The Developmental Toxicity of Haloperidol on Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Zebrafish Housing and Husbandry
2.2. Zebrafish Toxicity Testing
2.3. Lethal Dose (LD50) Determination
2.3.1. Deformity Assessment
2.3.2. Developmental Toxicity
2.3.3. Somatometric Measurements
2.4. Assessment of Haloperidol on the Cardiac Development Toxicity
2.5. Behavioral Analyses
2.5.1. Locomotor Activity
2.5.2. Touch-Evoked Motor Response (TMR) and Vibrational Startle Response (VSR)
2.6. Statistical Analyses
2.7. Ethics Statement
3. Results
3.1. Lethal Concentration (LD50) Determination
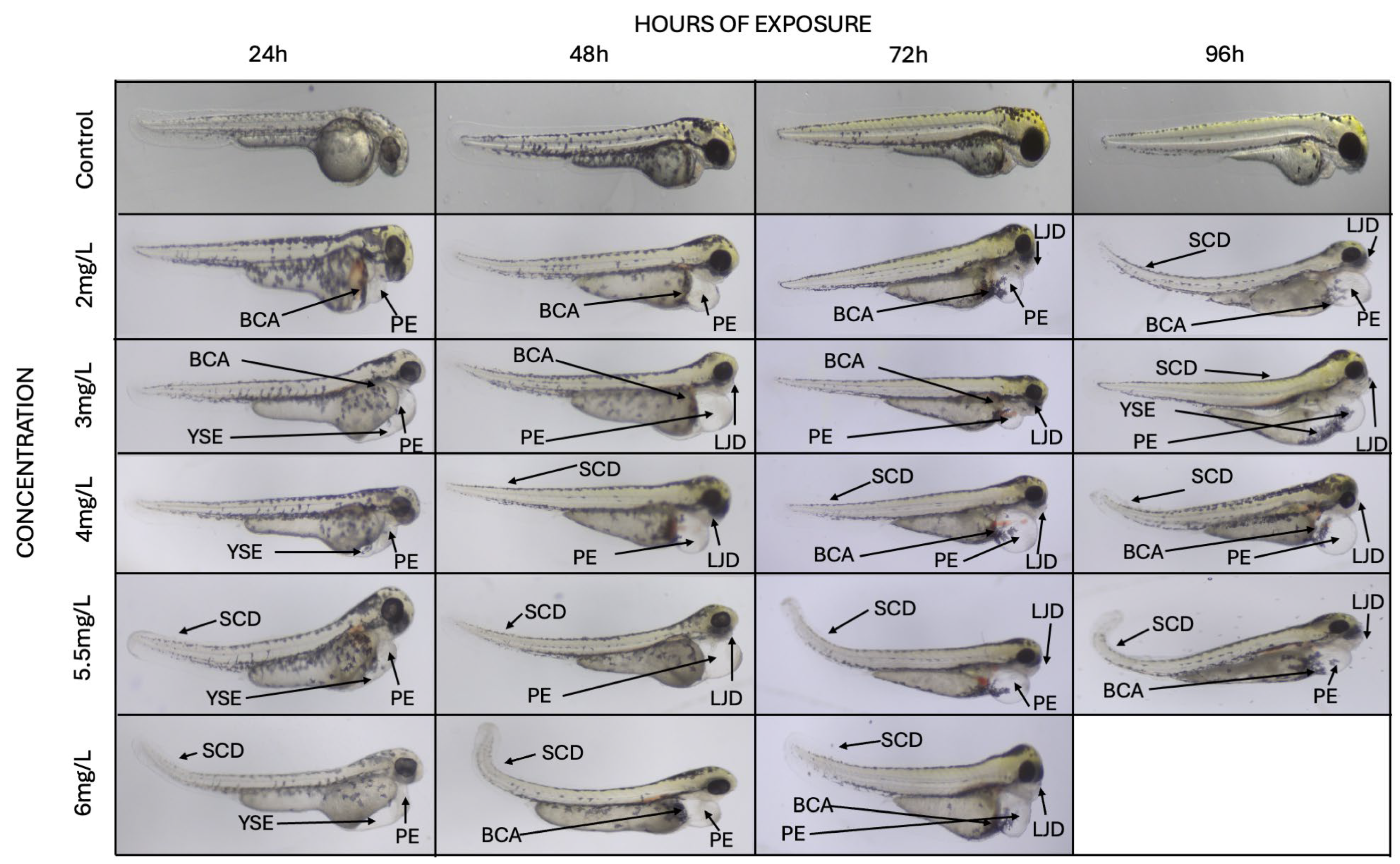
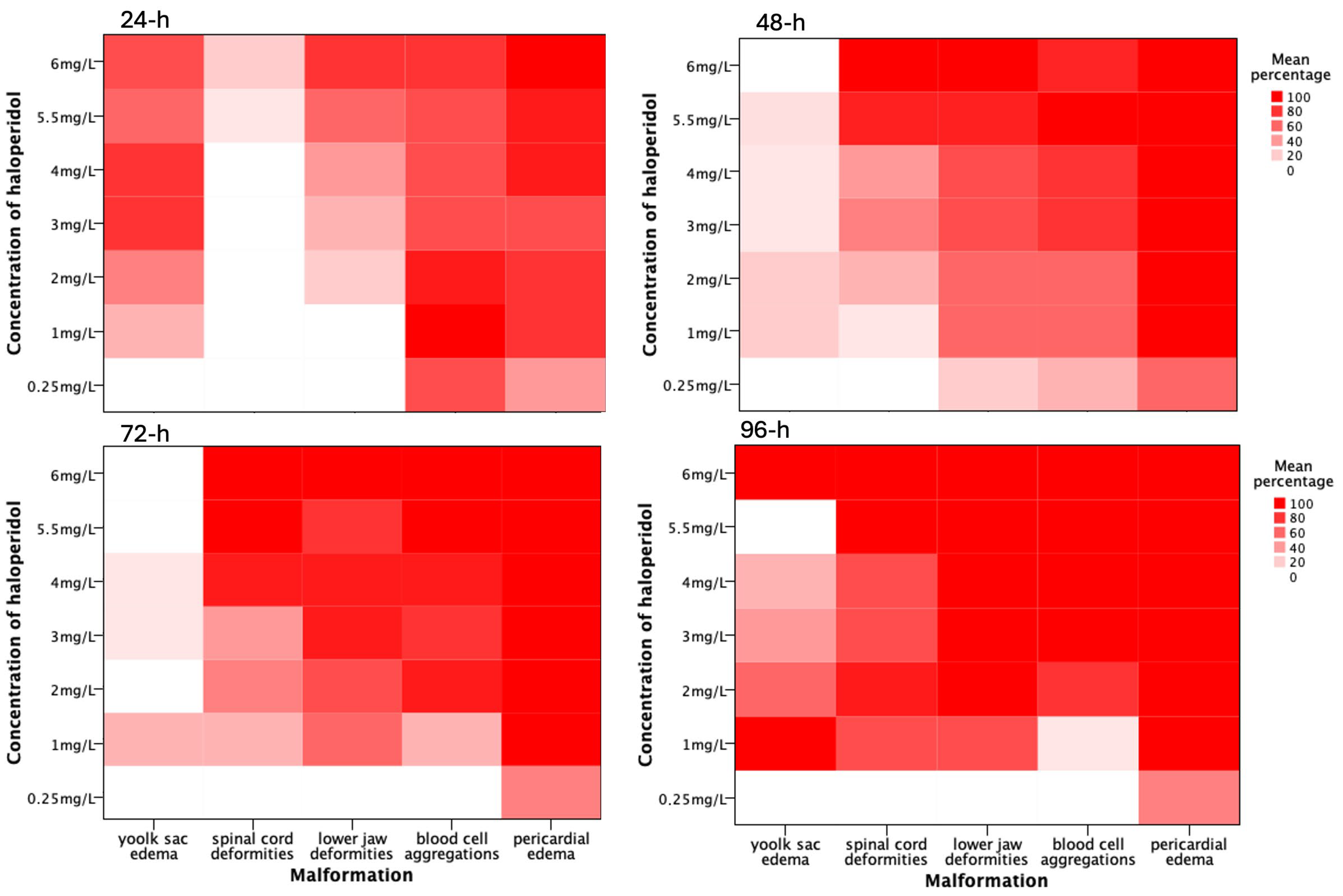
3.2. Morphological and Functional Alterations
3.2.1. Pericardial Edema
3.2.2. Blood Cell Aggregations
3.2.3. Skeletal Deformities
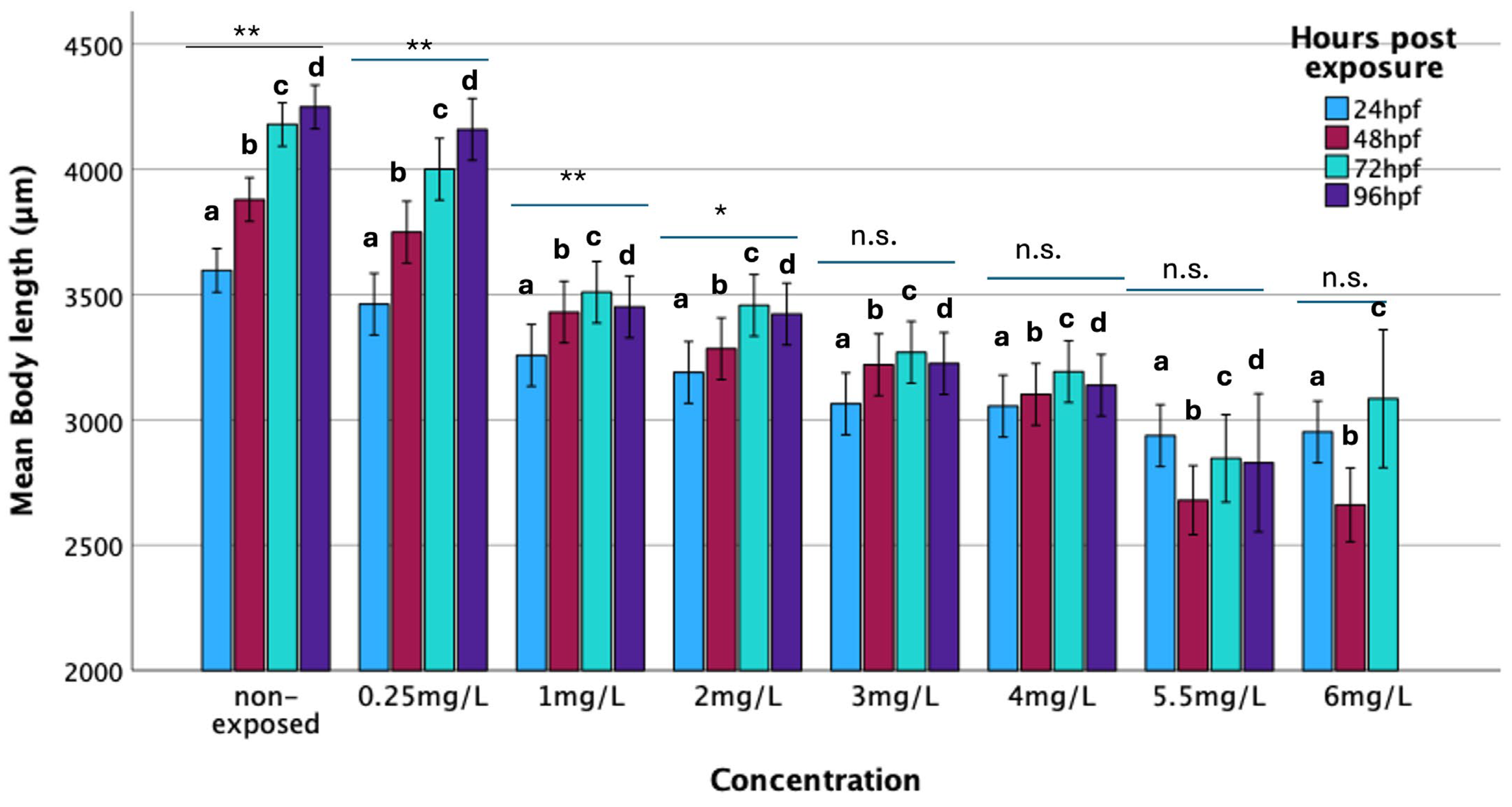
3.2.4. Body Length
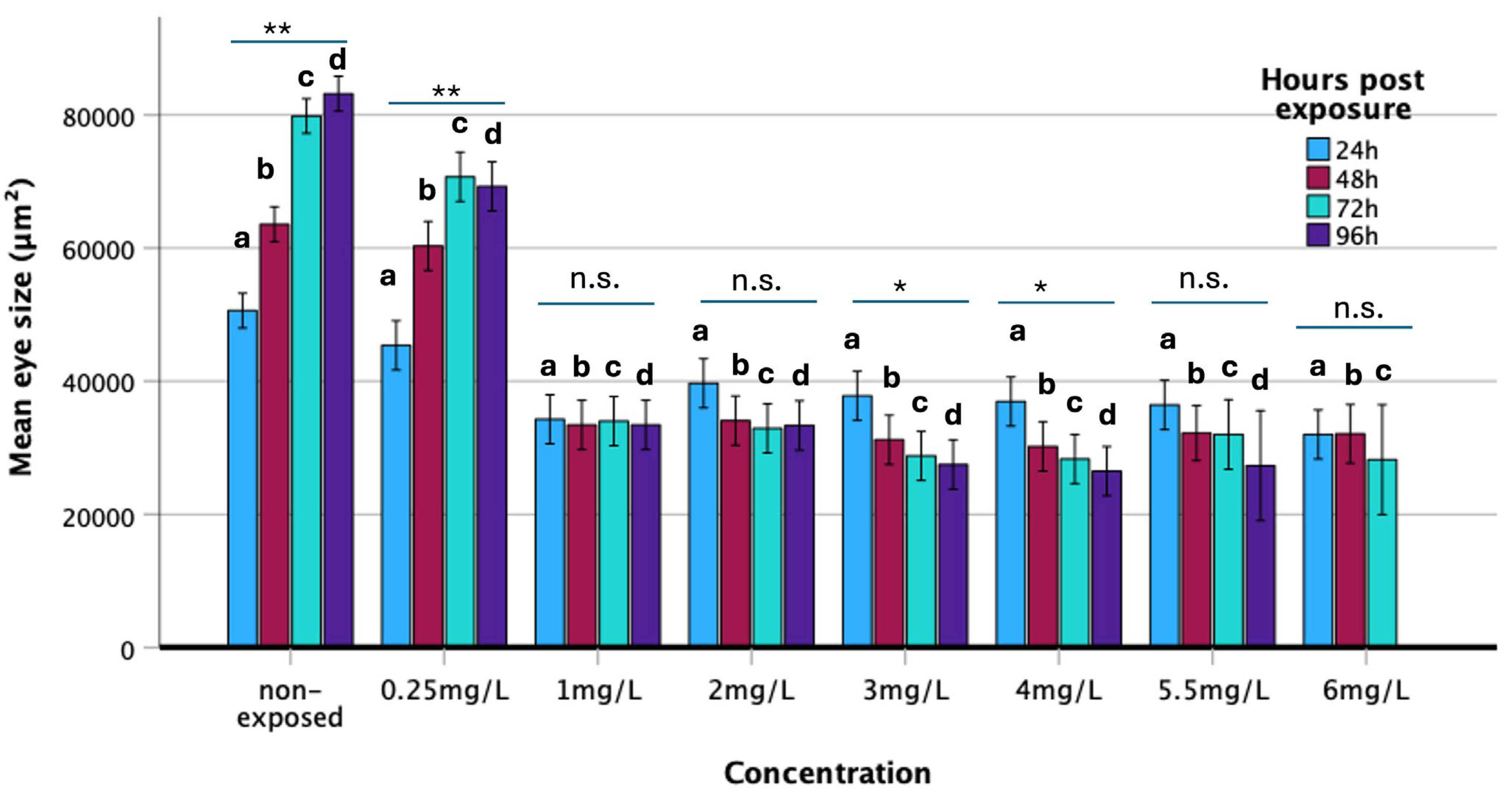
3.2.5. Eye Surface
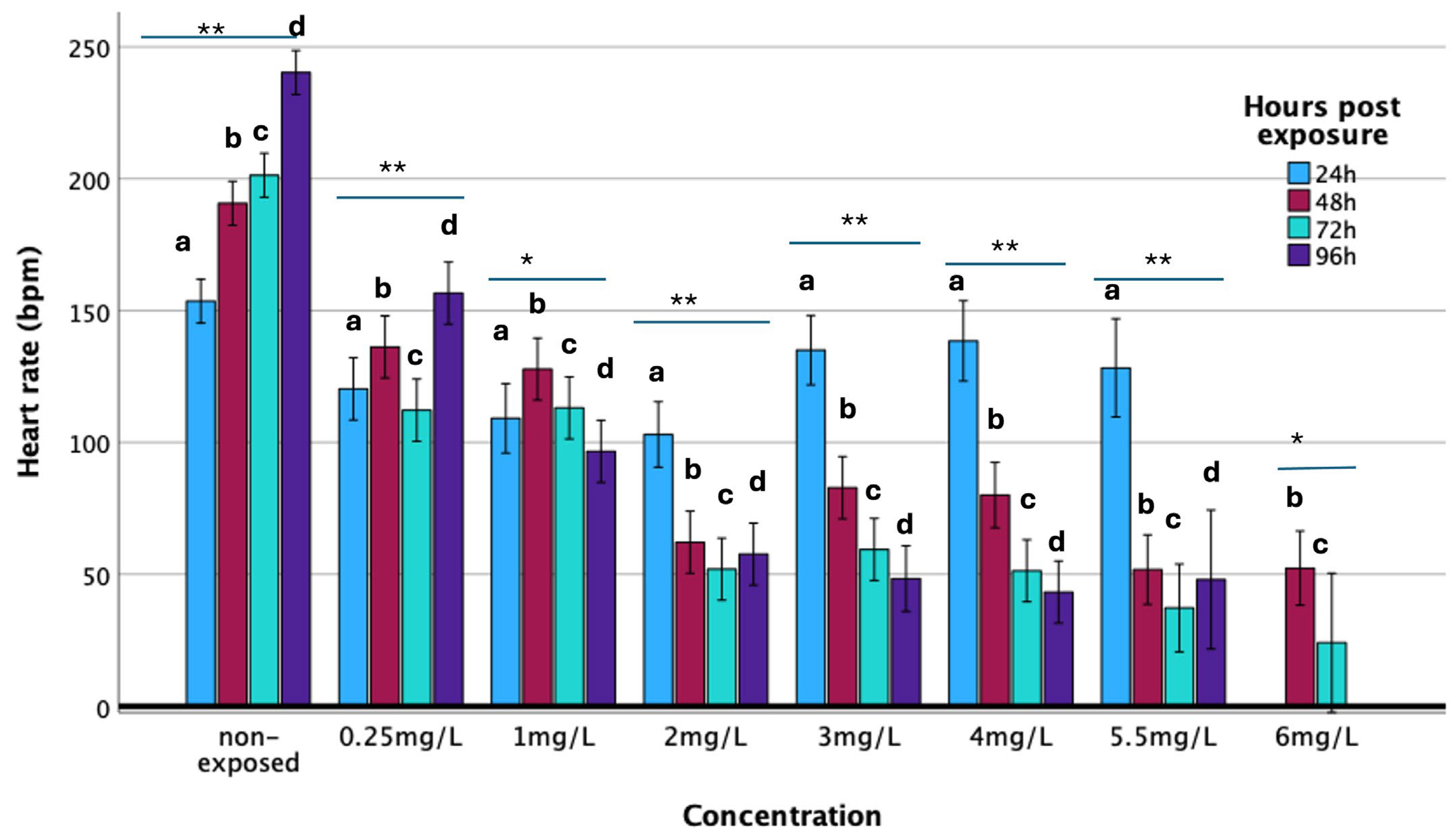
3.3. Heart Rate
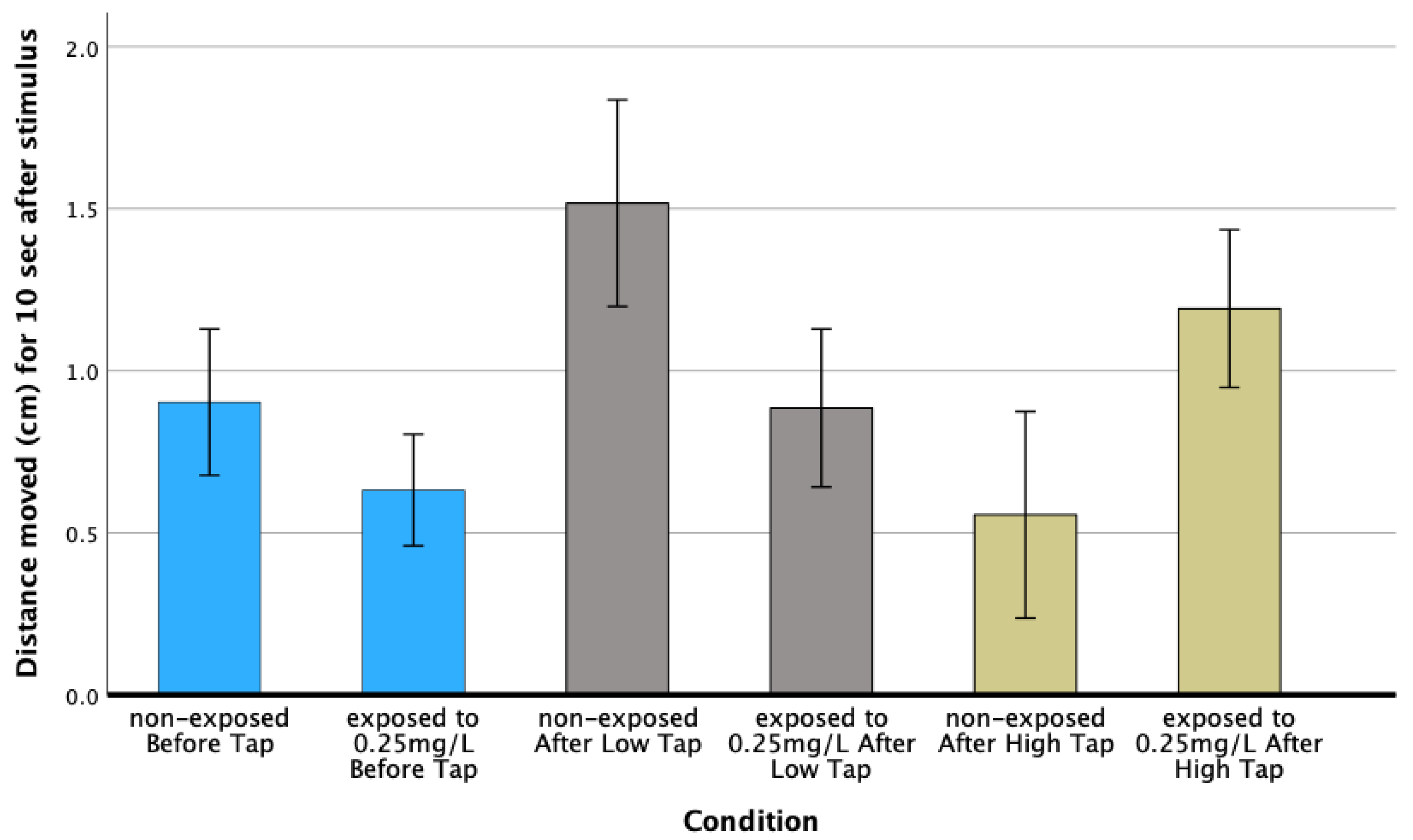
3.4. Behavioral Analysis
Larval Activity
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Bartolomeis, A.; Barone, A.; Begni, V.; Riva, M.A. Present and future antipsychotic drugs: A systematic review of the putative mechanisms of action for efficacy and a critical appraisal under a translational perspective. