Abstract
Background/Objectives: Neuromedin U (NMU) is a highly conserved gene encoding a neuropeptide involved in the regulation of feeding behavior and energy homeostasis. We aimed to analyze the association between NMU genetic and epigenetic variations and cardio-metabolic parameters in an Italian population to identify the role of these variants in cardio-metabolic risk. Methods: A total of 4028 subjects were randomly selected from the Moli-sani study cohort. NMU haplotypes were estimated using seven SNPs located in the gene body and in the promoter region; DNA methylation levels in the promoter region, previously associated with lipid-related variables in the same population, were also used. Results: Among the haplotypes inferred, the haplotype carrying the highest number of minor variants (frequency 16.6%), when compared with the most frequent haplotype, was positively associated with insulin levels, HOMA-IR, and diastolic blood pressure, and negatively with HDL-cholesterol. The multivariable analysis that considered methylation levels along with their interactions with SNPs showed that increased methylation levels in two close CpG sites were associated with higher levels of lipid-related variables. Conclusions: This study supports a role for NMU as a regulator of human metabolism. This finding suggests that NMU could be a potential target for preventive interventions against coronary and cerebrovascular diseases, and that NMU genetic and epigenetic variability may serve as a biomarker for cardio-metabolic risk.
1. Introduction
Metabolic disorders, such as insulin resistance, abdominal obesity, dyslipidemia, and hypertension, frequently occur together and are associated with an increased cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk [1]. An underlying pro-inflammatory condition frequently coexisting with these phenotypes, called metabolic inflammation, is considered the main reason for the increased CVD risk [2]. A chronic low-grade pro-inflammatory state often coexisting with these conditions, referred to as metabolic inflammation, is considered a major contributor to the elevated CVD risk [2]. Metabolic and inflammatory stress promote the onset and progression of CVD by activating complex molecular pathways that lead to endothelial dysfunction, plaque instability, and tissue damage [3]. However, the precise mechanisms linking metabolic disorders and inflammation are not yet fully understood [4,5].
Neuromedin U (NMU) is a neuropeptide expressed in several peripheral tissues that could be considered a potential bridge between metabolic disorders and inflammation and a good candidate as a biomarker in CVD risk assessment [6,7]. In fact, studies on murine models showed pleiotropic roles for this peptide in metabolic functions and inflammation, as well as in the regulation of blood pressure, hormone release, and tumorigenesis [8,9,10]. In addition to its peripheral actions, NMU is also highly expressed in the central nervous system, particularly in the hypothalamic paraventricular and dorsomedial nuclei, where it plays a key role in regulating feeding behavior, energy expenditure, and circadian rhythms [11,12]. The central administration of NMU has been shown to exert anorexigenic effects, to suppress food intake, and to activate the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis [13,14]. Studies in mice also indicate that NMU plays a role in stress response, anxiety-like behaviors, and locomotor activity [15].
In humans, NMU has been found to be involved in inflammatory and immune processes [16]. Our group also reported a role of this neuropeptide in potentiating platelet activation induced by several agonists like adenosine diphosphate, epinephrine, and serotonin [17]. Beyond experimental models, population studies on humans showed associations of NMU genetic variants with overweight and obesity in children and adults [18,19,20] as well as with food preferences [21] and bone density [22] in children. We have recently found NMU promoter methylation to be associated with metabolic and inflammatory indices in a cohort of adults [23].
In this study, we aimed at investigating the association between NMU genetic and epigenetic variability and several cardio-metabolic risk factors in an Italian general adult population. We firstly used a haplotype analysis approach, which allowed us to capture most of the existing combinations of genetic variants found in a population (haplotypes) confined to specific regions. We repeated the analyses, adding DNA methylation levels at single CpG sites.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
The study population was composed of a random subsample of 4028 participants from the Moli-sani study, a prospective cohort study established in 2005–2010 with an enrolment of 24,325 men and women (aged ≥ 35 years) randomly recruited from the general population of Molise, a Southern Mediterranean Italian region, with the purpose of investigating risk factors in the onset of cancer and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Exclusion criteria were pregnancy at the time of recruitment, mental impairments, current polytraumas or coma, or refusal to sign the informed consent [24,25,26].
The Moli-sani study complies with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Catholic University of Rome, Italy. All participants provided written informed consent.
The subsample size was selected to study the associations between continuous metabolic variables and haplotypes at a frequency higher than 10% to obtain adequate statistical power based on the expected results according to the literature. Subjects with unreliable questionnaires or with missing values for core variables were excluded.
The analyzed sub-cohort and the whole Moli-sani population showed similar values in all variables considered for the present study (Supplementary Table S1).
2.2. Data Collection
Detailed, structured questionnaires on medical history and lifestyles were administered to all subjects. A full description of the collected data is reported elsewhere [23].
Blood pressure (mm Hg) was measured by an automatic device (OMRON HEM-705CP, OMRON Healthcare, Shimogyo-ku, Kyoto, Japan) three times on the non-dominant arm, with the patient lying down for about 5 min. The second and the third measurements were averaged to compute the final measure. Body mass index (BMI) was calculated as weight (kg)/height (m)2. Waist and hip circumferences were measured according to the National Institutes of Health, Heart, Lung, and Blood Guidelines [27] to calculate the waist-to-hip ratio. Metabolic syndrome was defined according to Adult Treatment Panel III criteria [28].
