Clinical Performance of Analog and Digital 18F-FDG PET/CT in Pediatric Epileptogenic Zone Localization: Preliminary Results
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. PET/CT Acquisition Protocols
2.3. Qualitative Image Analysis
2.4. Quantitative Image Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Standard of Reference and Post-Surgical Outcome
3. Results
3.1. Visual and Quantitative Scoring, Interobserver Agreement
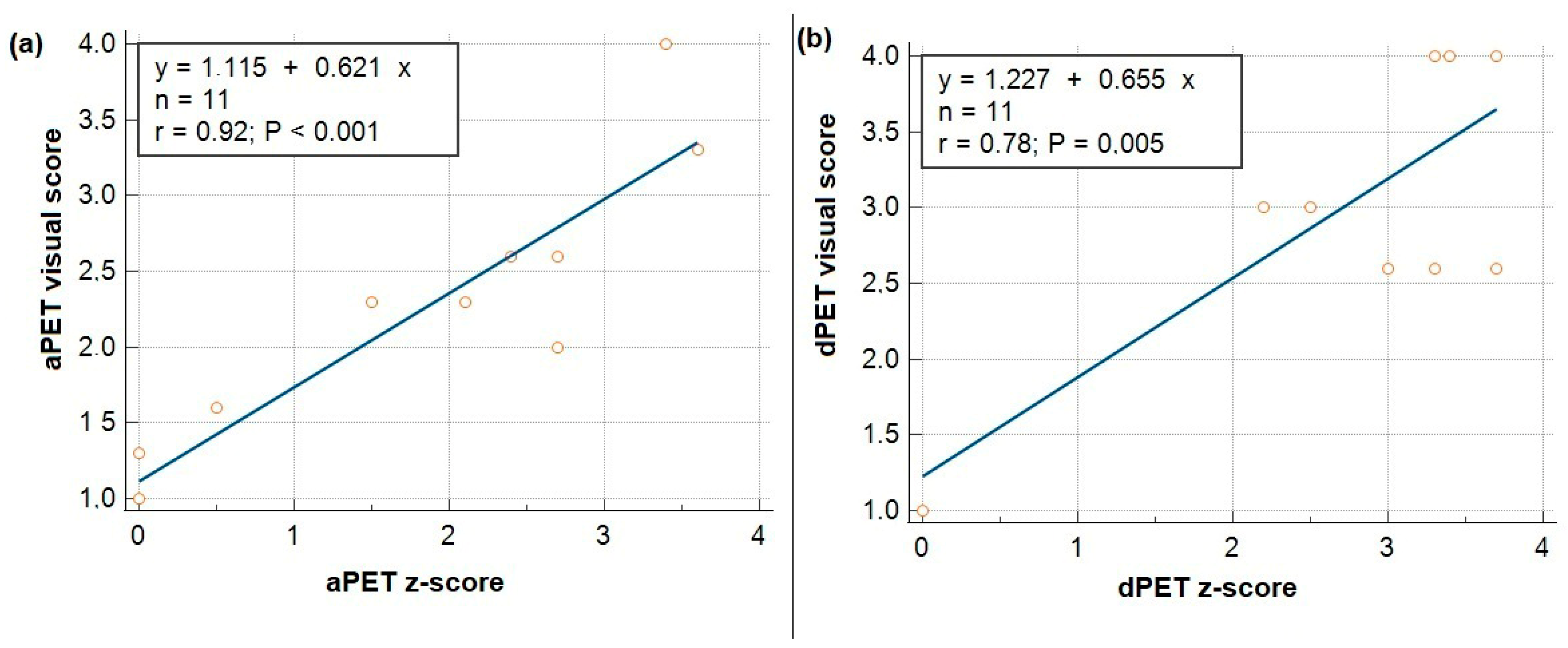
3.2. Correlation Between Visual and Z-Scores
3.3. Correlation Between PET and MRI Findings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- la Fougère, C.; Rominger, A.; Förster, S.; Geisler, J.; Bartenstein, P. PET and SPECT in Epilepsy: A Critical Review. Epilepsy Behav. 2009, 15, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffin, K.; Dedeurwaerdere, S.; Van Laere, K.; Van Paesschen, W. Neuronuclear Assessment of Patients with Epilepsy. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2008, 38, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, K.; Wang, J.; Fan, X.; Cui, B.; Ma, J.; Yang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, G.; Lu, J. Clinical Value of Hybrid TOF-PET/MR Imaging-Based Multiparametric Imaging in Localizing Seizure Focus in Patients with MRI-Negative Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boscolo Galazzo, I.; Mattoli, M.V.; Pizzini, F.B.; De Vita, E.; Barnes, A.; Duncan, J.S.; Jäger, H.R.; Golay, X.; Bomanji, J.B.; Koepp, M.; et al. Cerebral Metabolism and Perfusion in MR-Negative Individuals with Refractory Focal Epilepsy Assessed by Simultaneous Acquisition of (18)F-FDG PET and Arterial Spin Labeling. Neuroimage Clin. 2016, 11, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomás, J.; Pittau, F.; Hammers, A.; Bouvard, S.; Picard, F.; Vargas, M.I.; Sales, F.; Seeck, M.; Garibotto, V. The Predictive Value of Hypometabolism in Focal Epilepsy: A Prospective Study in Surgical Candidates. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 1806–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkovich, M.J.; Li, Y.; Desikan, R.S.; Barkovich, A.J.; Xu, D. Challenges in Pediatric Neuroimaging. Neuroimage 2019, 185, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayalakshmi, S.; Nanda, S.K.; Vooturi, S.; Vadapalli, R.; Sudhakar, P.; Madigubba, S.; Panigrahi, M. Focal Cortical Dysplasia and Refractory Epilepsy: Role of Multimodality Imaging and Outcome of Surgery. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Mora, D.A.; Carrió, I.; Flotats, A. Digital PET vs Analog PET: Clinical Implications? Semin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 52, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimalarathne, D.D.N.; Ruan, W.; Sun, X.; Liu, F.; Gai, Y.; Liu, Q.; Hu, F.; Lan, X. Impact of TOF on Brain PET with Short-Lived 11C-Labeled Tracers Among Suspected Patients With AD/PD: Using Hybrid PET/MRI. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 823292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Ocampo, F.; López-Mora, D.A.; Flotats, A.; Paillahueque, G.; Camacho, V.; Duch, J.; Fernández, A.; Domènech, A.; Estorch, M.; Carrió, I. Digital vs. Analog PET/CT: Intra-Subject Comparison of the SUVmax in Target Lesions and Reference Regions. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 1745–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, V.P.V.; Brady, S.; Ata, N.A.; Li, Y.; MacLean, J.; Zhang, B.; Sharp, S.E.; Trout, A.T. Simulated Reduced-Count Whole-Body FDG PET: Evaluation in Children and Young Adults Imaged on a Digital PET Scanner. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2022, 219, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, J. Overview of Surgical Treatment for Epilepsy. In The Treatment of Epilepsy; Shorvon, S., Perucca, E., Engel, J., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 709–722. ISBN 978-1-118-93700-6. [Google Scholar]
- Czarnetzki, C.; Spinelli, L.; Huppertz, H.-J.; Schaller, K.; Momjian, S.; Lobrinus, J.; Vargas, M.-I.; Garibotto, V.; Vulliemoz, S.; Seeck, M. Yield of Non-Invasive Imaging in MRI-Negative Focal Epilepsy. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metrard, G.; Besse, H.; Darsin-Bettinger, D.; Mouzoune, S.; Gauvain, S. New EANM Paediatric Dosage Card: Optimization of F-18 FDG-Administered Activities. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paldino, M.J.; Yang, E.; Jones, J.Y.; Mahmood, N.; Sher, A.; Zhang, W.; Hayatghaibi, S.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Seghers, V. Comparison of the Diagnostic Accuracy of PET/MRI to PET/CT-Acquired FDG Brain Exams for Seizure Focus Detection: A Prospective Study. Pediatr. Radiol. 2017, 47, 1500–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, K.; Togao, O.; Yamashita, K.; Momosaka, D.; Nakayama, T.; Kitamura, Y.; Kikuchi, Y.; Baba, S.; Sagiyama, K.; Ishimatsu, K.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy for the Epileptogenic Zone Detection in Focal Epilepsy Could Be Higher in FDG-PET/MRI than in FDG-PET/CT. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 2915–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Guo, K.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D.; Wang, Y.; Feng, L.; Wang, J.; Meng, X.; Ma, L.; He, H.; et al. Evaluating the Efficacy of CortexID Quantitative Analysis in Localization of the Epileptogenic Zone in Patients with Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Neurol. Ther. 2024, 13, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucca, A.; Manara, C.V.; Catalan, M.; Liccari, M.; Antonutti, L.; Lombardo, T.M.I.; Cenacchi, V.; Rangan, S.; Mingolo, S.; Crisafulli, C.; et al. Using Illusions to Understand Hallucinations: Differences in Perceptual Performances on Illusory Figures May Underscore Specific Visuoperceptual Impairments in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1256224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, L.D.; Cai, T.T.; DasGupta, A. Interval