Allosteric Inhibition of P-Glycoprotein-Mediated Efflux by DMH1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. P-gp Activity and Inhibition
2.2.1. DMH1 Cytotoxicity in Cell Lines with High and Low P-gp Expression
2.2.2. Assessment of DMH1 Inhibition of P-gp Activity Using Calcein AM Retention Assay
2.3. Kinetic Evaluation of DMH1 Effects on P-gp-Mediated Efflux
2.3.1. Inhibition of P-gp by DMH1 Enhancing Daunorubicin Accumulation
2.3.2. Kinetic Analysis of P-gp Inhibition by DMH1
2.4. Mechanistic Study of DMH1 Inhibition on P-Glycoprotein
2.4.1. P-gp ATPase Activity Assay
2.4.2. Molecular Modeling-ABCB1
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
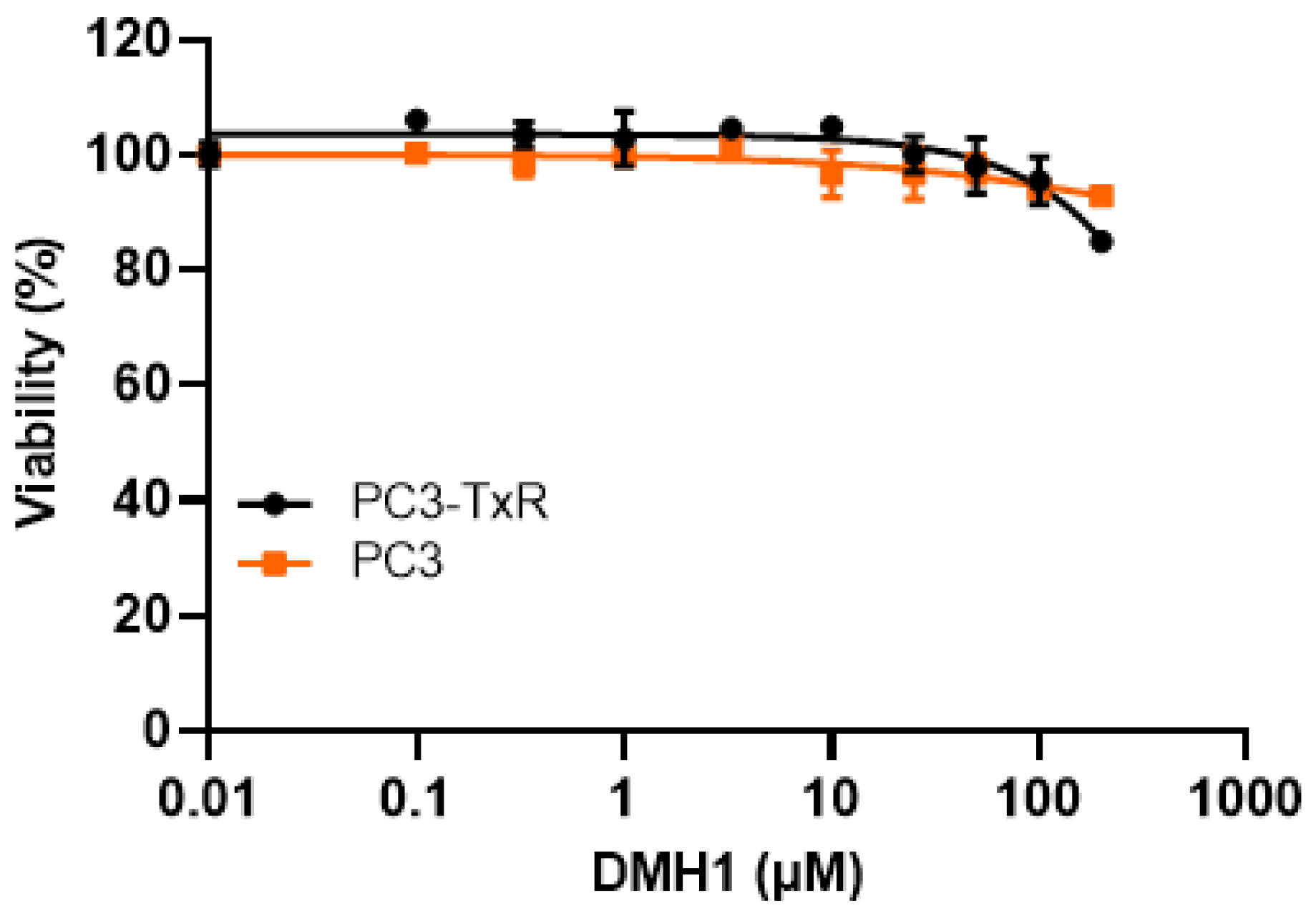
3.1. DMH1 Exhibits No Cytotoxicity in P-gp-Overexpressing or -Deficient Cells
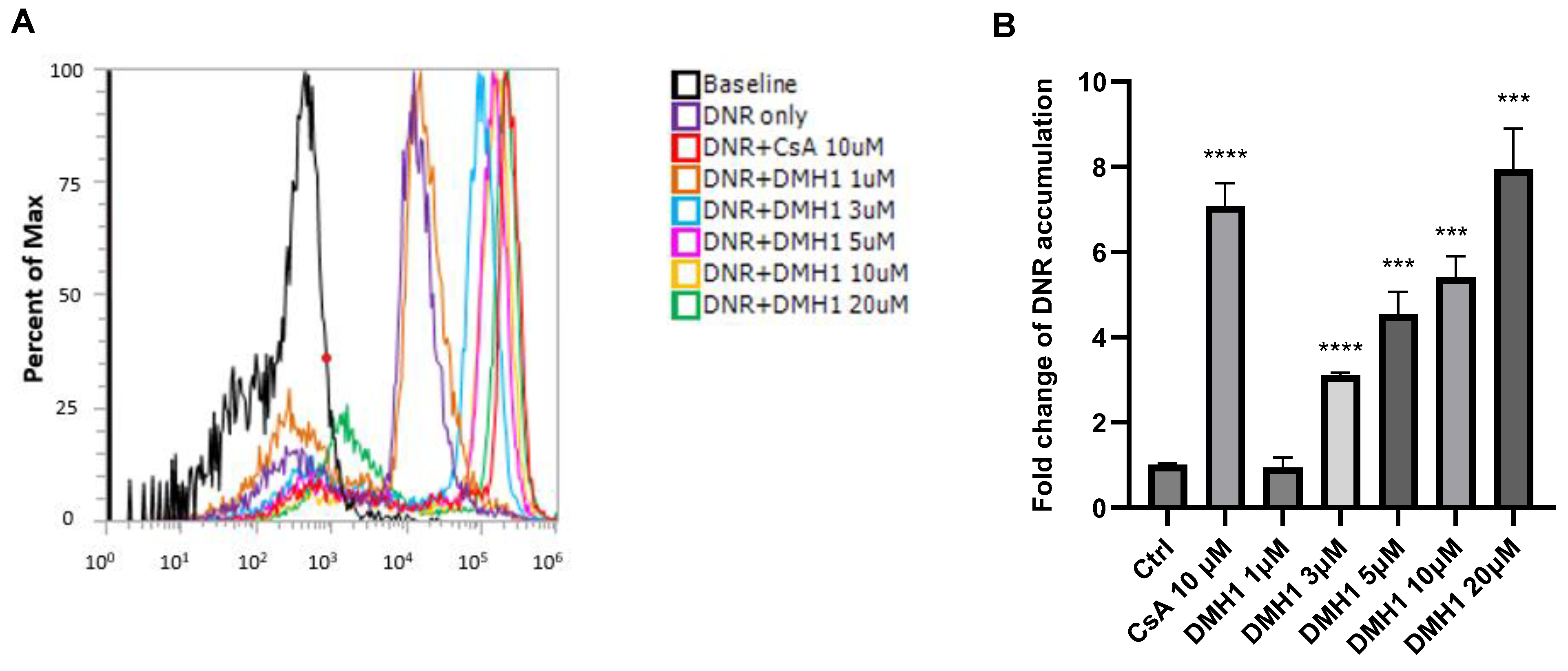
3.2. DMH1 Effectively Inhibits P-gp Efflux Function in Calcein AM Assays
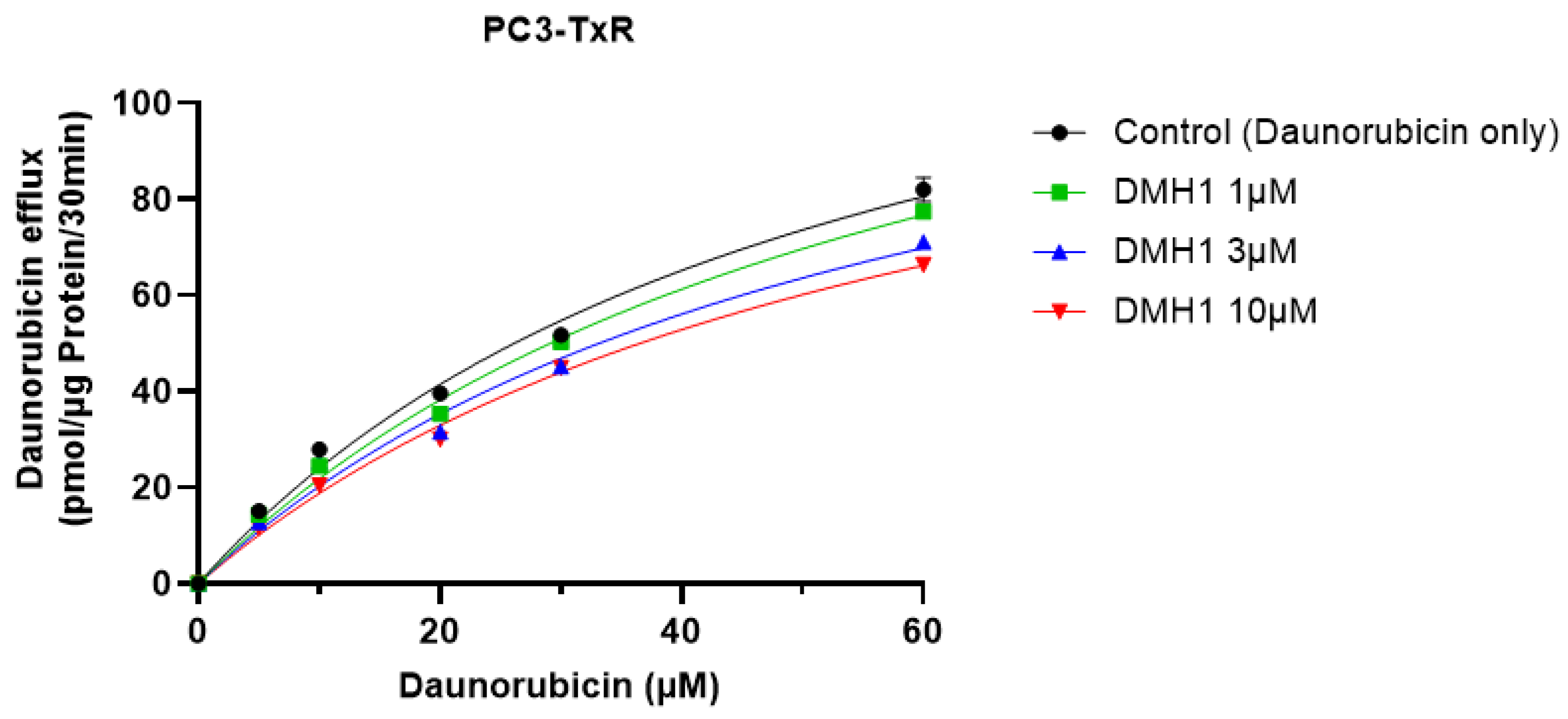
3.3. DMH1 Inhibits P-gp-Mediated Drug Efflux to Enhance Intracellular Accumulation of Daunorubicin
3.4. DMH1 Is a Noncompetitive Inhibitor of P-gp
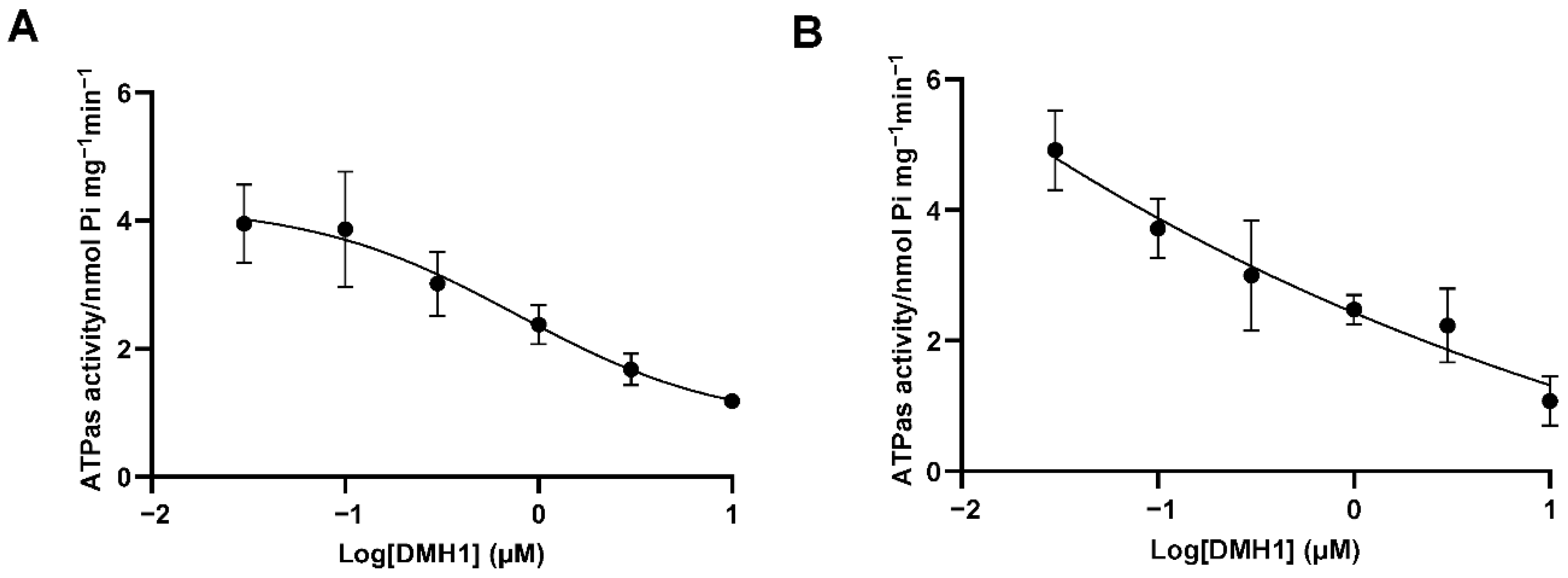
3.5. DMH1 Inhibits P-gp ATPase Activity Likely via Allosteric Interaction or Conformational Modulation
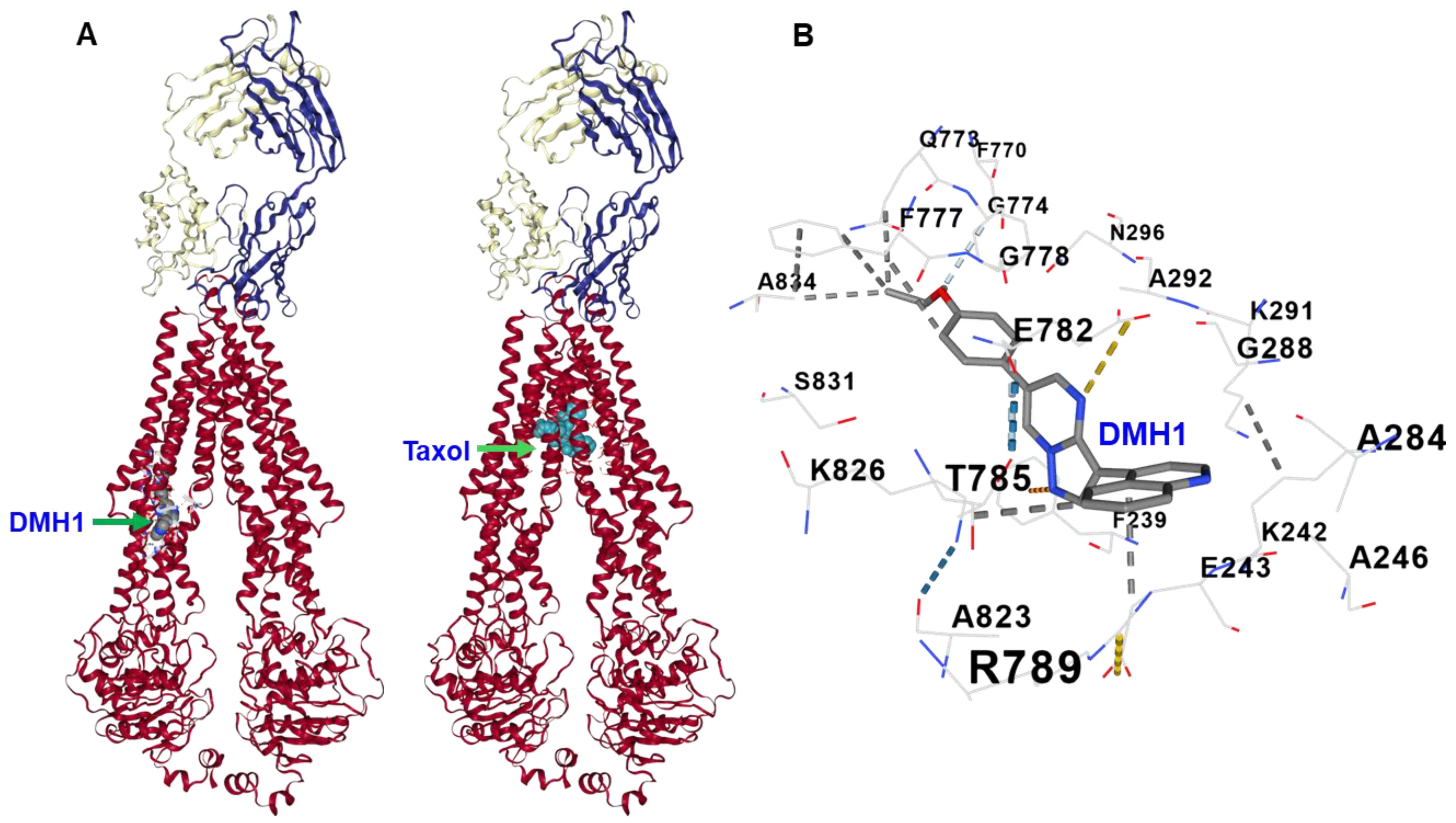
3.6. Molecular Docking Reveals That DMH1 Binds to an Allosteric Site of P-gp
