The Oncogenic Burden of Obesity: Mechanistic Links Between Adiposity and Gastrointestinal Cancers—A Comprehensive Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
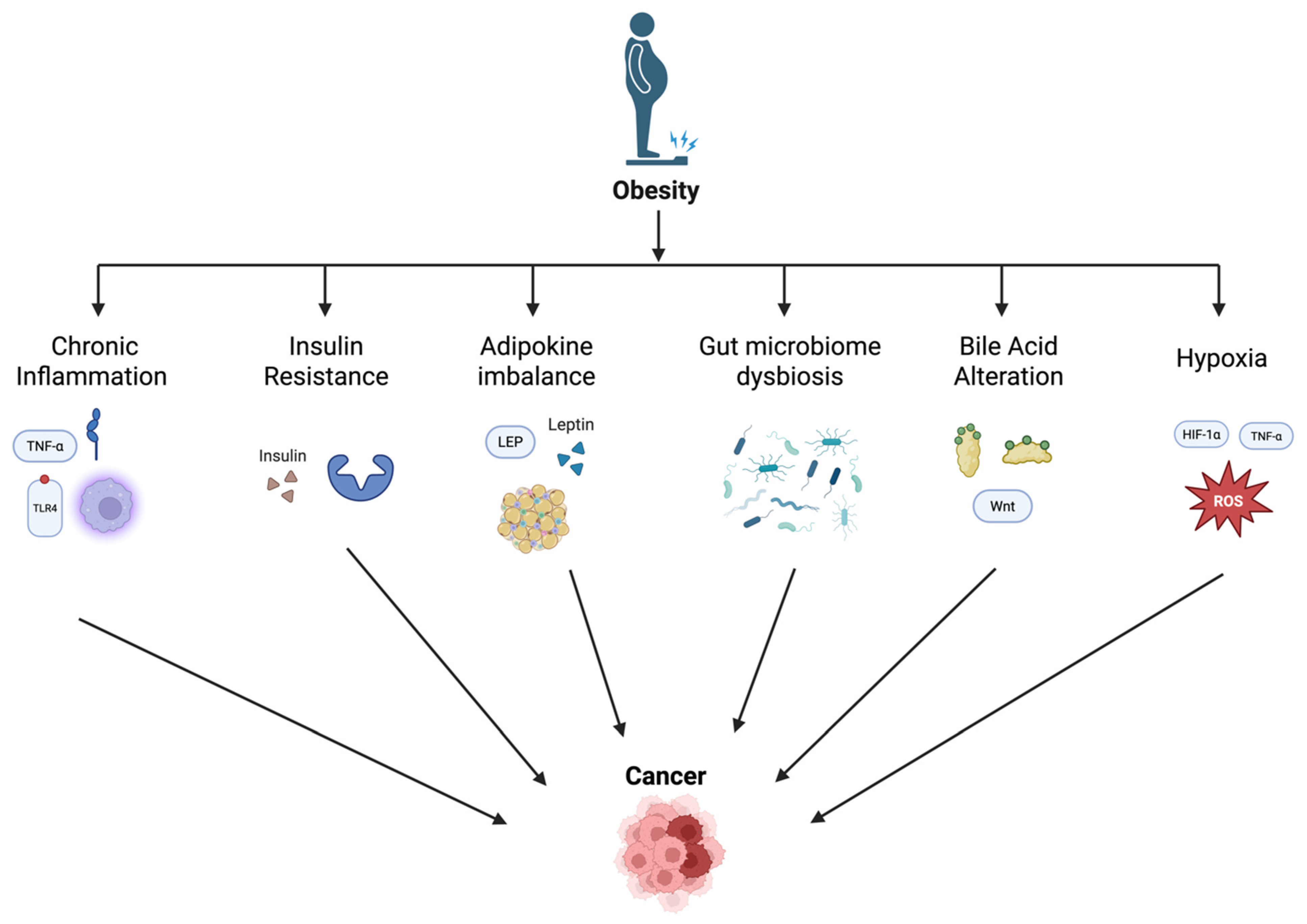
2. Mechanisms Linking Obesity and Gastrointestinal Cancer
2.1. Chronic Inflammation and Cytokine Dysregulation
2.2. Insulin Resistance and Hyperinsulinemia
2.3. Adipokine Imbalance
2.4. Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis
2.5. Bile Acid Metabolism Alterations
2.6. Hypoxia
2.7. Other Mechanisms
3. Obesity and Specific Gastrointestinal Cancers
3.1. Esophageal Adenocarcinoma
3.2. Gastric Cancer
3.3. Colorectal Cancer (CRC)
3.4. Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
3.5. Pancreatic Cancer
3.6. Gallbladder Cancer
3.7. Limitations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, M.; Gong, W.; Wang, S.; Li, Z. Trends in body mass index, overweight and obesity among adults in the USA, the NHANES from 2003 to 2018: A repeat cross-sectional survey. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e065425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anekwe, C.V.; Jarrell, A.R.; Townsend, M.J.; Gaudier, G.I.; Hiserodt, J.M.; Stanford, F.C. Socioeconomics of Obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2020, 9, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busebee, B.; Ghusn, W.; Cifuentes, L.; Acosta, A. Obesity: A Review of Pathophysiology and Classification. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2023, 98, 1842–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatterale, F.; Longo, M.; Naderi, J.; Raciti, G.A.; Desiderio, A.; Miele, C.; Beguinot, F. Chronic Adipose Tissue Inflammation Linking Obesity to Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divella, R.; De Luca, R.; Abbate, I.; Naglieri, E.; Daniele, A. Obesity and cancer: The role of adipose tissue and adipo-cytokines-induced chronic inflammation. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 2346–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Lyon, C.J.; Bergin, S.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Hsueh, W.A. Obesity, Inflammation, and Cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2016, 11, 421–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Cao, S.; Xu, R. Global trends and epidemiological shifts in gastrointestinal cancers: Insights from the past four decades. Cancer Commun. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Cao, Y. Obesity and Gastrointestinal Cancer: A Life Course Perspective. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e239921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Tang, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Sheng, J.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, W.; et al. Association of overweight/obesity and digestive system cancers: A meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis of prospective cohort studies. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0318256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Redondo-Flórez, L.; Beltrán-Velasco, A.I.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Martínez-Guardado, I.; Navarro-Jiménez, E.; Laborde-Cárdenas, C.C.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. The Role of Adipokines in Health and Disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, R.; Sutterwala, F.S.; Zhang, W. Obesity and cancer: Inflammation bridges the two. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2016, 29, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghusn, W.; Hurtado, M.D.; Acosta, A. Weight-centric treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Obes. Pillars 2022, 4, 100045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittelman, S.D. The Role of Diet in Cancer Prevention and Chemotherapy Efficacy. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2020, 40, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.B.; Lathigara, D.; Kaushal, D. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Impact of Bariatric Surgery on Future Cancer Risk. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, C.M.; Himbert, C.; Holowatyj, A.N.; Hursting, S.D. Energy balance and gastrointestinal cancer: Risk, interventions, outcomes and mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 683–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzyk, L.; Torres, A.; Maciejewski, R.; Torres, K. Obesity and Obese-related Chronic Low-grade Inflammation in Promotion of Colorectal Cancer Development. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 4161–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregor, M.F.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammatory mechanisms in obesity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 415–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahechu, P.; Zozaya, G.; Martí, P.; Hernández-Lizoáin, J.L.; Baixauli, J.; Unamuno, X.; Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V. NLRP3 Inflammasome: A Possible Link Between Obesity-Associated Low-Grade Chronic Inflammation and Colorectal Cancer Development. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfalzer, A.C.; Crott, J.W.; Koh, G.Y.; Smith, D.E.; Garcia, P.E.; Mason, J.B. Interleukin-1 Signaling Mediates Obesity-Promoted Elevations in Inflammatory Cytokines, Wnt Activation, and Epithelial Proliferation in the Mouse Colon. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2018, 38, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wei, H.; Zhou, Y.; Szeto, C.-H.; Li, C.; Lin, Y.; Coker, O.O.; Lau, H.C.H.; Chan, A.W.; Sung, J.J.; et al. High-Fat Diet Promotes Colorectal Tumorigenesis Through Modulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 135–149.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.A.; Nisar, S.; Singh, M.; Ashraf, B.; Masoodi, T.; Prasad, C.P.; Sharma, A.; Maacha, S.; Karedath, T.; Hashem, S.; et al. Cytokine- and chemokine-induced inflammatory colorectal tumor microenvironment: Emerging avenue for targeted therapy. Cancer Commun. 2022, 42, 689–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Grivennikov, S.I.; Karin, M. Implications of anti-cytokine therapy in colorectal cancer and autoimmune diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, ii100–ii103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Casado, G.; Jimenez-Gonzalez, A.; Rodriguez-Muñoz, A.; Tinahones, F.J.; González-Mesa, E.; Murri, M.; Ortega-Gomez, A. Neutrophils as indicators of obesity-associated inflammation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2025, 26, e13868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Kim, S.J.; Lei, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Tsung, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps in homeostasis and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, A.; Patruni, S.; Garciafigueroa, Y.; Phillips, B.; Engman, C.; Khatoon, N.; Shankar, K.; Rizvi, A.; Miller, S.; Giannoukakis, N.; et al. Significant lipid and neutrophil accumulation and active inflammasome in high BMI tumor regions of human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39 (Suppl. 3), 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericksen, R.E.; Rose, S.; Westphalen, C.B.; Shibata, W.; Muthupalani, S.; Tailor, Y.; Friedman, R.A.; Han, W.; Fox, J.G.; Ferrante, A.W.; et al. Obesity accelerates Helicobacter felis-induced gastric carcinogenesis by enhancing immature myeloid cell trafficking and TH17 response. Gut 2014, 63, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofman, P.M. Pathobiology of the neutrophil-intestinal epithelial cell interaction: Role in carcinogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2010, 16, 5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, M.; Yeon, J.; Park, S.; Park, J.H.Y.; Choi, M. Obesity-induced metabolic stresses in breast and colon cancer. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1229, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Rowitz, B.M.; Dailey, M.J. Insulin/IGF-1 enhances intestinal epithelial crypt proliferation through PI3K/Akt, and not ERK signaling in obese humans. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 243, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.-Q.; Buchsbaum, D.J. Monoclonal Antibodies in the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer. Immunotherapy 2009, 1, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, E.M.; Hintzsche, H.; Stopper, H. Signaling steps in the induction of genomic damage by insulin in colon and kidney cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 68, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Häring, M.