2.3. Biochemical Analyses
Blood samples were obtained between 07:00 and 09:00 from participants who had fasted overnight and had refrained from smoking for at least 6 h.
Hemochromocytometric analyses were performed on freshly collected blood by a cell counter (Coulter HMX, Beckman Coulter, IL, Milan, Italy) within 3 h of venipuncture.
Serum lipids and glucose were assayed by enzymatic reaction methods using an automatic analyzer (ILab 350, Instrumentation Laboratory, Milan, Italy). The concentration of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol was calculated using the Friedewald formula. These analyses were performed in the centralized Moli-sani laboratory. Insulin and apolipoprotein A-I and B measurements were performed using automated immunoassay on samples frozen in nitrogen vapor at Neuromed Biobanking Center and subsequently transferred to the BiomarCaRE project centralized laboratory [29]. The HOMA-IR (homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance) was calculated as insulin (mU/L)*glucose (mg/dL)/405 [30].
2.4. NMU Genetic Variant Analysis
NMU genotyping was performed on white blood cell DNA. Buffy coats of peripheral blood cells were freshly isolated from whole blood samples collected in sodium citrate and EDTA by centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 20 min at room temperature, frozen in nitrogen vapor, and stored at Neuromed Biobanking Centre until utilized (http://www.neuromed.it/biobanking-centre/, accessed on 12 April 2025) [31]. DNA was subsequently extracted using a silica matrix-based method, as previously described [32], its concentration verified with NanoDrop spectrophotometry, and samples stored at −20 °C until analyzed.
NMU spans chromosome region 4q12 (chr4: 55,595,231–55,636,298; GRCh38/hg38 Assembly), and it is composed of 9 exons. Two main NMU haplotype blocks were selected from Hapmap Project (CEU, TSI populations) and 1000 Genomes Project data using the Tagger Pairwise method on Haploview software (version 4.2; Broad Institute, Cambridge, MA, USA) [33] (Figure 1); one in the gene body (GTT, GCC, GTT, GCT, ATT)—tagged by rs3805383, rs6827359, rs12500837—and the other in the promoter region (TCTG, TCCT, CCCT, TATG, and TCTT), tagged by rs73236170, rs62308715, rs4865020 and rs55796004.
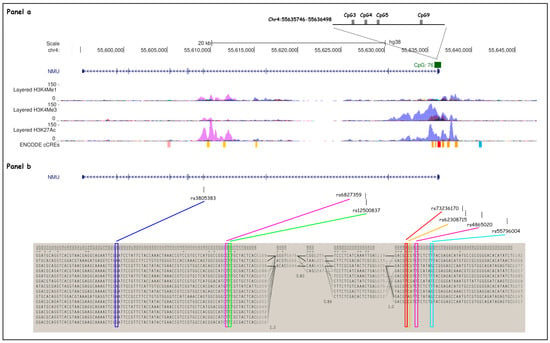
Figure 1.
Selected NMU SNP and haplotype block structures. (Panel a) NMU (chr4: 55,595,231–55,636,298; GRCh38/hg38 assembly) spans chromosome region 4q12 and is composed of nine exons (depicted as blue lines throughout the gene). H3K4Me1, H3K4Me3, and H3K27Ac profiles are displayed as colored overlaid histograms (Bernstein Laboratory at the Broad Institute and the University of California, Santa Cruz, and part of the ENCODE database). Four CpG sites from the CpG island 76 (chr4: 55,635,746–55,636,498, GRCh38/hg38 assembly) found to be significantly associated with methylation patterns in Marotta et al. 23. are shown as gray boxes. (Panel b) Seven SNPs (depicted as black lines on the top) were selected for the haplotype study: rs73236170, rs62308715, rs4865020, and rs55796004, located upstream of the NMU TSS, and rs3805383, rs6827359, and rs12500837 within the gene body. Two main haplotype blocks (chr4: 55,595,229–55,653,833; GRCh38/hg38 assembly) have been identified in NMU, in the gene body (block on the left) and in the promoter region (block on the right), respectively.
The SNP selection was based on the following criteria.
First, a set of SNP lists defining haplotypes with frequency higher than 10% was selected.
Second, we evaluated SNP type and position in the gene using the Genome Variation Server database as well as the correlation between SNPs in the same haplotype block (linkage disequilibrium, pairwise r2 threshold of 0.8).
Third, we considered SNPs that were previously associated with metabolic phenotypes in GWAS studies retrieved from literature or large genetic databases (GWAS Central, OMICS db in PubMed).
Moreover, we selected variants that could have a regulatory role in NMU gene expression. In particular, rs4865020 co-localizes with a CTCF binding region according to the ENCODE Candidate Cis-Regulatory Elements database and with moderate deposition of H3K4Me1 histone mark (Supplementary Figure S1).
Concerning the SNPs selected within the gene body, rs3805383 tags a region where there is a high presence of H3K27Ac and moderate presence of H3K4Me1 histone modifications, usually associated with transcriptional activation. Located at around 400 bp from another distal enhancer element, this SNP also tags a highly conserved region across species (Supplementary Figure S2).
The SNP set was enriched through imputation using the CEU and TSI populations from the Hapmap Project and 1000 Genomes Project as a reference set.
NMU variants were genotyped using a 7500 Fast Real-Time System (Applied Biosystems, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) with standard Taqman reagents and protocols. Positive and negative controls (homozygous allele 1, homozygous allele 2, heterozygous, no template control) were selected from the cohort.
