Gut Microbiome Signatures in Multiple Sclerosis: A Case-Control Study with Machine Learning and Global Data Integration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Stool Sample Processing and Sequencing
2.3. Sequence Data Processing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. Microbial Diversity
2.4.2. sPLS-DA
2.5. Additional Microbiome Data Collection
2.6. Literature Review for Taxonomic Feature Selection
2.7. Development of Machine Learning Models
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Demographic Characteristics of the Study Participants
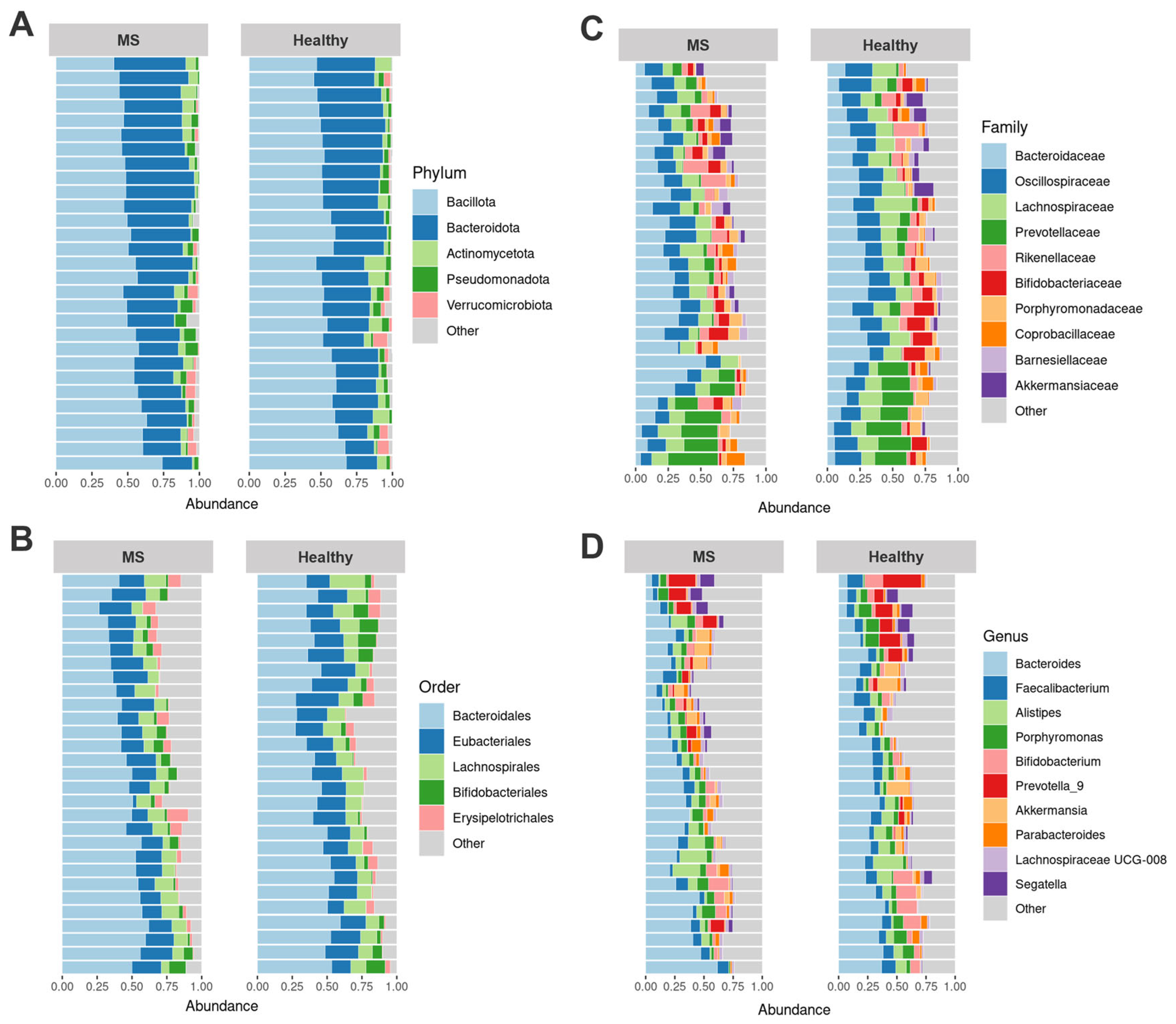
3.2. Differences in Gut Microbiota Composition of Healthy Controls and MS Patients
3.3. Bacterial Diversity Analysis
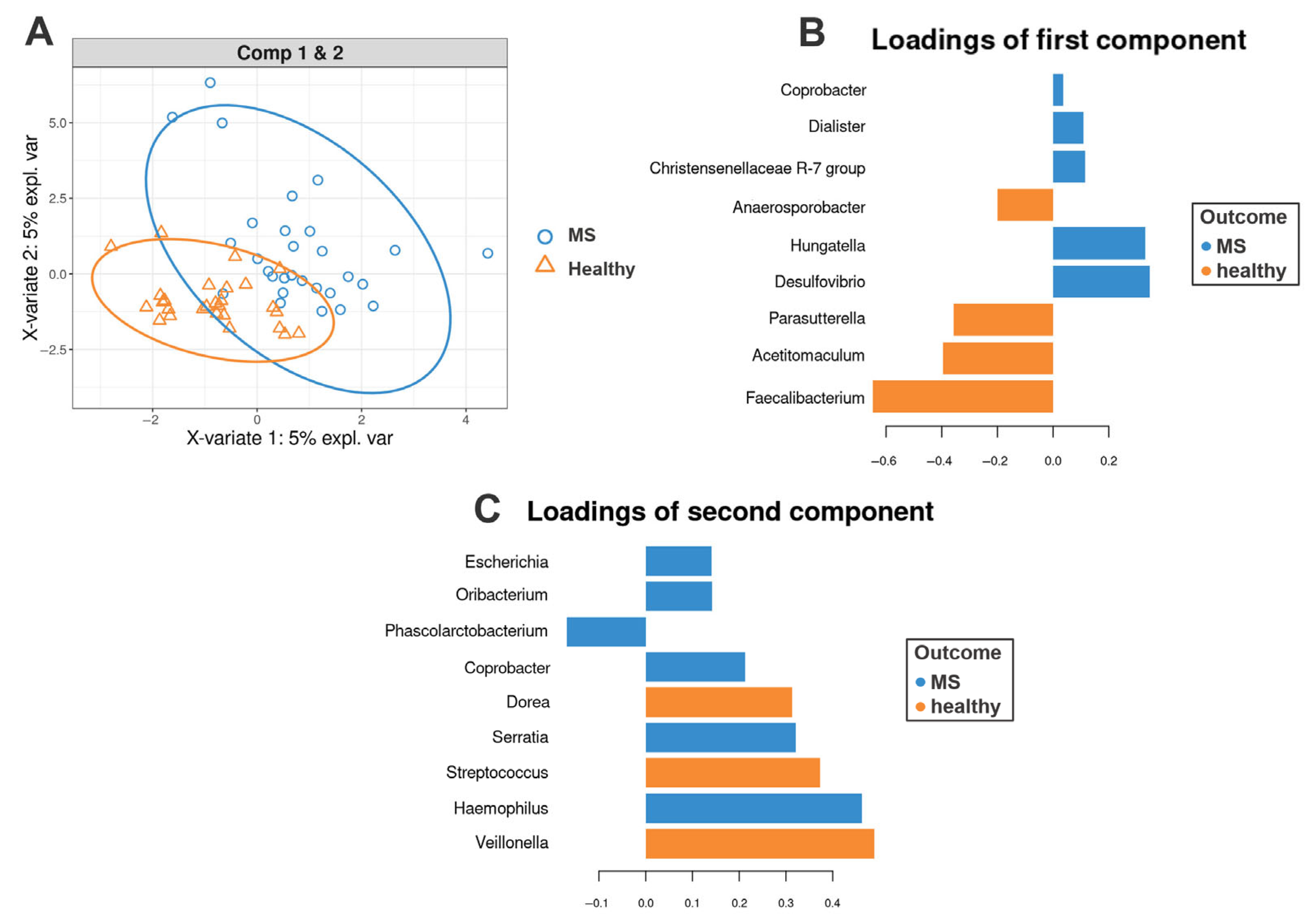
3.4. sPLS-DA Analysis Results
3.5. Dataset for the Global Analysis
- For MS patients: Age ≤ 70 years, BMI ≤ 36 kg/m2, and no antibiotic use for at least one month prior to fecal sample collection.
- For healthy volunteers: Age ≤ 50 years, BMI between 18.5 and 25 kg/m2, and the same antibiotic restriction.
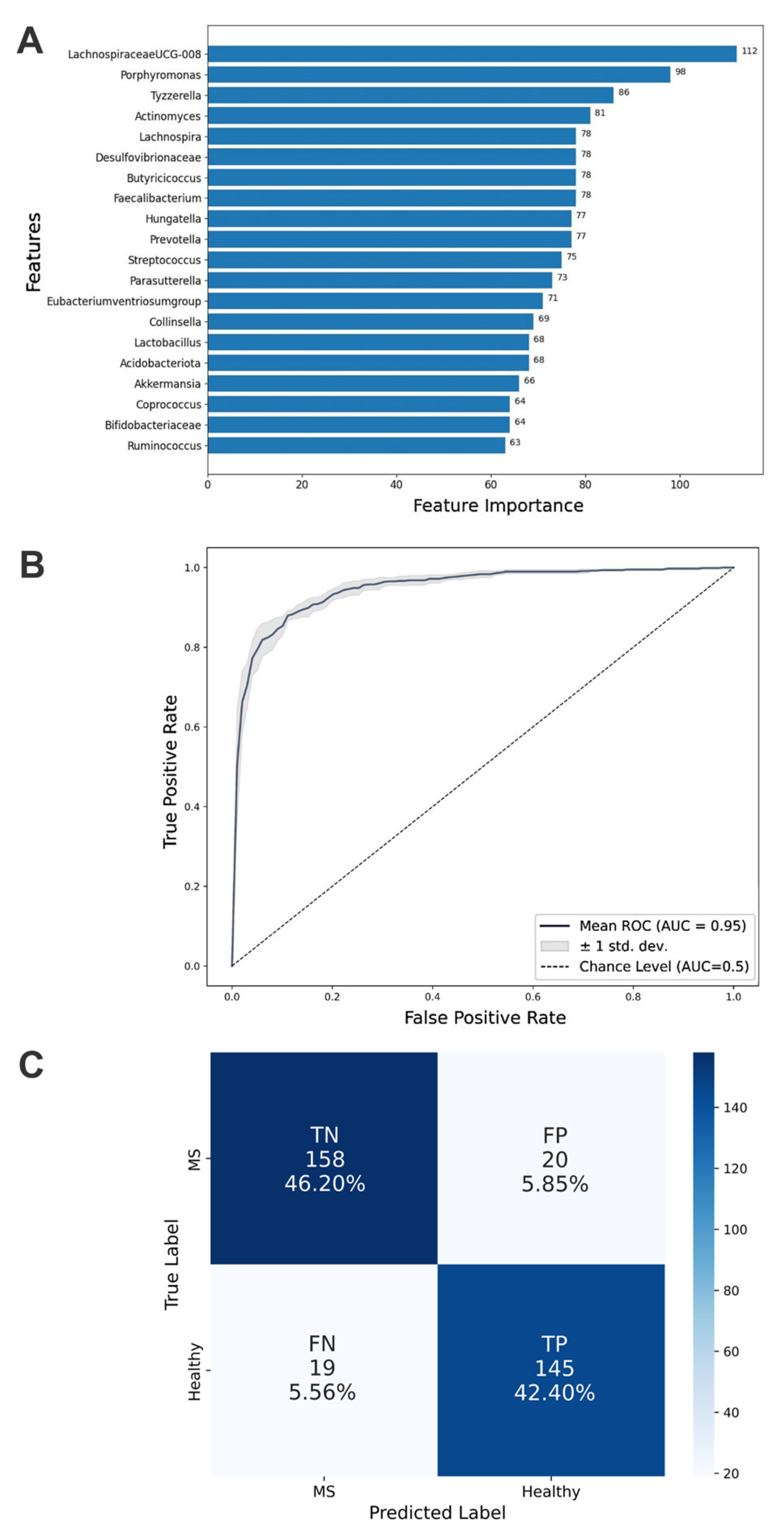
3.6. Development of an ML Algorithm for Microbiome Classification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC | Area Under Curve |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| CRC | Colorectal Cancer |
| DMTs | Disease-Modifying Therapies |
| EDSS | Expanded Disability Status Scale |
| IBD | Inflammatory Bowel Diseases |
| LightGBM | Light Gradient Boosting Machine |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MS | Multiple Sclerosis |
| RF | Random Forest |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| SCFAs | Short-Chain Fatty Acids |
| sPLS-DA | Sparse Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| T2D | Type 2 Diabetes |
| Tregs | Regulatory T-cells |
| XGB | eXtreme Gradient Boosting |
References
- Yamout, B.; Sahraian, M.; Bohlega, S.; Al-Jumah, M.; Goueider, R.; Dahdaleh, M.; Inshasi, J.; Hashem, S.; Alsharoqi, I.; Khoury, S.; et al. Consensus recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of multiple sclerosis: 2019 revisions to the MENACTRIMS guidelines. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2020, 37, 101459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, T.; Barcellos, L.F.; Alfredsson, L. Interactions between genetic, lifestyle and environmental risk factors for multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramagopalan, S.V.; Dobson, R.; Meier, U.C.; Giovannoni, G. Multiple sclerosis: Risk factors, prodromes, and potential causal pathways. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, F.; Shi, M.; Lang, Y.; Shen, D.; Jin, T.; Zhu, J.; Cui, L. Gut Microbiota in Multiple Sclerosis and Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis: Current Applications and Future Perspectives. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 8168717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Barreiro, L.; Eixarch, H.; Montalban, X.; Espejo, C. Combined therapies to treat complex diseases: The role of the gut microbiota in multiple sclerosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Haq, R.; Schlachetzki, J.C.M.; Glass, C.K.; Mazmanian, S.K. Microbiome-microglia connections via the gut-brain axis. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordoñez-Rodriguez, A.; Roman, P.; Rueda-Ruzafa, L.; Campos-Rios, A.; Cardona, D. Changes in Gut Microbiota and Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braniste, V.; Al-Asmakh, M.; Kowal, C.; Anuar, F.; Abbaspour, A.; Tóth, M.; Korecka, A.; Bakocevic, N.; Ng, L.G.; Kundu, P.; et al. The gut microbiota influences blood-brain barrier permeability in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 263ra158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erny, D.; Hrabě de Angelis, A.L.; Jaitin, D.; Wieghofer, P.; Staszewski, O.; David, E.; Keren-Shaul, H.; Mahlakoiv, T.; Jakobshagen, K.; Buch, T.; et al. Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fettig, N.M.; Osborne, L.C. Direct and indirect effects of microbiota-derived metabolites on neuroinflammation in multiple sclerosis. Microbes Infect. 2021, 23, 104814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Baumann, R.; Gao, X.; Mendoza, M.; Singh, S.; Sand, I.K.; Xia, Z.; Cox, L.M.; Chitnis, T.; Yoon, H.; et al. Gut microbiome of multiple sclerosis patients and paired household healthy controls reveal associations with disease risk and course. Cell 2022, 185, 3467–3486.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Covián, D.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Margolles, A.; Gueimonde, M.; de Los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.; Salazar, N. Intestinal Short Chain Fatty Acids and their Link with Diet and Human Health. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosorich, I.; Dalla-Costa, G.; Sorini, C.; Ferrarese, R.; Messina, M.J.; Dolpady, J.; Radice, E.; Mariani, A.; Testoni, P.A.; Canducci, F.; et al. High frequency of intestinal TH17 cells correlates with microbiota alterations and disease activity in multiple sclerosis. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronzini, M.; Maglione, A.; Rosso, R.; Matta, M.; Masuzzo, F.; Rolla, S.; Clerico, M. Feeding the gut microbiome: Impact on multiple sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1176016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsogka, A.; Kitsos, D.K.; Stavrogianni, K.; Giannopapas, V.; Chasiotis, A.; Christouli, N.; Tsivgoulis, G.; Tzartos, J.S.; Giannopoulos, S. Modulating the Gut Microbiome in Multiple Sclerosis Management: A Systematic Review of Current Interventions. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavakiotis, I.; Tsave, O.; Salifoglou, A.; Maglaveras, N.; Vlahavas, I.; Chouvarda, I. Machine Learning and Data Mining Methods in Diabetes Research. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubatan, J.; Levitte, S.; Patel, A.; Balabanis, T.; Wei, M.T.; Sinha, S.R. Artificial intelligence applications in inflammatory bowel disease: Emerging technologies and future directions. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 1920–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.M.; Manghi, P.; Asnicar, F.; Pasolli, E.; Armanini, F.; Zolfo, M.; Beghini, F.; Manara, S.; Karcher, N.; Pozzi, C.; et al. Metagenomic analysis of colorectal cancer datasets identifies cross-cohort microbial diagnostic signatures and a link with choline degradation. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrucci, D.; Teofani, A.; Unida, V.; Cerroni, R.; Biocca, S.; Stefani, A.; Desideri, A. Can Gut Microbiota Be a Good Predictor for Parkinson’s Disease? A Machine Learning Approach. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.J.; Banwell, B.L.; Barkhof, F.; Carroll, W.M.; Coetzee, T.; Comi, G.; Correale, J.; Fazekas, F.; Filippi, M.; Freedman, M.S.; et al. Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions of the McDonald criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illumina DNA Prep Reference Guide—Document #1000000025416, v09; Illumina: San Diego, CA, USA, 2020.
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. 2010. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 20 July 2024).
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, D.E.; Lu, J.; Langmead, B. Improved metagenomic analysis with Kraken 2. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahti, L.; Shetty, S. Tools for Microbiome Analysis in R Version. 2017. Available online: https://github.com/microbiome/microbiome (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- Oksanen, J.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P. The Vegan Package. Community Ecol. Package 2007, 10, 631–637. [Google Scholar]
