Velefibrinase: A Marine-Derived Fibrinolytic Enzyme with Multi-Target Antithrombotic Effects Across Diverse In Vivo Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animals
2.3. Assessment of Tail Vein Bleeding Time and Clotting Time
2.4. Evaluation of the In Vivo Antithrombotic Activity of Velefibrinase in a Model of Acute Pulmonary Thromboembolism
2.5. In Vivo Evaluation of the Antithrombotic Activity of Velefibrinase in a Carotid Artery Thrombosis Model
2.6. Cerebral I/R Injury Model
2.7. Evaluation of Neurological Deficits and Cerebral Infarct Volume in the Cerebral I/R Injury Model
2.8. Determination of the Antiplatelet and Anticoagulation Activity of Velefibrinase in a Cerebral I/R Injury Model
2.9. Detection of the Levels of TXB2/6-keto-PGF1a, Oxidative-Stress-Related Factors, and Inflammatory Cytokines in Plasma
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Velefibrinase Prolonged Blood BT and CT
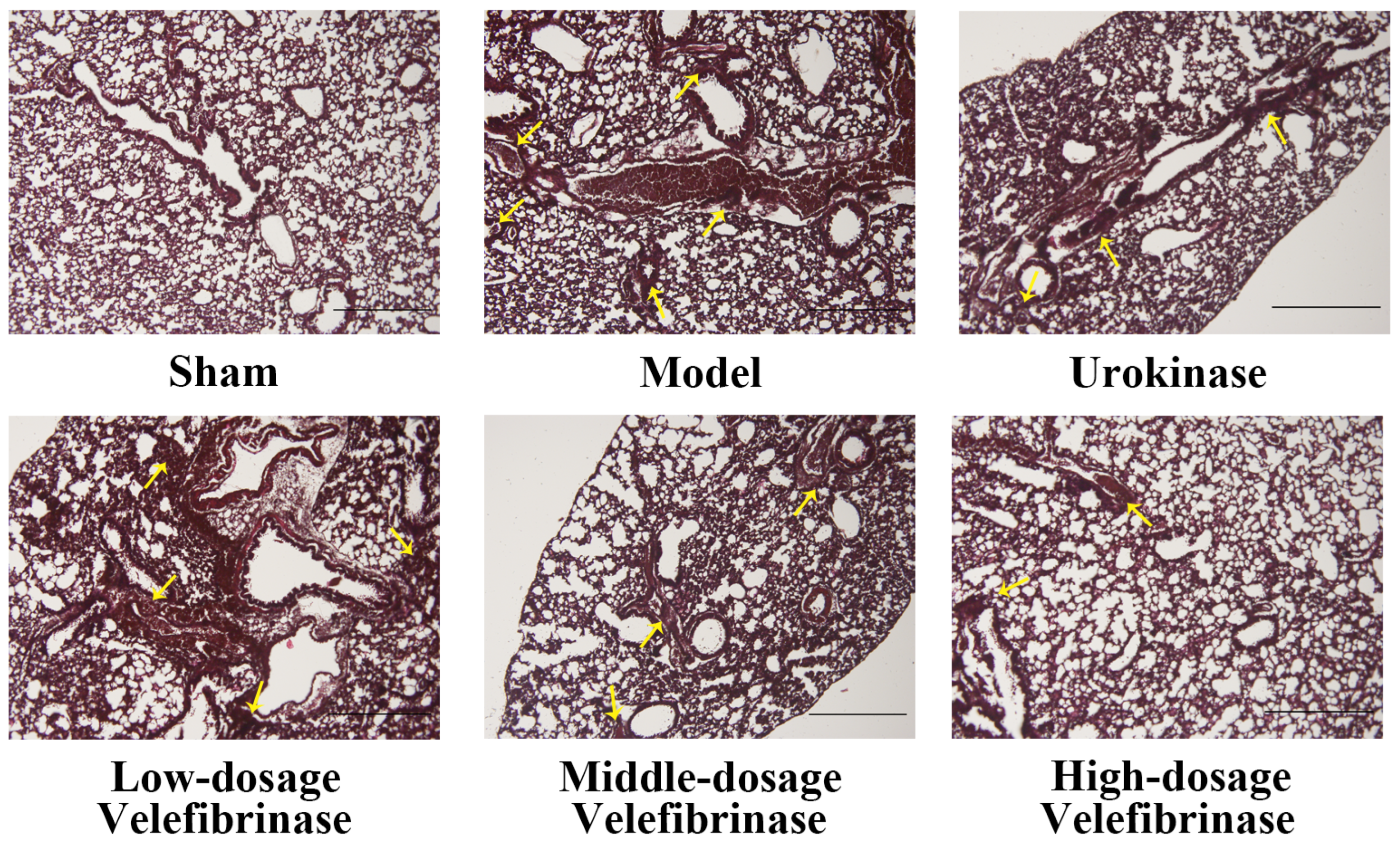
3.2. The Effect of Velefibrinase on Acute Pulmonary Thromboembolism
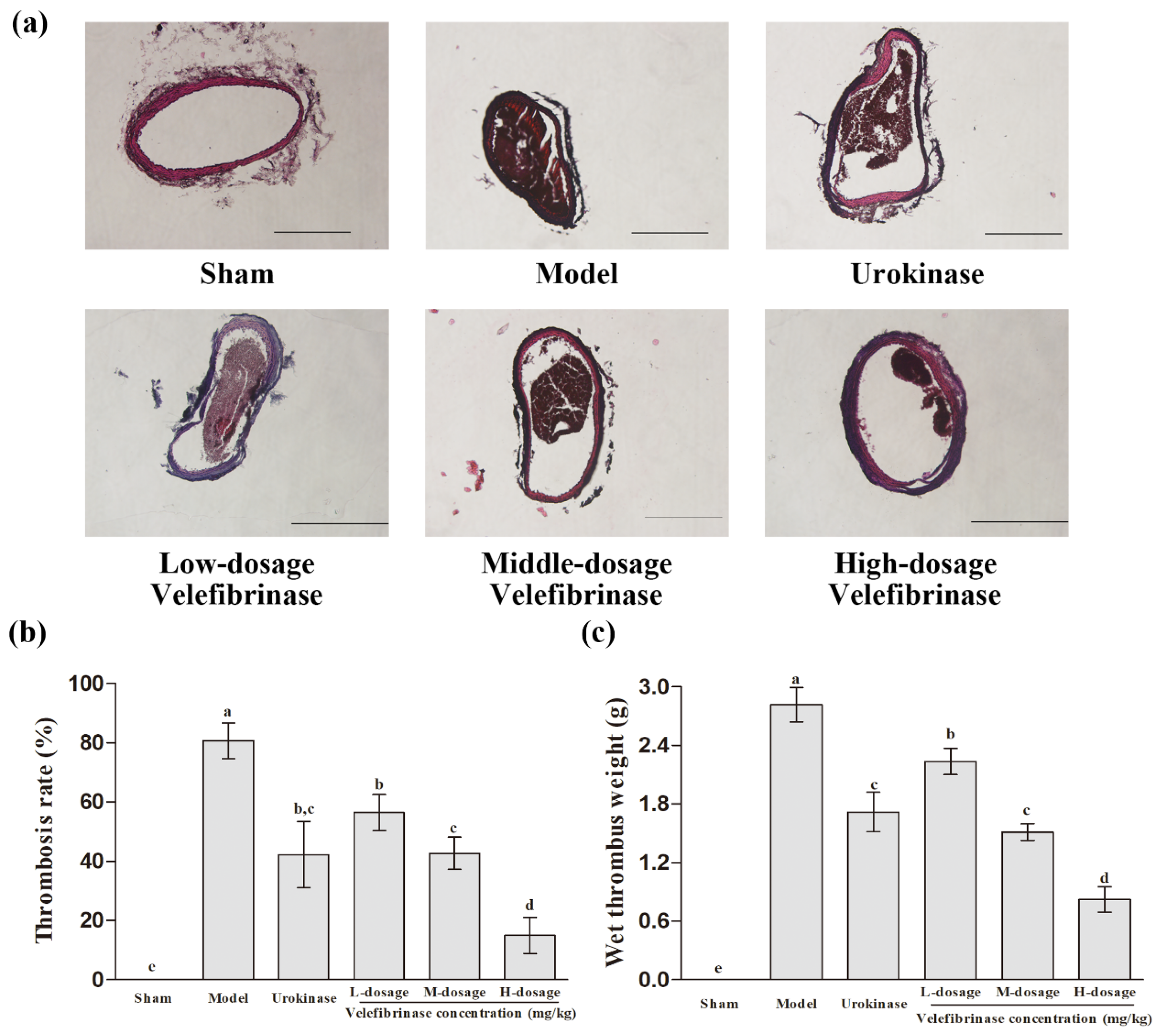
3.3. Velefibrinase Relieved the Infarction Resulting from FeCl3-Induced Carotid Arterial Thrombosis
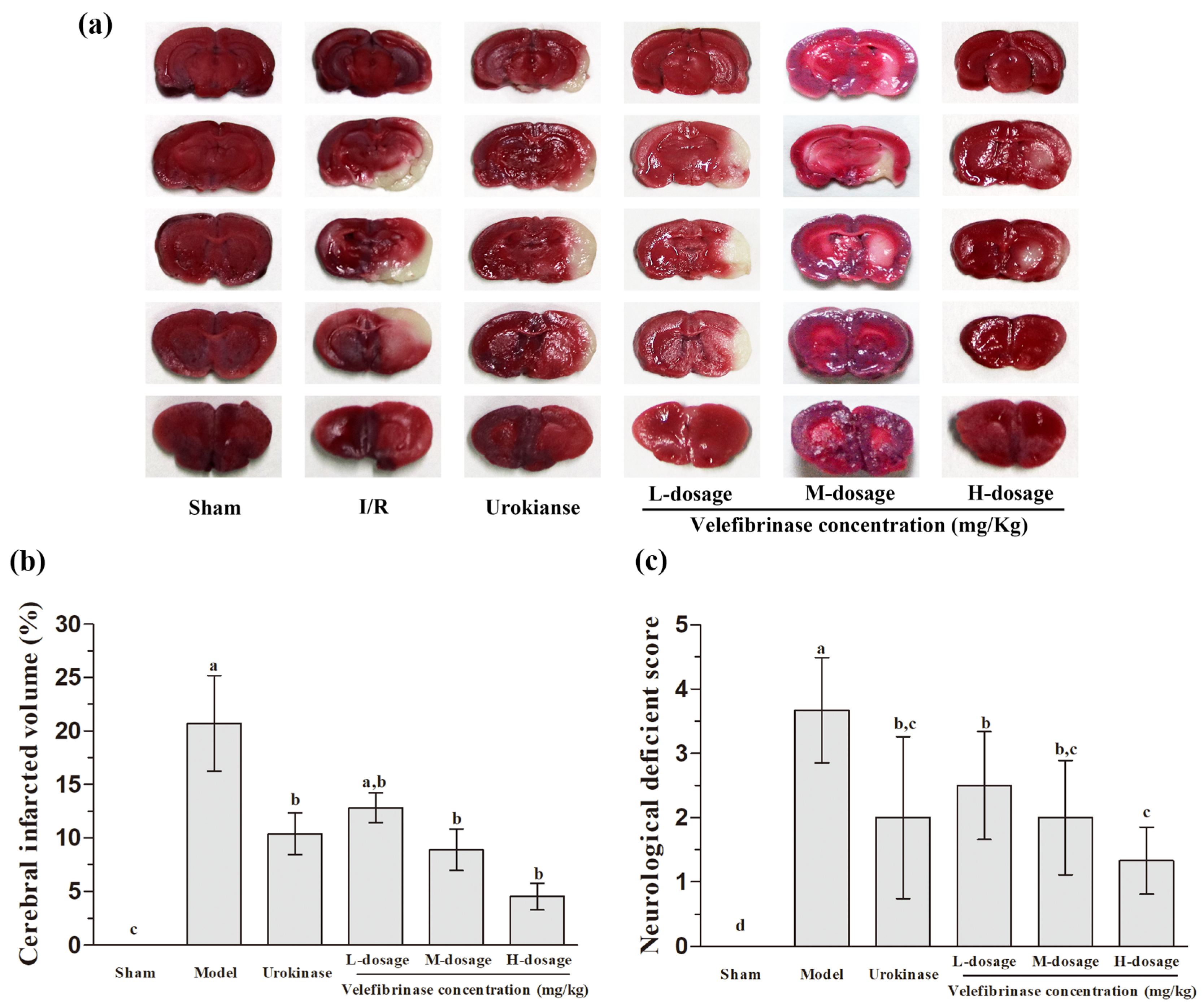
3.4. Velefibrinase Improved Brain Infarcts and Attenuated Neurological Deficits in MCAO/R Rats
3.5. The Effect of Velefibrinase on Platelet Aggregation and the Levels of TXB2 and 6-keto-PGF1a in MCAO/R Rats
3.6. The Effect of Velefibrinase on Coagulation Parameters in MCAO/R Rats
3.7. Velefibrinase Ameliorated Oxidative Stress and Reduced Inflammatory Cytokine Levels in MCAO/R Rats
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADP | Adenosine Diphosphate |
| aPTT | Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time |
| BT | Bleeding Time |
| CAT | Catalase |
| CT | Clotting Time |
| FIB | Fibrinogen |
| GSH-Px | Glutathione Peroxidase |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| I/R | Ischemia/Reperfusion |
| MCAO/R | Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion and Reperfusion |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| PPP | Platelet-Poor Plasma |
| PT | Prothrombin Time |
| SOD | Superoxide Dismutase |
| TTC | 2,3,5-Triphenyltetrazolium Chloride |
| TDs | Thrombotic Diseases |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-α |
