Serum Levels of Human Neutrophil Peptides 1–3 (HNP1–3) as Potential Biomarkers in Psoriasis and Associated Comorbidities
Abstract
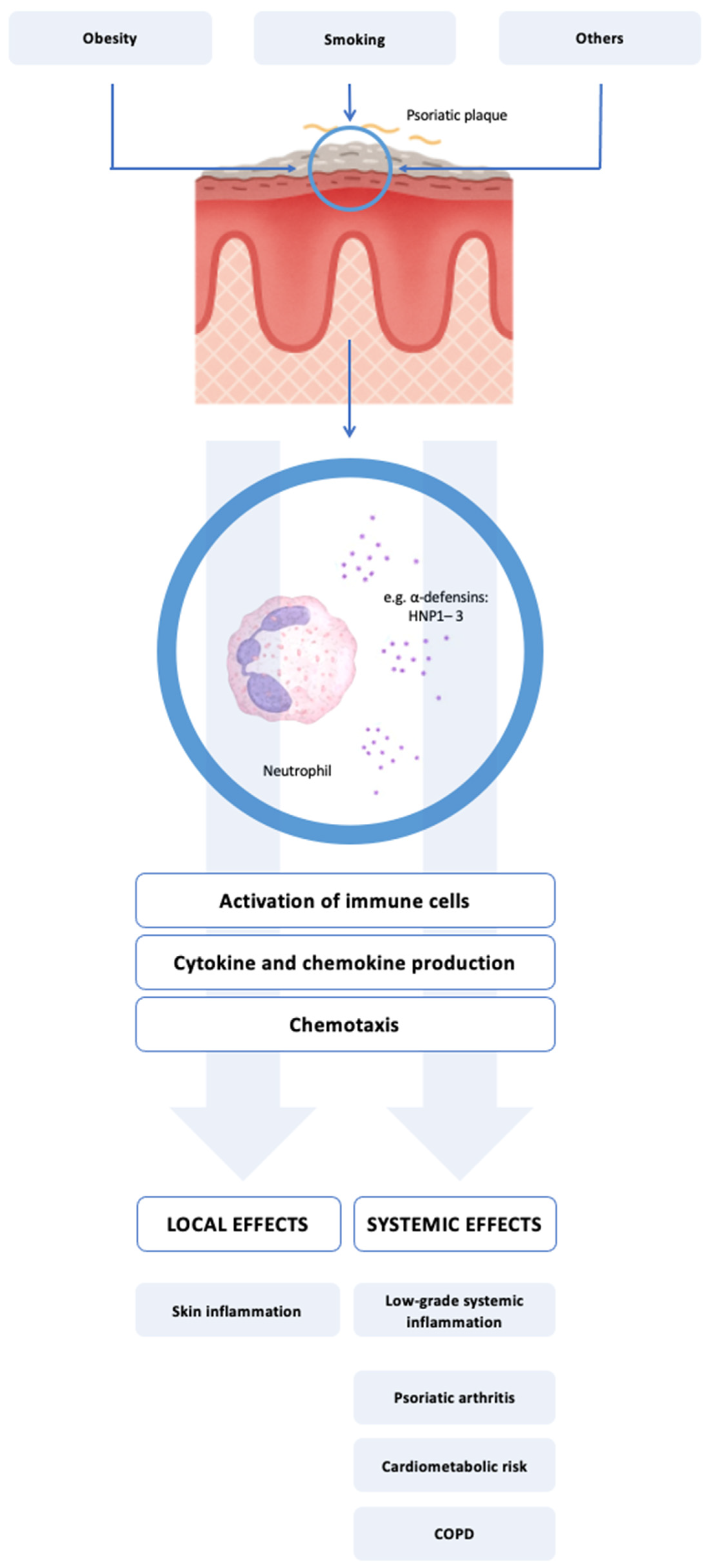
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Characteristics of the Study Population
2.3. Clinical Assessment
2.4. Blood Sample Collection and Biochemical Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Serum HNP1–3 Levels and Selected Comorbid Conditions
3.3. Serum HNP1–3 Levels and Their Association with Clinical Parameters
3.4. Serum HNP1–3 Levels and Their Association with Biochemical Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Relevance of Elevated HNP1–3 in Psoriasis and PsA
4.2. Associations with Clinical Features: WHR and Smoking
4.3. Correlations with Inflammatory Biomarkers
4.4. Mechanistic Implications: HNP1–3 as Immunomodulatory Mediators
4.5. Relevance in Psoriatic Arthritis and Other Comorbidities
4.6. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boehncke, W.H.; Schön, M.P. Psoriasis. Lancet 2015, 386, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendon, A.; Schäkel, K. Psoriasis Pathogenesis and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daudén, E.; Castañeda, S.; Suárez, C.; García-Campayo, J.; Blasco, A.J.; Aguilar, M.D.; Ferrándiz, C.; Puig, L.; Sánchez-Carazo, J.L. Clinical Practice Guideline for an Integrated Approach to Comorbidity in Patients with Psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2013, 27, 1387–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-T.; Yeh, H.-M.; Liu, S.-Y.; Chen, K.-T. Psoriatic Arthritis: Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. World J. Orthop. 2014, 5, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coto-Segura, P.; Eiris-Salvado, N.; González-Lara, L.; Queiro-Silva, R.; Martinez-Camblor, P.; Maldonado-Seral, C.; García-García, B.; Palacios-García, L.; Gomez-Bernal, S.; Santos-Juanes, J.; et al. Psoriasis, Psoriatic Arthritis and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 169, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Harskamp, C.T.; Armstrong, E.J. The Association between Psoriasis and Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. J. Hypertens. 2013, 31, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Harskamp, C.T.; Armstrong, E.J. The Association between Psoriasis and Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Nutr. Diabetes 2012, 2, e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, I.M.; Ellervik, C.; Yazdanyar, S.; Jemec, G.B.E. Meta-Analysis of Psoriasis, Cardiovascular Disease, and Associated Risk Factors. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 69, 1014–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.J.; Weng, C.L.; Zhao, Y.T.; Liu, Q.H.; Yin, R.X. Psoriasis and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 4992–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Voort, E.A.M.; Koehler, E.M.; Dowlatshahi, E.A.; Hofman, A.; Stricker, B.H.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Schouten, J.N.L.; Nijsten, T. Psoriasis Is Independently Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients 55 Years Old or Older: Results from a Population-Based Study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 70, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Lee, C.-H.; Chi, C.