Engineered Pseudomonas mirabilis-Derived Outer Membrane Vesicles Targeting Bone Microenvironment to Improve Osteoporosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain Culture Medium and Cultivation
2.2. Isolation and Characterization of OMVs
2.3. Synthesis of DSPE-PEG-Mal-Cys-SDSSD
2.4. PM-OMVs-BT Construction
2.5. Biophoton Imaging Analysis
2.6. In Vivo Safety
2.7. Cell Culture
2.8. Internalization Assay
2.9. Cell Viability
2.10. Osteogenesis Induction and Evaluation
2.11. Osteoclast Induction and Evaluation
2.12. Animal Experiment
2.13. Micro-CT
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Design and Characterization of Engineered PM-OMVs-BT
3.2. Distribution of PM-OMVs-BT In Vivo
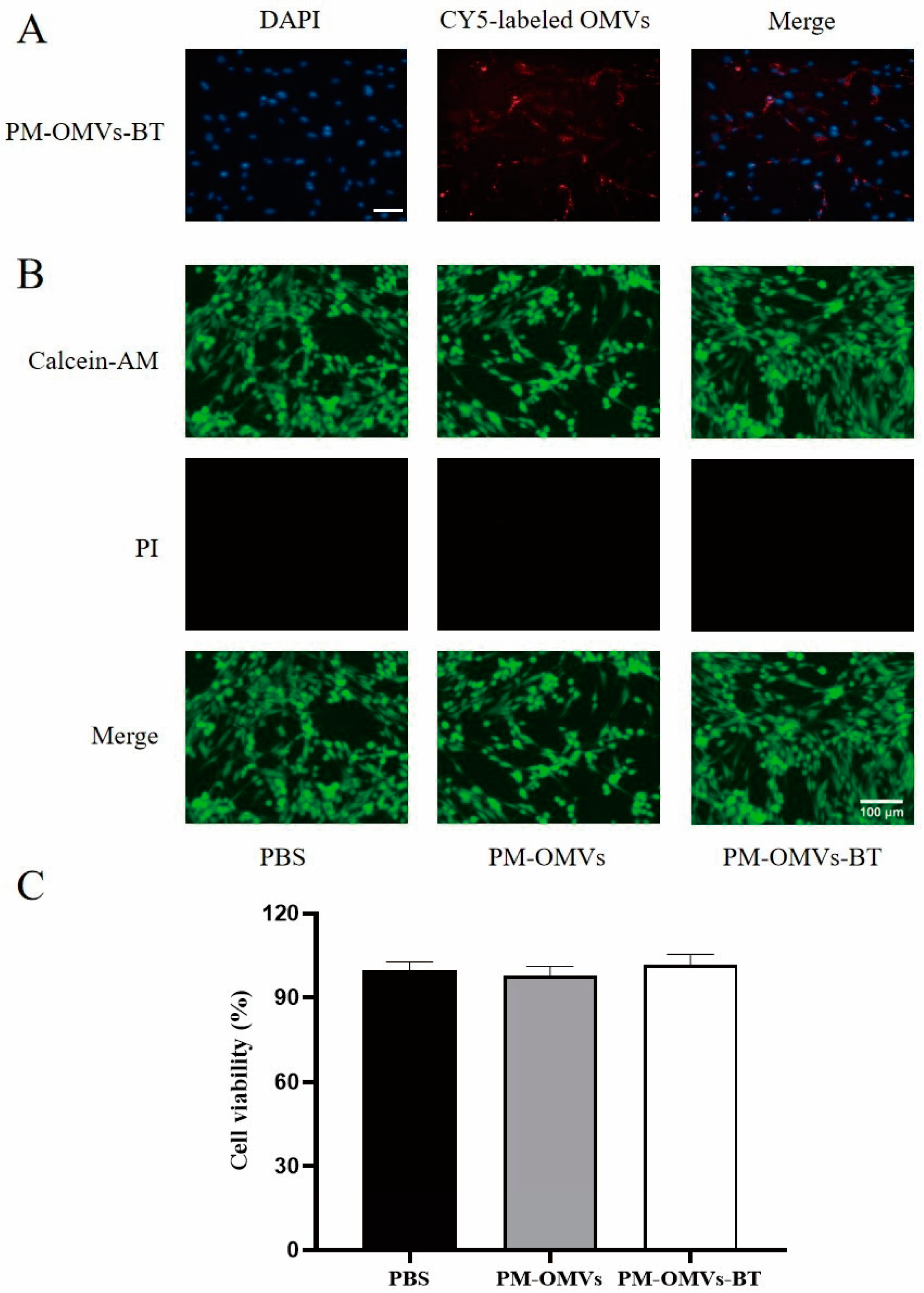
3.3. Cellular Uptake and Toxicity of PM-OMVs-BT In Vitro
3.4. Toxicity of PM-OMVs-BT In Vivo
3.5. PM-OMVs-BT Promote Osteogenesis In Vitro
3.6. PM-OMVs-BT Alleviate OP In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Eastell, R.; O’Neill, T.W.; Hofbauer, L.C.; Langdahl, B.; Reid, I.R.; Gold, D.T.; Cummings, S.R. Postmenopausal osteoporosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, J.Y.; Yang, Y.; Jung, H. Molecular Mechanisms and Emerging Therapeutics for Osteoporosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.L.; Shen, H.; Liu, A.; Dong, S.S.; Zhang, L.; Deng, F.Y.; Zhao, Q.; Deng, H.W. A road map for understanding molecular and genetic determinants of osteoporosis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Lv, B.; Li, Z.; Ma, C.; Gui, Z.; Geng, Y.; Liu, G.; Sang, L.; Xu, C.; Min, Q.; et al. Bone-Targeted Biomimetic Nanogels Re-Establish Osteoblast/Osteoclast Balance to Treat Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Small 2024, 20, e2303494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkawi, I.; Zmerly, H. Osteoporosis: Current Concepts. Joints 2018, 6, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenbroucke, A.; Luyten, F.P.; Flamaing, J.; Gielen, E. Pharmacological treatment of osteoporosis in the oldest old. Clin. Interv. Aging 2017, 12, 1065–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBoff, M.S.; Greenspan, S.L.; Insogna, K.L.; Lewiecki, E.M.; Saag, K.G.; Singer, A.J.; Siris, E.S. The clinician’s guide to prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporos. Int. 2022, 33, 2049–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, C.B.; Dagar, M. Osteoporosis in Older Adults. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 104, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langdahl, B. Treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis with bone-forming and antiresorptive treatments: Combined and sequential approaches. Bone 2020, 139, 115516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, I.R.; Billington, E.O. Drug therapy for osteoporosis in older adults. Lancet 2022, 399, 1080–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorg, D.J.; Fuertinger, D.H.; Cherif, A.; Bushinsky, D.A.; Mermelstein, A.; Raimann, J.G.; Kotanko, P. Modeling osteoporosis to design and optimize pharmacological therapies comprising multiple drug types. Elife 2022, 11, e76228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seely, K.D.; Kotelko, C.A.; Douglas, H.; Bealer, B.; Brooks, A.E. The Human Gut Microbiota: A Key Mediator of Osteoporosis and Osteogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Li, D.