| TTC | 2,3,5-Triphenyltetrazolium Chloride |
| TT | Thrombin Time |
References
- Salunke, A.S.; Nile, S.H.; Kharat, A.S. A comparative study on fibrinolytic enzymes extracted from six Bacillus spp. isolated from fruit-vegetable waste biomass. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 102149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, T.; Hsu, C.Y.; Khamrang, T.; Hsia, C.H.; Hsia, C.W.; Manubolu, M.; Sheu, J.R. Possible Molecular Targets of Novel Ruthenium Complexes in Antiplatelet Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, D.; Arora, N.; Kalita, B.; Sarma, R.; Islam, T.; Ghosh, S.S.; Devi, R.; Mukherjee, A.K. Anticoagulant mechanism, pharmacological activity, and assessment of preclinical safety of a novel fibrin(ogen)olytic serine protease from leaves of Leucas indica. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumdar, S.; Sarmah, B.; Gogoi, D.; Banerjee, S.; Ghosh, S.S.; Banerjee, S.; Chattopadhyay, P.; Mukherjee, A.K. Characterization, mechanism of anticoagulant action, and assessment of therapeutic potential of a fibrinolytic serine protease (Brevithrombolase) purified from Brevibacillus brevis strain FF02B. Biochimie 2014, 103, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, T.S.; Athimoolam, S.; Vijayaraghavan, P. Biosynthesis and Characterization of a Novel Fibrinolytic Alkaline Serine Protease from Newly Isolated Bacillus flexus BF12 for Biomedical Applications. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2021, 22, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Gao, Z.; Xing, S.; Long, J.; Li, C.; He, L.; Wang, X. Purification, characterization, and chemical modification of Bacillus velezensis SN-14 fibrinolytic enzyme. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 177, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, A.; Frey, M.E.; Munoz, F.; Fernandez, M.B.; Pedraza, A.; Galban, G.; Garcia, D.N.; Daleo, G.R.; Guevara, M.G. Fibrin(ogen)olytic and antiplatelet activities of a subtilisin-like protease from Solanum tuberosum (StSBTc-3). Biochimie 2016, 125, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marder, V.J.; Novokhatny, V. Direct fibrinolytic agents: Biochemical attributes, preclinical foundation and clinical potential. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharnaior, P.; Das, M.; Tamang, J.P. Therapeutic and Anti-Thrombotic Properties of Some Naturally Fermented Soybean Foods of the Eastern Himalayas. Fermentation 2023, 9, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernyshenko, V.; Platonova, T.; Makogonenko, Y.; Rebriev, A.; Mikhalovska, L.; Chernyshenko, T.; Komisarenko, S. Fibrin(ogen)olytic and platelet modulating activity of a novel protease from the Echis multisquamatis snake venom. Biochimie 2014, 105, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Hu, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, B.; Yang, W.; Lu, Y.; Li, P.; Du, S. Novel Pheretima guillelmi-derived antithrombotic protein DPf3: Identification, characterization, in vitro evaluation and antithrombotic mechanisms investigation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, S.M.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, M.S.; Park, B.R.; Kim, S.G.; Ahn, H.; Chun, H.S.; Shin, Y.K.; Kim, J.J.; et al. Purification and characterization of a novel fibrinolytic alpha chymotrypsin like serine metalloprotease from the edible mushroom, Lyophyllum shimeji. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2014, 117, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Pan, S.; Chen, G.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Liang, Z. Biochemical characteristics of a fibrinolytic enzyme purified from a marine bacterium, Bacillus subtilis HQS-3. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzkar, N.; Jahromi, S.T.; Vianello, F. Marine Microbial Fibrinolytic Enzymes: An Overview of Source, Production, Biochemical Properties and Thrombolytic Activity. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, H.; Yu, B.; Chen, G.; Liang, Z. Purification and Characterization of a Fibrinolytic Enzyme from Marine Bacillus velezensis Z01 and Assessment of Its Therapeutic Efficacy In Vivo. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedik, G.; Asan, H.; Özyurt, A.; Allı, H.; Asan, A.; Nazlı, H.; Sarp, Ö. Effect of gel formulation obtained from Fomes fomentarius on bleeding and clotting time: A pilot study. İstanb. J. Pharm. 2020, 50, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghmare, R.V. Influence of Blood Groups on Bleeding and Clotting Time. Int. Physiol. 2018, 6, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Tong, R.; Zhou, M.