Transcriptomic Profile of Perineural Invasion in Prostate Cancer Identifies Prognostic Gene Signatures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Gene Expression Analysis
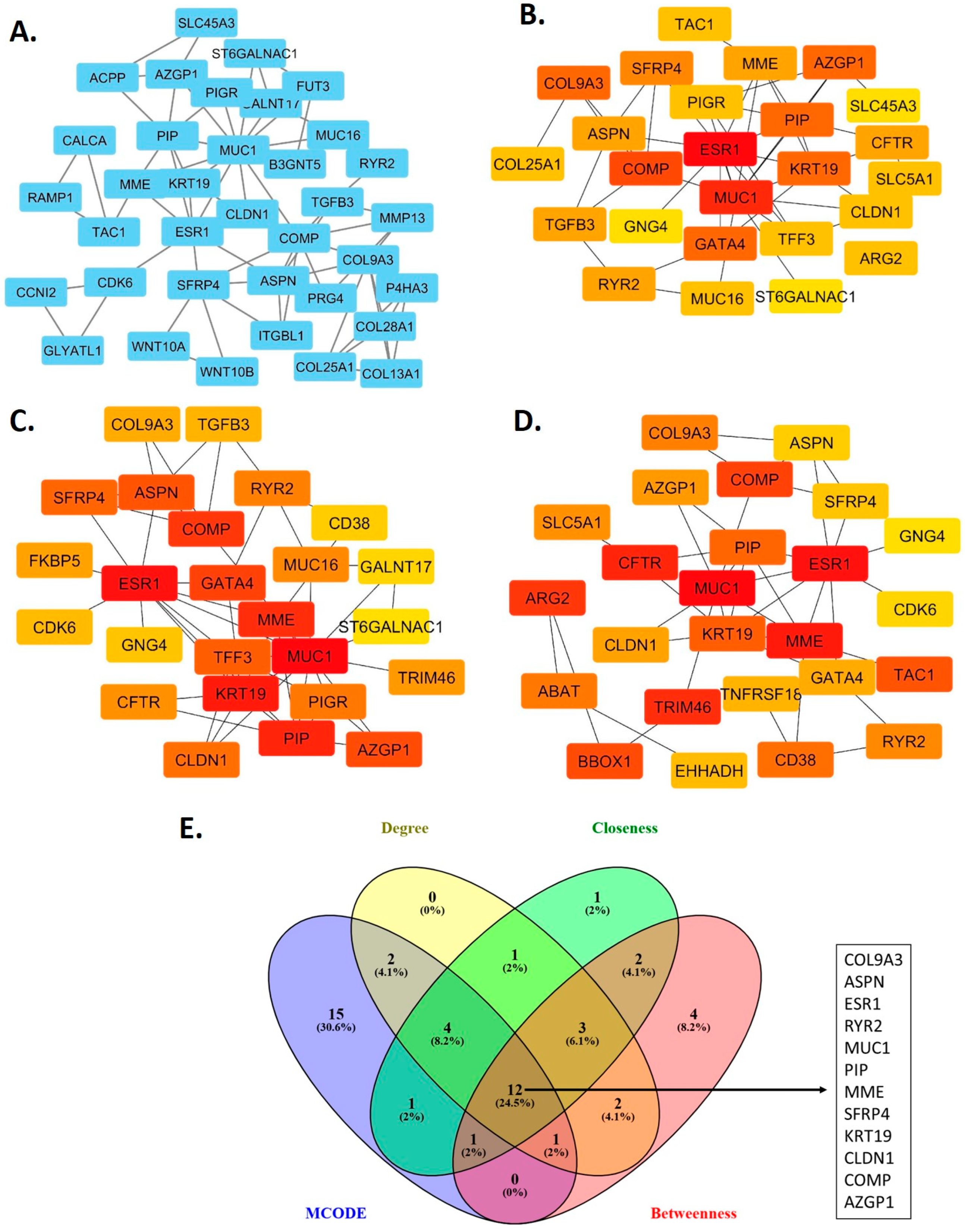
2.3. Construction of the Protein-Protein Interaction Network and Identification of Hub Genes
2.4. Functional Enrichment Analysis
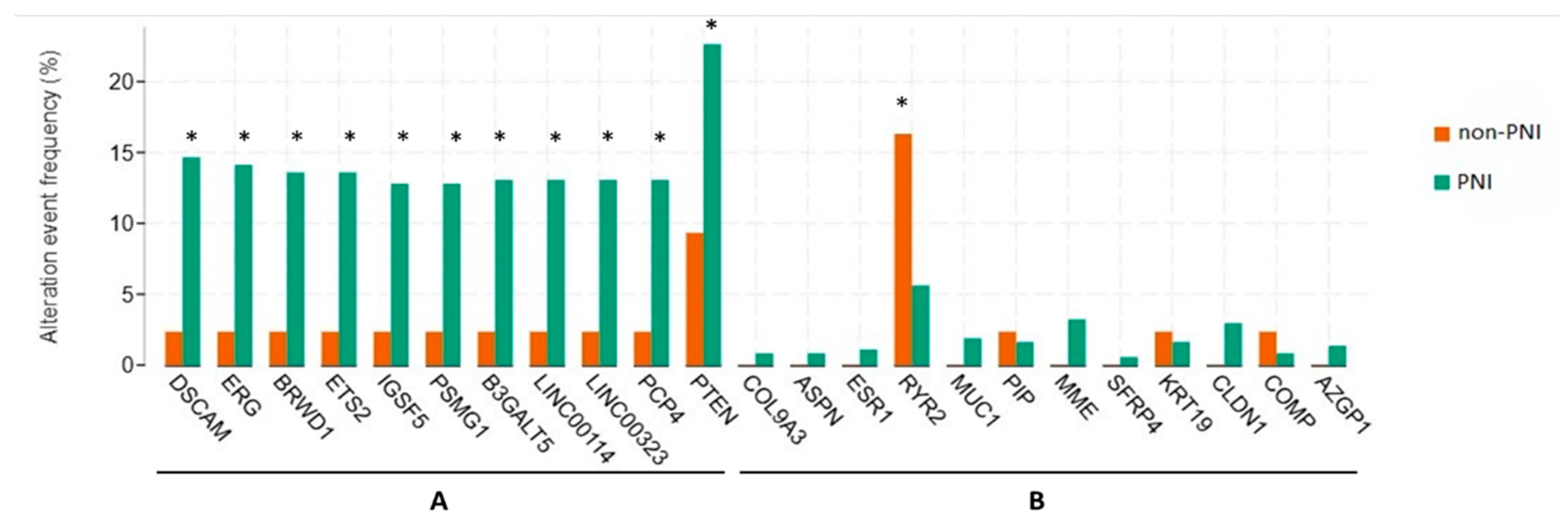
2.5. Genomic Alterations of Genes Compared Between PNI and Non-PNI Groups
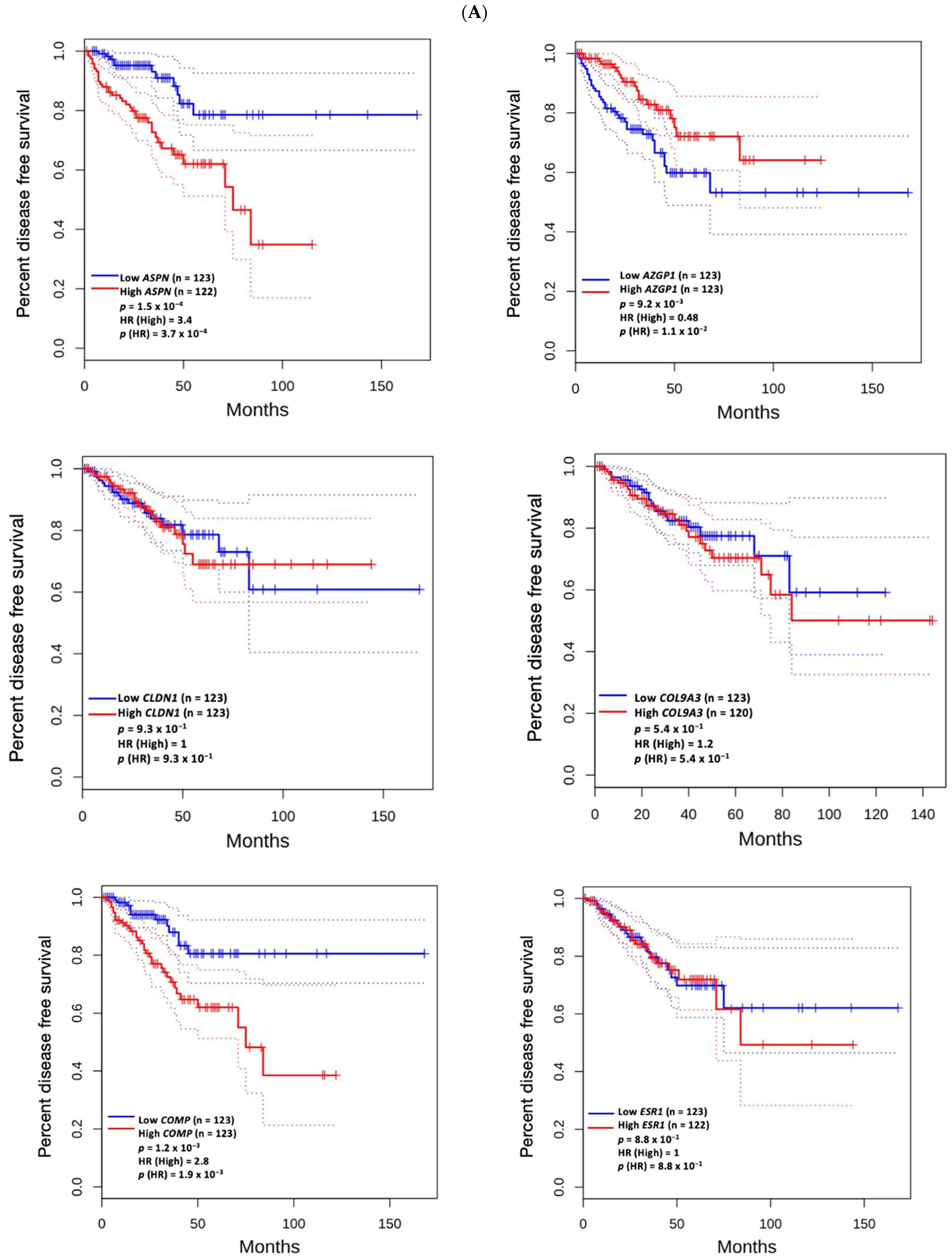
2.6. Prognostic Value of Genomic Alterations and Hub Genes
3. Results
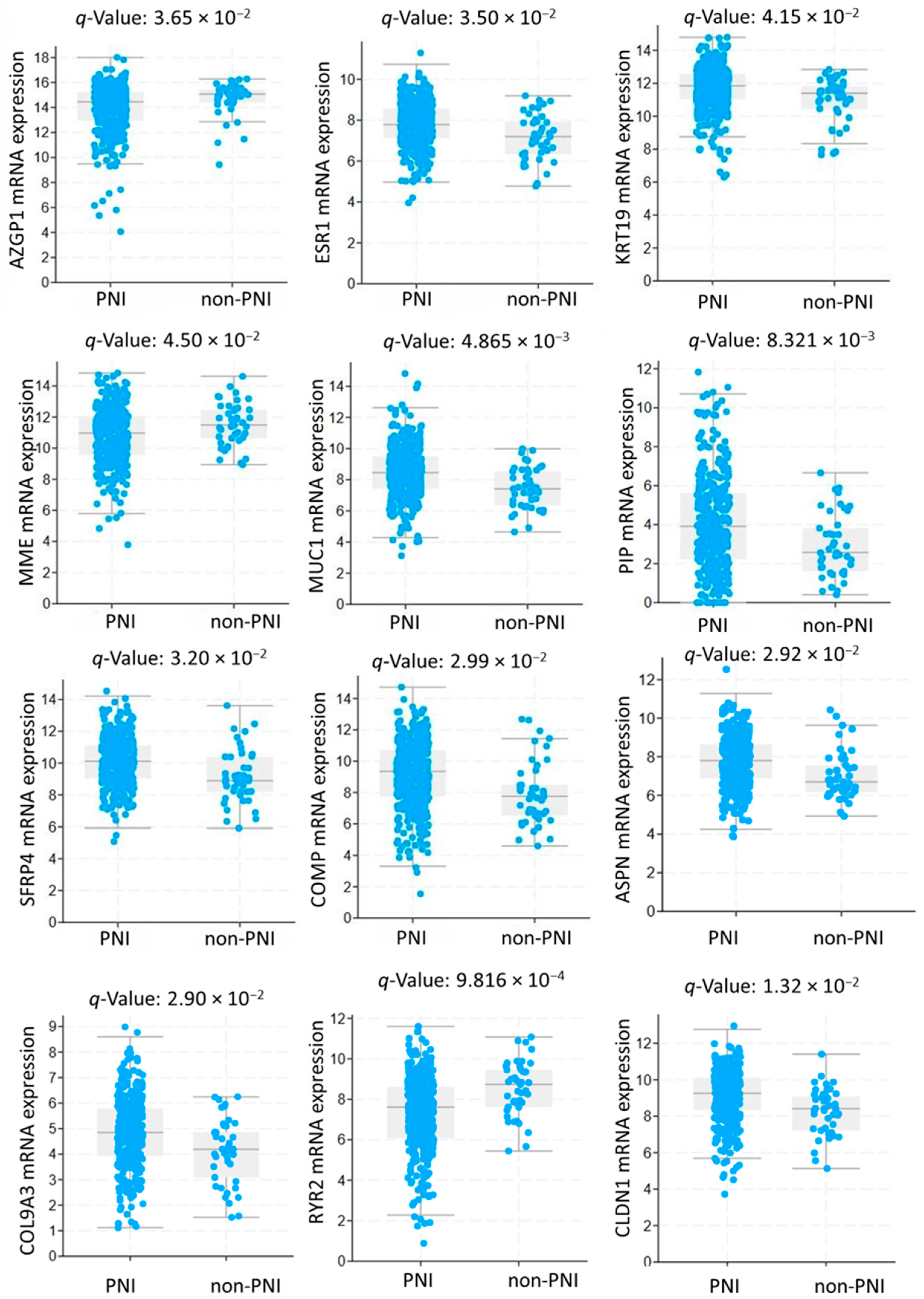
3.1. Study Population and Gene Expression Analysis
3.2. Hub Genes in the Protein-Protein Interaction Network
3.3. Genetic Alterations
3.4. Biological Processes and Pathways Underlying Perineural Invasion
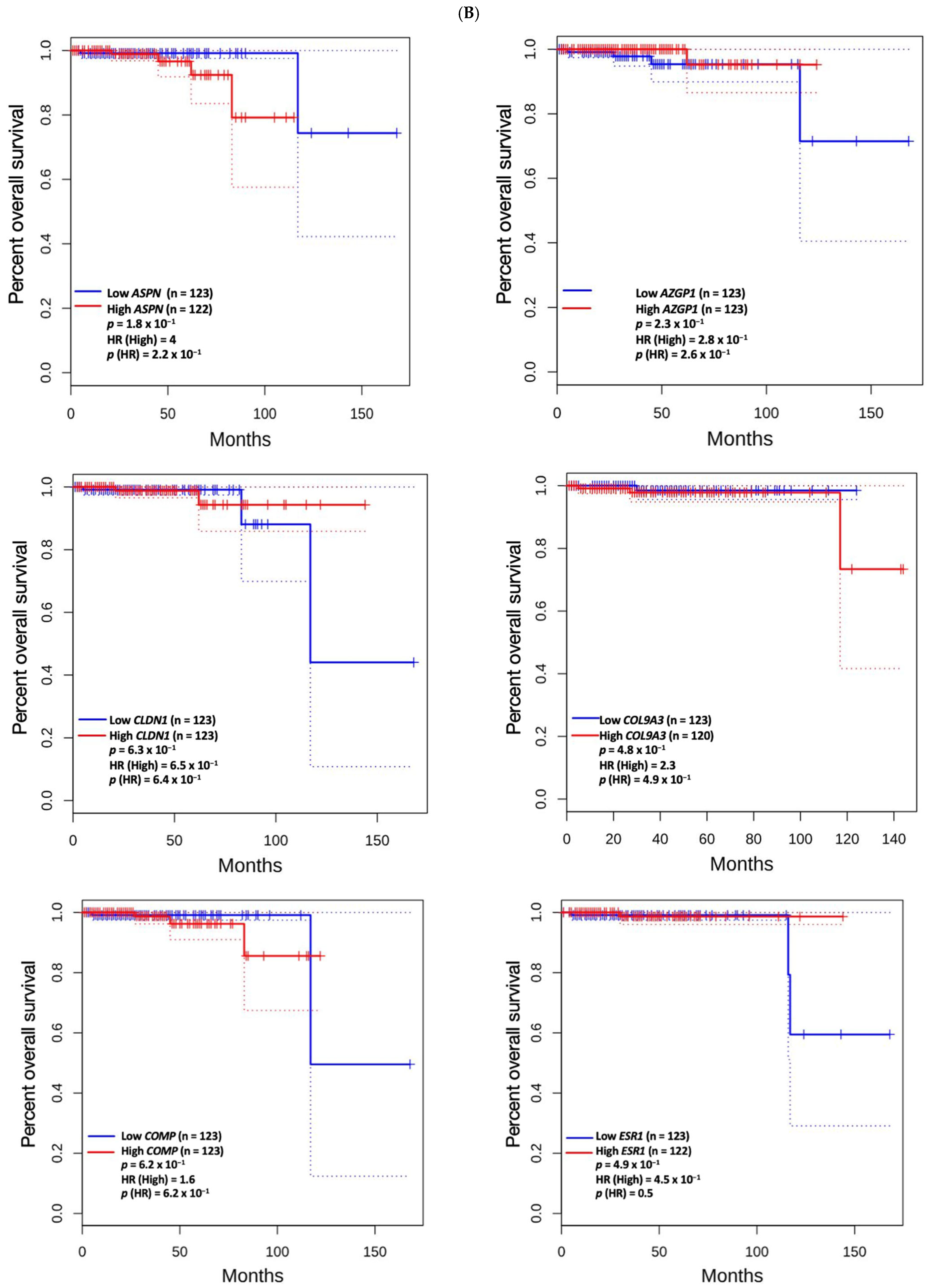
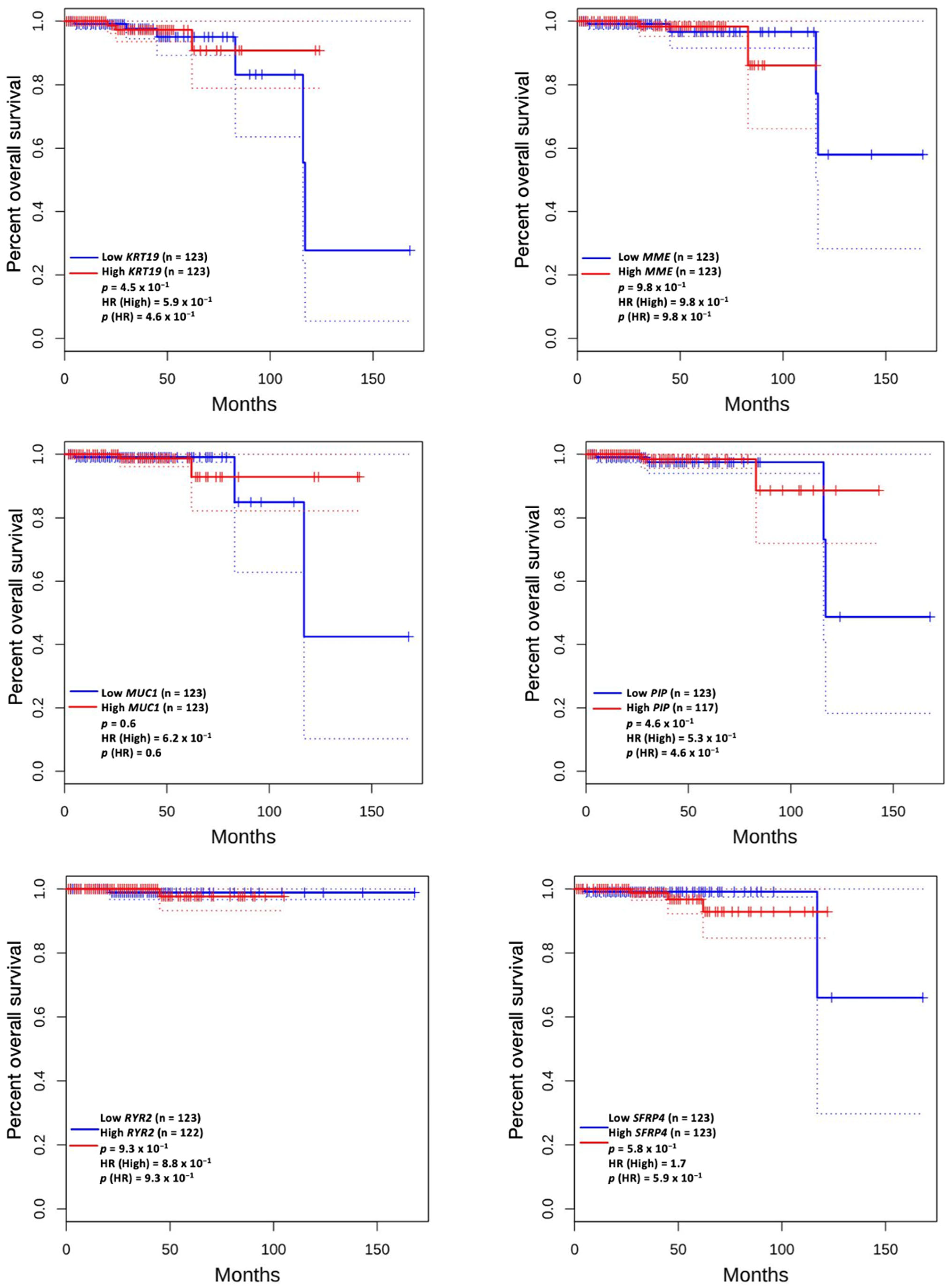
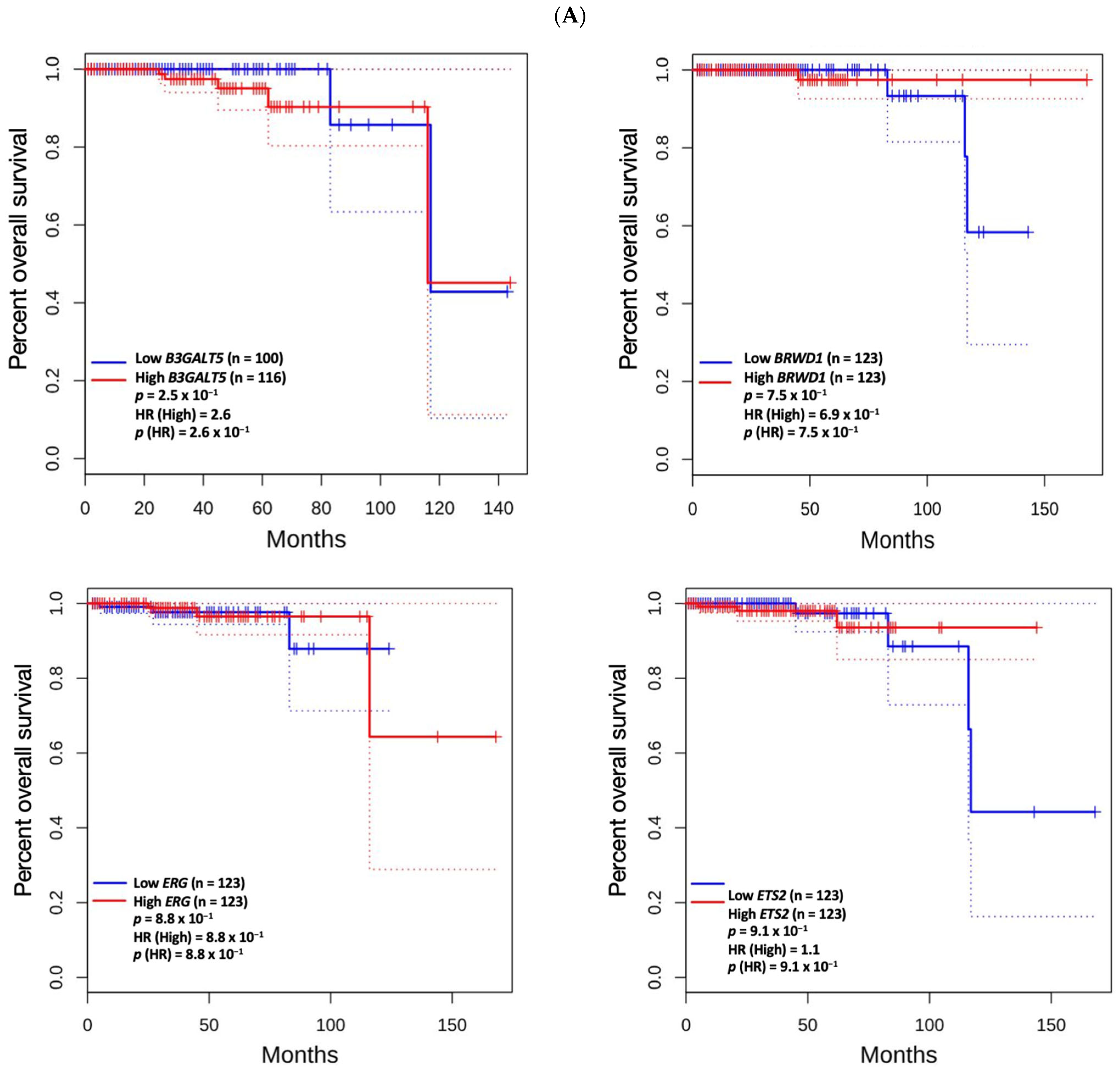
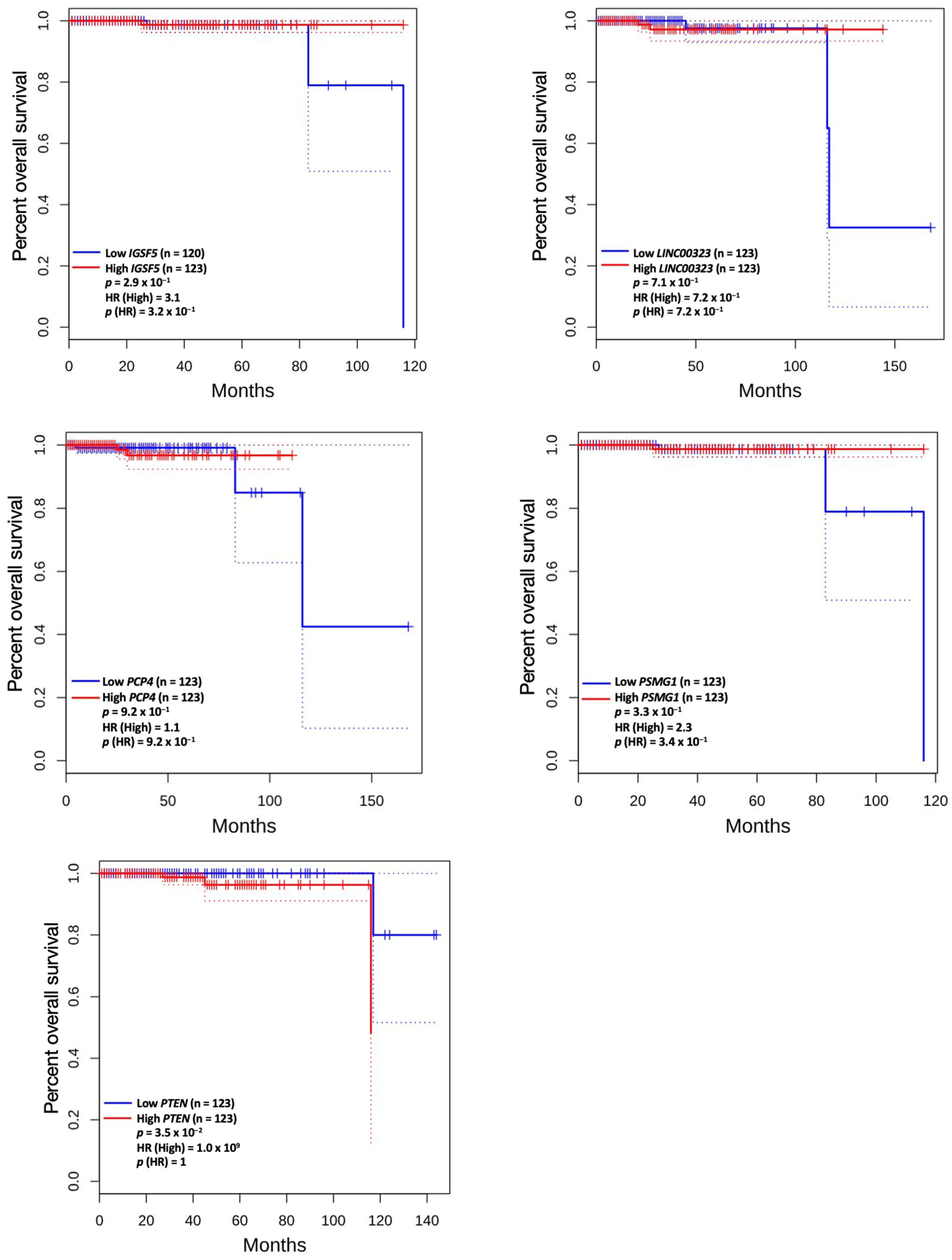
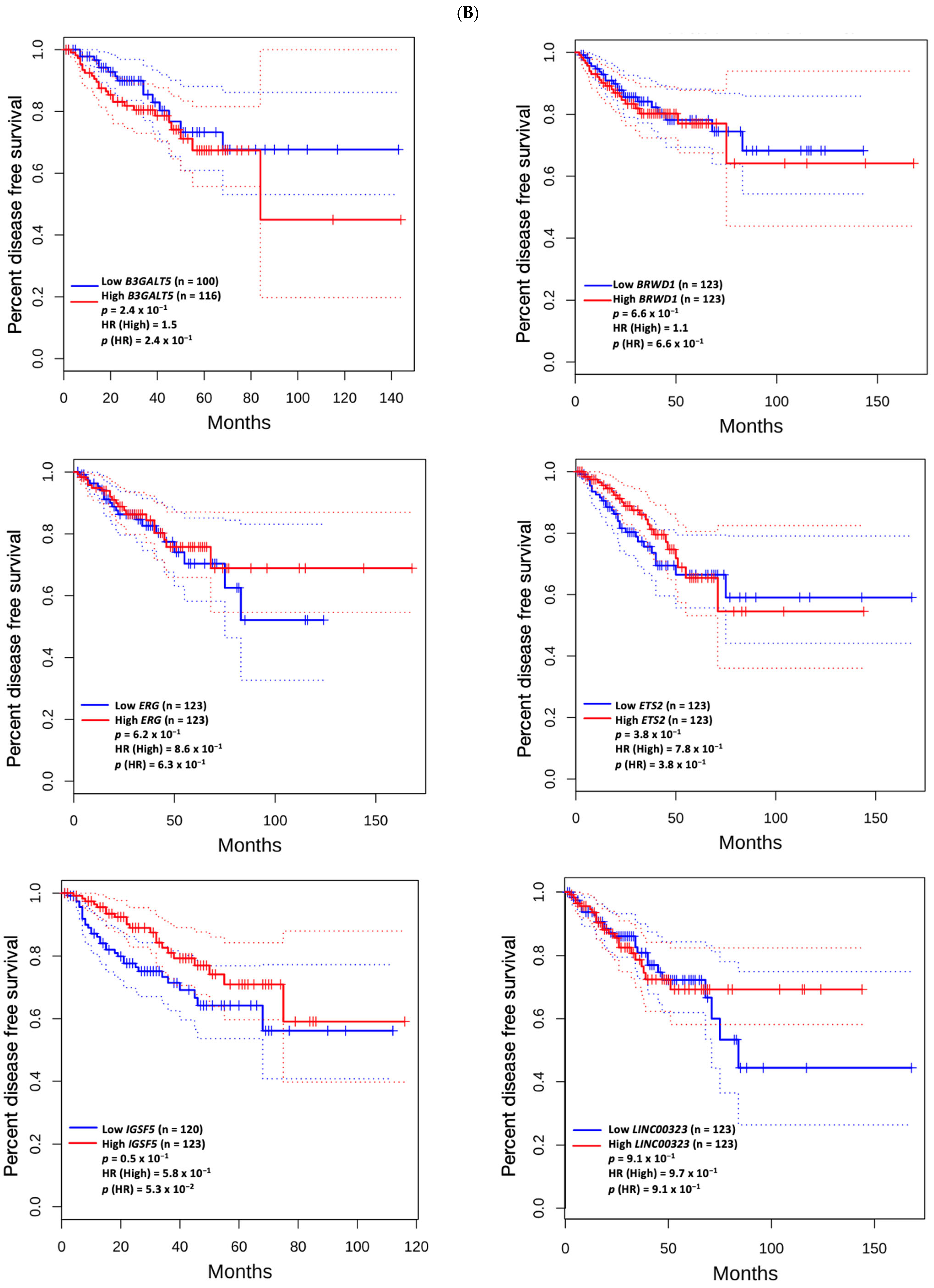
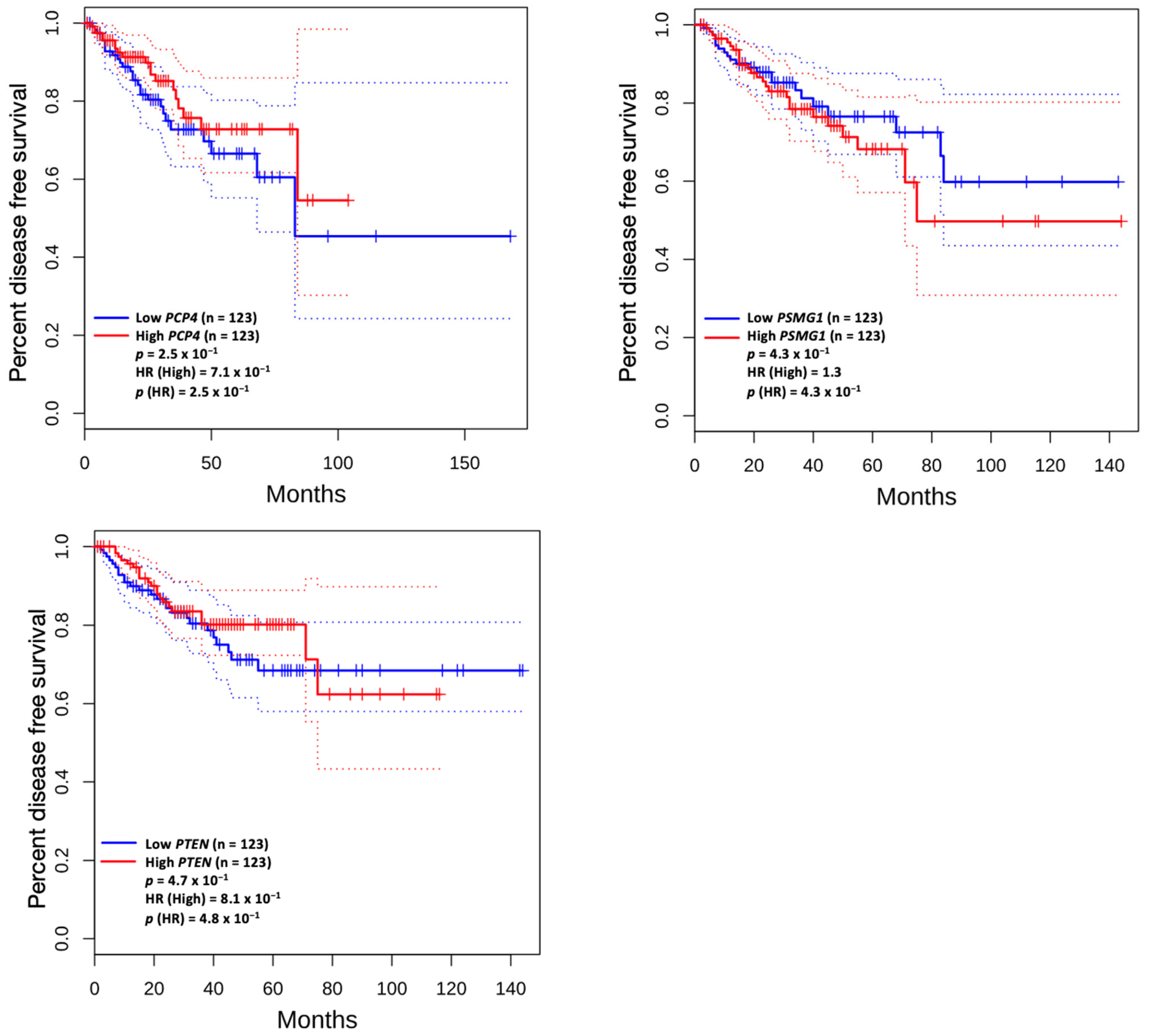
3.5. Prognostic Value of Genetic Alteration and Hub Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PNI | perineural invasion |
| TCGA | the cancer genome atlas |
| NGS | next-generation sequencing |
| FFPE | formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded |
| RSEM | RNA-seq by expectation-maximization |
| DEGs | differentially expressed genes |
| PPI | protein–protein interaction |
| STRING | search tool for the retrieval of interacting genes |
| MCODE | molecular complex detection |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| WP | WikiPathways |
| OS | overall survival |
| DFS | disease-free survival |
References
- Shoag, J.; Barbieri, C.E. Clinical variability and molecular heterogeneity in prostate cancer. Asian J. Androl. 2016, 18, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Ettinger, S.L.; Qu, S.; Xue, H.; Nabavi, N.; Choi, S.Y.C.; Bell, R.H.; Mo, F.; Haegert, A.M.; Gout, P.W.; et al. Metabolic heterogeneity signature of primary treatment-naïve prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 25928–25941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brönimann, S.; Pradere, B.; Karakiewicz, P.; Abufaraj, M.; Briganti, A.; Shariat, S.F. An overview of current and emerging diagnostic, staging and prognostic markers for prostate cancer. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 20, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, K.; Beltran, H. Future directions for precision oncology in prostate cancer. Prostate 2022, 82 (Suppl. S1), S86–S96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozzi, G.; Rocco, B.M.; Grasso, A.; Rosso, M.; Abed El Rahman, D.; Oliva, I.; Talso, M.; Costa, B.; Tafa, A.; Palumbo, C.; et al. Perineural invasion as a predictor of extraprostatic extension of prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand. J. Urol. 2013, 47, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.T.; Lee, S.; Yun, C.J.; Jeon, B.J.; Kim, J.M.; Ha, H.K.; Lee, W.; Chung, M.K. Prediction of perineural invasion and its prognostic value in patients with prostate cancer. Korean J. Urol. 2010, 51, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tollefson, M.K.; Karnes, R.J.; Kwon, E.D.; Lohse, C.M.; Rangel, L.J.; Mynderse, L.A.; Cheville, J.C.; Sebo, T.J. Prostate cancer Ki-67 (MIB-1) expression, perineural invasion, and gleason score as biopsy-based predictors of prostate cancer mortality: The Mayo model. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2014, 89, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teramoto, Y.; Numbere, N.; Wang, Y.; Miyamoto, H. Clinical Significance of Perineural Invasion by Prostate Cancer Detected on Needle Core Biopsy. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2023, 159, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeb, S.; Epstein, J.I.; Humphreys, E.B.; Walsh, P.C. Does perineural invasion on prostate biopsy predict adverse prostatectomy outcomes? BJU Int. 2010, 105, 1510–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zareba, P.; Flavin, R.; Isikbay, M.; Rider, J.R.; Gerke, T.A.; Finn, S.; Pettersson, A.; Giunchi, F.; Unger, R.H.; Tinianow, A.M.; et