Genotyping data were obtained by using the SDS v1.4 software (Applied Biosystems, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Primers and probes used in the assay for each SNP are listed in Supplementary Table S2. The quality of the genotyping was assured by Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (HWE, Chi-squared p > 0.05), concordance with population frequencies (Hapmap CEU and TSI, 1000 Genomes Project), concordance between duplicate samples (a locus for each DNA sample was repeated twice), and frequencies of rare haplotypes, as estimated from the software.
2.5. NMU DNA Methylation Analysis
Detailed methods were previously reported [21]. Briefly, NMU methylation analysis was performed on white blood cell DNA using the Pyrosequencer Q48 Autoprep (QIAGEN) platform using peripheral blood cells from a subsample of 1211 subjects included in this study. Amplicons covering 10 CpG sites from CpG island 76 (chr4: 55,635,746–55,636,498) in the promoter region were considered. All PCR amplifications were performed in duplicate. The two assays were tested using fully methylated and unmethylated controls (EpiTect PCR Control DNA Set, QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany). For the CpG-specific analysis, data were discarded when the duplicate measurements had a standard deviation (SD) ≥ 5%.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
All analyses were performed using R software (v3.2.1; https://www.R-project.org/, accessed on 12 April 2025) and SAS software (Version 9.4 for Windows©2009. SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). Mean and SD were computed for continuous variables (z-scores or log-transformed variables were used where appropriate) and frequencies for categorical variables (Table 1).

Table 1.
Population characteristics (Moli-sani N 3953).
Regression analyses were performed to evaluate associations between haplotypes and cardio-metabolic indices, using age and sex as covariates. The R Haplo.stats package (https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=haplo.stats, accessed on 12 April 2025) was used to estimate the haplotype frequencies based on the genotyped SNPs and to verify the associations between haplotypes and phenotypes (haplo.glm function, the most prevalent haplotype, was used for reference). Haplotypes with frequencies lower than 1% were excluded from the analysis.
The same analysis was then repeated using all the available genotypes in models including (i) single SNPs or (ii) all the available SNPs, along with age and sex. For the analysis including all the SNPs, a stepwise model with backward elimination was used to finally retain only the statistically significant associated genotypes.
We imputed the missing genotypes (n = 24 to 226 for the seven SNPs, Table 2 and Table 3) using the estimation function (haplo.em), which deals with sparse missing genotypes, imputing them based on the linkage found in the case-complete subsample. Moreover, using SAS/STAT software software (version 9.4, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA), we checked the Hapmap Project (CEU, TSI populations) and 1000 Genomes Project databases to identify and impute any other unmeasured SNPs tagging the haplotypes, or combinations of them, which were retrieved using combinations of measured tag SNPs.

Table 2.
Alleles and frequencies of the inferred haplotypes.

Table 3.
Characteristics and frequencies of the available NMU genotypes (measured plus imputed).
The best genetic model was checked for each haplotype/genotype–phenotype association using dominant, codominant, and recessive models for the analysis. The codominant/additive model was the best genetic model (i.e., the one with the smallest AIC) for the majority of the genotype–phenotype associations and thus was used for all subsequent analyses. A Benjamini–Hochberg false discovery rate (FDR) was used to adjust the results for multiple comparisons, accounting for a total of 13 phenotypes and a single haplotype block. FDR-adjusted p-values (pFDR) < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Since lipid-related variables were found to be associated with DNA methylation patterns of the NMU promoter region in the same study population [21], the analyses for these phenotypes were repeated, including both genotypes and the CpG methylation levels resulting from association (CpG3, CpG4, CpG5, CpG9).
Once we identified the genetic variants remaining statistically significant associated, the interactions between pairs of the associated SNPs and CpG sites were tested in models including the interaction and its constitutive terms. The significant interactions were then added to the final model.
3. Results
Following the genetic analysis and the related quality control of concordance between genotypes of duplicate samples, we excluded the 75 subjects with discordant results, leading to a final study population of 3953 subjects. Baseline characteristics are described in Table 1. The mean age was 55.7 years (±12.9 SD), and 48.7% were male. The prevalence of diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidaemia was 9.8%, 58.1%, and 33.7%, respectively. Participants with metabolic syndrome accounted for 28.1% of the studied population.
All genotyped SNPs were in Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (HWE), and the minor allele frequencies (MAFs) were similar to values reported in the HapMap Project database for the Tuscan (TSI) and Caucasian (CEU) populations (Supplementary Table S3).
Using data from the seven selected tag SNPs and considering the whole region comprising the two selected haplotype blocks, eight haplotypes (H1–H8) were inferred (Table 2).
Four additional SNPs were imputed, based on linkage with the retrieved haplotypes, allowing for coverage of the tract variability for 11 SNPs. The most frequent haplotype (H1, 25.2%) carried only one minor allele out of 11 loci, while the others included between one and five minor alleles. Genotype frequencies are reported in Table 3. The list of all SNPs in linkage disequilibrium (LD) with the 11 genotypes is reported in Supplementary Table S4.
3.1. Association Between Haplotypes and Metabolic Indices
Table 4 shows the associations between cardio-metabolic variables and haplotypes with a frequency greater than 10%, each carrying a different number of minor alleles, using the most frequent haplotype for reference (H1, including only one minor allele).

Table 4.
Associations between NMU haplotypes from both internal and promoter regions and cardio-metabolic indices.
