Maresin1 Alleviates Ischemia Reperfusion Injury After Lung Transplantation by Inhibiting Ferroptosis via the PKA-Hippo-YAP Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experiment Protocol
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Reagents
2.5. Histopathological Pathologic Analysis
2.6. The Lung Wet/Dry (W/D) Weight Ratio
2.7. Cell Viability and Injury Determination
2.8. Fe2+, MDA, 4-HNE, and GSH Measurements
2.9. Western Blotting
2.10. Lipid ROS Detection
2.11. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
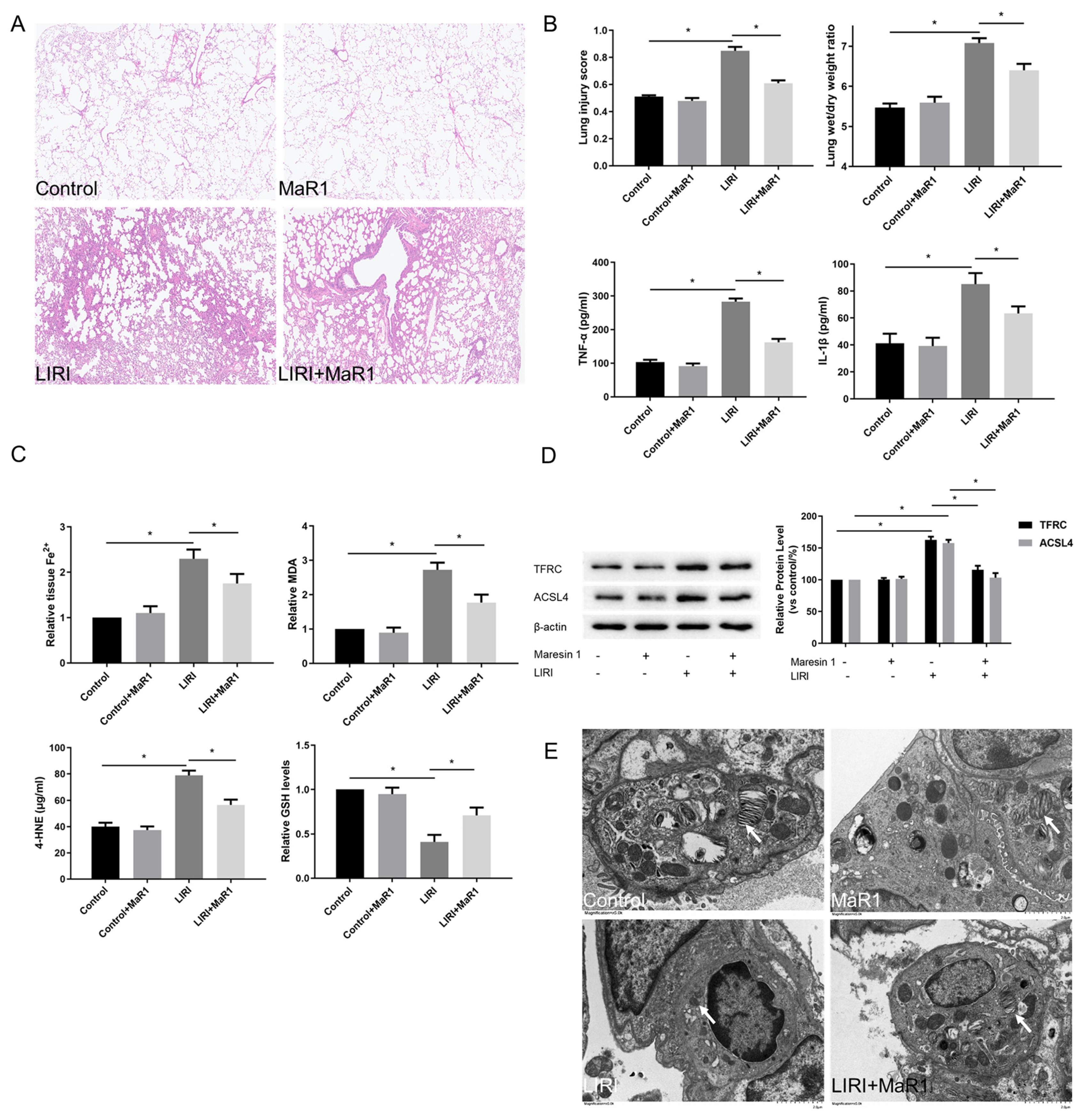
3.1. MaR1 Alleviates LIRI and Ferroptosis After Lung Transplantation
3.2. MaR1 Ameliorates LIRI by Inhibiting Ferroptosis
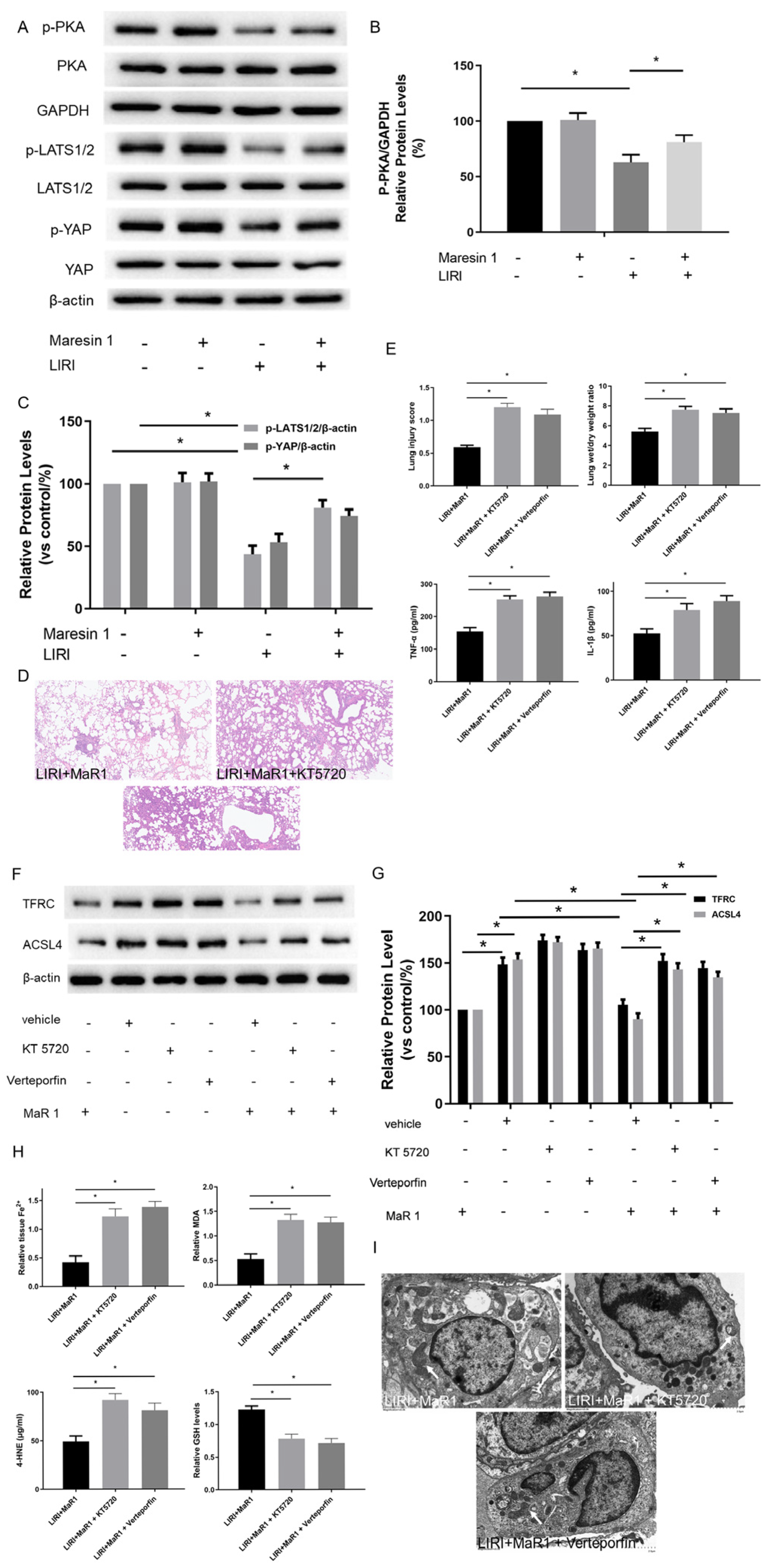
3.3. MaR1 Dampens Ferroptosis via Activating the PKA/LATS1/2/YAP Pathway in LIRI
3.4. MaR1 Inhibits Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-Induced Ferroptosis In Vitro
3.5. MaR1 Suppresses Ferroptosis by PKA/LATS1/2/YAP Activation In Vitro
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LIRI | Lung ischemia reperfusion injury |
| LT | Lung transplantation |
| H/R | Hypoxia reoxygenation culture |
| MaR1 | Maresin1 |
| TFRC | Transferrin receptor |
| ACSL4 | Acyl-CoA Synthetase Long Chain Family Member 4 |
| PKA | Protein kinase A |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| CCK-8 | Cell Counting Kit-8 |
| OD | Optical density |
| LGR6 | Leucine-rich repeat containing-GPCR 6 |
| MST1/2 | Mammalian STE20-like kinase 1/2 |
| LATS1/2 | Large tumor suppressor 1/2 |
| YAP | Yes-associated protein |
| TAZ | Transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding TEA domain (TEAD) |
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| GPCRs | G-protein-coupled receptors |
References
- de Perrot, M.; Liu, M.; Waddell, T.K.; Keshavjee, S. Ischemia-reperfusion-induced lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 490–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matot, I.; Einav, S.; Weiniger, C.F.; Pearl, R.G.; Abramovitch, R.; Joshi, B.V.; Jacobson, K.A. Lung injury after in vivo reperfusion: Outcome at 27 h after reperfusion. Anesthesiology 2008, 109, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Hengst, W.A.; Gielis, J.F.; Lin, J.Y.; Van Schil, P.E.; De Windt, L.J.; Moens, A.L. Lung ischemia-reperfusion injury: A molecular and clinical view on a complex pathophysiological process. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2010, 299, H1283–H1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Zhai, Z.; Wu, D.; Lin, Q.; Yang, Y.; Yang, M.; Ding, H.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, C. Inflammatory response and pneumocyte apoptosis during lung ischemia-reperfusion injury in an experimental pulmonary thromboembolism model. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2015, 40, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.D.; Tribble, C.G.; Gaughen, J.R., Jr.; Shockey, K.S.; Parrino, P.E.; Kron, I.L. Reduced neutrophil infiltration protects against lung reperfusion injury after transplantation. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1999, 67, 1428–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyker, P.D.; Webb, C.A.; Kiamanesh, D.; Flynn, B.C. Lung ischemia reperfusion injury: A bench-to-bedside review. Semin. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2013, 17, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, B.V.; Krishnadasan, B.; Farivar, A.S.; Woolley, S.M.; Thomas, R.; Van Rooijen, N.; Verrier, E.D.; Mulligan, M.S. Early activation of the alveolar macrophage is critical to the development of lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2003, 126, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, B.R.; Friedmann Angeli, J.P.; Bayir, H.; Bush, A.I.; Conrad, M.; Dixon, S.J.; Fulda, S.; Gascón, S.; Hatzios, S.K.; Kagan, V.E.; et al. Ferroptosis: A Regulated Cell Death Nexus Linking Metabolism, Redox Biology, and Disease. Cell 2017, 171, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kang, R.; Kroemer, G.; Tang, D. Ferroptosis in infection, inflammation, and immunity. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20210518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Shen, L.; Chen, Q.; Shu, Q. Targeting Ferroptosis as a Promising Therapeutic Strategy for Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, R.; Tian, D.; Liu, D.; Zhang, F.; Ning, S.; Yao, J.; et al. Ischemia-induced ACSL4 activation contributes to ferroptosis-mediated tissue injury in intestinal ischemia/reperfusion. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 2284–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, M.; Wang, R. Inhibition of ACSL4 attenuates ferroptotic damage after pulmonary ischemia-reperfusion. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 16262–16275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Pan, B.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Song, Z.; Zhang, E.; Wang, F.; Wang, W. Ischemia/reperfusion-activated ferroptosis in the early stage triggers excessive inflammation to aggregate lung injury in rats. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1181286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Zamel, R.; Bai, X.H.; Lu, C.; Keshavjee, S.; Keshavjee, S.; Liu, M. Ischemia-reperfusion induces death receptor-independent necroptosis via calpain-STAT3 activation in a lung transplant setting. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2018, 315, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuzzimati, M.; Hough, O.; Liu, M. Cell death and ischemia-reperfusion injury in lung transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2022, 41, 1003–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N. Pro-resolving lipid mediators are leads for resolution physiology. Nature 2014, 510, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcon, R.; Bento, A.F.; Dutra, R.C.; Bicca, M.A.; Leite, D.F.; Calixto, J.B. Maresin 1, a proresolving lipid mediator derived from omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, exerts protective actions in murine models of colitis. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 4288–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordgren, T.M.; Heires, A.J.; Wyatt, T.A.; Poole, J.A.; LeVan, T.D.; Cerutis, D.R.; Romberger, D.J. Maresin-1 reduces the pro-inflammatory response of bronchial epithelial cells to organic dust. Respir. Res. 2013, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N.; Dalli, J.; Karamnov, S.; Choi, A.; Park, C.K.; Xu, Z.Z.; Ji, R.R.; Zhu, M.; Petasis, N.A. Macrophage proresolving mediator maresin 1 stimulates tissue regeneration and controls pain. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 1755–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, E.; Wu, K.; Li, W.; Shi, L.; Wang, D.; Xie, G.; Yin, Y.; Deng, M.; et al. Maresin 1, a Proresolving Lipid Mediator, Mitigates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Injury in Mice. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 9203716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, N.; Burkett, P.R.; Dalli, J.; Abdulnour, R.E.; Colas, R.; Ramon, S.; Phipps, R.P.; Petasis, N.A.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Serhan, C.N.; et al. Cutting edge: Maresin-1 engages regulatory T cells to limit type 2 innate lymphoid cell activation and promote resolution of lung inflammation. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 863–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Minikes, A.M.; Gao, M.; Bian, H.; Li, Y.; Stockwell, B.R.; Chen, Z.N.; Jiang, X. Intercellular interaction dictates cancer cell ferroptosis via NF2-YAP signalling. Nature 2019, 572, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ye, R.; Qiu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Li, J. Role of extracellular matrix and YAP/TAZ in cell fate determination. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magesh, S.; Cai, D. Roles of YAP/TAZ in ferroptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 2022, 32, 729–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.H.; Camargo, F.D.; Yimlamai, D. Hippo Signaling in the Liver Regulates Organ Size, Cell Fate, and Carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.H.; Chi, J.T. Hippo pathway effectors YAP/TAZ as novel determinants of ferroptosis. Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2020, 7, 1699375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, J.; Huang, X.; Jiang, K.; Nie, J.; Qiao, X.; Li, J. Improvements of the surgical technique on the established mouse model of orthotopic single lung transplantation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungraithmayr, W.M.; Korom, S.; Hillinger, S.; Weder, W. A mouse model of orthotopic, single-lung transplantation. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2009, 137, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Huang, Y.T.; Lee, T.Y.; Chan, C.C.; Yeh, Y.C.; Lee, K.C.; Lin, H.C. Rho-kinase-dependent pathway mediates the hepatoprotective effects of sorafenib against ischemia/reperfusion liver injury in rats with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Liver Transpl. 2012, 18, 1371–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, J.M.; Makarewich, C.A.; Trappanese, D.; Gross, P.; Husain, S.; Dunn, J.; Lal, H.; Sharp, T.E.; Starosta, T.; Vagnozzi, R.J.; et al. Sorafenib cardiotoxicity increases mortality after myocardial infarction. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennenberg, M.; Trebicka, J.; Stark, C.; Kohistani, A.Z.; Heller, J.; Sauerbruch, T. Sorafenib targets dysregulated Rho kinase expression and portal hypertension in rats with secondary biliary cirrhosis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Xie, L.; Yin, S.; Zhou, J.; Yi, L.; Ye, L. The Gut Microbial Lipid Metabolite 14(15)-EpETE Inhibits Substance P Release by Targeting GCG/PKA Signaling to Relieve Cisplatin-Induced Nausea and Vomiting in Rats. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, C.E.; Welch, S.P.; Martin, B.R. Reversal of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol-induced tolerance by specific kinase inhibitors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 496, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Sun, Z.; Liu, H.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, W.; Tu, B.; Li, J.; Fan, C. Verteporfin attenuates trauma-induced heterotopic ossification of Achilles tendon by inhibiting osteogenesis and angiogenesis involving YAP/β-catenin signaling. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e23057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Chen, G. Verteporfin Promotes the Apoptosis and Inhibits the Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Cervical Cancer Cells by Downregulating SULT2B1 Expression. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e926780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Noda, K.; Philips, B.; Velayutham, M.; Stolz, D.B.; Gladwin, M.T.; Shiva, S.D.; Cunha, J. Nitrite attenuates mitochondrial impairment and vascular permeability induced by ischemia-reperfusion injury in the lung. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2020, 318, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.S.; Kawamura, T.; Lee, S.; Tochigi, N.; Shigemura, N.; Buchholz, B.M.; Kloke, J.D.; Billiar, T.R.; Toyoda, Y.; Nakao, A. Hydrogen inhalation ameliorates ventilator-induced lung injury. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wu, S.; Fan, J.; Meng, Z.; Gao, G.; Liu, T.; Wang, Q.; Xia, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, K. CYLD regulates cell ferroptosis through Hippo/YAP signaling in prostate cancer progression. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baz, M.A.; Ghio, A.J.; Roggli, V.L.; Tapson, V.F.; Piantadosi, C.A. Iron accumulation in lung allografts after transplantation. Chest 1997, 112, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, C.; Hathwar, V.; Richards, J.H.; Stonehuerner, J.; Ghio, A.J. Disruption of iron homeostasis in the lungs of transplant patients. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2005, 24, 1821–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Li, X.; Li, B.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Ji, Y.; Wang, X.; Wen, Z.; Fan, J.; et al. The mitochondrial-derived peptide MOTS-c suppresses ferroptosis and alleviates acute lung injury induced by myocardial ischemia reperfusion via PPARγ signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 953, 175835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Wei, D.; Gao, F.; Yang, X.; Yue, B.; Xiong, D.; Liu, M.; Xu, H.; Hu, C.; et al. Liproxstatin-1 Alleviates Lung Transplantation-induced Cold Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting Ferroptosis. Transplantation 2023, 107, 2190–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Xiao, J.; Shang, J.; Tan, Q.; Ping, F.; Huang, W.; Wu, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X. Inhibitor of apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53 inhibits ferroptosis and alleviates intestinal ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute lung injury. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 2635–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, P.; Birukov, K.G. Oxidized Phospholipids in Control of Endothelial Barrier Function: Mechanisms and Implication in Lung Injury. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 794437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, Y.; Yang, L.; Yang, Y.; Xu, J. Inhibition of keratinocyte ferroptosis suppresses psoriatic inflammation. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, F.; Li, D.; Yan, Y.; Wang, H. Transferrin receptor-mediated reactive oxygen species promotes ferroptosis of KGN cells via regulating NADPH oxidase 1/PTEN induced kinase 1/acyl-CoA synthetase long chain family member 4 signaling. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 4983–4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N.; Yang, R.; Martinod, K.; Kasuga, K.; Pillai, P.S.; Porter, T.F.; Oh, S.F.; Spite, M. Maresins: Novel macrophage mediators with potent antiinflammatory and proresolving actions. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Jiang, L.; Qin, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Su, B. Maresin 1 Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Kidney Injury via Inhibiting NOX4/ROS/NF-κB Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 782660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Fu, H.; Ji, L.; Li, N.; Zhang, D.; Su, L.; Hu, Z. Maresin1 Ameliorates Sepsis-Induced Microglial Neuritis Induced through Blocking TLR4-NF-κ B-NLRP3 Signaling Pathway. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, N.; Peng, S.; Fu, H.; Hu, Z.; Su, L. Maresin1 improves hippocampal neuroinflammation and cognitive function in septic rats by activating the SLC7A11/GPX4 ferroptosis signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 131, 111792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, F.; Wang, J. Maresin 1 Ameliorates Lung Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Suppressing Oxidative Stress via Activation of the Nrf-2-Mediated HO-1 Signaling Pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 9634803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Fu, G.; Li, W.; Sun, P.; Loughran, P.A.; Deng, M.; Scott, M.J.; Billiar, T.R. Maresin 1 protects the liver against ischemia/reperfusion injury via the ALXR/Akt signaling pathway. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Ji, C.; Wang, Y.N.; Liu, S.; Wang, M.; Xu, X.; Zhang, D. Maresin1 Suppresses High-Glucose-Induced Ferroptosis in Osteoblasts via NRF2 Activation in Type 2 Diabetic Osteoporosis. Cells 2022, 11, 2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Ma, X.; Bai, X. Maresin-1 inhibits high glucose induced ferroptosis in ARPE-19 cells by activating the Nrf2/HO-1/GPX4 pathway. BMC Ophthalmol. 