Inhibition of TPI1 Sensitizes Cisplatin-Resistant Oral Cancer to Ferroptosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.2. Tissue Specimens and Patients
2.3. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.4. Cell Culture
2.5. Chemical Inhibitors and Treatments
2.6. Cell Viability Assay
2.7. IC50 Assay
2.8. Creation of Cisplatin-Resistant Cell Lines and Transfection
2.9. Transfection
2.10. Western Blot Assay
2.11. Reverse Transcription-Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.12. 3-[4,5-Dimethyl-2-thiazolyl]-2,5 diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium Bromide (MTT) Assay
2.13. Transwell Migration Assay
2.14. Wound Healing Assays
2.15. Fe2+ Measurement
2.16. Measurement of ROS Production, GSH Level, and Lipid Peroxidation
2.17. In Vivo Assay
2.18. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
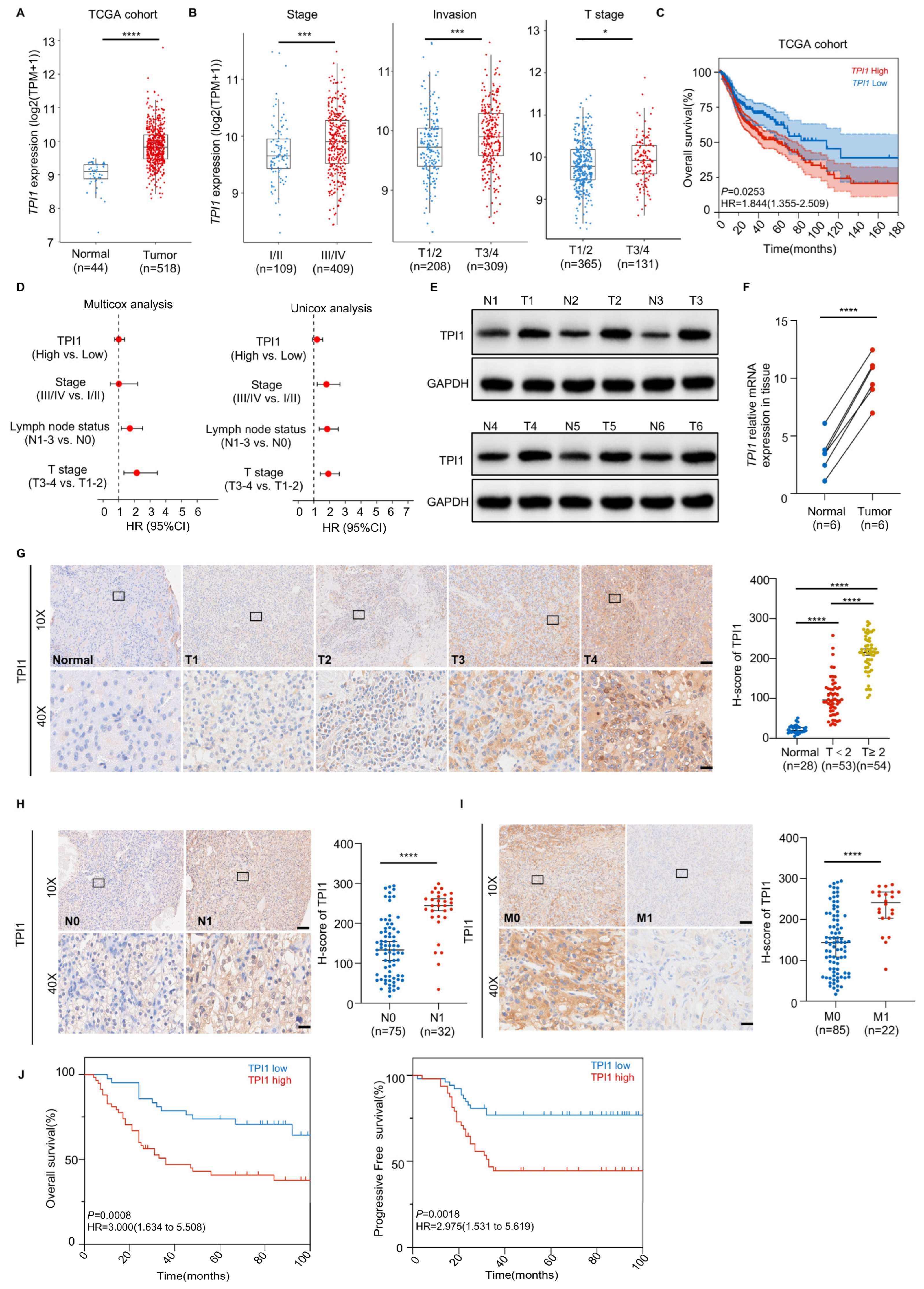
3.1. High TPI1 Levels in Oral Cancer Are Associated with Poor Prognosis and Serve as an Independent Predictive Biomarker
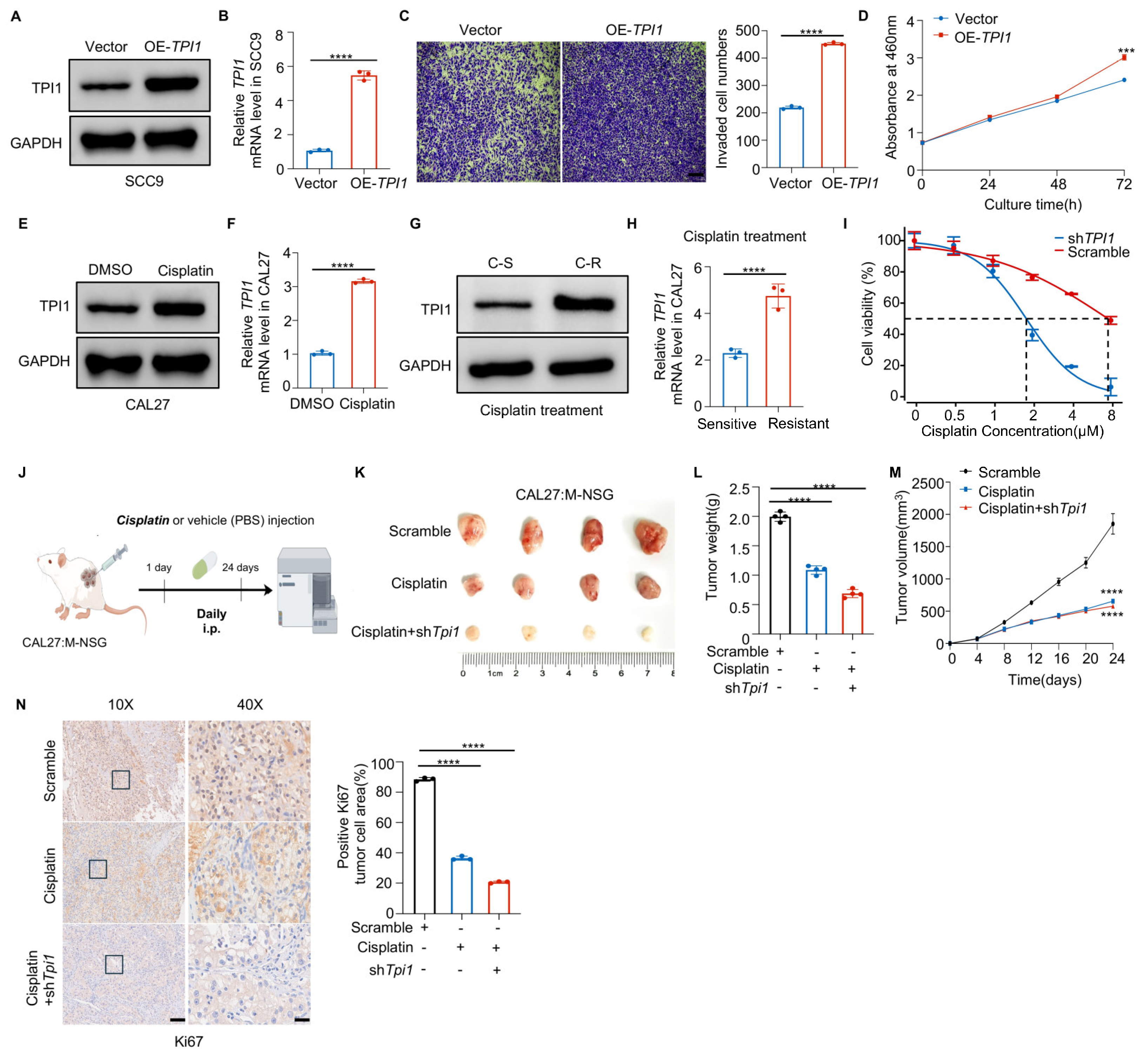
3.2. TPI1 Knockdown Impairs Oral Cancer Prognosis Both In Vitro and In Vivo
3.3. TPI1 Overexpression Accelerates Tumor Growth and Causes Cisplatin Resistance
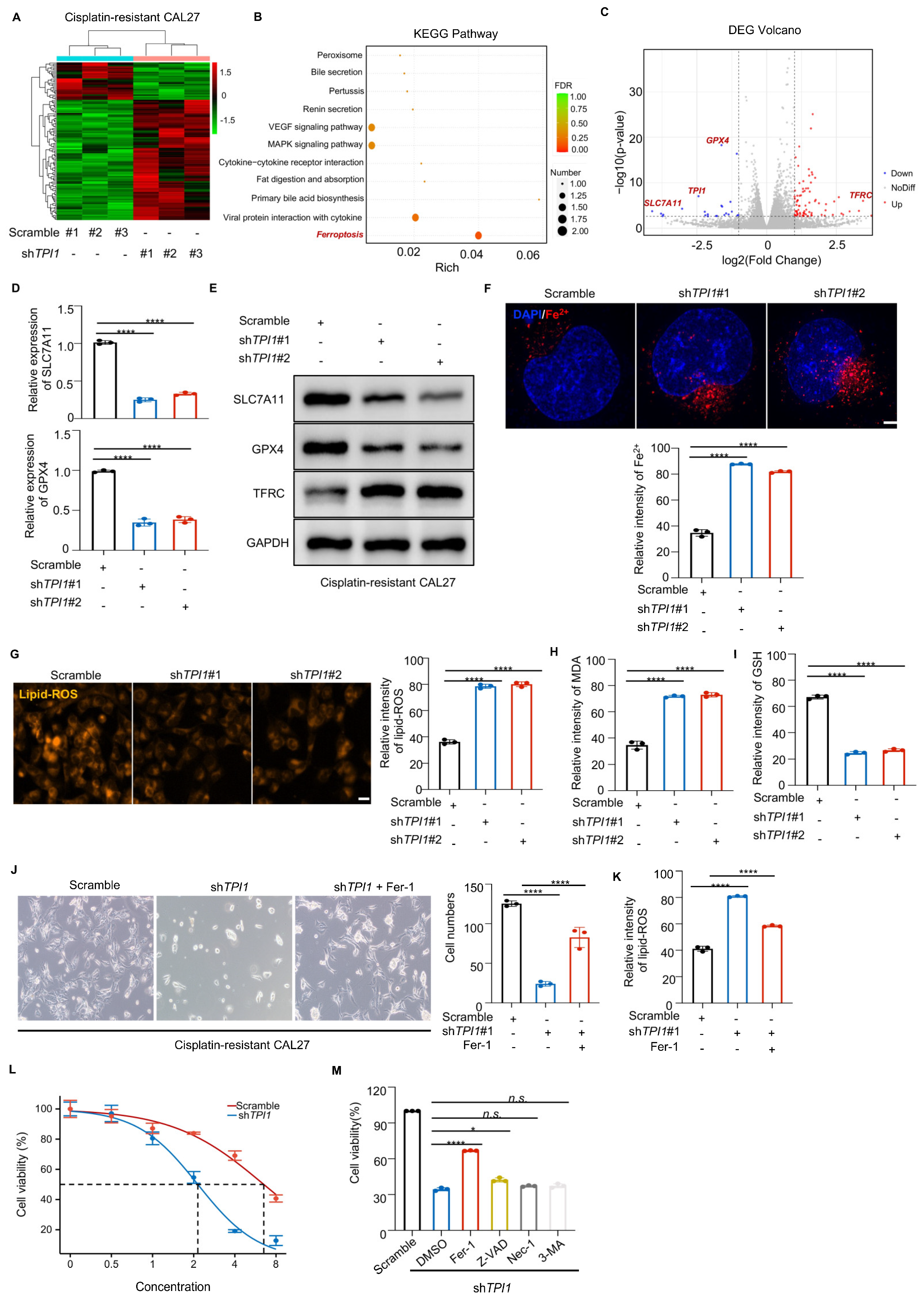
3.4. TPI1 Inhibition Triggered Ferroptosis in Cisplatin-Resistant Oral Cancer
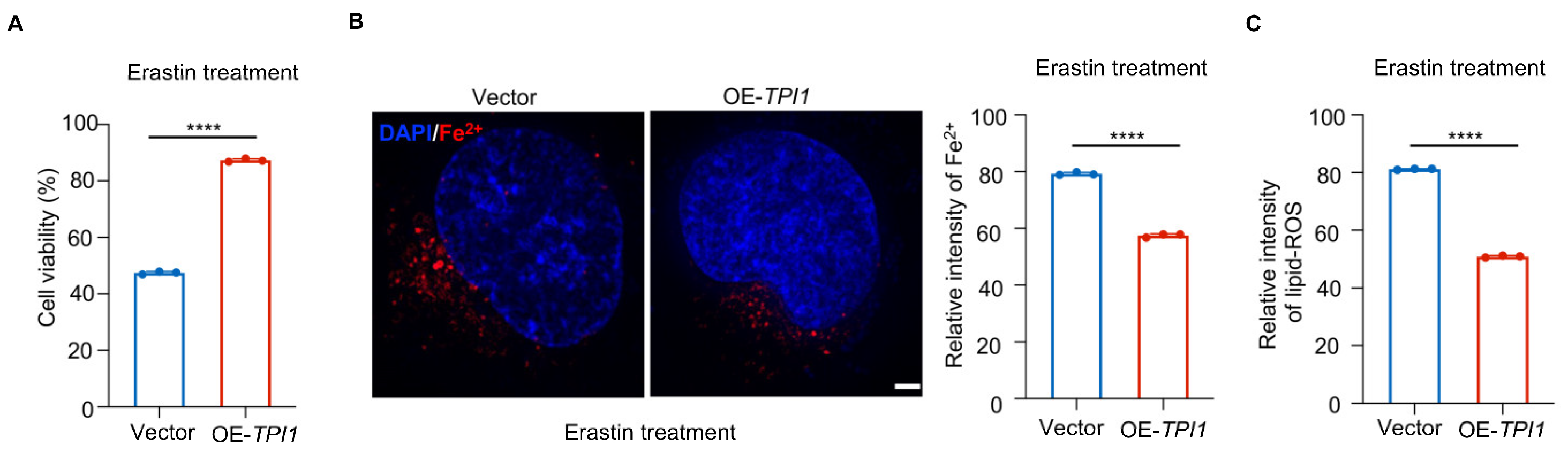
3.5. TPI1 Overexpression Protects Against Erastin-Induced Ferroptosis in Oral Cancer Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, E.H.; Shin, D.; Lee, J.; Jung, A.R.; Roh, J.L. CISD2 inhibition overcomes resistance to sulfasalazine-induced ferroptotic cell death in head and neck cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 432, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PDQ Supportive and Palliative Care Editorial Board. Oral Complications of Cancer Therapies (PDQ(R)): Patient Version. In PDQ Cancer Information Summaries; National Library of Medicine: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Aradya, A.; Kiran, P.K.; Raghavendra Swamy, K.N.; Doddawad, V.G.; Ranganatha, N.; Sravani, K. Oral Risk Factors in Patients with Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy—A Pilot Study. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2024, 35, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padure, A.; Horhat, R.; Talpos-Niculescu, I.C.; Scheusan, R.; Anghel, M.D.; Rusu, L.-C.; Lungeanu, D. Oral Mucositis in Adult Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy: Six-Month On-Treatment Follow-Up. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, H.; Haga, Y.; Lin, Y.; Tsujino, H.; Higashisaka, K.; Tsutsumi, Y. Osimertinib-tolerant lung cancer cells are susceptible to ferroptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 641, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, P.; Murialdo, R.; Barisione, C.; Lazzarini, E.; Garibaldi, S.; Fabbi, P.; Ruggeri, C.; Borile, S.; Carbone, F.; Armirotti, A.; et al. 5-fluorouracil causes endothelial cell senescence: Potential protective role of glucagon-like peptide 1. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 3713–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagioni, A.; Staderini, F.; Peri, S.; Versienti, G.; Schiavone, N.; Cianchi, F.; Papucci, L.; Magnelli, L. 5-Fluorouracil Conversion Pathway Mutations in Gastric Cancer. Biology 2020, 9, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, L.E.; Lalla, R.V. Dental Treatment Planning for the Patient with Oral Cancer. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 62, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rishi, G.; Huang, G.; Subramaniam, V.N. Cancer: The role of iron and ferroptosis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2021, 141, 106094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, B.R.; Jiang, X. The Chemistry and Biology of Ferroptosis. Cell Chem. Biol. 2020, 27, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedmann Angeli, J.P.; Krysko, D.V.; Conrad, M. Ferroptosis at the crossroads of cancer-acquired drug resistance and immune evasion. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Jin, S.; Chen, Y.; Guo, R. Ferroptosis in cancer therapy: A novel approach to reversing drug resistance. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhuo, Q.; Hu, Q.; Liu, M.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, G.; Xu, W.; Ji, S.; et al. Ferroptosis: Final destination for cancer? Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Palte, M.J.; Deik, A.A.; Li, H.; Eaton, J.K.; Wang, W.; Tseng, Y.-Y.; Deasy, R.; Kost-Alimova, M.; Dančík, V.; et al. A GPX4-dependent cancer cell state underlies the clear-cell morphology and confers sensitivity to ferroptosis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; You, J.H.; Shin, D.; Roh, J.L. Inhibition of Glutaredoxin 5 predisposes Cisplatin-resistant Head and Neck Cancer Cells to Ferroptosis. Theranostics 2020, 10, 7775–7786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.P. Metabolic control of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 1104–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Carlisle, A.E.; Peppers, A.; Park, S.J.; Doshi, M.B.; Spears, M.E.; Kim, D. xCT-Driven Expression of GPX4 Determines Sensitivity of Breast Cancer Cells to Ferroptosis Inducers. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Shan, D.; Li, S.; Zhang, S.; Zi, X.; Xing, F.; Shi, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, T.; Sun, X.; et al. A Novel Ferroptosis Related Gene Signature for Prognosis Prediction in Patients With Colon Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 654076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xu, B.; Han, Q.; Zhou, H.; Xia, Y.; Gong, C.; Dai, X.; Li, Z.; Wu, G. Ferroptosis: A Novel Anti-tumor Action for Cisplatin. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 50, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, G.; Ari, F. Therapeutic Targeting of Cancer Metabolism with Triosephosphate Isomerase. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e2000012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wang, D.; Lei, M.; Guo, Y.; Cui, Y.; Chen, F.; Sun, W.; Chen, X. TPI1 activates the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway to induce breast cancer progression by stabilizing CDCA5. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, T.; Miura, N.; Kato, S.; Masuda, T.; Ohashi, R.; Matsushita, A.; Matsuda, F.; Ohtsuki, S.; Katakura, A.; Honda, K. Identification of TPI1 As a potential therapeutic target in pancreatic cancer with dependency of TP53 mutation using multi-omics analysis. Cancer Sci. 2024, 115, 3622–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman-Luna, V.; Olvera-Rodriguez, L.; Bustamante-Villalobos, P.; Saab-Rincon, G. Characterization of a New Allelic Variant of Triosephosphate Isomerase from the LNCaP Human Prostate Cancer Cell Line: Enzyme Inhibition and Spectroscopic Studies. Curr. Enzym. Inhib. 