Functional Disruption of IQGAP1 by Truncated PALB2 in Two Cases of Breast Cancer: Implications for Proliferation and Invasion
Abstract
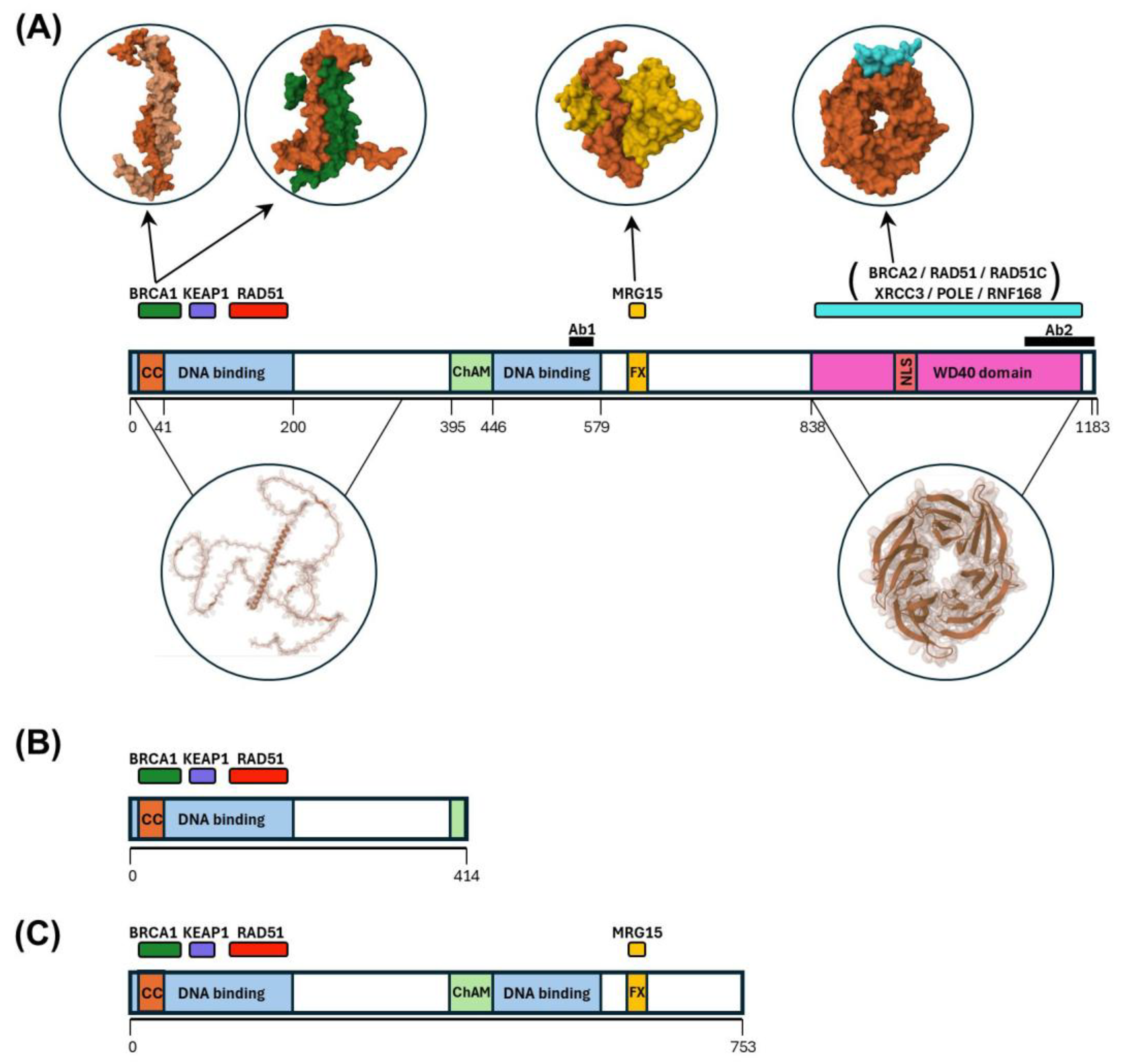
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Considerations
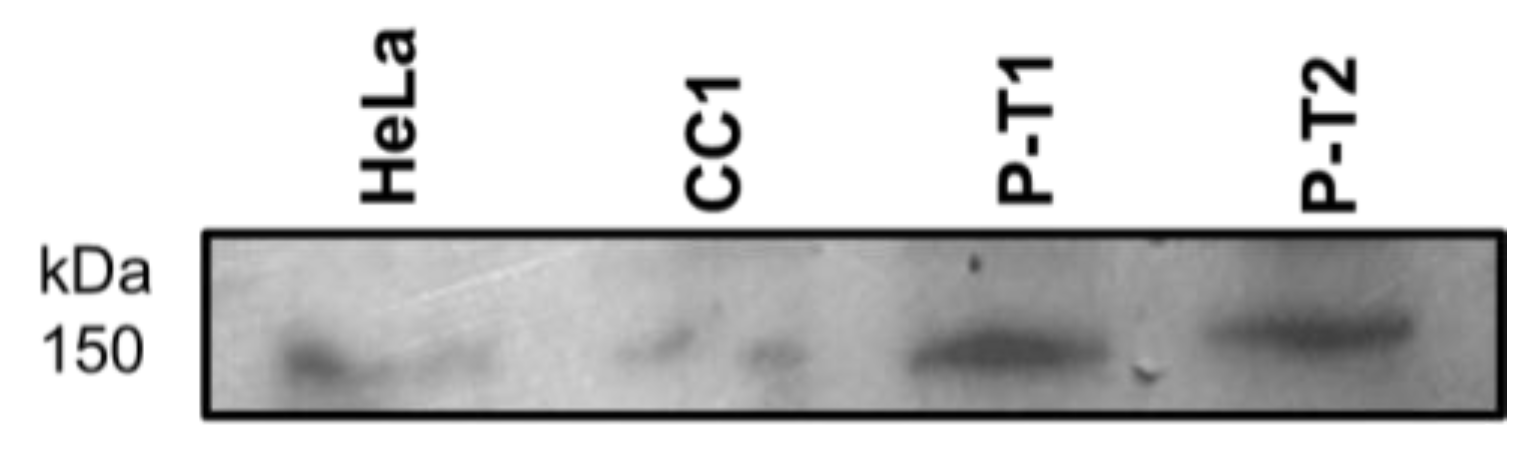
2.2. Patients with Truncated PALB2 Breast Carcinomas and Breast Cancer Controls
2.3. White Cell Purification and Protein Detection
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative Image Analysis
2.6. Quantitative Image Analysis
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. PALB2 Western Blot from Circulating White Cells
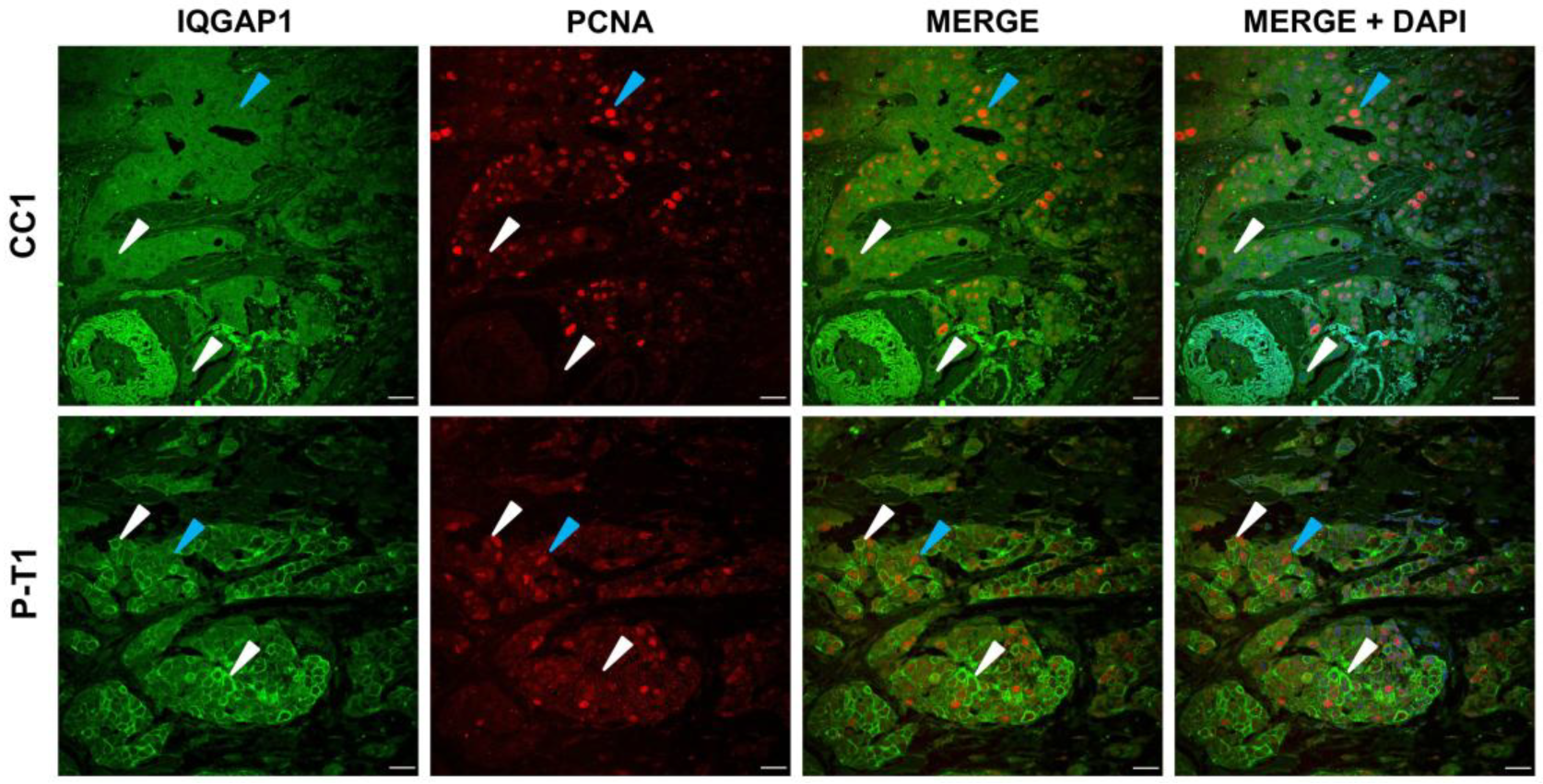
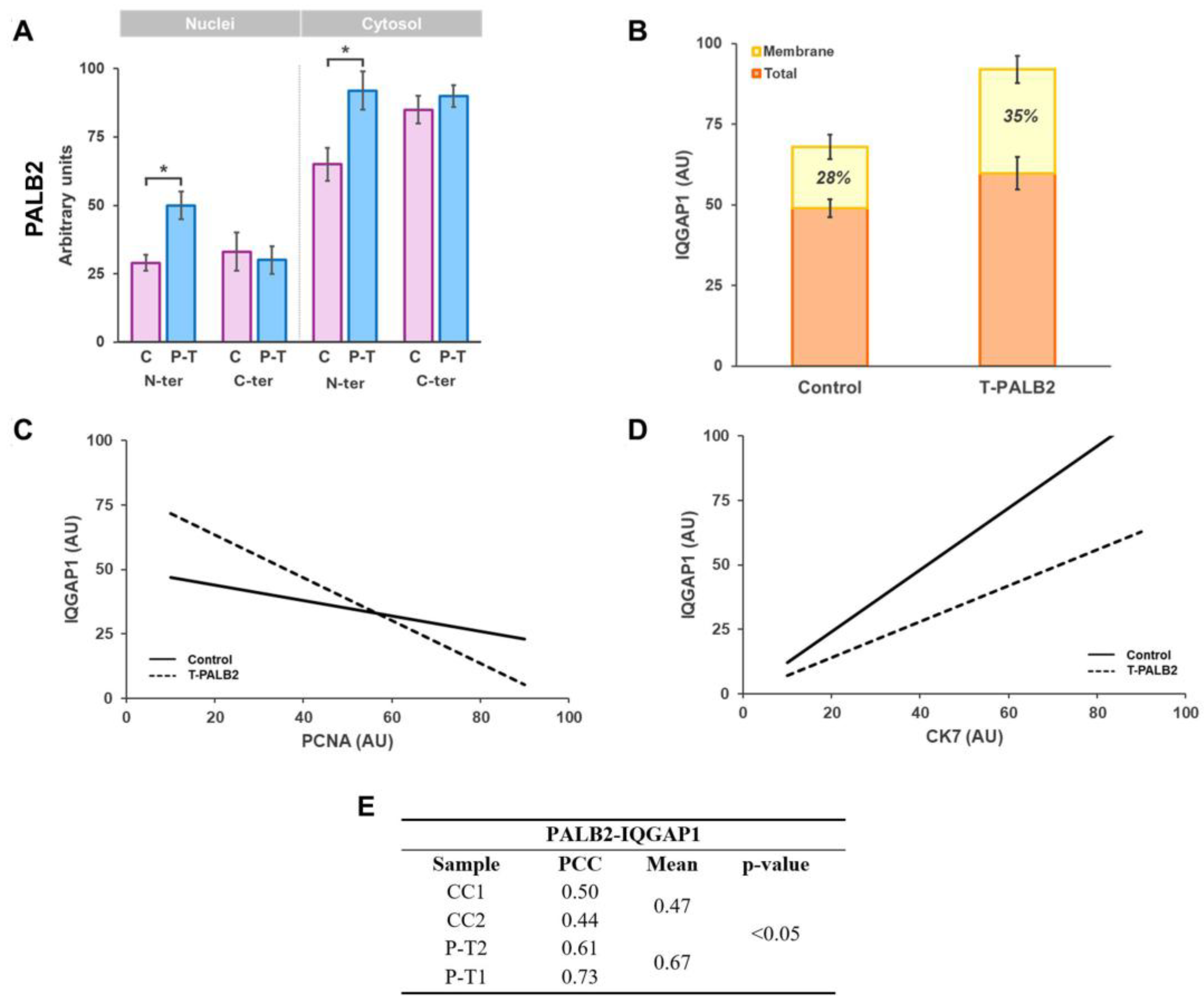
3.2. PALB2 and IQGAP1 Co-Expression in Breast IDC
3.3. IQGAP1 Expression and Cellular Proliferation in Tumor Breast with Truncated PALB2 Scaffold Protein
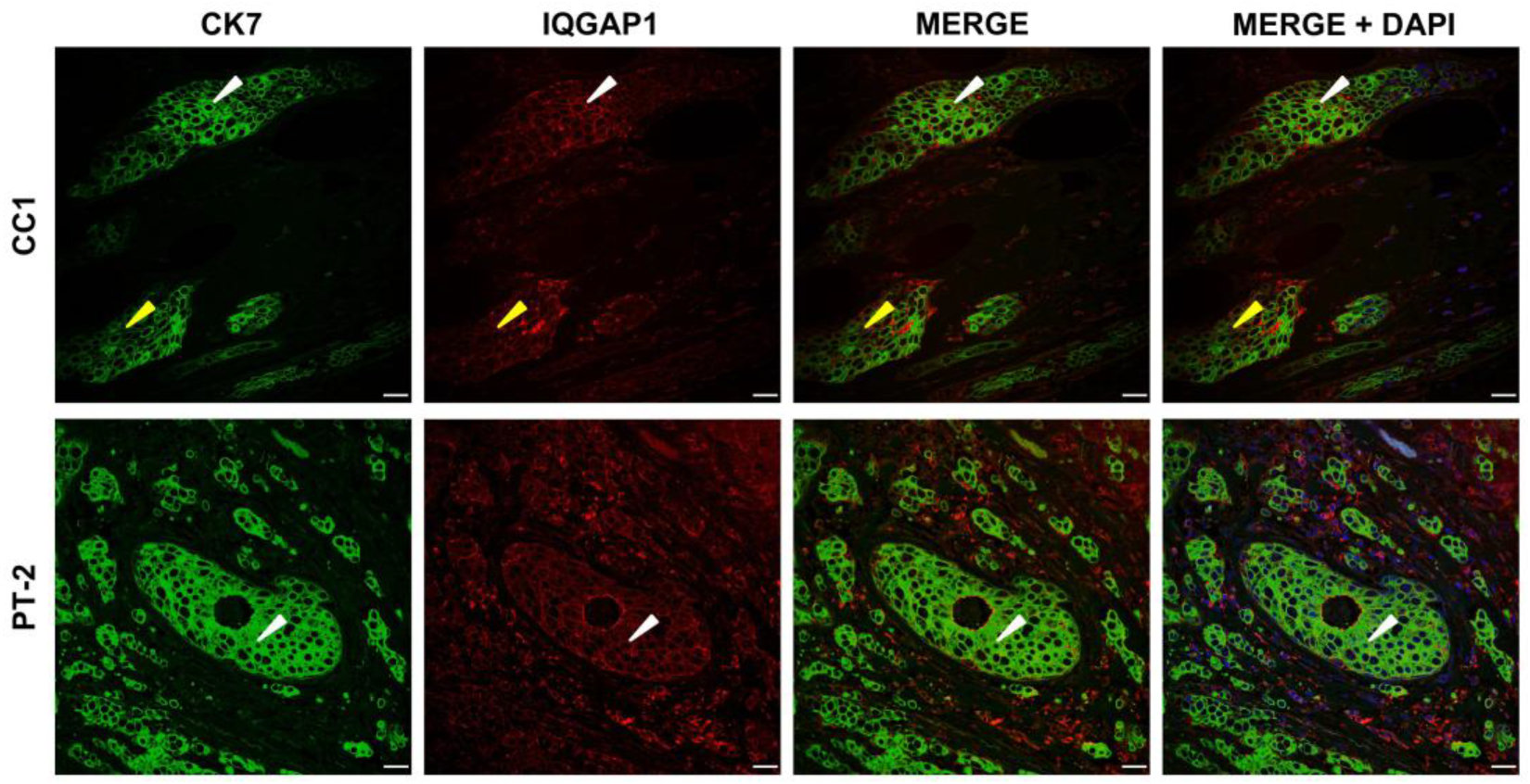
3.4. IQGAP1 Involvement in Cellular Migration and Invasion in IDC with Truncated PALB2
4. Discussion
4.1. Expression of PALB2 in Blood White Cells
4.2. Expression and Co-Localization of IQGAP1 and PALB2 Protein Variants in Breast Cancer Control and in PALB2-Truncated Breast Cancer as Revealed by Antibodies Directed at the N-Terminus or the C-Terminus
4.3. IQGAP1 Expression Varies During the Cell Cycle
4.4. Truncated PALB2 Elicits Changes in the Involvement of IQGAP1 in Invasion and Migration in Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
4.5. Discussion of the Study as a Whole
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IDC | invasive ductal carcinoma |
| PALB2 | partner and localizer of BRCA2 |
| HR | homologous recombination |
| IQGAP1 | IQ motif containing GTPase activating protein 1 |
| P-T | PALB2-truncated variant |