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 176, 106078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallee, F.R.; Nesbitt, L.; Jackson, C.; Sine, L.; Sethuraman, G. Relative Efficacy of Haloperidol and Pimozide in Children and Adolescents With Tourette’s Disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 1997, 154, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Galili-Mosberg, R.; Gil-Ad, I.; Weizman, A.; Melamed, E.; Offen, D. Haloperidol-Induced Neurotoxicity-Possible Implications for Tardive Dyskinesia. J. Neural Transm. 2000, 107, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emul, M.; Kalelioglu, T. Etiology of cardiovascular disease in patients with schizophrenia: Current perspectives. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2015, 11, 2493–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasumi, A.; Maeda, H.; Yoshida, K. Zebrafish as a model for haloperidol-induced catalepsy-like immobilization. Research Square 2021. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravliova, E.; Barbakadze, T.; Natsvlishvili, N.; Mikeladze, D.G. Haloperidol induces neurotoxicity by the NMDA receptor downstream signaling pathway, alternative from glutamate excitotoxicity. Neurochem. Int. 2007, 50, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, J.M.; Marder, S.R.; Schooler, N.R.; Wirshing, W.C.; Umbricht, D.; Baker, R.W.; Wirshing, D.A.; Safferman, A.; Ganguli, R.; McMeniman, M.; et al. Clozapine and Haloperidol in Moderately Refractory Schizophrenia A 6-Month Randomized and Double-Blind Comparison. JAMA Psychiatry 2025, 58, 965–972. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, W.A.; Chung, C.P.; Murray, K.T.; Hall, K.; Stein, C.M. Atypical Antipsychotic Drugs and the Risk of Sudden Cardiac Death. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, S.; Li, Q.; Cheetham, T.C.; Cooper, W.O.; Davis, R.L.; Dublin, S.; Hammad, T.A.; Li, D.-K.; Pawloski, P.A.; Pinheiro, S.P.; et al. Prevalence and trends in the use of antipsychotic medications during pregnancy in the U.S., 2001–2007: A population-based study of 585,615 deliveries. Arch. Women’s Ment. Health 2013, 16, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.V.S.; Cardoso, D.S.; Takada, S.H.; Echeverry, M.B. Prenatal exposition to haloperidol: A preclinical narrative review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 155, 105470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.Y.; Choi, T.I.; Lee, Y.R.; Choe, S.K.; Kim, C.H. Zebrafish as an animal model for biomedical research. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, P.R.; Bharani, K.K.; Khurana, A. Zebrafish Model for Biomedical Research. Zebrafish Model for Biomedical Research; Springer Nature: Berlin, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.N.; Patnaik, L. Flight for fish in drug discovery: A review of zebrafish-based screening of molecules. Biol. Lett. 2023, 19, 20220541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.J.; Teraoka, H.; Heideman, W.; Peterson, R.E. Zebrafish as a model vertebrate for investigating chemical toxicity. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 86, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trompouki, E.; Vianna Maurer-Morelli, C.; Adams, M.M.; Kafaligonul, H. Zebrafish—A Model Organism for Studying the Neurobiological Mechanisms Underlying Cognitive Brain Aging and Use of Potential Interventions. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of Embryonic Development of the Zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parichy, D.M.; Elizondo, M.R.; Mills, M.G.; Gordon, T.N.; Engeszer, R.E. Normal table of postembryonic zebrafish development: Staging by externally visible anatomy of the living fish. Dev. Dyn. 2009, 238, 2975–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamplin, O.J.; White, R.M.; Jing, L.; Kaufman, C.K.; Lacadie, S.A.; Li, P.; Taylor, A.M.; Zon, L.I. Small molecule screening in zebrafish: Swimming in potential drug therapies. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2012, 1, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postlethwait, J.H.; Yan, Y.L.; Gates, M.A.; Horne, S.; Amores, A.; Brownlie, A.; Donovan, A.; Egan, E.S.; Force, A.; Gong, Z.; et al. Vertebrate Genome Evolution and the Zebrafish Gene Map. Nat. Genet. 1988, 18, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihel, J.; Prober, D.A.; Arvanites, A.; Lam, K.; Zimmerman, S.; Jang, S.; Haggarty, S.J.; Kokel, D.; Rubin, L.L.; Peterson, R.T.; et al. Zebrafish behavioral profiling links drugs to biological targets and rest/wake regulation. Science 2010, 327, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnet, R.M.; Zizioli, D.; Taweedet, S.; Finazzi, D.; Memo, M. Zebrafish larvae as a behavioral model in neuropharmacology. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, B.; Mally, A.; Liedtke, D. Zebrafish embryos and larvae as alternative animal models for toxicity testing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassar, S.; Adatto, I.; Freeman, J.L.; Gamse, J.T.; Iturria, I.; Lawrence, C.; Muriana, A.; Peterson, R.T.; Van Cruchten, S.; Zon, L.I. Use of Zebrafish in Drug Discovery Toxicology. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 33, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieschke, G.J.; Currie, P.D. Animal models of human disease: Zebrafish swim into view. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.D.; Cerutti, D.T. Behavioral Neuroscience of Zebrafish; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Canadian Council on Animal Care. Guidelines on the Care and Use of Fish in Research, Teaching and Testing; Canadian Council on Animal Care: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council (US) Institute for Laboratory Animal Research. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Uematsu, T.; Yamada, K.; Matsuno, H.; Nakashima, M. The measurement of haloperidol and reduced haloperidol in neonatal hair as an index of placental transfer of maternal haloperidol. Ther. Drug Monit. 1991, 13, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huybrechts, K.F.; Hernández-Díaz, S.; Patorno, E.; Desai, R.J.; Mogun, H.; Dejene, S.Z.; Cohen, J.M.; Panchaud, A.; Cohen, L.; Bateman, B.T. Antipsychotic use in pregnancy and the risk for congenital malformations. JAMA Psychiatry 2016, 73, 