2015, 13, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tamesa, M.S.; Kuramitsu, Y.; Fujimoto, M.; Maeda, N.; Nagashima, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Oka, M.; Nakamura, K. Detection of autoantibodies against cyclophilin A and triosephosphate isomerase in sera from breast cancer patients by proteomic analysis. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 2168–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Ma, N.; Shang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Chen, T.; Guan, D.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, E.; Feng, Y.; et al. Triosephosphate isomerase 1 suppresses growth, migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 1048–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; Yang, J.; Shi, Y.; Lan, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhai, H.; Fan, D. Identification of triosephosphate isomerase as an anti-drug resistance agent in human gastric cancer cells using functional proteomic analysis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 134, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enríquez-Flores, S.; Flores-López, L.A.; Mora, I.D.l.M.-D.l.; García-Torres, I.; Gracia-Mora, I.; Gutiérrez-Castrellón, P.; Fernández-Lainez, C.; Martínez-Pérez, Y.; Olaya-Vargas, A.; de Vos, P.; et al. Naturally occurring deamidated triosephosphate isomerase is a promising target for cell-selective therapy in cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Li, R. Contemporary Treatment of Locally Advanced Oral Cancer. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2019, 20, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjioe, K.C.; Cardoso, D.M.; Oliveira, S.H.P.; Bernabe, D.G. Stress hormone norepinephrine incites resistance of oral cancer cells to chemotherapy. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2022, 29, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Target Sequence | |
|---|---|
| sh-TPI1 | F:CCGGTGATGTGGATGGCTTCCTTGTCTCGAGACAAGGAAGCCATCCACATCATTTTTG |
| R:AATTCAAAAATGATGTGGATGGCTTCCTTGTCTCGAGACAAGGAAGCCATCCACATCA | |
| Scramble | F:CCGGTTGGTGCTATGCGTGTACTGTCTCGAGAGTACACGCATAGCACCAATTTTTG |
| R:AATTCAAAAATTGGTGCTATGCGTGTACTGTCTCGAGAGTACACGCATAGCACCAA |
| Target Sequence | |
|---|---|
| TPI1 | F: ACTGCCTATATCGACTTCGCC |
| R: AAGCCCCATTAGTCACTTTGTAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.; Zheng, H.; Chen, Y.; Hao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, N. Inhibition of TPI1 Sensitizes Cisplatin-Resistant Oral Cancer to Ferroptosis. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051225
Wang D, Zheng H, Chen Y, Hao J, Zhou Y, Li N. Inhibition of TPI1 Sensitizes Cisplatin-Resistant Oral Cancer to Ferroptosis. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(5):1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051225
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Dandan, Huimin Zheng, Yumin Chen, Jialin Hao, Yuan Zhou, and Nan Li. 2025. "Inhibition of TPI1 Sensitizes Cisplatin-Resistant Oral Cancer to Ferroptosis" Biomedicines 13, no. 5: 1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051225
APA StyleWang, D., Zheng, H., Chen, Y., Hao, J., Zhou, Y., & Li, N. (2025). Inhibition of TPI1 Sensitizes Cisplatin-Resistant Oral Cancer to Ferroptosis. Biomedicines, 13(5), 1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051225