| CC | breast cancer control |
| TBS | Tris-buffered saline |
| LIF | Leica Image Format |
| PCC | Pearson correlation coefficient |
References
- Prakash, R.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, W.; Jasin, M. Homologous Recombination and Human Health: The Roles of BRCA1, BRCA2, and Associated Proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a016600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveryshetty, J.; Peterlini, T.; Ryzhikov, M.; Brahiti, N.; Dellaire, G.; Masson, J.-Y.; Korolev, S. Novel RNA and DNA Strand Exchange Activity of the PALB2 DNA Binding Domain and Its Critical Role for DNA Repair in Cells. eLife 2019, 8, e44063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriukha, Y.; Watkins, M.B.; Redington, J.M.; Chintalapati, N.; Ganti, A.; Dastvan, R.; Uversky, V.N.; Hopkins, J.B.; Pozzi, N.; Korolev, S. The Strand Exchange Domain of Tumor Suppressor PALB2 Is Intrinsically Disordered and Promotes Oligomerization-Dependent DNA Compaction. iScience 2024, 27, 111259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotoli, D.; Díaz-Flores, L.; Gutiérrez, R.; Morales, M.; Ávila, J.; Martín-Vasallo, P. AmotL2, IQGAP1, and FKBP51 Scaffold Proteins in Glioblastoma Stem Cell Niches. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2022, 70, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PDQ Cancer Genetics Editorial Board. BRCA1 and BRCA2: Cancer Risks and Management (PDQ®): Health Professional Version; National Cancer Institute (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sy, S.M.-H.; Huen, M.S.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, J. PALB2 Regulates Recombinational Repair through Chromatin Association and Oligomerization. