Glucocorticoids Downregulate PD-L1 in Glioblastoma Cells via GILZ-Mediated ERK Inhibition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Cell Cultures and Treatments
2.3. Western Blot Analysis
2.4. Flow Cytometry
2.5. GILZ Silencing
2.6. GILZ Overexpression via TAT-Fusion Protein
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
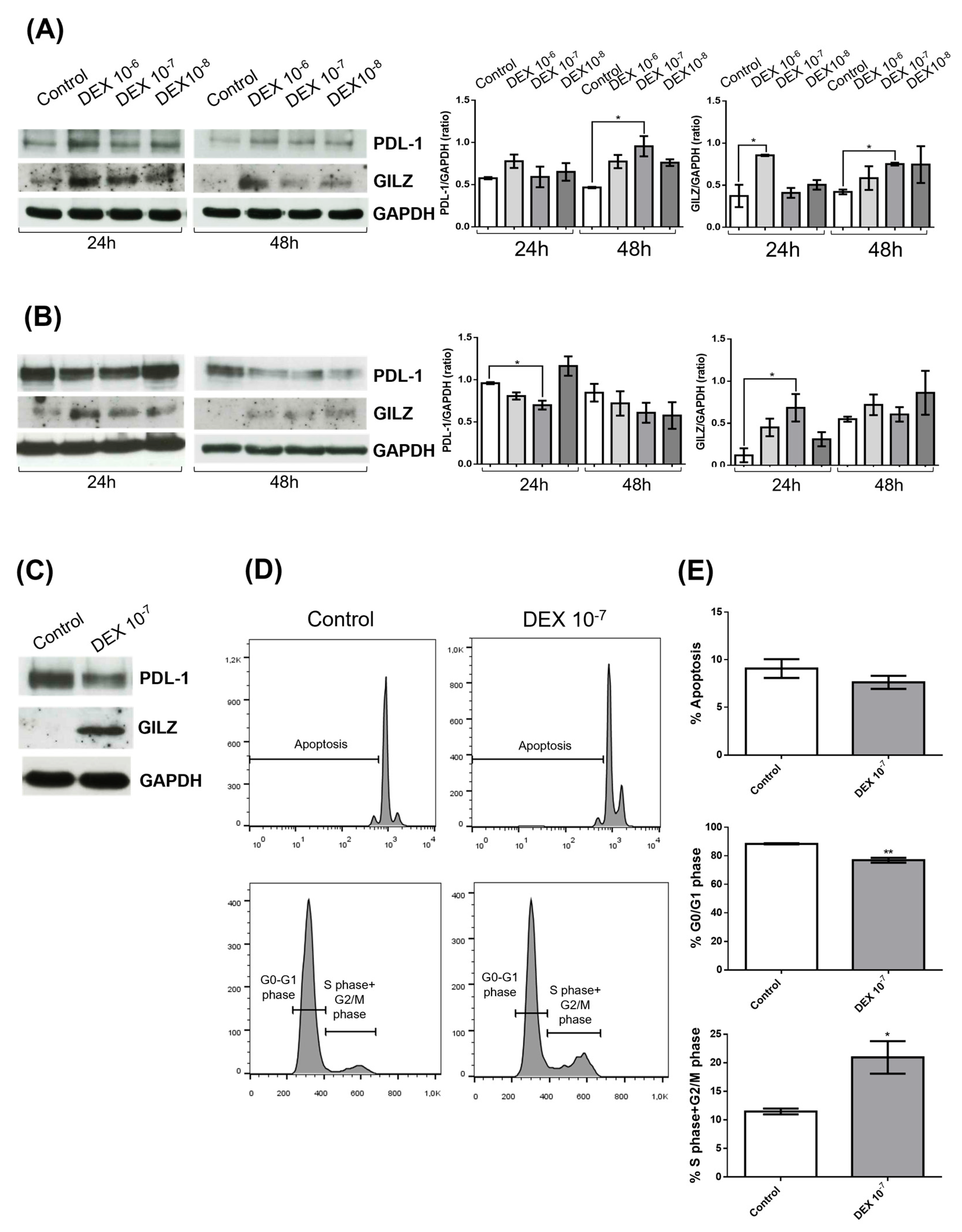
3.1. DEX Induces GILZ Expression but Differentially Regulates PD-L1 in GBM Cell Lines
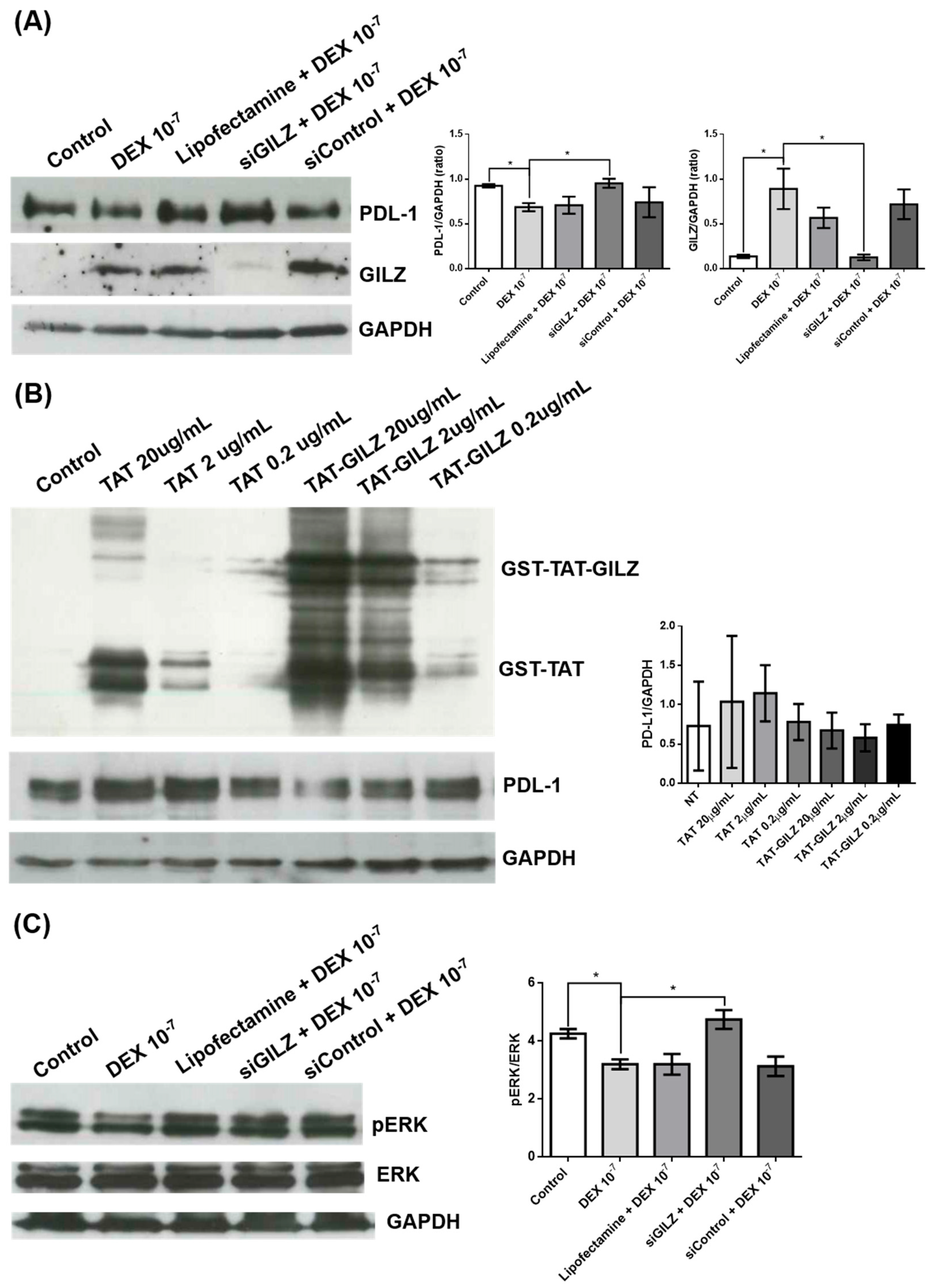
3.2. GILZ Mediates PD-L1 Downregulation via ERK Inhibition in U87 Cells
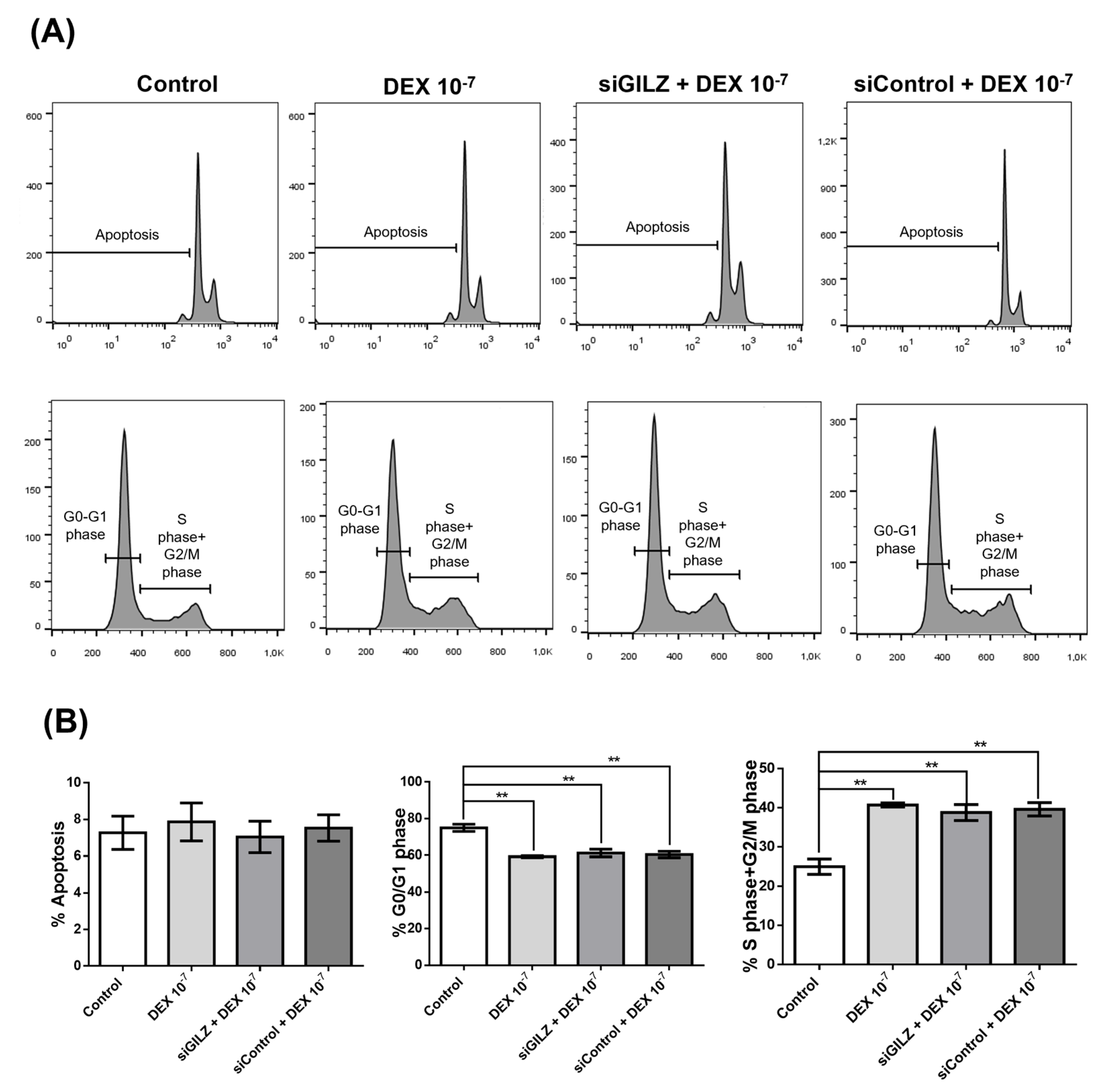
3.3. DEX Stimulates U87 Proliferation Independently of GILZ
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DEX | Dexamethasone |
| GR | Glucocorticoid Receptor |
| PD-L1 | Programmed Death-Ligand 1 |
| GILZ | Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper |
| siRNA | Small Interfering RNA |
| siGILZ | GILZ-targeting Small Interfering RNA |
| siControl | Control Small Interfering RNA |
| ERK | Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase |
| pERK | Phosphorylated Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase |
| AKT | Protein Kinase B |
| pAKT | Phosphorylated AKT |
| p21 | Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 1A |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase |
| SEM | Standard Error of the Mean |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
References
- Sharpe, A.H.; Pauken, K.E. The Diverse Functions of the PD1 Inhibitory Pathway. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, J. Functions of Immune Checkpoint Molecules Beyond Immune Evasion. In Regulation of Cancer Immune Checkpoints: Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms and Therapy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 201–226. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Kang, K.; Chen, P.; Zeng, Z.; Li, G.; Xiong, W.; Yi, M.; Xiang, B. Regulatory Mechanisms of PD-1/PD-L1 in Cancers. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohaegbulam, K.C.; Assal, A.; Lazar-Molnar, E.; Yao, Y.; Zang, X. Human Cancer Immunotherapy with Antibodies to the PD-1 and PD-L1 Pathway. Trends Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Schilling, B.; Liu, D.; Sucker, A.; Livingstone, E.; Jerby-Arnon, L.; Zimmer, L.; Gutzmer, R.; Satzger, I.; Loquai, C.; et al. Integrative Molecular and Clinical Modeling of Clinical Outcomes to PD1 Blockade