-F.; Rathjen, T.; Lockhart, S.M.; Sørensen, D.; Ussar, S.; Rasmussen, L.M.; Bertagnolli, M.M.; Kahn, C.R.; Rask-Madsen, C. Insulin resistance in vascular endothelial cells promotes intestinal tumour formation. Oncogene 2017, 36, 4987–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socol, C.T.; Chira, A.; Martinez-Sanchez, M.A.; Nuñez-Sanchez, M.A.; Maerescu, C.M.; Mierlita, D.; Rusu, A.V.; Ruiz-Alcaraz, A.J.; Trif, M.; Ramos-Molina, B. Leptin Signaling in Obesity and Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, M.; Biswas, R.; Ganguly, S.; Chakrabarti, N.; Chaudhuri, A.G. Leptin and obesity. Physiol. Int. 2020, 107, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klok, M.D.; Jakobsdottir, S.; Drent, M.L. The role of leptin and ghrelin in the regulation of food intake and body weight in humans: A review. Obes. Rev. 2007, 8, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, G.; Poursheikhani, A.; Yassi, M.; Hayatbakhsh, A.; Kerachian, M.; Kerachian, M.A. Obesity, diabetes and the risk of colorectal adenoma and cancer. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2019, 19, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, S.S.; Jang, K.-S.; Lee, K.H.; Choi, D.; Jang, S.J. Leptin expression correlates with favorable clinicopathologic phenotype and better prognosis in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 16, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.-Y.; Lee, Y.-H.; Na, H.-K.; Baek, J.-H.; Surh, Y.-J. Leptin induces SIRT1 expression through activation of NF-E2-related factor 2: Implications for obesity-associated colon carcinogenesis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 153, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazolini, N.P.; Cruz, A.L.; Werneck, M.B.; Viola, J.P.; Maya-Monteiro, C.M.; Bozza, P.T. Leptin activation of mTOR pathway in intestinal epithelial cell triggers lipid droplet formation, cytokine production and increased cell proliferation. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 2667–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Yu, Y.; Zides, C.G.; Beyak, M.J. Mechanisms of reduced leptin-mediated satiety signaling during obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 1212–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, V.; Arella, F.; Afonso, M.B.; Santos, A.A.; Rodrigues, C.M. Decoding the role of leptin and adiponectin in obesity-related gastrointestinal cancer. Clin. Sci. 2023, 137, 1095–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishihara, T.; Baba, M.; Matsuda, M.; Inoue, M.; Nishizawa, Y.; Fukuhara, A.; Araki, H.; Kihara, S.; Funahashi, T.; Tamura, S.; et al. Adiponectin deficiency enhances colorectal carcinogenesis and liver tumor formation induced by azoxymethane in mice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 6473–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, A.; Sugiyama, M.; Takahashi, H.; Hosono, K.; Endo, H.; Kato, S.; Yoneda, K.; Nozaki, Y.; Fujita, K.; Yoneda, M.; et al. Adiponectin inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth through the AMPK/mTOR pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2009, 34, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.-S.; Liu, X.; Nagel, J.M.; Chamberland, J.P.; Diakopoulos, K.N.; Brinkoetter, M.T.; Hatziapostolou, M.; Wu, Y.; Robson, S.C.; Iliopoulos, D.; et al. Salutary effects of adiponectin on colon cancer: In vivo and in vitro studies in mice. Gut 2013, 62, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byeon, J.; Jeong, J.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, S.; Nam, W.; Myung, S.; Kim, J.G.; Yang, S.; Kim, J.; Suh, D.J. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptor in relation to colorectal cancer progression. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2758–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tae, C.H.; Kim, S.-E.; Jung, S.-A.; Joo, Y.-H.; Shim, K.-N.; Jung, H.-K.; Kim, T.H.; Cho, M.-S.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, J.S. Involvement of adiponectin in early stage of colorectal carcinogenesis. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D. Human gut microbiome: Hopes, threats and promises. Gut 2018, 67, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuei, J.; Chau, T.; Mills, D.; Wan, Y.J.Y. Bile acid dysregulation, gut dysbiosis, and gastrointestinal cancer. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 239, 1489–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpiński, T.M.; Ożarowski, M.; Stasiewicz, M. Carcinogenic microbiota and its role in colorectal cancer development. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86 Pt 3, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Choi, J.; Cho, Y.; Hong, B.; Shon, H.; Kim, B.; Park, J.; Kim, W.; Kim, D. Mycobacterium potentiates protection from colorectal cancer by gut microbial alterations. Immunology 2023, 168, 493–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, J.; Zheng, X.; Ren, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, W.; Fu, W.; Wang, J.; Du, G. Tumorigenic bacteria in colorectal cancer: Mechanisms and treatments. Cancer Biol. Med. 2021, 19, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shariati, A.; Razavi, S.; Ghaznavi-Rad, E.; Jahanbin, B.; Akbari, A.; Norzaee, S.; Darban-Sarokhalil, D. Association between colorectal cancer and Fusobacterium nucleatum and Bacteroides fragilis bacteria in Iranian patients: A preliminary study. Infect. Agents Cancer 2021, 16, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobhani, I.; Tap, J.; Roudot-Thoraval, F.; Roperch, J.P.; Letulle, S.; Langella, P.; Corthier, G.; Van Nhieu, J.T.; Furet, J.P.; Pied, S. Microbial Dysbiosis in Colorectal Cancer (CRC) Patients. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelsberger, V.; Gerhard, M.; Mejías-Luque, R. Effects of Helicobacter pylori infection on intestinal microbiota, immunity and colorectal cancer risk. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1339750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Xu, F.; Deng, C.; Nie, X.; Zhong, L.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, X.; He, S. Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes the early occurrence of esophageal cancer through upregulation of IL-32/PRTN3 expression. Cancer Sci. 2023, 114, 2414–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Hu, Y.; Hou, S. An Exploration of Oral-Gut Pathogens Mediating Immune Escape of Pancreatic Cancer via miR-21/PTEN Axis. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 928846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; von Ehrlich-Treuenstätt, V.; Schardey, J.; Wirth, U.; Zimmermann, P.; Andrassy, J.; Bazhin, A.V.; Werner, J.; Kühn, F. Gut Barrier Dysfunction and Bacterial Lipopolysaccharides in Colorectal Cancer. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2023, 27, 1466–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manilla, V.; Di Tommaso, N.; Santopaolo, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; Ponziani, F.R. Endotoxemia and Gastrointestinal Cancers: Insight into the Mechanisms Underlying a Dangerous Relationship. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, L.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, M.; Jiang, Z.; Pan, J.; Yang, C.; Li, X.; et al. Cross-talk between the gut microbiota and monocyte-like macrophages mediates an inflammatory response to promote colitis-associated tumourigenesis. Gut 2020, 70, 1495–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Huang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Hua, J.; Yang, S.; Zhuang, J.; Wang, J.; Ye, J. Lipopolysaccharide increases the release of VEGF-C that enhances cell motility and promotes lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis through the TLR4- NF-κB/JNK pathways in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 73711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-W.; Wu, L.; Lu, W.; Chen, W.; Yan, W.; Qi, C.; Xuan, S.; Shang, A. Lipopolysaccharides increase the risk of colorectal cancer recurrence and metastasis due to the induction of neutrophil extracellular traps after curative resection. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 147, 2609–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Xu, M.; Dong, W.; Deng, B.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Luo, S.; Wang, W.; Qi, Y.; et al. Secondary bile acid-induced dysbiosis promotes intestinal carcinogenesis. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 2545–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, H.; Bernstein, C. Bile acids as carcinogens in the colon and at other sites in the gastrointestinal system. Exp. Biol. Med. 2023, 248, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Song, X.; Khan, S.; Li, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, S.; Dong, W.; Liu, W.; Wang, B.; et al. The gut microbiota at the intersection of bile acids and intestinal carcinogenesis: An old story, yet mesmerizing. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 1780–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehmas, L.C.; DeAngelo, A.B.; Hester, S.D.; Chorley, B.N.; Carswell, G.; Olson, G.R.; George, M.H.; Carter, J.H.; Eldridge, S.R.; Fisher, A.; et al. Metabolic Disruption Early in Life is Associated With Latent Carcinogenic Activity of Dichloroacetic Acid in Mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 159, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagathihalli, N.S.; Beesetty, Y.; Lee, W.; Washington, M.K.; Chen, X.; Lockhart, A.C.; Merchant, N.B. Novel mechanistic insights into ectodomain shedding of EGFR Ligands Amphiregulin and TGF-α: Impact on gastrointestinal cancers driven by secondary bile acids. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2062–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Ung, T.T.; Li, S.; Sah, D.K.; Park, S.Y.; Lian, S.; Jung, Y.D. Lithocholic Acid Induces miR21, Promoting PTEN Inhibition via STAT3 and ERK-1/2 Signaling in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhana, L.; Nangia-Makker, P.; Arbit, E.; Shango, K.; Sarkar, S.; Mahmud, H.; Hadden, T.; Yu, Y.; Majumdar, A.P.N. Bile acid: A potential inducer of colon cancer stem cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2016, 7, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, M.K.; Park, J.S.; Park, J.H.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, H.D.; Bae, W.K.; Chung, I.J.; Shin, B.A.; Jung, Y.D. Lithocholic acid upregulates uPAR and cell invasiveness via MAPK and AP-1 signaling in colon cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2010, 290, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’sUllivan, J.; Lysaght, J.; Donohoe, C.L.; Reynolds, J.V. Obesity and gastrointestinal cancer: The interrelationship of adipose and tumour microenvironments. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, N.; Jenab, M.; Gunter, M.J. Adiposity and gastrointestinal cancers: Epidemiology, mechanisms and future directions. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karczewski, J.; Begier-Krasińska, B.; Staszewski, R.; Popławska, E.; Gulczynska-Elhadi, K.; Dobrowolska, A. Obesity and the Risk of Gastrointestinal Cancers. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 2740–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagarde, C.B.; Kavalakatt, J.; Benz, M.C.; Hawes, M.L.; Arbogast, C.A.; Cullen, N.M.; McConnell, E.C.; Rinderle, C.; Hebert, K.L.; Khosla, M.; et al. Obesity-associated epigenetic alterations and the obesity-breast cancer axis. Oncogene 2024, 43, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madani, N.H.; Etemadi, A.; Nalini, M.; Poustchi, H.; Khajavi, A.; Mirzazade, E.; Mirfakhraei, H.; Pourshams, A.; Khoshnia, M.; Gharavi, A.; et al. Obesity and incident gastrointestinal cancers: Overall body size or central obesity measures, which factor matters? Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2021, 30, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Song, M.; Lee, D.H.; Giovannucci, E.L. The Role of Mendelian Randomization Studies in Deciphering the Effect of Obesity on Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2022, 114, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, M.Y.; Takeuchi, F.; Kato, N. Deciphering the genetic landscape of obesity: A data-driven approach to identifying plausible causal genes and therapeutic targets. J. Hum. Genet. 2023, 68, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, S.; Ekeanyanwu, R.; Jiang, Y.; Davis, D.; Spechler, S.J.; Souza, R.F. Obesity and its effects on the esophageal mucosal barrier. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2021, 321, G335–G343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, L.; Long, E.; Beales, I.L. Pathophysiological mechanisms linking obesity and esophageal adenocarcinoma. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2014, 5, 534–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renehan, A.G.; Tyson, M.; Egger, M.; Heller, R.F.; Zwahlen, M. Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Lancet 2008, 371, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyo, C.; Cook, M.B.; Kamangar, F.; Freedman, N.D.; Whiteman, D.C.; Bernstein, L.; Brown, L.M.; Risch, H.A.; Ye, W.; Sharp, L.; et al. Body mass index in relation to oesophageal and oesophagogastric junction adenocarcinomas: A pooled analysis from the International BEACON Consortium. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 1706–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Abraham, N.S.; El-Serag, H.B. Meta-Analysis: Obesity and the Risk for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Its Complications. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005, 143, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.-P. Risk Factors of Gastric Cancer and Lifestyle Modification for Prevention. J. Gastric Cancer 2024, 24, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Qiao, L. Obesity and gastric cancer. Front. Biosci. 2012, 17, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Yan, Z.; Cheng, J.; Gong, G.; Li, G. Body Mass Index and Risk of Gastric Cancer: A Meta-analysis of a Population with More Than Ten Million from 24 Prospective Studies. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2013, 22, 1395–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, A.; Corley, D.A. Body Mass Index and Adenocarcinomas of the Esophagus or Gastric Cardia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2006, 15, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, J.; Ren, D.; Yan, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. A rising trend of gastric cardia cancer in Gansu Province of China. Cancer Lett. 2008, 269, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrova, K.; Nimptsch, K.; Pischon, T. Obesity and colorectal cancer. Front. Biosci. 2013, 5, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasiuk, A.; Mosińska, P.; Fichna, J. The mechanisms linking obesity to colon cancer: An overview. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 12, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, S.J.D. Diet, microorganisms and their metabolites, and colon cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zheng, X.; Zong, X.; Li, Z.; Li, N.; Hur, J.; Fritz, C.D.; William, C., Jr.; Nickel, K.B.; Tipping, A.; et al. Metabolic syndrome, metabolic comorbid conditions and risk of early-onset colorectal cancer. Gut 2021, 70, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Lee, D.H.; Han, K.-D.; Shin, C.M.; Kim, N. Abdominal obesity, glucose intolerance and decreased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol as components of the metabolic syndrome are associated with the development of colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 33, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Wan, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wu, X. Metabolic syndrome and the risk of colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2021, 36, 2215–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marengo, A.; Rosso, C.; Bugianesi, E. Liver Cancer: Connections with Obesity, Fatty Liver, and Cirrhosis. Annu. Rev. Med. 2016, 67, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: From pathophysiology to therapeutics. Metabolism 2019, 92, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calle, E.E.; Rodriguez, C.; Walker-Thurmond, K.; Thun, M.J. Overweight, Obesity, and Mortality from Cancer in a Prospectively Studied Cohort of U.S. Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, S.; Aleksandrova, K.; Pischon, T.; Fedirko, V.; Jenab, M.; Trepo, E.; Boffetta, P.; Dahm, C.C.; Overvad, K.; Tjønneland, A.; et al. Abdominal obesity, weight gain during adulthood and risk of liver and biliary tract cancer in a European cohort. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.; Yang, H.I.; Yang, W.S.; Liu, C.J.; Chen, P.J.; You, S.L.; Wang, L.Y.; Sun, C.A.; Lu, S.N.; Chen, D.S.; et al. Metabolic Factors and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Chronic Hepatitis B/C Infection: A Follow-up Study in Taiwan. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothuraju, R.; Rachagani, S.; Junker, W.M.; Chaudhary, S.; Saraswathi, V.; Kaur, S.; Batra, S.K. Pancreatic cancer associated with obesity and diabetes: An alternative approach for its targeting. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, J.D.; Surana, R.; Valle, J.W.; Shroff, R.T. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2020, 395, 2008–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preziosi, G.; Oben, J.A.; Fusai, G. Obesity and pancreatic cancer. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 23, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gonzalez, A.B.; Sweetland, S.; Spencer, E. A meta-analysis of obesity and the risk of pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 89, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, S.C.; Orsini, N.; Wolk, A. Body mass index and pancreatic cancer risk: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 120, 1993–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, L.; de Gonzalez, A.B.; Hartge, P.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Park, Y.; Freedman, D.M.; Gail, M.H.; Alavanja, M.C.R.; Albanes, D.; Freeman, L.E.B.; et al. Body mass index, effect modifiers, and risk of pancreatic cancer: A pooled study of seven prospective cohorts. Cancer Causes Control 2010, 21, 1305–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, B.; Qiao, L. Association between obesity and gallbladder cancer. Front. Biosci. 2012, 17, 2550–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Gao, M.; Liu, N.; Zhang, G.; Xu, T.; Cui, W. Body Mass Index and Risk of Gallbladder Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8321–8334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.C.; Wolk, A. Obesity and the risk of gallbladder cancer: A meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 1457–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gastrointestinal Cancer | Mechanisms Linking Obesity to Cancer |
|---|---|
| Esophageal Adenocarcinoma | GERD and Barrett’s esophagus progression; VAT-induced cytokine inflammation; altered adipokines (↑ leptin, ↓ adiponectin) |
| Gastric Cancer (Cardia) | GERD-induced mucosal damage; elevated intra-abdominal pressure; insulin resistance; ↑ leptin and inflammation |
| Colorectal Cancer | Insulin resistance, adipokine imbalance, chronic inflammation; dietary effects on microbiota; metabolic syndrome |
| Hepatocellular Carcinoma | Lipid accumulation → MASLD/MASH → fibrosis and cirrhosis; inflammatory cytokine infiltration |
| Pancreatic Cancer | Free fatty acid infiltration; insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia; gut microbiome-mediated inflammation |
| Gallbladder Cancer | Gallstone formation from cholesterol supersaturation; delayed gallbladder emptying; hormonal changes (↑ estrogen) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, F.; Moore, J.; Markouli, M.; Ghusn, W. The Oncogenic Burden of Obesity: Mechanistic Links Between Adiposity and Gastrointestinal Cancers—A Comprehensive Narrative Review. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071571
Lee F, Moore J, Markouli M, Ghusn W. The Oncogenic Burden of Obesity: Mechanistic Links Between Adiposity and Gastrointestinal Cancers—A Comprehensive Narrative Review. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(7):1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071571
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Felicia, Jessica Moore, Mariam Markouli, and Wissam Ghusn. 2025. "The Oncogenic Burden of Obesity: Mechanistic Links Between Adiposity and Gastrointestinal Cancers—A Comprehensive Narrative Review" Biomedicines 13, no. 7: 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071571
APA StyleLee, F., Moore, J., Markouli, M., & Ghusn, W. (2025). The Oncogenic Burden of Obesity: Mechanistic Links Between Adiposity and Gastrointestinal Cancers—A Comprehensive Narrative Review. Biomedicines, 13(7), 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071571







