Development of LncRNA Biomarkers in Extracellular Vesicle of Amniotic Fluid Associated with Antenatal Hydronephrosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Sample Handling
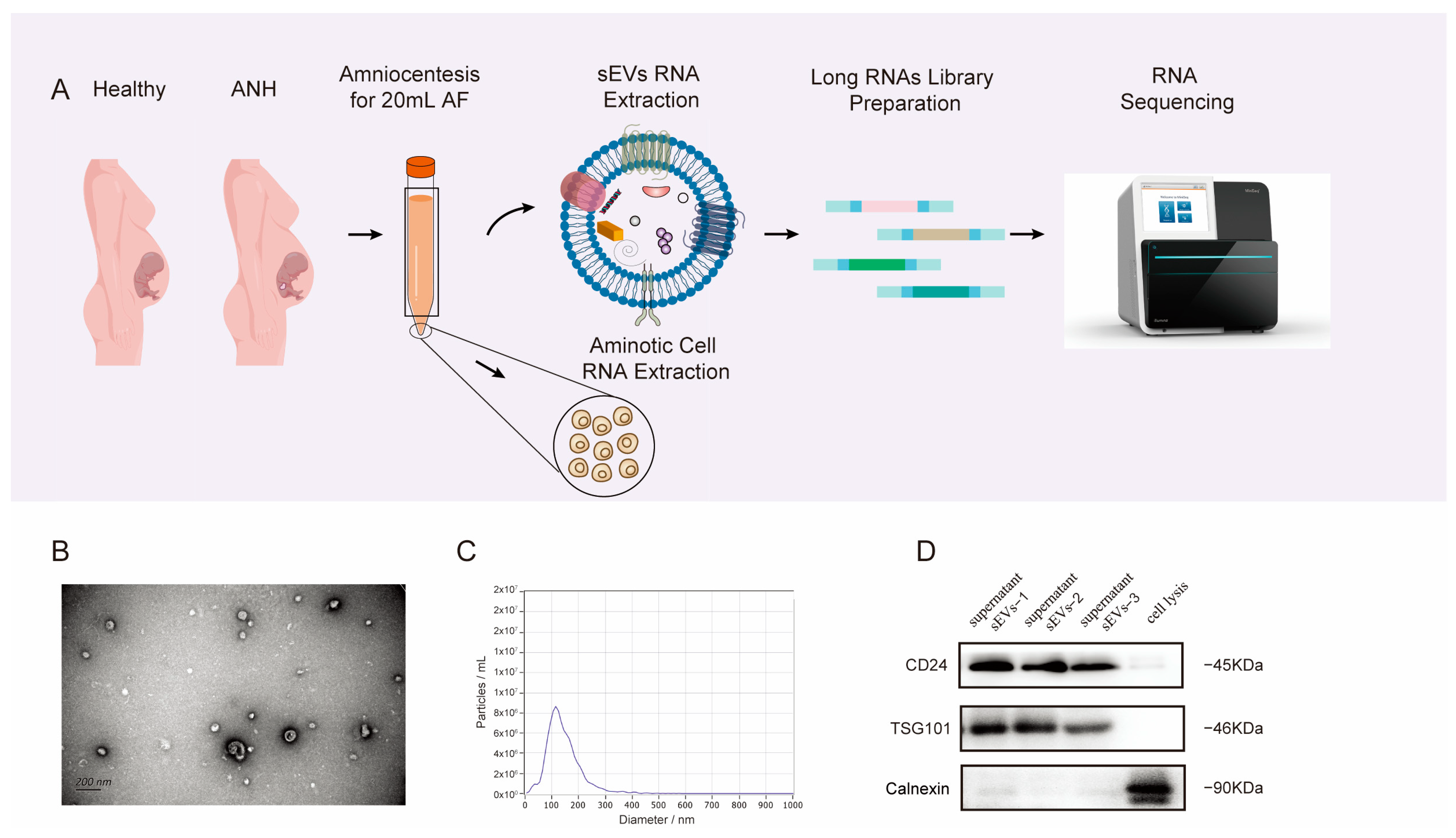
2.3. Isolation of sEVs by Size-Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
2.4. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.6. Western Blot (WB) Analysis
2.7. RNA Isolation and Sequencing
2.8. Known lncRNA Identification
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT–PCR) Analysis
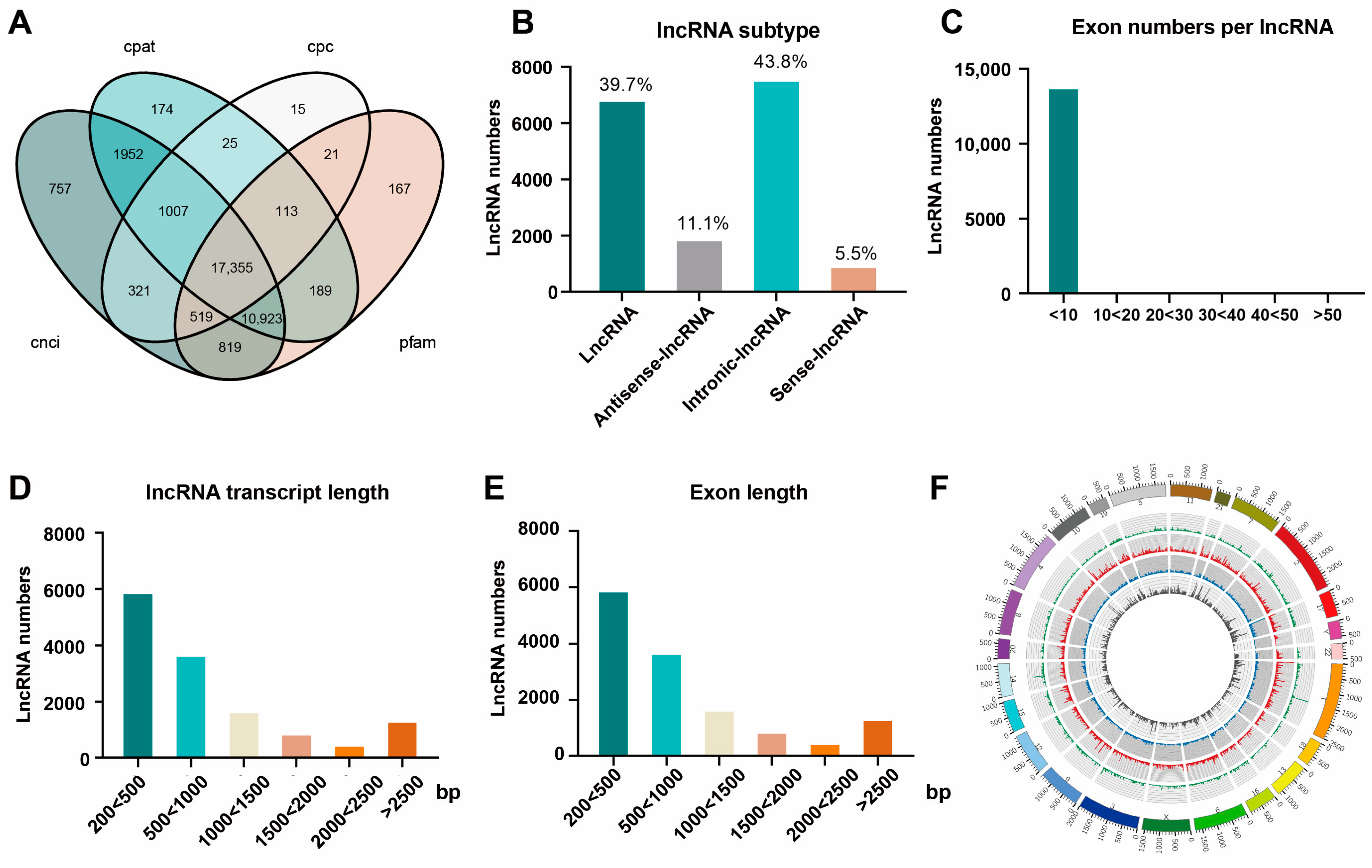
2.10. Prediction of Novel lncRNAs
2.11. Prediction of Novel lncRNA Target Genes
2.12. Differential Expression Analysis of Novel lncRNAs
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization and Properties of sEVs Isolated from AF
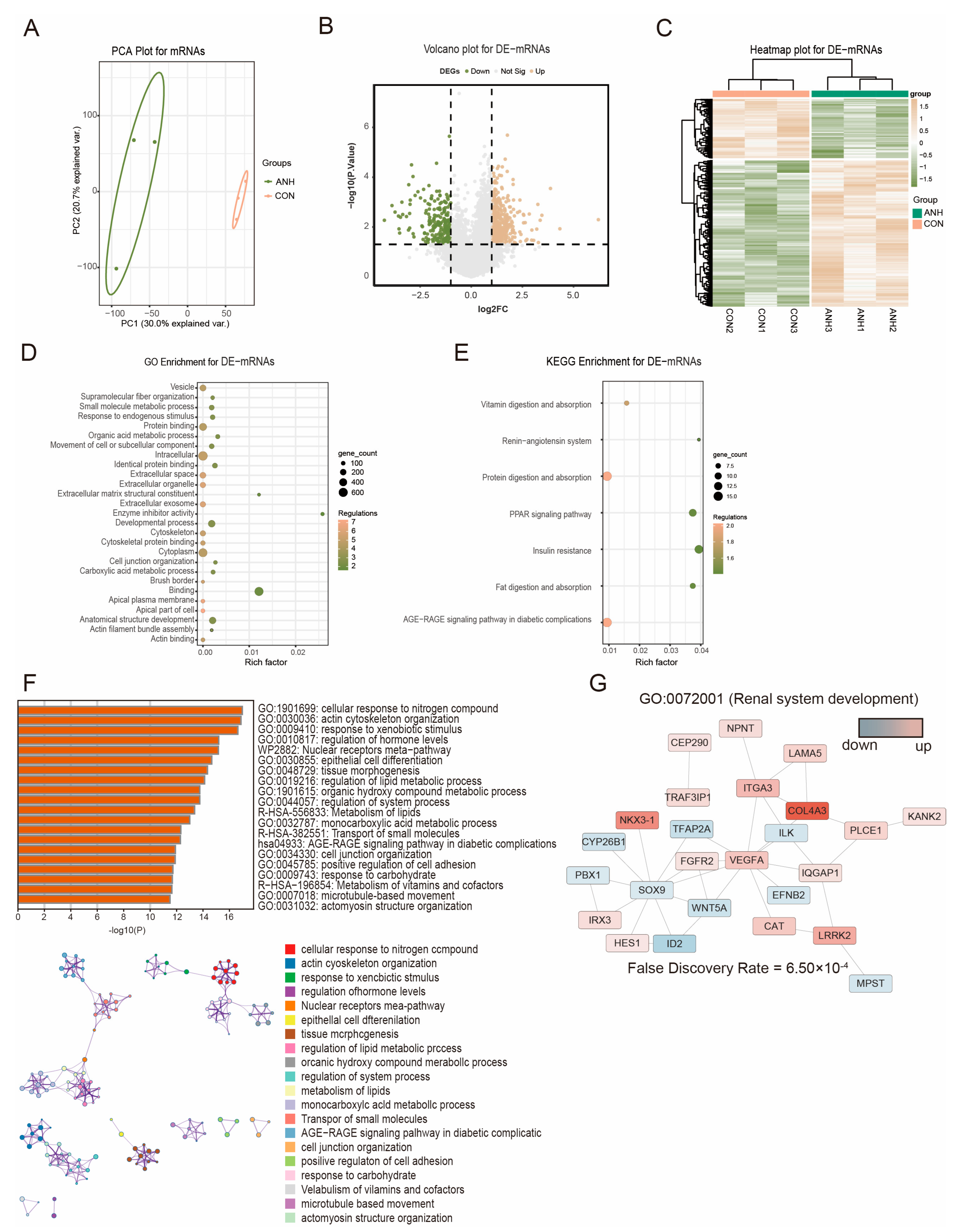
3.2. Differentially Expressed sEV-Derived mRNAs in ANH
3.3. Differential and Functional Analysis of Known sEV-Derived lncRNAs in ANH
3.4. Functional Analysis and Validation of the Known DE-lncRNAs in ANH
3.5. Prediction and Functional Analysis of the Novel DE-lncRNAs in ANH
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yalcinkaya, F.; Ozcakar, Z.B. Management of antenatal hydronephrosis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2020, 35, 2231–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Herndon, C.D.; Cooper, C.; Gatti, J.; Kirsch, A.; Kokorowski, P.; Lee, R.; Perez-Brayfield, M.; Metcalfe, P.; Yerkes, E.; et al. The Society for Fetal Urology consensus statement on the evaluation and management of antenatal hydronephrosis. J. Pediatr. Urol. 2010, 6, 212–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.S.; Cendron, M.; Kinnamon, D.D.; Nguyen, H.T. Antenatal hydronephrosis as a predictor of postnatal outcome: A meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2006, 118, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, M.G. Urinary biomarkers in hydronephrosis. Dan. Med. J. 2013, 60, B4582. [Google Scholar]
- Mallik, M.; Watson, A.R. Antenatally detected urinary tract abnormalities: More detection but less action. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2008, 23, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, L.J.; Malone, P.S.; Wellesley, D.G. Antenatal minimal hydronephrosis: Is its follow-up an unnecessary cause of concern? Prenat. Diagn. 1999, 19, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.S.; Darge, K. Multidisciplinary consensus on the classification of antenatal and postnatal urinary tract dilation (UTD classification system). Pediatr. Radiol. 