The Mechanism of Steroid Hormones in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: From Molecular Signaling to Clinical Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. An Epidemiological Overview of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
1.2. Basic Concepts and Classification of Steroid Hormones
1.3. The Association Between Steroid Hormones and Cancer
2. The Expression of Steroid Hormone Receptors in NSCLC
2.1. Estrogen Receptor Expression
2.2. Progesterone Receptor Expression
2.3. Androgen Receptor Expression
2.4. Glucocorticoid Receptor Expression
3. Molecular Signaling Pathways of Steroid Hormones in NSCLC
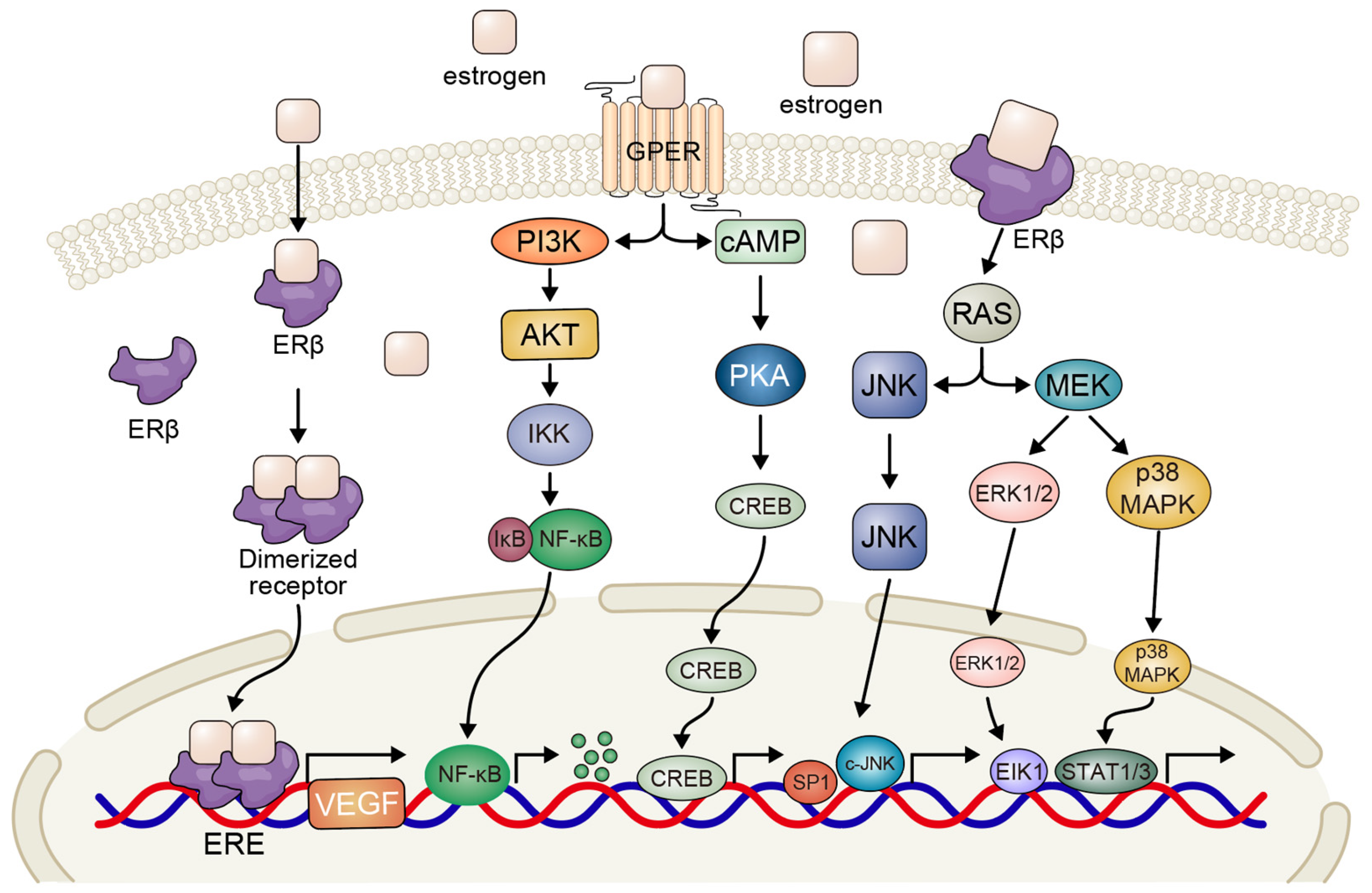
3.1. Estrogen-Mediated Signaling Pathways
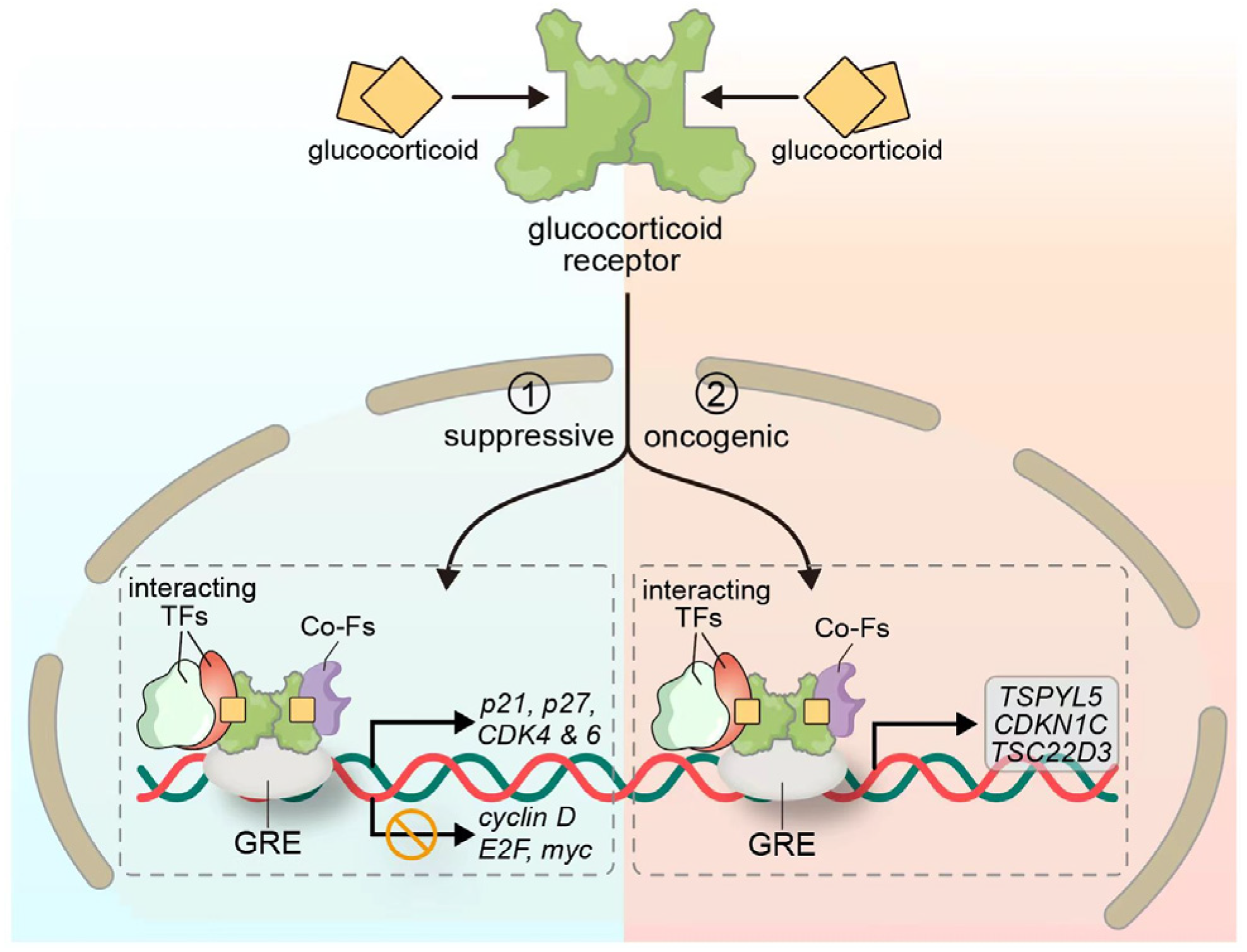
3.2. Glucocorticoid-Mediated Signaling Pathway
4. Clinical Application of Steroid Hormones in the Treatment of NSCLC
4.1. Application of GCs in the Treatment of NSCLC
4.2. Potential of Anti-Estrogen Therapy
4.3. Combination Therapy with Steroid Hormones and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
5. Future Directions and Challenges
5.1. Elucidation of Hormone Signaling Crosstalk and Resistance Mechanisms
5.2. Development of Selective Hormone-Based Therapeutics
5.3. Identification and Validation of Predictive Biomarkers
5.4. Addressing Sex- and Gender-Based Differences
5.5. Managing the Dual Roles of GCs
5.6. Enhancing Integration with Immunotherapy
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Aromatase inhibitor |
| AKT | Protein kinase B |
| AP-1 | Activator protein 1 |
| AR | Androgen receptor |
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| CDK | Cyclin-dependent kinase |
| CTLA-4 | Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| ER | Estrogen receptor |
| ERE | Estrogen response element |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| GC | Glucocorticoid |
| GPER | G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor |
| GR | Glucocorticoid receptor |
| GRE | Glucocorticoid response element |
| ICI | Immune checkpoint inhibitor |
| IGF1R | Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| LKB1 | Liver Kinase B1 |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| NK | Natural killer |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| PD-1 | Programmed death receptor 1 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed death ligand 1 |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| PKA | Protein kinase A |
| PR | Progesterone receptor |
| Rb | Retinoblastoma protein |
| SCLC | Small cell lung cancer |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Health Estimates (GHE). 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/global-health-estimates (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuta, K.; Ejima, A.; Abe, S.; Shimba, A. Control of immunity and allergy by steroid hormones. Allergol. Int. 2022, 71, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, W.; Waliszczak, G.; Jach, R.; Dulińska-Litewka, J. Steroid Receptors in Breast Cancer: Understanding of Molecular Function as a Basis for Effective Therapy Development. Cancers 2021, 13, 4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radkiewicz, C.; Dickman, P.W.; Johansson, A.L.V.; Wagenius, G.; Edgren, G.; Lambe, M.; Duell, E.J. Sex and survival in non-small cell lung cancer: A nationwide cohort study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.