- Rohart, F.; Gautier, B.; Singh, A.; Lê Cao, K.-A. mixOmics: An R package for ‘omics feature selection and multiple data integration. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.02754v3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.R.; Millman, K.J.; van der Walt, S.J.; Gommers, R.; Virtanen, P.; Cournapeau, D.; Wieser, E.; Taylor, J.; Berg, S.; Smith, N.J.; et al. Array programming with NumPy. Nature 2020, 585, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiba, T.; Sano, S.; Yanase, T.; Ohta, T.; Koyama, M. Optuna: A Next-generation Hyperparameter Optimization Framework. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–8 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Preziosi, G.; Gordon-Dixon, A.; Emmanuel, A. Neurogenic bowel dysfunction in patients with multiple sclerosis: Prevalence, impact, and management strategies. Degener. Neurol. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2018, 8, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrie, R.A.; Rudick, R.; Horwitz, R.; Cutter, G.; Tyry, T.; Campagnolo, D.; Vollmer, T. Vascular comorbidity is associated with more rapid disability progression in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2010, 74, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marck, C.H.; Neate, S.L.; Taylor, K.L.; Weiland, T.J.; Jelinek, G.A. Prevalence of Comorbidities, Overweight and Obesity in an International Sample of People with Multiple Sclerosis and Associations with Modifiable Lifestyle Factors. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, L.M.; Maghzi, A.H.; Liu, S.; Tankou, S.K.; Dhang, F.H.; Willocq, V.; Song, A.; Wasén, C.; Tauhid, S.; Chu, R.; et al. Gut Microbiome in Progressive Multiple Sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2021, 89, 1195–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takewaki, D.; Suda, W.; Sato, W.; Takayasu, L.; Kumar, N.; Kimura, K.; Kaga, N.; Mizuno, T.; Miyake, S.; Hattori, M.; et al. Alterations of the gut ecological and functional microenvironment in different stages of multiple sclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 22402–22412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, N.S.; Valenzuela, R.K.; Kitchner, T.; Le, T.; Mayer, J.; Tang, Z.Z.; Bayanagari, V.R.; Lu, Q.; Aston, P.; Anantharaman, K.; et al. Genetic risk score in multiple sclerosis is associated with unique gut microbiome. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozhieva, M.; Naumova, N.; Alikina, T.; Boyko, A.; Vlassov, V.; Kabilov, M.R. The Core of Gut Life: Firmicutes Profile in Patients with Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. Life 2021, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangi, S.; Gandhi, R.; Cox, L.M.; Li, N.; von Glehn, F.; Yan, R.; Patel, B.; Mazzola, M.A.; Liu, S.; Glanz, B.L.; et al. Alterations of the human gut microbiome in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cekanaviciute, E.; Yoo, B.B.; Runia, T.F.; Debelius, J.W.; Singh, S.; Nelson, C.A.; Kanner, R.; Bencosme, Y.; Lee, Y.K.; Hauser, S.L.; et al. Gut bacteria from multiple sclerosis patients modulate human T cells and exacerbate symptoms in mouse models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10713–10718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, J.D.; Chen, C.Y.; Knox, N.C.; Marrie, R.A.; El-Gabalawy, H.; de Kievit, T.; Alfa, M.; Bernstein, C.N.; Van Domselaar, G. A comparative study of the gut microbiota in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases—Does a common dysbiosis exist? Microbiome 2018, 6, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saresella, M.; Marventano, I.; Barone, M.; La Rosa, F.; Piancone, F.; Mendozzi, L.; d’Arma, A.; Rossi, V.; Pugnetti, L.; Roda, G.; et al. Alterations in Circulating Fatty Acid Are Associated with Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis and Inflammation in Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.; Gong, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, C.; Sun, X.