2015, 45, 787–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Merchant, M.L.; Rood, I.M.; Deegens, J.K.J.; Klein, J.B. Isolation and characterization of urinary extracellular vesicles: Implications for biomarker discovery. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 731–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergunay, T.; Collino, F.; Bianchi, G.; Sedrakyan, S.; Perin, L.; Bussolati, B. Extracellular vesicles in kidney development and pediatric kidney diseases. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2024, 39, 1967–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.I.; Andriole, S.; Evans, S.M. Genetics: Update on prenatal screening and diagnosis. Obstet. Gynecol. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 42, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.T.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, W.Z.; Li, Z.Q.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, L. The relationship between amniotic fluid miRNAs and congenital obstructive nephropathy. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 1754–1763. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dixon, C.L.; Sheller-Miller, S.; Saade, G.R.; Fortunato, S.J.; Lai, A.; Palma, C.; Guanzon, D.; Salomon, C.; Menon, R. Amniotic Fluid Exosome Proteomic Profile Exhibits Unique Pathways of Term and Preterm Labor. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 2229–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orczyk-Pawilowicz, M.; Jawien, E.; Deja, S.; Hirnle, L.; Zabek, A.; Mlynarz, P. Metabolomics of Human Amniotic Fluid and Maternal Plasma during Normal Pregnancy. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraldi, E.; Giordano, G.; Stocchero, M.; Moschino, L.; Zaramella, P.; Tran, M.R.; Carraro, S.; Romero, R.; Gervasi, M.T. Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis of Amniotic Fluid in the Prediction of Preterm Delivery and Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Re, M.; Marconcini, R.; Pasquini, G.; Rofi, E.; Vivaldi, C.; Bloise, F.; Restante, G.; Arrigoni, E.; Caparello, C.; Bianco, M.G.; et al. PD-L1 mRNA expression in plasma-derived exosomes is associated with response to anti-PD-1 antibodies in melanoma and NSCLC. Brit J. Cancer 2018, 118, 820–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.H.; Chen, K.K.; Zhang, J.T.; Xiao, B.F.; Huang, Z.H.; Ju, C.; Sun, J.; Zhang, F.F.; Lv, X.B.; Huang, G.F. The decade of exosomal long RNA species: An emerging cancer antagonist. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhan, A.; Soleimani, M.; Mandal, S.S. Long Noncoding RNA and Cancer: A New Paradigm. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3965–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, F.; Mendell, J.T. Functional Classification and Experimental Dissection of Long Noncoding RNAs. Cell 2018, 172, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, G.; Song, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Xia, K.; Chang, Y.; et al. Emerging role of exosome-derived long non-coding RNAs in tumor microenvironment. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Zhao, L.; Kong, G.; Liu, X.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, S.; Min, L. Combination of Size-Exclusion Chromatography and Ultracentrifugation Improves the Proteomic Profiling of Plasma-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles. Biol. Proced. Online 2020, 22, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, C.; Ferreira, Y.J.; Dragovic, R.A.; Redman, C.W.; Sargent, I.L. Extracellular vesicle sizing and enumeration by nanoparticle tracking analysis. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 19671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragovic, R.A.; Gardiner, C.; Brooks, A.S.; Tannetta, D.S.; Ferguson, D.J.; Hole, P.; Carr, B.; Redman, C.W.; Harris, A.L.; Dobson, P.J.; et al. Sizing and phenotyping of cellular vesicles using Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis. Nanomedicine 2011, 7, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Pol, E.; Coumans, F.A.; Grootemaat, A.E.; Gardiner, C.; Sargent, I.L.; Harrison, P.; Sturk, A.; van Leeuwen, T.G.; Nieuwland, R. Particle size distribution of exosomes and microvesicles determined by transmission electron microscopy, flow cytometry, nanoparticle tracking analysis, and resistive pulse sensing. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 12, 1182–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrugger, U.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, S.; Rupp, C.; Stoeck, A.; Runz, S.; Fogel, M.; Lugert, S.; Hager, H.D.; Abdel-Bakky, M.S.; Gutwein, P.; Altevogt, P. CD24 is a marker of exosomes secreted into urine and amniotic fluid. Kidney Int. 2007, 72, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Sanchez-Ferras, O.; Bouchard, M. Pax genes in renal development, disease and regeneration. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 44, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.; Buffin-Meyer, B.; Boizard, F.; Moussaoui, N.; Lescat, O.; Breuil, B.; Fedou, C.; Feuillet, G.; Casemayou, A.; Neau, E.; et al. Amniotic fluid peptides predict postnatal kidney survival in developmental kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2021, 99, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Shen, K.; Yao, R.; Fu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Xie, M.; Jian, W.; Guo, M.; et al. Multiomics-based study of amniotic fluid small extracellular vesicles identified Moesin as a biomarker for antenatal hydronephrosis. Clin. Transl. Med. 2023, 13, e1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Li, J.; Tang, C.; He, K.; Shan, D.; Yan, S.; Deng, G. A risk signature of necroptosis-related lncRNA to predict prognosis and probe molecular characteristics for male with bladder cancer. Medicine 2023, 102, e33664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statello, L.; Guo, C.J.; Chen, L.L.; Huarte, M. Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 96–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattick, J.S.; Amaral, P.P.; Carninci, P.; Carpenter, S.; Chang, H.Y.; Chen, L.L.; Chen, R.; Dean, C.; Dinger, M.E.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; et al. Long non-coding RNAs: Definitions, functions, challenges and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 430–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Cao, R.; Li, Q.; Yin, L. The Long Noncoding RNA-H19 Mediates the Progression of Fibrosis from Acute Kidney Injury to Chronic Kidney Disease by Regulating the miR-196a/Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling. Nephron 2022, 146, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, M.; Souabni, A.; Mandler, M.; Neubüser, A.; Busslinger, M. Nephric lineage specification by Pax2 and Pax8. Gene Dev. 2002, 16, 2958–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, A.; Chowdhury, K.; Gruss, P. Follicular cells of the thyroid gland require Pax8 gene function. Nat. Genet. 1998, 19, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakun, R.R.; Melamed, Z.; Perets, R. PAX8 in the Junction between Development and Tumorigenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng-Blichfeldt, J.P.; Stewart, B.J.; Clatworthy, M.R.; Williams, J.M.; Roper, K. Identification of a core transcriptional program driving the human renal mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition. Dev. Cell 2024, 59, 595–612.e598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorkova, O.; Wahlestedt, C. Oligonucleotide therapies for disorders of the nervous system. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Mendell, J.T. Antisense-Mediated Transcript Knockdown Triggers Premature Transcription Termination. Mol. Cell 2020, 77, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, L.S.; Larson, M.H.; Gilbert, L.A.; Doudna, J.A.; Weissman, J.S.; Arkin, A.P.; Lim, W.A. Repurposing CRISPR as an RNA-guided platform for sequence-specific control of gene expression. Cell 2013, 152, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, J.A.; Hamza, E.; Guerrero-Hue, M.; Rayego-Mateos, S.; Garcia-Caballero, C.; Vallejo-Mudarra, M.; Metzinger, L.; Metzinger-Le Meuth, V. Non-Coding RNAs in Kidney Diseases: The Long and Short of Them. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San Agustin, J.T.; Klena, N.; Granath, K.; Panigrahy, A.; Stewart, E.; Devine, W.; Strittmatter, L.; Jonassen, J.A.; Liu, X.; Lo, C.W.; et al. Genetic link between renal birth defects and congenital heart disease. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Song, R. Role of STAT3/mTOR pathway in chronic kidney injury. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 3302–3310. [Google Scholar]
- Vigolo, E.; Marko, L.; Hinze, C.; Muller, D.N.; Schmidt-Ullrich, R.; Schmidt-Ott, K.M. Canonical BMP signaling in tubular cells mediates recovery after acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.Y. Diverse roles of TGF-beta/Smads in renal fibrosis and inflammation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 1056–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, H.; Boen, J.R.A.; De Moudt, S.; Hendrickx, J.O.; Leloup, A.J.A.; Jacobs, G.; De Meyer, G.R.Y.; De Keulenaer, G.W.; Guns, P.D.F.; Segers, V.F.M. Neuregulin-1 compensates for endothelial nitric oxide synthase deficiency. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2021, 320, H2416–H2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Huang, L.; Luo, W.; Yu, W.; Hu, X.; Guan, X.; Cai, Y.; Zou, C.; Yin, H.; Xu, Z.; et al. Inhibition of STAT3 in tubular epithelial cells prevents kidney fibrosis and nephropathy in STZ-induced diabetic mice. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Patient | ANH-1 | ANH-2 | ANH-3 | Con-1 | Con-2 | Con-3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 30 | 36 | 28 | 40 | 32 | 35 | |
| Amniocentesis week | 24+ | 24+ | 23+ | 23+ | 19+ | 20+ | |
| Karyotype & CNV | 46, XY | 46, XY | 46, XX | 46, XY | 46, XY | 46, XX | |
| Unilateral/Bilateral ANH | Bilateral | Bilateral | Bilateral | ||||
| US Second trimester | Grading system (grade) | 1 L: III; 2 R: II | L: III–IV; R: II | L: III; R: II | |||
| APD (mm) | L: 15.8; R: 11 | L: 34; R: 18 | L: 31; R: 26 | ||||
| Renal pelvis splitting | √ | √ | √ | ||||
| Distention of the renal pelvis and calyces | √ | √ | √ | ||||
| Ureteral obstruction/dilatation | Obstruction (L) | Obstruction (L) Dilatation (L) | Obstruction (L) | ||||