The analysis considering the contrast with the haplotype carrying the highest number of minor alleles (H8, five minor alleles, frequency 16.6%) showed a positive association between haplotype copy number and glucose metabolism-related variables, in particular with insulin levels (standardized variable, β ± SE = 0.11 ± 0.04, p = 0.002) and the derived variable HOMA-IR (0.09 ± 0.03, p = 0.013).
A positive association was also found with diastolic (0.09 ± 0.03, p = 0.008) but not systolic blood pressure. Regarding lipid metabolism, a negative association with HDL-cholesterol (−0.09 ± 0.03, p = 0.006) was found. These associations survived FDR correction.
The other haplotypes did not show FDR-significant associations, although a nominally significant association was found for H8 with hypercholesterolemia (OR = 0.82, 95% CI = 0.71–0.96). Supplementary Table S5 reports the results for haplotypes with a frequency lower than 10%.
3.2. Association Between SNPs and Metabolic Indices
Table 5 reports the genotypes associated with the cardio-metabolic variables, including those resulting in statistically significant differences in the previous haplotype analysis and in the previous DNA methylation analyses (lipid-related variables) performed in the same study population [21].

Table 5.
Associations between NMU SNPs and cardio-metabolic indices previously found to be significantly associated with H8 and with NMU CpG sites [18].
Only the SNPs that survived backward elimination of non-significant results have been reported. As for insulin and the HOMA index, beyond rs28451532 tagging the H2 haplotype (standardized variable, β ± SE = 0.09 ± 0.03, p = 0.003, and 0.08 ± 0.03, p = 0.006, respectively), rs12501006 (H5—haplotype frequency 3.2%, and rare haplotypes) was also associated (0.12 ± 0.06, p = 0.048, and 0.18 ± 0.06, p = 0.002). As for lipids, five SNPs located in the coding region of NMU were retained in the final model.
Very similar results were observed for total, LDL-, and HDL-cholesterol levels, which were associated positively with rs11945489 and rs3805383 and negatively with rs140220080 and rs6827359. Non-HDL variables and apolipoprotein B were also positively associated with rs73236170. No associations were found with diastolic blood pressure. A full list of results for all studied variables, for models including a single variant in each model or the whole set of genotypes, is reported in Supplementary Table S6a,b.
3.3. Association Between SNPs, CpG Methylation Levels, and Metabolic Indices
Table 6 reports the results of the models investigating the association between both genetic variants and CpG sites with lipid-related variables, which were found to be significantly associated with NMU methylation in our previous work [21].

Table 6.
Associations between NMU SNPs, CpG methylation levels, and their interactions with total and LDL-cholesterol and apolipoprotein B levels.
First, we used multivariable models and, following a backward elimination of non-significant variables, we found that both SNPs and CpGs remained statistically significant in all analyses (R-squared from 0.034 to 0.045). In the analysis including the interaction terms between SNP–CpG pairs, those between the SNPs rs73236170 or rs3805383 and CpG sites 4 or 5 were also retained in the final models (R-squared improved by 0.01 for LDL-cholesterol and apolipoprotein B). Supplementary Table S7 reports the associations between genetic and epigenetic variants, showing no significant associations.
4. Discussion
We report the relation between NMU genetic variability and a number of cardio-metabolic parameters in a general population of Italian adults using a haplotype-based approach. The main result is the identification of an NMU haplotype, ACTCCCT (haplotype frequency = 16.6%), significantly associated with increased insulin levels and the derived variable HOMA-IR, as well as with increased diastolic blood pressure and decreased HDL-cholesterol levels. Following our previous results on the associations between DNA methylation patterns at CpG sites located in the NMU promoter and lipid-related variables, in this study, we validated and replicated our findings using a combination of SNPs and specific CpG sites that were both found to explain lipid-related variability.
Our results support the role of NMU in the regulation of insulin production/release, previously observed in experimental studies [34], and suggest a potential influence of NMU in the development of insulin sensitivity and related metabolic disorders. We found associations between genetic variants linked with the H8 haplotype and insulin resistance, measured through insulin levels and the HOMA index. This finding was previously observed in studies on transgenic mouse models [35]. NMU plays a crucial role in glucose homeostasis. Although NMU treatment of isolated human islets suppresses insulin production and secretion, acting like a decretin hormone [36], it also appears to improve glucose tolerance [37]. In fact, peripheral treatment with NMU results in elevated GLP-1 levels in mice and improved glucose tolerance via NMUR1 signaling [38]. All these effects could also be due to an indirect effect on glucose homeostasis, mediated by vagus-dependent reduction of gastric emptying following meals, and to the reduced peaks of nutrient absorption [39]. It is worth noting that NMU also exerts multiple central effects, which may influence metabolic phenotypes indirectly. NMU has been shown to suppress appetite, regulate circadian behavior, and modulate the stress response via central nervous system pathways. These neurobehavioral effects could interact with peripheral mechanisms [7,20]. Future studies combining laboratory and behavioral assessments with genetic and epigenetic profiling may help clarify how central and peripheral NMU functions converge in the pathogenesis of cardio-metabolic diseases.
Beyond the association with glucose-related parameters, we also found associations between the same genetic variants and other metabolic parameters. Insulin resistance is the main underlying condition of metabolic syndrome, since insulin has beneficial effects on blood pressure, metabolism of lipids, and cholesterol-binding lipoproteins [40,41]. This suggests that the effect on insulin may be the driving phenotype in the associations reported in this study.