938–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrana, N.; Koren, G.; Pivovarov, J.; Etwel, F.; Nulman, I. Pregnancy Outcomes Following in Utero Exposure to Second-Generation Antipsychotics: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2015, 35, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, C.G.; Blackwell, K.A.; Bartley, C.; Hay, M.; Yonkers, K.A.; Bloch, M.H. Obstetric and neonatal outcomes after antipsychotic medication exposure in pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 125, 1224–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, P.M.U.D.; Kaur, S.; Boddeda, J.; Wani, S.M. Haloperidol Induced Sudden Cardiac Arrest—Report of a Very Rare Case and Review of Literature. Case Rep. Psychiatry 2020, 2020, 1836716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glassman, A.H.; Thomas Bigger, J. Antipsychotic Drugs: Prolonged QTc Interval, Torsade de Pointes, and Sudden Death. Am. J. Psychiatry 2001, 158, 1774–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sackerman, J.; Donegan, J.J.; Cunningham, C.S.; Nguyen, N.N.; Lawless, K.; Long, A.; Benno, R.H.; Gould, G.G. Zebrafish Behavior in Novel Environments: Effects of Acute Exposure to Anxiolytic Compounds and Choice of Danio Rerio Line NIH Public Access. Int. J. Comp. Psychol. 2010, 23, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, G.; Maeda, H.; Kikura-Hanajiri, R.; Yoshida, K.I.; Hayashi, Y.K. The psychoactive drug 25B-NBOMe recapitulates rhabdomyolysis in zebrafish larvae. Forensic Toxicol. 