in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1916–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topalian, S.L.; Taube, J.M.; Anders, R.A.; Pardoll, D.M. Mechanism-Driven Biomarkers to Guide Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Cancer Therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jammihal, T.; Saliby, R.M.; Labaki, C.; Soulati, H.; Gallegos, J.; Peris, A.; McCurry, D.; Yu, C.; Shah, V.; Poduval, D.; et al. Immunogenomic Determinants of Exceptional Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibition in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Nat. Cancer 2025, 6, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haanen, J.B.A.G.; Robert, C. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Prog. Tumor. Res. 2015, 42, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lei, Q.; Wang, D.; Sun, K.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Resistance Mechanisms of Anti-PD1/PDL1 Therapy in Solid Tumors. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhen, T.; Cidlowski, J.A. Antiinflammatory Action of Glucocorticoids—New Mechanisms for Old Drugs. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1711–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.R. Anti-Inflammatory Functions of Glucocorticoid-Induced Genes. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2007, 275, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayroldi, E.; Cannarile, L.; Adorisio, S.; Delfino, D.V.; Riccardi, C. Role of Endogenous Glucocorticoids in Cancer in the Elderly. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pufall, M.A. Glucocorticoids and Cancer. In Glucocorticoid Signaling: From Molecules to Mice to Man; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 315–333. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.N.; LaRiviere, M.; Macduffie, E.; White, C.A.; Jordan-Luft, M.M.; Anderson, E.; Ziegler, M.; Radcliff, J.A.; Jones, J. Use of Glucocorticoids in Patients with Cancer: Potential Benefits, Harms, and Practical Considerations for Clinical Practice. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 13, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adorisio, S.; Cannarile, L.; Delfino, D.V.; Ayroldi, E. Glucocorticoid and PD-1 Cross-Talk: Does the Immune System Become Confused? Cells 2021, 10, 2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayroldi, E.; Riccardi, C. Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper (GILZ): A New Important Mediator of Glucocorticoid Action. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 3649–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Adamio, F.; Zollo, O.; Moraca, R.; Ayroldi, E.; Bruscoli, S.; Bartoli, A.; Cannarile, L.; Migliorati, G.; Riccardi, C. A New Dexamethasone-Induced Gene of the Leucine Zipper Family Protects T Lymphocytes from TCR/CD3-Activated Cell Death. Immunity 1997, 7, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruscoli, S.; Velardi, E.; Di Sante, M.; Bereshchenko, O.; Venanzi, A.; Coppo, M.; Berno, V.; Mameli, M.G.; Colella, R.; Cavaliere, A.; et al. Long Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper (L-GILZ) Protein Interacts with Ras Protein Pathway and Contributes to Spermatogenesis Control. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 1242–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayroldi, E.; Migliorati, G.; Bruscoli, S.; Marchetti, C.; Zollo, O.; Cannarile, L.; D’Adamio, F.; Riccardi, C. Modulation of T-Cell Activation by the Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper Factor via Inhibition of Nuclear Factor κB. Blood 2001, 98, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayroldi, E.; Zollo, O.; Bastianelli, A.; Marchetti, C.; Agostini, M.; Di Virgilio, R.; Riccardi, C. GILZ Mediates the Antiproliferative Activity of Glucocorticoids by Negative Regulation of Ras Signaling. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1605–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, M.C.; Cannarile, L.; Ronchetti, S.; Delfino, D.V.; Riccardi, C.; Ayroldi, E. L-GILZ Binds and Inhibits Nuclear Factor κB Nuclear Translocation in Undifferentiated Thyroid Cancer Cells. J. Chemother. 2020, 32, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayroldi, E.; Marchetti, C.; Riccardi, C. The Novel Partnership of L-GILZ and P53: A New Affair in Cancer? Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2015, 2, e975087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grugan, K.D.; Ma, C.; Singhal, S.; Krett, N.L.; Rosen, S.T. Dual Regulation of Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper (GILZ) by the Glucocorticoid Receptor and the PI3-Kinase/AKT Pathways in Multiple Myeloma. J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 110, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebson, L.; Wang, T.; Jiang, Q.; Whartenby, K.A. Induction of the Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper Gene Limits the Efficacy of Dendritic Cell Vaccines. Cancer Gene Ther. 2011, 18, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Maxwell, R.; Luksik, A.S.; Garzon-Muvdi, T.; Hung, A.L.; Kim, E.S.; Wu, A.; Xia, Y.; Belcaid, Z.; Gorelick, N.; Choi, J.; et al. Contrasting Impact of Corticosteroids on Anti-PD-1 Immunotherapy Efficacy for Tumor Histologies Located within or Outside the Central Nervous System. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1500108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, N.; Maruhashi, T.; Sugiura, D.; Shimizu, K.; Okazaki, I.; Okazaki, T. Glucocorticoids Potentiate the Inhibitory Capacity of Programmed Cell Death 1 by Up-Regulating Its Expression on T Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 19896–19906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quatrini, L.; Vacca, P.; Tumino, N.; Besi, F.; Di Pace, A.L.; Scordamaglia, F.; Martini, S.; Munari, E.; Mingari, M.C.; Ugolini, S.; et al. Glucocorticoids and the Cytokines IL-12, IL-15, and IL-18 Present in the Tumor Microenvironment Induce PD-1 Expression on Human Natural Killer Cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, K.; Gu, B.; Zhang, P.; Wu, X. Dexamethasone Enhances Programmed Cell Death 1 (PD-1) Expression during T Cell Activation: An Insight into the Optimum Application of Glucocorticoids in Anti-Cancer Therapy. BMC Immunol. 2015, 16, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouyan, A.; Ghorbanlo, M.; Eslami, M.; Jahanshahi, M.; Ziaei, E.; Salami, A.; Mokhtari, K.; Shahpasand, K.; Farahani, N.; Meybodi, T.E.; et al. Glioblastoma Multiforme: Insights into Pathogenesis, Key Signaling Pathways, and Therapeutic Strategies. Mol. Cancer 2025, 24, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Du, A.; Li, J.; Han, H.; Feng, P.; Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; Tian, G.; Yu, H.; Zhang, B.; et al. Transitioning from Molecular Methods to Therapeutic Methods: An In-depth Analysis of Glioblastoma. Oncol. Rep. 2025, 53, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inggas, M.A.M.; Patel, U.; Wijaya, J.H.; Otinashvili, N.; Menon, V.R.; Iyer, A.K.; Turjman, T.; Dadwal, S.; Gadaevi, M.; Ismayilova, A.; et al. The Role of Temozolomide as Adjuvant Therapy in Glioblastoma Management: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Cancer 2025, 25, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, F.; Augello, F.R.; Artone, S.; Ayroldi, E.; Giusti, I.; Dolo, V.; Cifone, M.G.; Cinque, B.; Palumbo, P. Cyclooxygenase-2 Upregulated by Temozolomide in Glioblastoma Cells Is Shuttled in Extracellular Vesicles Modifying Recipient Cell Phenotype. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 933746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikfalvi, A.; da Costa, C.A.; Avril, T.; Barnier, J.-V.; Bauchet, L.; Brisson, L.; Cartron, P.F.; Castel, H.; Chevet, E.; Chneiweiss, H.; et al. Challenges in Glioblastoma Research: Focus on the Tumor Microenvironment. Trends Cancer 2023, 9, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.; Pang, L.; Dunterman, M.; Lesniak, M.S.; Heimberger, A.B.; Chen, P. Macrophages and Microglia in Glioblastoma: Heterogeneity, Plasticity, and Therapy. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Hambardzumyan, D. Immune Microenvironment in Glioblastoma Subtypes. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nduom, E.K.; Wei, J.; Yaghi, N.K.; Huang, N.; Kong, L.-Y.; Gabrusiewicz, K.; Ling, X.; Zhou, S.; Ivan, C.; Chen, J.Q.; et al. PD-L1 Expression and Prognostic Impact in Glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2016, 18, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akintola, O.O.; Reardon, D.A. The Current Landscape of Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Glioblastoma. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 32, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinnadurai, M.; McDonald, K.L. Immune Checkpoint Inhibition and Its Relationship with Hypermutation Phenoytype as a Potential Treatment for Glioblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 132, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinelli, D.; Giusti, R.; Mazzotta, M.; Filetti, M.; Krasniqi, E.; Pizzuti, L.; Landi, L.; Tomao, S.; Cappuzzo, F.; Ciliberto, G.; et al. Palliative- and Non-Palliative Indications for Glucocorticoids Use in Course of Immune-Checkpoint Inhibition. Current Evidence and Future Perspectives. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2021, 157, 103176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, P.; Sabatier, J.-M. Rethinking Corticosteroids Use in Oncology. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1551111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, J.A.; Rodgers, L.T.; Kryscio, R.J.; Hartz, A.M.S.; Bauer, B. Characterization and Comparison of Human Glioblastoma Models. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camphausen, K.; Purow, B.; Sproull, M.; Scott, T.; Ozawa, T.; Deen, D.F.; Tofilon, P.J. Influence of In Vivo Growth on Human Glioma Cell Line Gene Expression: Convergent Profiles under Orthotopic Conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 8287–8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.; Liu, Y. Differences in Protein Expression between the U251 and U87 Cell Lines. Turk. Neurosurg. 