-C. Association of Psoriasis With Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2018, 154, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ke, R.; Shi, W.; Yan, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Chai, L.; Li, M. Association between Psoriasis and Asthma Risk: A Meta-Analysis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2018, 39, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungprasert, P.; Srivali, N.; Thongprayoon, C. Association between Psoriasis and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2016, 27, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kong, L.; Li, F.; Chen, C.; Xu, R.; Wang, H.; Peng, S.; Zhou, M.; Li, B. Association between Psoriasis and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ger, T.-Y.; Fu, Y.; Chi, C.-C. Bidirectional Association Between Psoriasis and Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.M.; Famenini, S.; Wu, J.J. Incidence of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Patients with Psoriasis: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Perm. J. 2017, 21, 16–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mleczko, M.; Gerkowicz, A.; Krasowska, D. Co-Occurrence of Psoriasis and Asthma in the Pediatric Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, G.; Dua, S.; Mathur, A.; Acquah, S.O.; Salvatore, M.; Beasley, M.B.; Padilla, M.L. Concomitant Interstitial Lung Disease with Psoriasis. Can. Respir. J. 2019, 2019, 5919304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, U.; Gislason, G.H.; Hansen, P.R. Sarcoidosis in Patients with Psoriasis: A Population-Based Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukmanji, A.; Basmadjian, R.B.; Vallerand, I.A.; Patten, S.B.; Tang, K.L. Risk of Depression in Patients With Psoriatic Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2021, 25, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, J.; Ding, R.; Zhou, L.; Chen, X.; Shen, E. Epidemiology of Psoriasis and Comorbid Diseases: A Narrative Review. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 880201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowes, M.A.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Krueger, J.G. Immunology of Psoriasis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 227–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Cid, R.; Riveira-Munoz, E.; Zeeuwen, P.L.J.M.; Robarge, J.; Liao, W.; Dannhauser, E.N.; Giardina, E.; Stuart, P.E.; Nair, R.; Helms, C.; et al. Deletion of the Late Cornified Envelope LCE3B and LCE3C Genes as a Susceptibility Factor for Psoriasis. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilchie, A.L.; Wuerth, K.; Hancock, R.E.W. Immune Modulation by Multifaceted Cationic Host Defense (Antimicrobial) Peptides. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, J.; Dressel, S.; Wittersheim, M.; Cordes, J.; Meyer-Hoffert, U.; Mrowietz, U.; Fölster-Holst, R.; Proksch, E.; Schröder, J.-M.; Schwarz, T.; et al. Enhanced Expression and Secretion of Antimicrobial Peptides in Atopic Dermatitis and after Superficial Skin Injury. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittmann, M.; McGonagle, D.; Werfel, T. Cytokines as Therapeutic Targets in Skin Inflammation. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014, 25, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierkarre, H.; Harder, J.; Cuthbert, R.; Emery, P.; Leuschner, I.; Mrowietz, U.; Hedderich, J.; McGonagle, D.; Gläser, R. Differential Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis as a Novel Contributory Mechanism for Skin and Joint Disease Heterogeneity. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 45, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Biragyn, A.; Hoover, D.M.; Lubkowski, J.; Oppenheim, J.J. Multiple Roles of Antimicrobial Defensins, Cathelicidins, and Eosinophil-Derived Neurotoxin in Host Defense. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 22, 181–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, E.; Sato, Y.; Minagawa, A.; Okuyama, R. Pathogenesis of Psoriasis and Development of Treatment. J. Dermatol. 2018, 45, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rycyk-Bojarzyńska, A.; Kasztelan-Szczerbińska, B.; Cichoż-Lach, H.; Surdacka, A.; Roliński, J. Human Neutrophil Alpha-Defensins Promote NETosis and Liver Injury in Alcohol-Related Liver Cirrhosis: Potential Therapeutic Agents. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, W.; Gladman, D.; Helliwell, P.; Marchesoni, A.; Mease, P.; Mielants, H. Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis: Development of New Criteria from a Large International Study. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 2665–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Physical Status: The Use and Interpretation of Anthropometry, Report of a WHO Expert Committee; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995; Volume 854.
- Wensveen, F.M.; Valentić, S.; Šestan, M.; Turk Wensveen, T.; Polić, B. The “Big Bang” in Obese Fat: Events Initiating Obesity-Induced Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 2446–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.-L.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Q.-Y.; Bai, J.; He, Z.-Y.; Zhang, J.-Q.; Li, M.-H.; Deng, J.-M.; Liu, G.-N.; Zhong, X.-N. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Induced by Cigarette Smoke Activate Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells. Thorax 2017, 72, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yao, W.-Z.; Xia, G.-G.; Sun, D.-J. The expression and implications of human alpha-defensin 1-3 in serum and induced sputum in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi Chin. J. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2008, 31, 410–413. [Google Scholar]
- Heijink, I.H.; Pouwels, S.D.; Leijendekker, C.; de Bruin, H.G.; Zijlstra, G.J.; van der Vaart, H.; ten Hacken, N.H.T.; van Oosterhout, A.J.M.; Nawijn, M.C.; van der Toorn, M. Cigarette Smoke-Induced Damage-Associated Molecular Pattern Release from Necrotic Neutrophils Triggers Proinflammatory Mediator Release. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 52, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, M.T.; Gauss, K.A. Structure and Regulation of the Neutrophil Respiratory Burst Oxidase: Comparison with Nonphagocyte Oxidases. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 76, 760–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, A.; Thompson, P.R.; Segal, B.H.; Urban, C.F. Nicotine Induces Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 100, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, C.; Kushner, I. Acute-Phase Proteins and Other Systemic Responses to Inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Németh, T.; Mócsai, A. The Role of Neutrophils in Autoimmune Diseases. Immunol. Lett. 2012, 143, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.U.