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. Gut dysbiosis and lack of short chain fatty acids in a Chinese cohort of patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 129, 104468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chia, N.; Kalari, K.R.; Yao, J.Z.; Novotna, M.; Paz Soldan, M.M.; Luckey, D.H.; Marietta, E.V.; Jeraldo, P.R.; Chen, X.; et al. Multiple sclerosis patients have a distinct gut microbiota compared to healthy controls. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozhieva, M.; Naumova, N.; Alikina, T.; Boyko, A.; Vlassov, V.; Kabilov, M.R. Primary progressive multiple sclerosis in a Russian cohort: Relationship with gut bacterial diversity. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, M.; Mendozzi, L.; D’Amico, F.; Saresella, M.; Rampelli, S.; Piancone, F.; La Rosa, F.; Marventano, I.; Clerici, M.; d’Arma, A.; et al. Influence of a High-Impact Multidimensional Rehabilitation Program on the Gut Microbiota of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascanelli, S.; Bombardini, C.; Chimisso, L.; Carcoforo, P.; Turroni, S.; D’Amico, F.; Caniati, M.L.; Baldi, E.; Tugnoli, V.; Morotti, C.; et al. Trans-anal irrigation in patients with multiple sclerosis: Efficacy in treating disease-related bowel dysfunctions and impact on the gut microbiota: A monocentric prospective study. Mult. Scler. J. Exp. Transl. Clin. 2022, 8, 20552173221109771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.K.; Ito, N.; Mindur, J.E.; Kumar, H.; Youssef, M.; Suresh, S.; Kulkarni, R.; Rosario, Y.; Balashov, K.E.; Dhib-Jalbut, S.; et al. Fecal Lcn-2 level is a sensitive biological indicator for gut dysbiosis and intestinal inflammation in multiple sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1015372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Yan, X.; Shao, L.; Liu, X.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, L.; Yu, K.; Zhao, L. Alterations of the Fecal Microbiota in Chinese Patients With Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 590783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallè, F.; Valeriani, F.; Cattaruzza, M.S.; Gianfranceschi, G.; Liguori, R.; Antinozzi, M.; Mederer, B.; Liguori, G.; Romano Spica, V. Mediterranean Diet, Physical Activity and Gut Microbiome Composition: A Cross-Sectional Study among Healthy Young Italian Adults. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kato, K.; Murakami, H.; Hosomi, K.; Tanisawa, K.; Nakagata, T.; Ohno, H.; Konishi, K.; Kawashima, H.; Chen, Y.A.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of gut microbiota of a healthy population and covariates affecting microbial variation in two large Japanese cohorts. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Tun, H.M.; Liu, Q.; Yeoh, Y.K.; Mak, J.W.Y.; Chan, F.K.; Ng, S.C. Gut microbiome signatures reflect different subtypes of irritable bowel syndrome. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2157697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healey, G.; Murphy, R.; Butts, C.; Brough, L.; Whelan, K.; Coad, J. Habitual dietary fibre intake influences gut microbiota response to an inulin-type fructan prebiotic: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over, human intervention study. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 119, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Cuesta-Zuluaga, J.; Corrales-Agudelo, V.; Carmona, J.A.; Abad, J.M.; Escobar, J.S. Body size phenotypes comprehensively assess cardiometabolic risk and refine the association between obesity and gut microbiota. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailén, M.; Bressa, C.; Martínez-López, S.; González-Soltero, R.; Montalvo Lominchar, M.G.; San Juan, C.; Larrosa, M. Microbiota Features Associated with a High-Fat/Low-Fiber Diet in Healthy Adults. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 583608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakan, D.B.; Maji, A.; Sharma, A.K.; Saxena, R.; Pulikkan, J.; Grace, T.; Gomez, A.; Scaria, J.; Amato, K.R.; Sharma, V.K. The unique composition of Indian gut microbiome, gene catalogue, and associated fecal metabolome deciphered using multi-omics approaches. GigaScience 2019, 8, giz004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, J.; Smith, K.R.; Crouch, A.L.; Sharma, V.; Yi, F.; Vargova, V.; LaMoia, T.E.; Dupont, L.M.; Serna, V.; Tang, F.; et al. High-dose saccharin supplementation does not induce gut microbiota changes or glucose intolerance in healthy humans and mice. Microbiome 2021, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; van Dijk, L.; Rijnaarts, I.; Hermes, G.D.A.; de Roos, N.M.; Witteman, B.J.M.; de Wit, N.J.W.; Govers, C.; Smidt, H.; Zoetendal, E.G. Methanogen Levels Are Significantly Associated with Fecal Microbiota Composition and Alpha Diversity in Healthy Adults and Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0165322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Chen, J.; Ren, X.; Yang, C.; Liu, S.; Bai, X.; Shan, S.; Dong, X. Gut Microbiota Composition Changes in Constipated Women of Reproductive Age. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 557515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancabelli, L.; Milani, C.; Lugli, G.A.; Turroni, F.; Mangifesta, M.; Viappiani, A.; Ticinesi, A.; Nouvenne, A.; Meschi, T.; van Sinderen, D.; et al. Unveiling the gut microbiota composition and functionality associated with constipation through metagenomic analyses. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Zhang, Z.; Seethaler, B.; Nazare, J.A.; Sánchez, C.R.; Roumain, M.; Muccioli, G.G.; Bindels, L.B.; Cani, P.D.; et al. Metabolite profiling reveals the interaction of chitin-glucan with the gut microbiota. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1810530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgo, F.; Garbossa, S.; Riva, A.; Severgnini, M.; Luigiano, C.; Benetti, A.; Pontiroli, A.E.; Morace, G.; Borghi, E. Body Mass Index and Sex Affect Diverse Microbial Niches within the Gut. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaike, A.H.; Paul, D.; Bhute, S.; Dhotre, D.P.; Pande, P.; Upadhyaya, S.; Reddy, Y.; Sampath, R.; Ghosh, D.; Chandraprabha, D.; et al. The Gut Microbial Diversity of Newly Diagnosed Diabetics but Not of Prediabetics Is Significantly Different from That of Healthy Nondiabetics. mSystems 2020, 5, e00578-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.Y. LightGBM: A Highly Efficient Gradient Boosting Decision Tree. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 3146–3154. [Google Scholar]
- Thirion, F.; Sellebjerg, F.; Fan, Y.; Lyu, L.; Hansen, T.H.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Quinquis, B.; Stankevic, E.; Søndergaard, H.B.; et al. The gut microbiota in multiple sclerosis varies with disease activity. Genome Med. 2023, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, T.; Kong, J.Y.; Stothard, P.; Willing, B.P. Defining the Role of Parasutterella, a Previously Uncharacterized Member of the Core Gut Microbiota. ISME J. 2019, 13, 1520–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troci, A.; Zimmermann, O.; Esser, D.; Krampitz, P.; May, S.; Franke, A.; Berg, D.; Leypoldt, F.; Stürner, K.H.; Bang, C. B-cell-depletion