2023, 23, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.; Salloum, R.; Xin, M.; Lu, Q.R. The G protein Gαs acts as a tumor suppressor in sonic hedgehog signaling-driven tumorigenesis. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, N.; Libreros, S.; Norris, P.C.; de la Rosa, X.; Serhan, C.N. Maresin 1 activates LGR6 receptor promoting phagocyte immunoresolvent functions. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 5294–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.H.; Guan, K.L. Interplay between YAP/TAZ and Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2018, 28, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Jiao, Z.; Yu, F.X. The Hippo signaling pathway in development and regeneration. Cell. Rep. 2024, 43, 113926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Xie, W.; Wang, X.; Du, Z.; Zheng, C.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Z.; Ji, Z. Ischemia-inhibited ferric chelate reductase 1 improves ferroptosis-mediated intestinal ischemia injury via Hippo signaling. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 132, 111900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Hu, M.; He, M.; Wang, X.; Sun, D.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Fu, J.; Cai, J.; Ma, T.; et al. TNFAIP3 Interacting Protein 3 Is an Activator of Hippo-YAP Signaling Protecting Against Hepatic Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Hepatology 2021, 74, 2133–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, T.; Zhai, P.; Sciarretta, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jeong, J.I.; Ikeda, S.; Park, J.; Hsu, C.P.; Tian, B.; Pan, D.; et al. NF2 Activates Hippo Signaling and Promotes Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in the Heart. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, S.; Jeong, M.; Tonnus, W.; Feldmann, F.; Hofmans, S.; Goossens, V.; Takahashi, N.; Bräsen, J.H.; Lee, E.W.; Van der Veken, P.; et al. Sorafenib tosylate inhibits directly necrosome complex formation and protects in mouse models of inflammation and tissue injury. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, P.; Wu, Y.; Wan, L.; Sun, X.; Sun, Q. Maresin1 Alleviates Ischemia Reperfusion Injury After Lung Transplantation by Inhibiting Ferroptosis via the PKA-Hippo-YAP Signaling Pathway. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071594
Deng P, Wu Y, Wan L, Sun X, Sun Q. Maresin1 Alleviates Ischemia Reperfusion Injury After Lung Transplantation by Inhibiting Ferroptosis via the PKA-Hippo-YAP Signaling Pathway. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(7):1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071594
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Peng, You Wu, Li Wan, Xiangfu Sun, and Quanchao Sun. 2025. "Maresin1 Alleviates Ischemia Reperfusion Injury After Lung Transplantation by Inhibiting Ferroptosis via the PKA-Hippo-YAP Signaling Pathway" Biomedicines 13, no. 7: 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071594
APA StyleDeng, P., Wu, Y., Wan, L., Sun, X., & Sun, Q. (2025). Maresin1 Alleviates Ischemia Reperfusion Injury After Lung Transplantation by Inhibiting Ferroptosis via the PKA-Hippo-YAP Signaling Pathway. Biomedicines, 13(7), 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071594