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, G.; Lu, D.; Meng, G.; et al. Circadian nuclear receptor Rev-erbα is expressed by platelets and potentiates platelet activation and thrombus formation. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 2317–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, Y.; Li, J.S.; Zhao, P.; Bai, Y.P.; Feng, S.X.; Liu, X.F.; Wang, Y.; Bian, Q.Q.; Li, J.Z. Long-Term Effects of TCM Yangqing Kangxian Formula on Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats via Regulating Nuclear Factor-κB Signaling. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 2089027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, S.; Yoon, J.; Park, D.H.; Shin, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; Cho, S.S. Purification and partial characterization of a low molecular fibrinolytic serine metalloprotease C142 from the culture supernatant of Bacillus subtilis C142. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Zhu, T.; Dong, X.; Nan, F.; Meng, X.; Zhou, P.; Sun, G.; Sun, X. HMGB1-triggered inflammation inhibition of notoginseng leaf triterpenes against cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury via MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Sun, G.; Ye, J.; Xu, H.; Sun, X. Suppression of NADPH oxidase- and mitochondrion-derived superoxide by Notoginsenoside R1 protects against cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury through estrogen receptor-dependent activation of Akt/Nrf2 pathways. Free Radic. Res. 2014, 48, 823–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.; Wang, M.; Jin, R.; Li, G. Blocking of PI3-kinase beta protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by reducing platelet activation and downstream microvascular thrombosis in rats. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-W.; Choi, J.-H.; Park, S.-E.; Kim, S.; Sapkota, K.; Kim, S.-J. Purification and characterization of a fibrinolytic enzyme from Petasites japonicus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ten Cate, H.; Gupta, A.K.; Chopra, B.S.; Vaid, B.; Sagar, A.; Raut, S.; Badmalia, M.D.; Ashish; Khatri, N. Protective effects of gelsolin in acute pulmonary thromboembolism and thrombosis in the carotid artery of mice. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Osmolovskiy, A.; Singh, R. Microbial Fibrinolytic Enzymes as Anti-Thrombotics: Production, Characterisation and Prodigious Biopharmaceutical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, D.; Ge, L.; Wang, T.; Ma, Z.; Han, Y.; Duan, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, W.; Yuan, J.; et al. Catestatin prevents endothelial inflammation and promotes thrombus resolution in acute pulmonary embolism in mice. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20192236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, L.K.; Kline, J.A. Fibrinolytics for the treatment of pulmonary embolism. Transl. Res. 2020, 225, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckly, A.; Hechler, B.; Freund, M.; Zerr, M.; Cazenave, J.P.; Lanza, F.; Mangin, P.H.; Gachet, C. Mechanisms underlying FeCl3-induced arterial thrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zennadi, R. Oxidative Stress and Thrombosis during Aging: The Roles of Oxidative Stress in RBCs in Venous Thrombosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Zhou, G.-S.; Liu, X.; Tang, Y.-P.; Liu, R.; Liu, P.; Li, N.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; et al. A Novel Antithrombotic Protease from Marine Worm Sipunculus nudus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Wang, F.; Ge, W.; Meng, X.; Fan, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Ding, M.; Gu, S.; Xing, X.; et al. Scutellarin attenuates oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through PI3K/Akt-mediated Nrf2 signaling pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 957, 175979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, H.-Q.; Lu, L.; Fu, D.-L.; Liu, A.-J.; Li, J.-H.; Zheng, G.-Q. Ginsenoside Rg1 provides neuroprotection against blood brain barrier disruption and neurological injury in a rat model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion through downregulation of aquaporin 4 expression. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; McGowan, E.M.; Ren, N.; Lal, S.; Nassif, N.; Shad-Kaneez, F.; Qu, X.; Lin, Y. Nattokinase: A Promising Alternative in Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. Biomark. Insights 2018, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, M.; Zhou, J.; Ye, T.; Xie, X.; Ni, D.; Ye, J.; Han, Q.; Di, C.; Guo, L.; et al. Shuxuening injection protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through reducing oxidative stress, inflammation and thrombosis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Zhou, P.; Sun, Y.; Meng, X.; Dai, Z.; Sun, G.; Sun, X. Protective Effects and Target Network Analysis of Ginsenoside Rg1 in Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury: A Comprehensive Overview of Experimental Studies. Cells 2018, 7, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-H.; Li, Q.; Deng, Z.-H.; Ji, X.; Jiang, X.; Ge, X.; Bo, Q.-Q.; Cui, J.-Y.; Zhang, L.-Z.; Liu, J.-K.; et al. Neanthes japonica (Iznka) fibrinolytic enzyme reduced cerebral infarction, cerebral edema and increased antioxidation in rat models of focal cerebral ischemia. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 489, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, C.-L.; Zhai, F.-G.; Guan, L.-X.; Yang, J. Neuroprotective Effect of the Ginsenoside Rg1 on Cerebral Ischemic Injury In Vivo and In Vitro Is Mediated by PPARγ-Regulated Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Pathways. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 7842082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosawa, Y.; Nirengi, S.; Homma, T.; Esaki, K.; Ohta, M.; Clark, J.F.; Hamaoka, T. A single-dose of oral nattokinase potentiates thrombolysis and anti-coagulation profiles. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.-J.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, J.; An, G.; Kim, D.; Kwon, Y.-R.; Lee, A.M.; Kim, Y.-B.; Kim, H.-H. Abstract W P262: Neuroprotective Effect of Nattokinase Mediated by Inhibition of Platelet Aggregation and Thrombosis in Photothrombotic Stroke. Stroke 2015, 46, AWP262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Song, Z.; Han, M.; Yu, B.; Lv, G.; Han, N.; Liu, Z.; Yin, J. Evaluation of the antithrombotic activity of Zhi-Xiong Capsules, a Traditional Chinese Medicinal formula, via the pathway of anti-coagulation, anti-platelet activation and anti-fibrinolysis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 1622–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, M.; Qi, H. Sulfation, anticoagulant and antioxidant activities of polysaccharide from green algae Enteromorpha linza. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 58, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Groups | Dose (mg/kg) | BT (s) | CT (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | - | 173.17 ± 10.93 d | 122.67 ± 7.79 c |