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Yan, J.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X.; Cao, H. Crosstalk between the gut microbiota and postmenopausal osteoporosis: Mechanisms and applications. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 110, 108998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, S.; Omata, Y.; Hofmann, J.; Bottcher, M.; Iljazovic, A.; Sarter, K.; Albrecht, O.; Schulz, O.; Krishnacoumar, B.; Kronke, G.; et al. Short-chain fatty acids regulate systemic bone mass and protect from pathological bone loss. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Liu, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Xie, H.; Wei, C.; Mei, C.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, N.; Qin, K.; et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG ameliorates osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats by regulating the Th17/Treg balance and gut microbiota structure. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2190304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Xiao, H.M.; Liu, H.M.; Lv, W.Q.; Greenbaum, J.; Gong, R.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.C.; Peng, C.; Xu, X.J.; et al. Gut microbiota impacts bone via Bacteroides vulgatus-valeric acid-related pathways. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Han, Y.; Hu, Y.; Geng, Z.; Su, J. Bacterial extracellular vesicles-based therapeutic strategies for bone and soft tissue tumors therapy. Theranostics 2022, 12, 6576–6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Song, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, F.; Ji, N.; Wang, M.; Zhou, G.; Han, R.; Liu, X.; Weng, W.; et al. Synthetic biology-based bacterial extracellular vesicles displaying BMP-2 and CXCR4 to ameliorate osteoporosis. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.C.P.; Jiao, M.; Xingxuan, C.; Wei, J. Extracellular vesicles derived from host and gut microbiota as promising nanocarriers for targeted therapy in osteoporosis and osteoarthritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1051134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.C.; Lin, S.W.; Li, I.C.; Chen, Y.P.; Tzu, S.Y.; Chou, W.; Chen, C.C.; Lin, W.C.; Chen, Y.L.; Lin, W.H. Lactobacillus plantarum GKM3 and Lactobacillus paracasei GKS6 Supplementation Ameliorates Bone Loss in Ovariectomized Mice by Promoting Osteoblast Differentiation and Inhibiting Osteoclast Formation. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Rao, S.S.; Yue, T.; Tan, Y.J.; Yin, H.; Chen, L.J.; Luo, M.J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.Y.; Hong, C.G.; et al. Glucocorticoid-induced loss of beneficial gut bacterial extracellular vesicles is associated with the pathogenesis of osteonecrosis. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabg8335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapra, L.; Shokeen, N.; Porwal, K.; Saini, C.; Bhardwaj, A.; Mathew, M.; Mishra, P.K.; Chattopadhyay, N.; Dar, H.Y.; Verma, B.; et al. Bifidobacterium longum Ameliorates Ovariectomy-Induced Bone Loss via Enhancing Anti-Osteoclastogenic and Immunomodulatory Potential of Regulatory B Cells (Bregs). Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 875788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Cong, R.; Yang, L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Q. A novel lncRNA LNC_000052 leads to the dysfunction of osteoporotic BMSCs via the miR-96-5p-PIK3R1 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Mo, L.; Ou, J.; Fang, Q.; Wu, H.; Wu, Y.; Nandakumar, K.S. Proteus mirabilis Vesicles Induce Mitochondrial Apoptosis by Regulating miR96-5p/Abca1 to Inhibit Osteoclastogenesis and Bone Loss. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 833040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Ji, N.; Wang, M.; Zhou, G.; Han, R.; Liu, X.; Weng, W.; et al. Bone-targeted engineered bacterial extracellular vesicles delivering miRNA to treat osteoporosis. Compos. Part. B Eng. 2023, 267, 111047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Yu, N.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Gong, F.; Lin, W.; He, X.; Wang, S.; et al. Bone-targeting exosome nanoparticles activate Keap1/Nrf2/GPX4 signaling pathway to induce ferroptosis in osteosarcoma cells. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Guo, Y.; Kong, L.; Shi, J.; Liu, P.; Li, R.; Geng, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, D. A bone-targeted engineered exosome platform delivering siRNA to treat osteoporosis. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 10, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, S.; Chen, C.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, B.; Wu, W. Engineered Pseudomonas mirabilis-Derived Outer Membrane Vesicles Targeting Bone Microenvironment to Improve Osteoporosis. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040847
Lin S, Chen C, Zheng Y, Wu B, Wu W. Engineered Pseudomonas mirabilis-Derived Outer Membrane Vesicles Targeting Bone Microenvironment to Improve Osteoporosis. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(4):847. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040847
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Sanfu, Chonggang Chen, Yuhui Zheng, Baofang Wu, and Wenhua Wu. 2025. "Engineered Pseudomonas mirabilis-Derived Outer Membrane Vesicles Targeting Bone Microenvironment to Improve Osteoporosis" Biomedicines 13, no. 4: 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040847
APA StyleLin, S., Chen, C., Zheng, Y., Wu, B., & Wu, W. (2025). Engineered Pseudomonas mirabilis-Derived Outer Membrane Vesicles Targeting Bone Microenvironment to Improve Osteoporosis. Biomedicines, 13(4), 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040847