Our haplotype analysis showed that the most significantly associated variants are mainly located in the gene body. This suggests a possible link with changes in mRNA structure and its processing. However, many of these variants are in linkage with others distributed across the gene region, including the upstream promoter of DNA methylation. These variants may act as regulatory elements [42,43]. Worth noting is rs3805383, which is linked to the H8 haplotype and found to be significantly associated with lipid-related variables in genotype association analyses. This variant co-localizes with an active enhancer since it is located in a region with high deposition of both H3K27Ac and H3K4Me1 histone marks [44] (Supplementary Figure S2). As a consequence, the presence of gene variants in these regions is likely to influence the enhancer activity, potentially leading to an altered gene expression [44].
Methods based on haplotypes are more powerful in disease gene mapping than those based on single variation markers [45]. Moreover, since NMU haplotype blocks are short and highly conserved across different species, a high impact on peptide function and/or transcription regulation was expected for human genetic variations of this tract. However, we took advantage of the tag SNPs measured and imputed; thus, we also performed genotype–phenotype associations. We identified variants in the promoter region associated with cholesterol (both HDL- and non-HDL cholesterol content in the same direction) and apolipoprotein B levels. In our previous study focusing on NMU methylation measured in a Moli-sani sub-cohort [23], which included some of the subjects involved in this analysis, we also found an association between NMU DNA methylation and lipid-related variables. Adding this methylation contribution to the genetic analyses, we interestingly found that both CpG methylation levels and SNPs, both located in the promoter region, as well as their interactions, were significantly associated with lipid-related parameters. Moreover, in our previous study, we also found an association between those CpG sites and inflammatory variables [23]. This finding suggests that NMU could be one of the factors linking inflammation and metabolic disorders in subjects with cardio-metabolic diseases. This result strengthened the suggestion to further study NMU and other genes belonging to its pathway as markers or as potential targets for interventions on lipid-related, inflammatory, and cardio-metabolic diseases.
The main strengths of this study are the availability of a large, homogenous population, which represents a good setting for genetic studies, and the wealth of standardized cardio-metabolic measures. We also acknowledge some limitations. Although a confounding effect should be excluded due to the genetic study design, we cannot rule out a modification of the genetic effect due to some factors not taken into account here, like diet or physical activity. A further limitation is the use of a single discovery cohort, without any replication. Caution is necessary in extending these results to larger population contexts, since data were collected in a single Italian region. However, the main characteristics of our population sample are comparable to those of the Italian Cardiovascular Epidemiology Observatory [46]. For this reason, our sample could be considered representative of at least the Italian population. In addition, a further limitation of our study is the absence of NMU gene variant-dependent expression analyses. Future studies leveraging CRISPR-based functional assays will be necessary to determine whether NMU variants directly modulate NMU transcription or influence it through alternative regulatory mechanisms.
5. Conclusions
These results suggest the presence of a functional genetic and epigenetic variant(s) of the neuromedin U gene influencing phenotypic variation in metabolic indices, encouraging further studies on NMU variants as biomarkers for risk assessment of cardio-metabolic disorders. Our study also opens up future investigation to characterize the functional role of the identified NMU variants. By integrating functional genetic and epigenetic approaches, it will be possible to better unravel the contribution of the neuropeptide NMU in the pathophysiology of cardio-metabolic disturbances including CVD.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biomedicines13081906/s1, Supplementary Table S1. Anthropometrical and biochemical variables of the sub-cohort sample (N = 4031) and the whole Moli-sani cohort population (N = 24,325). Supplementary Figure S1. Rs4865020 in the putative regulatory/promoter NMU region co-localized with a CTCF binding site region. Supplementary Figure S2. Rs3805383 in the NMU gene body tags the H3K27Ac and H3K4Me1 histone marks. Supplementary Table S2. Primers and probes of the allelic discrimination assay. Supplementary Table S3. Characteristics of the NMU SNPs and frequencies of measured genotypes. Supplementary Table S4. List of SNPs in linkage disequilibrium (LD = 1) with those SNPs analyzed in the haplotypes studied. Supplementary Table S5. Association between haplotypes with frequencies lower than 10% from both promoter and internal regions and cardio-metabolic indices. Supplementary Table S6a,b Association between promoter/internal SNPs and cardiometabolic indices. Supplementary Table S7. Association between genetic variants and CpG methylation levels.