Estimation for a Binomial Proportion. Statist. Sci. 2001, 16, 101–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, J.; Wiebe, S.; French, J.; Sperling, M.; Williamson, P.; Spencer, D.; Gumnit, R.; Zahn, C.; Westbrook, E.; Enos, B. Practice Parameter: Temporal Lobe and Localized Neocortical Resections for Epilepsy: Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology, in Association with the American Epilepsy Society and the American Association of Neurological Surgeons. Neurology 2003, 60, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, C.; Dickson, J.C.; Teotónio, R.; Ell, P.; Duncan, J.S. The Utility of 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose PET (FDG PET) in Epilepsy Surgery. Epilepsy Res. 2014, 108, 1306–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbrenner, M.; Duncan, J.S.; Dickson, J.; Rathore, C.; Wächter, B.; Aygun, N.; Menon, R.N.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Holtkamp, M.; Ilyas-Feldmann, M. Utility of 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography in Presurgical Evaluation of Patients with Epilepsy: A Multicenter Study. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 1238–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, R.N.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Parameswaran, R.; Thomas, B.; Kesavadas, C.; Abraham, M.; Vilanilam, G.; Sarma, S.P. Does F-18 FDG-PET Substantially Alter the Surgical Decision-Making in Drug-Resistant Partial Epilepsy? Epilepsy Behav. 2015, 51, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, H.; Gao, C.; Zhang, G.; Xu, L.; Lv, M.; Chai, W. Imaging the Effects of Propofol on Human Cerebral Glucose Metabolism Using Positron Emission Tomography. J. Int. Med. Res. 2008, 36, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepes, Z.; Arato, V.; Csikos, C.; Hegedus, E.; Esze, R.; Nagy, T.; Joszai, I.; Emri, M.; Kertesz, I.; Trencsenyi, G. In Vivo Evaluation of Brain [18F]F-FDG Uptake Pattern Under Different Anaesthesia Protocols. Vivo 2024, 38, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perillo, T.; Perillo, S.; Pinto, A. Machine Learning in Neuroimaging of Epilepsy: A Narrative Review. J. Med. Imaging Interv. Radiol. 2024, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Dong, C.; Zhou, H.; Wu, B.; Tang, Y.; Gong, J.; Ye, W.; Hu, Y.; et al. Machine Learning Techniques Based on 18F-FDG PET Radiomics Features of Temporal Regions for the Classification of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Patients from Healthy Controls. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1377538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuvoli, S.; Bianconi, F.; Rondini, M.; Lazzarato, A.; Marongiu, A.; Fravolini, M.L.; Cascianelli, S.; Amici, S.; Filippi, L.; Spanu, A.; et al. Differential Diagnosis of Alzheimer Disease vs. Mild Cognitive Impairment Based on Left Temporal Lateral Lobe Hypomethabolism on 18F-FDG PET/CT and Automated Classifiers. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, I.; Sachpekidis, C.; Prenosil, G.; Viscione, M.; Bohn, K.P.; Mingels, C.; Shi, K.; Ashar-Oromieh, A.; Rominger, A. Digital PET/CT Allows for Shorter Acquisition Protocols or Reduced Radiopharmaceutical Dose in [18F]-FDG PET/CT. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2021, 35, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippi, L.; Danieli, R. Unlocking the Brain’s Secrets: The NeuroEXPLORER Revolution in PET Imaging. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2025, 8, 783–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, S.E.; Kwan, B.Y.M.; Jurkiewicz, M.T.; Samargandy, L.; Iacobelli, M.; Steven, D.A.; Lam Shin Cheung, V.; Moran, G.; Prato, F.S.; Thompson, R.T.; et al. An Evaluation of the Diagnostic Equivalence of 18F-FDG-PET between Hybrid PET/MRI and PET/CT in Drug-Resistant Epilepsy: A Pilot Study. Epilepsy Res. 2021, 172, 106583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, G.B.; Yoon, H.S.; Kim, K.Y.; Lee, M.S.; Yang, B.Y.; Jeong, J.M.; Lee, D.S.; Song, I.C.; Kim, S.-K.; Kim, D.; et al. Simultaneous Multiparametric PET/MRI with Silicon Photomultiplier PET and Ultra-High-Field MRI for Small-Animal Imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, H.; Lerche, C. Advances in Clinical PET/MRI Instrumentation. PET Clin. 2016, 11, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, T.; Hacker, M.; Goh, V. PET/MRI-Knocking on the Doors of the Rich and Famous. Br. J. Radiol. 2017, 90, 20170347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.F.; Hall, P.S.; Hulme, C.T.; Dunn, J.A.; McConkey, C.C.; Rahman, J.K.; McCabe, C.; Mehanna, H. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of PET-CT-Guided Management for Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 85, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Xiao, L.; Deng, C.; Zhu, H.; Gao, X.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Liu, D.; Feng, L.; Hu, S. [18F]FDG PET Metabolic Patterns in Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy with Different Pathological Types. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodore, W.H. Antiepileptic Drugs and Cerebral Glucose Metabolism. Epilepsia 1988, 29 (Suppl. S2), 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, K.; Catana, C.; Qi, J.; Li, Q. PET Image Reconstruction Using Deep Image Prior. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 1655–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, J.; Oktem, O. Learned Primal-Dual Reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catana, C. Principles of Simultaneous PET/MR Imaging. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2017, 25, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


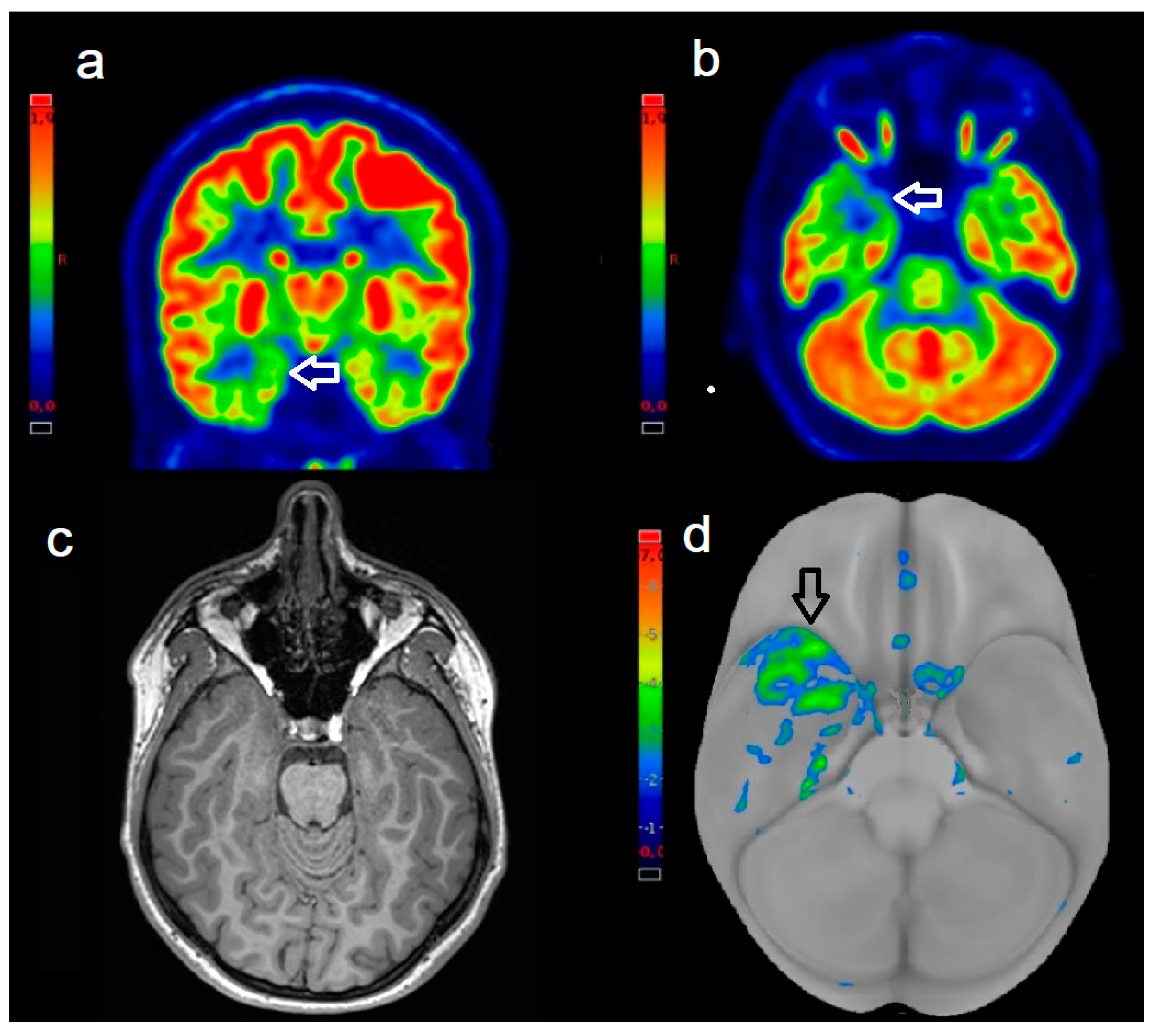
| Patient | Age | Sex | Epilepsy Duration (Years) | PET Device | PET Detection | EZ Location | MRI Findings | Histopathology | Engel Scale |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11 | F | 2 | aPET | + | R temp | − | Gliosis | Class I |