-S.; O’Sullivan, K.M. The Expanding Role of Extracellular Traps in Inflammation and Autoimmunity: The New Players in Casting Dark Webs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Stehr, A.M.; Naschberger, E.; Knopf, J.; Herrmann, M.; Stürzl, M. No NETs No TIME: Crosstalk between Neutrophil Extracellular Traps and the Tumor Immune Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1075260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Chertov, O.; Bykovskaia, S.N.; Chen, Q.; Buffo, M.J.; Shogan, J.; Anderson, M.; Schröder, J.M.; Wang, J.M.; Howard, O.M.; et al. Beta-Defensins: Linking Innate and Adaptive Immunity through Dendritic and T Cell CCR6. Science 1999, 286, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funderburg, N.; Lederman, M.M.; Feng, Z.; Drage, M.G.; Jadlowsky, J.; Harding, C.V.; Weinberg, A.; Sieg, S.F. Human β-Defensin-3 Activates Professional Antigen-Presenting Cells via Toll-like Receptors 1 and 2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18631–18635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Frade, J.M.; del Real, G.; Serrano, A.; Hernanz-Falcón, P.; Soriano, S.F.; Vila-Coro, A.J.; de Ana, A.M.; Lucas, P.; Prieto, I.; Martínez-A, C.; et al. Blocking HIV-1 Infection via CCR5 and CXCR4 Receptors by Acting in Trans on the CCR2 Chemokine Receptor. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, P.Y.; Ohtake, T.; Brandt, C.; Strickland, I.; Boguniewicz, M.; Ganz, T.; Gallo, R.L.; Leung, D.Y.M. Endogenous Antimicrobial Peptides and Skin Infections in Atopic Dermatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Yamasaki, K. Psoriasis and Antimicrobial Peptides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lande, R.; Ganguly, D.; Facchinetti, V.; Frasca, L.; Conrad, C.; Gregorio, J.; Meller, S.; Chamilos, G.; Sebasigari, R.; Riccieri, V.; et al. Neutrophils Activate Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells by Releasing Self-DNA-Peptide Complexes in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 73ra19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffen, S.L.; Jain, R.; Garg, A.V.; Cua, D.J. IL-23-IL-17 Immune Axis: Discovery, Mechanistic Understanding, and Clinical Testing. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, A.M.; Naik, P.; Giles, J.T.; Darrah, E. PAD Enzymes in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathogenic Effectors and Autoimmune Targets. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadaki, G.; Kambas, K.; Choulaki, C.; Vlachou, K.; Drakos, E.; Bertsias, G.; Ritis, K.; Boumpas, D.T.; Thompson, P.R.; Verginis, P.; et al. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Exacerbate Th1-Mediated Autoimmune Responses in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Promoting DC Maturation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 2542–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehkamp, J.; Salzman, N.H.; Porter, E.; Nuding, S.; Weichenthal, M.; Petras, R.E.; Shen, B.; Schaeffeler, E.; Schwab, M.; Linzmeier, R.; et al. Reduced Paneth Cell Alpha-Defensins in Ileal Crohn’s Disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18129–18134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Feature | Psoriasis Patients (n = 49) | Controls (n = 49) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic | |||