-Y.D.; Cramb, S.M.; Baade, P.D.; Youlden, D.R.; Nwogu, C.; Reid, M.E. The International Epidemiology of Lung Cancer: Latest Trends, Disparities, and Tumor Characteristics. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 1653–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Lara, V.; Avila-Costa, M.R. An Overview of Lung Cancer in Women and the Impact of Estrogen in Lung Carcinogenesis and Lung Cancer Treatment. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 600121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Lara, V.; Ramírez-Tirado, L.A.; Barrón, F.; Zatarain-Barrón, Z.L.; Flores-Estrada, D.; Arrieta, O. Characteristics of non-small cell lung cancer: Differences by sex and hormonal status in a Mexican population. Salud Publica Mex. 2019, 61, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postow, M.A.; Sidlow, R.; Hellmann, M.D. Immune-Related Adverse Events Associated with Immune Checkpoint Blockade. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, A.J.; Hutchinson, M.-K.N.D.; Sonnemann, H.M.; Jung, J.; Fecci, P.E.; Ratnam, N.M.; Zhang, W.; Song, H.; Bailey, R.; Davis, D.; et al. Dexamethasone-induced immunosuppression: Mechanisms and implications for immunotherapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.H.; Chu, N.M.; Kao, S.H. Estrogen, Estrogen Receptor and Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaker, R.; Lee, U.J.; Strange, T.J.; Sison, C.P.; Kwok, Y.F.R.; Niazi, M.R.K.; Gut, T.; Seetharamu, N.; Castellanos, M.R. Estrogen receptor subtypes and survival outcomes in non-small cell lung cancer. Pathol.–Res. Pract. 2025, 268, 155843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, K.; Miki, Y.; Ono, K.; Mori, M.; Kakinuma, H.; Kou, Y.; Kudo, N.; Koguchi, M.; Niikawa, H.; Suzuki, S.; et al. Highly concordant coexpression of aromatase and estrogen receptor β in non–small cell lung cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2010, 41, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rades, D.; Setter, C.; Dahl, O.; Schild, S.E.; Noack, F. The prognostic impact of tumor cell expression of estrogen receptor-α, progesterone receptor, and androgen receptor in patients irradiated for nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer 2011, 118, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prekovic, S.; Schuurman, K.; Mayayo-Peralta, I.; Manjón, A.G.; Buijs, M.; Yavuz, S.; Wellenstein, M.D.; Barrera, A.; Monkhorst, K.; Huber, A.; et al. Glucocorticoid receptor triggers a reversible drug-tolerant dormancy state with acquired therapeutic vulnerabilities in lung cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, P.K.; Thomas, P.A.; Walker, M.J.; Briele, H.A.; Das Gupta, T.K.; Beattie, C.W. Steroid receptors in human lung cancer cytosols. Cancer Lett. 1982, 16, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Li, B.; Ou-Yang, L. Role of estrogen receptors in health and disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 839005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, N.M.; Stabile, L.P. Estrogen Receptor ß in Cancer: To ß(e) or not to ß(e)? Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez-Garbán, D.C.; Chen, H.; Goodglick, L.; Fishbein, M.C.; Pietras, R.J. Targeting Aromatase and Estrogen Signaling in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1155, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Bai, Y.; Xiong, L.; Zhang, L.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wu, X.; Long, D.; Yang, J.; Yu, L.; et al. Interaction of estrogen receptor β5 and interleukin 6 receptor in the progression of non–small cell lung cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 120, 2028–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Yu, W.; Chang, C.; Miyamoto, H.; Liu, X.; Jiang, K.; Yeh, S. Estrogen receptor α promotes lung cancer cell invasion via increase of and cross-talk with infiltrated macrophages through the CCL2/CCR2/MMP9 and CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling pathways. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 1779–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nose, N.; Sugio, K.; Oyama, T.; Nozoe, T.; Uramoto, H.; Iwata, T.; Onitsuka, T.; Yasumoto, K. Association Between Estrogen Receptor-β Expression and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation in the Postoperative Prognosis of Adenocarcinoma of the Lung. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smida, T.; Bruno, T.C.; Stabile, L.P. Influence of Estrogen on the NSCLC Microenvironment: A Comprehensive Picture and Clinical Implications. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Wu, R.; Jiang, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Chen, W.; Li, W. Overexpression of estrogen receptor beta is a prognostic marker in non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 8686–8697. [Google Scholar]
- Skjefstad, K.; Grindstad, T.; Khanehkenari, M.R.; Richardsen, E.; Donnem, T.; Kilvaer, T.; Andersen, S.; Bremnes, R.M.; Busund, L.-T.; Al-Saad, S. Prognostic relevance of estrogen receptor α, β and aromatase expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Steroids 2016, 113, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, M.R.; Fanous, E.; Thaker, R.; Flory, M.J.; Seetharamu, N.; Dhar, M.; Starr, A.; Strange, T.J. Expression patterns and clinical significance of estrogen receptor in non-small cell lung cancer. Pathol.–Res. Pract. 2022, 241, 154298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-T.; Chang, Y.-L.; Shih, J.-Y.; Lee, Y.-C. The significance of estrogen receptor β in 301 surgically treated non–small cell lung cancers. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2005, 130, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, J.A., II; Hayashi, K. Progesterone Actions and Resistance in Gynecological Disorders. Cells 2022, 11, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, R.; Morgese, F.; Santinelli, A.; Onofri, A.; Biscotti, T.; Brunelli, A.; Caramanti, M.; Savini, A.; De Lisa, M.; Ballatore, Z.; et al. Hormonal receptors in lung adenocarcinoma: Expression and difference in outcome by sex. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 82648–82657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanov, I.P.; Bogush, T.A.; Scherbakov, A.M.; Grishanina, A.N.; Bogush, E.A.; Ravcheeva, A.B.; Kosorukov, V.S. Prognostic value of progesterone receptor expression in non-small cell lung cancer tissue. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2025, 194, 817–825. [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi, H.; Suzuki, T.; Suzuki, S.; Niikawa, H.; Lu, L.; Miki, Y.; Moriya, T.; Hayashi, S.-I.; Handa, M.; Kondo, T.; et al. Progesterone Receptor in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer—A Potent Prognostic Factor and Possible Target for Endocrine Therapy. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 6450–6458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raso, M.G.; Behrens, C.; Herynk, M.H.; Liu, S.; Prudkin, L.; Ozburn, N.C.; Woods, D.M.; Tang, X.; Mehran, R.J.; Moran, C.; et al. Immunohistochemical Expression of Estrogen and Progesterone Receptors Identifies a Subset of NSCLCs and Correlates with EGFR Mutation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5359–5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maasberg, M.; Rotsch, M.; Jaques, G.; Enderle-Schmidt, U.; Weehle, R.; Havemann, K. Androgen receptors, androgen-dependent proliferation, and 5 alpha-reductase activity of small-cell lung cancer cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 1989, 43, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegfried, J.M. Smoking Out Reproductive Hormone Actions in Lung Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hu, C.; Li, M.; Zhou, W.; Wang, R.; Xiao, Y. Androgen receptor suppresses lung cancer invasion and increases cisplatin response via decreasing TPD52 expression. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 3709–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Siddiqui, S.; Singh, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Upadhyay, V.; Sethi, A.; Trivedi, A.K. Dexamethasone induces cancer mitigation and irreversible senescence in lung cancer cells via damaging cortical actin and sustained hyperphosphorylation of pRb. Steroids 2023, 198, 109269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-S.; Lien, H.-C.; Yeh, P.-Y.; Kuo, S.-H.; Chang, W.-C.; Kuo, M.-L.; Cheng, A.-L. Glucocorticoid receptor expression in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: Clinicopathological correlation and in vitro effect of glucocorticoid on cell growth and chemosensitivity. Lung Cancer 2006, 53, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, K.E.; Li, L.S.; Carstens, R.; Park, H.; Girard, L.; Avila, K.; Wei, S.; Kollipara, R.; Timmons, B.; Sudderth, J.; et al. Glucocorticoid mediated inhibition of LKB1 mutant non-small cell lung cancers. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1025443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez-Garban, D.C.; Mah, V.; Alavi, M.; Maresh, E.L.; Chen, H.-W.; Bagryanova, L.; Horvath, S.; Chia, D.; Garon, E.; Goodglick, L.; et al. Progesterone and estrogen receptor expression and activity in human non-small cell lung cancer. Steroids 2011, 76, 910–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegfried, J.M.; Gubish, C.T.; Rothstein, M.E.; Henry, C.; Stabile, L.P. Combining the Multitargeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Vandetanib with the Antiestrogen Fulvestrant Enhances Its Antitumor Effect in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liao, Y.; Fan, S.; Fu, X.; Xiong, J.; Zhou, S.; Zou, M.; Wang, J. G-Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor Antagonist G15 Decreases Estrogen-Induced Development of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2019, 27, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belous, A.R.; Hachey, D.L.; Dawling, S.; Roodi, N.; Parl, F.F. Cytochrome P450 1B1–Mediated Estrogen Metabolism Results in Estrogen-Deoxyribonucleoside Adduct Formation. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spivack, S.D.; Hurteau, G.J.; Reilly, A.A.; Aldous, K.M.; Ding, X.; Kaminsky, L.S. CYP1B1 expression in human lung. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2001, 29, 916–922. [Google Scholar]
- Kawai, H.; Ishii, A.; Washiya, K.; Konno, T.; Kon, H.; Yamaya, C.; Ono, I.; Ogawa, J. Combined overexpression of EGFR and estrogen receptor alpha correlates with a poor outcome in lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 4693–4698. [Google Scholar]
- Hershberger, P.A.; Stabile, L.P.; Kanterewicz, B.; Rothstein, M.E.; Gubish, C.T.; Land, S.; Shuai, Y.; Siegfried, J.M.; Nichols, M. Estrogen receptor beta (ERβ) subtype-specific ligands increase transcription, p44/p42 mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) activation and growth in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 116, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, N.; Rodriguez, M.S.; Silveyra, P. Role of sex hormones in lung cancer. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 246, 2098–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier, A.M.; Anunciato, A.K.O.; Rosenstock, T.R.; Glezer, I. Gene Expression Control by Glucocorticoid Receptors during Innate Immune Responses. Front. Endocrinol. 2016, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, N.Z.; Cidlowski, J.A. Glucocorticoid receptor isoforms generate transcription specificity. Trends Cell Biol. 2006, 16, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Yamamura, S.; Essilfie-Quaye, S.; Cosio, B.G.; Ito, M.; Barnes, P.J.; Adcock, I. Histone deacetylase 2–mediated deacetylation of the glucocorticoid receptor enables NF-κB suppression. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlais, D.; Couture, C.; Balsalobre, A.; Drouin, J. The Stat3/GR Interaction Code: Predictive Value of Direct/Indirect DNA Recruitment for Transcription Outcome. Mol. Cell 2012, 47, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groeneweg, F.L.; Karst, H.; de Kloet, E.R.; Joëls, M. Rapid non-genomic effects of corticosteroids and their role in the central stress response. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 209, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, R.H.; Cidlowski, J.A. The biology of the glucocorticoid receptor: New signaling mechanisms in health and disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayayo-Peralta, I.; Zwart, W.; Prekovic, S. Duality of glucocorticoid action in cancer: Tumor-suppressor or oncogene? Endocrine-Related Cancer. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2021, 28, R157–R171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, A.K.; Hu, J.; Basu, S.; Hay, J.; Reibman, J.; Yie, T.-A.; Tchou-Wong, K.M.; Rom, W.N.; Lee, T.C. Glucocorticoids Inhibit Lung Cancer Cell Growth through Both the Extracellular Signal-Related Kinase Pathway and Cell Cycle Regulators. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2002, 27, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papavassiliou, K.A.; Anagnostopoulos, N.; Papavassiliou, A.G. Glucocorticoid Receptor Signaling in NSCLC: Mechanistic Aspects and Therapeutic Perspectives. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xia, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Martin, V.; Li, Q.; Lin, S.; Chen, J.; Calmette, J.; Lu, M.; et al. Stress–glucocorticoid–TSC22D3 axis compromises therapy-induced antitumor immunity. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1428–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, P.; Rosati, R.; Mamdani, H.; Wright, R.E.; Hussain, Z.; Naeem, A.; Dzinic, S.; Polin, L.; Gavande, N.S.; Ratnam, M. Senescence-associated secretory proteins induced in lung adenocarcinoma by extended treatment with dexamethasone enhance migration and activation of lymphocytes. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2022, 72, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kernéis, S.; Blanc, K.; Caliez, J.; Canouï, E.; Loubinoux, J.; Gauzit, R.; Nguyen, Y.-L.; Casetta, A.; Lefebvre, A.; Regnard, J.-F.; et al. Epidemiology and Appropriateness of Antibiotic Prescribing in Severe Pneumonia After Lung Resection. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2019, 108, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, A.; Skalsky, K.; Avni, T.; Carrara, E.; Leibovici, L.; Paul, M. Corticosteroids for pneumonia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 1–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, R.; Tobian, A.A.R.; Shaz, B.H. Noninfectious transfusion-associated adverse events and their mitigation strategies. Blood 2019, 133, 1831–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, M.; Wendel, S.; Bercovitz, R.S.; Cid, J.; Cohn, C.; Dunbar, N.M.; Apelseth, T.O.; Popovsky, M.; Stanworth, S.J.; Tinmouth, A.; et al. Transfusion reactions: Prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. Lancet 2016, 388, 2825–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez-Garbán, D.C.; Chen, H.-W.; Fishbein, M.C.; Goodglick, L.; Pietras, R.J. Estrogen receptor signaling pathways in human non-small cell lung cancer. Steroids 2007, 72, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietras, R.; Marquez, D.; Chen, H.; Tsai, E.; Weinberg, O.; Fishbein, M. Estrogen and growth factor receptor interactions in human breast and non-small cell lung cancer cells. Steroids 2005, 70, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Shen, H.; Guo, R.; Sun, J.; Gao, W.; Shu, Y. Combine therapy of gefitinib and fulvestrant enhances antitumor effects on NSCLC cell lines with acquired resistance to gefitinib. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2012, 66, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traynor, A.M.; Schiller, J.H.; Stabile, L.P.; Kolesar, J.M.; Eickhoff, J.C.; Dacic, S.; Hoang, T.; Dubey, S.; Marcotte, S.M.; Siegfried, J.M. Pilot study of gefitinib and fulvestrant in the treatment of post-menopausal women with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2008, 64, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Liao, Y.; Qiu, W.; Li, L.; Li, D.; Cao, X.; Ai, B. Targeting Toll-like receptor 4 with CLI-095 (TAK-242) enhances the antimetastatic effect of the estrogen receptor antagonist fulvestrant on non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 22, 2074–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabile, L.P.; Siegfried, J.M. Estrogen receptor pathways in lung cancer. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2004, 6, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swedenborg, E.; Power, K.A.; Cai, W.; Pongratz, I.; Rüegg, J. Regulation of estrogen receptor beta activity and implications in health and disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 3873–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.U.; Yeo, C.D. Update on adjuvant therapy in completely resected NSCLC patients. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 13, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghaei, H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Horn, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Steins, M.; Ready, N.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Vokes, E.E.; Felip, E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Chemotherapy for PD-L1–Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Ren, J.; Xue, Q.; Luan, R.; Ding, D.; Tan, J.; Su, X.; Yang, J. Anti PD 1/PD L1 and anti CTLA 4 associated checkpoint inhibitor pneumonitis in non small cell lung cancer: Occurrence, pathogenesis and risk factors (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2023, 63, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.A.; Herynk, M.H.; Cascone, T.; Saigal, B.; Nilsson, M.B.; Tran, H.; Ramachandran, S.; Diao, L.; Wang, J.; Le, X.; et al. Estrogen Promotes Resistance to Bevacizumab in Murine Models of NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 2051–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Song, B.; Tong, S.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, H.; Guo, J.; Tian, X.; Chang, R.; Wu, J. Research Progress on the Anticancer Activity of Plant Polysaccharides. Recent Pat. Anti-Cancer Drug Discov. 2024, 19, 573–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laugesen, K.; Sørensen, H.T.; Jorgensen, J.O.L.; Petersen, I. Prenatal exposure to glucocorticoids and the prevalence of overweight or obesity in childhood. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2022, 186, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veneziani, I.; Alicata, C.; Moretta, L.; Maggi, E. Human toll-like receptor 8 (TLR8) in NK cells: Implication for cancer immunotherapy. Immunol. Lett. 2023, 261, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, I.; Salfity, S.; Seshacharyulu, P.; Rachagani, S.; Thomas, A.; Das, S.; Majhi, P.D.; Nimmakayala, R.K.; Vengoji, R.; Lele, S.M.; et al. MUC16 Regulates TSPYL5 for Lung Cancer Cell Growth and Chemoresistance by Suppressing p53. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3906–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Receptor | Expression in NSCLC | Gender Association | Prognostic Value | Therapeutic Implications | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERα/ERβ | ERβ ↑ (more common) | ↑ in females | Favorable (ERβ) | Anti-estrogens | [12,13] |
| PR | Low/moderate | Variable | Unclear | Limited studies | [14] |