Reverses Dysbiosis of the Microbiome in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moles, L.; Delgado, S.; Gorostidi-Aicua, M.; Sepúlveda, L.; Alberro, A.; Iparraguirre, L.; Suárez, J.A.; Romarate, L.; Arruti, M.; Muñoz-Culla, M.; et al. Microbial dysbiosis and lack of SCFA production in a Spanish cohort of patients with multiple sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 960761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiodini, R.J.; Dowd, S.E.; Chamberlin, W.M.; Galandiuk, S.; Davis, B.; Glassing, A. Microbial Population Differentials between Mucosal and Submucosal Intestinal Tissues in Advanced Crohn’s Disease of the Ileum. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, S.; Kim, S.; Suda, W.; Oshima, K.; Nakamura, M.; Matsuoka, T.; Chihara, N.; Tomita, A.; Sato, W.; Kim, S.W.; et al. Dysbiosis in the Gut Microbiota of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis, with a Striking Depletion of Species Belonging to Clostridia XIVa and IV Clusters. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, Z.; Liu, Z.; Yang, W.; Huai, Y. Changes in Gut Microbiota in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis Based on 16s rRNA Gene Sequencing Technology: A Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2024, 23, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Lee, G.; Son, H.; Koh, H.; Kim, E.S.; Unno, T.; Shin, J.H. Butyrate producers, “The Sentinel of Gut”: Their intestinal significance with and beyond butyrate, and prospective use as microbial therapeutics. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1103836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kibbie, J.J.; Dillon, S.M.; Thompson, T.A.; Purba, C.M.; McCarter, M.D.; Wilson, C.C. Butyrate directly decreases human gut lamina propria CD4 T cell function through histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibition and GPR43 signaling. Immunobiology 2021, 226, 152126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacca, M.; Celano, G.; Calabrese, F.M.; Portincasa, P.; Gobbetti, M.; De Angelis, M. The Controversial Role of Human Gut Lachnospiraceae. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letchumanan, G.; Abdullah, N.; Marlini, M.; Baharom, N.; Lawley, B.; Omar, M.R.; Mohideen, F.B.S.; Addnan, F.H.; Fariha, M.M.N.; Ismail, Z.; et al. Gut Microbiota Composition in Prediabetes and Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review of Observational Studies. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 943427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, P. Gut microbiota and its metabolites in depression: From pathogenesis to treatment. EBioMedicine 2023, 90, 104527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, J.; Ni, Q.; Sun, W.; Li, L.; Feng, X. The links between gut microbiota and obesity and obesity related diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 147, 112678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, P.P.; Chin, V.K.; Looi, C.Y.; Wong, W.F.; Madhavan, P.; Yong, V.C. The Microbiome and Irritable Bowel Syndrome—A Review on the Pathophysiology, Current Research and Future Therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, R.; Wang, J.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, J.; Ma, X.; Gou, X.; He, X.; Cheng, C.; Wang, W.; Zheng, J.; et al. Relationship between Gut Microbiota and Lymphocyte Subsets in Chinese Han Patients with Spinal Cord Injury. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 986480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.J.; Yang, J.; Seo, H.; Lee, W.H.; Lee, D.H.; Kym, S.