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.G. and L.I.; methodology, A.M., F.N., A.G., F.G. and B.I.; validation, A.M., F.N. and A.D.C. (Amalia De Curtis); formal analysis, F.G., A.P., S.C. and A.D.C. (Augusto Di Castelnuovo); investigation, A.M., F.N., B.I. and A.D.C. (Amalia De Curtis); data curation, S.C., A.G. and A.D.C. (Amalia De Curtis); writing—original draft preparation, A.M. and F.N.; writing—review and editing, F.G., L.I., A.M., S.G., F.N., B.I., A.P., A.D.C. (Amalia De Curtis), A.G., A.D.C. (Augusto Di Castelnuovo), S.C., C.C., M.B.D. and G.d.G.; visualization, S.C. and F.G.; supervision, F.G. and L.I.; project administration, C.C. and L.I.; F.G. and L.I. contributed equally to this work as last authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The enrolment phase of the Moli-sani study was supported by research grants from the Pfizer Foundation (Rome, Italy), the Italian Ministry of University and Research (MIUR, Rome, Italy)—Programma Triennale di Ricerca, Decreto no.1588, and the Instrumentation Laboratory, Milan, Italy. Laboratory analyses of the Moli-sani study were partially supported by BiomarCaRE (Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Risk Assessment in Europe: European Commission Seventh Framework Programme FP7/2007-2013, HEALTH-F2-2011-278913, L.I.). The work reported in this manuscript was partially supported by the European Union NextGenerationEU through the Italian Ministry of University and Research under PNRR M4C2-I1.3 PE6 project PE00000019 “Heal Italia” (CUP: B23D22000580004).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Catholic University of Rome, Italy (P99, A.931/03-138-04, 11 February 2004).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. The data are stored in an institutional repository (https://repository.neuromed.it (accessed on 31 July 2025)) and their access is restricted by the ethical approvals and the legislation of the European Union.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Moli-sani study participants who enthusiastically joined the study, and to the Associazione Cuore Sano ETS (Campobasso, Italy) for its support of our research communication activities. The authors would like to thank the colleagues at the Neuromed Biobanking Center for the management of samples and for their valuable support and cooperation. F.N. and F.G: were supported by the Fondazione Umberto Veronesi ETS, which is gratefully acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CCTF | CCCTC-binding factor |
| CEU | Caucasian population, Utah residents with Northern and Western European ancestry |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| FDR | False discovery rate |
| GWAS | Genome-wide association study |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance |
| HWE | Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| MAF | Minor allele frequency |
| NMU | Neuromedin U |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SE | Standard error |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
| TSI | Tuscan population |
Appendix A. Moli-sani Study Investigators
The enrolment phase of the Moli-sani study was conducted at the Research Laboratories of the Catholic University in Campobasso (Italy). The follow-up of the Moli-sani cohort is being conducted at the Research Unit of Epidemiology and Prevention at the IRCCS Neuromed, Pozzilli, Italy.
- Steering Committee: Licia Iacoviello *# (Chairperson), Giovanni de Gaetano *, Maria Benedetta Donati *.
- Scientific Secretariat: Chiara Cerletti * (Coordinator), Marialaura Bonaccio *, Americo Bonanni *, Simona Costanzo *°, Amalia De Curtis *, Augusto Di Castelnuovo *, Alessandro Gialluisi *#, Francesco Gianfagna °, Mariarosaria Persichillo *.
- Safety and Ethical Committee: JosVermylen (Catholic University, Leuven, Belgio) (Chairperson), Renzo Pegoraro (Pontificia Accademia per la Vita, Roma, Italy), Antonio G. Spagnolo (Catholic University, Roma, Italy).
- External Event Adjudicating Committee: Deodato Assanelli (Brescia, Italy), Livia Rago (Campobasso, Italy).
- Baseline and Follow-up Data Management: Simona Costanzo *° (Coordinator), Sabatino Orlandi *, Teresa Panzera *.
- Data Analysis: Augusto Di Castelnuovo * (Coordinator), Marialaura Bonaccio *, Francesca Bracone *, Simona Costanzo *°, Giuseppe Di Costanzo *, Simona Esposito *, Alessandro Gialluisi *#, Anwal Ghulam °, Francesco Gianfagna °, Martina Morelli *†, Maria Loreto MuñozVenegas *†, Antonietta Pepe *, Emilia Ruggiero *§.
- Biobank, Molecular and Genetic Laboratory: Amalia De Curtis * (Coordinator), Concetta Civitillo *†, Alisia Cretella *†, Sara Magnacca *.
- Recruitment Staff: Mariarosaria Persichillo * (Coordinator), Francesca Bracone *, Giuseppe Di Costanzo *, Martina Morelli *†.
- Communication and Press Office: Americo Bonanni *.
- Regional Institutions: Direzione Generale per la Salute—Regione Molise; Azienda Sanitaria Regionale del Molise (ASReM, Italy); Agenzia Regionale per la Protezione Ambientale del Molise (ARPA Molise, Italy); Molise Dati Spa (Campobasso, Italy); Offices of vital statistics of the Molise region.
- Hospitals: Presidi Ospedalieri ASReM: Ospedale A. Cardarelli—Campobasso, Ospedale F. Veneziale—Isernia, Ospedale San Timoteo—Termoli (CB), Ospedale Ss. Rosario—Venafro (IS), Ospedale Vietri—Larino (CB), Ospedale San Francesco Caracciolo—Agnone (IS); Casa di Cura Villa Maria—Campobasso; Responsible Research Hospital—Campobasso; IRCCS Neuromed—Pozzilli (IS).
- * Research Unit of Epidemiology and Prevention, IRCCS Neuromed, Pozzilli, Italy.
- # Department of Medicine and Surgery, LUM University “Giuseppe Degennaro”, Casamassima, Italy.
- ° Department of Medicine and Surgery, University of Insubria, Varese, Italy.
- § Fellow of the Fondazione Umberto Veronesi, Italy.
- † Fondazione Veronesi—Piattaforma UMBERTO.
- Moli-sani study past investigators are available at https://www.moli-sani.org/?page_id=173 (accessed on 12 April 2025).