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 18302–18310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buisson, R.; Masson, J.-Y. PALB2 Self-Interaction Controls Homologous Recombination. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 10312–10323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, A.W.; Swift, S.; Lord, C.J.; Ashworth, A.; Pearl, L.H. Structural Basis for Recruitment of BRCA2 by PALB2. EMBO Rep. 2009, 10, 990–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Feng, W.; Sy, S.M.H.; Huen, M.S.Y. ATM-Dependent Phosphorylation of the Fanconi Anemia Protein PALB2 Promotes the DNA Damage Response. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 27545–27556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlskog, J.K.; Larsen, B.D.; Achanta, K.; Sørensen, C.S. ATM/ATR-mediated Phosphorylation of PALB2 Promotes RAD51 Function. EMBO Rep. 2016, 17, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducy, M.; Sesma-Sanz, L.; Guitton-Sert, L.; Lashgari, A.; Gao, Y.; Brahiti, N.; Rodrigue, A.; Margaillan, G.; Caron, M.C.; Côté, J.; et al. The Tumor Suppressor PALB2: Inside Out. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2019, 44, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luijsterburg, M.S.; Typas, D.; Caron, M.-C.; Wiegant, W.W.; van den Heuvel, D.; Boonen, R.A.; Couturier, A.M.; Mullenders, L.H.; Masson, J.-Y.; van Attikum, H. A PALB2-Interacting Domain in RNF168 Couples Homologous Recombination to DNA Break-Induced Chromatin Ubiquitylation. eLife 2017, 6, e20922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadeski, L.; Mataraza, J.M.; Jeong, H.