| Urokinase | 0.44 | 195.67 ± 10.41 b,c | 134.83 ± 8.33 b |
| L-dosage (Velefibrinase) | 0.22 | 185.33 ± 12.94 c,d | 135.33 ± 9.42 b |
| M-dosage (Velefibrinase) | 0.44 | 200.50 ± 14.32 a,b | 141.50 ± 6.47 b |
| H-dosage (Velefibrinase) | 0.88 | 212.33 ± 13.50 a | 166.50 ± 7.82 a |
| Groups | Dose (mg/kg) | No. Dead/No. Tested | Protection (%) | Lung Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | - | 0 | 100 | 0.76 ± 0.03 e |
| Model | - | 6 | 0 | 1.10 ± 0.06 a |
| Urokinase | 0.44 | 2 | 66.67 | 0.95 ± 0.04 b,c |
| L-dosage (Velefibrinase) | 0.22 | 3 | 50 | 0.99 ± 0.05 b |
| M-dosage (Velefibrinase) | 0.44 | 3 | 50 | 0.94 ± 0.03 c |
| H-dosage (Velefibrinase) | 0.88 | 2 | 66.67 | 0.88 ± 0.05 d |
| Groups | Dose (mg/kg) | Platelet Aggregation Rate (%) | TXB2 (pg/mL) | 6-keto-PGF1a (pg/mL) | Ratio of TXB2 to 6-keto-PGF1a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sham | - | 45.92 ± 4.80 d | 279.36 ± 15.02 e | 542.27 ± 14.61 d | 1.94 ± 0.09 a |
| I/R | - | 74.97 ± 5.50 a | 595.36 ± 21.62 a | 448.73 ± 29.51 e | 0.75 ± 0.06 e |
| Urokinase | 0.34 | 64.48 ± 7.05 b | 466.45 ± 17.18 c | 669.36 ± 18.56 a,b | 1.44 ± 0.08 c |
| L-dosage (Velefibrinase) | 0.17 | 68.45 ± 6.06 a,b | 522.09 ± 18.28 b | 616.82 ± 21.49 c | 1.18 ± 0.05 d |
| M-dosage (Velefibrinase) | 0.34 | 61.68 ± 5.40 b,c | 467.91 ± 21.99 c | 652.09 ± 20.44 b | 1.40 ± 0.07 c |
| H-dosage (Velefibrinase) | 0.68 | 56.70 ± 8.91 c | 393.18 ± 13.88 d | 695.18 ± 17.74 a | 1.77 ± 0.04 b |
| Groups | Dose (mg/kg) | aPTT (s) | PT (INR) | TT (s) | FIB (g/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sham | - | 40.82 ± 3.73 a | 2.92 ± 0.28 a | 34.13 ± 2.55 a | 3.85 ± 0.18 d |
| I/R | - | 23.22 ± 3.99 c | 2.27 ± 0.21 b | 23.27 ± 2.52 d | 5.33 ± 0.73 a |
| Urokinase | 0.34 | 27.83 ± 2.58 b | 2.67 ± 0.27 a | 27.38 ± 2.99 c | 4.82 ± 0.42 b |
| L-dosage (Velefibrinase) | 0.17 | 28.15 ± 2.34 b | 2.34 ± 0.21 b | 27.55 ± 3.61 c | 4.81 ± 0.32 b |
| M-dosage (Velefibrinase) | 0.34 | 31.30 ± 3.00 b | 2.69 ± 0.27 a | 29.37 ± 2.23 b,c | 4.29 ± 0.31 c |
| H-dosage (Velefibrinase) | 0.68 | 37.77 ± 4.47 a | 2.79 ± 0.26 a | 31.98 ± 2.97 a,b | 4.02 ± 0.19 c,d |
