Effects of In Vitro Fermented Pleurotus eryngii on Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Immunomodulation in a Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Colonic Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Generation of Fermentation-Derived Supernatants
2.2. Cell Culture of Caco-2 Cells and Bacterial LPS
2.3. Exposure of Caco-2 Cells to FSs and LPS Treatment
2.4. Preparation of Samples for TJ Gene Expression
2.5. Preparation of Samples for Cytokine and Receptor Gene Expression
2.6. Quantification of Cytokines’ Release
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Preservative Influence of P. eryngii FSs on Intestinal Barrier’s Integrity via TJ Gene Upregulation
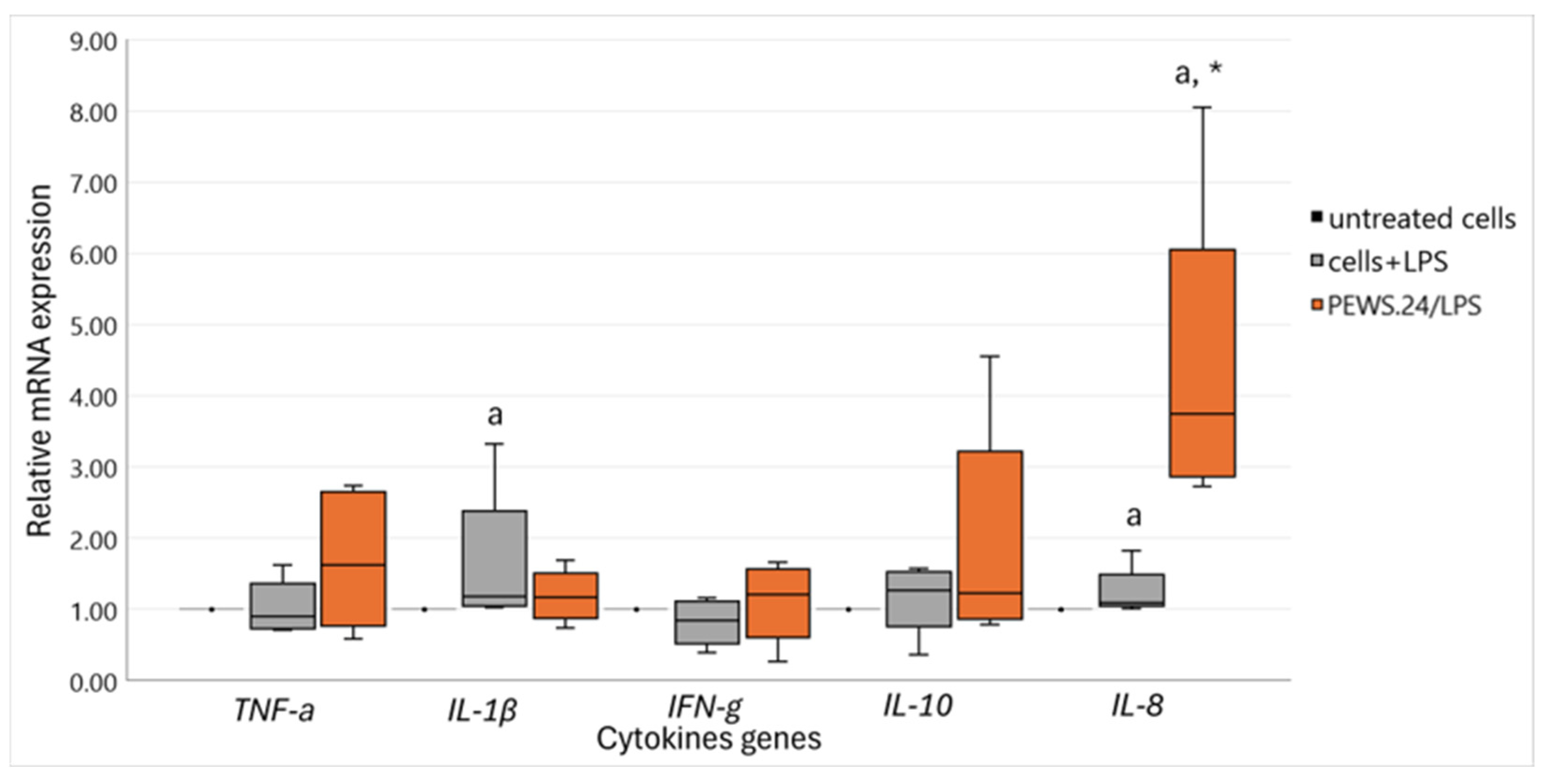
3.2. Immunomodulatory Impact of FS-PEWS on Cytokine mRNA Expression Levels in the LPS-Stimulated Caco-2 Cells
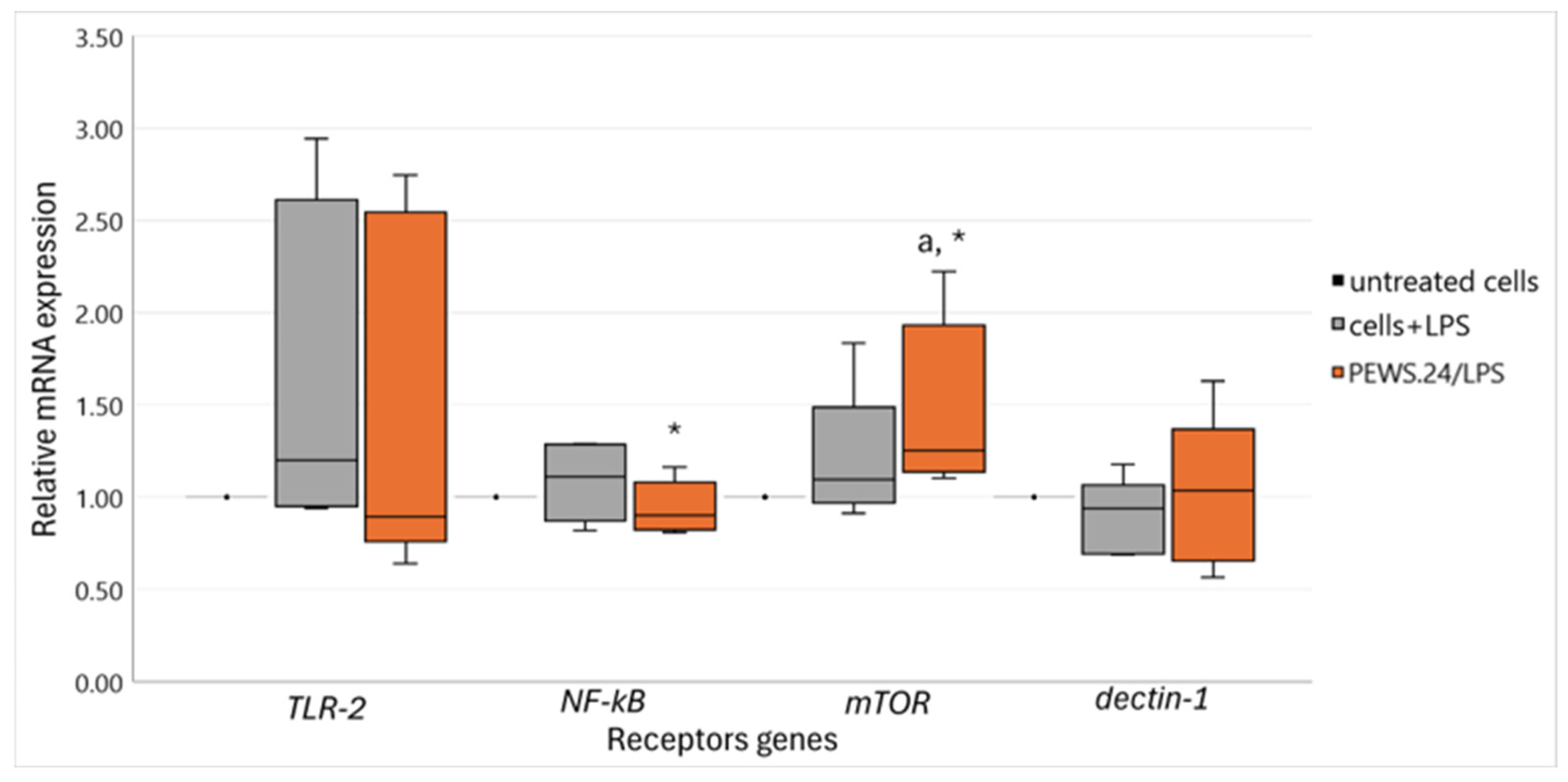
3.3. Effect of FS-PEWS in the LPS-Stimulated Caco-2 Cells Linked to Intestinal Immune Regulation and Metabolism-Related Receptor mRNA Expression Levels
3.4. Undetectable Cytokines Released in Caco-2 Cell Culture Supernatants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bischoff, S.; Barbara, G.; Buurman, W.; Ockhuizen, T.; Schulzke, J.; Serino, M.; Tilg, H.; Watson, A.; Wells, J. Intestinal permeability—A new target for disease prevention and therapy. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014, 14, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincenzo, F.; Gaudio, A.; Petito, V.; Lopetuso, L.; Scaldaferri, F. Gut microbiota, intestinal permeability, and systemic inflammation: A narrative review. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2024, 19, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, F.; Balas, I.; Robinson, M.; Bakdash, G. Border Control: The Role of the Microbiome in Regulating Epithelial Barrier Function. Cells 2024, 13, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, G.P.; Lee, S.; Mazmanian, S. Gut biogeography of the bacterial microbiota. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragonnaud, E.; Biragyn, A. Gut microbiota as the key controllers of “healthy” aging of elderly people. Immun. Ageing 2021, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, A.; Aparicio, R.; Clark, R.; Rera, M.; Walker, D. Intestinal barrier dysfunction: An evolutionarily conserved hallmark of aging. Dis. Model. Mech. 2023, 16, dmm049969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, N.; Noti, M. The aging gut microbiome and its impact on host immunity. Genes Immun. 2021, 22, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevaranjan, N.; Puchta, A.; Schulz, C.; Naidoo, A.; Szamosi, J.; Verschoor, C.; Loukov, D.; Schenck, L.; Jury, J.; Foley, K.; et al. Age-Associated Microbial Dysbiosis Promotes Intestinal Permeability, Systemic Inflammation, and Macrophage Dysfunction. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 21, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walrath, T.; Dyamenahalli, K.U.; Hulsebus, H.J.; McCullough, R.L.; Idrovo, J.P.; Boe, D.M.; McMahan, R.H.; Kovacs, E.J. Age-related changes in intestinal immunity and the microbiome. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2021, 109, 1045–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.; Kell, D.; Pretorius, E. The Role of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Cell Signalling in Chronic Inflammation. Chronic Stress 2022, 8, 24705470221076390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Yan, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ge, W.; Wu, J.; Du, P.; Chen, Y. Boosting mTOR-dependent autophagy via upstream TLR4-MyD88-MAPK signalling and downstream NF-κB pathway quenches intestinal inflammation and oxidative stress injury. eBioMedicine 2018, 35, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M.; Prescott, S.; Reimer, R.; Salminen, S.; Scott, K.; Stanton, C.; Swanson, K.; Cani, P.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, E.; Odle, J.; Blikslager, A.; Ziegler, A. Probiotics, Prebiotics and Epithelial Tight Junctions: A Promising Approach to Modulate Intestinal Barrier Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, E. Prebiotics and Probiotics in Digestive Health. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayachandran, M.; Xiao, J.; Xu, B. A Critical Review on Health Promoting Benefits of Edible Mushrooms through Gut Microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxami, G.; Kerezoudi, E.; Mitsou, E.; Koutrotsios, G.; Zervakis, G.; Pletsa, V.; Kyriacou, A. Fermentation Supernatants of Pleurotus eryngii Mushroom Ameliorate Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Dysfunction in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Caco-2 Cells via Upregulation of Tight Junctions. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlassopoulou, M.; Paschalidis, N.; Savvides, A.L.; Saxami, G.; Mitsou, E.K.; Kerezoudi, Ε.; Koutrotsios, G.; Zervakis, G.I.; Georgiadis, P.; Kyriacou, A.; et al. Immunomodulating Activity of Pleurotus eryngii Mushrooms Following Their In Vitro Fermentation by Human Fecal Microbiota. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerezoudi, E.; Vlasopoulou, M.; Mitsou, E.; Saxami, G.; Koutrotsios, G.; Taflampa, I.; Mountzouris, K.; Rangel, I.; Brummer, R.; Zervakis, G.I.; et al. In vitro fermentation of whole matrix, digested products and β-glucan enriched extract of Pleurotus eryngii mushrooms distinctively impact the fecal microbiota of healthy older adults. Hum. Nutr. Metab. 2024. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsou, E.K.; Saxami, G.; Stamoulou, E.; Kerezoudi, E.; Terzi, E.; Koutrotsios, G.; Bekiaris, G.; Zervakis, G.I.; Mountzouris, K.C.; Pletsa, V.; et al. Effects of Rich in B-Glucans Edible Mushrooms on Aging Gut Microbiota Characteristics: An In Vitro Study. Molecules 2020, 25, 2806–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxami, G.; Karapetsas, A.; Lamprianidou, E.; Kotsianidis, I.; Chlichlia, A.; Tassou, C.; Zoumpourlis, V.; Galanis, A. Two potential probiotic lactobacillus strains isolated from olive microbiota exhibit adhesion and anti-proliferative effects in cancer cell lines. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 24, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, S.; Wu, M.; Li, B.; Ruan, Z.; Hu, X. Dietary l-tryptophan alleviated LPS-induced intestinal barrier injury by regulating tight junctions in a Caco-2 cell monolayer model. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 2390–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Moran, T.; Swanson, E.; Julian, C.; Harris, J.; Bonen, D.; Hedl, M.; Nicolae, D.; Abraham, C.; Cho, J. Regulation of IL-8 and IL-1beta expression in Crohn’s disease associated NOD2/CARD15 mutations. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, 1715–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furrie, E.; Macfarlane, S.; Kennedy, A.; Cummings, J.; Walsh, S.; O’neil, D.; Macfarlane, G. Synbiotic therapy (Bifidobacterium longum/Synergy 1) initiates resolution of inflammation in patients with active ulcerative colitis: A randomised controlled pilot trial. Gut 2005, 54, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duary, R.K.; Batish, V.; Grover, S. Immunomodulatory activity of two potential probiotic strains in LPS-stimulated HT-29 cells. Genes Nutr. 2014, 9, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, M.; Lin, Y.; Xie, S.; Huang, T.; Liu, P.; Nie, R.; Meng, Q.; Luo, N.; Chen, Y.; et al. IL-33 promotes IL-10 production in macrophages: A role for IL-33 in macrophage foam cell formation. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Govers, C.; Wichers, H.; Mes, J. Macrophages treated with non-digestible polysaccharides reveal a transcriptionally unique phenotype. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 36, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminsky, L.; Al-Sadi, R.; Ma, T. IL-1β and the Intestinal Epithelial Tight Junction Barrier. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 767456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sadi, R.; Boivin, M.; Ma, T. Mechanism of cytokine modulation of epithelial tight junction barrier. Front. Biosci. 2009, 14, 2765–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wei, X.; Ding, M.; Luo, Z.; Tan, X.; Zheng, Z. Daidzein Protects Caco-2 Cells against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Injury by Suppressing PI3K/AKT and P38 Pathways. Molecules 2022, 27, 8928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Nighot, M.; Al-Sadi, R.; Alhmoud, T.; Nighot, P.; Ma, T. Lipopolysaccharide Regulation of Intestinal Tight Junction Permeability Is Mediated by TLR4 Signal Transduction Pathway Activation of FAK and MyD88. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 4999–5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minato, K.; Ohara, A.; Mizuno, M. A Proinflammatory Effect of the β-Glucan from Pleurotus cornucopiae Mushroom on Macrophage Action. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 8402405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanput, W.; Reitsma, M.; Kleinjans, L.; Mes, J.; Savelkoul, H.; Wichers, H. β-Glucans are involved in immune-modulation of THP-1 macrophages. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 822–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, S.; O’Brien, T.; Ledwith, A.; Chen, S.; Johnston, H.C.; Hackett, E.; O’Sullivan, M.; Charles-Messance, H.; Dempsey, E.; Yadav, S.; et al. β-glucans from Agaricus bisporus mushroom products drive Trained Immunity. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1346706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicchese, J.; Evans, S.; Hult, C.; Joslyn, L.; Wessler, T.; Millar, J.; Marino, S.; Cilfone, N.; Mattila, J.; Linderman, J.; et al. Dynamic balance of pro- and anti-inflammatory signals controls disease and limits pathology. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 285, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stehle, J., Jr.; Leng, X.; Kitzman, D.; Nicklas, B.; Kritchevsky, S.; High, K. Lipopolysaccharide-Binding Protein, a Surrogate Marker of Microbial Translocation, Is Associated with Physical Function in Healthy Older Adults. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2012, 67, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; He, Q.; Wu, S.; Zhang, K.; Xu, Z.; Kang, J.; Quan, F. Catalpol ameliorates LPS-induced inflammatory response by activating AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway in rat intestinal epithelial cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 960, 176125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegler, C.; Ölander, M.; Wiśniewski, J.; Lundquist, P.; Zettl, K.; Åsberg, A.; Hjelmesæth, J.; Andersson, T.; Artursson, P. Global variability analysis of mRNA and protein concentrations across and within human tissues. NAR Genom. Bioinform. 2019, 2, lqz010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnik, Y.; Buchauer, L.; Ben-Moshe, S.; Averbukh, I.; Levin, Y.; Savidor, A.; Eilam, R.; Moor, A.; Itzkovitz, S. Spatial discordances between mRNAs and proteins in the intestinal epithelium. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 1680–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortelny, N.; Overall, C.; Pavlidis, P.; Freue, G. Can we predict protein from mRNA levels? Nature 2017, 547, E19–E20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, M.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy: New insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Bhardwaj, A. β-glucans: A potential source for maintaining gut microbiota and the immune system. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1143682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata-Martínez, P.; Bergón-Gutiérrez, M.; Fresno, C. Dectin-1 Signaling Update: New Perspectives for Trained Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 812148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers, C.; Plüss, C.; Ricklin, D. The Promiscuous Profile of Complement Receptor 3 in Ligand Binding, Immune Modulation, and Pathophysiology. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 662164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volman, J.; Mensink, R.; Buurman, W.; Onning, G.; Plat, J. The absence of functional dectin-1 on enterocytes may serve to prevent intestinal damage. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 22, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen-Kedar, S.; Baram, L.; Elad, H.; Brazowski, E.; Guzner-Gur, H.; Dotan, I. Human intestinal epithelial cells respond to β-glucans via Dectin-1 and Syk. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 3729–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernet-Camard, M.; Coconnier, M.; Hudault, S.; Servin, A. Differential expression of complement proteins and regulatory decay accelerating factor in relation to differentiation of cultured human colon adenocarcinoma cell lines. Gut 1996, 38, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyam, A.; Kannan, L.; Matsumoto, N.; Geha, M.; Lapchak, P.; Bosse, R.; Shi, G.; Dalle Lucca, J.; Tsokos, M.; Tsokos, G. Intracellular Activation of Complement 3 Is Responsible for Intestinal Tissue Damage during Mesenteric Ischemia. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjan, P.; Sahasrabudhe, N.; Haan, B.D.; Vos, P.D. Immune effects of β-glucan are determined by combined effects on Dectin-1, TLR2, 4 and 5. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 37, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laval, L.; Martin, R.; Natividad, J.; Chain, F.; Miquel, S.; Maredsous, C.D.; Capronnier, S.; Sokol, H.; Verdu, E.; Hylckama Vlieg, J.V.; et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus CNCM I-3690 and the commensal bacterium Faecalibacterium prausnitzii A2-165 exhibit similar protective effects to induced barrier hyper-permeability in mice. Gut Microbes 2015, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synytsya, A.; Míčková, K.; Synytsya, A.; Jablonský, I.; Spěváček, J.; Erban, V.; Kováříková, E.; Čopíková, J. Glucans from fruit bodies of cultivated mushrooms Pleurotus ostreatus and Pleurotus eryngii: Structure and potential prebiotic activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 76, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petraglia, T.; Latronico, T.; Fanigliulo, A.; Crescenzi, A.; Liuzzi, G.M.; Rossano, R. Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharides from the Edible Mushroom Pleurotus eryngii. Molecules 2023, 28, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Wu, Q.; Lin, Z.; Liu, S.; Su, Q.; Pan, Y. Therapeutic effects of chitin from Pleurotus eryngii on high-fat diet induced obesity in rats. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2020, 19, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reis, F.S.; Barros, L.; Martins, A.; Ferreira, I.C. Chemical composition and nutritional value of the most widely appreciated cultivated mushrooms: An inter-species comparative study. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moutia, I.; Lakatos, E.; Kovács, A.J. Impact of Dehydration Techniques on the Nutritional and Microbial Profiles of Dried Mushrooms. Foods 2024, 13, 3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coşkun, N.; Sarıtaş, S.; Jaouhari, Y.; Bordiga, M.; Karav, S. The Impact of Freeze Drying on Bioactivity and Physical Properties of Food Products. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Primer Sequences (5′–3′) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Human β-actin F | GCGCGGCTACAGCTTCA | [20] |
| Human β-actin R | CTTAATGTCACGCACGATTTCC | [20] |
| Human ZO-1 F | TTCACGCAGTTACGAGCAAG | [21] |
| Human ZO-1 R | TTGGTGTTTGAAGGCAGAGC | [21] |
| Human Occludin F | ACAAGCGGTTTTATCCAGAGTC | [21] |
| Human Occludin R | GTCATCCACAGGCGAAGTTAAT | [21] |
| Human Claudin-1 F | TGGTCAGGCTCTCTTCACTG | [21] |