| AR | Low/moderate | ↑ in males | Poor prognosis | Under investigation | [15] |
| GR | Widely expressed | No clear link | Context-dependent | Corticosteroids, GR modulators | [16] |
| Steroid Receptor | Crosstalk Pathway | Molecular Mechanism | Functional Outcomes | Therapeutic Implications | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERβ (±ERα) | EGFR | Estrogen promotes EGFR phosphorylation and activates downstream PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling; reciprocal compensation between pathways | Enhances proliferation and survival; may lead to TKI resistance | Combining anti-estrogens with EGFR-TKIs to overcome resistance | [45] |
| ERβ | MAPK/ERK, PI3K/AKT | ERβ-selective ligands activate MAPK and AKT pathways | Promotes tumor cell growth and proliferation | Dual targeting of ERβ and MAPK/PI3K pathways | [43,44] |
| ER | VEGF | Estrogen increases VEGF expression; anti-estrogen + EGFR-TKI reduces VEGF secretion | Promotes angiogenesis and tumor vascularization | Use of anti-estrogens in combination with anti-angiogenic or EGFR-targeted therapies | [40,41] |
| GPER | MAPK, cAMP/PKA | Membrane-bound GPER activates non-genomic cascades; G15 inhibits E2-induced proliferation | Stimulates rapid proliferation and migration | GPER antagonists as novel anti-proliferative agents | [42] |
| GR | STAT3 | GR cooperates with activated STAT3 to transactivate TSPYL5, which suppresses p53 | Promotes tumor growth and drug resistance | Targeting STAT3-GR axis or TSPYL5 expression to restore drug sensitivity | [56] |
| GR | NF-κB/AP-1 | GR inhibits NF-κB and AP-1 via protein–protein interaction; HDAC2-mediated deacetylation enhances repression | Reduces inflammation but may suppress anti-tumor immunity | Use selective GR modulators to balance anti-inflammatory and immune activation | [50,51] |
| GR | ERK/MAPK and Cell Cycle | Dexamethasone via GR suppresses ERK signaling, downregulates Cyclin D/E2F/Myc, upregulates p21/p27 | Induces cell cycle arrest and senescence | GR agonism beneficial in LKB1-mutant NSCLC or steroid-sensitive tumors | [37] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, Y.; Zheng, C. The Mechanism of Steroid Hormones in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: From Molecular Signaling to Clinical Application. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081992
Wang Y, Zhou Y, Yao Y, Zheng C. The Mechanism of Steroid Hormones in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: From Molecular Signaling to Clinical Application. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(8):1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081992
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yao, Ying Zhou, Yao Yao, and Caihong Zheng. 2025. "The Mechanism of Steroid Hormones in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: From Molecular Signaling to Clinical Application" Biomedicines 13, no. 8: 1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081992
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhou, Y., Yao, Y., & Zheng, C. (2025). The Mechanism of Steroid Hormones in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: From Molecular Signaling to Clinical Application. Biomedicines, 13(8), 1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081992