References
- Chait, A.; den Hartigh, L.J. Adipose Tissue Distribution, Inflammation and Its Metabolic Consequences, Including Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galmés, S.; Cifre, M.; Palou, A.; Oliver, P.; Serra, F. A Genetic Score of Predisposition to Low-Grade Inflammation Associated with Obesity May Contribute to Discern Population at Risk for Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2019, 11, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardu, C.; Paolisso, G.; Marfella, R. Inflammatory Related Cardiovascular Diseases: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Targets. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 2565–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C375–C391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koliaki, C.; Liatis, S.; Kokkinos, A. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: Revisiting an old relationship. Metabolism 2019, 92, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, V.G.; O’DRiscoll, L. Neuromedin U: A multifunctional neuropeptide with pleiotropic roles. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teranishi, H.; Hanada, R. Neuromedin U, a Key Molecule in Metabolic Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamino, N.; Kangawa, K.; Matsuo, H. Neuromedin U-8 and U-25: Novel uterus stimulating and hypertensive peptides identified in porcine spinal cord. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1985, 130, 1078–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przygodzka, P.; Soboska, K.; Sochacka, E.; Boncela, J. Neuromedin U: A Small Peptide in the Big World of Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Liang, Z.; Xue, L. Neuromedin U: Potential roles in immunity and inflammation. Immunology 2021, 162, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalbøge, L.S.; Pedersen, S.L.; Secher, T.; Holst, B.; Vrang, N.; Jelsing, J. Neuromedin U inhibits food intake partly by inhibiting gastric emptying. Peptides 2015, 69, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.D.; Wang, R.; Pong, S.-S.; Mellin, T.N.; Strack, A.; Guan, X.-M.; Zeng, Z.; Williams, D.L.; Feighner, S.D.; Nunes, C.N.; et al. Identification of receptors for neuromedin U and its role in feeding. Nature 2000, 406, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malendowicz, L.K.; Ziolkowska, A.; Rucinski, M. Neuromedins U and S involvement in the regulation of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis. Front. Endocrinol. 2012, 3, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanadaa, R.; Nakazato, M.; Murakamic, N.; Sakiharad, S.; Yoshimatsua, H.; Toshinaib, K.; Hanadae, T.; Sudad, T.; Kangawaf, K.; Matsukurab, S.; et al. A role for neuromedin U in stress response. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 289, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wren, A.M.; Small, C.J.; Abbott, C.R.; Jethwa, P.H.; Kennedy, A.R.; Murphy, K.G.; Stanley, S.A.; Zollner, A.N.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. Hypothalamic actions of neuromedin U. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 4227–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cardoso, V.; Chesné, J.; Ribeiro, H.; García-Cassani, B.; Carvalho, T.; Bouchery, T.; Shah, K.; Barbosa-Morais, N.L.; Harris, N.; Veiga-Fernandes, H. Neuronal regulation of type 2 innate lymphoid cells via neuromedin U. Nature 2017, 549, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grippi, C.; Izzi, B.; Gianfagna, F.; Noro, F.; Falcinelli, E.; Di Pardo, A.; Amico, E.; Donati, M.; de Gaetano, G.; Iacoviello, L.; et al. Neuromedin U potentiates ADP- and epinephrine-induced human platelet activation. Thromb. Res. 2017, 159, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainerová, I.; Torekov, S.S.; Ek, J.; Finková, M.; Borch-Johnsen, K.; Jørgensen, T.; Madsen, O.D.; Lebl, J.; Hansen, T.; Pedersen, O. Association between neuromedin U gene variants and overweight and obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 5057–5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianfagna, F.; Grippi, C.; Ahrens, W.; Bailey, M.E.S.; Börnhorst, C.; De Henauw, S.; Foraita, R.; Koni, A.C.; Krogh, V.; Mårild, S.; et al. The role of neuromedin U in adiposity regulation. Haplotype analysis in European children from the IDEFICS Cohort. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botticelli, L.; Di Bonaventura, E.M.; Del Bello, F.; Giorgioni, G.; Piergentili, A.; Quaglia, W.; Bonifazi, A.; Cifani, C.; Di Bonaventura, M.V.M. The neuromedin U system: Pharmacological implications for the treatment of obesity and binge eating behavior. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 195, 106875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grippi, C.; Ahrens, W.; Buchecker, K.; Chadjigeorgiou, C.; De Henauw, S.; Koni, A.C.; Foraita, R.; Lissner, L.; Molnár, D.; Moreno, L.A.; et al. Association between variants of neuromedin U gene and taste thresholds and food preferences in European children: Results from the IDEFICS study. Appetite 2019, 142, 104376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianfagna, F.; Cugino, D.; Ahrens, W.; Bailey, M.E.S.; Bammann, K.; Herrmann, D.; Koni, A.C.; Kourides, Y.; Marild, S.; Molnár, D.; et al. Understanding the links among neuromedin U gene, beta2-adrenoceptor gene and bone health: An observational study in European children. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotta, A.; Noro, F.; Parisi, R.; Gialluisi, A.; Tirozzi, A.; De Curtis, A.; Costanzo, S.; Di Castelnuovo, A.; Cerletti, C.; Donati, M.B.; et al. NMU DNA methylation in blood is associated with metabolic and inflammatory indices: Results from the Moli-sani study. Epigenetics 2021, 16, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacoviello, L.; Bonanni, A.; Costanzo, S.; De Curtis, A.; Di Castelnuovo, A.; Olivieri, M.; Zito, F.; Donati, M.B.; de Gaetano, G. The Moli-Sani Project, a randomized, prospective cohort study in the Molise region in Italy; design, rationale and objectives. Ital. J. Public Health 2007, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Castelnuovo, A.; Costanzo, S.; Persichillo, M.; Olivieri, M.; de Curtis, A.; Zito, F.; Donati, M.B.; de Gaetano, G.; Iacoviello, L. MOLI-SANI Project Investigators. Distribution of short and lifetime risks for cardiovascular disease in Italians. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2012, 19, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Castelnuovo, A.; de Curtis, A.; Costanzo, S.; Persichillo, M.; Olivieri, M.; Zito, F.; Donati, M.B.; de Gaetano, G.; Iacoviello, L.; MOLI-SANI Project Investigators. Association of D-dimer levels with all-cause mortality in a healthy adult population: Findings from the MOLI-SANI study. Haematologica 2013, 98, 1476–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Guidelines on the Identification Evaluation Treatment of Overweight Obesity in Adults—The Evidence Report National Institutes of Health. Obes. Res. 1998, 6 (Suppl. S2), 51S–209S, Erratum in Obes. Res. 1998, 6, 464.