| Human Claudin-1 R | TTGGATAGGGCCTTGGTGTT | [21] |
| Human IL-1β F | ACAGATGAAGTGCTCCTTCCA | [22] |
| Human IL-1β R | GTCGGAGATTCGTAGCTGGAT | [22] |
| Human TNF-α F | TCTCGAACCCCGAGTGACAA | [23] |
| Human TNF-α R | TATCTCTCAGCTCCACGCCA | [23] |
| Human IFN-γ F | ATCCAGTTACTGCCGGTTTG | [24] |
| Human IFN-γ R | GAAGCACCAGGCATGAAATC | [24] |
| Human IL-6 F | AGACAGCCACTCACCTCTTCAG | NM_000600 |
| Human IL-6 R | TTCTGCCAGTGCCTCTTTGCTG | NM_000600 |
| Human IL-8 F | GAGAGTGATTGAGAGTGGACCAC | NM_000584 |
| Human IL-8 R | CACAACCCTCTGCACCCAGTTT | NM_000584 |
| Human IL-10 F | GGAGAACCTGAAGACCCTCA | [25] |
| Human IL-10 R | GATGTCAAACTCACTCATGGC | [25] |
| Human IL-13 F | ACGGTCATTGCTCTCACTTGCC | NM_002188 |
| Human IL-13 R | CTGTCAGGTTGATGCTCCATACC | NM_002188 |
| Human IL-17 F | CGGACTGTGATGGTCAACCTGA | NM_002190 |
| Human IL-17 R | GCACTTTGCCTCCCAGATCACA | NM_002190 |
| Human Dectin-1 F | AACCACAGCTACCCAAGAAAAC | [26] |
| Human Dectin-1 R | GGGCACACTACACAGTTGGTC | [26] |
| Human TLR-2 F | CTTCACTCAGGAGCAGCAAGCA | NM_003264 |
| Human TLR-2 R | ACACCAGTGCTGTCCTGTGACA | NM_003264 |
| Human TLR-4 F | CCCTGAGGCATTTAGGCAGCTA | NM_138554 |
| Human TLR-4 R | AGGTAGAGAGGTGGCTTAGGCT | NM_138554 |
| Human NF-kB F | GGGGATGGTGAGAAGGTTGG | NM_001319226.2 |
| Human NF-kB R | GCAGTGCCATCTGTGGTTGA | NM_001319226.2 |
| Human CR3 F | AAGTCCTCGTTGTCCGTTCC | MW027613.1 |
| Human CR3 R | CTGCAGCCATTTAACAGCCC | MW027613.1 |
| Human mTOR F | GCCGCGCGAATATTAAAGGA | NM_001386500.1 |
| Human mTOR R | CTGGTTTCCTCATTCCGGCT | NM_001386500.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kerezoudi, E.N.; Saxami, G.; Zervakis, G.I.; Pletsa, V.; Brummer, R.J.; Kyriacou, A.; Rangel, I. Effects of In Vitro Fermented Pleurotus eryngii on Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Immunomodulation in a Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Colonic Model. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020430
Kerezoudi EN, Saxami G, Zervakis GI, Pletsa V, Brummer RJ, Kyriacou A, Rangel I. Effects of In Vitro Fermented Pleurotus eryngii on Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Immunomodulation in a Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Colonic Model. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(2):430. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020430
Chicago/Turabian StyleKerezoudi, Evangelia N., Georgia Saxami, Georgios I. Zervakis, Vasiliki Pletsa, Robert J. Brummer, Adamantini Kyriacou, and Ignacio Rangel. 2025. "Effects of In Vitro Fermented Pleurotus eryngii on Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Immunomodulation in a Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Colonic Model" Biomedicines 13, no. 2: 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020430
APA StyleKerezoudi, E. N., Saxami, G., Zervakis, G. I., Pletsa, V., Brummer, R. J., Kyriacou, A., & Rangel, I. (2025). Effects of In Vitro Fermented Pleurotus eryngii on Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Immunomodulation in a Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Colonic Model. Biomedicines, 13(2), 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020430







