Efficacy of EA575 as an Antitussive and Mucoactive Agent in Preclinical In Vivo Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Test Item
2.3. Basic Information on In Vivo Studies
2.4. Antitussive Evaluation In Vivo
2.4.1. Animal Housing and Randomization
2.4.2. Bleomycin Challenge and Treatment
2.4.3. Tussive Assay and Enhanced Pause Assessment
2.4.4. Bronchoalveolar Lavage—Cell Counts
2.5. Mucoactivity Assessment In Vivo
2.5.1. Animal Housing and Randomization
2.5.2. Treatment
2.5.3. Determination of Phenol Red in BALF
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
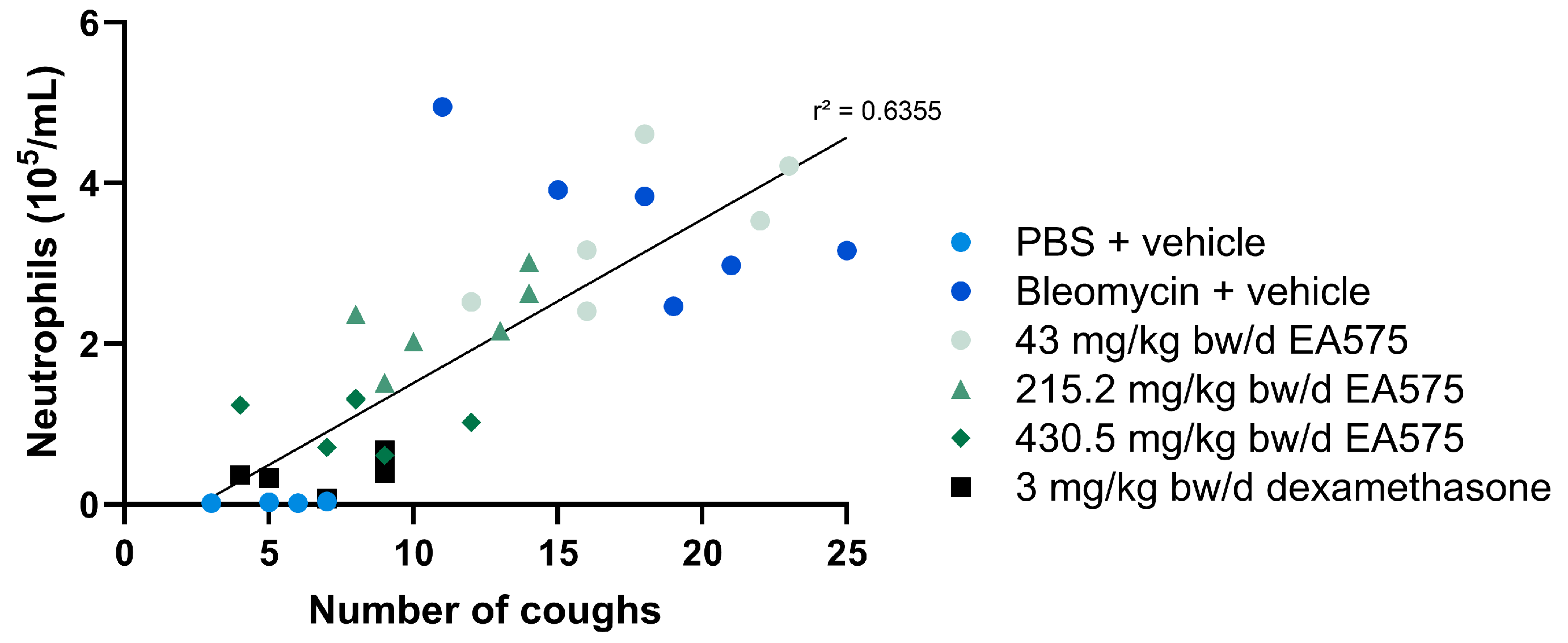
3.1. EA575 Reduces Cough Events in Acute Lung Inflammation Model
3.2. EA575 Alleviates Inflammatory Cell Influx in BALF of an Acute Lung Inflammation Model
3.3. EA575 Attenuates Enhanced Pause in Acute Lung Inflammation Model
3.4. EA575 Increases Phenol Red Secretion in BALF
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BALF | Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid |
| BLM | Bleomycin |
| bw | Body weight |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PRR | Pattern-recognition receptor |
| RSV | Respiratory syncytial virus |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
References
- EMA. Assessment Report on Hedera helix L., Folium. In EMA/HMPC/325715/2017; Committee on Herbal Medicinal Products (HMPC): Amsterdam, the Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Seifert, G.; Upstone, L.; Watling, C.P.; Vogelberg, C. Ivy Leaf Dry Extract Ea 575 for the Treatment of Acute and Chronic Cough in Pediatric Patients: Review and Expert Survey. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2023, 39, 1407–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Völp, A.; Schmitz, J.; Bulitta, M.; Raskopf, E.; Acikel, C.; Mösges, R. Ivy Leaves Extract Ea 575 in the Treatment of Cough during Acute Respiratory Tract Infections: Meta-Analysis of Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trials. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardos, P.; Dinh, Q.T.; Fuchs, K.H.; Gillissen, A.; Klimek, L.; Koehler, M.; Sitter, H.; Worth, H. German Respiratory Society Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Adults Suffering from Acute, Subacute and Chronic Cough. Respir. Med. 2020, 170, 105939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greunke, C.; Hage-Hulsmann, A.; Sorkalla, T.; Keksel, N.; Haberlein, F.; Haberlein, H. A Systematic Study on the Influence of the Main Ingredients of an Ivy Leaves Dry Extract on the Beta2-Adrenergic Responsiveness of Human Airway Smooth Muscle Cells. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 31, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte-Michels, J.; Runkel, F.; Gokorsch, S.; Haberlein, H. Ivy Leaves Dry Extract Ea 575® Decreases Lps-Induced Il-6 Release from Murine Macrophages. Pharmazie 2016, 71, 158–161. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Meurer, F.; Häberlein, H.; Franken, S. Ivy Leaf Dry Extract Ea 575® Has an Inhibitory Effect on the Signalling Cascade of Adenosine Receptor A2b. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čolić, M.; Tomić, S.; Bekić, M.; Dubovina, A.; Häberlein, H.; Rademaekers, A.; Mašić, S.; Bokonjić, D. Ivy Leaf Dry Extract Ea 575® Is a Potent Immunomodulator Acting on Dendritic Cells. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meurer, F.; Schulte-Michels, J.; Haberlein, H.; Franken, S. Ivy Leaves Dry Extract Ea 575® Mediates Biased Β2-Adrenergic Receptor Signaling. Phytomedicine 2021, 90, 153645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte-Michels, J.; Keksel, C.; Haberlein, H.; Franken, S. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Ivy Leaves Dry Extract: Influence on Transcriptional Activity of Nfkappab. Inflammopharmacology 2019, 27, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussmann, H.; Schulte-Michels, J.; Bingel, M.; Meurer, F.; Aatz, S.; Haberlein, F.; Franken, S.; Haberlein, H. A Comparative Study on the Influence of an Ivy Preparation and an Ivy/Thyme Combination on the Beta2-Adrenergic Signal Transduction. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giembycz, M.A.; Newton, R. Beyond the Dogma: Novel Beta2-Adrenoceptor Signalling in the Airways. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 27, 1286–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmotte, P.; Ressmeyer, A.R.; Bai, Y.; Sanderson, M.J. Mechanisms of Airway Smooth Muscle Relaxation Induced by Β2-Adrenergic Agonists. Front. Biosci.-Landmark 2010, 15, 750–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, S.A. Regulation of Surfactant Secretion. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.-Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2001, 129, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokry, A.A.; El-Shiekh, R.A.; Kamel, G.; Bakr, A.F.; Ramadan, A. Bioactive Phenolics Fraction of Hedera helix L. (Common Ivy Leaf) Standardized Extract Ameliorates Lps-Induced Acute Lung Injury in the Mouse Model through the Inhibition of Proinflammatory Cytokines and Oxidative Stress. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, P.M.N.; Brito, M.C.; de Sá, P.G.S.; Ribeiro, L.A.A.; Rolim, L.A.; Silva, F.S. Analytical and Pharmacological Validation of the Quantification of Phenol Red in a Mouse Model: An Optimized Method to Evaluate Expectorant Drugs. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2019, 98, 106586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plevkova, J.; Brozmanova, M.; Matloobi, A.; Poliacek, I.; Honetschlager, J.; Buday, T. Animal Models of Cough. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2021, 290, 103656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordag, N.; Biasin, V.; Schnoegl, D.; Valzano, F.; Jandl, K.; Nagy, B.M.; Sharma, N.; Wygrecka, M.; Kwapiszewska, G.; Marsh, L.M. Machine Learning Analysis of the Bleomycin Mouse Model Reveals the Compartmental and Temporal Inflammatory Pulmonary Fingerprint. iScience 2020, 23, 101819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, P.; Upagupta, C.; Vierhout, M.; Ayaub, E.; Bellaye, P.S.; Gauldie, J.; Shimbori, C.; Inman, M.; Ask, K.; Kolb, M.R.J. The Importance of Interventional Timing in the Bleomycin Model of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1901105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, N.I.; Schnapp, A.; Park, J.E. Pharmacologic Differentiation of Inflammation and Fibrosis in the Rat Bleomycin Model. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izbicki, G.; Segel, M.J.; Christensen, T.G.; Conner, M.W.; Breuer, R. Time Course of Bleomycin-Induced Lung Fibrosis. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2002, 83, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumo, T.; Kondo, M.; Nagai, A. Effects of a Leukotriene B4 Receptor Antagonist on Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 34, 1444–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Ying, S.; Wang, Y. Increased Expression of Transient Receptor Potential Channels and Neurogenic Factors Associates with Cough Severity in a Guinea Pig Model. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Ying, S.; Zhao, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. Increased Expression of Lung Trpv1/Trpa1 in a Cough Model of Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Guinea Pigs. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqvi, K.F.; Mazzone, S.B.; Shiloh, M.U. Infectious and Inflammatory Pathways to Cough. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2023, 85, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Zhou, W.; Sun, J.; Li, C.; Zhong, B.; Lai, K. Ifn-Γ Enhances the Cough Reflex Sensitivity Via Calcium Influx in Vagal Sensory Neurons. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 868–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGovern, A.E.; Short, K.R.; Kywe Moe, A.A.; Mazzone, S.B. Translational Review: Neuroimmune Mechanisms in Cough and Emerging Therapeutic Targets. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 1392–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, C.; Staiger, C.; Wegener, T. Ivy in Everyday Paediatric Use: Administration of Ea 575® to Schoolchildren for the Treatment of Acute Bronchitis. Z. Für Phytother. 2015, 36, 192–196. [Google Scholar]
- Oróstegui, D.M.; Sánchez-Vanegas, G.; Castro, F.V.; Manzanares, A.B.; Monterrosa-Blanco, A.; Castro, G.E.; Narvaez, A.G.V. Clinical Evolution of Acute Bronchitis In colombian Children between 2 and 14 Years Treated with Hedera helix Ea575 Syrup. Rev. Colomb. Cienc. Quim.-Farm. 2023, 52, 781–795. [Google Scholar]
- Hamelmann, E.; Schwarze, J.; Takeda, K.; Oshiba, A.; Larsen, G.L.; Irvin, C.G.; Gelfand, E.W. Noninvasive Measurement of Airway Responsiveness in Allergic Mice Using Barometric Plethysmography. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 156, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheijden, K.A.; Henricks, P.A.; Redegeld, F.A.; Garssen, J.; Folkerts, G. Measurement of Airway Function Using Invasive and Non-Invasive Methods in Mild and Severe Models for Allergic Airway Inflammation in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundblad, L.K.A.; Irvin, C.G.; Hantos, Z.; Sly, P.; Mitzner, W.; Bates, J.H.T. Penh Is Not a Measure of Airway Resistance! Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 30, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, K.S.; Song, H.K.; Hwang, Y.H.; Chae, S.; Kim, H.K.; Jang, S.; Kim, Y.H.; Choo, B.K.; Yang, W.K.; Kim, S.H.; et al. Ethanol Extract of Veronica Persica Ameliorates House Dust Mite-Induced Asthmatic Inflammation by Inhibiting Stat-3 and Stat-6 Activation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 152, 113264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyss, D.; Bonneau, O.; Trifilieff, A. Synergistic Effect of Formoterol and Mometasone in a Mouse Model of Allergic Lung Inflammation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 152, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriquez, A.R.; Snow, S.J.; Schladweiler, M.C.; Miller, C.N.; Dye, J.A.; Ledbetter, A.D.; Richards, J.E.; Mauge-Lewis, K.; McGee, M.A.; Kodavanti, U.P. Adrenergic and Glucocorticoid Receptor Antagonists Reduce Ozone-Induced Lung Injury and Inflammation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 339, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condor Capcha, J.M.; Kamiar, A.; Robleto, E.; Saad, A.G.; Cui, T.; Wong, A.; Villano, J.; Zhong, W.; Pekosz, A.; Medina, E.; et al. Growth Hormone–Releasing Hormone Receptor Antagonist Mia-602 Attenuates Cardiopulmonary Injury Induced by Bsl-2 Rvsv-Sars-Cov-2 in Hace2 Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2308342120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menachery, V.D.; Gralinski, L.E.; Baric, R.S.; Ferris, M.T. New Metrics for Evaluating Viral Respiratory Pathogenesis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tang, X.X. Abnormal Airway Mucus Secretion Induced by Virus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 701443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, B.K. Secretion Properties, Clearance, and Therapy in Airway Disease. Transl. Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsamo, R.; Lanata, L.; Egan, C.G. Mucoactive Drugs. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2010, 19, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, C.; Rottger-Luer, P.; Staiger, C. A Valuable Option for the Treatment of Respiratory Diseases: Review on the Clinical Evidence of the Ivy Leaves Dry Extract Ea 575(R). Planta Medica 2015, 81, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, A.; Kehr, M.S.; Giannetti, B.M.; Bulitta, M.; Staiger, C. A Randomized, Controlled, Double-Blind, Multi-Center Trial to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of a Liquid Containing Ivy Leaves Dry Extract (Ea 575®) Vs. Placebo in the Treatment of Adults with Acute Cough. Die Pharm. 2016, 71, 504–509. [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer, A.; Ludwig, F.; Giannetti, B.M.; Bulitta, M.; Wacker, A. Efficacy of Two Dosing Schemes of a Liquid Containing Ivy Leaves Dry Extract Ea 575 Versus Placebo in the Treatment of Acute Bronchitis in Adults. ERJ Open Res. 2019, 5, 00019–02019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malerba, M.; Ragnoli, B. Ambroxol in the 21st Century: Pharmacological and Clinical Update. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2008, 4, 1119–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delavoie, F.; Molinari, M.; Milliot, M.; Zahm, J.M.; Coraux, C.; Michel, J.; Balossier, G. Salmeterol Restores Secretory Functions in Cystic Fibrosis Airway Submucosal Gland Serous Cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2009, 40, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte-Michels, J.; Wolf, A.; Aatz, S.; Engelhard, K.; Sieben, A.; Martinez-Osuna, M.; Häberlein, F.; Häberlein, H. α-Hederin Inhibits G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2-Mediated Phosphorylation of β2-Adrenergic Receptors. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieben, A.; Prenner, L.; Sorkalla, T.; Wolf, A.; Jakobs, D.; Runkel, F.; Häberlein, H. α-Hederin, but Not Hederacoside C and Hederagenin from Hedera helix, Affects the Binding Behavior, Dynamics, and Regulation of β2-Adrenergic Receptors. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 3477–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hufnagel, M.; Rademaekers, A.; Weisert, A.; Häberlein, H.; Franken, S. Efficacy of EA575 as an Antitussive and Mucoactive Agent in Preclinical In Vivo Models. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071673
Hufnagel M, Rademaekers A, Weisert A, Häberlein H, Franken S. Efficacy of EA575 as an Antitussive and Mucoactive Agent in Preclinical In Vivo Models. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(7):1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071673
Chicago/Turabian StyleHufnagel, Matthias, André Rademaekers, Anika Weisert, Hanns Häberlein, and Sebastian Franken. 2025. "Efficacy of EA575 as an Antitussive and Mucoactive Agent in Preclinical In Vivo Models" Biomedicines 13, no. 7: 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071673
APA StyleHufnagel, M., Rademaekers, A., Weisert, A., Häberlein, H., & Franken, S. (2025). Efficacy of EA575 as an Antitussive and Mucoactive Agent in Preclinical In Vivo Models. Biomedicines, 13(7), 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071673