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, J.G.; Jang, I.J.; Kim, Y.K.; et al. Colorectal Cancer Diagnostic Model Utilizing Metagenomic and Metabolomic Data of Stool Microbial Extracellular Vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, G.; Tap, J.; Voigt, A.Y.; Sunagawa, S.; Kultima, J.R.; Costea, P.I.; Amiot, A.; Böhm, J.; Brunetti, F.; Habermann, N.; et al. Potential of fecal microbiota for early-stage detection of colorectal cancer. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2014, 10, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Yang, J.; Wong, K.C. Human disease prediction from microbiome data by multiple feature fusion and deep learning. iScience 2022, 25, 104081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, M.; Zhang, L. DeepMicro: Deep representation learning for disease prediction based on microbiome data. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantoni, C.; Lin, Q.; Dorsett, Y.; Ghezzi, L.; Liu, Z.; Pan, Y.; Chen, K.; Han, Y.; Li, Z.; Xiao, H.; et al. Alterations of host-gut microbiome interactions in multiple sclerosis. EBioMedicine 2022, 76, 103798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremlett, H.; Zhu, F.; Arnold, D.; Bar-Or, A.; Bernstein, C.N.; Bonner, C.; Forbes, J.D.; Graham, M.; Hart, J.; Knox, N.C.; et al. The gut microbiota in pediatric multiple sclerosis and demyelinating syndromes. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2021, 8, 2252–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, T.L.; Wang, Q.; Mirza, A.; Dwyer, D.; Wu, Q.; Dowling, C.A.; Martens, J.W.S.; Yang, J.; Krementsov, D.N.; Mao-Draayer, Y. Identification of commensal gut microbiota signatures as predictors of clinical severity and disease progression in multiple sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-López, V.; Méndez-Miralles, M.Á.; Vela-Yebra, R.; Fríes-Ramos, A.; Sánchez-Pellicer, P.; Ruzafa-Costas, B.; Núñez-Delegido, E.; Gómez-Gómez, H.; Chumillas-Lidón, S.; Picó-Monllor, J.A.; et al. Gut Microbiota as a Potential Predictive Biomarker in Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. Genes 2022, 13, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, R.E.; Iizumi, T.; Battaglia, T.; Liu, M.; Perez-Perez, G.I.; Herbert, J.; Blaser, M.J. Gut microbiome of treatment-naïve MS patients of different ethnicities early in disease course. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussamet, L.; Montassier, E.; Mathé, C.; Garcia, A.; Morille, J.; Shah, S.; Dugast, E.; Wiertlewski, S.; Gourdel, M.; Bang, C.; et al. Investigating the metabolite signature of an altered oral microbiota as a discriminant factor for multiple sclerosis: A pilot study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellizoni, F.P.; Leite, A.Z.; Rodrigues, N.C.; Ubaiz, M.J.; Gonzaga, M.I.; Takaoka, N.N.C.; Mariano, V.S.; Omori, W.P.; Pinheiro, D.G.; Matheucci Junior, E.; et al. Detection of Dysbiosis and Increased Intestinal Permeability in Brazilian Patients with Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynders, T.; Devolder, L.; Valles-Colomer, M.; Van Remoortel, A.; Joossens, M.; De Keyser, J.; Nagels, G.; D’Hooghe, M.; Raes, J. Gut microbiome variation is associated to Multiple Sclerosis phenotypic subtypes. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2020, 7, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | MS (n = 29) | Healthy (n = 27) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) * | 33.9 ± 11.1 (19–60 years) | 31.0 ± 10.8 (19–60 years) | 0.34 a |
| Sex (M/F) | (13/16) | (11/16) | 1 b |
| BMI, kg/m2 * | 24.8 ± 5.9 (18.6–46.9) | 21.9 ± 2.5 (18.5–27.7) | 0.051 a |
| Gastritis, n (%) | 10 (34.5) | 0 (0) | 0.001 c |
| Constipation, n (%) | 5 (17.2) | 0 (0) | 0.052 c |
| Overweight (BMI 25–29.9 kg/m2), n (%) | 6 (20.7) | 1 (3.7) | 0.1 c |
| Obesity (BMI > 30 kg/m2), n (%) | 4 (13.8) | 0 (0) | 0.11 c |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 3 (10.3) | 0 (0) | 0.24 c |