-W.; Li, Z.; Sacks, D.B. IQGAP1 Stimulates Proliferation and Enhances Tumorigenesis of Human Breast Epithelial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 1008–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotoli, D.; Pérez-Rodríguez, N.; Morales, M.; Maeso, M.; Ávila, J.; Mobasheri, A.; Martín-Vasallo, P. IQGAP1 in Podosomes/Invadosomes Is Involved in the Progression of Glioblastoma Multiforme Depending on the Tumor Status. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, A.M.; Schuldt, K.M.; Rajasekaran, K.; Hwang, D.; Riese, M.J.; Rao, S.; Thakar, M.S.; Malarkannan, S. IQGAP1: Insights into the Function of a Molecular Puppeteer. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 65, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, W.; Fan, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H. Ras GTPase-Activating-Like Protein IQGAP1 (IQGAP1) Promotes Breast Cancer Proliferation and Invasion and Correlates with Poor Clinical Outcomes. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 3315–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wang, T.; Gao, H.; Yue, X.; Bian, W.; Mei, J.; Zhang, Y. The Interplay between IQGAP1 and Small GTPases in Cancer Metastasis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 135, 111243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, J.D.; Tian, C.; Lamar, J.M.; Rickelt, S.; Abbruzzese, G.; Liu, X.; Hynes, R.O. The Scaffold Protein IQGAP1 Is Crucial for Extravasation and Metastasis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starita, L.M.; Machida, Y.; Sankaran, S.; Elias, J.E.; Griffin, K.; Schlegel, B.P.; Gygi, S.P.; Parvin, J.D. BRCA1-Dependent Ubiquitination of γ-Tubulin Regulates Centrosome Number. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 24, 8457–8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, B.P.; Starita, L.M.; Parvin, J.D. Overexpression of a Protein Fragment of RNA Helicase A Causes Inhibition of Endogenous BRCA1 Function and Defects in Ploidy and Cytokinesis in Mammary Epithelial Cells. Oncogene 2003, 22, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, M.J.; Murata, K.; Hwang, D.-S.; Parvin, J.D. Inhibition of BRCA1 in Breast Cell Lines Causes the Centrosome Duplication Cycle to Be Disconnected from the Cell Cycle. Oncogene 2006, 25, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.A.; Antonisamy, W.J.; Yakirevich, E. IQGAP1 Control of Centrosome Function Defines Distinct Variants of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 2493–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, J.H.; Dunn, K.W. Statistical Tests for Measures of Colocalization in Biological Microscopy. J. Microsc. 2013, 252, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stauffer, W.; Sheng, H.; Lim, H.N. EzColocalization: An ImageJ Plugin for Visualizing and Measuring Colocalization in Cells and Organisms. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, J.; Parmryd, I. Quantifying Colocalization by Correlation: The Pearson Correlation Coefficient Is Superior to the Mander’s Overlap Coefficient. Cytometry Part A 2010, 77A, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armitage, P.; Berry, G.; Matthews, J.N.S. Statistical Methods in Medical Research, 4th ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Tot, T. Cytokeratins 20 and 7 as Biomarkers. Eur. J. Cancer 2002, 38, 758–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liang, S.; Fang, L.; Chen, L.; Tang, M.; Xu, Y.; Fu, A.; Yang, J.; Wei, Y. Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of HepG2 Cells Treated with Quercetin Suggests IQGAP1 Involved in Quercetin-Induced Regulation of Cell Proliferation and Migration. OMICS 2009, 13, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Hirasawa, A. Homologous Recombination Deficiencies and Hereditary Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Kojima, Y.; Takeuchi, S. Causative Genes of Homologous Recombination Deficiency (HRD)-Related Breast Cancer and Specific Strategies at Present. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoes-da-Silva, M.M.; Barisic, M. How Does the Tubulin Code Facilitate Directed Cell Migration? Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2025, 53, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyukgolcigezli, I.; Tenekeci, A.K.; Sahin, I.H. Opportunities and Challenges in Antibody–Drug Conjugates for Cancer Therapy: A New Era for Cancer Treatment. Cancers 2025, 17, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, V.J.; Osman, M.A. The Antipsychotic Drug Haldol Modulates IQGAP1-Signaling and Inhibits Cell Proliferation in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cell Lines. MicroPubl. Biol. 2023, 2023, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Primary Antibodies | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target | Host/Class | Dilution | Source | Cat.# | ||
| PALB2 (N-ter) | Rabbit polyclonal | 1:100 | Invitrogen 1 | PA5-48258 | ||
| PALB2 (C-ter) | Rabbit polyclonal | 1:200 | Bioss 2 | BS-0588R | ||
| IQGAP1 | Rabbit polyclonal | 1:500 | Millipore 3 | ABT186 | ||
| IQGAP1 | Mouse monoclonal | 1:100 | SC Biotechnology 4 | sc-376021 | ||
| PCNA | Mouse monoclonal | 1:100 | Novus 5 | NB500-106 | ||
| Β-tubulin | Mouse monoclonal | 1:100 | SC Biotechnology 4 | sc-101527 | ||
| CK7 | Rabbit monoclonal | RTU | Biocare Medical 6 | VLTR339G20 | ||
| Secondary Antibodies | ||||||