al. Perineural Invasion and Risk of Lethal Prostate Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2017, 26, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fromont, G.; Godet, J.; Pires, C.; Yacoub, M.; Dore, B.; Irani, J. Biological significance of perineural invasion (PNI) in prostate cancer. Prostate 2012, 72, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. The Molecular Taxonomy of Primary Prostate Cancer. Cell 2015, 163, 1011–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bruijn, I.; Kundra, R.; Mastrogiacomo, B.; Tran, T.N.; Sikina, L.; Mazor, T.; Li, X.; Ochoa, A.; Zhao, G.; Lai, B.; et al. Analysis and Visualization of Longitudinal Genomic and Clinical Data from the AACR Project GENIE Biopharma Collaborative in cBioPortal. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 3861–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Franceschini, A.; Wyder, S.; Forslund, K.; Heller, D.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Roth, A.; Santos, A.; Tsafou, K.P.; et al. STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D447–D452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader, G.D.; Hogue, C.W.V. An automated method for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinform. 2003, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, C.H.; Chen, S.H.; Wu, H.H.; Ho, C.W.; Ko, M.T.; Lin, C.Y. cytoHubba: Identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst. Biol. 2014, 8 (Suppl. 4), S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raudvere, U.; Kolberg, L.; Kuzmin, I.; Arak, T.; Adler, P.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J. g:Profiler: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists (2019 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W191–W198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoabi, Y.; Shomron, N. Processing and Analysis of RNA-seq Data from Public Resources. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2243, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Warner, M.; Wang, L.; He, W.W.; Zhao, R.; Guan, X.; Botero, C.; Huang, B.; Ion, C.; Coombes, C.; et al. Drivers and suppressors of triple-negative breast cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2104162118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, C.; Wu, M.; Chen, G.; Yu, G.; Ji, D.; Wang, S. Identification of molecular characteristics induced by radiotherapy in rectal cancer based on microarray data. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 2777–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; He, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, W.; Jiang, L.; Yan, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, S.; et al. Identification of potential key genes and pathways predicting pathogenesis and prognosis for triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkus-Adamczyk, K.; Brodaczewska, K.; Majewska, A.; Kieda, C. Microenvironment commits breast tumor ECs to dedifferentiation by micro-RNA-200-b-3p regulation and extracellular matrix remodeling. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1125077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochette, A.; Boufaied, N.; Scarlata, E.; Hamel, L.; Brimo, F.; Whitaker, H.C.; Ramos-Montoya, A.; Neal, D.E.; Dragomir, A.; Aprikian, A.; et al. Asporin is a stromally expressed marker associated with prostate cancer progression. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, C.; Chang, Y.; Bian, Z.; Zhao, X. Impact of NR5A2 and RYR2 3’UTR polymorphisms on the risk of breast cancer in a Chinese Han population. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 183, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maris, P.; Blomme, A.; Palacios, A.P.; Costanza, B.; Bellahcène, A.; Bianchi, E.; Gofflot, S.; Drion, P.; Trombino, G.E.; Di Valentin, E.; et al. Asporin Is a Fibroblast-Derived TGF-β1 Inhibitor and a Tumor Suppressor Associated with Good Prognosis in Breast Cancer. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Min, L.; Li, H.