| 2 | 13 | M | 3 | aPET | + | L temp | +/C | HS | Class I |
| 3 * | 17 | M | 6 | aPET | + | R temp-occip | +/C | Gliosis | Class I |
| 4 | 8 | M | 2 | aPET | − | L front | + | FCD | Class III |
| 5 | 11 | F | 3 | aPET | − | Left temp | + | HS | Class I |
| 6 | 10 | M | 4 | aPET | + | R temp | − | Gliosis | Class II |
| 7 | 9 | M | 2 | aPET | − | L front | + | FCD | Class I |
| 8 | 15 | M | 3 | aPET | + | L temp | +/C | HS | Class II |
| 9 | 13 | M | 4 | aPET | + | L temp | +/C | Temp cyst | Class I |
| 10 | 9 | F | 2 | aPET | + | R temp | − | HS | Class I |
| 11 | 12 | F | 3 | aPET | + | L front | +/C | FCD | Class II |
| 12 | 15 | M | 4 | dPET | + | R temp | +/C | HS | Class I |
| 13 | 7 | F | 2 | dPET | + | L front | +/C | FCD | Class I |
| 14 | 9 | M | 3 | dPET | + | R temp | − | HS | Class I |
| 15 | 11 | F | 4 | dPET | + | L temp | +/C | HS | Class I |
| 16 | 13 | F | 5 | dPET | + | R temp | − | HS | Class I |
| 17 | 10 | M | 2 | dPET | − | L front | + | FCD | Class I |
| 18 | 16 | M | 3 | dPET | + | R temp | +/C | HS | Class I |
| 19 | 12 | F | 3 | dPET | + | L temp | − | Gliosis | Class I |
| 20 | 10 | M | 2 | dPET | + | L temp | +/C | ODG WHO 2 | Class III |
| 21 | 9 | M | 3 | dPET | + | R temp | +/C | HS | Class II |
| 22 | 12 | F | 4 | dPET | + | L front-temp | − | Gliosis | Class I |
| Device | Average Visual Scores | ICC | 95% (CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observer 1 | Observer 2 | Observer 3 | |||
| aPET | 2.1 ± 0.9 | 2.2 ± 1.1 | 2 ± 0.8 | 0.63 | 0.2–0.8 |
| dPET | 3.1 ± 0.8 | 3 ± 1 | 3.1 ± 0.8 | 0.91 | 0.7–0.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bagni, O.; Danieli, R.; Bianconi, F.; Palumbo, B.; Filippi, L. Clinical Performance of Analog and Digital 18F-FDG PET/CT in Pediatric Epileptogenic Zone Localization: Preliminary Results. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1887. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081887
Bagni O, Danieli R, Bianconi F, Palumbo B, Filippi L. Clinical Performance of Analog and Digital 18F-FDG PET/CT in Pediatric Epileptogenic Zone Localization: Preliminary Results. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(8):1887. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081887
Chicago/Turabian StyleBagni, Oreste, Roberta Danieli, Francesco Bianconi, Barbara Palumbo, and Luca Filippi. 2025. "Clinical Performance of Analog and Digital 18F-FDG PET/CT in Pediatric Epileptogenic Zone Localization: Preliminary Results" Biomedicines 13, no. 8: 1887. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081887
APA StyleBagni, O., Danieli, R., Bianconi, F., Palumbo, B., & Filippi, L. (2025). Clinical Performance of Analog and Digital 18F-FDG PET/CT in Pediatric Epileptogenic Zone Localization: Preliminary Results. Biomedicines, 13(8), 1887. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081887