| Parenchymal thinning (mm) | L: 3; R:4.1 | L: 2; R: 4.6 | L: 3.5; R: 5 | ||||
| US Third trimester | Grading system (grade) | L: IV; R: II | L: IV; R: II | L: IV; R: II | |||
| APD (mm) | L: 25; R: 20 | L: 25.1; R: 8.6 | L: 58; R: 11 | ||||
| Ureteral obstruction/dilatation | Obstruction (L) Dilatation (R) | Obstruction (L) | Obstruction (L) | ||||
| Parenchymal thinning (mm) | L: 3; R: 4.4 | L: 2.6; R: 7.8 | L: 1.6; R: 6.6 | ||||
| RPA (Renal pelvis aspiration) (times: volume (mL)) | 1st (L): 3 | 1st (L): 15 | 1st (L): 10 2nd (L): 52 3rd (L): 70 4th (L): 110 | ||||
| Diagnosis after birth | UPJO | UPJO (operation: nephron-ureterectomy | UPJO (operation: right nephron-ureterectomy) | ||||
| Evaluation renal function | Average sodium (mmol) | 47.6 | 45.1 | 49.8 | |||
| Average creatinine (µmol/L) | 182.8 | 164.9 | 135 | ||||
| ID | Symbol | logFC | t | p Value | Regulated in ANH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENST00000521945 | SFTA3 | −1.83448 | −5.43091 | 0.004118 | up |
| ENST00000454380 | AC116366.2 | −1.34567 | −6.9862 | 0.001489 | up |
| ENST00000439928 | SPATA13 | −1.01094 | −3.05002 | 0.0332 | up |
| ENST00000455153 | CDR1 | −1.60484 | −3.20392 | 0.028291 | up |
| ENST00000523568 | AC105052.3 | −1.48765 | −2.67951 | 0.049575 | up |
| ENST00000508166 | GBA3 | 1.48944 | 3.500571 | 0.021009 | down |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yao, R.; Fu, Y.; Dai, L.; Jian, W.; Zhang, W.; Li, J. Development of LncRNA Biomarkers in Extracellular Vesicle of Amniotic Fluid Associated with Antenatal Hydronephrosis. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030668
Fu Y, Liu Q, Yao R, Fu Y, Dai L, Jian W, Zhang W, Li J. Development of LncRNA Biomarkers in Extracellular Vesicle of Amniotic Fluid Associated with Antenatal Hydronephrosis. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(3):668. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030668
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Ying, Qiaoshu Liu, Ruojin Yao, Yimei Fu, Lei Dai, Wenyan Jian, Weishe Zhang, and Jingzhi Li. 2025. "Development of LncRNA Biomarkers in Extracellular Vesicle of Amniotic Fluid Associated with Antenatal Hydronephrosis" Biomedicines 13, no. 3: 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030668
APA StyleFu, Y., Liu, Q., Yao, R., Fu, Y., Dai, L., Jian, W., Zhang, W., & Li, J. (2025). Development of LncRNA Biomarkers in Extracellular Vesicle of Amniotic Fluid Associated with Antenatal Hydronephrosis. Biomedicines, 13(3), 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030668