| Age, years ± SD | 47.5 ± 12.6 | 45.7 ± 10.9 | ns |
| Male, n (%) | 36 (73.5) | 38 (77.6) | ns |
| Clinical | |||
| Psoriasis duration, years ± SD | 17.6 ± 12.7 | N/A | |
| PASI, mean ± SD | 15.8 ± 9.9 | N/A | |
| PsA, n (%) | 12 (24.5) | N/A | |
| WHR, mean ± SD | 0.96 ± 0.1 | 0.93 ± 0.1 | ns |
| BMI, mean ± SD (kg/m2) | 28.3 ± 4.7 | 27.4 ± 2.9 | ns |
| Hyperlipidemia, n (%) | 21 (42.8) | 24 (49) | ns |
| AHT, n (%) | 15 (30.1) | 17 (34.7) | ns |
| DM, n (%) | 4 (8.1) | 6 (12.2) | ns |
| CHD, n (%) | 4 (8.1) | 2 (4) | ns |
| COPD, n (%) | 3 (6.1) | 4 (8.1) | ns |
| Asthma, n (%) | 2 (4) | 2 (4) | ns |
| Crohn’s disease, n (%) | 1 (2) | 0 (0) | ns |
| SLE, n (%) | 1 (2) | 0 (0) | ns |
| Smoking cigarettes, n (%) | 18 (36.7) | 15 (30.6) | ns |
| Cigarette pack-years, mean ± SD | 16.9 ± 13 | 14.1 ± 10.1 | ns |
| Intensity (cigarettes/day), mean ± SD | 14.8 ± 7 | 13.2 ± 8.8 | ns |
| Respiratory infections in last 6 weeks, n (%) | 2 (4) | 2 (4) | ns |
| Biochemical | |||
| ESR, mean ± SD (mm/h) | 26.15 ± 19.46 | 21.09 ± 20.8 | ns |
| CRP, mean ± SD (mg/L) | 6.62 ± 7.86 | 5.01 ± 5.81 | ns |
| IL-6, mean ± SD (pg/mL) | 4.86 ± 10.31 | 3.12 ± 11.02 | ns |
| Group | n | Mean HNP1–3 Concentration ± SD (ng/mL) | p Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy controls | 49 | 2.52 ± 0.84 | |
| Psoriasis (total) | 49 | 3.85 ± 0.76 | <0.001 |
| with AHT | 15 | 3.49 ± 0.41 | ns |
| with PsA | 12 | 4.21 ± 0.69 | <0.001 |
| with CHD | 4 | 3.89 ± 0.81 | N/A * |
| with DM | 4 | 3.71 ± 0.91 | N/A |
| with COPD | 3 | 4.12 ± 0.71 | N/A * |
| with asthma | 2 | 4.05 ± 0.55 | N/A * |
| with Crohn’s disease | 1 | 4.01 | N/A * |
| with SLE | 1 | 4.14 | N/A * |
| Variable | β Coefficient | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| WHR | 1.77 | 0.62–2.91 | <0.01 |
| Smoking status | 0.45 | 0.21–0.69 | <0.001 |
| Age (adjusted) | - | - | ns |
| Sex (adjusted) | - | - | ns |
| Variable Pair | Pearson r | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| HNP1–3 vs. CRP | −0.089 | 0.701 |
| HNP1–3 vs. ESR | 0.505 | 0.019 |
| HNP1–3 vs. IL-6 | 0.561 | 0.008 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mleczko, M.; Kowalska-Kępczyńska, A.; Gerkowicz, A.; Kowal, M.; Krasowska, D. Serum Levels of Human Neutrophil Peptides 1–3 (HNP1–3) as Potential Biomarkers in Psoriasis and Associated Comorbidities. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1635. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071635
Mleczko M, Kowalska-Kępczyńska A, Gerkowicz A, Kowal M, Krasowska D. Serum Levels of Human Neutrophil Peptides 1–3 (HNP1–3) as Potential Biomarkers in Psoriasis and Associated Comorbidities. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(7):1635. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071635
Chicago/Turabian StyleMleczko, Mateusz, Anna Kowalska-Kępczyńska, Agnieszka Gerkowicz, Małgorzata Kowal, and Dorota Krasowska. 2025. "Serum Levels of Human Neutrophil Peptides 1–3 (HNP1–3) as Potential Biomarkers in Psoriasis and Associated Comorbidities" Biomedicines 13, no. 7: 1635. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071635
APA StyleMleczko, M., Kowalska-Kępczyńska, A., Gerkowicz, A., Kowal, M., & Krasowska, D. (2025). Serum Levels of Human Neutrophil Peptides 1–3 (HNP1–3) as Potential Biomarkers in Psoriasis and Associated Comorbidities. Biomedicines, 13(7), 1635. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071635