| Target | Conjugation | Host/Class | Dilution | Source | Cat.# | |
| Rabbit IgG | FITC | Goat polyclonal | 1:200 | Sigma-Aldrich 7 | F9887 | |
| Mouse IgG | DyLight® 650 | Goat polyclonal | 1:100 | Abcam 8 | ab97018 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Rodríguez, N.-D.; Martín-Ramírez, R.; González-Fernández, R.; Maeso, M.d.C.; Ávila, J.; Martín-Vasallo, P. Functional Disruption of IQGAP1 by Truncated PALB2 in Two Cases of Breast Cancer: Implications for Proliferation and Invasion. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1804. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081804
Pérez-Rodríguez N-D, Martín-Ramírez R, González-Fernández R, Maeso MdC, Ávila J, Martín-Vasallo P. Functional Disruption of IQGAP1 by Truncated PALB2 in Two Cases of Breast Cancer: Implications for Proliferation and Invasion. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(8):1804. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081804
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Rodríguez, Natalia-Dolores, Rita Martín-Ramírez, Rebeca González-Fernández, María del Carmen Maeso, Julio Ávila, and Pablo Martín-Vasallo. 2025. "Functional Disruption of IQGAP1 by Truncated PALB2 in Two Cases of Breast Cancer: Implications for Proliferation and Invasion" Biomedicines 13, no. 8: 1804. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081804
APA StylePérez-Rodríguez, N.-D., Martín-Ramírez, R., González-Fernández, R., Maeso, M. d. C., Ávila, J., & Martín-Vasallo, P. (2025). Functional Disruption of IQGAP1 by Truncated PALB2 in Two Cases of Breast Cancer: Implications for Proliferation and Invasion. Biomedicines, 13(8), 1804. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081804







