Healthy vs. HCC | HCC detection (all stages) | AFP alone AUC 0.889; combined panel + AFP AUC 0.989 (sens/spec ~97%/98%) | (panel of ↑/↓) | [71] |
| miRNA | Target(s)/Function | Context | Predictive Value | Dysregulation (High/Low) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. Systemic Therapy Response | |||||
| miR-21 | PTEN (tumor suppressor) | Sorafenib response | Sorafenib resistance marker | ↑ in resistant cells | [75] |
| miR-30d | —(secreted biomarker) | Sorafenib response | Sorafenib responder marker | ↑ in responders | [68,76] |
| miR-486-3p | FGFR4, EGFR (oncogenes) | Sorafenib resistance | Sorafenib resistance marker | ↓ in resistant tumors | [77] |
| miR-25 | FBXW7 (autophagy regulator) | Sorafenib resistance | Sorafenib resistance marker | ↑ in resistant tumors | [97] |
| miR-423-5p | Autophagy-related genes | Sorafenib response | Sorafenib response biomarker | ↑ in resistant tumors | [98] |
| B. Locoregional-Therapy Response | |||||
| miR-21 | PTEN | TACE | Early TACE failure | ↑ in refractoriness | [84] |
| miR-26a | Cyclin D2/E2 | TACE | Early TACE failure | ↑ in refractoriness | [84] |
| miR-29a-3p | (DNMT-related) | TACE | Early TACE failure | ↑ in refractoriness | [84] |
| miR-1271 | (tumor-suppressive) | TACE response | Poor TACE response marker | ↓ in non-responders | [80] |
| miR-214 | (tumor-suppressive) | TACE response | Poor TACE response marker | ↓ in non-responders | [99] |
| miR-133b | (tumor-suppressive) | TACE response | Poor TACE response marker | ↓ in non-responders | [83] |
| miR-335 | (tumor-suppressive) | TACE response | Poor TACE response marker | ↓ in non-responders | [100] |
| C. Recurrence after Curative Therapy | |||||
| miR-122 | Cyclin G1, ADAM17 (oncogenes) | Post-resection | ↑ recurrence risk (↓ RFS) | ↓ in tumors | [86] |
| miR-15b | Bcl-w (anti-apoptotic) | Post-resection | ↓ recurrence risk (↑ RFS) | ↑ in non-recurrers | [87] |
| miR-34a | Bcl-2, Cyclins | Post-ablation (RFA) | Early recurrence marker | ↓ in recurrences | [88] |
| miR-483-3p | IGF2 locus, multiple | Post-resection (advanced HCC) | Recurrence predictor | ↓ in recurrences | [89] |
| miR-3201 | —(biomarker candidate) | Curative therapy (resection/RFA) | Responder vs. non-responder | ↓ in complete responders | [90] |
| miR-215-5p | (exosomal oncogenic signals) | Curative therapy (exosomal, serum) | Shorter DFS (poor prognosis) | ↑ in recurrences | [96] |
| miR-92b | (exosomal oncogenic signals) | Post-surgery (exosomal, serum) | Recurrence marker | ↑ in recurrences | [91] |
| D. Overall/Disease-Free Survival | |||||
| miR-221 | PTEN, CDKN1B (tumor suppressors) | General prognosis | Poor OS/DFS (high risk) | ↑ in poor outcome | [94] |
| 3-miR signature (miR-139-3p, miR-760, miR-7-5p) | (various tumor suppressors) | General prognosis (TCGA signature) | Risk score for OS | ↓ (low-risk) or ↑ (high-risk) | [95] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liapopoulos, D.; Sarantis, P.; Biniari, T.; Bousou, T.-E.; Trifylli, E.-M.; Anastasiou, I.A.; Kokkali, S.; Korakaki, D.; Pantzios, S.; Koustas, E.; et al. MicroRNA Landscape in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Metabolic Re-Wiring, Predictive and Diagnostic Biomarkers, and Emerging Therapeutic Targets. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2243. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092243
Liapopoulos D, Sarantis P, Biniari T, Bousou T-E, Trifylli E-M, Anastasiou IA, Kokkali S, Korakaki D, Pantzios S, Koustas E, et al. MicroRNA Landscape in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Metabolic Re-Wiring, Predictive and Diagnostic Biomarkers, and Emerging Therapeutic Targets. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(9):2243. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092243
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiapopoulos, Dimitris, Panagiotis Sarantis, Theodora Biniari, Thaleia-Eleftheria Bousou, Eleni-Myrto Trifylli, Ioanna A. Anastasiou, Stefania Kokkali, Dimitra Korakaki, Spyridon Pantzios, Evangelos Koustas, and et al. 2025. "MicroRNA Landscape in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Metabolic Re-Wiring, Predictive and Diagnostic Biomarkers, and Emerging Therapeutic Targets" Biomedicines 13, no. 9: 2243. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092243
APA StyleLiapopoulos, D., Sarantis, P., Biniari, T., Bousou, T.-E., Trifylli, E.-M., Anastasiou, I. A., Kokkali, S., Korakaki, D., Pantzios, S., Koustas, E., Elefsiniotis, I., & Karamouzis, M. V. (2025). MicroRNA Landscape in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Metabolic Re-Wiring, Predictive and Diagnostic Biomarkers, and Emerging Therapeutic Targets. Biomedicines, 13(9), 2243. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092243