2017, 35, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mersereau, E.J.; Poitra, S.L.; Espinoza, A.; Crossley, D.A.; Darland, T. The effects of cocaine on heart rate and electrocardiogram in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 172–173, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Muñoz, F.; Alamo, C. Monoaminergic Neurotransmission: The History of the Discovery of Antidepressants from 1950s Until Today. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 1563–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raschi, E.; Vasina, V.; Poluzzi, E.; De Ponti, F. The hERG K+ channel: Target and antitarget strategies in drug development. Pharmacol. Res. 2008, 57, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruni, G.; Rennekamp, A.J.; Velenich, A.; McCarroll, M.; Gendelev, L.; Fertsch, E.; Taylor, J.; Lakhani, P.; Lensen, D.; Evron, T.; et al. Zebrafish behavioral profiling identifies multitarget antipsychotic-like compounds. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irons, T.D.; Kelly, P.E.; Hunter, D.L.; MacPhail, R.C.; Padilla, S. Acute administration of dopaminergic drugs has differential effects on locomotion in larval zebrafish. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2013, 103, 792–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, F.R.C.; de Matos, L.W.; dos Santos Sampaio, M.D.F.; Carey, R.J.; Carrera, M.P. Opposite effects of low versus high dose haloperidol treatments on spontaneous and apomorphine induced motor behavior: Evidence that at a very low dose haloperidol acts as an indirect dopamine agonist. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 229, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auffret, M.; Drapier, S.; Vérin, M. The Many Faces of Apomorphine: Lessons from the Past and Challenges for the Future. Drugs R D 2018, 18, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemberling, M.; Bailey, T.J.; Hyde, D.R.; Poss, K.D. The zebrafish as a model for complex tissue regeneration. Trends Genet. 2013, 29, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leonardos, M.; Georgalis, C.; Sergiou, G.; Leonardos, D.; Lakkas, L.; Alexiou, G.A. The Developmental Toxicity of Haloperidol on Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081794
Leonardos M, Georgalis C, Sergiou G, Leonardos D, Lakkas L, Alexiou GA. The Developmental Toxicity of Haloperidol on Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(8):1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081794
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeonardos, Maximos, Charis Georgalis, Georgia Sergiou, Dimitrios Leonardos, Lampros Lakkas, and George A. Alexiou. 2025. "The Developmental Toxicity of Haloperidol on Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos" Biomedicines 13, no. 8: 1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081794
APA StyleLeonardos, M., Georgalis, C., Sergiou, G., Leonardos, D., Lakkas, L., & Alexiou, G. A. (2025). The Developmental Toxicity of Haloperidol on Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos. Biomedicines, 13(8), 1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081794