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Silva, R.; Vilas-Boas, V.; Carmo, H.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; Carvalho, F.; de Lourdes Bastos, M.; Remião, F. Modulation of P-glycoprotein efflux pump: Induction and activation as a therapeutic strategy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 149, 1–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, A.; Kowal, J.; Broude, E.; Roninson, I.; Locher, K.P. Structural insight into substrate and inhibitor discrimination by human P-glycoprotein. Science 2019, 363, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binkhathlan, Z.; Lavasanifar, A. P-glycoprotein inhibition as a therapeutic approach for overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer: Current status and future perspectives. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2013, 13, 326–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilotto Heming, C.; Muriithi, W.; Wanjiku Macharia, L.; Niemeyer Filho, P.; Moura-Neto, V.; Aran, V. P-glycoprotein and cancer: What do we currently know? Heliyon 2022, 8, e11171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawara, I.; Kataoka, I.; Morishita, Y.; Hamada, H.; Tsuruo, T.; Itoyama, S.; Mori, S. Tissue distribution of P-glycoprotein encoded by a multidrug-resistant gene as revealed by a monoclonal antibody, MRK 16. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 1926–1929. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cordon-Cardo, C.; O’Brien, J.P.; Casals, D.; Rittman-Grauer, L.; Biedler, J.L.; Melamed, M.R.; Bertino, J.R. Multidrug-resistance gene (P-glycoprotein) is expressed by endothelial cells at blood-brain barrier sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimecki, W.T.; Futscher, B.W.; Grogan, T.M.; Dalton, W.S. P-glycoprotein expression and function in circulating blood cells from normal volunteers. Blood 1994, 83, 2451–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, K.; Tiriveedhi, V. Perplexing Role of P-Glycoprotein in Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Liu, K. P-gp Inhibition-Based Strategies for Modulating Pharmacokinetics of Anticancer Drugs: An Update. Curr. Drug Metab. 2016, 17, 806–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Zhou, P.; Asenso, J.; Yang, X.D.; Wang, C.; Wei, W. Advances in plant-based inhibitors of P-glycoprotein. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 867–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinić, J.; Podolski-Renić, A.; Jeremić, M.; Pešić, M. Potential of Natural-Based Anticancer Compounds for P-Glycoprotein Inhibition. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 4334–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmeira, A.; Sousa, E.; Vasconcelos, M.H.; Pinto, M.M. Three decades of P-gp inhibitors: Skimming through several generations and scaffolds. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 1946–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szakács, G.; Váradi, A.; Ozvegy-Laczka, C.; Sarkadi, B. The role of ABC transporters in drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and toxicity (ADME-Tox). Drug Discov. Today 2008, 13, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Shi, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, P.; Deng, M.; Huang, C.; Hu, T.; Jiang, L.; Li, J. Mammalian drug efflux transporters of the ATP binding cassette (ABC) family in multidrug resistance: A review of the past decade. Cancer Lett. 2016, 370, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, W.D.; Cheng, G.; Yehuda, A.G.; Ashby, C.R., Jr.; Chen, Z.S.; Cheng, X.D.; Qin, J.J. Medicinal chemistry strategies to discover P-glycoprotein inhibitors: An update. Drug Resist. Updates 2020, 49, 100681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Lee, R.; Chang, A.; Fan, J.; Labib, C.; Parsa, C.; Orlando, R.; Andresen, B.; Huang, Y. DMH1, a small molecule inhibitor of BMP type i receptors, suppresses growth and invasion of lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hover, L.D.; Young, C.D.; Bhola, N.E.; Wilson, A.J.; Khabele, D.; Hong, C.C.; Moses, H.L.; Owens, P. Small molecule inhibitor of the bone morphogenetic protein pathway DMH1 reduces ovarian cancer cell growth. Cancer Lett. 2015, 368, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, J.; Mondal, A.; Foty, R.; Jia, D.; Langenfeld, J. Bone morphogenetic protein receptor inhibitors suppress the growth of glioblastoma cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2022, 477, 1583–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Wang, Z.; Ba, Y.; Aguilar, J.; Kyan, A.; Zhong, L.; Hao, J. BMP signaling inhibition overcomes chemoresistance of prostate cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2023, 13, 4073–4086. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Jung, J.E.; Choi, S.I.; Kim, S.S.; Oh, Y.T.; Kim, T.H.; Choi, E.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, H.; Kim, E.O.; et al. Inhibition of BMP signaling overcomes acquired resistance to cetuximab in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Lett. 2018, 414, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Ravula, R.; Shi, L.; Song, Y.; Yeung, S.; Liu, M.; Lau, B.; Hao, J.; Wang, J.; Lam, C.W.; et al. Overcoming chemoresistance in prostate cancer with Chinese medicine Tripterygium wilfordii via multiple mechanisms. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 61246–61261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, I.; Croop, J. P-glycoprotein multidrug resistance and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1288, F37–F54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ka Yan Ho, R.L.; Huang, Y.; Chow, M.S.S.; Kei Lam, C.W.; Zuo, Z. Enhanced anti-tumor efficacy and mechanisms associated with docetaxel-piperine combination- in vitro and in vivo investigation using a taxane-resistant prostate cancer model. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 3338–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machioka, K.; Izumi, K.; Kadono, Y.; Iwamoto, H.; Naito, R.; Makino, T.; Kadomoto, S.; Natsagdorj, A.; Keller, E.T.; Zhang, J.; et al. Establishment and characterization of two cabazitaxel-resistant prostate cancer cell lines. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 16185–16196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahon, F.X.; Belloc, F.; Lagarde, V.; Chollet, C.; Moreau-Gaudry, F.; Reiffers, J.; Goldman, J.M.; Melo, J.V. MDR1 gene overexpression confers resistance to imatinib mesylate in leukemia cell line models. Blood 2003, 101, 2368–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledwitch, K.V.; Barnes, R.W.; Roberts, A.G. Unravelling the complex drug-drug interactions of the cardiovascular drugs, verapamil and digoxin, with P-glycoprotein. Biosci. Rep. 2016, 36, e00309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varma, M.V.; Ashokraj, Y.; Dey, C.S.; Panchagnula, R. P-glycoprotein inhibitors and their screening: A perspective from bioavailability enhancement. Pharmacol. Res. 2003, 48, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, A.B.; Ling, V. Effect of quercetin on Hoechst 33342 transport by purified and reconstituted P-glycoprotein. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1997, 53, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drori, S.; Eytan, G.D.; Assaraf, Y.G. Potentiation of anticancer-drug cytotoxicity by multidrug-resistance chemosensitizers involves alterations in membrane fluidity leading to increased membrane permeability. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 228, 1020–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moesgaard, L.; Pedersen, M.L.; Uhd Nielsen, C.; Kongsted, J. Structure-based discovery of novel P-glycoprotein inhibitors targeting the nucleotide binding domains. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Vmax (pmol/µg Protein/30 min) | Km (µM) | |
|---|---|---|
| Daunorubicin only | 180.10 ± 14.00 | 59.16 ± 7.44 |
| +1 µM DMH1 | 154.78 ± 3.03 | 61.03 ± 2.14 |
| +3 µM DMH1 | 135.66 ± 6.87 * | 59.47 ± 4.72 |
| +10 µM DMH1 | 132.64 ± 2.34 ** | 59.95 ± 2.95 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Xie, C.; Chou, M.; Hao, J. Allosteric Inhibition of P-Glycoprotein-Mediated Efflux by DMH1. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081798
Wang Z, Xie C, Chou M, Hao J. Allosteric Inhibition of P-Glycoprotein-Mediated Efflux by DMH1. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(8):1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081798
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhijun, Chen Xie, Maggie Chou, and Jijun Hao. 2025. "Allosteric Inhibition of P-Glycoprotein-Mediated Efflux by DMH1" Biomedicines 13, no. 8: 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081798
APA StyleWang, Z., Xie, C., Chou, M., & Hao, J. (2025). Allosteric Inhibition of P-Glycoprotein-Mediated Efflux by DMH1. Biomedicines, 13(8), 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081798