2017, 27, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motaln, H.; Koren, A.; Gruden, K.; Ramšak, Ž.; Schichor, C.; Lah, T.T. Heterogeneous Glioblastoma Cell Cross-Talk Promotes Phenotype Alterations and Enhanced Drug Resistance. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 40998–41017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayroldi, E.; Petrillo, M.G.; Bastianelli, A.; Marchetti, M.C.; Ronchetti, S.; Nocentini, G.; Ricciotti, L.; Cannarile, L.; Riccardi, C. L-GILZ Binds P53 and MDM2 and Suppresses Tumor Growth through P53 Activation in Human Cancer Cells. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riccardi, C.; Nicoletti, I. Analysis of Apoptosis by Propidium Iodide Staining and Flow Cytometry. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1458–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Chen, J.-F.; Li, X.-G.; Shi, Y.-H.; Tang, Z.; Liu, W.-R.; Zhang, X.; Huang, A.; Luo, X.-M.; Gao, Q.; et al. KRAS Acting through ERK Signaling Stabilizes PD-L1 via Inhibiting Autophagy Pathway in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruera, S.; Suarez-Almazor, M.E. The Effects of Glucocorticoids and Immunosuppressants on Cancer Outcomes in Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 928390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokito, T.; Azuma, K.; Kawahara, A.; Ishii, H.; Yamada, K.; Matsuo, N.; Kinoshita, T.; Mizukami, N.; Ono, H.; Kage, M.; et al. Predictive Relevance of PD-L1 Expression Combined with CD8+ TIL Density in Stage III Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Receiving Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 55, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, W.J.; Gilbert, M.R. Glucocorticoids and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Glioblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 2021, 151, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayroldi, E.; Cannarile, L.; Delfino, D.V.; Riccardi, C. A Dual Role for Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper in Glucocorticoid Function: Tumor Growth Promotion or Suppression? Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redjimi, N.; Gaudin, F.; Touboul, C.; Emilie, D.; Pallardy, M.; Biola-Vidamment, A.; Fernandez, H.; Prévot, S.; Balabanian, K.; Machelon, V. Identification of Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper as a Key Regulator of Tumor Cell Proliferation in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2009, 8, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, F.; Trinh, A.; Balayssac, S.; Maboudou, P.; Dekiouk, S.; Malet-Martino, M.; Quesnel, B.; Idziorek, T.; Kluza, J.; Marchetti, P. Metabolic Rewiring in Cancer Cells Overexpressing the Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper Protein (GILZ): Activation of Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation and Sensitization to Oxidative Cell Death Induced by Mitochondrial Targeted Drugs. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 85, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurgali, K.; Rudd, J.A.; Was, H.; Abalo, R. Editorial: Cancer Therapy: The Challenge of Handling a Double-Edged Sword. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1007762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayayo-Peralta, I.; Zwart, W.; Prekovic, S. Duality of Glucocorticoid Action in Cancer: Tumor-Suppressor or Oncogene? Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2021, 28, R157–R171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cathelin, D.; Met, Ö.; Svane, I.M. Silencing of the Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper Improves the Immunogenicity of Clinical-Grade Dendritic Cells. Cytotherapy 2013, 15, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vétillard, M.; Schlecht-Louf, G. Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper: Fine-Tuning of Dendritic Cells Function. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adorisio, S.; Renga, G.; Delfino, D.V.; Ayroldi, E. Glucocorticoids Downregulate PD-L1 in Glioblastoma Cells via GILZ-Mediated ERK Inhibition. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081793
Adorisio S, Renga G, Delfino DV, Ayroldi E. Glucocorticoids Downregulate PD-L1 in Glioblastoma Cells via GILZ-Mediated ERK Inhibition. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(8):1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081793
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdorisio, Sabrina, Giorgia Renga, Domenico Vittorio Delfino, and Emira Ayroldi. 2025. "Glucocorticoids Downregulate PD-L1 in Glioblastoma Cells via GILZ-Mediated ERK Inhibition" Biomedicines 13, no. 8: 1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081793
APA StyleAdorisio, S., Renga, G., Delfino, D. V., & Ayroldi, E. (2025). Glucocorticoids Downregulate PD-L1 in Glioblastoma Cells via GILZ-Mediated ERK Inhibition. Biomedicines, 13(8), 1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081793