| Groups | Dose (mg/kg) | MDA (μmol/mg pro) | SOD (U/mg pro) | CAT (U/mg pro) | GSH-Px (U/mg pro) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sham | - | 2.39 ± 0.06 c | 38.09 ± 5.82 a | 15.42 ± 1.24 a | 6.52 ± 0.72 a |
| I/R | - | 4.87 ± 0.44 a | 12.94 ± 2.35 d | 5.68 ± 0.85 f | 2.20 ± 0.52 e |
| Urokinase | 0.34 | 4.21 ± 0.50 b | 18.21 ± 3.93 c | 8.76 ± 1.14 d | 3.58 ± 0.28 c |
| L-dosage (Velefibrinase) | 0.17 | 4.41 ± 0.54 a,b | 17.66 ± 3.73 c,d | 7.40 ± 0.98 e | 2.84 ± 0.31 d |
| M-dosage (Velefibrinase) | 0.34 | 4.18 ± 0.49 b | 22.03 ± 4.20 c | 10.07 ± 0.94 c | 3.45 ± 0.41 c |
| H-dosage (Velefibrinase) | 0.68 | 3.99 ± 0.30 b | 27.76 ± 3.98 b | 11.88 ± 0.84 b | 4.26 ± 0.39 b |
| Groups | Dose (mg/kg) | TNF-α (pg/mL) | IL-1β (pg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sham | - | 47.83 ± 3.96 d | 90.74 ± 17.81 e |
| I/R | - | 65.00 ± 4.16 a | 293.56 ± 36.76 a |
| Urokinase | 0.34 | 57.19 ± 2.47 b | 221.66 ± 17.75 c |
| L-dosage (Velefibrinase) | 0.17 | 57.73 ± 4.89 b | 252.93 ± 23.79 b |
| M-dosage (Velefibrinase) | 0.34 | 52.50 ± 4.44 c | 190.99 ± 19.41 d |
| H-dosage (Velefibrinase) | 0.68 | 50.83 ± 2.60 c,d | 171.83 ± 18.81 d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Yu, B.; Xie, C.; Liu, M.; Long, T.; Liang, Z. Velefibrinase: A Marine-Derived Fibrinolytic Enzyme with Multi-Target Antithrombotic Effects Across Diverse In Vivo Models. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061277
Zhou Y, Yu B, Xie C, Liu M, Long T, Liang Z. Velefibrinase: A Marine-Derived Fibrinolytic Enzyme with Multi-Target Antithrombotic Effects Across Diverse In Vivo Models. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(6):1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061277
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yuting, Bo Yu, Chaoyin Xie, Manli Liu, Tiantian Long, and Zhiqun Liang. 2025. "Velefibrinase: A Marine-Derived Fibrinolytic Enzyme with Multi-Target Antithrombotic Effects Across Diverse In Vivo Models" Biomedicines 13, no. 6: 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061277
APA StyleZhou, Y., Yu, B., Xie, C., Liu, M., Long, T., & Liang, Z. (2025). Velefibrinase: A Marine-Derived Fibrinolytic Enzyme with Multi-Target Antithrombotic Effects Across Diverse In Vivo Models. Biomedicines, 13(6), 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061277