- Bener, A.; Zirie, M.; Musallam, M.; Khader, Y.S.; Al-Hamaq, A.O. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome according to Adult Treatment Panel III and International Diabetes Federation criteria: A population-based study. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2009, 7, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, T.; Hughes, M.; Tuovinen, T.; Schillert, A.; Conrads-Frank, A.; RuijterHd Schnabel, R.B.; Kee, F.; Salomaa, V.; Siebert, U.; Thorand, B.; et al. BiomarCaRE: Rationale and design of the European BiomarCaRE project including 300,000 participants from 13 European countries. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 29, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacoviello, L.; De Curtis, A.; Donati, M.B.; de Gaetano, G. Biobanks for cardiovascular epidemiology and prevention. Future Cardiol. 2014, 10, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malferrari, G.; Monferini, E.; DeBlasio, P.; Diaferia, G.; Saltini, G.; Del Vecchio, E.; Rossi-Bernardi, L.; Biunno, I. High-qualitygenomic DNA from human wholeblood and mononuclearcells. BioTechniques 2002, 33, 1228–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, J.C.; Fry, B.; Maller, J.; Daly, M.J. Haploview: Analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sakoda, H.; Nakazato, M. Neuromedin U suppresses insulin secretion by triggering mitochondrial dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress in pancreatic β-cells. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, T.J.; Spar, B.D.; Markowitz, L.; Maguire, M.; Golovko, A.; Yang, S.; Farley, C.; Cook, J.A.; Tetzloff, G.; Hoos, L.; et al. Transgenic overexpression of neuromedin U promotes leanness and hypophagia in mice. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 185, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfa, R.W.; Park, S.; Skelly, K.R.; Poffenberger, G.; Jain, N.; Gu, X.; Kockel, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Powers, A.C.; et al. Suppression of insulin production and secretion by a decretin hormone. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 323–334, Erratum in Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2018.01.003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, H.; He, J.; Sun, H.; Zhu, D.; Bi, Y. Peripheral Administration of NMU Promotes White Adipose Tissue Beiging and Improves Glucose Tolerance. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 2021, 6142096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Peier, A.M.; Desai, K.; Hubert, J.; Du, X.; Yang, L.; Qian, Y.; Kosinski, J.R.; Metzger, J.M.; Pocai, A.; Nawrocki, A.R.; et al. Effects of peripherally administered neuromedin U on energy and glucose homeostasis. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 2644–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarry, A.C.; Merah, N.; Cisse, F.; Cayetanot, F.; Fiamma, M.N.; Willemetz, A.; Gueddouri, D.; Barka, B.; Valet, P.; Guilmeau, S.; et al. Neuromedin U is a gut peptide that alters oral glucose tolerance by delaying gastric emptying via direct contraction of the pylorus and vagal-dependent mechanisms. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 5377–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T. Pathophysiology of Diabetic Dyslipidemia. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2018, 25, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahiru, E.; Hsiao, R.; Phillipson, D.; Watson, K.E. Mechanisms and Treatment of Dyslipidemia in Diabetes. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2021, 23, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, K.L.; Rapkins, R.W.; Olivier, J.; Zhao, L.; Nozue, K.; Lu, D.; Tiwari, S.; Kuroiwa-Trzmielina, J.; Brewer, J.; Wheeler, H.R.; et al. The T genotype of the MGMT C>T (rs16906252) enhancer single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) is associated with promoter methylation and longer survival in glioblastoma patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzi, B.; Pistoni, M.; Cludts, K.; Akkor, P.; Lambrechts, D.; Verfaillie, C.; Verhamme, P.; Freson, K.; Hoylaerts, M.F. Allele-specific DNA methylation reinforces PEAR1 enhancer activity. Blood 2016, 128, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plank, J.L.; Dean, A. Enhancer function: Mechanistic and genome-wide insights come together. Mol. Cell. 2014, 55, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, H. Haplotype-association analysis. Adv. Genet. 2008, 60, 335–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanuzzo, D.; Lo Noce, C.; Pilotto, L.; Palmieri, L.; Donfrancesco, C.; Dima, F.; Gattone, M.; Goldoni, C.A.; Boccanelli, A.; Iacoviello, L.; et al. Osservatorio Epidemiologico Cardiovascolare 2008–2011: Primi risultati [Cardiovascularepidemiologic observatory 2008–2011: Preliminary results]. G. Ital. Di Cardiol. 2010, 11, 25–30. (In Italian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).