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, S.; Guo, Q.; Zhu, S.; Li, P.; Zhang, S. Asporin represses gastric cancer apoptosis via activating LEF1-mediated gene transcription independent of β-catenin. Oncogene 2021, 40, 4552–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakan, S.; Leduc, Y.; Lamarre, D.; Brunet, G.; Poirier, G.G. Immunoelectron microscopical distribution of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase in the mammalian cell nucleus. Exp. Cell Res. 1988, 179, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, H.B.; Li, J.; Meniel, V.S.; Fennell, C.M.; Waring, P.; Montgomery, K.G.; Rebello, R.J.; Macpherson, A.A.; Koushyar, S.; Furic, L.; et al. Identification of Pik3ca Mutation as a Genetic Driver of Prostate Cancer That Cooperates with Pten Loss to Accelerate Progression and Castration-Resistant Growth. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 764–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulholland, D.J.; Tran, L.M.; Li, Y.; Cai, H.; Morim, A.; Wang, S.; Plaisier, S.; Garraway, I.P.; Huang, J.; Graeber, T.G.; et al. Cell autonomous role of PTEN in regulating castration-resistant prostate cancer growth. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 792–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armenia, J.; Wankowicz, S.A.M.; Liu, D.; Gao, J.; Kundra, R.; Reznik, E.; Chatila, W.K.; Chakravarty, D.; Han, G.C.; Coleman, I.; et al. The long tail of oncogenic drivers in prostate cancer. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, A.P.G.; Cavalheiro, R.P.; Porto, C.S.; Vicente, C.M. Estrogen Receptor Signaling Pathways Involved in Invasion and Colony Formation of Androgen-Independent Prostate Cancer Cells PC-3. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonkhoff, H.; Fixemer, T.; Hunsicker, I.; Remberger, K. Estrogen receptor expression in prostate cancer and premalignant prostatic lesions. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonkhoff, H. Estrogen receptor signaling in prostate cancer: Implications for carcinogenesis and tumor progression. Prostate 2018, 78, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yegnasubramanian, S.; Kowalski, J.; Gonzalgo, M.L.; Zahurak, M.; Piantadosi, S.; Walsh, P.C.; Bova, G.S.; De Marzo, A.M.; Isaacs, W.B.; Nelson, W.G. Hypermethylation of CpG islands in primary and metastatic human prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 1975–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, A.E. Can a single model explain both breast cancer and prostate cancer? Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 2007, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Huang, H. Interplay Among PI3K/AKT, PTEN/FOXO and AR Signaling in Prostate Cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1210, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnero, A. The PKB/AKT pathway in cancer. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnero, A.; Blanco-Aparicio, C.; Renner, O.; Link, W.; Leal, J.F. The PTEN/PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in cancer, therapeutic implications. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2008, 8, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhao, J.; Sun, J.; Tian, C.; Jiang, Q.; Ding, C.; Gan, Q.; Shu, P.; Wang, X.; Qin, J.; et al. Demethylation of the SFRP4 Promoter Drives Gastric Cancer Progression via the Wnt Pathway. Mol. Cancer Res. 2021, 19, 1454–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernreuther, C.; Daghigh, F.; Möller, K.; Hube-Magg, C.; Lennartz, M.; Lutz, F.; Rico, S.D.; Fraune, C.; Dum, D.; Luebke, A.M.; et al. Secreted Frizzled-Related Protein 4 (SFRP4) Is an Independent Prognostic Marker in Prostate Cancers Lacking TMPRSS2: ERG Fusions. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2020, 26, 2709–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandsmark, E.; Andersen, M.K.; Bofin, A.M.; Bertilsson, H.; Drabløs, F.; Bathen, T.F.; Rye, M.B.; Tessem, M.B. SFRP4 gene expression is increased in aggressive prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.; He, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, C.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bao, Z.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, R.; Cao, M.; et al. SFRP4 Is a Potential Biomarker for the Prognosis and Immunotherapy for Gastric Cancer. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 8829649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.W.; Tao, L.Y.; Yang, J.Y.; Jiang, Y.S.; Fu, X.L.; Liu, W.; Huo, Y.M.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.F.; Hua, R.; et al. SFRP4 is a prognostic marker and correlated with Treg cell infiltration in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Yu, B.; Deng, Y.; Sheng, W.; Peng, Z.; Qin, W.; Du, X. SFRP4 was overexpressed in colorectal carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 136, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Cao, K.; Han, T.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhang, G.T.; Xu, L.F.; Lian, H.B.; Li, X.G.; Guo, H.Q. Perineural invasion status, Gleason score and number of positive cores in biopsy pathology are predictors of positive surgical margin following laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Asian J. Androl. 2017, 19, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Atti, L. Prognostic significance of perineural invasion in patients who underwent radical prostatectomy for localized prostate cancer. J. BUON 2016, 21, 1219–1223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kobylewski, S.E.; Henderson, K.A.; Eckhert, C.D. Identification of ryanodine receptor isoforms in prostate DU-145, LNCaP, and PWR-1E cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 425, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eminaga, O.; Wei, W.; Hawley, S.J.; Auman, H.; Newcomb, L.F.; Simko, J.; Hurtado-Coll, A.; Troyer, D.A.; Carroll, P.R.; Gleave, M.E.; et al. MUC1 Expression by Immunohistochemistry Is Associated with Adverse Pathologic Features in Prostate Cancer: A Multi-Institutional Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risk, M.C.; Knudsen, B.S.; Coleman, I.; Dumpit, R.F.; Kristal, A.R.; LeMeur, N.; Gentleman, R.C.; True, L.D.; Nelson, P.S.; Lin, D.W. Differential gene expression in benign prostate epithelium of men with and without prostate cancer: Evidence for a prostate cancer field effect. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 5414–5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, J.O.; White, J.; Elhussin, I.; Duduyemi, B.M.; Karanam, B.; Yates, C.; Wang, H. Molecular and pathological subtypes related to prostate cancer disparities and disease outcomes in African American and European American patients. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 928357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, S.C.; Nagel, S.; Junginger, J.; Hewicker-Trautwein, M.; Wagner, S.; Heisterkamp, A.; Ngezahayo, A.; Nolte, I.; Murua Escobar, H. Claudin-1, -3, -4 and -7 gene expression analyses in canine prostate carcinoma and mammary tissue derived cell lines. Neoplasma 2016, 63, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, R.M.; Qiu, Z.; Marti, G.E.W.; Peterson, E.E.; Marques, F.J.G.; Bermudez, A.; Wei, Y.; Nolley, R.; Lam, N.; Polasko, A.L.; et al. AZGP1 deficiency promotes angiogenesis in prostate cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aktan, C.; Mamidanna, S.; Cobb, C.; Atalar, C.; Chan, J.; Breneman, C.M.; Argun, O.; Sayan, M. Transcriptomic Profile of Perineural Invasion in Prostate Cancer Identifies Prognostic Gene Signatures. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081789
Aktan C, Mamidanna S, Cobb C, Atalar C, Chan J, Breneman CM, Argun O, Sayan M. Transcriptomic Profile of Perineural Invasion in Prostate Cancer Identifies Prognostic Gene Signatures. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(8):1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081789
Chicago/Turabian StyleAktan, Cagdas, Swati Mamidanna, Caryn Cobb, Ceren Atalar, Jacqueline Chan, Christina M. Breneman, Okan Argun, and Mutlay Sayan. 2025. "Transcriptomic Profile of Perineural Invasion in Prostate Cancer Identifies Prognostic Gene Signatures" Biomedicines 13, no. 8: 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081789
APA StyleAktan, C., Mamidanna, S., Cobb, C., Atalar, C., Chan, J., Breneman, C. M., Argun, O., & Sayan, M. (2025). Transcriptomic Profile of Perineural Invasion in Prostate Cancer Identifies Prognostic Gene Signatures. Biomedicines, 13(8), 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081789