| Dataset ID | Country | N (Controls) | N (Cases) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current study | Russia | 27 | 29 | - |
| Cox L. M. et al., 2021 | USA | 15 | 327 | [38] |
| Takewaki D. et al., 2022 | Japan | - | 98 | [39] |
| Elsayed N. S. et al., 2023 | USA | - | 83 | [40] |
| Kozhieva M. et al., 2021 | Russia | - | 63 | [41] |
| Jangi S. et al., 2016 | USA | - | 60 | [42] |
| Cekanaviciute E. et al., 2017 | USA | - | 57 | [43] |
| Forbes J. D. et al., 2018 | Canada | - | 40 | [44] |
| Saresella M. et al., 2020 | Italy | - | 35 | [45] |
| Zeng Q. et al., 2019 | China | - | 30 | [46] |
| Chen J. et al., 2016 | USA | - | 30 | [47] |
| Kozhieva M. et al., 2019 | Russia | - | 15 | [48] |
| Barone M. et al., 2021 | Italy | - | 15 | [49] |
| Ascanelli S. et al., 2022 | Italy | - | 12 | [50] |
| Yadav S. K. et al., 2022 | USA | 13 | 13 | [51] |
| Ling Z. et al., 2020 | China | 18 | 21 | [52] |
| Gallè F. et al., 2020 | Italy | 107 | - | [53] |
| Park J. et al., 2021 | Japan | 92 | - | [54] |
| Su Q. et al., 2023 | China | 90 | - | [55] |
| Healey G. et al., 2018 | New Zealand | 75 | - | [56] |
| De La Cuesta-Zuluaga J. et al., 2018 | Colombia | 63 | - | [57] |
| Bailén M. et al., 2020 | Spain | 52 | - | [58] |
| Dhakan D. B. et al., 2019 | India | 49 | - | [59] |
| Serrano J. et al., 2021 | USA | 44 | - | [60] |
| Wang T. et al., 2022 | Netherlands | 33 | - | [61] |
| Li H. et al., 2021 | China | 30 | - | [62] |
| Mancabelli L. et al., 2017 | Italy | 23 | - | [63] |
| Rodriguez J. et al., 2020 | Belgium | 20 | - | [64] |
| Borgo F. et al., 2018 | Italy | 10 | - | [65] |
| Gaike A. H. et al., 2020 | India | 16 | - | [66] |
| Metric | ML Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | XGB | SVM | LightGBM | |
| Precision | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.83 | 0.90 |
| Recall | 0.82 | 0.87 | 0.48 | 0.84 |
| F1-score | 0.85 | 0.88 | 0.60 | 0.87 |
| Accuracy | 0.86 | 0.89 | 0.70 | 0.88 |
| Cross-validation accuracy | 0.84 | 0.85 | 0.69 | 0.87 |
| Precision | Recall | F1-Score | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy controls | 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.88 |
| MS patients | 0.89 | 0.92 | 0.91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neklesova, M.V.; Sogomonyan, K.S.; Golovkin, I.A.; Shirokiy, N.I.; Vershinina, S.O.; Tsvetikova, S.A.; Korzhova, J.E.; Zakharova, M.N.; Gnedovskaya, E.V. Gut Microbiome Signatures in Multiple Sclerosis: A Case-Control Study with Machine Learning and Global Data Integration. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081806
Neklesova MV, Sogomonyan KS, Golovkin IA, Shirokiy NI, Vershinina SO, Tsvetikova SA, Korzhova JE, Zakharova MN, Gnedovskaya EV. Gut Microbiome Signatures in Multiple Sclerosis: A Case-Control Study with Machine Learning and Global Data Integration. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(8):1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081806
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeklesova, Margarita V., Karine S. Sogomonyan, Ivan A. Golovkin, Nikolay I. Shirokiy, Sofia O. Vershinina, Sofia A. Tsvetikova, Julia E. Korzhova, Mariya N. Zakharova, and Elena V. Gnedovskaya. 2025. "Gut Microbiome Signatures in Multiple Sclerosis: A Case-Control Study with Machine Learning and Global Data Integration" Biomedicines 13, no. 8: 1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081806
APA StyleNeklesova, M. V., Sogomonyan, K. S., Golovkin, I. A., Shirokiy, N. I., Vershinina, S. O., Tsvetikova, S. A., Korzhova, J. E., Zakharova, M. N., & Gnedovskaya, E. V. (2025). Gut Microbiome Signatures in Multiple Sclerosis: A Case-Control Study with Machine Learning and Global Data Integration. Biomedicines, 13(8), 1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081806







